Submitted:
15 December 2025
Posted:
16 December 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Background on DES and THEDES
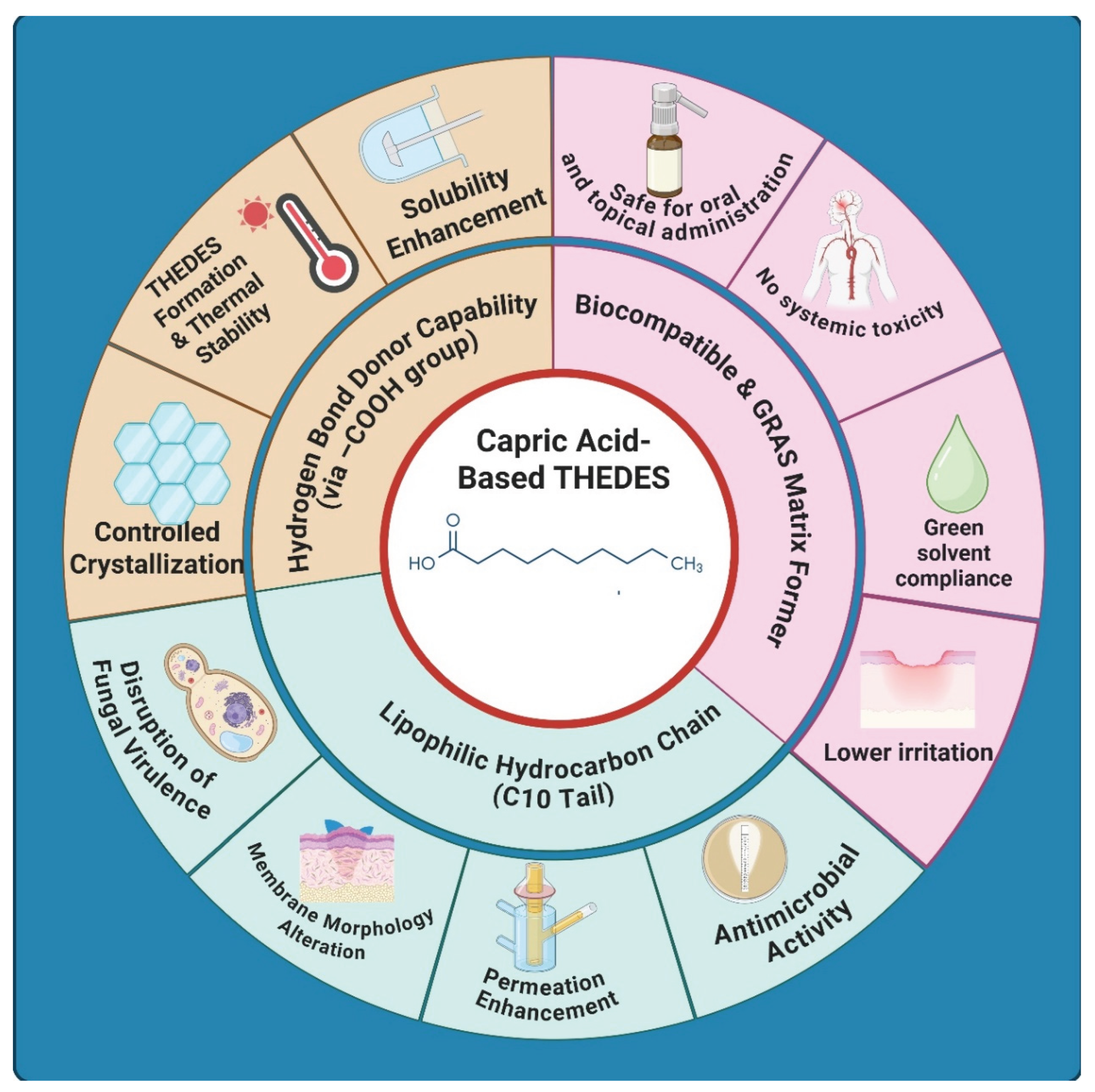
3. Capric Acid as a Functional Component in Multicomponent Therapeutic Deep Eutectic Systems
4. Preparation and Characterization of Capric Acid-Based THEDES
5. Role of CA in Promoting Real DES Formation: Insights from Solid–Liquid Phase Diagrams
6. Pharmaceutical Applications
7. Mechanisms of Drug–Solvent Interactions
8. Safety, Toxicity, and Regulatory Considerations
9. Challenges and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CA | Capric Acid |
| ILs | Ionic Liquids |
| THEDES | Therapeutic Deep Eutectic Systems |
| DES | Dee Eutectic Solvent |
| DESy | Deep Eutectic System |
References
- Endluri Dharmik Chandu, Sakhinamma Chejerla, Chandra Yadala Prapurna. Unmasking the purity: reviewingsources and detection methods of organic volatile impurities. International Journal of Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Medical Sciences 2023.
- Kerton Francesca M. Solvent Systems for Sustainable Chemistry. 2016.
- Adwan Samer, Qasmieh Madeiha, Al-Akayleh Faisal, Ali Agha Ahmed S. Recent Advances in Ocular Drug Delivery: Insights into Lyotropic Liquid Crystals. Pharmaceuticals 2024. [Epub ahead of print]. [CrossRef]
- Nakaweh Abdeh, Al-Akayleh Faisal, Al-Remawi Mayyas, Abdallah Qasem, Agha Ahmed SA Ali. Deep eutectic system-based liquisolid nanoparticles as drug delivery system of curcumin for in-vitro colon cancer cells. J Pharm Innov 2024; 19 (2): 18.
- Al-Mawla Layaly, Al-Akayleh Faisal, Daadoue Saifeddin, Mahyoob Waseem, Al-Tameemi Badralbdoor, Al-Remawi Mayyas, Adwan Samer, Agha Ahmed S. A. Ali. Development, Characterization, and Ex Vivo Permeation Assessment of Diclofenac Diethylamine Deep Eutectic Systems Across Human Skin. J Pharm Innov 2023; 18 (4): 2196-2209. [CrossRef]
- Al-Akayleh Faisal, Alkhawaja Bayan, Al-Zoubi Nizar, Abdelmalek Suzanne M. A., Daadoue Saifeddin, AlAbbasi Diala, Al-Masri Shoroq, Ali Agha Ahmed S. A., Olaimat Ali R., Woodman Tim. Novel therapeutic deep eutectic system for the enhancement of ketoconazole antifungal activity and transdermal permeability. J Mol Liq 2024; 413: 125975. [CrossRef]
- Al-Akayleh Faisal, Alkhawaja Bayan, Al-Remawi Mayyas, Al-Zoubi Nizar, Nasereddin Jehad, Woodman Tim, Nisrein Jaber, Ahmad Mohammad I. A., AbuQatouseh Luay, Omari Derar, Agha Ahmed S. A. Ali. An Investigation into the Preparation, Characterization, and Therapeutic Applications of Novel Gefitinib/Capric Acid Deep Eutectic Systems. J Pharm Innov 2024; 19 (6): 79. [CrossRef]
- Rifai Alaa, Bayan Alkhawaja, Faisal Al-Akayleh, Mayyas Al-Remawi, Jehad Nasereddin, Safwan Abdel Rahim, Tim Woodman, and Ali Agha Ahmed Saad Abdulbari. Eutectic-based self-emulsifying drug delivery system for enhanced oral delivery of risperidone. J Dispersion Sci Technol: 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Silva Joana M., Pereira Carolina V., Mano Francisca, Silva Eduardo, Castro Vânia I. B., Sá-Nogueira Isabel, Reis Rui Luís, Paiva Alexandre, Matias Ana A., Duarte Ana Rita Cruz. Therapeutic Role of Deep Eutectic Solvents Based on Menthol and Saturated Fatty Acids on Wound Healing. ACS Applied Bio Materials 2019; 2: 4346 - 4355.
- Al-Akayleh Faisal, Mohammed Ali Hiba Hani, Ghareeb Mowafaq M., Al-Remawi Mayyas. Therapeutic deep eutectic system of capric acid and menthol: Characterization and pharmaceutical application. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 2019; 53. [CrossRef]
- Ali Hiba Hani Mohammed, Ghareeb Mowafaq Mohammed, Al-Remawi Mayyas, Al-Akayleh Faisal. New insight into single phase formation of capric acid/menthol eutectic mixtures by Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy and differential scanning calorimetry. Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Research 2020; 19: 361-369.
- Alkhawaja Bayan, Al-Akayleh Faisal, Nasereddin Jehad, Kamran Muhammad, Woodman Tim, Al-Rubaye Zaid, Qinna Nidal, Al-Remawi Mayyas, Olaimat Ali R. Structural insights into novel therapeutic deep eutectic systems with capric acid using 1D, 2D NMR and DSC techniques with superior gut permeability. RSC advances 2024; 14 (21): 14793-14806.
- Alkhawaja Bayan, Al-Akayleh Faisal, Al-Rubaye Zaid, AlDabet Ghayda, Bustami Muna, Smairat Maisa’a, Agha Ahmed S. A. A., Nasereddin Jehad, Qinna Nidal, Michael Andreas, Watts Andrew G. Dissecting the stability of Atezolizumab with renewable amino acid-based ionic liquids: Colloidal stability and anticancer activity under thermal stress. Int J Biol Macromol 2024; 270: 132208. [CrossRef]
- Al-Akayleh Faisal, Al-Remawi Mayyas, Agha Ahmed, Abu-Nameh Eyad. Applications and risk assessments of ionic liquids in chemical and pharmaceutical domains: an updated overview. Jordan Journal of Chemistry (JJC) 2023; 18 (2): 53-76.
- Paiva Alexandre, Craveiro Rita, Aroso Ivo M., Martins Marta, Reis Rui Luís, Duarte Ana Rita Cruz. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents – Solvents for the 21st Century. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering 2014; 2: 1063-1071.
- Pitacco W., Samorì C., Pezzolesi L., Gori V., Grillo A., Tiecco M., Vagnoni M., Galletti P. Extraction of astaxanthin from Haematococcus pluvialis with hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents based on oleic acid. Food Chem 2022; 379: 132156. [CrossRef]
- Liu Yiwen, Wu Yujing, Liu Jinming, Wang Wenxi, Yang Qingliang, Yang Gensheng. Deep eutectic solvents: recent advances in fabrication approaches and pharmaceutical applications. Int J Pharm 2022: 121811.
- Lomba Laura, García Cristina Belén, Ribate María Pilar, Giner Beatriz, Zuriaga Estefanía. Applications of Deep Eutectic Solvents Related to Health, Synthesis, and Extraction of Natural Based Chemicals. Applied Sciences 2021.
- Gotor-Fernández Vicente, Paul Caroline E. Deep eutectic solvents for redox biocatalysis. J Biotechnol 2019; 293: 24-35.
- Wang Zhaoyang, Wang Simin, Zhang Yuan, Bi Wentao. Switching from deep eutectic solvents to deep eutectic systems for natural product extraction. Green Chemical Engineering 2025; 6 (1): 36-53. [CrossRef]
- Al-Akayleh Faisal, Al-Remawi Mayyas, Abdel-Rahem Rami A, Al-Adham Ibrahim SI, Aburub Faisal, Agha Ahmed SA Ali. AI-Driven Strategies in Prebiotic Research: Addressing Challenges and Advancing Human Health. 2025 1st International Conference on Computational Intelligence Approaches and Applications (ICCIAA). IEEE; 2025:1-5.
- Aroso Ivo M., Silva João Carlos, Mano Francisca, Ferreira Ana S.D., Dionísio Madalena, Sá-Nogueira Isabel, Barreiros Susana, Reis Rui Luís, Paiva Alexandre, Duarte Ana Rita Cruz. Dissolution enhancement of active pharmaceutical ingredients by therapeutic deep eutectic systems. European journal of pharmaceutics and biopharmaceutics : official journal of Arbeitsgemeinschaft fur Pharmazeutische Verfahrenstechnik eV 2016; 98: 57-66.
- Hložek Tomáš, Bosáková Tereza, Bosáková Zuzana, Tůma Petr. Hydrophobic eutectic solvents for endocrine disruptors purification from water: Natural and synthetic estrogens study. Sep Purif Technol 2022; 303: 122310. [CrossRef]
- van den Bruinhorst Adriaan, Costa Gomes Margarida. Is there depth to eutectic solvents? Current Opinion in Green and Sustainable Chemistry 2022; 37: 100659. [CrossRef]
- Toxicity studies of select ionic liquids (1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride, 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride, 1-butyl-1-methylpyrrolidinium chloride, and n-butylpyridinium chloride) administered in drinking water to Sprague Dawley (Hsd:Sprague Dawley SD) rats and B6C3F1/N mice. Toxic Rep Ser 2022; 103.
- Yoon Bo Kyeong, Jackman Joshua A., Kim Min Chul, Sut Tun Naw, Cho Nam-Joon. Correlating Membrane Morphological Responses with Micellar Aggregation Behavior of Capric Acid and Monocaprin. Langmuir : the ACS journal of surfaces and colloids 2017; 33 11: 2750-2759.
- Trenzado Jose L., Benito Cristina, Atilhan Mert, Aparicio Santiago. Hydrophobic Deep eutectic Solvents based on cineole and organic acids. J Mol Liq 2023; 377: 121322. [CrossRef]
- Tan Sue Woon, Yoon Bo Kyeong, Jackman Joshua A. Membrane-Disruptive Effects of Fatty Acid and Monoglyceride Mitigants on E. coli Bacteria-Derived Tethered Lipid Bilayers. Molecules 2024; 29.
- Al-Akayleh Faisal, Adwan Samer, Khanfar Mai S., Idkaidek Nasir M, Al-Remawi Mayyas. A Novel Eutectic-Based Transdermal Delivery System for Risperidone. AAPS PharmSciTech 2020; 22.
- Suchodolski Jakub, Derkacz Daria, Bernat Przemysław, Krasowska Anna. Capric acid secreted by Saccharomyces boulardii influences the susceptibility of Candida albicans to fluconazole and amphotericin B. Sci Rep 2021; 11.
- Bakr El-Nassan Hala. Applications of therapeutic deep eutectic solvents (THEDESs) as antimicrobial and anticancer agents. Pharmaceutical Development and Technology 2024; 29: 1084 - 1092.
- Daadoue Saifeddin, Al-Remawi Mayyas, Al-Mawla Layaly, Idkaidek Nasir M, Khalid Ruwaida M., Al-Akayleh Faisal. Deep Eutectic Liquid as Transdermal Delivery Vehicle of Risperidone. J Mol Liq 2021.
- Trombino Sonia, Siciliano Carlo, Procopio Debora, Curcio Federica, Laganà Annarita S., Di Gioia Maria L., Cassano Roberta. Deep Eutectic Solvents for Improving the Solubilization and Delivery of Dapsone. Pharmaceutics 2022. [Epub ahead of print]. [CrossRef]
- Swebocki Tomasz, Barras Alexandre, Abderrahmani Amar, Haddadi Kamel, Boukherroub Rabah. Deep Eutectic Solvents Comprising Organic Acids and Their Application in (Bio)Medicine. Int J Mol Sci 2023. [Epub ahead of print]. [CrossRef]
- Silva Joana M., Silva Eduardo, Reis Rui L., Duarte Ana Rita C. A closer look in the antimicrobial properties of deep eutectic solvents based on fatty acids. Sustainable Chemistry and Pharmacy 2019; 14: 100192. [CrossRef]
- Alkhawaja Bayan, Al-Akayleh Faisal, Nasereddin Jehad, Malek Suzanne Abdel, Alkhawaja Nour, Kamran Muhammad, Al-Rubaye Zaid, Smairat Maisa’a, Al-Remawi Mayyas, Aburayyan Walid Salem. Levofloxacin–fatty acid systems: dual enhancement through deep eutectic formation and solubilization for pharmaceutical potential and antibacterial activity. AAPS PharmSciTech 2023; 24 (8): 244.
- Li Menghan, Yuan Jing, Yang Qinghua, Liu Zhuoni, Meng Shengxi, Wang Xiaoyong, Peng Changjun, Yin Tianxiang. Therapeutic deep eutectic solvents based on natural product matrine and caprylic acid: Physical properties, cytotoxicity and formation of surfactant free microemulsion. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 2023; 90: 105177.
- Kim J., Gao Y., Zhao Z., Rodrigues D., Tanner E. E. L., Ibsen K., Sasmal P. K., Jaladi R., Alikunju S., Mitragotri S. A deep eutectic-based, self-emulsifying subcutaneous depot system for apomorphine therapy in Parkinson’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2022; 119 (9). [CrossRef]
- Kahwaji Samer, Johnson Michel B., Kheirabadi Ali C., Groulx Dominic, White Mary Anne. Stable, low-cost phase change material for building applications: The eutectic mixture of decanoic acid and tetradecanoic acid. Applied Energy 2016; 168: 457-464. [CrossRef]
- Deepika, Juneja Shreya, Pandey Siddharth. Water Miscibility, Surface Tension, Density, and Dynamic Viscosity of Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents Composed of Capric Acid, Menthol, and Thymol. J Chem Eng Data 2022; 67 (11): 3400-3413. [CrossRef]
- Li Zhuocheng, Zhang Enhui, Li Weimin, Liu Haichao. Tribological study of two ammonium chloride-decanoic acid deep eutectic solvents (DESs) as high-performance lubricants. Friction 2024; 12 (11): 2441-2457. [CrossRef]
- Kyriakoudi Anastasia, Tsiouras Alexandros, Mourtzinos Ioannis. Extraction of Lycopene from Tomato Using Hydrophobic Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents Based on Terpenes and Fatty Acids. Foods 2022. [Epub ahead of print]. [CrossRef]
- Majidi Elham, Bakhshi Hamid. Hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents characterization and performance for efficient removal of heavy metals from aqueous media. Journal of Water Process Engineering 2024; 57: 104680.
- Wu Jieyu, Yin Tianxiang. Insight into the physicochemical properties and bioactivities of therapeutic deep eutectic solvents based on matrine and fatty acids. J Mol Liq 2022; 360: 119560.
- Yu Kunyang, Jia Minjie, Liu Yushi, Yang Yingzi. Binary decanoic acid/polyethylene glycol as a novel phase change material for thermal energy storage: Eutectic behaviors and energy conservation evaluation. Journal of Energy Storage 2023; 68: 107663.
- He Hongdou, Li Xinmei, Yuan Dan, Huang Xinyu, Qiu Zhenpeng, Hong Yi, He Jianhua, Guo Yujie, Lu Shan. Novel therapeutic deep eutectic solvents based on mirtazapine and medium-chain fatty acids for enhancing the transdermal delivery of mirtazapine. Int J Pharm 2025; 670: 125133.
- Li Bin, Xiao Ting, Guo Shiqi, Wu Yan, Lai Rongrong, Liu Ziyi, Luo Weixuan, Xu Yuehong. Oxymatrine-fatty acid deep eutectic solvents as novel penetration enhancers for transdermal drug delivery: Formation mechanism and enhancing effect. Int J Pharm 2023; 637: 122880.
- Panbachi Shaida, Beranek Josef, Kuentz Martin. Abiraterone acetate fixed-dosed combinations with ibuprofen-based therapeutic eutectic and deep eutectic solvents. Int J Pharm 2025; 671: 125279. [CrossRef]
- Al-Akayleh Faisal, Alkhawaja Bayan, Al-Zoubi Nizar, Abdelmalek Suzanne M. A., Daadoue Saifeddin, AlAbbasi Diala, Al-Masri Shoroq, Ali Agha Ahmed S. A., Rifai Alaa, Olaimat Ali R., Habashneh Lubna, Al-Remawi Mayyas, Woodman Tim. Optimized ethylcellulose films incorporating a novel clotrimazole deep eutectic system for enhanced permeation and antifungal activity. Int J Pharm 2025; 685: 126207. [CrossRef]
- Fan Chen, Sebbah Tarik, Liu Yang, Cao Xueli. Terpenoid-capric acid based natural deep eutectic solvent: Insight into the nature of low viscosity. Cleaner engineering and technology 2021; 3: 100116.
- fda.gov. Nonclinical Studies for the Safety Evaluation of Pharmaceutical Excipients. 2018.
- https://www.fda.gov/. Substances Added to Food (formerly EAFUS). 2025.
- García Cristina B., Concha Julia, Culleré Laura, Lomba Laura, Sangüesa Estela, Ribate Mª P. Has the Toxicity of Therapeutic Deep Eutectic Systems Been Assessed? Applied Sciences 2023. [Epub ahead of print]. [CrossRef]
- Mohammed Taghreed Hassanin Ibrahim, Zainal-Abidin Mohamad Hamdi, El Enshasy Hesham Ali, Tan Li Ting, Kristianto Sonny, Putri Rury Eryna. Development of therapeutic deep eutectic solvent with anti-oxidant and anti-microbial properties for potential pharmaceutical applications. J Mol Struct 2025; 1329: 141397.
- Patel Dhruv, Suthar Krunal J, Balsora Hemant Kumar, Patel Dhara, Panda Swapna Rekha, Bhavsar Nirav. Estimation of density and viscosity of deep eutectic solvents: Experimental and machine learning approach. Asia-Pacific Journal of Chemical Engineering 2024; 19 (6): e3151.
- Subba Navin, Das Nilimesh, Sen Pratik. Partial viscosity decoupling of solute solvation, rotation, and translation dynamics in lauric acid/menthol deep eutectic solvent: modulation of dynamic heterogeneity with length scale. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B 2020; 124 (31): 6875-6884.
- Abel Grace, Amobonye Ayodeji, Bhagwat Prashant, Mohite Sachin Balaso, Karpoormath Rajshekhar, Permaul Kugen, Pillai Santhosh. Structural and physicochemical characterisation of binary glutamine-based deep eutectic solvents. J Mol Liq 2024; 414: 126065.
- Lomba Laura, Ribate Mª Pilar, Sangüesa Estela, Concha Julia, Garralaga M ª Pilar, Errazquin Diego, García Cristina B, Giner Beatriz. Deep eutectic solvents: are they safe? Applied Sciences 2021; 11 (21): 10061.
- Abdelquader Magdy M., Li Shu, Andrews Gavin P., Jones David S. Therapeutic deep eutectic solvents: A comprehensive review of their thermodynamics, microstructure and drug delivery applications. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 2023; 186: 85-104. [CrossRef]
- Oyoun Feras, Toncheva Antoniya, Henríquez Luis Castillo, Grougnet Raphael, Laoutid Fouad, Mignet Nathalie, Alhareth Khair, Corvis Yohann. Deep eutectic solvents: an eco-friendly design for drug engineering. ChemSusChem 2023; 16 (20): e202300669.
- López-Flores Francisco Javier, Ramirez-Marquez Cesar, González-Campos J Betzabe, Ponce-Ortega José María. Machine learning for predicting and optimizing physicochemical properties of deep eutectic solvents: review and perspectives. Ind Eng Chem Res 2024; 64 (6): 3103-3117.
- Cysewski Piotr, Jeliński Tomasz, Przybyłek Maciej, Mai Anna, Kułak Julia. Experimental and machine-learning-assisted design of pharmaceutically acceptable deep eutectic solvents for the solubility improvement of non-selective COX inhibitors ibuprofen and ketoprofen. Molecules 2024; 29 (10): 2296.
- Mohan Mood, Jetti Karuna Devi, Smith Micholas Dean, Demerdash Omar N, Kidder Michelle K, Smith Jeremy C. Accurate machine learning for predicting the viscosities of deep eutectic solvents. J Chem Theory Comput 2024; 20 (9): 3911-3926.
- Ayres Lucas B, Bandara Madhushi, McMillen Colin D, Pennington William T, Garcia Carlos D. eutXG: A Machine-Learning Model to Understand and Predict the Melting Point of Novel X-Bonded Deep Eutectic Solvents. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering 2024; 12 (30): 11260-11273.
- Tavares Duarte de Alencar Luan Vittor, Rodríguez-Reartes Sabrina Belén, Tavares Frederico Wanderley, Llovell Fèlix. Assessing viscosity in sustainable deep eutectic solvents and cosolvent mixtures: an artificial neural network-based molecular approach. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering 2024; 12 (21): 7987-8000.
- Hosseini SM, Pierantozzi M. Density, viscosity and CO2 solubility modeling of deep eutectic solvents from various neural network approaches. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers 2025; 169: 105988.
- Christodoulou Stella, Cousseau Camille, Limanton Emmanuelle, Toucouere Lorris, Gauffre Fabienne, Legouin Béatrice, Maron Laurent, Paquin Ludovic, Poteau Romuald. Efficient machine-learning-based new tools to design eutectic mixtures and predict their viscosity. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering 2024; 12 (52): 18537-18554.
- Al-Akayleh Faisal, Ali Agha Ahmed S. A., Olaimat Ali R., Qinna Nidal A. Rationalizing Polysaccharide Extraction with Deep Eutectic Solvents: From Supramolecular Architecture to Emerging AI-Guided Solvent Design. Polysaccharides 2025. [Epub ahead of print]. [CrossRef]
- Al-Remawi Mayyas, Aburub Faisal, Al-Akayleh Faisal, Abdel-Rahem Rami A, Agha Ahmed SA Ali. Artificial Intelligence in Lipidomics: Advancing Biomarker Discovery, Pathway Analysis, and Precision Medicine. 2025 1st International Conference on Computational Intelligence Approaches and Applications (ICCIAA). IEEE; 2025:01-05.
- Al-Akayleh Faisal, Ali Agha Ahmed SA, Abdel Rahem Rami A, Al-Remawi Mayyas. A mini review on the applications of artificial intelligence (AI) in surface chemistry and catalysis. Tenside Surfactants Detergents 2024; 61 (4): 285-296.
- Al-Akayleh Faisal, Agha Ahmed SA Ali. Trust, ethics, and user-centric design in AI-integrated genomics. 2024 2nd International Conference on Cyber Resilience (ICCR). IEEE; 2024:1-6.
- Al-Remawi Mayyas, Abdel-Rahem Rami A, Al-Akayleh Faisal, Aburub Faisal, Agha Ahmed SA Ali. Transforming Obesity Care Through Artificial Intelligence: Real-Case Implementations and Personalized Solutions. 2025 1st International Conference on Computational Intelligence Approaches and Applications (ICCIAA). IEEE; 2025:1-5.
- Aburub Faisal, Al-Remawi Mayyas, Abdel-Rahem Rami A, Al-Akayleh Faisal, Agha Ahmed SA Ali. AI-Driven Whole-Exome Sequencing: Advancing Variant Interpretation and Precision Medicine. 2025 1st International Conference on Computational Intelligence Approaches and Applications (ICCIAA). IEEE; 2025:1-5.
- Al-Adham Ibrahim SI, Agha Ahmed SA Ali, Al-Akayleh Faisal, Al-Remawi Mayyas, Jaber Nisrein, Al Manasur Manar, Collier Phillip J. Prebiotics Beyond the Gut: Omics Insights, Artificial Intelligence, and Clinical Trials in Organ-Specific Applications. Probiotics Antimicrob 2025: 1-22.
- Al-Remawi Mayyas, Agha Ahmed SA Ali, Al-Akayleh Faisal, Aburub Faisal, Abdel-Rahem Rami A. Artificial intelligence and machine learning techniques for suicide prediction: Integrating dietary patterns and environmental contaminants. Heliyon 2024; 10 (24).
- Ghunaim Lama, Agha Ahmed Saad Abdulbari Ali, Aburjai Talal. Integrating artificial intelligence and advanced genomic technologies in unraveling autism spectrum disorder and gastrointestinal comorbidities: a multidisciplinary approach to precision medicine. Jordan Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2024; 17 (3): 567-581.
- Al-Akayleh Faisal, Al-Remawi Mayyas, Agha Ahmed SA Ali. AI-driven physical rehabilitation strategies in post-cancer care. 2024 2nd International Conference on Cyber Resilience (ICCR). IEEE; 2024:1-6.
- Aburub Faisal, Agha Ahmed SA Ali. AI-driven psychological support and cognitive rehabilitation strategies in post-cancer care. 2024 2nd international conference on cyber resilience (ICCR). IEEE; 2024:1-6.
- Liu Yang, Kashima Hisashi. Chemical property prediction under experimental biases. Sci Rep 2022; 12 (1): 8206.
- Al-Akayleh Faisal, Abdel-Rahem Rami A, Al-Remawi Mayyas, Aburub Faisal, Al-Adham Ibrahim SI, Agha Ahmed SA Ali. AI-Driven Tools and Methods for Wound Healing: Towards Precision Wound Care and Optimized Outcomes. 2025 1st International Conference on Computational Intelligence Approaches and Applications (ICCIAA). IEEE; 2025:01-05.
- Aburub Faisal, Al-Akayleh Faisal, Abdel-Rahem Rami A, Al-Remawi Mayyas, Agha Ahmed SA Ali. AI-Driven Transcriptomics: Advancing Gene Expression Analysis and Precision Medicine. 2025 1st International Conference on Computational Intelligence Approaches and Applications (ICCIAA). IEEE; 2025:1-5.
- Ghunaim Lama, Agha Ahmed SA Ali, Al-Samydai Ali, Aburjai Talal. The future of pediatric care: AI and ML as catalysts for change in genetic syndrome management. Jordan Medical Journal 2024; 58 (4).
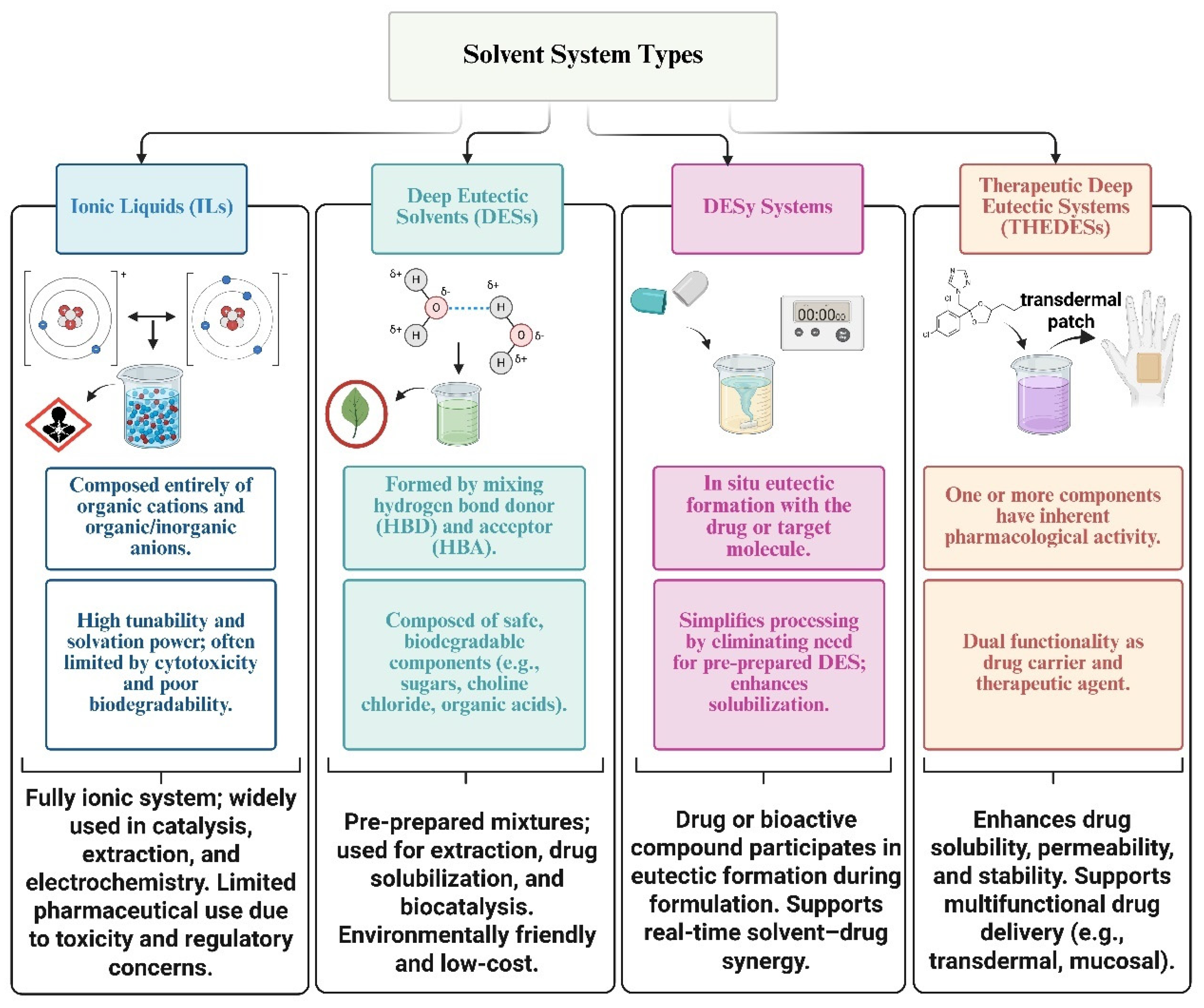
| Feature | ES | DES | ILs | DESy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Composition | Organic/inorganic blends of solid compounds | Mixtures of H-bond donors and acceptors (ionic or non-ionic) | Pure salts: discrete organic cations and inorganic/organic anions | In situ mixtures formed with the active compound as part of the eutectic system |
| Melting Behavior | Sharp melting point at eutectic composition (solid or semisolid at RT) | Depressed melting point; liquid at or near room temperature | Liquid at room temperature due to bulky asymmetric ions | Formed dynamically during application; liquid under process conditions |
| Type of Interactions | Weak van der Waals and minimal hydrogen bonding | Extensive hydrogen bonding network | Electrostatic (ionic) interactions | Hydrogen bonding and solvation driven by target molecule–solvent synergy |
| Polarity and Solubility | Moderate; limited to polar solutes | Polar; excellent for solubilizing poorly soluble APIs | Broad—dissolves both polar and non-polar compounds | Typically polar; designed to improve solubility of target APIs |
| Tunable Properties | Limited | Highly tunable via component selection and ratio adjustments | Highly tunable via cation/anion selection | Moderately tunable via selection of in situ interacting components and formulation conditions (e.g., temperature, water content). |
| Therapeutic Functionality | Typically absent | Possible if one or more components have inherent biological activity (THEDES) | Generally inert in drug delivery unless functionalized | Yes; active compound contributes to both therapeutic and solvent function |
| Toxicity and Biocompatibility | Depends on components | Often low (especially with natural components like fatty acids, amino acids, sugars) | Variable; some ILs have cytotoxicity and environmental concerns | Generally favorable if composed of GRAS or natural components |
| Environmental Impact | Moderate to high (based on solvents used) | Low (especially for NaDES and THEDES based on natural compounds) | Often high; requires careful design for biodegradability | Low; reduced processing steps and mild preparation conditions |
| Example Systems | Benzoic acid–urea | Choline chloride–urea, choline chloride–capric acid, menthol–ibuprofen | 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride ([Bmim]Cl), [EtPy][BF₄] | In situ systems formed with kiwifruit or date seed polysaccharides |
| Applications | Melting point depression, food, metallurgy | Green extraction, pharmaceutical formulation, topical/transdermal delivery (THEDES) | Organic synthesis, catalysis, electrochemistry, solubilization | Prebiotic extraction, drug solubilization, biocompatible formulations |
| Reference | [23] | [24] | [25] | [20] |
| Components with CA | Ratio | Observation | Application | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tetradecanoic acid (myristic acid) | CA: Myristic acid = 82:18 (mol%) or 78:22 (wt%) | Smooth, homogeneous, congruent melt; no phase separation | As a phase change material (PCM) of potential interest for passive temperature control in buildings | [39] |
| Myristic acid, Lauric acid, Steric acid | Molar Ratio (CA: Myristic acid) 3:1 Molar Ratio (CA: Lauric acid) 2:1 Molar Ratio (CA: Stearic acid) 4:1 |
Pasty-like solid Transparent liquid White solid |
Synergistic antimicrobial activity | [35] |
| Thymol, Menthol |
(Thymol: CA) 0.33: 0.67 0.50: 0.50 0.67: 0.33 (Menthol: CA) 0.33: 0.67 0.50: 0.50 0.67: 0.33 |
Homogeneous liquid Homogeneous liquid Homogeneous liquid Homogeneous liquid Homogeneous liquid Homogeneous liquid |
Reported physical properties and their dependence on constituents/composition of the NADESs will enhance their utility and help establish them as novel alternate media in science and technology. | [40] |
| Gefitinib | (Gefitinib: CA) 80: 20 ≤70: 30 Extreme ratios |
Clear liquid Pasty Powder/solid |
Enhance Gefitinib solubility and exhibit a synergistic cytotoxic effect against EGFR-expressing cell lines | [7] |
| Tetrabutylammonium chloride (TBAC), methyl tricaprylmethylammonium chloride (TOMAC) | (TBAC:CA) 1:2 (TOMAC:CA) 1:2 |
Clear, viscous fluid Clear, viscous fluid |
Have the potential to be a novel class of lubricants | [41] |
| Cineole | (Cineole: CA) 1: 1 |
Clear, low-viscosity liquid |
Very low viscous and dense fluid, with suitable properties for several solubilization technologies. its suitability to penetrate and stabilize cell membranes may lead to adverse outcomes when living organisms are exposed to this hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent.
|
[27] |
|
Droperidol |
(Droperidol: CA) 0.9:0.1 (D1) 0.8:0.2 (D2) 0.7:0.3 (D3) ≤0.6:0.4 (D4–D8) |
Clear eutectic liquid; ¹H NMR showed Δδ = +0.08–0.09 ppm at protons adjacent to piperidine N; DOSY confirmed reduced CA diffusion; DSC showed no melting peaks; highest intestinal flux (1.182 mg cm⁻² s⁻¹ at 15 min). Homogeneous liquid; similar NMR shifts; DSC revealed CA recrystallization on cooling (−8.1 °C); slightly lower flux than D1. Partial melting; depressed CA melting at 17.7 °C in DSC; signs of phase separation. Pasty mixtures; recrystallization and Tg observed in DSC; weak interaction. |
Solvent-free THEDES platform for enhancing droperidol solubility and intestinal permeability; suitable for green pharmaceutical formulation. |
[12] |
| Aripiprazole | (Aripiprazole: CA) 0.9:0.1 (A1) 0.8:0.2 (A2) ≤0.7:0.3 (A3–A8) |
Clear eutectic liquid; downfield shifts in amide (Δδ = +0.62 ppm) and piperazine CH₂ (Δδ = +0.10 ppm); strong H-bonding confirmed. Similar spectral shifts: eutectic liquid maintained; no residual crystallinity. Heterogeneous pastes; DSC showed unincorporated CA (e.g., CA melting at 18.7 °C in A3); weak or absent interactions. |
Hydrogen-bond-stabilized eutectic systems enabling improved solubility and biopharmaceutical performance of aripiprazole. | [12] |
| Lauric acid | (Lauric acid: CA) 1:2 |
Clear, homogeneous liquid; lowest density (0.859 g/cm³); Newtonian flow; visually stable. Lycopene yield 7.51 mg/100 g FW, total carotenoids 8.04 mg/100 g. | Green solvent for lycopene extraction; practical operating window established. | [42] |
| Lauric acid |
(CA : Lauric Acid) 1:1 2:1 |
Transparent liquid; thicker flow (shear-thickening). Lycopene 2.98 mg/100 g. Transparent liquid; more viscous feel; Lycopene 3.19 mg/100 g. |
Alternative HNADES with moderate performance. Lower-performing variant. |
[42] |
| Dodecanoic acid |
(Dodecanoic cid:CA) 1:2 |
Clear, uniform liquid; noticeably viscous; stable hydrophobic phase. Effective for Cu²⁺, Co²⁺, Ni²⁺ extraction |
Green solvent for metal recovery; applicable in wastewater treatment. | [43] |
| Matrine | (Matrine:CA) 1:1 |
Slightly yellowish homogeneous liquid; density and viscosity decrease with temperature; moderate thermal stability |
better antibacterial activity on S. aureus as compared with matrine | [44] |
| Polyethylene glycol |
Weigh% Mass Ratio (polyethylene glycol:CA) 1:1 |
Congruent eutectic at ~22.9 °C with high latent heat (173.9 J g⁻¹); reduced supercooling, faster crystallization, stable after 200 cycles, negligible corrosion. |
Thermal energy storage for solar passive buildings; energy saving (≈4.9 kWh·kg⁻¹·yr⁻¹), cost-effective, and carbon neutral within ~3 years. | [45] |
| Mirtazapine |
(Mirtazapine:CA) 1:2 |
Light-yellow transparent viscous liquid; no crystals (polarized microscopy) |
Transdermal delivery of MTZ to bypass first-pass metabolism; promising topical antidepressant THEDES. | [46] |
| Levofloxacine: |
(CA:Levofloxacin) 9:1, 8:2, 7:3 (DES liquids formed at these ranges; eutectic ~80:20–70:30 |
Clear liquids (THDES); DES formation confirmed by ¹H NMR & ATR-FTIR (H-bonding) and DSC (melting point depression; excess CA signal decreases with more LEV). |
Green THDES to enhance LEV performance: solubilization + antibacterial synergy; potential to combat resistance. | [36] |
| Ketoconazole: | Molar Ratio (Ketoconazole: CA) 1:5 |
Clear, stable liquid at room temperature for ≥5 months. |
Enhanced antifungal efficacy, solubility, and transdermal permeability using a green, stable THEDES system. | [6] |
| Oxymatrine: | (Oxymatrine: CA) 1: 1 |
Stable transparent DES. |
Biocompatible, low-toxicity enhancer; suitable when high safety is prioritized. | [47] |
| Ibuprofen: | (Ibuprofen: CA) 1:3 |
Clear, stable liquid at 37 °C. |
Effective transient eutectic solubilizer; excellent for dual-drug oral systems when combined with surfactant; balances high solubility and moderate release. | [48] |
|
Clotrimazole
|
(Clotrimazole:CA) 1:1 1:2 1:3 1:4 1:5 |
Solid at RT (not a DES) Transparent liquid; physically stable ≥1 year (DES candidate) Eutectic point; transparent liquid Transparent liquid; physically stable (DES candidate) Solid at RT (not a DES) |
Therapeutic DES (THEDES) for enhanced antifungal potency and skin permeation | [49] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





