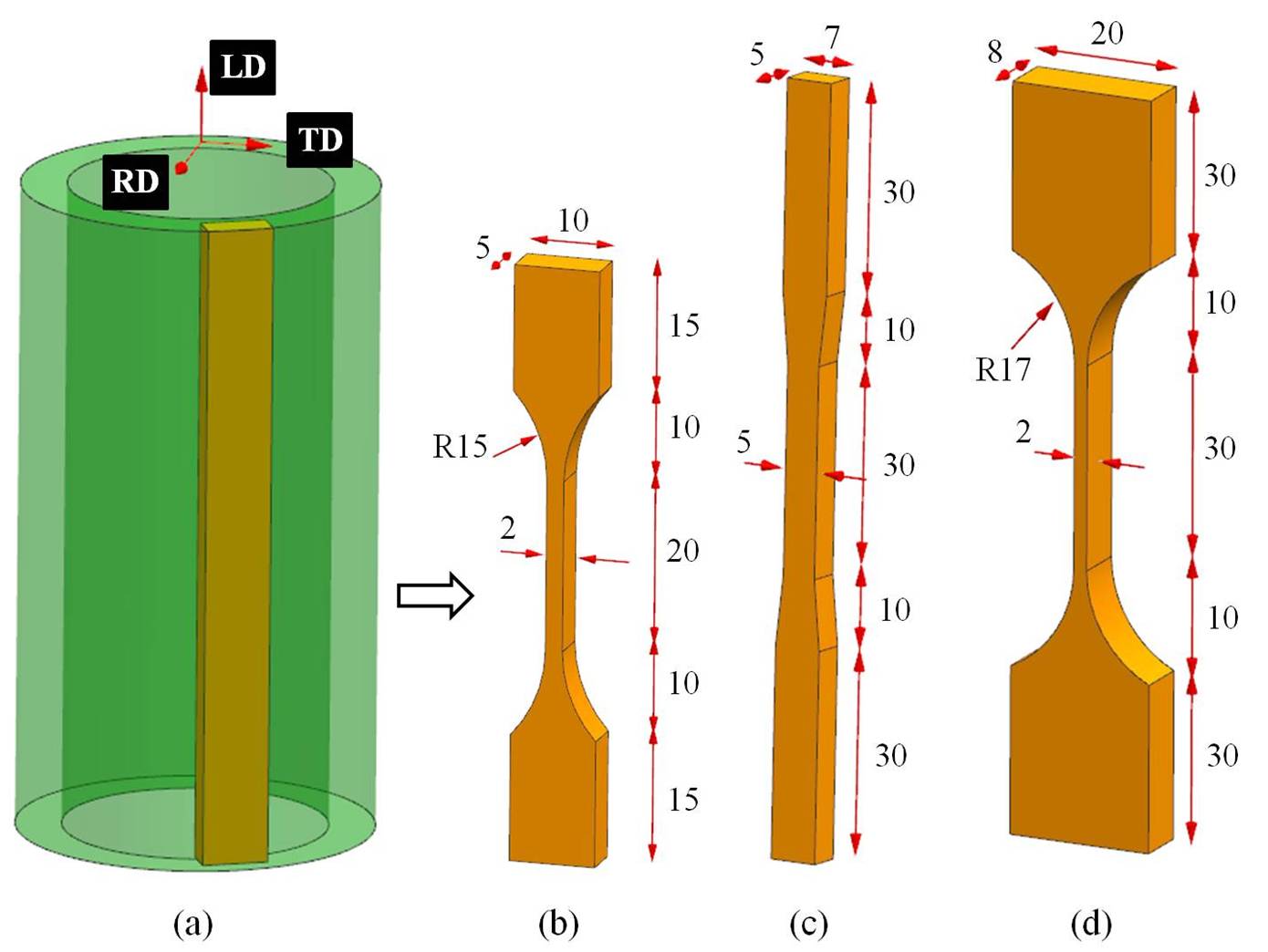
In this paper, quasi-static axial compression tests are performed on the nodal Moso bamboos to study the size effect on energy absorption of the bamboos and the damage pattern of the multiple bamboo columns. Experimental results show that under the same moisture content, growth age and growing environment, the specific energy absorption (SEA) of the test samples increases with the increase of the out-diameter and thickness of the bamboo columns, indicating that size effect exists for energy absorption of the Moso Bamboos. For the multiple bamboo columns, there are mainly three failure modes for the constituent single bamboo columns: splitting above the node, splitting below the node and splitting through the node. Also, the tensile tests are conducted on three kinds of dog-bone shaped bamboo samples to investigate the macroscopic tensile fracture mode in the longitudinal direction of Moso bamboos. Results show that there is no direct relationship between the fracture pattern and moisture content of the bamboos, as well as the growth age of the bamboos. However, the tensile loading rate and the shape of the dog-bone shaped bamboo sample could affect the macroscopic fracture pattern of the bamboos in some cases.