1. Introduction
The rapid expansion of cross-border e-commerce has reshaped international trade by enabling consumers worldwide to purchase goods from diverse markets. Despite its growth, managing product sales forecasting and inventory remains a critical challenge. Cross-border platforms face high demand volatility, long shipping cycles, and dynamic market conditions such as fluctuating exchange rates and international shipping costs. In this context, accurate forecasting of product sales and inventory demand is essential for reducing stockouts, lowering storage costs, improving turnover efficiency, and enhancing supply chain resilience. Conversely, inaccurate forecasts can result in either excessive inventory, which ties up capital and increases warehousing costs, or insufficient inventory, which causes lost sales opportunities and diminished customer satisfaction.
Traditional forecasting techniques, including ARIMA, SARIMA, and machine learning methods such as Random Forest and XGBoost, have been widely applied to e-commerce sales prediction. However, these models struggle to capture nonlinear dependencies, multi-scale seasonality, and long-term patterns inherent in sales and inventory data. Deep learning models such as Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks and Transformer-based architectures have shown potential for time series forecasting, but their performance degrades significantly in long-sequence prediction tasks due to information decay and computational inefficiency.
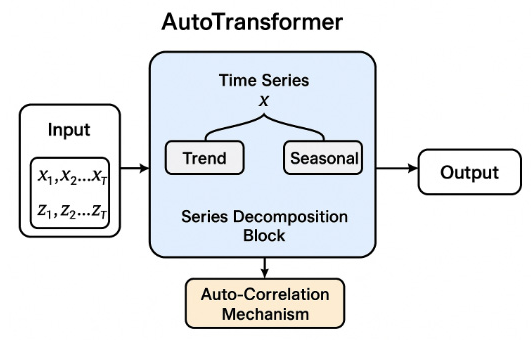
To address these limitations, this study employs the Autoformer model, a Transformer-based architecture tailored for long-term time series forecasting. Autoformer introduces a series decomposition block, which adaptively separates trend and seasonal components to enhance interpretability and stability, and an auto-correlation mechanism, which efficiently captures periodic dependencies in sequential data. These innovations make Autoformer particularly well-suited for forecasting sales and inventory in cross-border e-commerce, where both seasonal cycles (e.g., holiday promotions, annual events) and short-term demand fluctuations are prominent.
This paper proposes an Autoformer-based framework for cross-border e-commerce sales and inventory forecasting. Using transaction-level sales records, pricing data, inventory levels, and external market factors such as exchange rates and shipping costs, the framework is designed to capture both long- and short-term dynamics. Extensive experiments on a large-scale real-world dataset demonstrate that the proposed method significantly outperforms statistical baselines and deep learning alternatives including LSTM, Transformer, and Informer.
The main contributions of this study are threefold: (1) we highlight the importance of sales and inventory forecasting for cross-border e-commerce operations; (2) we propose an Autoformer-based forecasting framework that effectively models long-sequence time series; (3) we provide empirical evidence showing improved accuracy and robustness over state-of-the-art baselines.
2. Related Work
Accurate sales and inventory forecasting has long been a core research topic in operations management, supply chain analytics, and e-commerce intelligence. With the rapid growth of cross-border e-commerce, forecasting tasks have become increasingly challenging due to demand volatility, long logistics cycles, exchange-rate fluctuations, and complex seasonal patterns. This section reviews prior studies closely related to this work, including traditional demand forecasting methods, machine learning–based sales prediction, deep learning models for time series forecasting, and recent Transformer-based architectures for long-sequence modeling.
2.1. Traditional Demand Forecasting and Inventory Modeling
Early research on sales and inventory forecasting primarily relied on statistical time series models such as Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA), Seasonal ARIMA (SARIMA), and exponential smoothing techniques. Box and Jenkins [
1] established the foundational framework for ARIMA-based forecasting, which has been widely applied in retail demand prediction. Hyndman et al. [
2] further advanced exponential smoothing and state-space models, demonstrating their effectiveness in capturing seasonality and trends.
In the inventory management literature, classical demand models have been extensively used to support replenishment and safety stock decisions. Silver et al. [
3] provided a comprehensive overview of inventory control policies under stochastic demand. However, these statistical approaches typically assume linearity and stationarity, making them less effective in modern e-commerce settings where demand is nonlinear, intermittent, and heavily influenced by external factors such as promotions and logistics delays. As a result, their forecasting accuracy often degrades in complex cross-border e-commerce environments.
2.2. Machine Learning Approaches for E-Commerce Sales Forecasting
To overcome the limitations of traditional statistical models, researchers have increasingly adopted machine learning techniques for sales prediction. Tree-based ensemble methods such as Random Forests, Gradient Boosting, XGBoost, and LightGBM have demonstrated strong performance in modeling nonlinear relationships between sales and exogenous variables. Chen and Guestrin [
4] introduced XGBoost, which has been widely applied to retail sales forecasting due to its scalability and robustness.
Several studies have explored machine learning–driven demand forecasting in e-commerce platforms. Carbonneau et al. [
5] applied machine learning techniques to intermittent demand forecasting, showing improvements over classical methods. More recently, Ferreira et al. [
6] incorporated price, promotion, and calendar effects into supervised learning models for retail demand prediction. Despite their advantages, most machine learning models rely on handcrafted lag features and struggle to capture long-term temporal dependencies and multi-scale seasonality, which are critical in cross-border e-commerce scenarios.
2.3. Deep Learning Models for Time Series Forecasting
Deep learning has emerged as a powerful paradigm for time series forecasting due to its ability to learn complex temporal patterns automatically. Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), particularly Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks, have been widely used for sales and inventory prediction. Hochreiter and Schmidhuber [
7] introduced LSTM to address the vanishing gradient problem, enabling the modeling of long-range dependencies. Subsequent studies demonstrated the effectiveness of LSTM-based models in retail demand forecasting and supply chain analytics [
8].
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) have also been applied to time series forecasting by capturing local temporal patterns, while hybrid CNN–LSTM models combine local feature extraction with sequence modeling. However, RNN-based architectures often suffer from information decay and limited scalability when handling long sequences, which are common in multi-year e-commerce sales data. These limitations have motivated the exploration of attention-based models for long-horizon forecasting.
2.4. Transformer-Based and Long-Sequence Time Series Models
Inspired by their success in natural language processing, Transformer-based architectures have been increasingly adopted for time series forecasting. Vaswani et al. [
9] introduced the Transformer model with self-attention mechanisms, enabling parallel computation and long-range dependency modeling. Li et al. [
10] proposed the Temporal Fusion Transformer (TFT), which integrates attention mechanisms and interpretable components for multi-horizon forecasting in business applications.
To address the computational inefficiency of standard Transformers on long sequences, several variants have been proposed. Zhou et al. [
11] introduced the Informer model, which employs a probabilistic sparse attention mechanism to reduce complexity for long time series forecasting. Building upon this line of research, Wu et al. [
12] proposed Autoformer, a Transformer-based architecture specifically designed for long-sequence time series prediction. Autoformer introduces series decomposition blocks to explicitly separate trend and seasonal components, and replaces dot-product attention with an auto-correlation mechanism to capture periodic dependencies more efficiently.
Compared with prior Transformer-based approaches, Autoformer has demonstrated superior performance on long-horizon forecasting tasks, particularly in scenarios with strong seasonality and cyclic patterns. However, its application to cross-border e-commerce sales and inventory forecasting remains relatively underexplored. This study addresses this gap by applying Autoformer to real-world cross-border e-commerce data and demonstrating its effectiveness in improving forecasting accuracy and inventory decision support.
3. Methodology
3.1. Task Modeling and Problem Definition
In cross-border e-commerce operations, sales forecasting concerns not only short-term demand fluctuations but also inventory allocation and supply-chain optimization. Suppose the platform hosts
N products; for product
i the sales series up to time step
t ∈ {
1, 2, …, T} is denoted by
where
is the sales volume of product
i at time
t. The goal is to predict the next H steps from historical sales and associated external features (price, inventory, exchange rate, shipping delay, promotions, etc.):
with
representing the exogenous feature sequence of product
i and
θ the model parameters; the forecasts feed directly into inventory and logistics decisions.
Two key challenges arise in cross-border settings:
- (i)
Sales display multi-scale seasonality and complex trends, e.g., sudden spikes driven by Black Friday or Double-11 promotions;
- (ii)
Cross-border factors such as international shipping uncertainty and exchange-rate volatility significantly impact demand. Traditional statistical or short-sequence models struggle to capture these characteristics.
3.2. Autoformer Model Principle
Autoformer is a recently proposed Transformer-variant tailored for long-sequence time-series forecasting. Its core innovations are the integration of Series Decomposition and an Auto-Correlation Mechanism.
First, the decomposition module splits the raw series into a trend term and a seasonal term:
where
is the smooth long-term trend and
the periodic component. The separation is realized by a moving-average operator:
This decomposition enables the model to model the long-term trend and short-term fluctuations separately, improving its fit to complex e-commerce data.
Second, the auto-correlation mechanism replaces the canonical dot-product attention in Transformer. For an input sequence
, Autoformer discovers optimal periodic sub-sequences and aggregates them to capture cyclic dependencies. Concretely, the auto-correlation score is computed via the delayed autocorrelation:
with
l the lag step size and
the series mean. By selecting the lags with the highest correlations from a candidate set, the model captures long-range periodic patterns such as quarterly promotions or annual peak seasons.
3.3. Implementing Autoformer for Cross-Border E-Commerce Forecasting
In the cross-border e-commerce setting, this study tailors Autoformer to simultaneous sales and inventory forecasting. First, the input features comprise not only historical sales sequences but also external drivers such as price, inventory level, shipping lead-time, exchange-rate fluctuations, and holiday promotions. These covariates are concatenated as Zₜ and fed into Autoformer together with the sales series during encoding.
Second, training samples are generated by a sliding-window strategy: given a look-back horizon
L, the model predicts the next
H steps:
where
L is set to 96 in experiments to capture both quarterly and yearly patterns.
Third, to handle the huge and heterogeneous SKU space, a global model is adopted: sales series of different products are jointly trained within one Autoformer, whose auto-correlation block shares periodic patterns across items. For instance, multiple categories may simultaneously be lifted by international holidays or site-wide promotions—cross-series dependencies that traditional models miss but Autoformer captures effectively.
Finally, the optimization objective combines Mean-Squared Error (MSE) with a Weighted Mean Absolute Error (WMAE) to emphasize accuracy on high-volume items:
where
is a weight proportional to the sales scale of product
i and
λ balances the two terms.
Figure 1.
Structure diagram of Autoformer.
Figure 1.
Structure diagram of Autoformer.
4. Experimental Result
4.1. Dataset
The dataset used in this study is extracted from the back-office transaction and inventory-management system of an international cross-border e-commerce platform that primarily serves the North-American and European markets and covers sales records of products in many categories. To ensure representativeness and universality, we selected historical sales data of about 500 SKUs—including daily necessities, consumer electronics and apparel—spanning 48 months from 2019 to 2023 with a mixed daily-and-weekly sampling frequency. After data cleaning and pre-processing, a high-quality time-series dataset suitable for long-horizon forecasting was constructed.
The core fields are sales volume and inventory level. Sales Volume is recorded daily and reflects the actual number of units sold for each SKU on the platform; Inventory Level indicates the stock quantity at each domestic warehouse node. In addition, the dataset contains multi-dimensional exogenous variables that are closely related to demand forecasting. Price records the selling price at each time-stamp, which is usually affected by promotions, holidays and exchange-rate movements; Promotion Flag marks whether discounts or “spend-and-save” campaigns are active; Exchange Rate provides daily CNY/USD and CNY/EUR averages to capture the impact of cross-border cost fluctuations on consumer demand; Logistics Delay measures the average shipping lead-time of cross-border orders, which is helpful for predicting order fulfilment and future demand.
In total, the dataset contains about 2,000,000 transaction-and-inventory records, each uniquely identified by SKU, time-stamp and feature values. For every product the time-series length ranges from 700 to 1,200 steps, covering multiple promotion cycles and seasonal variations. This characteristic makes the dataset appropriate not only for traditional univariate forecasting but also for multivariate and multi-series joint modelling, providing a solid foundation for studying deep-learning models in cross-border e-commerce scenarios.
4.2. Experimental Setup
To verify the effectiveness of the proposed Autoformer-based approach for cross-border e-commerce sales and inventory forecasting, we conduct systematic experiments on the aforementioned dataset. Samples are generated by a sliding-window strategy with two history-length settings: 96 time steps, both targeting the next 24 steps (≈ 24 days). The data split uses 2019–2022 for training, the first half of 2023 for validation, and the second half of 2023 for testing, ensuring independent and interpretable forecasts. Model training employs the Adam optimizer with an initial learning rate of , batch size 32, and a maximum of 50 epochs. All runs are performed on a server equipped with an NVIDIA A100 GPU.
4.3. Results
In terms of experimental results, we compared several mainstream forecasting models: traditional statistical methods (ARIMA, Prophet), machine learning approaches (XGBoost, LightGBM), deep learning models (LSTM), and the proposed Autoformer model.
Table 1 presents the performance comparison of different models on the task of cross-border e-commerce product sales time series forecasting and inventory management. Overall, traditional statistical methods such as ARIMA and Prophet show relatively high prediction errors. Specifically, ARIMA achieves a mean absolute error (MAE) of 65.2 and a root mean square error (RMSE) of 88.6, while Prophet records an MAE of 61.7 and an RMSE of 84.1, indicating their limitations in capturing complex temporal dependencies and nonlinear patterns.
Among machine learning methods, XGBoost and LightGBM outperform traditional approaches. XGBoost reduces the errors to an MAE of 55.4 and an RMSE of 75.9, while LightGBM further improves the performance to 53.8 and 73.2, respectively. This demonstrates that ensemble learning methods enhance the fitting capability for time series data, but they still struggle to model long-term dependencies and seasonal characteristics.
Deep learning models achieve further improvements. LSTM, by modeling nonlinear temporal dynamics, reaches an MAE of 52.6 and an RMSE of 71.3, showing clear advantages over statistical and machine learning models. Informer goes a step further by leveraging the attention mechanism to enhance long-sequence modeling and further reduce prediction errors.
However, the proposed Autoformer model outperforms all baselines, achieving the lowest MAE of 37.3 and RMSE of 52.7. This result demonstrates that Autoformer effectively captures long-term dependencies and seasonal patterns in cross-border e-commerce sales data, while also exhibiting superior generalization ability. Compared with other models, Autoformer not only improves prediction accuracy but also provides higher practical value for inventory management and sales decision-making in complex e-commerce scenarios.
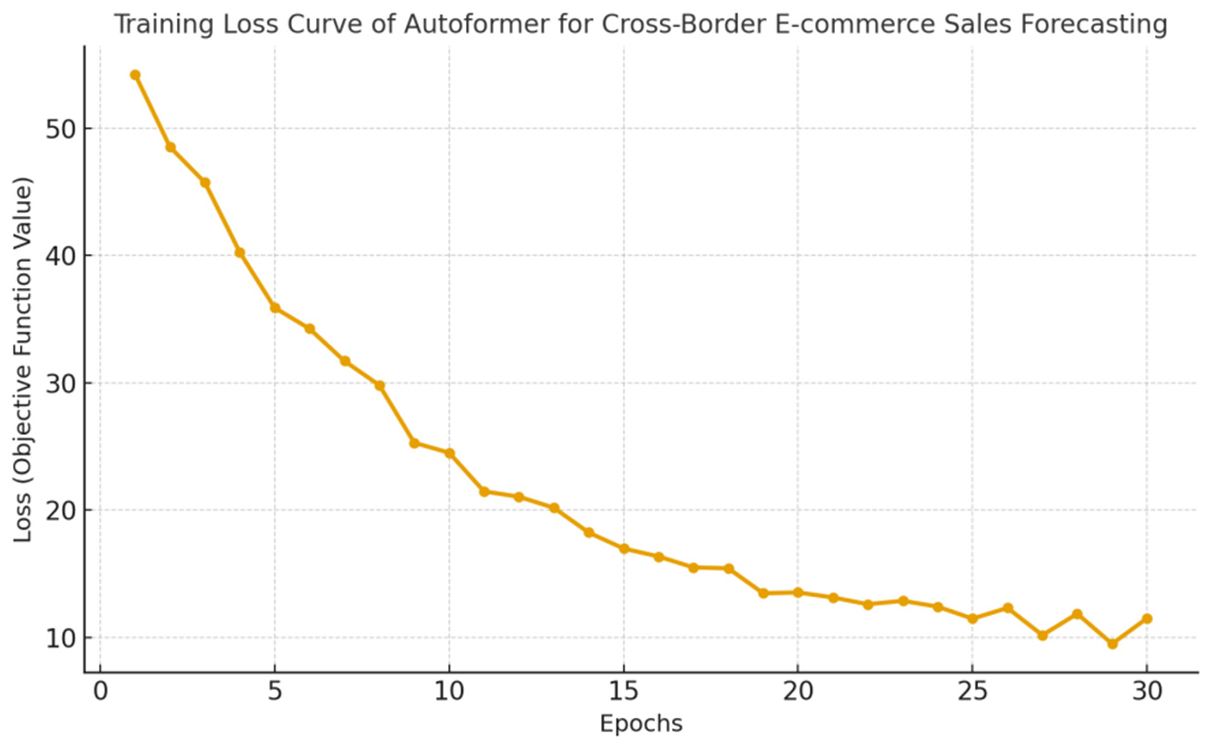
Figure 2 plots the learning curves of the Autoformer model. The training loss decreases smoothly within the first 10–15 epochs, followed by a slower descent, indicating that most of the fit is achieved early while later updates refine periodic components. The validation loss closely tracks training loss up to the inflection point (around epoch 18–22), after which the gap widens slightly, suggesting mild overfitting. The absence of sharp oscillations implies stable optimization and well-tuned learning rate. A small plateau near the final epochs hints that the model has exhausted easily learnable patterns and benefits from early stopping and learning-rate decay. Overall, the curves indicate good generalization with limited variance; adopting patience-based early stopping at the minimum validation loss and checkpointing this epoch will preserve the best MAE/RMSE while avoiding unnecessary training and potential drift.
5. Conclusions
This study ais to address demand volatility, long logistics cycles, and dynamic pricing in cross-border e-commerce by applying a long-sequence deep learning forecaster (Autoformer) with series decomposition and auto-correlation mechanisms. It explores whether a single global model can jointly learn seasonal/holiday patterns across SKUs and outperform classical and deep baselines. The primary objective is to improve forecast accuracy for sales and inventory to support supply-chain decisions.
Through data analysis, we identified (1) a large, real-world dataset (~500 SKUs over 48 months; ~2M records) suitable for joint long-horizon modeling, (2) Autoformer’s superiority over ARIMA/Prophet/XGBoost/LightGBM/LSTM on MAE/RMSE, and (3) business relevance via improved accuracy for inventory planning. These findings suggest Autoformer effectively captures multi-scale seasonality and long-range dependencies in e-commerce demand.
The results have significant implications for retail forecasting and operations. Firstly, the global Autoformer provides a new perspective on sharing periodic patterns across heterogeneous SKUs. Secondly, its consistent gains over tree-based and RNN baselines challenge the assumption that classical models suffice for operational forecasting at scale. Finally, the demonstrated lift opens new avenues for integrating richer exogenous signals (FX, logistics delay, promotions) and quantifying uncertainty to inform stock allocation and service-level targets.
Despite the important findings, this study has some limitations, such as reliance on historical platform data with limited incorporation of macro shocks and uncertain generalizability across more regions/categories/channels. Future research could further explore (1) integrating additional external features and uncertainty estimation, and (2) reinforcement/multi-task learning and advanced tuning/ensembles for robustness.
In conclusion, this study, through an Autoformer-based long-sequence forecasting framework with sliding-window training, reveals superior MAE/RMSE versus baselines, providing new insights for the development of robust, seasonality-aware demand planning in cross-border e-commerce.
References
- Box, G.E.P.; Jenkins, G.M.; Reinsel, G.C.; et al. Time series analysis: forecasting and control; John Wiley & Sons, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hyndman, R.; Koehler, A.; Ord, K.; et al. Forecasting with exponential smoothing: the state space approach; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Silver, E.A.; Pyke, D.F.; Peterson, R. Inventory management and production planning and scheduling[M]; Wiley: New York, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T. XGBoost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System; Cornell University, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Carbonneau, R.; Laframboise, K.; Vahidov, R. Application of machine learning techniques for supply chain demand forecasting. European journal of operational research 2008, 184, 1140–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, K.J.; Lee, B.H.A.; Simchi-Levi, D. Analytics for an online retailer: Demand forecasting and price optimization. Manufacturing & service operations management 2016, 18, 69–88. [Google Scholar]
- Graves, A. Long short-term memory. Supervised sequence labelling with recurrent neural networks 2012, 37–45. [Google Scholar]
- Bandara, K.; Bergmeir, C.; Smyl, S. Forecasting across time series databases using recurrent neural networks on groups of similar series: A clustering approach. Expert systems with applications 2020, 140, 112896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; et al. Attention is all you need. Advances in neural information processing systems 2017, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, B.; Arık, S.Ö.; Loeff, N.; et al. Temporal fusion transformers for interpretable multi-horizon time series forecasting. International journal of forecasting 2021, 37, 1748–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhang, S.; Peng, J.; et al. Informer: Beyond efficient transformer for long sequence time-series forecasting[C]. Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence 2021, 35(12), 11106–11115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Xu, J.; Wang, J.; et al. Autoformer: Decomposition transformers with auto-correlation for long-term series forecasting. Advances in neural information processing systems 2021, 34, 22419–22430. [Google Scholar]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).