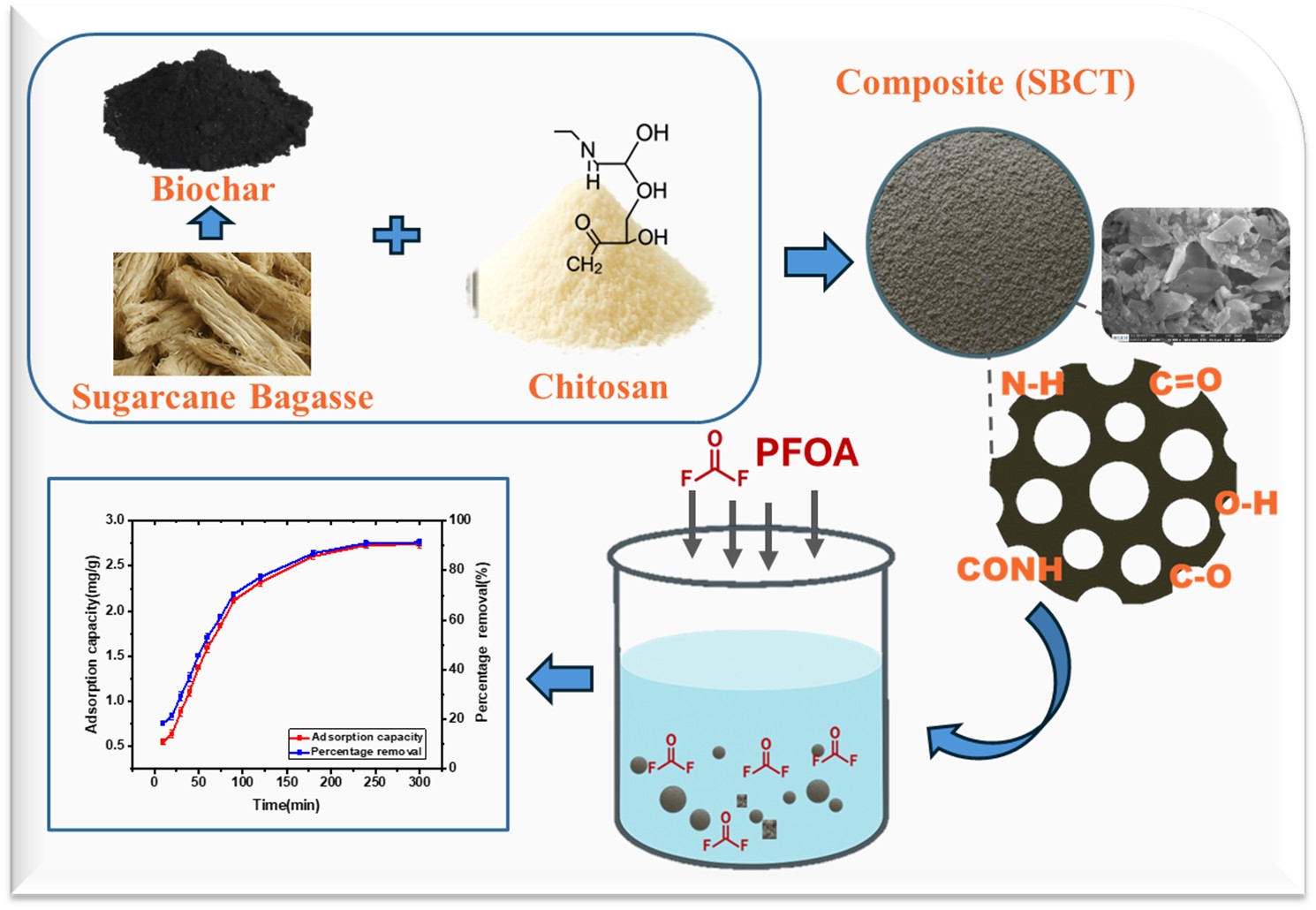
Recently, several studies from developing economies have reported the presence of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in water bodies, with a dominance of Perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA), a potential endocrine disruptor. In this study, an engineered sugarcane bagasse biochar–chitosan composite (SBCT) was designed, synthesized, and evaluated as an adsorption medium for the removal of PFOA from aqueous systems at concentrations up to 500 ppb in water. Batch adsorption experiments were conducted to investigate the effects of initial PFOA concentration, contact time, pH, adsorbent dosage, and temperature. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) showed that SBCT has a significant porous structure. The composite showed over 90% of PFOA removal from water. Further, the presence of peaks corresponding to C-F bonds after adsorption by Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy analysis confirms the adsorption of PFOA on SBCT. The protonated amine groups (NH₃⁺) in chitosan enhanced the adsorption of anionic PFOA through electrostatic attraction with carboxyl groups (COO⁻). The Kinetic study revealed that Pseudo-first order best described the adsorption process, with equilibrium adsorption capacity (qeq) of 2.78 mg/g, suggesting that physisorption is the predominant mechanism. The Langmuir Isotherm model gave the best fit, establishing a maximum adsorption capacity (qmax) of 9.08 mg/g. Thermodynamic analysis revealed that the adsorption process was spontaneous and exothermic, consistent with physisorption. The regeneration capacity of the SBCT composite demonstrated exceptional reusability across five adsorption-desorption cycles with methanol. The adsorption kinetics, equilibrium behavior, and regeneration efficiency suggest that SBCT is a viable low-cost adsorbent for batch adsorption-based treatment systems targeting PFOA removal, particularly in decentralized and resource-constrained water treatment applications.