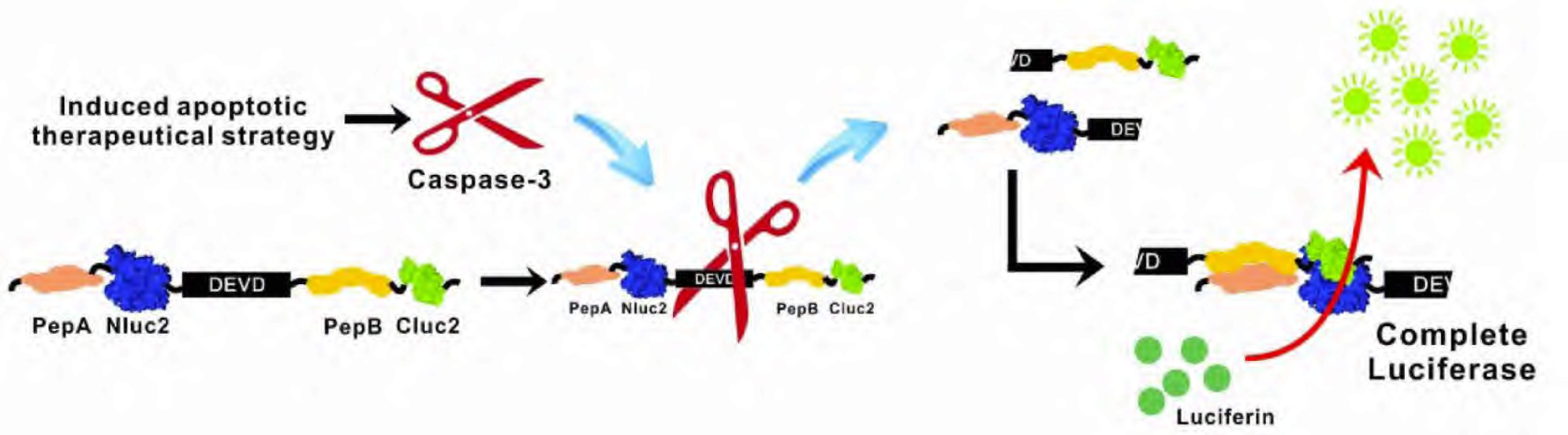
Breast cancer is the most common malignancies in women and the second leading cause of cancer death in women. Triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) subtype is a breast cancer subset without ER, PR and HER2 expression, limiting treatment options and presenting a poorer survival rate. Thus, we investigated whether HDACi would be used as potential anti-cancer therapy on breast cancer cells. In this study, we found TNBC and HER2-enrich breast cancers are extremely sensitive to Panobinostat, Belinostat of HDACi via experiments of cell viability assay, apoptotic marker identification and flow cytometry measurement. On the other hand, we developed a bioluminescence based live cell non-invasive apoptosis detection sensor (IADS) detection system to evaluate the quantitative and kinetic analyses of apoptotic cell death by HDAC treatment on breast cancer cells. In addition, the use of HDACi may also be accompanied with chemotherapeutic agent such as doxorubicin to synergic drug sensitivity on TNBC cell (MDA-MB-231), but not in breast normal epithelia cells (MCF-10A), providing therapeutic benefits against breast tumor in clinic.