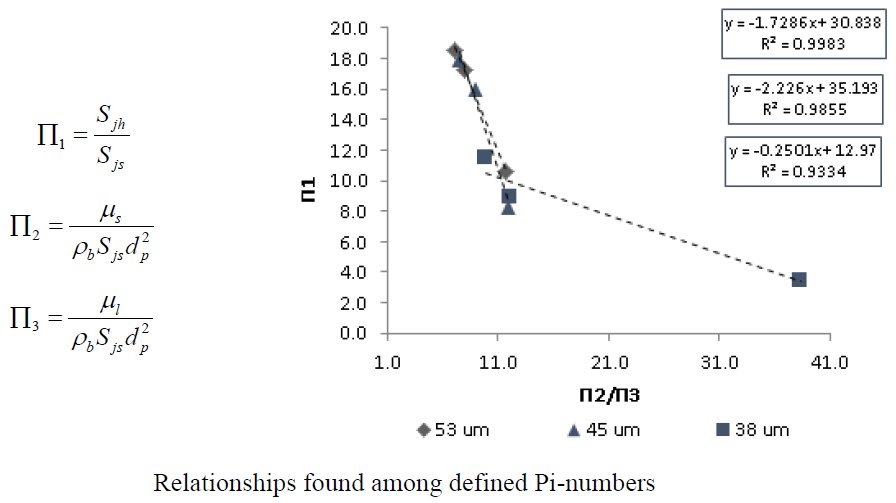
A rheological modifier was used to prepare solutions with viscosities of 1, 4, 6 and 8 cp, which exhibited Newtonian behavior. These solutions were later used to prepare suspensions of monosize quartz (53, 45 and 38 microns) at 60 % in solids. Monosize grinding tests in a laboratory ball mill were performed to determine breakage parameters, with different ball diameters. A model was developed to determine the specific rate of breakage in terms of the system rheology. With this model, it was demonstrated that an increase in suspending fluid viscosity until 6 cp, leads to an increased fracture rate and consequently affects the grinding degree. The above test is considered as an alternative for improving and optimizing such operations with excellent quality products with low energy and steel consumption, thereby minimizing environmental impact.