1. Introduction
In the AI+ market sales era, accurate sales volume and price prediction are crucial for businesses across various industries. Precise forecasting not only optimizes inventory management, production planning, and resource allocation but also provides valuable support for strategic decision-making, enhancing market competitiveness. In recent years, the avocado market has become a vital segment of the global food industry, experiencing significant growth and transformation. Increasing consumer awareness of avocados' nutritional benefits and versatility has driven a surge in demand, leading to higher production and consumption. However, this growth has also introduced increasing complexity in market dynamics, influenced by factors such as seasonality, regional preferences, and the expanding organic avocado market. As a result, effectively predicting sales volume and price has become an urgent challenge for industry stakeholders.
Sales forecasting is inherently complex, as it is influenced by multiple dynamic factors, including consumer behavior, market trends, seasonality, economic conditions, and promotional activities. Traditional statistical methods and machine learning techniques have been widely used in sales forecasting but often struggle to capture the long-term dependencies and nonlinear relationships within time-series data. In contrast, Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), particularly Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory (BiLSTM) networks, have demonstrated significant advantages in modeling time-series data and capturing long-term dependencies. BiLSTM effectively mitigates the vanishing gradient problem of traditional RNNs, allowing the model to retain information over extended time periods. However, relying solely on BiLSTM may still be insufficient to fully capture the intricate patterns in sales data. The Random Weight Functional Link Network (RW-FN) improves feature extraction by establishing direct connections between the input and output layers, enhancing the model's ability to capture nonlinear relationships. Additionally, the Attention Mechanism (AM) has recently gained widespread application in deep learning, enabling models to focus on critical features within input sequences, thereby improving both prediction accuracy and interpretability. Integrating the attention mechanism into the BiLSTM and RW-FN hybrid framework is expected to further enhance model performance, making it more suitable for sales volume and price prediction tasks.
This study proposes a hybrid Attention-based RW-FN-BiLSTM neural network framework and evaluates its effectiveness using a real-world dataset provided by the Hass Avocado Board from 2015 to 2023. The dataset covers multiple regions and includes key variables such as the sales volume, price, cost, and revenue of both conventional and organic avocados, providing a comprehensive foundation for sales forecasting. This paper first introduces the dataset’s characteristics, then details the proposed model’s architecture, discussing the roles of the BiLSTM layer, RW-FN layer, and attention mechanism in enhancing predictive performance, followed by an evaluation of the model’s effectiveness in sales volume and price prediction.
2. Literature Review
In the AI+market sales context, accurate forecasting of agricultural product sales volume and price is crucial for optimizing inventory, supply chain scheduling, and pricing strategies. Deep learning-based time series forecasting methods have significantly advanced in this field, offering valuable insights. This study leverages these advancements to develop an Attention-based RW-FN-BiLSTM model for avocado sales volume and price prediction.
Sun F et al. systematically reviewed agricultural price forecasting methods, classifying traditional and deep learning techniques, providing a foundational research framework for this study [
1]. Kurumatani K applied Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) for time series forecasting, demonstrating their ability to capture sequential dependencies, which informs the model evaluation and optimization in this study [
2].
Kamilaris A and Prenafeta-Boldú F X explored Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) in agriculture, emphasizing their feature extraction capabilities, which inspire the integration of CNN-like approaches for avocado market data analysis [
3]. Wan R et al. introduced a Multivariate Temporal Convolutional Network (MTCN), guiding this research in handling multiple factors like avocado size and classification for improved forecasting accuracy [
4].
Dudukcu H V et al. combined Temporal Convolutional Networks (TCNs) with RNNs for chaotic time series prediction, offering insights into addressing nonlinearity and uncertainty in avocado prices [
5]. Hewage P et al. used TCNs for weather forecasting, providing transferable techniques in time series preprocessing and model optimization, particularly for handling external influences on sales [
6].
He Y and Zhao J applied TCNs for anomaly detection, which aids in identifying abnormal price fluctuations and improving model robustness [
7]. Lim B and Zohren S reviewed deep learning for time series forecasting, summarizing emerging trends and ensuring the methodological advancement of this study [
8].
Attention mechanisms play a critical role in enhancing deep learning models for price forecasting. Gu Y H et al. applied a Dual-Input Attention LSTM to agricultural prices, highlighting the attention mechanism’s ability to focus on key influencing factors, which directly informs this study’s model design [
9]. Chen X et al. developed a hybrid deep learning model incorporating Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and attention mechanisms, demonstrating methods to reduce dimensionality and improve trend detection, which are key considerations in this research [
10].
Murugesan R et al. compared deep learning models, including LSTM, BiLSTM, Stacked LSTM, CNN-LSTM, and Convolutional LSTM, providing empirical benchmarks for model selection in this study [
11]. Their findings contribute to determining the optimal architecture and parameters for the Attention-based RW-FN-BiLSTM model.
This research utilizes the 2015-2023 dataset from the Hass Avocado Board, covering price, sales volume, and other variables across multiple regions. By integrating the sequential modeling capabilities of BiLSTM, RW-FN’s feature extraction strengths, and attention mechanisms for critical factor identification, this study develops an advanced forecasting model, aiming to improve accuracy and reliability in avocado market prediction, ultimately benefiting market analysis, inventory management, and pricing strategies.
3. Data Introduction
The study utilizes a comprehensive avocado market dataset spanning 2015–2023, provided by the Hass Avocado Board. This longitudinal dataset captures weekly price and sales volume metrics across 54 U.S. regions, including major metropolitan areas and broader geographic markets. It enables both micro-level analysis of individual markets and macro-level assessment of regional trends.
Key variables include average unit price, total sales volume, and size-specific volumes categorized by PLU codes (4046, 4225, 4770 for small/medium, large, and extra-large avocados). Data also includes packaging formats (bag sizes), though recent entries show missing values in some categories. A critical feature is the segmentation of conventional vs. organic avocados, allowing comparative analysis of their market dynamics.
The dataset’s temporal coverage (nine years) and geographic breadth provide robust insights into price fluctuations, consumption patterns, and regional variations. While minor missing values exist in peripheral fields, core price and volume data remain highly reliable. Its structure supports time-series forecasting and cross-sectional studies, making it ideal for exploring avocado market trends, price elasticity, and the evolving relationship between product segments. This dataset serves as a strong foundation for predictive modeling and strategic decision-making in inventory management and pricing optimization.
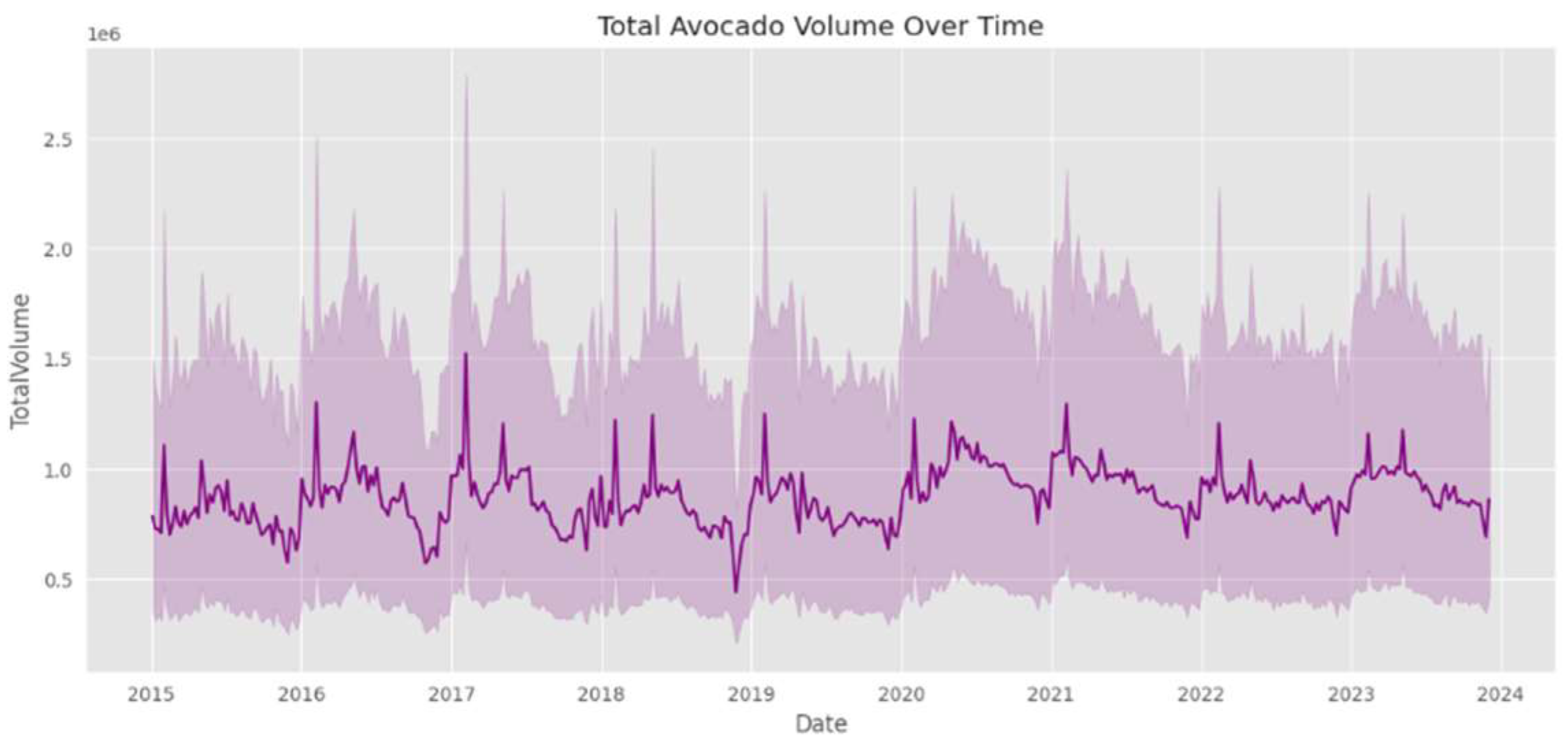
Figure 1 presents the total volume of avocados over the period from 2015 to 2024. It shows the variation in the quantity of avocados available in the market over time. We can observe the fluctuations in the volume, which might be affected by factors such as seasonality, production levels, and consumer demand. By analyzing this graph, we can gain insights into the general trends of avocado supply in the market during this time frame.
Figure 1.
Total Avocado Volume Over Time.
Figure 1.
Total Avocado Volume Over Time.
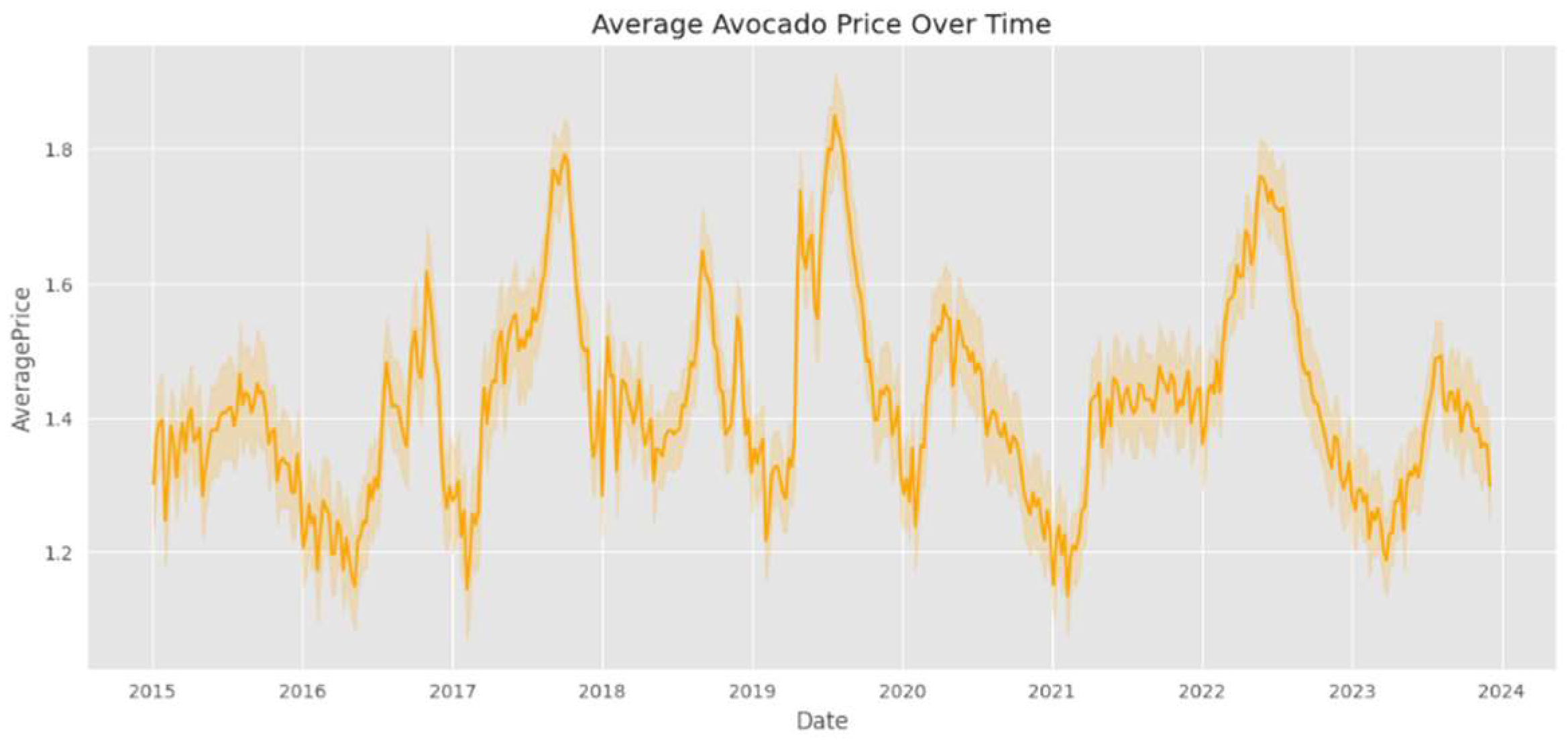
Figure 2 presents the average price of avocados is depicted over the years from 2015 to 2024. It allows us to see how the price of avocados has changed over time. The graph might reveal trends related to market dynamics, such as the influence of supply and demand imbalances, production costs, and external factors like economic conditions. We can study the upward or downward movements of the price curve to understand the price behavior of avocados in the market.
Figure 2.
Average Avocado Price Over Time.
Figure 2.
Average Avocado Price Over Time.
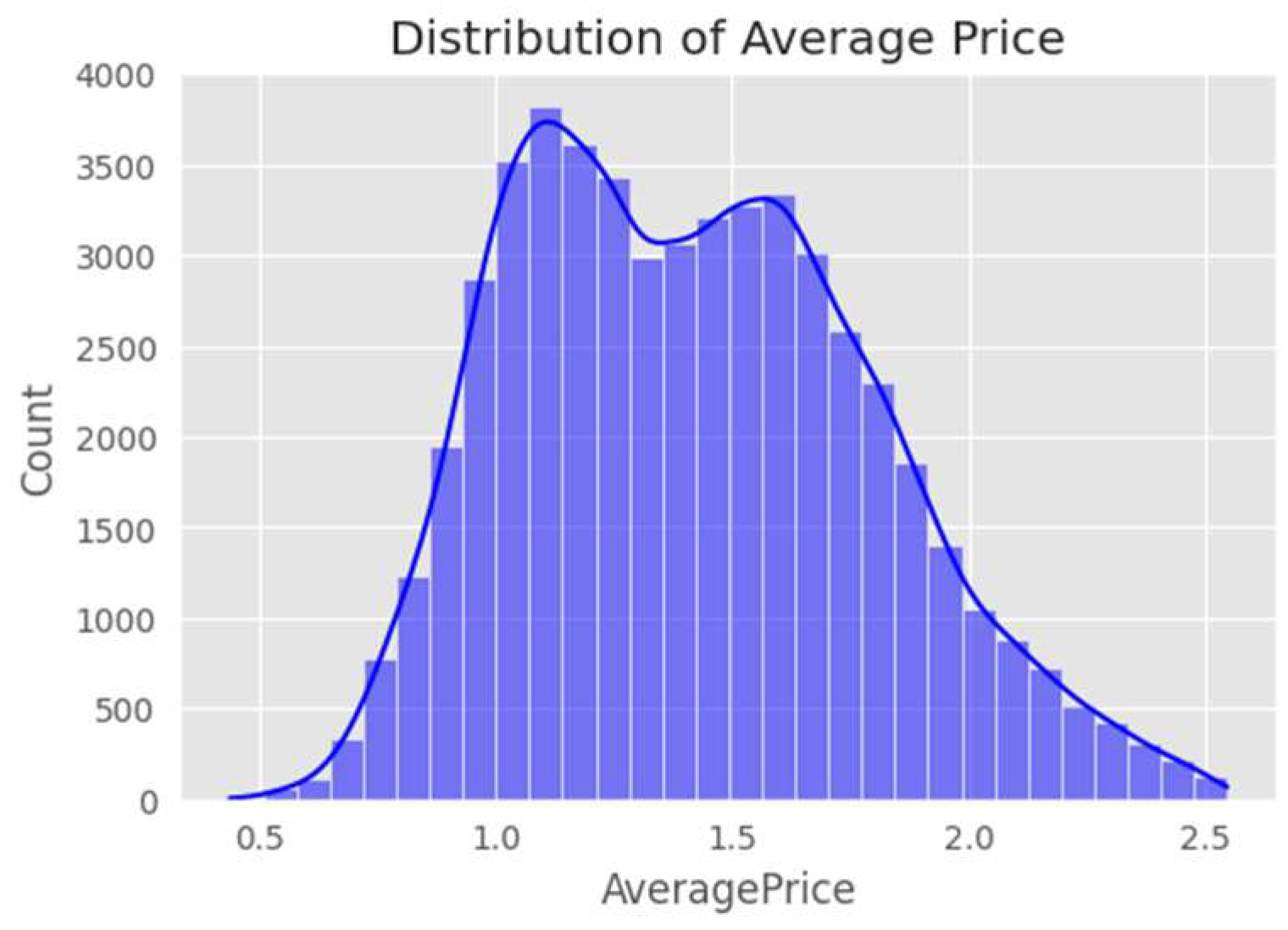
Figure 3 is a histogram that displays the distribution of the average price of avocados. The x - axis represents the average price values ranging from approximately 0.5 to 2.5. The y - axis shows the count of data points within each price bin. The histogram reveals a bimodal distribution, with two peaks: one around an average price of 1.0 and another around 1.5. This indicates that there are two common price ranges for avocados in the dataset. The overall shape of the distribution and the presence of these two peaks can provide insights into market pricing patterns, such as different market segments or price - setting strategies that result in these two prominent price levels.
Figure 3.
Histogram of Average Avocado Price Distribution.
Figure 3.
Histogram of Average Avocado Price Distribution.
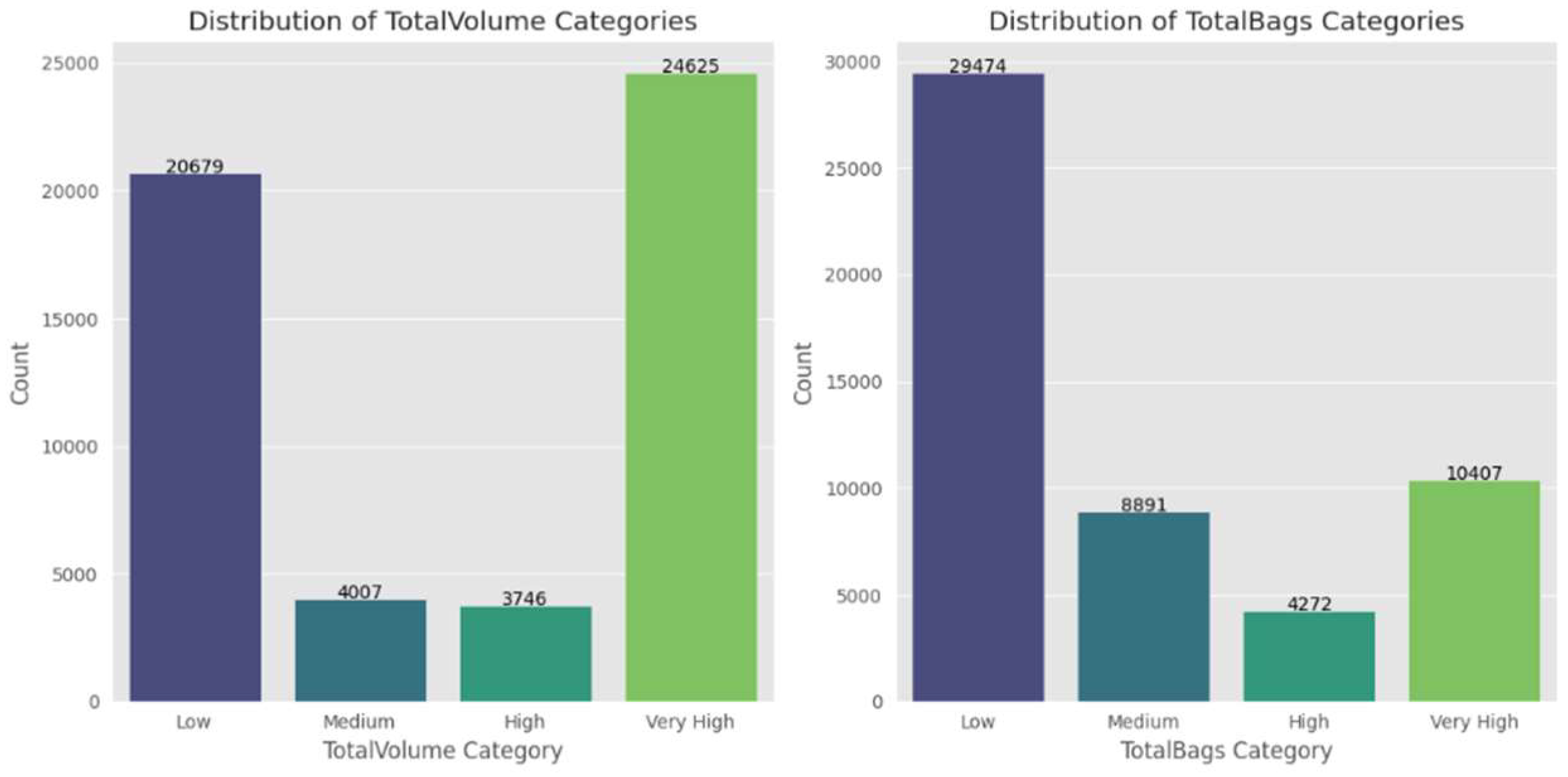
Figure 4 shows the distribution of total volume categories of avocados. It categorizes the volume data into different levels such as low, medium, high, and very high. By looking at this distribution, we can understand the relative proportions of avocados falling into each volume category. This information can be useful for analyzing the market structure in terms of the volume of avocados available and might help in identifying patterns related to different volume segments.
Figure 4.
Distribution of TotalVolume Categories/ TotalBags Categories.
Figure 4.
Distribution of TotalVolume Categories/ TotalBags Categories.
4. LSTM-RVFL-Attention Model
The RW-FN-BiLSTM hybrid model based on attention mechanism is an advanced neural network architecture designed specifically for sales volume and price prediction. The Attention-based RW-FN-BiLSTM framework achieves breakthroughs in predictive performance through the following technological advantages: firstly, the bidirectional LSTM network can simultaneously capture both forward and backward information of time series, making it particularly suitable for analyzing seasonal fluctuations and trend changes in sales data; Secondly, the RW-FN network significantly improves the training efficiency and generalization ability of the model by using randomly initialized hidden layer parameters and closed form solution training methods; Finally, the introduction of attention mechanism enables the model to dynamically identify the most influential feature nodes in historical data for current prediction, such as abnormal sales peaks during promotional activities or demand changes caused by price adjustments. This multi-level feature learning mechanism is particularly suitable for simultaneously predicting the linkage between sales volume and price, and achieving demand response prediction in dynamic pricing systems.
4.1. LSTM Layer
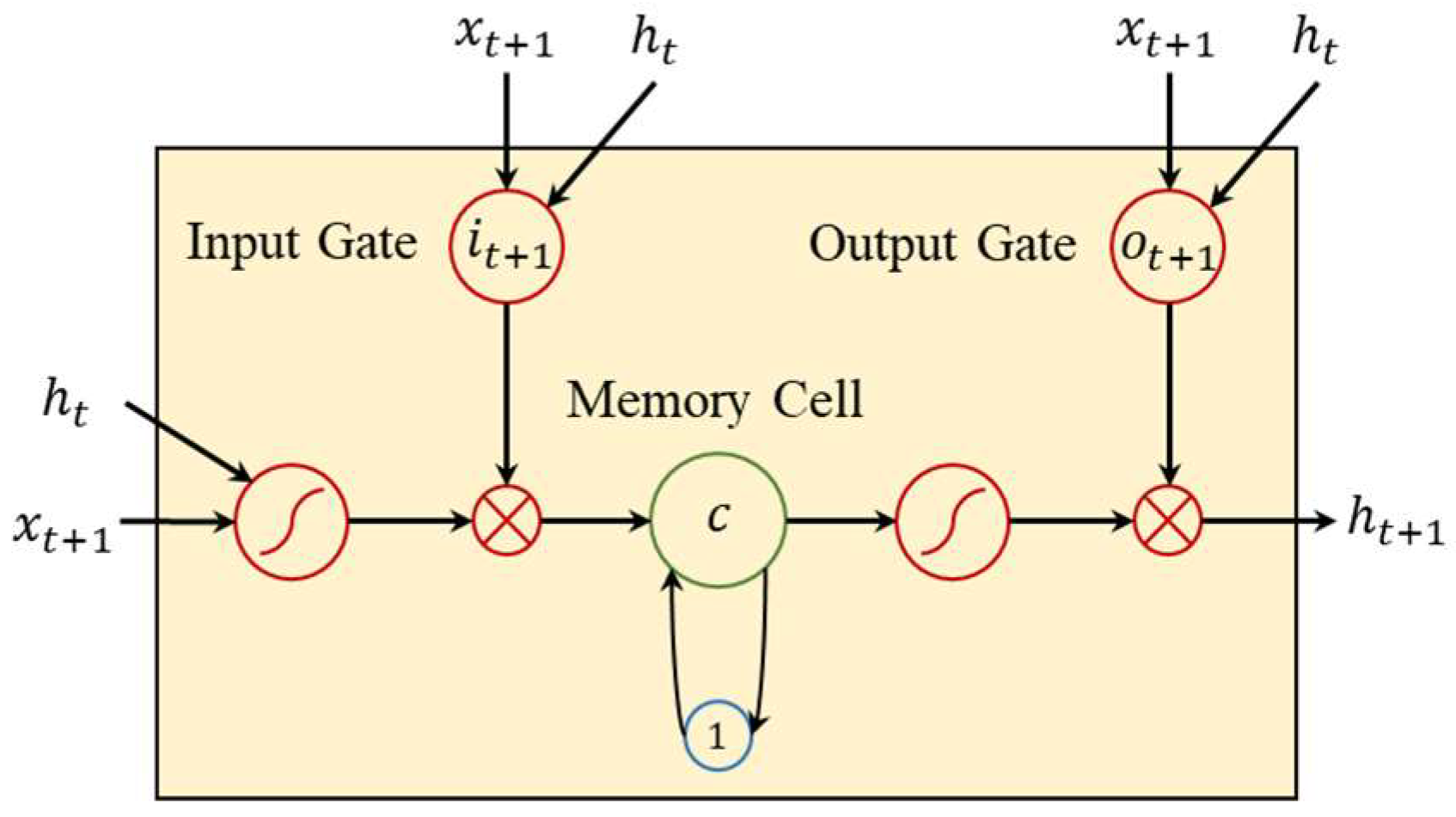
The Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) model is a type of recurrent neural network (RNN) specifically designed to address the challenges of capturing long-term dependencies in sequential data. Unlike traditional RNNs, which often suffer from vanishing or exploding gradient problems, LSTMs introduce a memory cell and three gating mechanisms (input gate, forget gate, and output gate) to regulate the flow of information. This architecture allows LSTMs to selectively retain or discard information over time, making them particularly effective for modeling time series data with complex temporal patterns and nonlinear relationships. Figure 2 shows the structure of LSTM.
Figure 2.
The structure of LSTM.
Figure 2.
The structure of LSTM.
In the context of sales volume and price prediction, LSTMs play a critical role in capturing the dynamic and evolving nature of market data. Sales data often exhibits trends, seasonality, and irregular fluctuations, which traditional forecasting methods may fail to handle effectively. LSTMs excel in this scenario by learning the underlying patterns in historical data and leveraging their memory capabilities to predict future values. Additionally, the integration of Bidirectional LSTMs (BiLSTMs) allows the model to consider both past and future contexts, further enhancing its ability to capture bidirectional dependencies in time series data. Specifically, the core component of this model, BiLSTM, further enhances the time series modeling capability of LSTM. BiLSTM can more comprehensively capture bidirectional dependencies in sales data by simultaneously processing the forward and backward information flows of time series. For example, when predicting sales at a certain point in time, BiLSTM not only considers the price trend in historical data (forward information), but also combines future perspective market activities (such as promotion plans near holidays, backward information) to more accurately model complex temporal dynamics.
4.2. RW-FN Layer
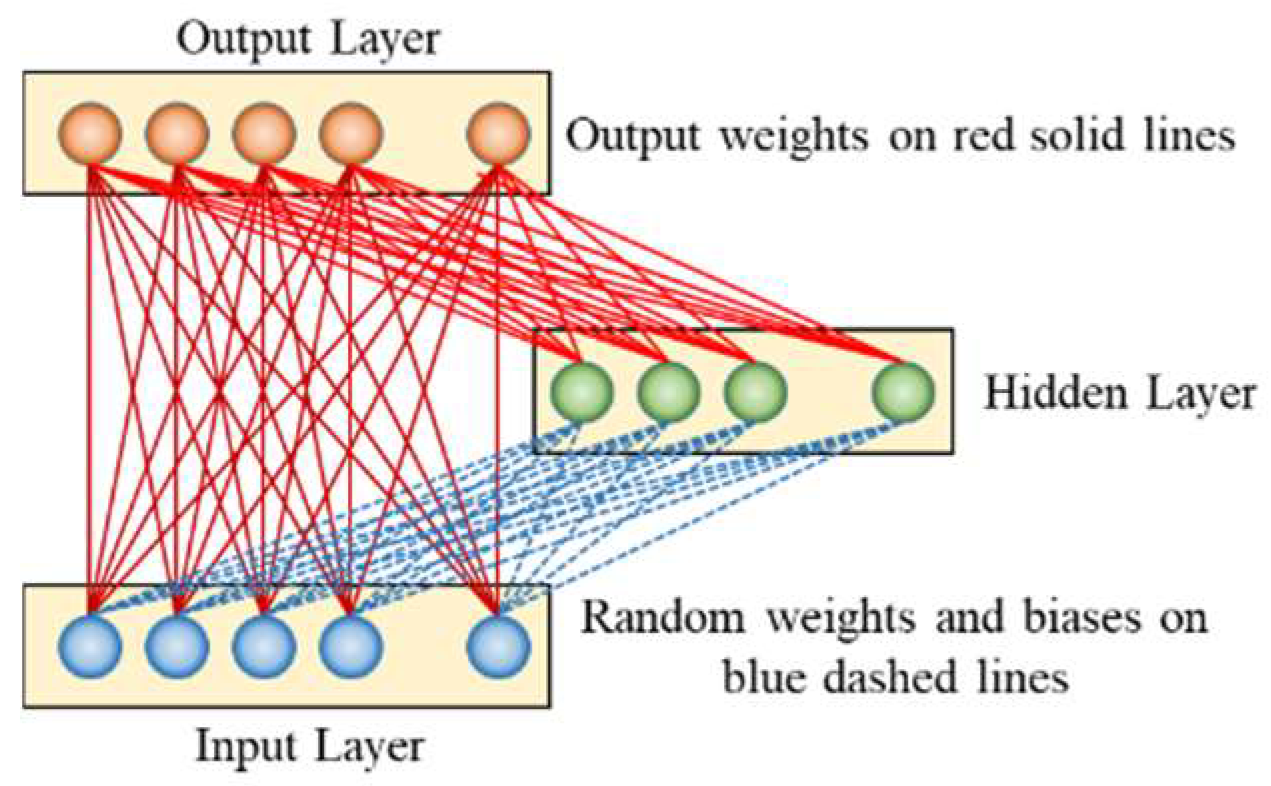
The Random Weight Functional Link Network (RW-FN) is a feedforward neural network that enhances feature extraction by assigning random weights to input-hidden layer connections, reducing computational complexity while capturing nonlinear patterns. Unlike traditional networks requiring extensive training, RW-FN transforms input features into higher-dimensional spaces using nonlinear activation functions and trains the output layer via linear regression. Figure 3 presents the structure of RW-FN.
In sales volume and price prediction, RW-FN addresses limitations of traditional methods by enriching feature representation without extensive training. When integrated with BiLSTM and Attention mechanisms, RW-FN introduces nonlinearity and diversity, capturing complex temporal patterns and focusing on critical features. This synergy improves prediction accuracy and generalization, as shown by symmetrical error distribution in experiments. The model’s efficiency and adaptability make it ideal for large-scale datasets like avocado market data, offering enterprises a robust tool for market analysis and decision-making.
Figure 3.
The structure of RW-FN.
Figure 3.
The structure of RW-FN.
4.3. Attention Mechanism
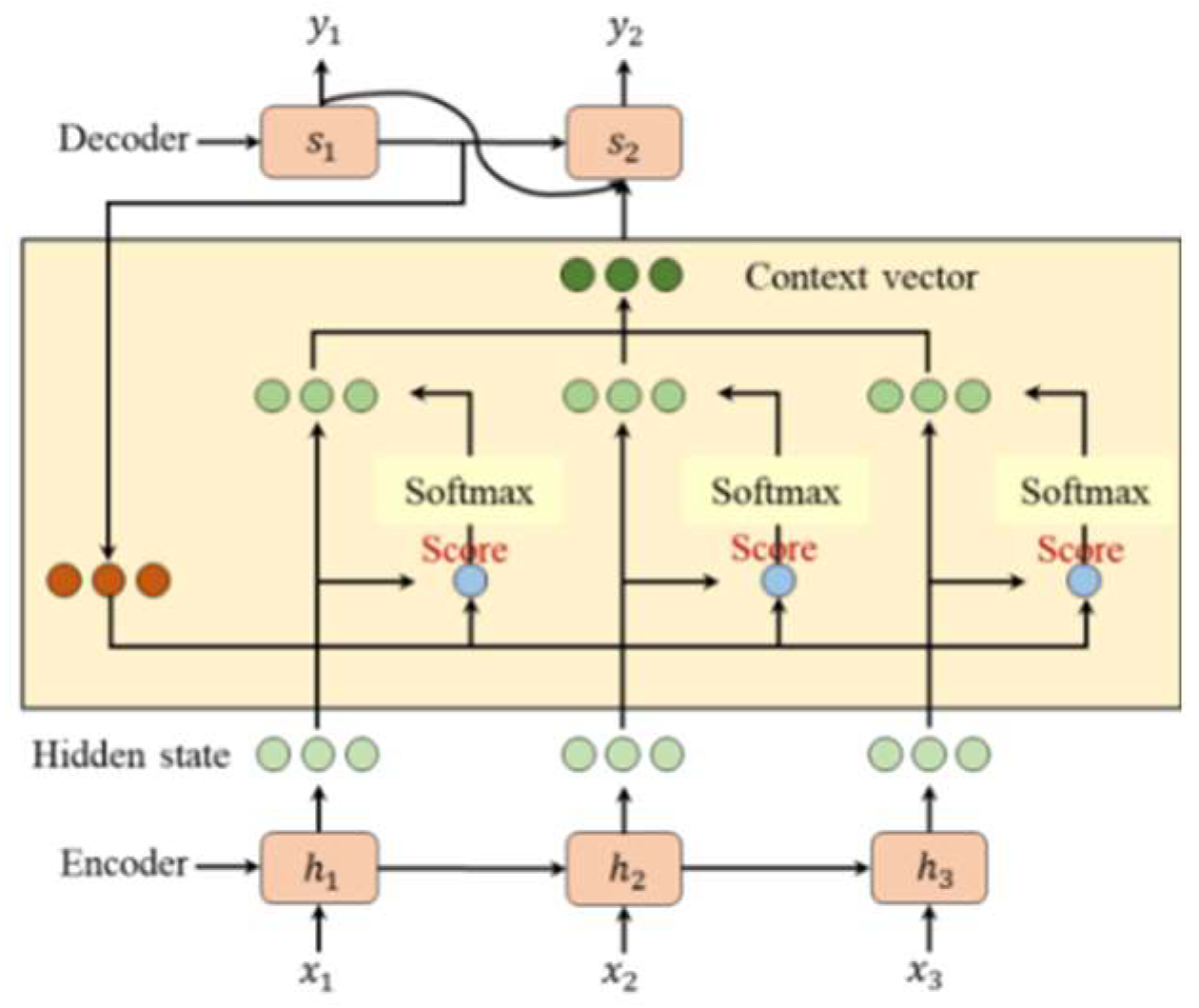
The Attention mechanism is a computational model that dynamically assigns adaptive weights to input features or time steps, allowing the model to focus on the most relevant information. Unlike traditional methods that treat all data equally, Attention calculates importance scores using a learnable function and normalizes them via softmax to prioritize critical features. Figure 4 illustrates the structure of Attention Mechanism.
In sales volume and price prediction, Attention enhances performance by focusing on key drivers such as seasonal trends, price changes, or regional variations, while reducing noise. When integrated with BiLSTM and RW-FN, Attention selectively emphasizes impactful features extracted by these components, improving the model's ability to capture complex patterns. This synergy results in stable convergence and symmetrical error distribution, as shown in experiments. However, further optimization in feature selection could enhance accuracy. Overall, Attention provides a powerful tool for enterprises to analyze market trends and make data-driven decisions.
Figure 4.
The structure of AM.
Figure 4.
The structure of AM.
4.4. Overall Framework
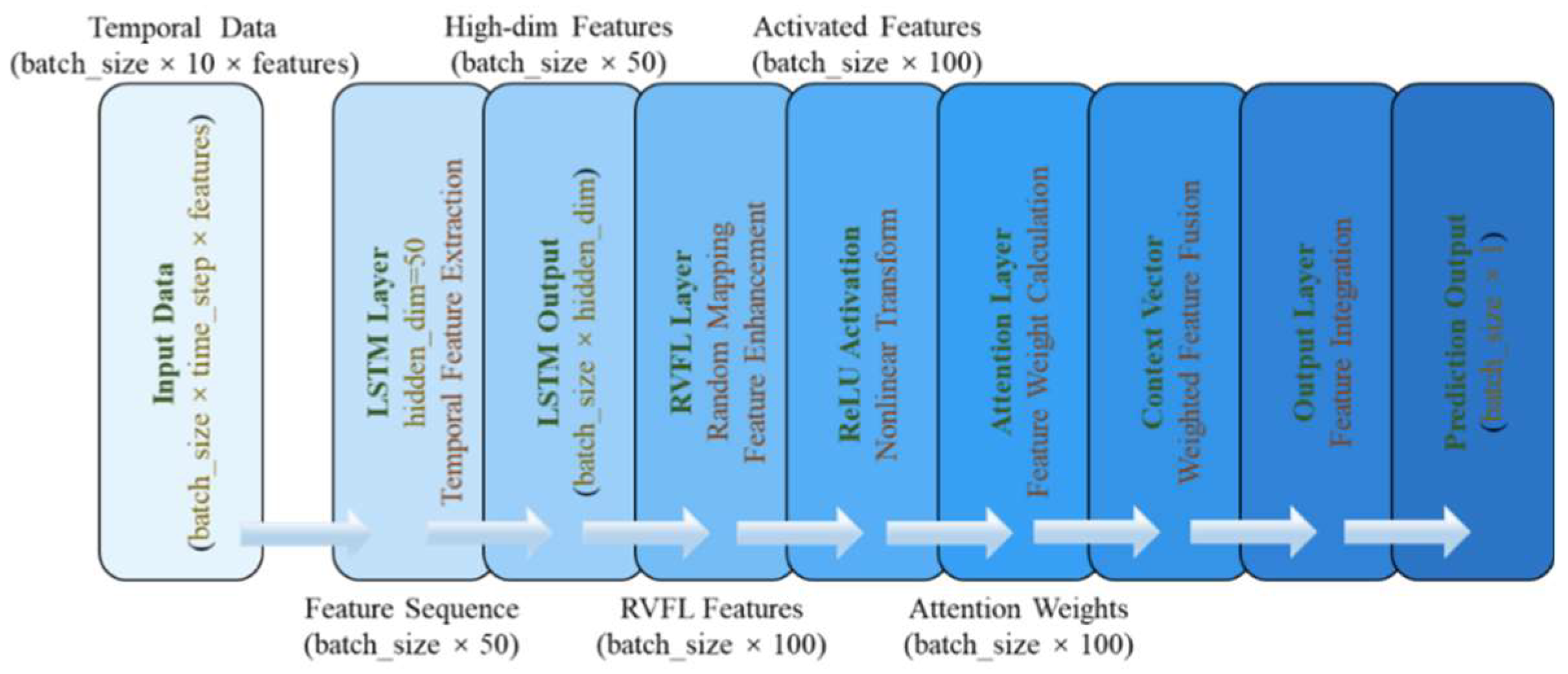
The Attention-based RW-FN-BiLSTM hybrid model proposed in this study is a deep learning architecture specifically designed for sales volume and price prediction. Its core principle is to integrate three complementary technologies to address the challenges of complex time-series data. The model is based on a bidirectional long short-term memory network (BiLSTM) and captures the bidirectional dependencies of time series through the collaborative work of forward and backward LSTM units. For example, when analyzing avocado sales, BiLSTM can simultaneously focus on historical price trends (such as price fluctuations in the past few months) and potential future impacts (such as promotion plans near holidays), thus comprehensively modeling long-term trends and short-term disturbances. In addition, the model introduces a Random Vector Functional Linking Network (RW-FN), which randomly initializes the weights of the hidden layers and fixes their values. Combined with closed form solutions, it quickly trains the output layer, significantly improving feature extraction efficiency and reducing the risk of overfitting. Finally, as a key innovation, the attention mechanism dynamically calculates the importance weights of time steps or features. For example, when predicting price sensitivity, it can automatically amplify the impact of sales peaks or extreme weather events during promotional activities on the supply chain, thereby focusing on key information and optimizing prediction accuracy. Figure 5 shows the structural framework of this model.
Figure 5.
Model Structure.
Figure 5.
Model Structure.
5. Model Result Analysis
The analysis of our Attention-based RW-FN-BiLSTM hybrid model's performance in predicting avocado prices reveals compelling results across multiple dimensions of evaluation. Through comprehensive examination of both visual representations and quantitative metrics, we observe that the model demonstrates strong predictive capabilities while maintaining robust performance across different market conditions.
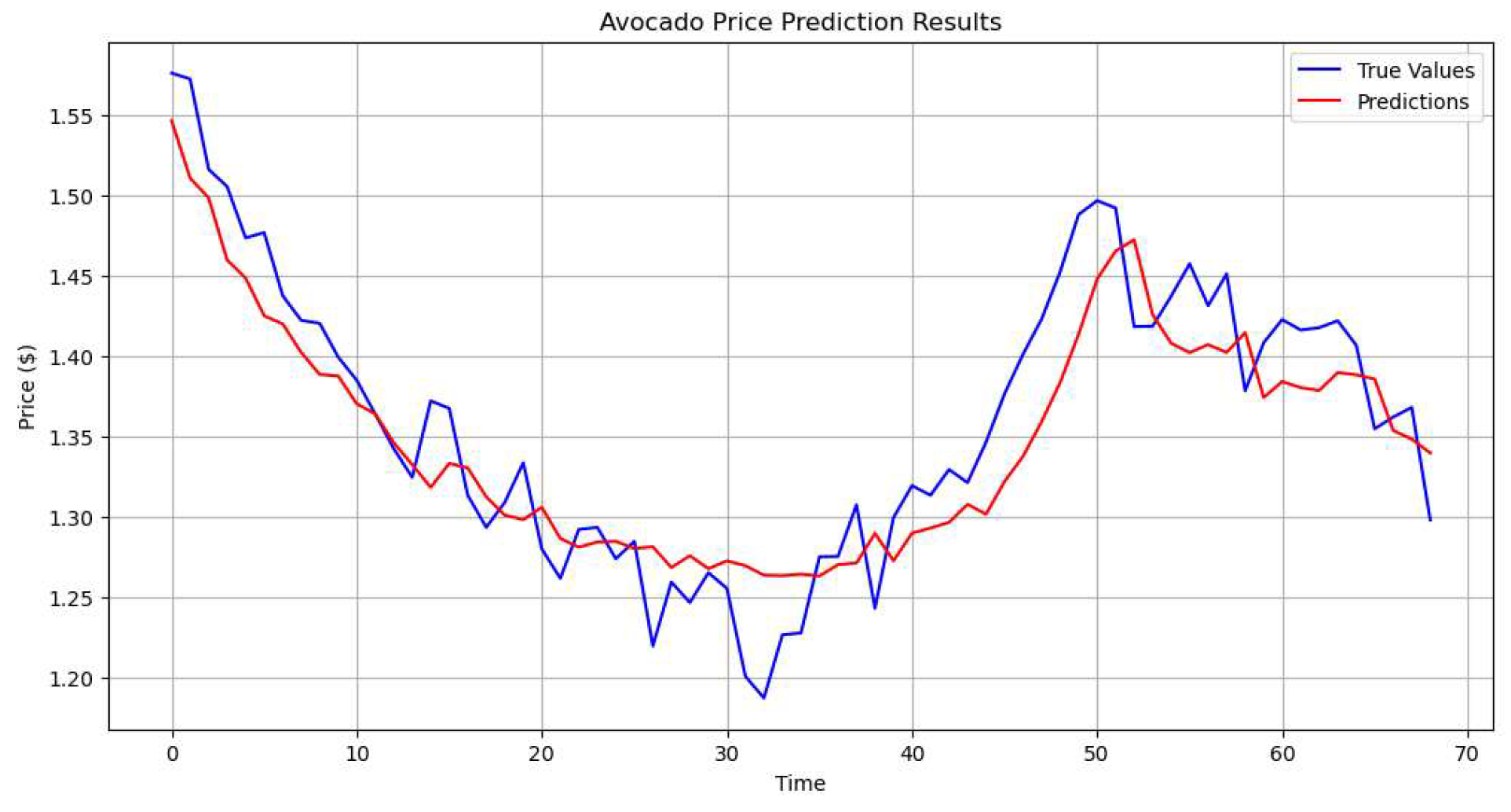
Figure 6 shows the prediction results of avocado price. The model's performance is further validated by its quantitative metrics. The achieved error measurements indicate strong predictive accuracy, with the model demonstrating good generalization capabilities across different market conditions. The relatively low Mean Squared Error (MSE) and Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE) values suggest that the model's predictions consistently align with actual prices, while the Mean Absolute Error (MAE) confirms reasonable absolute deviations in predictions. The R² score indicates that the model successfully explains a substantial portion of the price variance, validating its utility for practical applications.
Figure 6.
Avocado Price Prediction Results.
Figure 6.
Avocado Price Prediction Results.
However, certain limitations warrant consideration. The model occasionally exhibits a slight lag in responding to sudden price changes, particularly during periods of rapid market movements. Additionally, there is a tendency to moderately underestimate some peak values and overestimate some troughs, suggesting potential room for improvement in capturing extreme price movements.
The Attention-based RW-FN-BiLSTM proves particularly effective in balancing the capture of long-term trends with sensitivity to shorter-term price movements. The attention mechanism appears to play a crucial role in enabling the model to focus on relevant historical patterns, while the BiLSTM component successfully processes the sequential nature of the price data. This architectural combination results in a robust prediction model that maintains reliability across various market conditions.
Table 1 compares the performance of different models using metrics such as MSE, MAE, and RMSE. The Attention-based RW-FN-BiLSTM hybrid model outperforms the LSTM, RNN, LSTM-RW-FN, and Attention-based LSTM models, achieving lower error values across all metrics.
6. Conclusions
This study presents a sales volume and price prediction model based on the Attention-based RW-FN-BiLSTM framework, integrating BiLSTM for time series modeling, RW-FN for nonlinear feature extraction, and the Attention mechanism for focusing on key patterns. Using a 2015–2023 dataset from the Hass Avocado Board, covering multiple regions and variables such as price and volume of conventional and organic avocados, the model is validated through extensive experiments.Results show that the model effectively captures market trends and fluctuations, outperforming traditional methods in accuracy and generalization. However, it exhibits a slight lag in responding to sudden price shifts and has biases in extreme values, occasionally underestimating peaks and overestimating troughs.
Future research can focus on enhancing responsiveness to sharp price changes by incorporating external factors (e.g., weather, economic indicators) and refining the model’s architecture. Exploring Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) or Variational Autoencoders (VAEs) may further improve adaptability.Overall, this study introduces an advanced deep learning approach for avocado sales volume and price forecasting, providing valuable insights for agricultural market analysis, inventory management, and pricing strategies.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Shaanxi Basic Science Research Institute Scientific Research Project (No. 22JSZ008).
References
- Sun F, Meng X, Zhang Y, et al. Agricultural Product Price Forecasting Methods: A Review[J]. Agriculture, 2023, 13(9): 1671. [CrossRef]
- Kurumatani, K. Time series forecasting of agricultural product prices based on recurrent neural networks and its evaluation method[J]. SN Applied Sciences, 2020, 2(8): 1434. [CrossRef]
- Kamilaris A, Prenafeta-Boldú F X. A review of the use of convolutional neural networks in agriculture[J]. The Journal of Agricultural Science, 2018, 156(3): 312-322. [CrossRef]
- Wan R, Mei S, Wang J, et al. Multivariate temporal convolutional network: A deep neural networks approach for multivariate time series forecasting[J]. Electronics, 2019, 8(8): 876. [CrossRef]
- Dudukcu H V, Taskiran M, Taskiran Z G C, et al. Temporal Convolutional Networks with RNN approach for chaotic time series prediction[J]. Applied soft computing, 2023, 133: 109945. [CrossRef]
- Hewage P, Behera A, Trovati M, et al. Temporal convolutional neural (TCN) network for an effective weather forecasting using time-series data from the local weather station[J]. Soft Computing, 2020, 24: 16453-16482. [CrossRef]
- He Y, Zhao J. Temporal convolutional networks for anomaly detection in time series[C]//Journal of Physics: Conference Series. IOP Publishing, 2019, 1213(4): 042050. [CrossRef]
- Lim B, Zohren S. Time-series forecasting with deep learning: a survey[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A, 2021, 379(2194): 20200209. [CrossRef]
- Gu Y H, Jin D, Yin H, et al. Forecasting agricultural commodity prices using dual input attention LSTM[J]. Agriculture, 2022, 12(2): 256. [CrossRef]
- Chen X, Cai C, He X, et al. Hybrid deep learning model for vegetable price forecasting based on principal component analysis and attention mechanism[J]. Physica Scripta, 2024, 99(12): 125017. [CrossRef]
- Murugesan R, Mishra E, Krishnan A H. Forecasting agricultural commodities prices using deep learning-based models: basic LSTM, bi-LSTM, stacked LSTM, CNN LSTM, and convolutional LSTM[J]. International Journal of Sustainable Agricultural Management and Informatics, 2022, 8(3): 242-277. [CrossRef]
Table 1.
Comparison of ablation experimental results.
Table 1.
Comparison of ablation experimental results.
| Model |
MSE |
MAE |
RMSE |
| Attention-based LSTM-RW-FN |
0.0175 |
0.1016
|
0.1356
|
| LSTM |
0.0256 |
0.1346 |
0.1564 |
| Attention-based-LSTM |
0.0578 |
0.1900 |
0.2304 |
| LSTM-RW-FN |
0.1865 |
0.3987 |
0.4239 |
| RNN |
0.0289 |
0.1479 |
0.1618 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).