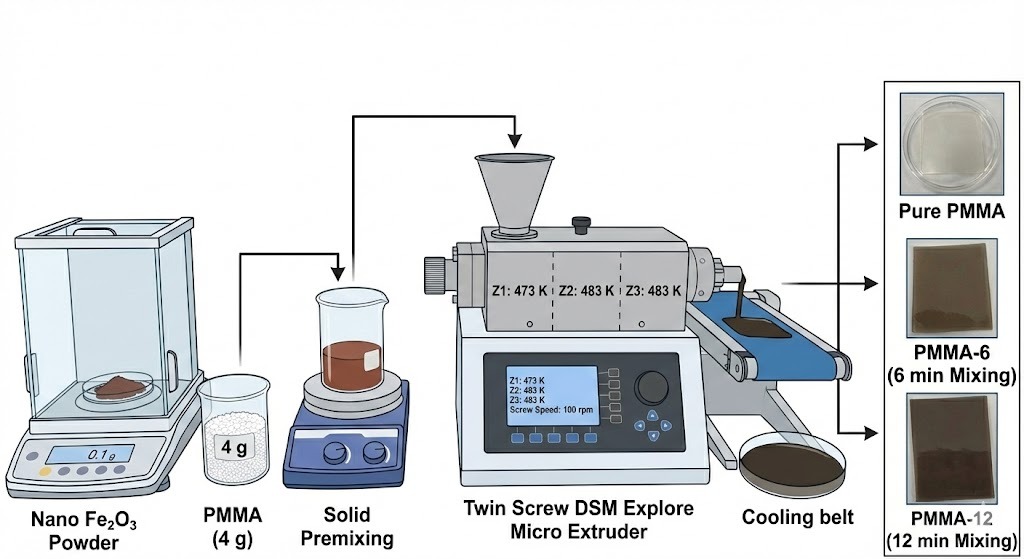
Fe₂O₃ nanoparticles reinforced in a polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) matrix structure were synthesized by the melting method. Fe₂O₃ was added in an amount of 2.5% by weight. Mixing times of 6 and 12 minutes were used, and materials with different homogenization properties were produced. In the final section, optimized binary nanocomposites were characterized by x-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM), revealing the strong interaction of the PMMA matrix with nanometal particles. Differential thermal analysis (DTA) was used to determine the thermal behavior of Fe₂O₃-reinforced PMMA nanocomposite. Activation energies of thermal degradation were calculated by using the Kissinger, Takhor, and Augis-Bennett methods. The increasing of the mixing time in the extruder also contributed to material homogenization. In addition, the Fe₂O₃ supplement lowered the polymer degradation temperature and increased the activation energy. Depending on the increasing mixing time, a decrease was observed in the maximum mass loss temperature (Tx) of the samples.