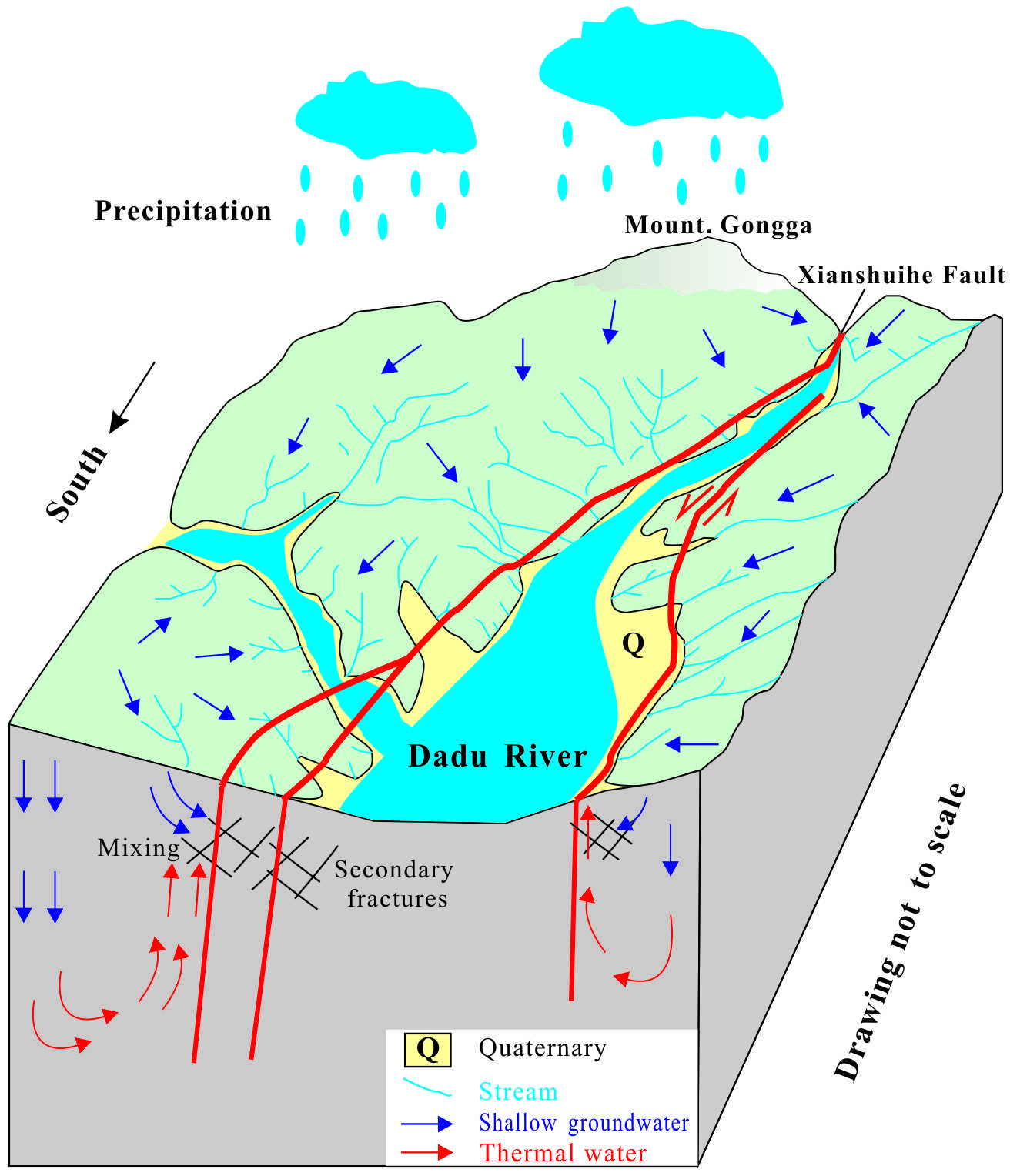
The utilization for water resource has been of great concern to human life. To assess the natural water system in Kangding County, the integrated methods of hydrochemcial analysis, multivariate statistics and geochemical modelling were conducted on surface water, groundwater and thermal water samples. Surface water and groundwater were dominated by Ca-HCO3 type, while thermal water belonged to Ca-HCO3 and Na-Cl type. The analyzing results concluded the driving factors that affect hydrochemical components. Following the results of the combined assessments, hydrochemcial process was controlled by the dissolution of carbonate and silicate minerals with slight influence from anthropogenic activity. The mixing model of groundwater and thermal water was calculated using silica-enthalpy method, yielding cold-water fraction of 0.56-0.79 and estimated reservoir temperature of 130-199 oC, respectively. δD and δ18O isotopes suggested surface water, groundwater and thermal springs were of meteoric origin. Thermal water should have deep circulation through the Xianshuihe fault zone, while groundwater flows through secondary fractures where it recharges with thermal water. Those analytical results were used to construct a hydrological conceptual model, providing a better understanding of the natural water system in Kangding County.