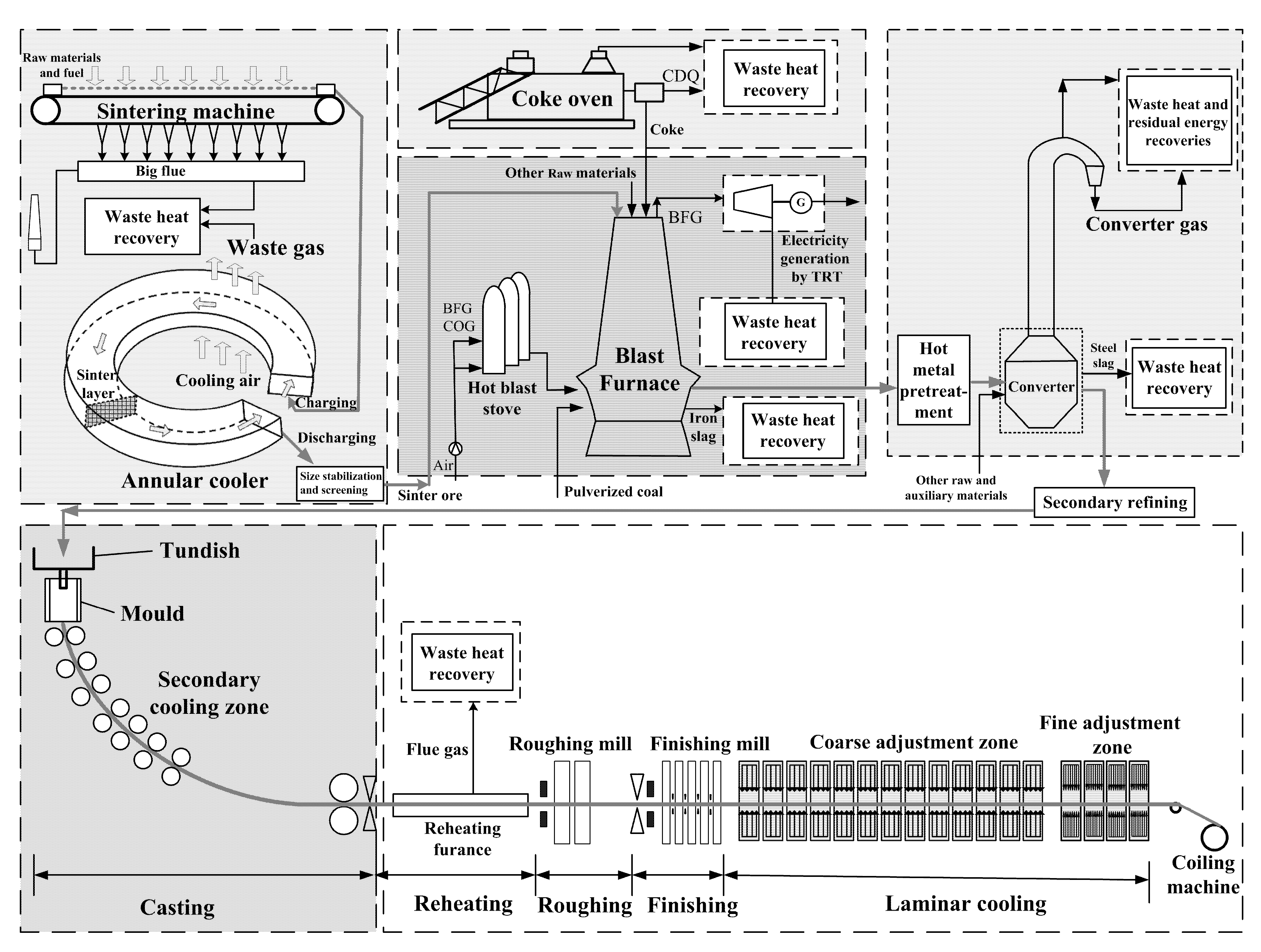
Combining modern thermodynamics theory branches, including finite time thermodynamics or entropy generation minimization, constructal theory and entransy theory, with metallurgical process engineering, this paper provides a new exploration on generalized thermodynamic optimization theory for iron and steel production processes. The theoretical core is to thermodynamically optimize performances of elemental packages, working procedure modules, functional subsystems, and whole process of iron and steel production processes with real finite-resource and/or finite-size constraints with various irreversibilities toward saving energy, decreasing consumption, reducing emission and increasing yield, and to achieve the comprehensive coordination among the material flow, energy flow and environment of the hierarchical process systems. A series of application cases of the theory are reviewed. It can provide a new angle of view for the iron and steel production processes from thermodynamics, and can also provide some guidelines for other process industries.