Submitted:
22 January 2026
Posted:
26 January 2026
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
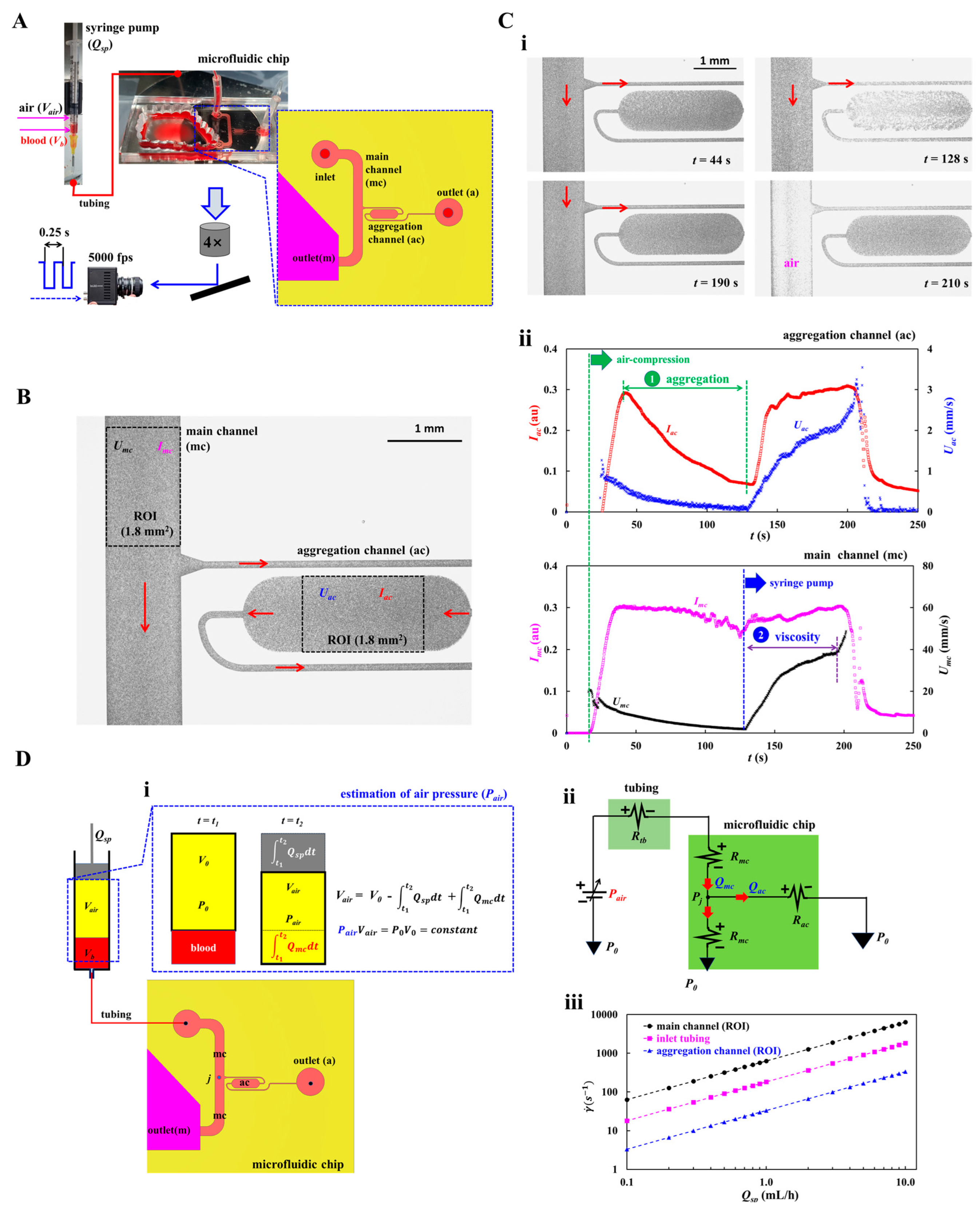
2.1. A Microfluidic Rheometry for Probing Biomechanical Properties from Blood Flows
2.2. Quantification of Image Intensity and Blood Flow-Rate in Main and Aggregation Channels
2.3. Mathematical Representation of Proposed Microfluidic System
2.4. Preparation of Test Blood
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
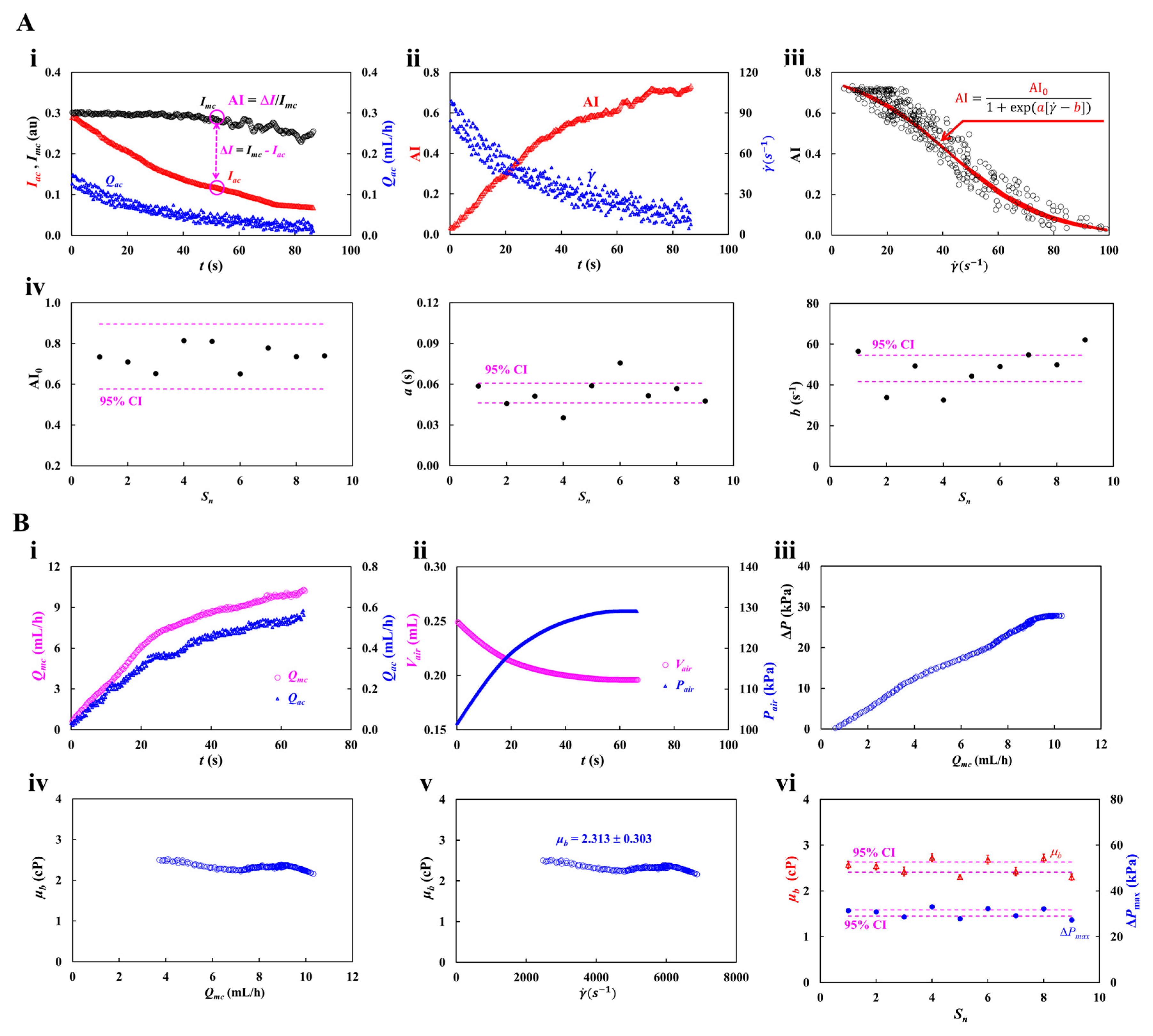
3.1. Proposed Protocols of Flow-Dependent RBCs Aggregation and Blood Viscosity
3.2. Accuracy Validation of Viscosity Measured by the Proposed Method for RBCs-Free Solution
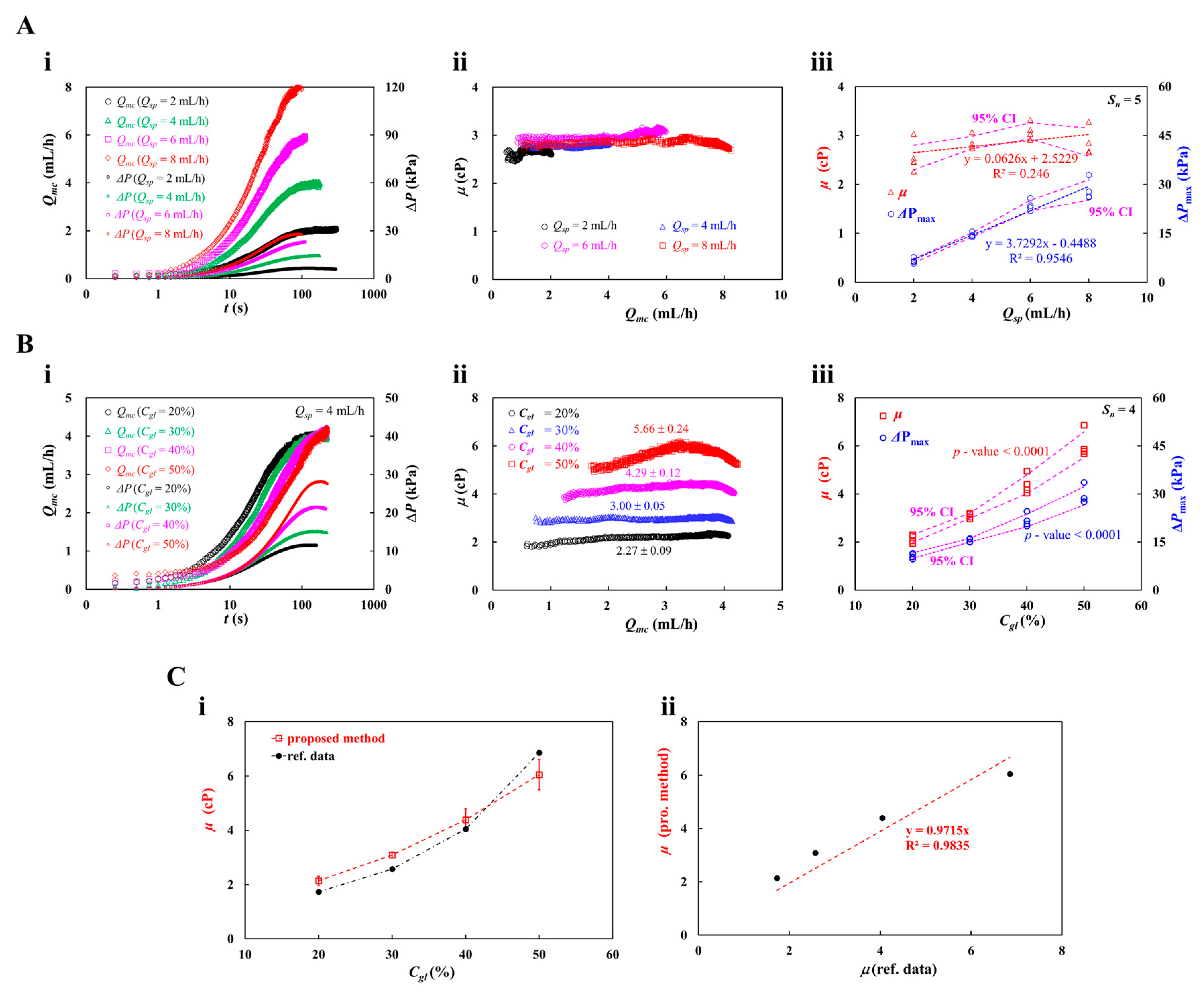
3.3. Determination of Supplied Blood Flow-Rate (Qsp) with Syringe Pump
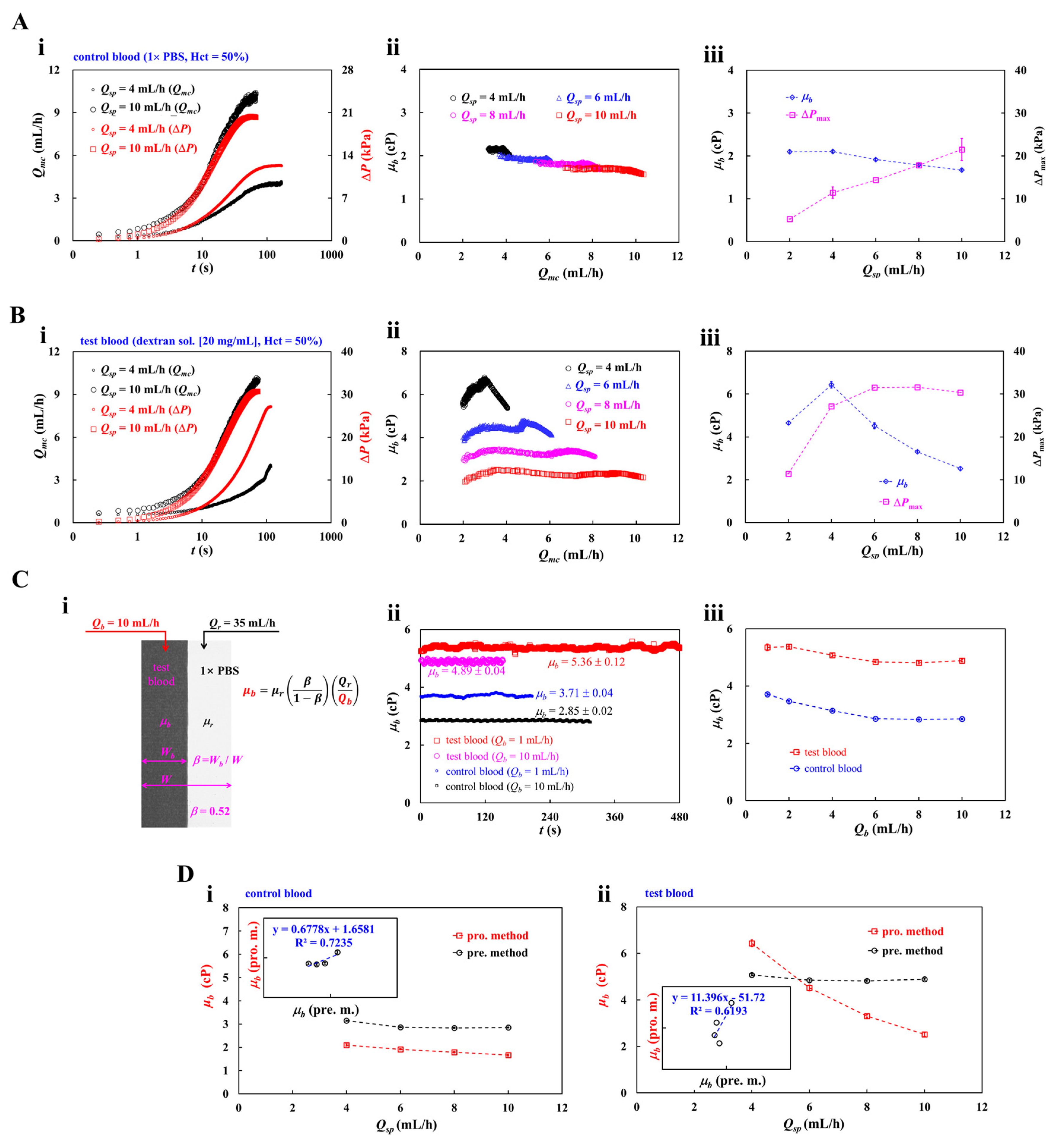
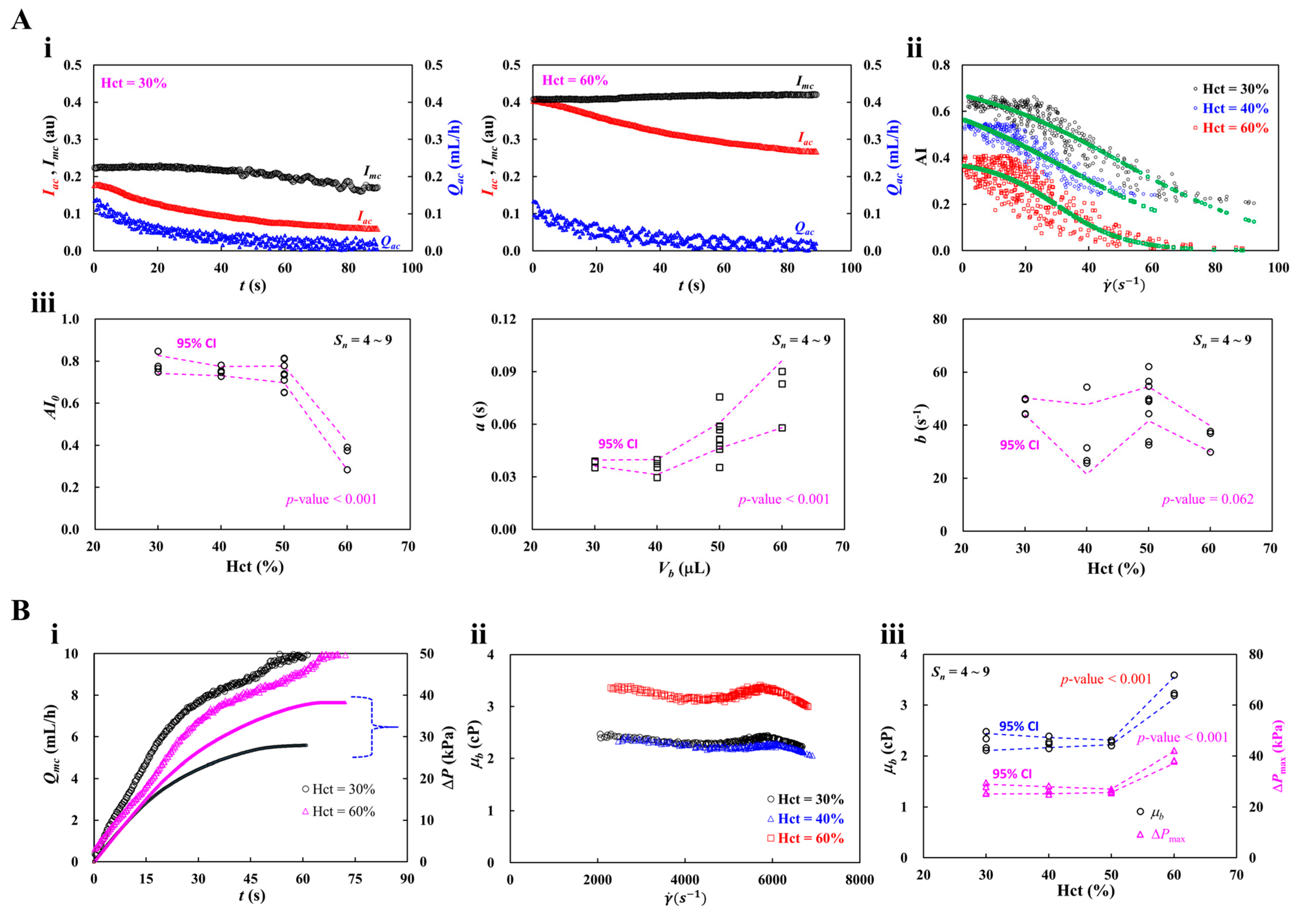
3.4. Contribution of Hematocrit (Hct)
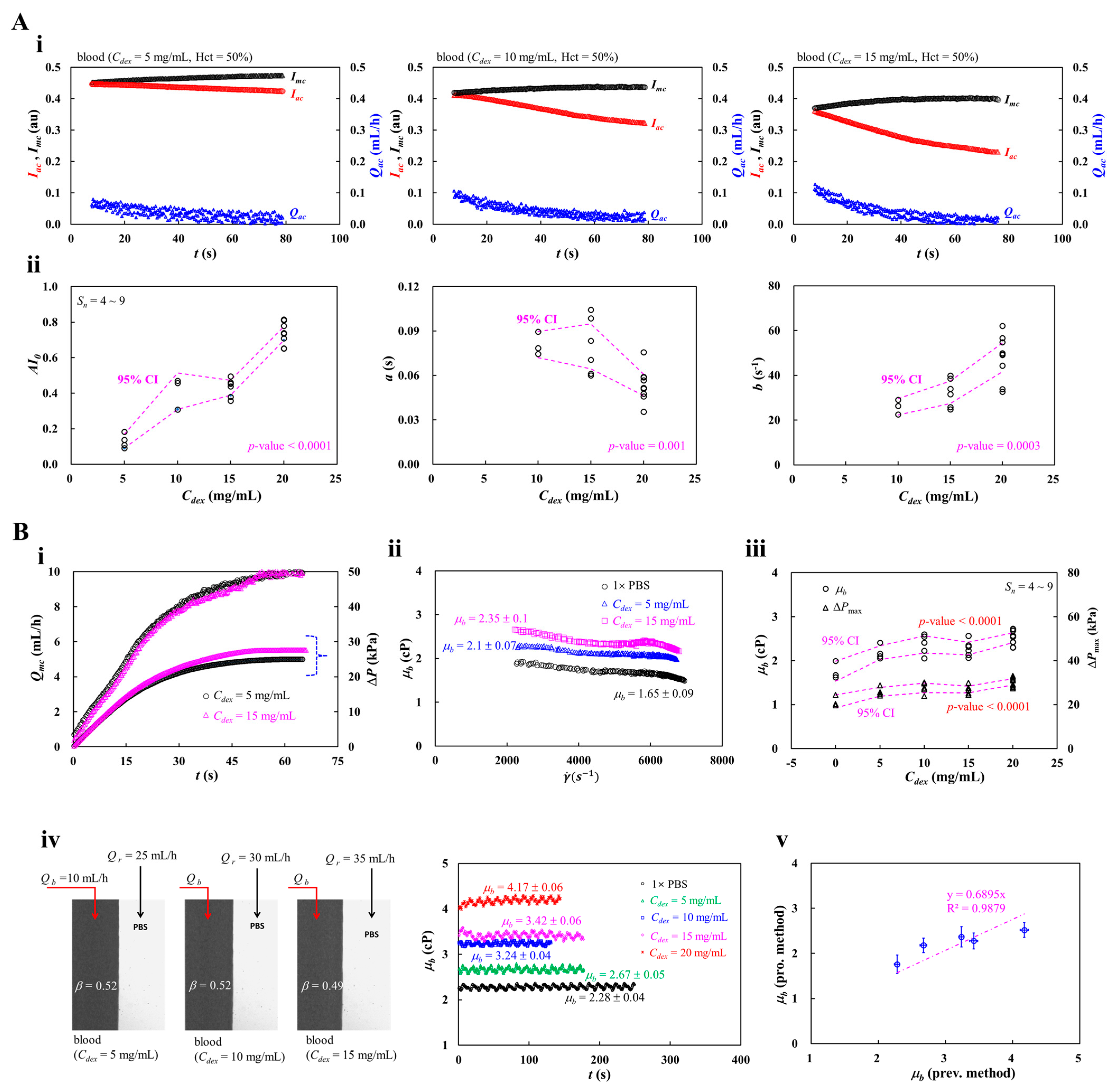
3.5. Contribution of Blood Medium (Dextran Concentration)
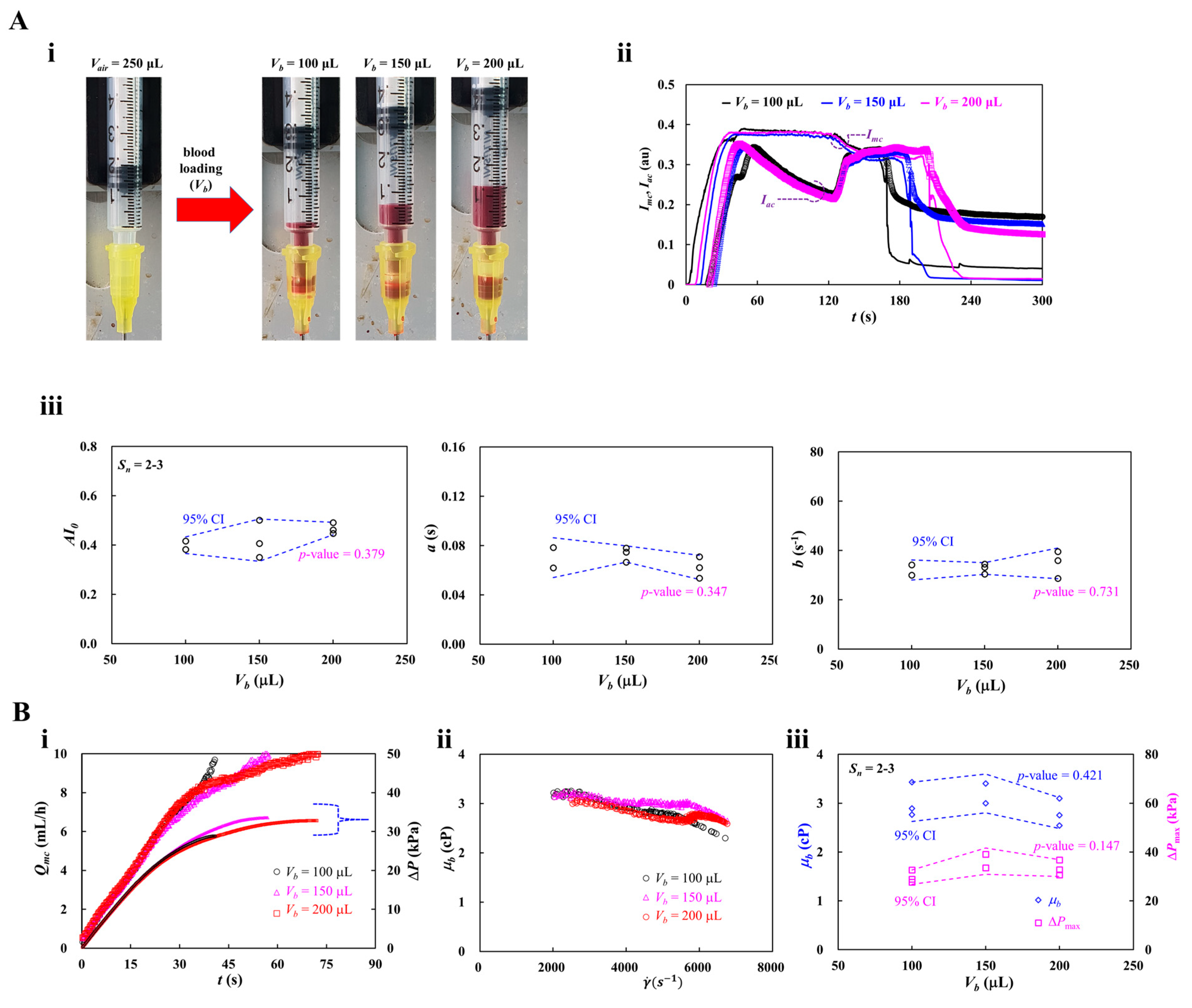
3.6. Contribution of Blood-Loading Volume (Vb) into a Driving Syringe
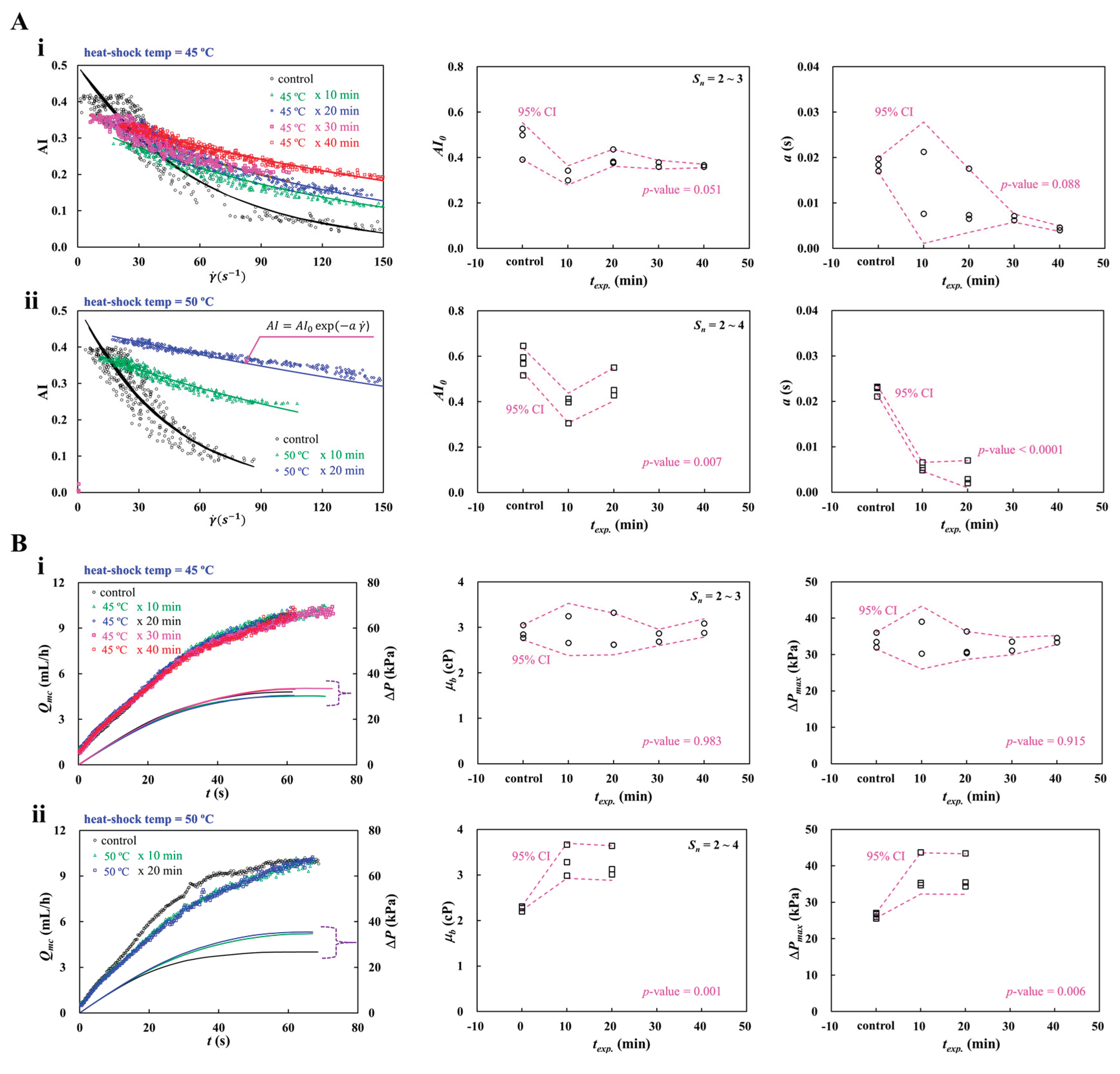
3.7. Detection of Heat-Shocked RBCs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, H.; Zhbanov, A.; Yang, S. Microfluidic systems for blood and blood cell characterization. Biosensors (Basel) 2022, 13, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigorev, G.V.; Lebedev, A.V.; Wang, X.; Qian, X.; Maksimov, G.V.; Lin, L. Advances in microfluidics for single red blood cell analysis. Biosensors (Basel) 2023, 13, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isiksacan, Z.; D'Alessandro, A.; Wolf, S.M.; McKenna, D.H.; Tessier, S.N.; Kucukal, E.; Gokaltun, A.A.; William, N.; Sandlin, R.D.; Bischof, J.; Mohandas, N.; Busch, M.P.; Elbuken, C.; Gurkan, U.A.; Toner, M.; Acker, J.P.; Yarmush, M.L.; Usta, O.B. Assessment of stored red blood cells through lab-on-a-chip technologies for precision transfusion medicine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2023, 120, e2115616120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakolidakhrabadi, A.; Stark, M.; Bacher, U.; Legros, M.; Bessire, C. Optimization of microfluidics for point-of-care blood sensing. Biosensors (Basel) 2024, 14, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, S.A.; Woodward, M.; Rumley, A.; Tunstall-Pedoe, H.D.; Lowe, G.D. Plasma and blood viscosity in the prediction of cardiovascular disease and mortality in the Scottish Heart Health Extended Cohort Study. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2017, 24, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, G.D.; Lee, A.J.; Rumley, A.; Price, J.F.; Fowkes, F.G. Blood viscosity and risk of cardiovascular events: the Edinburgh artery study. Br. J. Haematol. 1997, 96, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhtiaridoost, S.; Musuroi, C.; Volmer, M.; Florescu, M. Optoelectronic microfluidic device for point-of-care blood plasma viscosity measurement. Lab Chip 2024, 24, 3305–3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.N.; Yao, D.J. Development of a microfluidic viscometer for non-Newtonian blood analog fluid analysis. Bioengineering (Basel) 2024, 11, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.J. A microfluidic-based blood viscometer. Physics of Fluids 2025, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyawali, P.; Ziegler, D.; Cailhier, J.F.; Denault, A.; Cloutier, G. Quantitative measurement of erythrocyte aggregation as a systemic inflammatory marker by ultrasound imaging: a systematic review. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2018, 44, 1303–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ami, R.B.; Barshtein, G.; Zeltser, D.; Goldberg, Y.; Shapira, I.; Roth, A.; Keren, G.; Miller, H.; Prochorov, V.; Eldor, A.; Berliner, S.; Yedgar, S. Parameters of red blood cell aggregation as correlates of the inflammatory state. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2001, 280, H1982–H1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charansonney, O.L.; Meseguer, E.; Goube, P.; Vicaut, E. Erythrocyte aggregation kinetics for studying the vascular phase of inflammation in patients with suspected acute coronary syndrome or acute stroke. Sci Rep 2025, 15, 38049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mury, P.; Faes, C.; Millon, A.; Mura, M.; Renoux, C.; Skinner, S.; Nicaise, V.; Joly, P.; Della Schiava, N.; Lermusiaux, P.; Connes, P.; Pialoux, V. Higher Daily Physical Activity Level Is Associated with Lower RBC Aggregation in Carotid Artery Disease Patients at High Risk of Stroke. Front Physiol 2017, 8, 1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholivand, A.; Korculanin, O.; Dahlhoff, K.; Babaki, M.; Dickscheid, T.; Lettinga, M.P. Effect of in-plane and out-of-plane bifurcated microfluidic channels on the flow of aggregating red blood cells. Lab Chip 2024, 24, 2317–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.J. Assessment of continuous flow-dependent red cell aggregation using a microfluidic chip. Applied Sciences 2025, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.J. Microfluidic chip for quantitatively assessing hemorheological parameters. Micromachines 2025, 16, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadaf, A.; Seu, K.G.; Thaman, E.; Fessler, R.; Konstantinidis, D.G.; Bonar, H.A.; Korpik, J.; Ware, R.E.; McGann, P.T.; Quinn, C.T.; Kalfa, T.A. Automated Oxygen Gradient Ektacytometry: A Novel Biomarker in Sickle Cell Anemia. Front Physiol 2021, 12, 636609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisson, C.; Nader, E.; Renoux, C.; Gauthier, A.; Poutrel, S.; Bertrand, Y.; Stauffer, E.; Virot, E.; Hot, A.; Fort, R.; Cannas, G.; Joly, P.; Connes, P. Shear-Stress-Gradient and Oxygen-Gradient Ektacytometry in Sickle Cell Patients at Steady State and during Vaso-Occlusive Crises. Cells 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rab, M.A.E.; Kanne, C.K.; Boisson, C.; Bos, J.; van Oirschot, B.A.; Houwing, M.E.; Renoux, C.; Bartels, M.; Rijneveld, A.W.; Nur, E.; Cnossen, M.H.; Joly, P.; Nader, E.; Fort, R.; Connes, P.; van Wijk, R.; Sheehan, V.A.; van Beers, E.J. Oxygen gradient ektacytometry-derived biomarkers are associated with acute complications in sickle cell disease. Blood Adv 2024, 8, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, B.E.; Russell, B.; Grigg, M.J.; Zhang, R.; William, T.; Amir, A.; Lau, Y.L.; Chatfield, M.D.; Dondorp, A.M.; Anstey, N.M.; Yeo, T.W. Reduced red blood cell deformability in Plasmodium knowlesi malaria. Blood Adv 2018, 2, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renoux, C.; Faivre, M.; Bessaa, A.; Da Costa, L.; Joly, P.; Gauthier, A.; Connes, P. Impact of surface-area-to-volume ratio, internal viscosity and membrane viscoelasticity on red blood cell deformability measured in isotonic condition. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 6771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.C.; Wood, D.K. High-throughput quantification of red blood cell deformability and oxygen saturation to probe mechanisms of sickle cell disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2023, 120, e2313755120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.J.; Serhrouchni, S.; Makhro, A.; Bogdanova, A.; Lee, S.S. Simple assessment of red blood cell deformability using blood pressure in capillary channels for effective detection of subpopulations in red blood cells. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 38576–38588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Xie, L.; Yang, J.; Gong, X.; Sun, D.; Zhang, C. A microfluidic device for detecting the deformability of red blood cells. Biosensors (Basel) 2025, 15, 758. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kajitani, K.; Ohtani, T.; Higuchi, R.; Chimura, M.; Sera, F.; Tsai, C.D.; Ueda, Y.; Nishimura, J.I.; Sakata, Y. An on-chip deformability checker demonstrates that the severity of iron deficiency is associated with increased deformability of red blood cells. Sci Rep 2025, 15, 19994. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Luo, S.; Huang, J.; Chen, C.; Chen, R.; Li, F. A microfluidic approach for assessing the rheological properties of healthy versus thalassemic red blood cells. Micromachines (Basel) 2025, 16, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, J.; Park, C.-A.; Kim, A.-K.; Jeon, H.R.; Kim, D.-I.; Shin, S. Ultrasensitive microfluidic detection of red blood cell deformability: Age-related decline in deformability. Physics of Fluids 2025, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jou, J.M.; Lewis, S.M.; Briggs, C.; Lee, S.H.; De La Salle, B.; McFadden, S.; International Council for Standardization in; H. ICSH review of the measurement of the erythocyte sedimentation rate. Int J Lab Hematol 2011, 33, 125–32. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Y.J. Multiple-parameter sensing using an autonomous blood flow in a microfluidic chip. Results in Engineering 2025, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passos, A.; Louka, M.; Vryonidis, C.; Inglezakis, A.; Loizou, C.; Nikiphorou, E.; Psarelis, S.; Kaliviotis, E. Red blood cell sedimentation rate measurements in a high aspect ratio microchannel. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc 2022, 82, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshabaheebwa, S.; Delianides, C.A.; Patwardhan, A.A.; Evans, E.N.; Sekyonda, Z.; Bode, A.; Apio, F.M.; Mutuluuza, C.K.; Sheehan, V.A.; Suster, M.A.; Gurkan, U.A.; Mohseni, P. A miniaturized wash-free microfluidic assay for electrical impedance-based assessment of red blood cell-mediated microvascular occlusion. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2024, 258, 116352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, D.C.; Higgins, J.M.; Wood, D.K. Quantifying the unique mechanical properties of irreversibly sickled cells in sickle cell disease. Blood Vessel Thromb Hemost 2025, 2, 100077. [Google Scholar]
- Szafraniec, H.M.; Valdez, J.M.; Iffrig, E.; Lam, W.A.; Higgins, J.M.; Pearce, P.; Wood, D.K. Feature tracking microfluidic analysis reveals differential roles of viscosity and friction in sickle cell blood. Lab Chip 2022, 22, 1565–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Ye, T.; Yang, B.; Wang, S.; Li, X. Temporal-spatial heterogeneity of hematocrit in microvascular networks. Physics of Fluids 2023, 35, 021906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, B.J.; Zhu, L.T.; Chen, Z.; Ouyang, B.; Luo, Z.H. Review on Blood Flow Dynamics in Lab-on-a-Chip Systems: An Engineering Perspective. Chem Bio Eng 2024, 1, 26–43. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Harasek, M.; Gfohler, M. From soft lithography to 3D printing: current status and future of microfluidic device fabrication. Polymers (Basel) 2025, 17, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonova, N.; Khristov, K. Microrheological and microfluidic approaches for evaluation of the mechanical properties of blood cells. Applied Sciences 2025, 15, 8291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.J.; Lee, S.J. In vitro and ex vivo measurement of the biophysical properties of blood using microfluidic platforms and animal models. Analyst 2018, 143, 2723–2749. [Google Scholar]
- Del Giudice, F. A review of microfluidic devices for rheological characterisation. Micromachines (Basel) 2022, 13, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, I.; Berg, K.E.; Henry, C.S. Viscosity measurements utilizing a fast-flow microfluidic paper-based device. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical 2020, 319, 128240. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, H.; Jang, I.; Song, S.; Bae, S.C. Development of a paper-based viscometer for blood plasma using colorimetric analysis. Anal Chem 2019, 91, 4868–4875. [Google Scholar]
- Man, Y.; Maji, D.; An, R.; Ahuja, S.P.; Little, J.A.; Suster, M.A.; Mohseni, P.; Gurkan, U.A. Microfluidic electrical impedance assessment of red blood cell-mediated microvascular occlusion. Lab Chip 2021, 21, 1036–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaturvedi, A.; Nagaraj, S.K.; Gorthi, S.S.; Seelamantula, C.S. An efficient microscale technique for determining the erythrocyte sedimentation rate. SLAS Technol 2017, 22, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, K.W.; Lee, K.; Ahn, B.; Furlani, E.P. Design of pressure-driven microfluidic networks using electric circuit analogy. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 515–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilimi, Z.; Papay, Z.E.; Basa, B.; Orekhova, X.; Kallai-Szabo, N.; Antal, I. Microfluidic rheology: an innovative method for viscosity measurement of gels and various pharmaceuticals. Gels 2024, 10, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.J.; Lee, Y.S.; Zhbanov, A.; Yang, S. A physiometer for simultaneous measurement of whole blood viscosity and its determinants: hematocrit and red blood cell deformability. Analyst 2019, 144, 3144–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.J.; Yeom, E.; Lee, S.J. Microfluidic biosensor for monitoring temporal variations of hemorheological and hemodynamic properties using an extracorporeal rat bypass loop. Anal Chem 2013, 85, 10503–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapadia, W.; V Giri, N.; Qin, N.; Zhao, P.; Phan, C.-M.; Haines, L.; Jones, L.; Ren, C.L. A novel microfluidic viscometer for measuring viscosity of ultrasmall volumes of Newtonian and non-Newtonian liquids. Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering 2025, 35, 055005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khnouf, R.; Karasneh, D.; Abdulhay, E.; Abdelhay, A.; Sheng, W.; Fan, Z.H. Microfluidics-based device for the measurement of blood viscosity and its modeling based on shear rate, temperature, and heparin concentration. Biomed Microdevices 2019, 21, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riera-Llobet, C.; Méndez-Mora, L.; Cabello-Fusarés, M.; Hernández-Machado, A. Altered blood rheology in multiwidth microchannels: Hematocrit and tonicity variation. Physics of Fluids 2023, 35, 082017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez-Mora, L.; Cabello-Fusares, M.; Ferre-Torres, J.; Riera-Llobet, C.; Lopez, S.; Trejo-Soto, C.; Alarcon, T.; Hernandez-Machado, A. Microrheometer for biofluidic analysis: electronic detection of the fluid-front advancement. Micromachines (Basel) 2021, 12, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trejo-Soto, C.; Costa-Miracle, E.; Rodriguez-Villarreal, I.; Cid, J.; Alarcon, T.; Hernandez-Machado, A. Capillary Filling at the Microscale: Control of Fluid Front Using Geometry. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0153559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phu Pham, L.H.; Bautista, L.; Vargas, D.C.; Luo, X. A simple capillary viscometer based on the ideal gas law. RSC Adv 2018, 8, 30441–30447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.J. Microfluidic viscometer using capillary pressure sensing. Physics of Fluids 2023, 35, 121907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, N.; Ram, R.; Bishnoi, V.; Sarkar, A. A low-cost and disposable capillary-based paper sensor for measuring blood-plasma viscosity using a smartphone app. Microfluidics and Nanofluidics 2023, 27, 41. [Google Scholar]
- Uno, M.O.; Omori, M.; Sakamoto, K. Nonwoven-fabric-based microfluidic devices for solution viscosity measurements. Sensors & Diagnostics 2024, 3, 1551–1561. [Google Scholar]
- Mustafa, A.; Haider, D.; Barua, A.; Tanyeri, M.; Erten, A.; Yalcin, O. Machine learning based microfluidic sensing device for viscosity measurements. Sensors & Diagnostics 2023, 2, 1509–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eidi, A. Blood Viscosity Biosensor Based on Electromagnetic Resonator. Cardiovasc Eng Technol 2023, 14, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.; Ye, P.; Chen, C.; Zhang, J.; Xu, L.; Tan, F. Comparing of frequency shift and impedance analysis method based on QCM sensor for measuring the blood viscosity. Sensors (Basel) 2022, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, D.; Liu, X.; Xie, Y.; Shan, J.; Huang, H.; Yu, X.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, W.; Li, Z. Point-of-care blood coagulation assay based on dynamic monitoring of blood viscosity using droplet microfluidics. ACS Sens 2022, 7, 2170–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.F.; Hsu, P.S.; Tsai, C.S.; Pan, P.C.; Chen, Y.L. Significantly increased low shear rate viscosity, blood elastic modulus, and RBC aggregation in adults following cardiac surgery. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 7173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nader, E.; Skinner, S.; Romana, M.; Fort, R.; Lemonne, N.; Guillot, N.; Gauthier, A.; Antoine-Jonville, S.; Renoux, C.; Hardy-Dessources, M.D.; Stauffer, E.; Joly, P.; Bertrand, Y.; Connes, P. Blood rheology: key parameters, impact on blood flow, role in sickle cell disease and effects of exercise. Front Physiol 2019, 10, 1329. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.A.; Farooqi, H.M.U.; Paeng, D.G. Axial shear rate: A hemorheological factor for erythrocyte aggregation under Womersley flow in an elastic vessel based on numerical simulation. Comput Biol Med 2023, 157, 106767. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, S.; Nam, J.H.; Hou, J.X.; Suh, J.S. A transient, microfluidic approach to the investigation of erythrocyte aggregation: the threshold shear-stress for erythrocyte disaggregation. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc 2009, 42, 117–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhart, W.H.; Piety, N.Z.; Shevkoplyas, S.S. Influence of red blood cell aggregation on perfusion of an artificial microvascular network. Microcirculation 2017, 24, e12317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.A.; Paeng, D.G. Numerical simulation of spatiotemporal red blood cell aggregation under sinusoidal pulsatile flow. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 9977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charansonney, O.L.; Morel, P.; Dufaux, J.; Vicaut, E. Description and validation of a new, simple, easy-to handle, point-of-care technique for measuring erythrocyte aggregation kinetics. Sci Rep 2022, 12, 14798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandrova-Watanabe, A.; Abadjieva, E.; Ivanova, M.; Gartcheva, L.; Langari, A.; Guenova, M.; Tiankov, T.; Nikolova, E.V.; Krumova, S.; Todinova, S. Quantitative assessment of red blood cell disaggregation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia via software image flow analysis. Fluids 2025, 10, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namgung, B.; Lee, T.; Tan, J.K.S.; Poh, D.K.H.; Park, S.; Chng, K.Z.; Agrawal, R.; Park, S.Y.; Leo, H.L.; Kim, S. Vibration motor-integrated low-cost, miniaturized system for rapid quantification of red blood cell aggregation. Lab Chip 2020, 20, 3930–3937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, J.; Wan, N.; Bao, H.; Li, J. Quantitative measurement and evaluation of red blood cell aggregation in normal blood based on a modified Hanai equation. Sensors (Basel) 2019, 19, 1095. [Google Scholar]
- Isiksacan, Z.; Serhatlioglu, M.; Elbuken, C. In vitro analysis of multiple blood flow determinants using red blood cell dynamics under oscillatory flow. Analyst 2020, 145, 5996–6005. [Google Scholar]
- Isiksacan, Z.; Erel, O.; Elbuken, C. A portable microfluidic system for rapid measurement of the erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 4682–4690. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.J. Continuous and simultaneous measurement of the biophysical properties of blood in a microfluidic environment. Analyst 2016, 141, 6583–6597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, J.H.; Xue, S.; Lim, H.; Shin, S. Study of erythrocyte aggregation at pulsatile flow conditions with backscattering analysis. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc 2012, 50, 257–66. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Y.J. Biomechanical assessment of red blood cells in pulsatile blood flows. Micromachines (Basel) 2023, 14, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omura, M.; Yagi, K.; Nagaoka, R.; Hasegawa, H. Contrast analysis in ultrafast ultrasound blood flow imaging of jugular vein. J Med Ultrason (2001) 2023, 50, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.A.; Paeng, D.G. Spatiotemporal blood viscosity by local hematocrit under pulsatile flow: Whole blood experiments and computational analysis. Comput Biol Med 2025, 198, 111253. [Google Scholar]
- Maung Ye, S.S.; Kim, S. A mechanistic model of cross-bridge migration in RBC aggregation and disaggregation. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 2022, 10, 1049878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenech, M.; Garcia, D.; Meiselman, H.J.; Cloutier, G. A particle dynamic model of red blood cell aggregation kinetics. Ann Biomed Eng 2009, 37, 2299–309. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Tan, W.; Lu, Y.; Cao, W.; Zhu, G. A needle tip CCEA microfluidic device based on enhanced Dean flow for cell washing. Microsyst Nanoeng 2021, 7, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ernits, M.; Reinsalu, O.; Kyritsakis, A.; Linko, V.; Zadin, V. Low-cost, open-source, high-precision pressure controller for multi-channel mcrofluidics. Biosensors (Basel) 2025, 15, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akh, L.; Jung, D.; Frantz, W.; Bowman, C.; Neu, A.C.; Ding, X. Microfluidic pumps for cell sorting. Biomicrofluidics 2023, 17, 051502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.J. Red blood cell sedimentation index using shear stress of blood flow in microfluidic channel. Biosensors (Basel) 2022, 12, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.J. Microfluidic-based biosensor for blood viscosity and erythrocyte sedimentation rate using disposable fluid delivery system. Micromachines (Basel) 2020, 11, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.J. Blood viscometer using capillary blood flow under disposable compliance pump. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences 2024, 277, 109456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Jeong, S.; Kang, Y.J. Ultrasound standing wave-based cell-to-liquid separation for measuring viscosity and aggregation of blood sample. Sensors (Basel) 2020, 20, 2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thielicke, W.; Stamhuis, E.J. PIVlab – towards user-friendly, affordable and accurate digital particle image velocimetry in MATLAB. Journal of Open Research Software 2014, 2, e30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloosterman, A.; Poelma, C.; Westerweel, J. Flow rate estimation in large depth-of-field micro-PIV. Experiments in Fluids 2010, 50, 1587–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.J. Microfluidic-based effective monitoring of bloods by measuring RBC aggregation and blood viscosity under stepwise varying shear rates. Korea-Australia Rheology Journal 2020, 32, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kounov, N.B.; Petrov, V.G. Determination of erythrocyte aggregation. Math. Biosci. 1999, 157, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Villarreal, A.I.; Carmona-Flores, M.; Colomer-Farrarons, J. Effect of temperature and flow rate on the cell-free area in the microfluidic channel. Membranes (Basel) 2021, 11, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellini, M.A.; Baskurt, O.; Castellini, J.M.; Meiselman, H.J. Blood rheology in marine mammals. Front Physiol 2010, 1, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krisher, J.A.; Malinauskas, R.A.; Day, S.W. The effect of blood viscosity on shear-induced hemolysis using a magnetically levitated shearing device. Artif Organs 2022, 46, 1027–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.Y.; Lee, S.L.; Kim, E.; Kang, J.; Jung, S.; Kim, N.; Jung, J.; Lee, D.H.; Roh, Y.H.; Lee, D. Whole Blood Viscosity Reference Intervals and Its Correlation with Hematology and Serum Chemistry in Cats Using Scanning Capillary Method. Animals (Basel) 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskurt, O.K.; Meiselman, H.J. Blood rheology and hemodynamics. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2003, 29, 435–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehri, R.; Mavriplis, C.; Fenech, M. Red blood cell aggregates and their effect on non-Newtonian blood viscosity at low hematocrit in a two-fluid low shear rate microfluidic system. PLoS One 2018, 13, e0199911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadek, S.H.; Rubio, M.; Lima, R.; Vega, E.J. Blood particulate analogue fluids: A review. Materials (Basel) 2021, 14, 2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knüppel, F.; Thomas, I.; Wurm, F.-H.; Torner, B. Suitability of different blood-analogous fluids in determining the pump characteristics of a ventricular assist device. Fluids 2023, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenzen, P.S.; Dingfelder, F.; Muller, M.; Arosio, P. Portable microfluidic viscometer for formulation development and in situ quality control of protein and antibody solutions. Anal Chem 2024, 96, 13185–13190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, N.-S. Formula for the viscosity of a glycerol−water mixture. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research 2008, 47, 3285–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhbanov, A.; Yang, S. Effects of Aggregation on Blood Sedimentation and Conductivity. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0129337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabry, T.L. Mechanism of rbc aggregation and sedimentation. Blood 1987, 70, 1572–1576. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zydney, A.L.; Oliver, J.D.; Colton, C.K. A constitutive equation for the viscosity of stored red cell suspensions: Effect of hematocrit, shear rate, and suspending phase. J. Rheol. 1991, 35, 1639–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.J. Microfluidic-based measurement method of red blood cell aggregation under hematocrit variations. Sensors (Basel) 2017, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.S.; Lee, S.J. In vitro hemorheological study on the hematocrit effect of human blood flow in a microtube. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2008, 40, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.J. Quantitative monitoring of dynamic blood flows using coflowing laminar streams in a sensorless approach. Applied Sciences 2021, 11, 7260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Wang, W.S.; Vanapalli, S.A. Microfluidic viscometers for shear rheology of complex fluids and biofluids. Biomicrofluidics 2016, 10, 043402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillot, P.; Panizza, P.; Salmon, J.-B.; Joanicot, M.; Colin, A. Viscosimeter on a microfluidic chip. Langmuir 2006, 22, 6438–6445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.J. Microfluidic-based technique for measuring RBC aggregation and blood viscosity in a continuous and simultaneous fashion. Micromachines (Basel) 2018, 9, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskurt, O.K.; Boynard, M.; Cokelet, G.C.; Connes, P.; Cooke, B.M.; Forconi, S.; Liao, F.; Hardeman, M.R.; Jung, F.; Meiselman, H.J.; Nash, G.; Nemeth, N.; Neu, B.; Sandhagen, B.; Shin, S.; Thurston, G.; Wautier, J.L. International Expert Panel for Standardization of Hemorheological, M. New guidelines for hemorheological laboratory techniques. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2009, 42, 75–97. [Google Scholar]
- Baskurt, O.K.; Uyuklu, M.; Hardeman, M.R.; Meiselman, H.J. Photometric measurements of red blood cell aggregation: light transmission versus light reflectance. J. Biomed. Opt. 2009, 14, 054044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trejo-Soto, C.; Hernandez-Machado, A. Normalization of blood viscosity according to the hematocrit and the shear rate. Micromachines (Basel) 2022, 13, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.J. Biomechanical investigation of red cell sedimentation using blood shear stress and blood flow image in a capillary chip. Micromachines (Basel) 2023, 14, 1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber-Fishkin, S.; Seidner, H.S.; Gunter, G.; Frame, M.D. Erythrocyte aggregation in sudden flow arrest is linked to hyperthermia, hypoxemia, and band 3 availability. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2022, 20, 2284–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flormann, D.; Aouane, O.; Kaestner, L.; Ruloff, C.; Misbah, C.; Podgorski, T.; Wagner, C. The buckling instability of aggregating red blood cells. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 7928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Shirshin, E.; Rovnyagina, N.; Yaya, F.; Boujja, Z.; Priezzhev, A.; Wagner, C. Dextran adsorption onto red blood cells revisited: single cell quantification by laser tweezers combined with microfluidics. Biomed Opt Express 2018, 9, 2755–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neu, B.; Wenby, R.; Meiselman, H.J. Effects of dextran molecular weight on red blood cell aggregation. Biophys. J. 2008, 95, 3059–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Yu, L.; Chen, Z. Velocity variation assessment of red blood cell aggregation with spectral domain Doppler optical coherence tomography. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 38, 3210–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.J. Periodic and simultaneous quantification of blood viscosity and red blood cell aggregation using a microfluidic platform under in-vitro closed-loop circulation. Biomicrofluidics 2018, 12, 024116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matrai, A.A.; Varga, G.; Tanczos, B.; Barath, B.; Varga, A.; Horvath, L.; Bereczky, Z.; Deak, A.; Nemeth, N. In vitro effects of temperature on red blood cell deformability and membrane stability in human and various vertebrate species. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc 2021, 78, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckmann, D.M.; Bowers, S.; Stecker, M.; Cheung, A.T. Hematocrit, volume expander, temperature, and shear rate effects on blood viscosity. Anesth. Analg. 2000, 91, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zupančič Valant, A.; Žiberna, L.; Papaharilaou, Y.; Anayiotos, A.; Georgiou, G.C. The influence of temperature on rheological properties of blood mixtures with different volume expanders—implications in numerical arterial hemodynamics simulations. Rheol. Acta 2011, 50, 389–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lee, S.; Oh, J.E.; Shin, W.J.; Min, W.K.; Gwak, M. Hemolysis of irradiated leukoreduced red blood cells during rapid warming: An in vitro experimental study. J. Dent. Anesth. Pain Med. 2015, 15, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walt, J.H.V.D.; Russell, W.J. The effect of heating on the osmotic fragility of stored blood Br. J. Anaesth. 1978, 50, 815–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.L.; Li, H.; Qiang, Y.; Buffet, P.; Dao, M.; Karniadakis, G.E. Computational modeling of biomechanics and biorheology of heated red blood cells. Biophys. J. 2021, 120, 4663–4671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepock, J.R.; Frey, H.E.; Bayne, H.; Markus, J. Relationship of hyperthermia-induced hemolysis of human erythrocytes to the thermal denaturation of membrane proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1989, 980, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Perazzo, A.; Peng, Z.; Young, Y.-N.; Feng, Z.; Wood, D.K.; Higgins, J.M.; Stone, H.A. The effect of rigid cells on blood viscosity: linking rheology and sickle cell anemia. Soft Matter 2022, 18, 554–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




