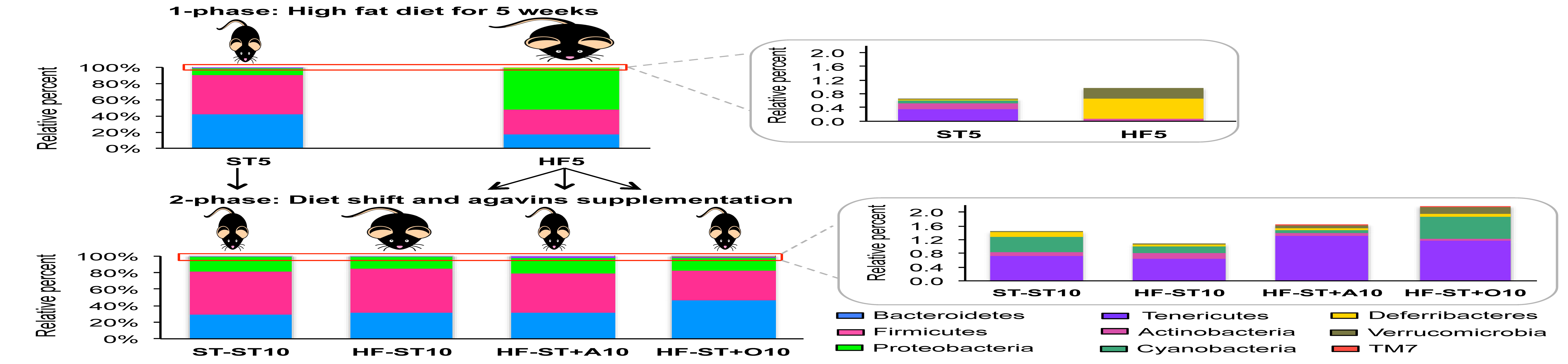
Agavins consumption has lead to accelerate body weight loss in mice. We investigated the changes on cecal microbiota and short chain fatty acids (SCFA) associated to body weight loss in overweight mice. Firstly, mice were fed with standard (ST5) or high fat (HF5) diet for 5 weeks. Secondly, overweight mice were shifted to standard diet alone (HF-ST10) or supplemented with agavins (HF-ST+A10) or oligofructose (HF-ST+O10), five more weeks. Cecal contents were collected before and after supplementation to determine microbiota and SCFA concentrations. At the end of first phase, HF5 mice showed a significant increase of body weight, which was associated with reduction of cecal microbiota diversity (PD whole tree; non-parametric t-test, P < 0.05), increased Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio and reduced SCFA concentrations (t-test, P < 0.05). After diet shifted, HF-ST10 normalized its microbiota, increase its diversity and SCFA levels, whereas agavins (HF-ST+A10) or oligofructose (HF-ST+O10) led to partial microbiota restoration, with normalization of the Firmicutes/Bacteroides ratio as well as higher SCFA levels (P < 0.1). Moreover, agavins noticeably enriched Klebsiella and Citrobacter (LDA > 3.0); this enrichment has not been reported previously under a prebiotic treatment. In conclusion, agavins or oligofructose modulated cecal microbiota composition, reduced extent of diversity and increased SCFA. Furthermore, identification of bacteria enriched by agavins, opens opportunities to explore new probiotics.