Submitted:
07 January 2026
Posted:
14 January 2026
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
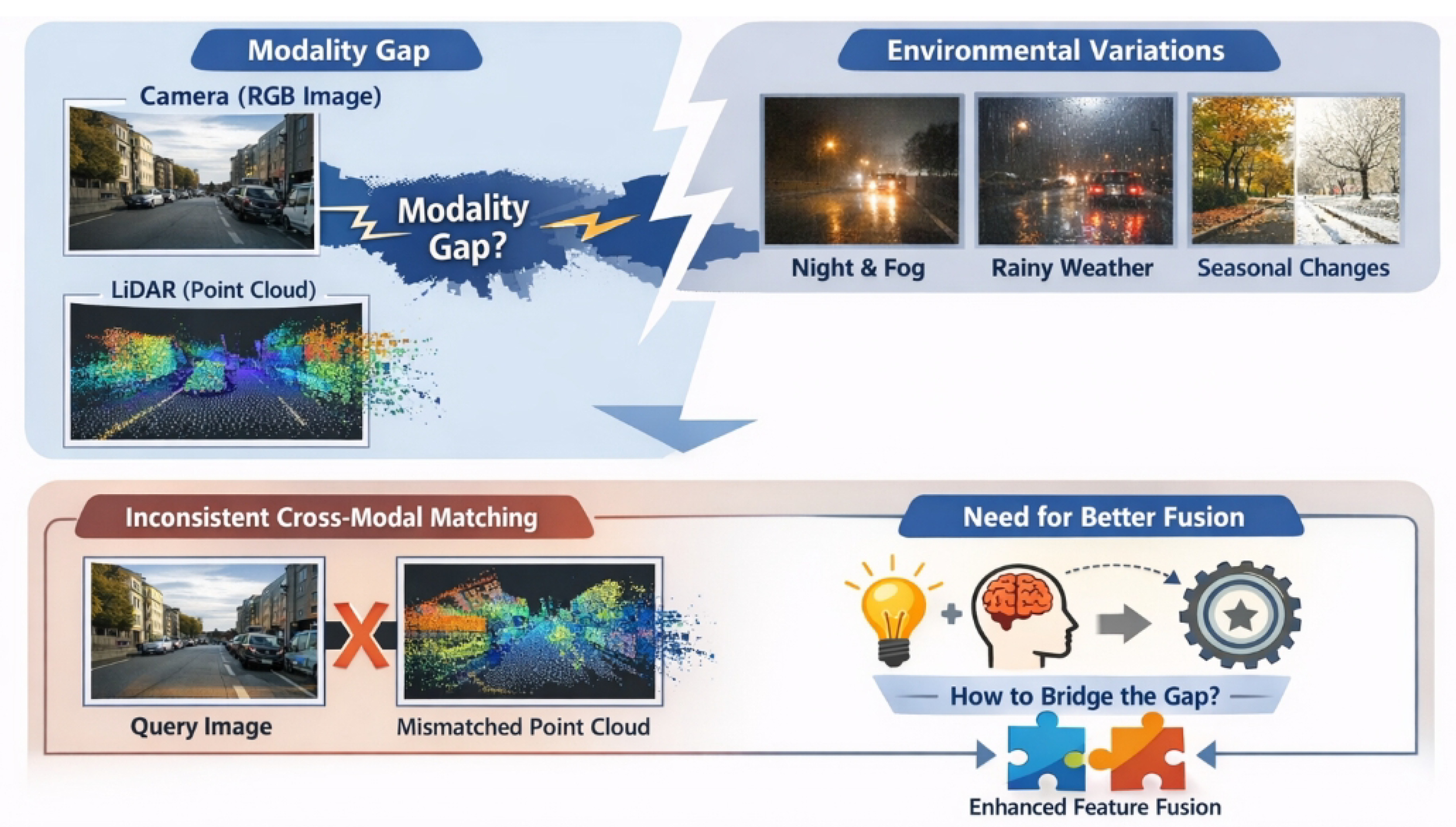
- We propose AttnLink, a novel framework for Image-to-PointCloud place recognition, which incorporates an Adaptive Depth Completion Network and an Attention-Guided Cross-Modal Feature Encoder to enhance the quality of geometric information and the discriminability of multi-modal features.
- We introduce a Multi-Head Attention Fusion Network that adaptively integrates local and semantic features, learning to focus on salient regions and cues for generating highly robust and discriminative global descriptors.
- We develop an improved training strategy utilizing an Adaptive Triplet Loss with Online Hard Negative Mining, which significantly accelerates model convergence and boosts overall recognition performance.
2. Related Work
2.1. Image-to-PointCloud Place Recognition
2.2. Cross-Modal Feature Learning and Attention Mechanisms
3. Method
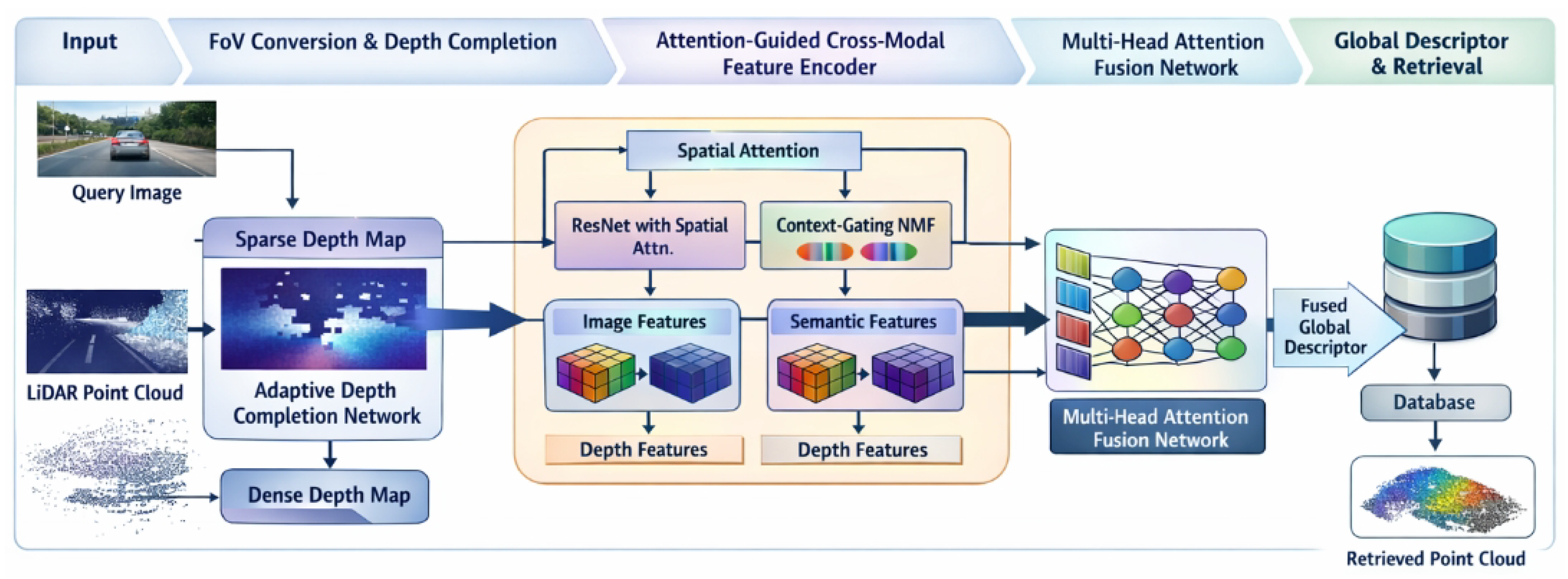
3.1. Overall Architecture
3.2. FoV Conversion and Adaptive Depth Completion
3.3. Attention-Guided Cross-Modal Feature Encoder
3.3.1. Local Feature Extraction with Spatial Attention
3.3.2. Context-Aware Semantic Clustering
3.3.3. Multi-Head Attention Fusion Network
3.4. Training Strategy
3.4.1. Adaptive Triplet Loss
3.4.2. Online Hard Negative Mining
4. Experiments
4.1. Experimental Setup
4.1.1. Datasets
4.1.2. Training Details
4.1.3. Data Preprocessing
4.2. Performance Comparison with State-of-the-Art
4.3. Runtime Efficiency Analysis
4.4. Human Evaluation
4.5. Generalization to Challenging Real-World Scenarios
4.6. Robustness to Varying Input Quality
4.7. Analysis of Multi-Head Attention Fusion Weights
5. Conclusion
References
- Li, W.; Gao, C.; Niu, G.; Xiao, X.; Liu, H.; Liu, J.; Wu, H.; Wang, H. UNIMO: Towards Unified-Modal Understanding and Generation via Cross-Modal Contrastive Learning. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 11th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (Volume 1: Long Papers). Association for Computational Linguistics, 2021, pp. 2592–2607. [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Stefani, E.; Wu, Q.; Thomason, J.; Wang, X. Vision-and-Language Navigation: A Survey of Tasks, Methods, and Future Directions. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 60th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers). Association for Computational Linguistics, 2022, pp. 7606–7623. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Tian, Z.; He, Y.; Liu, S.; Chen, H.; Yuan, F.; Peng, Y. Enhanced mean field game for interactive decision-making with varied stylish multi-vehicles. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2509.00981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Lin, Z.; Zhao, D.; Zhao, W.; Flynn, D.; Ansari, S.; Wei, C. Evaluating scenario-based decision-making for interactive autonomous driving using rational criteria: A survey. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2501.01886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Tian, Z.; Lan, J.; Zhao, D.; Wei, C. Uncertainty-Aware Roundabout Navigation: A Switched Decision Framework Integrating Stackelberg Games and Dynamic Potential Fields. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 2025, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yu, Y.; Niu, D.; Guo, W.; Xu, Y. ConFEDE: Contrastive Feature Decomposition for Multimodal Sentiment Analysis. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 61st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers). Association for Computational Linguistics, 2023, pp. 7617–7630. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Z.; Yuan, B.; Tao, D. On robust cross-view consistency in self-supervised monocular depth estimation. Machine Intelligence Research 2024, 21, 495–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhao, H.; Hao, X.; Yuan, B.; Li, X. STViT+: improving self-supervised multi-camera depth estimation with spatial-temporal context and adversarial geometry regularization. Applied Intelligence 2025, 55, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, S.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, J.; Tao, D. Simdistill: Simulated multi-modal distillation for bev 3d object detection. Proceedings of the Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence 2024, Vol. 38, 7460–7468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Bohndiek, S.E.; Li, Z.; Zhang, C.; Tan, Q. Mechanical-scan-free multicolor super-resolution imaging with diffractive spot array illumination. Nature Communications 2024, 15, 4135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Liu, G.; Kong, Z.; Tan, Q. Creation of super-resolution hollow beams with long depth of focus using binary optics. Applied Physics Express 2019, 13, 012003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Xiao, H.; Kong, Z.; Tan, Q. Axial multifocus beams formed by binary optical elements. IEEE Photonics Journal 2019, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Luo, L.; Ye, N.; Ren, Y.; Du, S.; Wang, M.; Xu, J.; Ai, R.; Gu, W.; Chen, X. ModaLink: Unifying Modalities for Efficient Image-to-PointCloud Place Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, IROS 2024, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, October 14-18, 2024. IEEE, 2024, pp. 3326–3333. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, Q.; Shen, J. Visual In-Context Learning for Large Vision-Language Models. Proceedings of the Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics, ACL 2024, Bangkok, Thailand and virtual meeting 2024, 2024, 15890–15902. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Shen, J.; Cheng, Y. Weak to strong generalization for large language models with multi-capabilities. In Proceedings of the The Thirteenth International Conference on Learning Representations, 2025.
- Zhou, Y.; Geng, X.; Shen, T.; Tao, C.; Long, G.; Lou, J.G.; Shen, J. Thread of thought unraveling chaotic contexts. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2311.08734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, W.; Zhao, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J. VQ-Insight: Teaching VLMs for AI-Generated Video Quality Understanding via Progressive Visual Reinforcement Learning. arXiv arXiv:2506.18564.
- Li, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J. Q-insight: Understanding image quality via visual reinforcement learning. arXiv arXiv:2503.22679. [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, J. AvatarShield: Visual Reinforcement Learning for Human-Centric Video Forgery Detection. arXiv arXiv:2505.15173.
- Cai, Z.; Xiao, W.; Sun, H.; Luo, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, K.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Chang, L.W.; Gu, J.; et al. R-KV: Redundancy-aware KV Cache Compression for Reasoning Models. In Proceedings of the The Thirty-ninth Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, R.; Yin, F.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, W.; Xia, W.; Yang, Y. Learning quality-aware dynamic memory for video object segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, 2022; Springer; pp. 468–486. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Bai, S.; Li, G.; Wang, Y.; Tang, Y. Open-vocabulary segmentation with semantic-assisted calibration. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2024; pp. 3491–3500. [Google Scholar]
- Han, K.; Liu, Y.; Liew, J.H.; Ding, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Feng, J.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Global knowledge calibration for fast open-vocabulary segmentation. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, 2023; pp. 797–807. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Wen, J.; Han, Y. EP-SAM: An Edge-Detection Prompt SAM Based Efficient Framework for Ultra-Low Light Video Segmentation. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2025-2025 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), 2025; IEEE; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Xu, G.; Deng, J.; Cheng, J.; Zheng, C.; Zhou, H.; Peng, N.; Zhu, X.; Huang, M. On the Safety of Conversational Models: Taxonomy, Dataset, and Benchmark. In Proceedings of the Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: ACL 2022, 2022; Association for Computational Linguistics; pp. 3906–3923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Liu, Y.; Mei, J.; Zeng, M. MediaSum: A Large-scale Media Interview Dataset for Dialogue Summarization. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 2021 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, 2021; Association for Computational Linguistics; pp. 5927–5934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xiong, Y.; Horowitz, R.; Wang, Y.; Han, Y. Hybrid Perception and Equivariant Diffusion for Robust Multi-Node Rebar Tying. In Proceedings of the 2025 IEEE 21st International Conference on Automation Science and Engineering (CASE), 2025; IEEE; pp. 3164–3171. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Xu, H.; Tian, J.; Wang, W.; Yan, M.; Bi, B.; Ye, J.; Chen, H.; Xu, G.; Cao, Z.; et al. mPLUG: Effective and Efficient Vision-Language Learning by Cross-modal Skip-connections. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 2022 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, 2022; Association for Computational Linguistics; pp. 7241–7259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Li, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhan, J.; Wang, P.; Zhou, Y.; Qiu, X. SpeechGPT: Empowering Large Language Models with Intrinsic Cross-Modal Conversational Abilities. In Proceedings of the Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2023, 2023; Association for Computational Linguistics; pp. 15757–15773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gui, M.; Jiang, Y.; Jia, Z.; Bach, N.; Wang, T.; Huang, Z.; Tu, K. ITA: Image-Text Alignments for Multi-Modal Named Entity Recognition. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 2022 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, 2022; Association for Computational Linguistics; pp. 3176–3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Lv, T.; Cui, L.; Wei, F.; Wang, G.; Lu, Y.; Florencio, D.; Zhang, C.; Che, W.; et al. LayoutLMv2: Multi-modal Pre-training for Visually-rich Document Understanding. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 11th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (Volume 1: Long Papers). Association for Computational Linguistics, 2021, pp. 2579–2591. [CrossRef]
- Hendricks, L.A.; Nematzadeh, A. Probing Image-Language Transformers for Verb Understanding. In Proceedings of the Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: ACL-IJCNLP 2021; Association for Computational Linguistics, 2021; pp. 3635–3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Wu, Y.; Liu, J.; Yang, S.; Zhang, Y. Template-Based Named Entity Recognition Using BART. In Proceedings of the Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: ACL-IJCNLP 2021; Association for Computational Linguistics, 2021; pp. 1835–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L. AI-Powered Financial Insights: Using Large Language Models to Improve Government Decision-Making and Policy Execution. Journal of Industrial Engineering and Applied Science 2025, 3, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L. Leveraging large language models for anomaly event early warning in financial systems. European Journal of AI, Computing & Informatics 2025, 1, 69–76. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, L.; et al. Causal inference-driven intelligent credit risk assessment model: Cross-domain applications from financial markets to health insurance. Academic Journal of Computing & Information Science 2025, 8, 8–14. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, J.; Tang, K.; Zhou, Y.; Cui, X.; Han, Q. The causal impact of gut microbiota and metabolites on myopia and pathological myopia: a mediation Mendelian randomization study. Scientific Reports 2025, 15, 12928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Liang, T.; Ji, X.; Shao, Y.; Zhao, P.; Li, X. LINC00488 induces tumorigenicity in retinoblastoma by regulating microRNA-30a-5p/EPHB2 Axis. Ocular Immunology and Inflammation 2023, 31, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Cui, X. Multi-omics Mendelian Randomization Reveals Immunometabolic Signatures of the Gut Microbiota in Optic Neuritis and the Potential Therapeutic Role of Vitamin B6. Molecular Neurobiology 2025, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, F.; Zhang, L.; Yin, S.; Zhao, X.; Liu, S.; Li, B.; Liu, Y. A Novel Global Feature-Oriented Relational Triple Extraction Model based on Table Filling. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 2021 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. Association for Computational Linguistics, 2021, pp. 2646–2656. [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Cahyawijaya, S.; Liu, Z.; Fung, P. Multimodal End-to-End Sparse Model for Emotion Recognition. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 2021 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies. Association for Computational Linguistics, 2021, pp. 5305–5316. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhan, P.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Xu, Z. Multimodal Fusion with Co-Attention Networks for Fake News Detection. In Proceedings of the Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: ACL-IJCNLP 2021. Association for Computational Linguistics, 2021, pp. 2560–2569. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Lin, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Qin, B.; Zhu, L.N. A Text-Centered Shared-Private Framework via Cross-Modal Prediction for Multimodal Sentiment Analysis. In Proceedings of the Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: ACL-IJCNLP 2021. Association for Computational Linguistics, 2021, pp. 4730–4738. Association for Computational Linguistics. [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Song, Y. Reinforced Cross-modal Alignment for Radiology Report Generation. In Proceedings of the Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: ACL 2022; Association for Computational Linguistics, 2022; pp. 448–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, C.; Feng, F.; Wen, L.; Ma, C.; Xie, P. Counterfactual Inference for Text Classification Debiasing. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 11th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (Volume 1: Long Papers). Association for Computational Linguistics, 2021, pp. 5434–5445. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Cheng, H.; Klopfer, R.; Gormley, M.R.; Schaaf, T. Effective Convolutional Attention Network for Multi-label Clinical Document Classification. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 2021 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. Association for Computational Linguistics, 2021, pp. 5941–5953. [CrossRef]
- Ansell, A.; Ponti, E.; Korhonen, A.; Vulić, I. Composable Sparse Fine-Tuning for Cross-Lingual Transfer. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 60th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers). Association for Computational Linguistics, 2022, pp. 1778–1796. [CrossRef]
- Angell, R.; Monath, N.; Mohan, S.; Yadav, N.; McCallum, A. Clustering-based Inference for Biomedical Entity Linking. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 2021 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies. Association for Computational Linguistics, 2021, pp. 2598–2608. [CrossRef]
| Method | Correct Match (%) | Plausible Match (%) | Incorrect Match (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LEA-I2P-Rec* | 85.2 | 9.8 | 5.0 |
| Ours (AttnLink) | 90.5 | 7.2 | 2.3 |
| Method | R@1 | R@1% |
|---|---|---|
| MIM-I2P-Rec | 38.5 | 75.1 |
| PSM-I2P-Rec* | 45.2 | 79.8 |
| LEA-I2P-Rec* | 58.7 | 88.3 |
| Ours (AttnLink) | 62.1 | 90.2 |
| Input Condition | Description | R@1 | R@1% |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normal Input | Original KITTI quality | 93.0 | 99.8 |
| Varying Depth Sparsity | |||
| Sparsity (75%) | 75% of original LiDAR points | 92.2 | 99.5 |
| Sparsity (50%) | 50% of original LiDAR points | 90.1 | 98.9 |
| Sparsity (25%) | 25% of original LiDAR points | 87.5 | 97.2 |
| Varying Image Noise | |||
| Image Noise (StdDev 0.05) | Gaussian noise, | 91.8 | 99.2 |
| Image Noise (StdDev 0.10) | Gaussian noise, | 89.9 | 98.6 |
| Image Noise (StdDev 0.15) | Gaussian noise, | 86.3 | 96.5 |
| Condition | Weight for | Weight for | Weight for | Weight for |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Good Illumination | 0.35 | 0.25 | 0.20 | 0.20 |
| Low Illumination | 0.15 | 0.38 | 0.12 | 0.35 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




