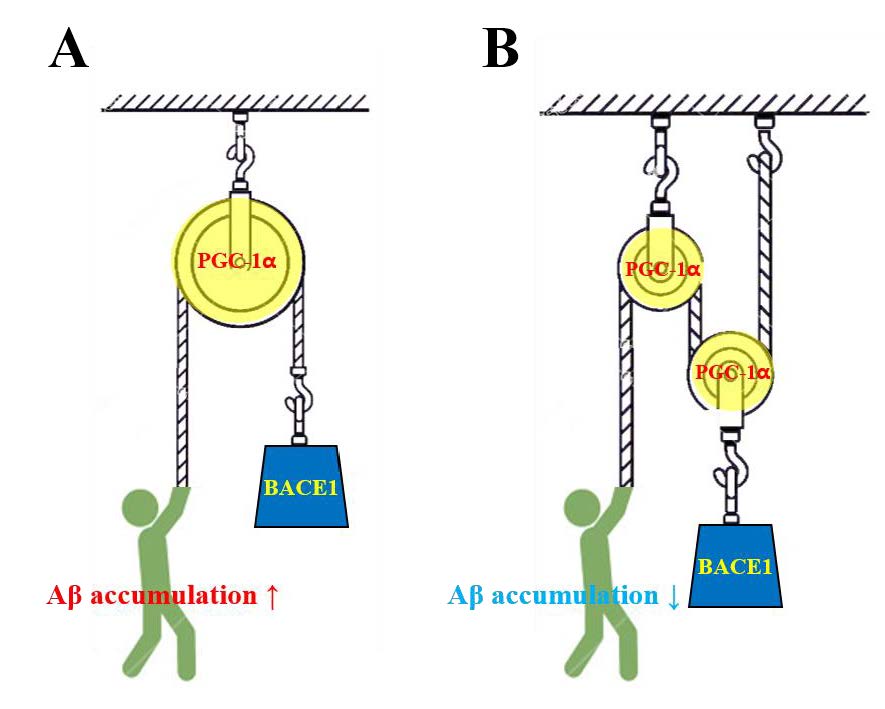
Irisin, a skeletal muscle-secreted myokine, produced in response to physical exercise, has protective functions in both the central and the peripheral nervous systems, including the regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factors and modification of telomere length. Such beneficial effects may inhibit or delay the emergence of neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s disease (AD). This review is based on the hypothesis that irisin produced by physical exercise helps control AD progression. Herein, we describe the physiology of irisin and its potential role in delaying or preventing AD. Although current and ongoing studies on irisin show promising results, further research is required to clarify its potential as a meaningful therapeutic target for treating human diseases.