Submitted:
19 December 2025
Posted:
19 December 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
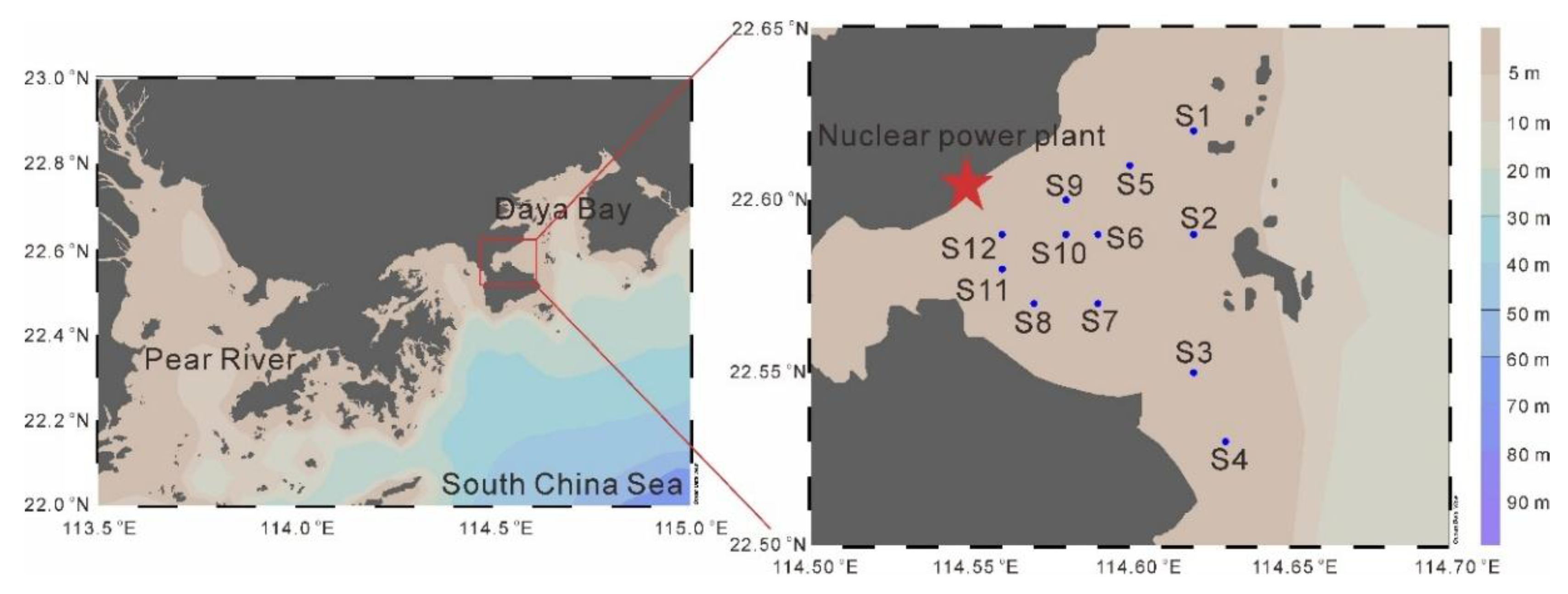
2.1. Study Area and Time
2.2. Field Sampling and Trawling
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Environmental Parameters
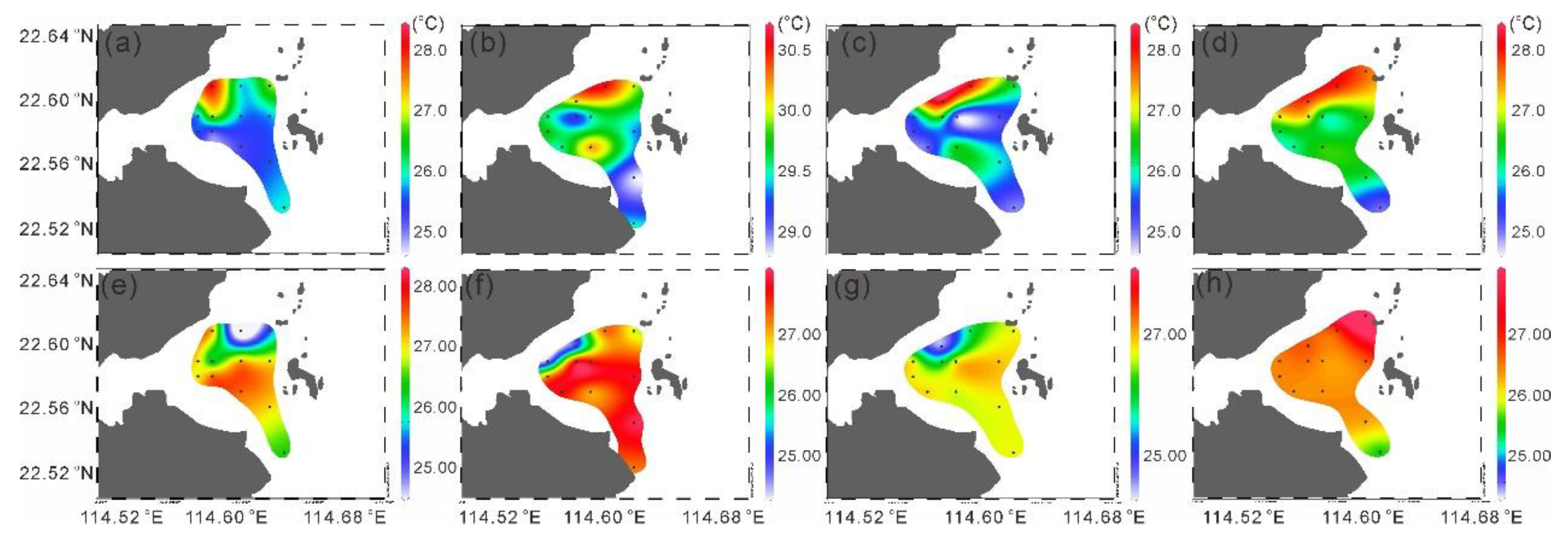
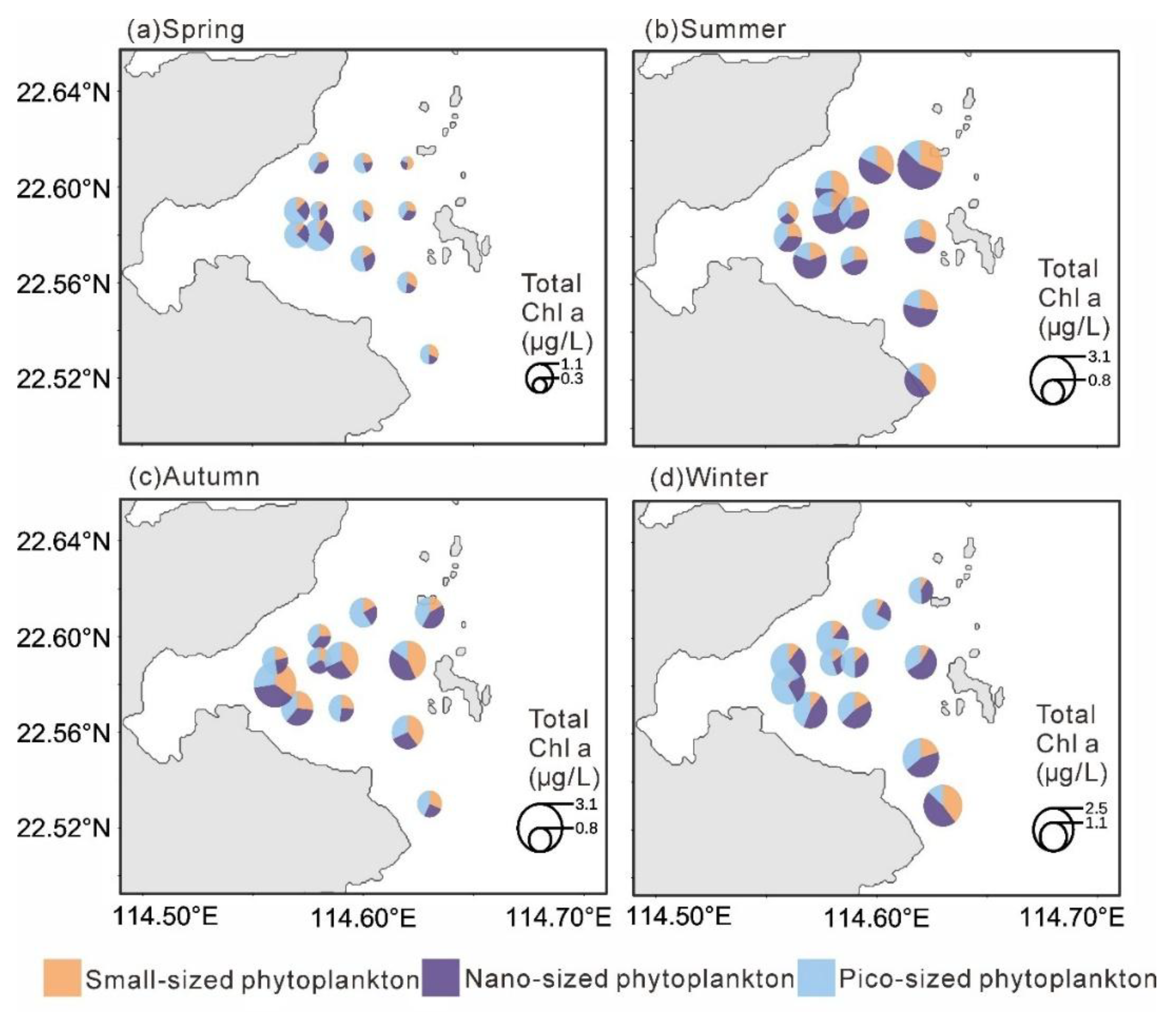
3.2. Mesozooplankton Community
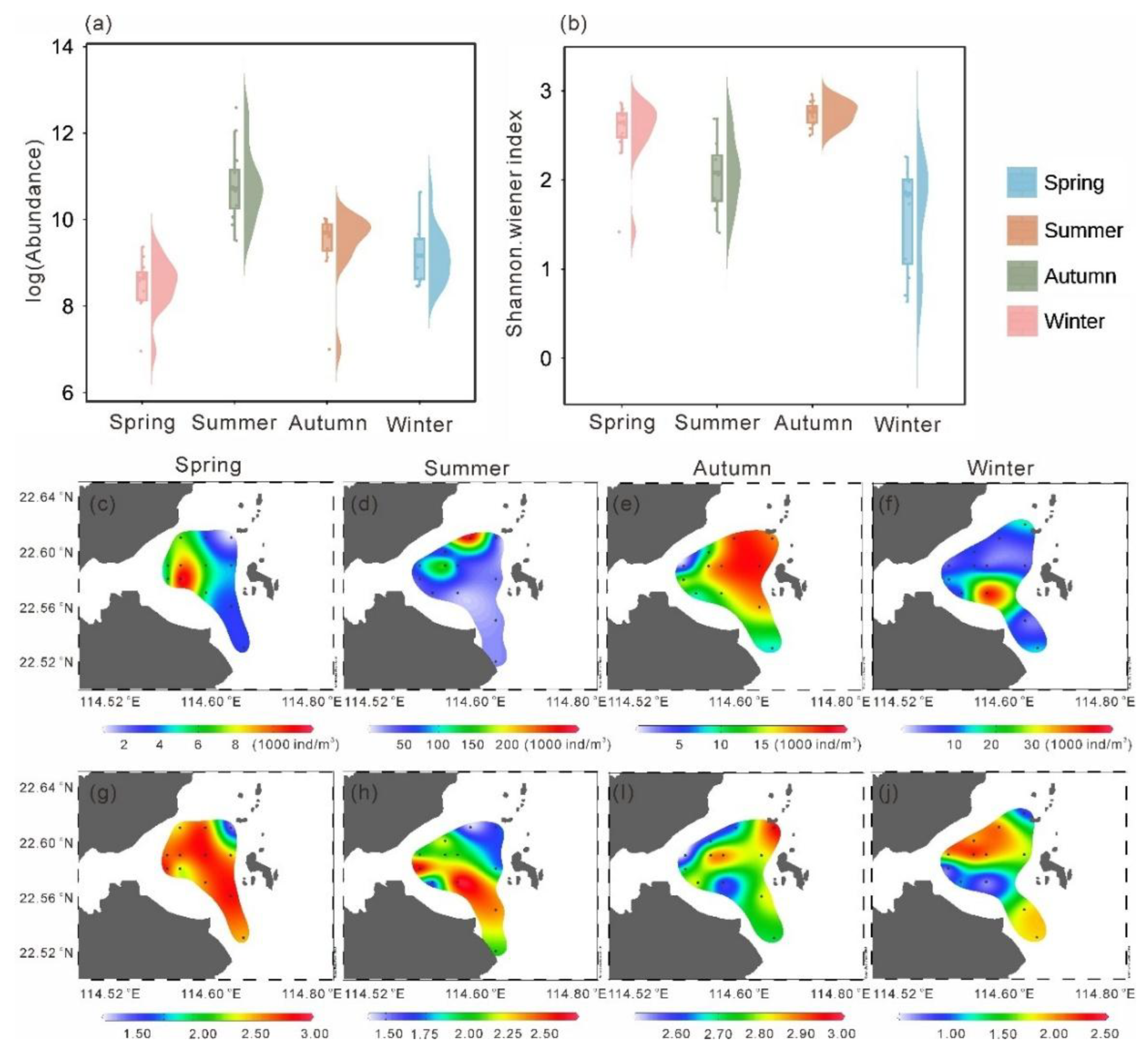
3.2.1. Abundance and Diversity of Mesozooplankton
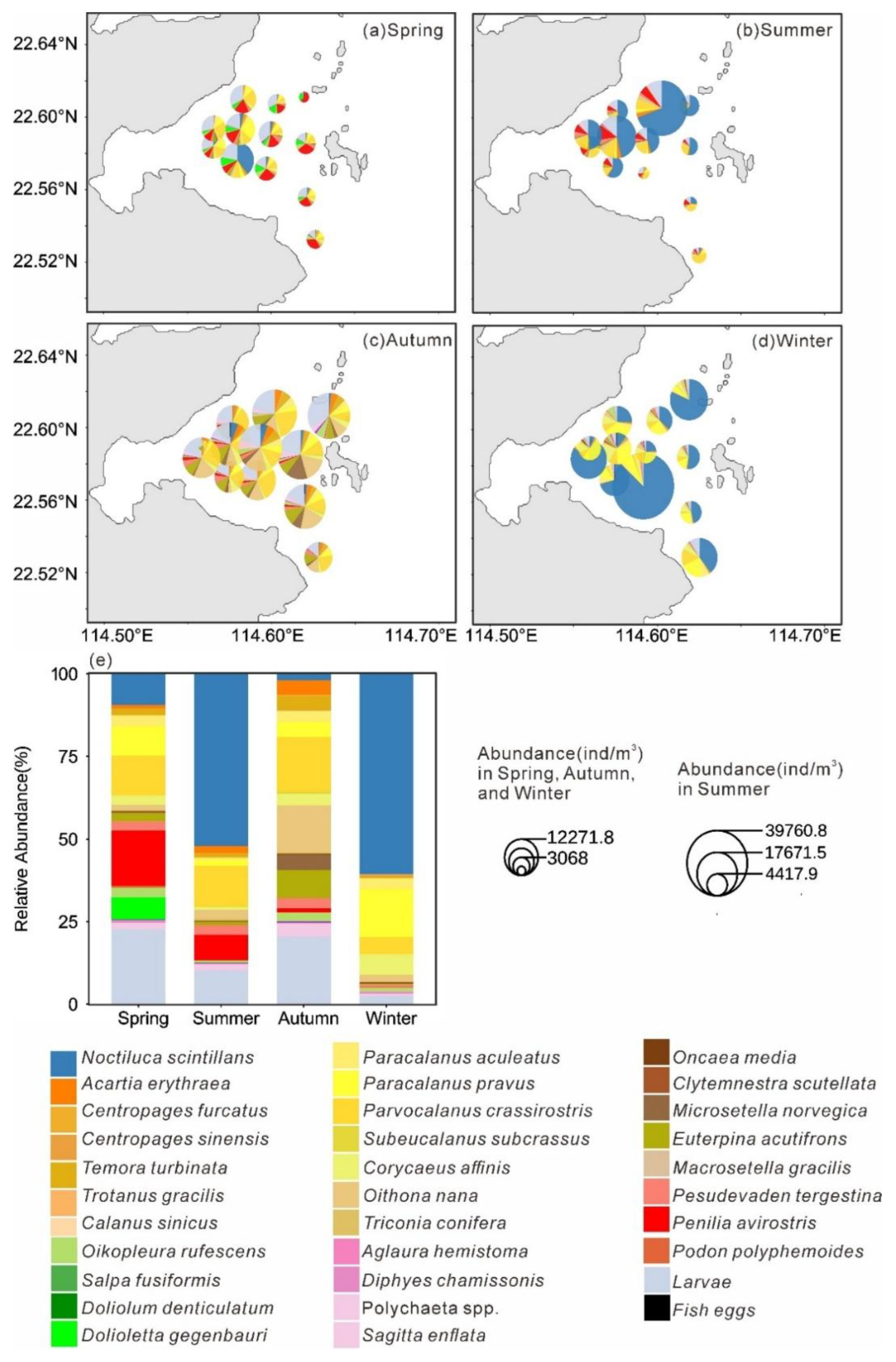
3.2.2. Species Composition of Mesozooplankton
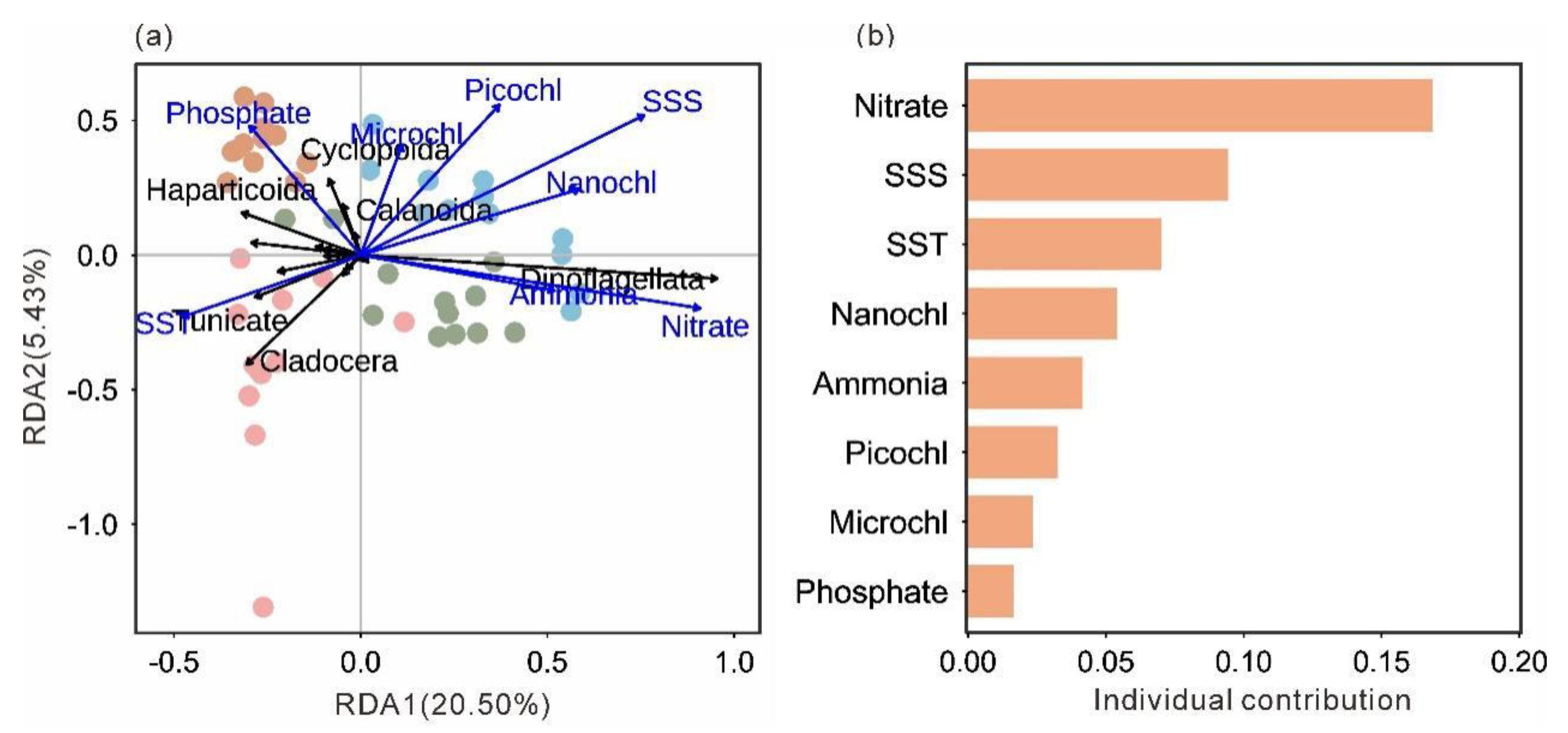
3.2.3. Relationships Between Mesozooplankton Groups and Environmental Factors
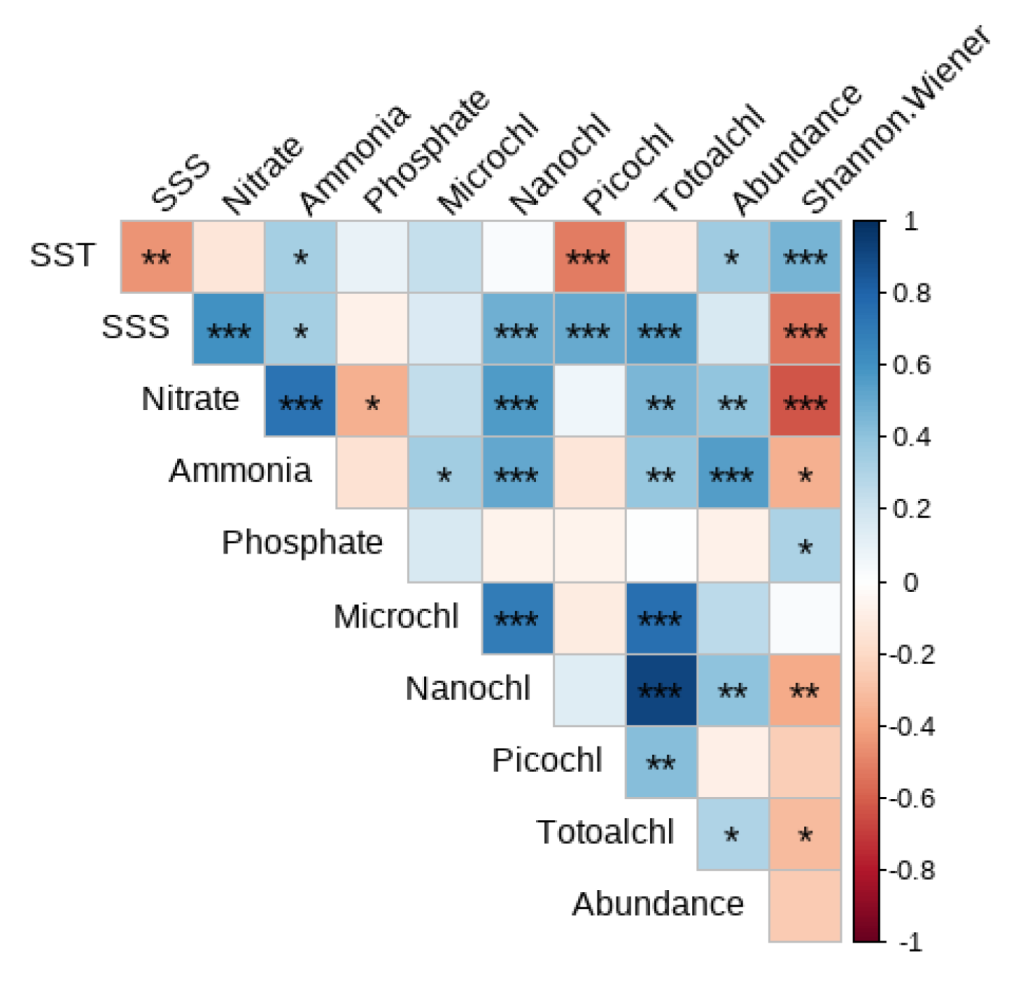
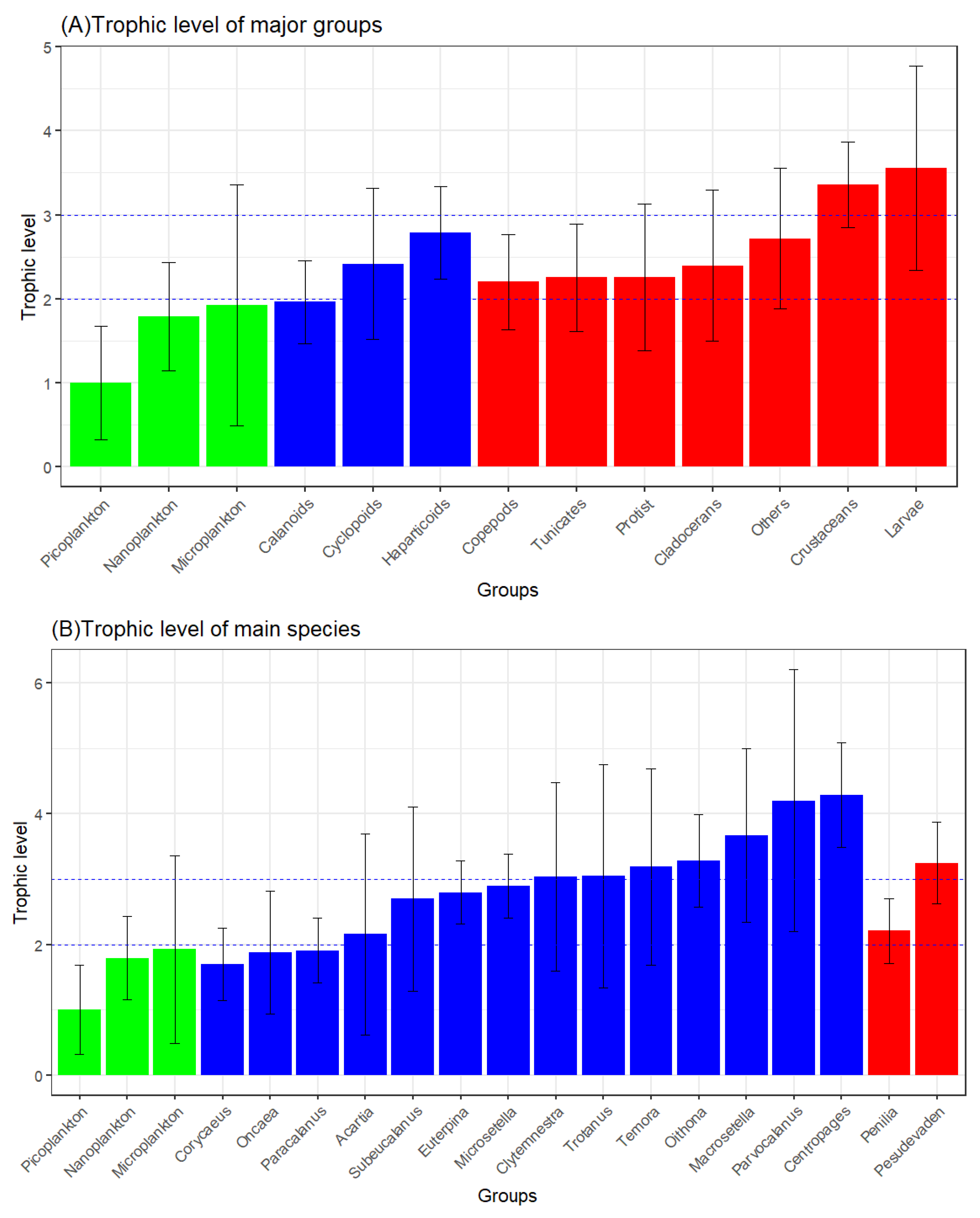
3.3. Trophic Level Classification of Plankton
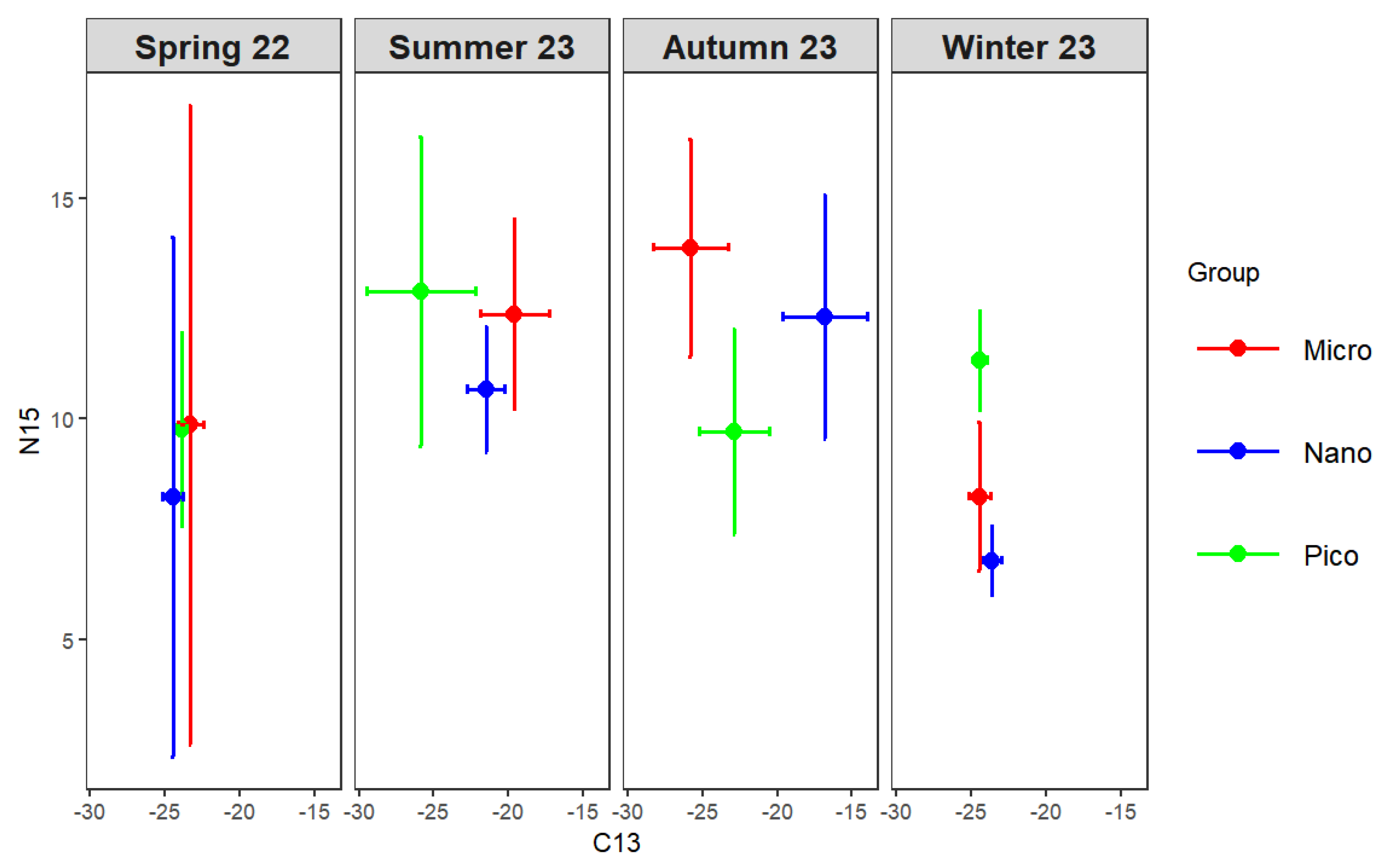
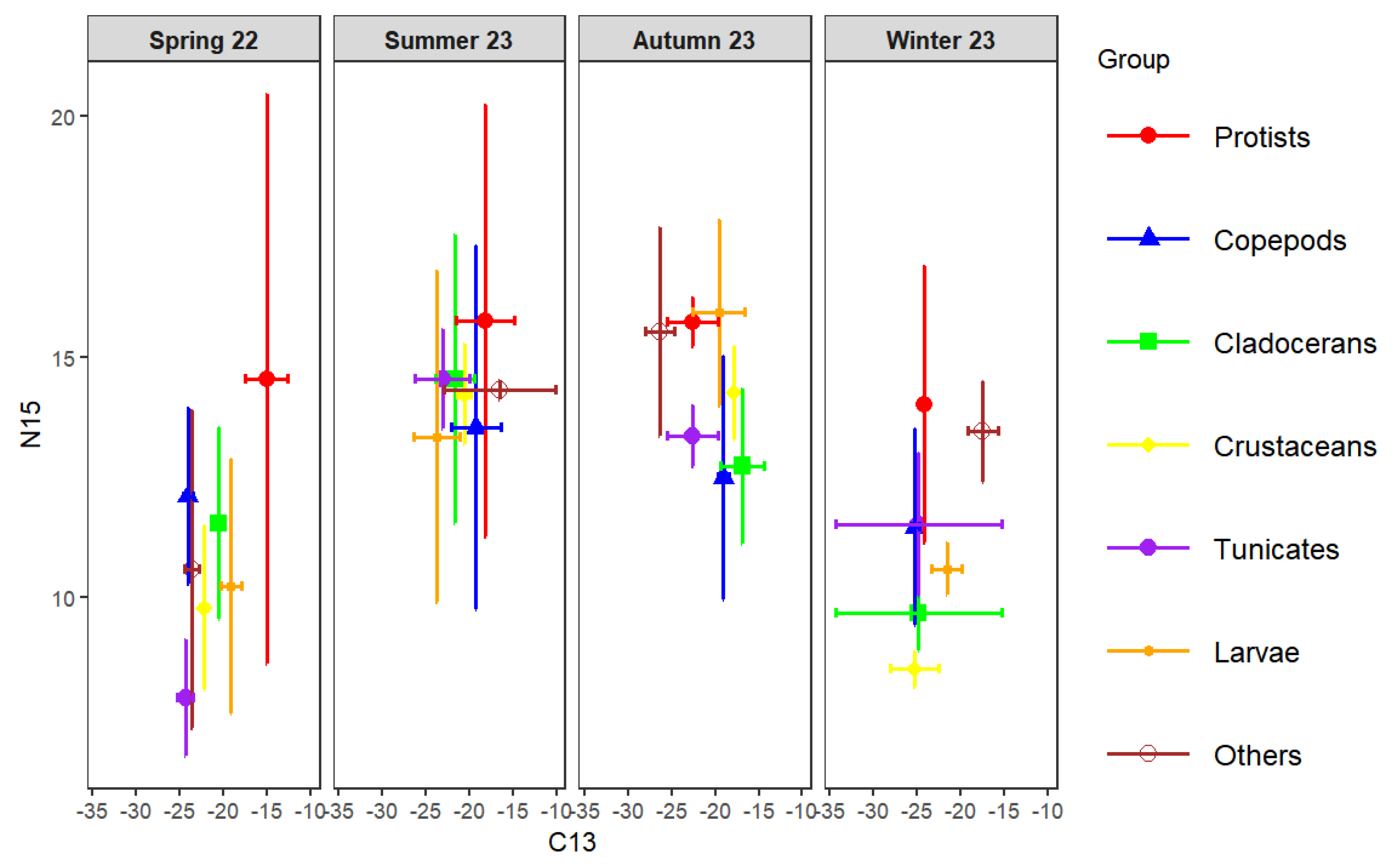
3.3.1. Stable Carbon and Nitrogen Isotope Ratios of Size-Fractionated Phytoplankton and Main Mesozooplankton
3.3.2. The Trophic Levels and Feeding Habits of Plankton
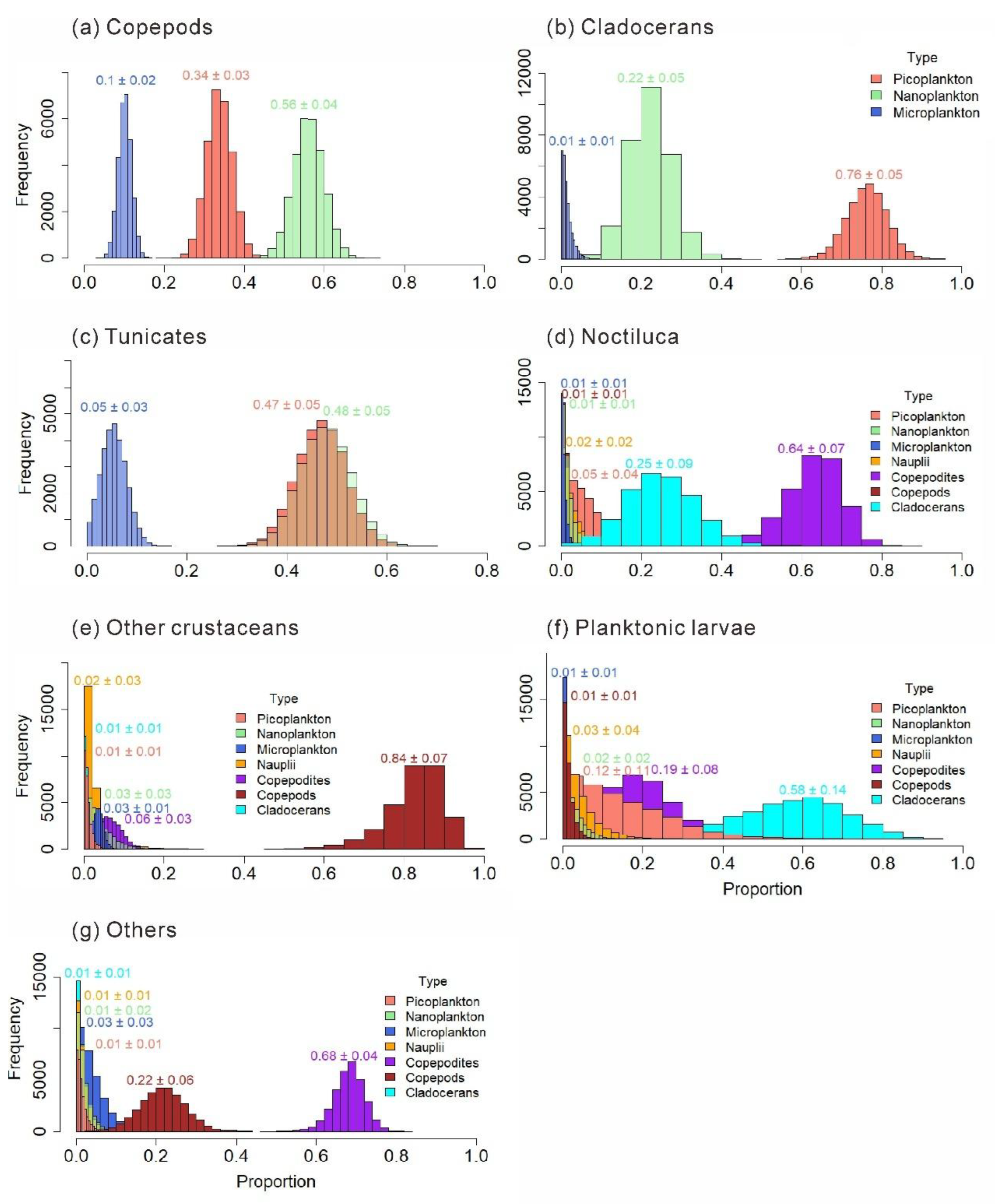
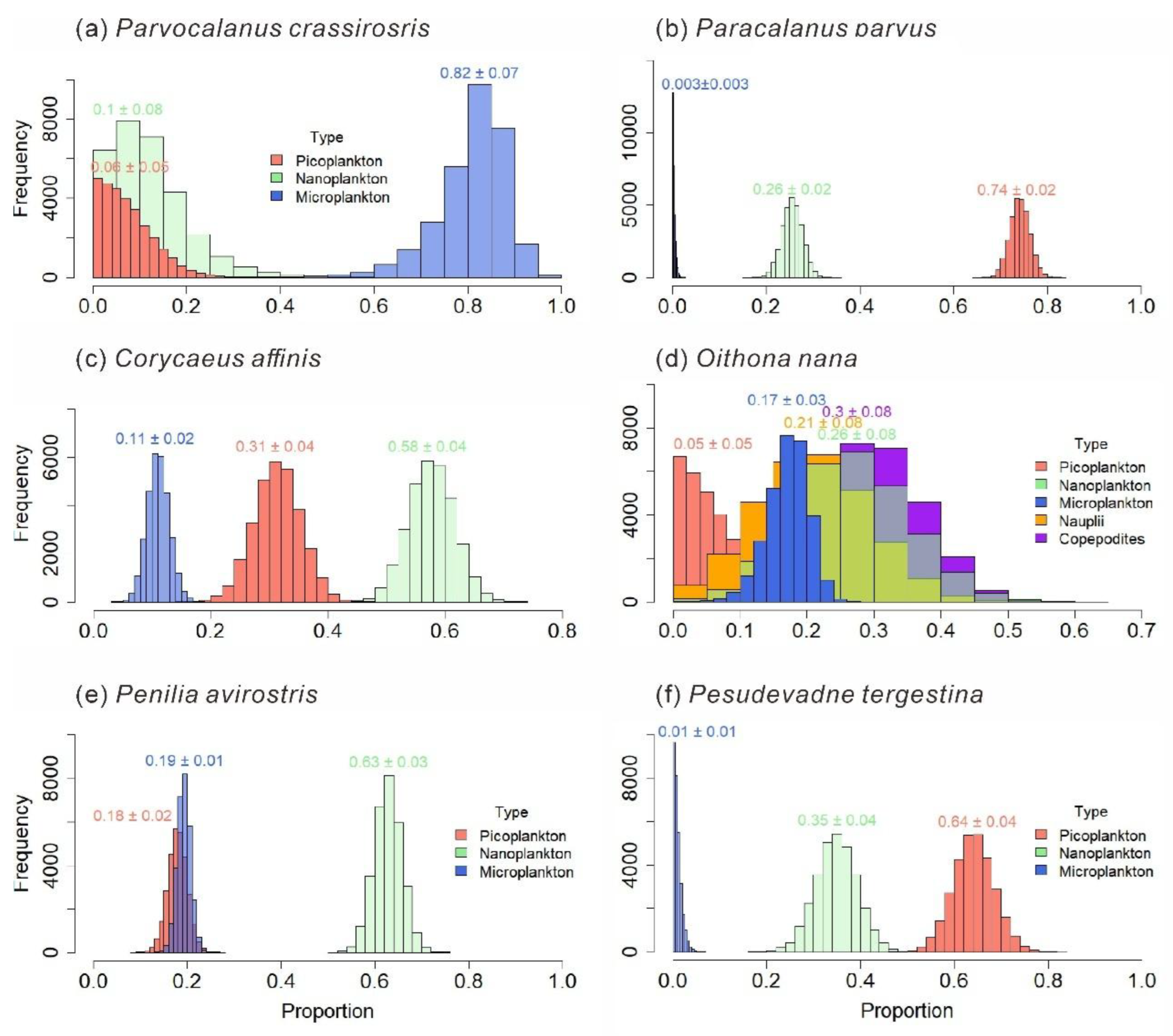
3.4. Food Composition and Feeding Preferences of Mesozooplankton
3.4.1. Food Composition and Feeding Preferences of Mesozooplankton Groups
3.4.2. Food Composition and Feeding Preferences of Mesozooplankton Species
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatiotemporal Variations and Environmental Drivers of the Mesozooplankton Community Structure in Daya Bay
4.2. Feeding Habits and Selectivity of Dominant Mesozooplankton Groups
4.3. Trophic Structure in the Thermal Discharge Area of Daya Bay Nuclear Power Plant
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Al-Azri, A. R.; Piontkovski, S. A.; Al-Hashmi, K. A.; Goes, J. I.; Gomes, H. D.; Glibert, P. M. Mesoscale and nutrient conditions associated with the massive 2008 Cochlodinium polykrikoides bloom in the Sea of Oman/Arabian Gulf. Estuaries and Coasts 2014, 37, 325–338. [Google Scholar]
- An, L. N.; Wang, L.; Huang, H.; Ou, D. Y.; Li, W. W. Population dynamics of Acetes chinensis and its response to environmental factors in western Daya Bay. Journal of Applied Oceanography (in Chinese). 2021, 40(3), 403–412. [Google Scholar]
- Atienza, D.; Saiz, E.; Calbet, A. Feeding ecology of the marine cladoceran Penilia avirostris: natural diet, prey selectivity and daily ration. Marine Ecology Progress Series 2006, 315, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bode, A.; Alvarez-Ossorio, M. T.; Barquero, S.; Lorenzo, J.; Louro, A.; Varela, M. Seasonal variations in upwelling and in the grazing impact of copepods on phytoplankton off A Coruña (Galicia, NW Spain). Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 2003, 297(1), 85–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M; Kim, D.; Liu, H.; Kang, C.-K. Variability in copepod trophic levels and feeding selectivity based on stable isotope analysis in Gwangyang Bay of the southern coast of the Korean Peninsula. Biogeosciences 2018, 15, 2055–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, L.; Qiu, D. In situ diets of the bloom-forming dinoflagellate Noctiluca scintillans in Daya Bay. Harmful Algae 2023, 130, 102546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, F. Y.; Wang, X. H.; Jia, X. P.; Yang, S. Y.; Liao, X. L.; Li, C. H. Seasonal succession of zooplankton species composition and dominant species in Daya Bay, northern South China Sea. Journal of Fisheries of China (in Chinese). 2013, 37(8), 1213–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanelli, E.; Menicucci, S.; Malavolti, S.; De Felice, A.; Leonori, I. Spatial changes in community composition and food web structure of mesozooplankton across the Adriatic basin (Mediterranean Sea). Biogeosciences 2022, 19(6), 1833–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fender, C. K.; Décima, M.; Gutiérrez-Rodríguez, A.; Selph, K. E.; Safi, K. A.; Stukel, M. R. Feeding selectivity and niche characteristics in Southern Ocean salps. Journal of Plankton Research 2024, fbae072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Seoane, R.; Viana, I. G.; Bode, A. Seasonal upwelling influence on trophic indices of mesozooplankton in a coastal food web estimated from δ15N in amino acids. Progress in Oceanography 2023, 219, 103149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Lei, M.; Cheng, F.; Hu, S. In situ food compositions reveal niche partitioning in small marine cladocerans and copepods in Daya Bay, South China Sea. Marine Ecology Progress Series 2023, 716, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.; Wang, Y.-S. Modeling the ecosystem response of the semi-closed Daya Bay to the thermal discharge from two nearby nuclear power plants. Ecotoxicology 2020, 29(6), 736–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenmochi, A.; Hirai, J.; Obayashi, Y.; Yoshikawa, T.; Nishikawa, J. Feeding habits and ecological roles of marine cladocerans in offshore zooplankton food-web in Suruga Bay, Japan. Journal of Oceanography 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordubel, K.; Baschek, B.; Hieronymi, M.; Voynova, Y. G.; Möller, K. O. Improving the sampling of red Noctiluca scintillans to understand its impact on coastal ecosystem dynamics. Journal of Plankton Research 2024, 46(3), 251–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Peres-Neto, P. R. Generalizing hierarchical and variation partitioning in multiple regression and canonical analyses using the rdacca.hp R package. Methods in Ecology and Evolution 2022, 13(4), 782–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, Q.; Mohamat-Yusuff, F.; Mohamed, K. N.; Zainordin, N. S.; Hassan, M. Z. Impacts of thermal and cold discharge from power plants on marine benthos and its mitigation measures: a systematic review. Frontiers in Marine Science 2024, 11, 1465289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Yin, J.; Tan, Y.; Huang, L.; Song, X. Short-term variation in zooplankton community from Daya Bay with outbreaks of Penilia avirostris**This research was supported by the Knowledge Innovation Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (SQ201307), the Public Science and Technology Research Funds Projects of Ocean (No. 201305030) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41276159, 31101619, 41130855 and 41276161). Oceanologia 2014, 56(3), 583–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Chen, M.; Wang, C. The Dynamics of Trophic Cascades on Phytoplankton Induced by Mesozooplankton in Coastal Water, Daya Bay, Northern South China Sea. Microorganisms 2024, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, X.; Tan, Y.; Huang, L.; Chen, Q.; Li, K.; Liu, Y. Spatiotemporal variations and influencing factors of macro-mesozooplankton in Daya Bay. Marine Environmental Science (in Chinese). 2011, 30, 640–645. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, M. Ecological study on thaliaceans in Daya Bay. In Collections of Papers on Marine Ecology in the Daya Bay II; Ocean Press: Beijing, 1990; pp. 390–396. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.; Cao, H.; Liu, M.; Qi, F.; Zhang, S.; Xu, J. The influence of thermal discharge from power plants on the biogeochemical environment of Daya Bay during high primary productivity seasons. Marine Pollution Bulletin 2025, 211, 117408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Ma, N.; Sun, M.; Yang, J.; Li, X.; Nie, W.; et al. Impact of climate change on frequency and community structure of red tide events in the northern South China Sea. Climate Dynamics 2025, 63(1), 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Huang, H.; Xie, F.; Song, X. High-temperature thermal discharge inhibits plankton community metabolism in a partly eutrophicated bay in China. Frontiers in Marine Science 2023, 9, 1016074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q. X.; Zhou, L. B.; Zhang, W. R.; Zhang, L.; Tan, Y. H.; Han, T. T.; et al. Rising temperature contributed to the outbreak of macrozooplankton Creseis acicula by enhancing its feeding and assimilation for algal food near the coastal Daya Bay Nuclear Power Plant. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety 2022, 238, 113606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michener, R. H.; Kaufman, L. Stable isotope ratios as tracers in marine food webs: An update. Stable Isotopes in Ecology and Environmental Science 2007, 2, 238–282. [Google Scholar]
- Owens, N. J. P. Natural variations in 15N in the marine environment. Advances in Marine Biology 1987, 24, 389–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Diego-McGlone, M. L.; Yñiguez, A. T.; Benico, G.; Lum, W. M.; Hii, K. S.; Leong, S. C. Y.; et al. Fish Kills Related to Harmful Algal Bloom Events in Southeast Asia. Sustainability 2024, 16(23), 10521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parnell, A. C.; Inger, R.; Bearhop, S.; Jackson, A. L. Source partitioning using stable isotopes: Coping with too much variation. PLoS One 2010, 5, e9672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parnell, A. C.; Phillips, D. L.; Bearhop, S.; Semmens, B. X.; Ward, E. J.; Moore, J. W.; Jackson, A. L.; Grey, J.; Kelly, D. J.; Inger, R. Bayesian stable isotope mixing models. Environmetrics 2013, 24, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, D. M. Using stable isotopes to estimate trophic position: Models, methods, and assumptions. Ecology 2002, 83, 703–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susana, C.-N.; Igor, F.-U.; Antonio, B.; Sergio, H.-T.; Pamela, H.; Ruben, E. Assessing the food web structure of the mesozooplankton community in the highly variable coastal upwelling system of the southeast Pacific. Progress in Oceanography 2025, 239, 103580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A. W.; Ward, A. C.; Sweeney, C. P.; Sutherland, K. R. Host-specific symbioses and the microbial prey of a pelagic tunicate (Pyrosoma atlanticum). ISME Communications 2021, 1(1), 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, A. W.; Sweeney, C. P.; Sutherland, K. R. Selective and differential feeding on marine prokaryotes by mucous mesh feeders. Environmental Microbiology 2023, 25(4), 880–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.-X.; Gu, Y.-G.; Liu, Q.-X.; Zhang, S.-F.; Rao, Y.-Y.; Liu, H.-X.; et al. Research on the seasonal variation of zooplankton community in Daya Bay, South China Sea. Frontiers in Marine Science 2023, 10, 1110160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, C.; Ke, Z.; Li, K.; Liu, J.; Zhou, L.; Lian, X.; Tan, Y. Effects of terrestrial inputs and seawater intrusion on zooplankton community structure in Daya Bay, South China Sea. Marine Pollution Bulletin 2021, 167, 112331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Tang, D.; Yao, L.; Chen, P.; Jia, X.; Li, C. Long-Term Water Temperature Variations in Daya Bay, China Using Satellite and In Situ Observations. Terrestrial, Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences (Oc). 2010, 21(2), 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Chen, G. B.; Wang, T.; Zhang, S. F.; Dai, M.; Yu, J.; et al. Acoustic study on the outbreak of Creseis acicula near the Daya Bay Nuclear Power Plant during the summer of 2020. Marine Pollution Bulletin 2021, 165, 112144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xiong, L.; Li, J.; Huang, X. Long-term changes of nutrients and biocenoses indicating the anthropogenic influences on ecosystem in Jiaozhou Bay and Daya Bay, China. Marine Pollution Bulletin 2021, 168, 112406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, D.; Cheng, Y.; Gong, F. Long-Term Changes and Factors That Influence Changes in Thermal Discharge from Nuclear Power Plants in Daya Bay, China. Remote Sensing 2022, 14(3), 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Liu, J.; Ke, Z.; Xiang, C.; Zhang, L.; et al. Role of jellyfish in mesozooplankton community stability in a subtropical bay under the long-term impacts of temperature changes. Science of The Total Environment 2022, 849, 157627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




