Submitted:
05 December 2025
Posted:
09 December 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Inclusion Criteria and Exclusion Criteria
2.2. Quality Assessment and Data Analysis (Figure 1 and Table S1-S3)
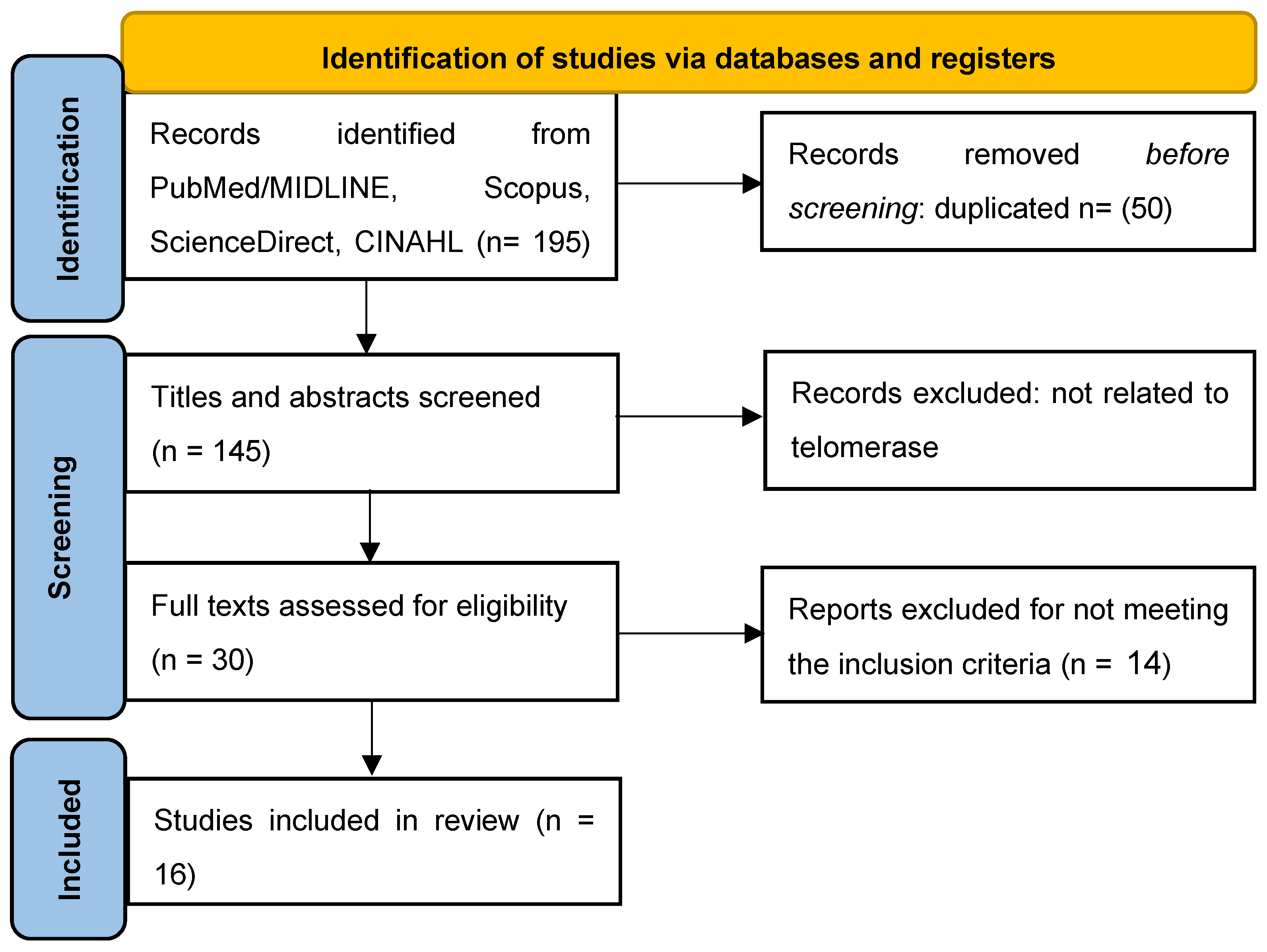
3. Results
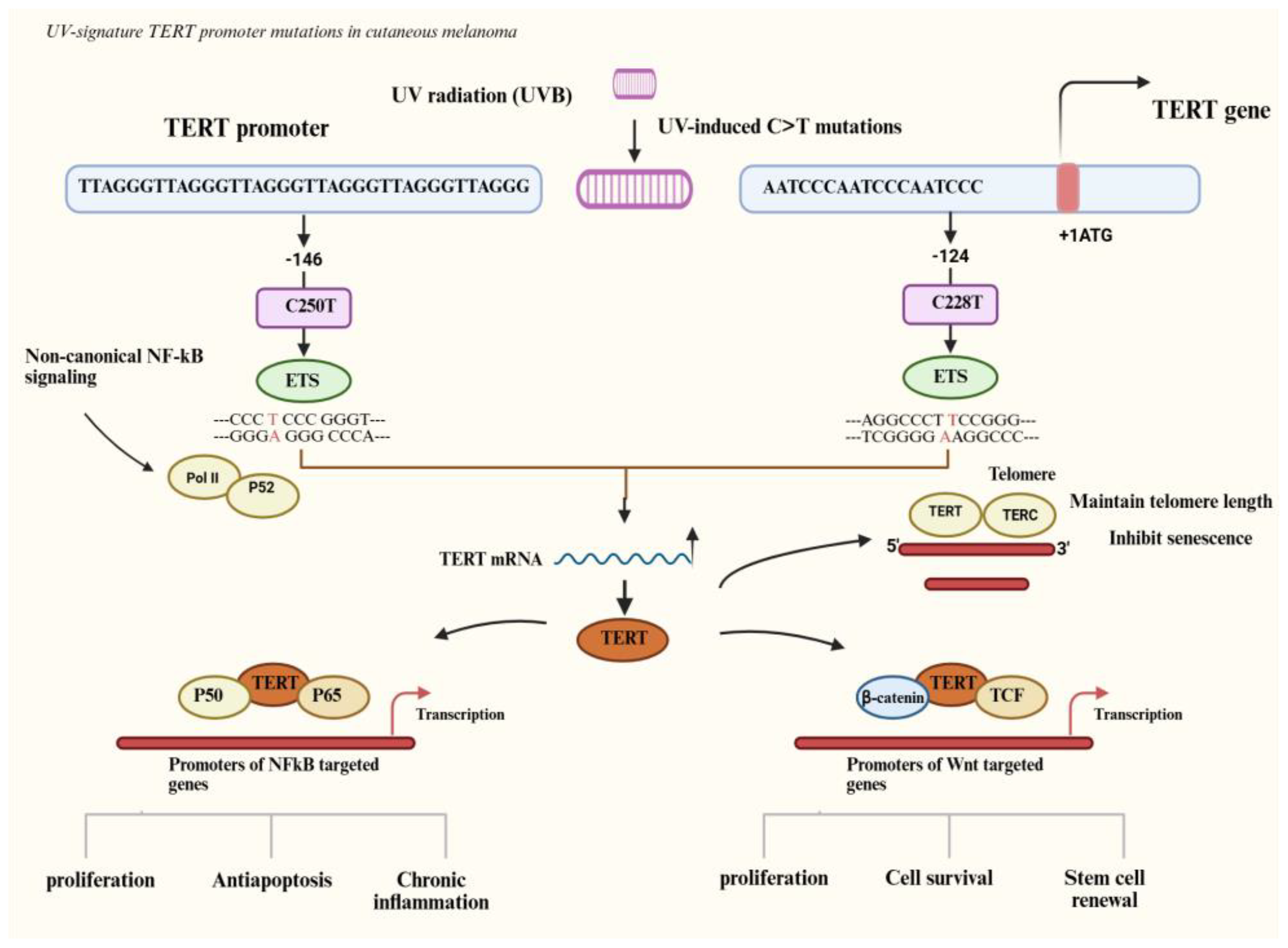
3.1. TERT Promoter Mutations as Drivers of Proliferation
3.3. Therapeutic Targeting of Telomerase in Melanoma
4. Discussion
Limitations of This Study
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABC | ATP-binding cassette |
| ALT | Alternative lengthening of telomeres |
| BRAF | v-Raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B |
| BRAF V600E | A common activating mutation in the BRAF gene that leads to constitutive activation of the MAPK pathway |
| CRISPR | Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats |
| EGFR | epidermal growth factors receptor |
| EXTEND | Expression based telomerase enzymatic activity detection |
| ETS | E26 transformation specific (Erythroblast transformation specific) |
| G1-S/G2-M phases | Cell cycle phases |
| GABP | GA-binding protein |
| GO | Gene ontology |
| hTERT | Human telomerase reverse transcriptase |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| MEK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| miRNA | Micro-ribonucleic acid |
| mRNA | Messenger ribonucleic acid |
| MSI-H | Microsatellite instability-high |
| N/A | Not available |
| NF-kB | Nuclear factor kappa -light-chain- enhancer of activated B cells |
| NF1 | Neurofibromin |
| NRAS | Neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog |
| PMCA4 | Plasma membrane calcium ATpase4 |
| PSF | Pathway signal flow |
| RNA-seq | RNA sequencing |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SEER | Surveillance, epidemiology and end results |
| TCGA | The cancer Genome atlas |
| TEL | Telomerase dependent pathway (telomerase positive phenotype) |
| TERT | Telomerase reverse transcriptase |
| TF | Transcription factor |
| TICCA | Transient, immediate, complete and combinatory attack |
| TME | Tumor microenvironment |
| TMM | Telomere maintenance mechanism |
| TPP1 | Telomerase processivity protein 1 |
| UV | Ultraviolet |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
| WT | Wild type |
References
- Okobi, O.E., et al., Trends in melanoma incidence, prevalence, stage at diagnosis, and survival: an analysis of the United States Cancer Statistics (USCS) Database. Cureus, 2024. 16(10). [CrossRef]
- Wagle, N.S., et al., Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2025. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 2025. [CrossRef]
- Rudolph, P., et al., Telomerase activity in melanocytic lesions: a potential marker of tumor biology. The American journal of pathology, 2000. 156(4): p. 1425-1432.
- Ramirez, R.D., et al., Progressive increase in telomerase activity from benign melanocytic conditions to malignant melanoma. Neoplasia, 1999. 1(1): p. 42-49. [CrossRef]
- Parris, C., et al., Telomerase activity in melanoma and non-melanoma skin cancer. British journal of cancer, 1999. 79(1): p. 47-53. [CrossRef]
- Horn, S., et al., TERT promoter mutations in familial and sporadic melanoma. Science, 2013. 339(6122): p. 959-961. [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.W., et al., Highly recurrent TERT promoter mutations in human melanoma. Science, 2013. 339(6122): p. 957-959. [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y., et al., TERT promoter mutations and telomerase in melanoma. Journal of oncology, 2022. 2022(1): p. 6300329. [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.W., et al., Specific association of human telomerase activity with immortal cells and cancer. Science, 1994. 266(5193): p. 2011-2015. [CrossRef]
- Blackburn, E.H., E.S. Epel, and J. Lin, Human telomere biology: a contributory and interactive factor in aging, disease risks, and protection. Science, 2015. 350(6265): p. 1193-1198. [CrossRef]
- Shay, J.W., et al., Telomerase and cancer. Human molecular genetics, 2001. 10(7): p. 677-685.
- Lincz, L.F., et al., Quantification of hTERT splice variants in melanoma by SYBR green real-time polymerase chain reaction indicates a negative regulatory role for the β deletion variant. Neoplasia, 2008. 10(10): p. 1131-1137. [CrossRef]
- Blagoev, K.B., Cell proliferation in the presence of telomerase. PLoS One, 2009. 4(2): p. e4622. [CrossRef]
- Cristofari, G. and J. Lingner, Telomere length homeostasis requires that telomerase levels are limiting. The EMBO journal, 2006. 25(3): p. 565-574. [CrossRef]
- Noureen, N., et al., Integrated analysis of telomerase enzymatic activity unravels an association with cancer stemness and proliferation. Nature communications, 2021. 12(1): p. 139. [CrossRef]
- Delyon, J., et al., TERT expression induces resistance to BRAF and MEK inhibitors in BRAF-mutated melanoma in vitro. Cancers, 2023. 15(11): p. 2888. [CrossRef]
- Blanco-García, L., et al., pTERT C250T mutation: A potential biomarker of poor prognosis in metastatic melanoma. Heliyon, 2023. 9(8). [CrossRef]
- Ali, J.H. and M. Walter, Combining old and new concepts in targeting telomerase for cancer therapy: transient, immediate, complete and combinatory attack (TICCA). Cancer Cell International, 2023. 23(1): p. 197. [CrossRef]
- Guterres, A.N. and J. Villanueva, Targeting telomerase for cancer therapy. Oncogene, 2020. 39(36): p. 5811-5824.
- Lipinska, N., et al., Telomerase and drug resistance in cancer. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 2017. 74(22): p. 4121-4132.
- Boccardi, V. and L. Marano, Aging, cancer, and inflammation: the telomerase connection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2024. 25(15): p. 8542. [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.-y., et al., Targeting telomere dynamics as an effective approach for the development of cancer therapeutics. International Journal of Nanomedicine, 2024: p. 3805-3825. [CrossRef]
- Welfer, G.A. and B.D. Freudenthal, Recent advancements in the structural biology of human telomerase and their implications for improved design of cancer therapeutics. NAR cancer, 2023. 5(1): p. zcad010. [CrossRef]
- Hakobyan, M., H. Binder, and A. Arakelyan, Pan-cancer analysis of telomere maintenance mechanisms. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2024. 300(6). [CrossRef]
- Sanford, S.L. and P.L. Opresko, UV light-induced dual promoter mutations dismantle the telomeric guardrails in melanoma. DNA repair, 2023. 122: p. 103446. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G., et al., Induction of telomere dysfunction prolongs disease control of therapy-resistant melanoma. Clinical Cancer Research, 2018. 24(19): p. 4771-4784. [CrossRef]
- Robinson, N.J. and W.P. Schiemann, Telomerase in cancer: function, regulation, and clinical translation. Cancers, 2022. 14(3): p. 808. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S. and S. Chowdhury, Emerging mechanisms of telomerase reactivation in cancer. Trends in cancer, 2022. 8(8): p. 632-641. [CrossRef]
- Baylie, T., et al., The role of telomere and telomerase in cancer and novel therapeutic target: narrative review. Frontiers in Oncology, 2025. 15: p. 1542930. [CrossRef]
- Kozyra, P., D. Krasowska, and M. Pitucha, New potential agents for malignant melanoma treatment—most recent studies 2020–2022. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2022. 23(11): p. 6084.
- Chun-On, P., et al., TPP1 promoter mutations cooperate with TERT promoter mutations to lengthen telomeres in melanoma. Science, 2022. 378(6620): p. 664-668. [CrossRef]
- Shay, J.W. and W.E. Wright, Telomeres and telomerase: three decades of progress. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2019. 20(5): p. 299-309. [CrossRef]
- Cesare, A.J. and R.R. Reddel, Alternative lengthening of telomeres: models, mechanisms and implications. Nature reviews genetics, 2010. 11(5): p. 319-330. [CrossRef]
- Jafri, M.A., et al., Roles of telomeres and telomerase in cancer, and advances in telomerase-targeted therapies. Genome medicine, 2016. 8(1): p. 69. [CrossRef]
- Mizukoshi, E. and S. Kaneko, Telomerase-targeted cancer immunotherapy. International journal of molecular sciences, 2019. 20(8): p. 1823.
- Satyanarayana, A., M.P. Manns, and K.L. Rudolph, Telomeres, telomerase and cancer: an endless search to target the ends. Cell Cycle, 2004. 3(9): p. 1136-1148. [CrossRef]
- Barthel, F.P., et al., Systematic analysis of telomere length and somatic alterations in 31 cancer types. Nature genetics, 2017. 49(3): p. 349-357. [CrossRef]
- Bell, R.J., et al., The transcription factor GABP selectively binds and activates the mutant TERT promoter in cancer. Science, 2015. 348(6238): p. 1036-1039. [CrossRef]
- Vallarelli, A.F., et al., TERT promoter mutations in melanoma render TERT expression dependent on MAPK pathway activation. Oncotarget, 2016. 7(33): p. 53127. [CrossRef]
- Heidenreich, B., et al., TERT promoter mutations and telomere length in adult malignant gliomas and recurrences. Oncotarget, 2015. 6(12): p. 10617. [CrossRef]
- Leão, R., et al., Combined genetic and epigenetic alterations of the TERT promoter affect clinical and biological behavior of bladder cancer. International journal of cancer, 2019. 144(7): p. 1676-1684. [CrossRef]
- Shay, J.W., Role of telomeres and telomerase in aging and cancer. Cancer discovery, 2016. 6(6): p. 584-593. [CrossRef]
- Nardin C, Laheurte C, Puzenat E, Boullerot L, Ramseyer M, Marguier A, Jacquin M, Godet Y, Aubin F, Adotevi O. Naturally Occurring Telomerase-Specific CD4 T-Cell Immunity in Melanoma. J Invest Dermatol. 2022 Feb;142(2):435-444. Epub 2021 Aug 2. PMID: 34352265. [CrossRef]
- Aamdal E, Inderberg EM, Ellingsen EB, Rasch W, Brunsvig PF, Aamdal S, Heintz KM, Vodák D, Nakken S, Hovig E, Nyakas M, Guren TK, Gaudernack G. Combining a Universal Telomerase Based Cancer Vaccine With Ipilimumab in Patients With Metastatic Melanoma—Five-Year Follow Up of a Phase I/IIa Trial. Front Immunol. 2021 May 11;12:663865. PMID: 34046035; PMCID: PMC8147687. [CrossRef]
| Author/years/ Reference |
Purpose | Settings | Sample size | Study design | Main findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boccardi V (2024) [21] | To review the relationship between telomeres/telomerase, aging, inflammation and cancer. | Division of Gerontology & Geriatrics, U. Perugia (Italy) & affiliated medical/surgical depts, Poland. | N/A | Narrative review. | Describes how telomere shortening and telomerase dysregulation link chronic inflammation, aging and cancer, & summarizes telomerase-targeted therapies. |
| Guo Y (2022) [8] |
To review the role of TERT promoter mutations and telomerase in melanoma biology, prognosis and treatment. | Dept of Oncology/Plastic & Burns Surgery, 1st Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical U., China. | N/A | Narrative review. | Describes how hotspot TERT RT promoter mutations increase TERT/telomerase activity, link to aggressive disease and poor prognosis, Outlines emerging telomerase-targeted and combina-tion therapies in melanoma. |
| Lipinska (2017) [20] | To review the mechanisms linking telomerase activity with drug resistance in cancer. | Dept of Clinical Chemistry and Molecular Diagnostics, Poznan U. of Medical Sciences, Poland. | N/A | Narrative review. | Describes how hTERT activation, mitochondrial translocation and vault/ABC transporter pathways contribute to chemoresistance and cancer cell survival. |
| Haj Ali (2023) [18] |
To summarize classical and novel approaches in telomerase-targeted cancer therapy and propose the TICCA concept. | Institute of Laboratory Medicine, Charité Berlin & University of Rostock, Germany. | N/A | Narrative review. | Reviews mechanisms of telomerase inhibition and introduces the TICCA strategy (Transient, Immediate, Complete, and Combinatory Attack) as a combined therapeutic model integrating CRISPR/Cas9, telomere deprotection, and hybrid inhibitors for improved long-term cancer control. |
| Tao H (2024) [22] |
To review the therapeutic potential of targeting telomere dynamics in cancer. | Institute of Medicinal Biotechnology, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing. | N/A | Narrative review. | Summarizes telomere- and telomerase-targeted drugs in clinical and preclinical stages, highlighting their chemotherapeutic and immunotherapeutic potential and integration into nanomedicine systems. |
| Welfer GA (2023) [23] | To summarize recent advances in human telomerase structural biology and implications for drug design. | U. Kansas Medical Center, Kansas City, USA. | N/A | Narrative review. | Reviews new cryo-EM structures of human telomerase, elucidating mechanisms of recruitment, telomere synthesis, and structural targets for rational inhibitor development. |
| Hakobyan M (2024) [24] | To perform a pan-cancer analysis of telomere maintenance mechanisms (TMM) across 33 cancer types. | Institute of Molecular Biology NAS RA, Armenia; U. Leipzig, Germany. | 11,123 TCGA samples. | Bioinformatics-based pan-cancer analysis. | Identified five distinct TMM phenotypes integrating telomerase (TEL) and ALT pathways; ALT and TEL coactivation correlated with worse survival and higher activity in MSI-H tumors. |
| Sanford SL (2022)[25] | To discuss how UV-induced promoter mutations in TERT and TPP1 cooperate to bypass telomere-based barriers in carcinogenesis. | U. Pittsburgh, USA. | N/A | Commentary/mechanistic review. | Highlights TERT and TPP1 promoter mutations as sequential UV-driven “hits” that cooperate to sustain telomere maintenance and melanoma progression. |
| Blanco-García L, 2023 [17] | To assess pTERT mutations/methylation in tissue & plasma of advanced melanoma and relate them to TERT expression and prognosis. | Hospital 12 de Octubre, Madrid, Spain. | 53 pts (88 tumors; 25 plasma). | Retrospective cohort. | C250T mutation linked to higher TERT expression and poor survival; pTERT hypermethylation enriched in WT tumors. |
| Zhang (2018) [26] |
To test telomerase-targeted nucleoside 6-thio-dG in therapy-resistant melanoma. | The Wistar Institute, Philadelphia, USA. | Several human melanoma cell lines and xenografts). | Preclinical experimental study. | 6-thio-dG induces telomere dysfunction, apoptosis, and tumor control in therapy-resistant melanoma. |
| Robinson N (2022) [27] | To review telomerase functions, regulation, and clinical applications in cancer. | Case Comprehensive Cancer Center, Case Western Reserve U., USA. | N/A | Comprehensive review. | Summarizes telomerase’s telomeric and extratelomeric roles, regulatory mechanisms, and its translational potential as a biomarker and therapeutic target. |
| Delyon J (2023) [16] |
To assess how TERT expression influences resistance to BRAF and MEK inhibitors in BRAF-mutated melanoma. | INSERM U976 and Hospital Saint Louis, U. Paris Cité, France. | 48 patients + in vitro cell lines. | Translational and in vitro study. | High TERT expression correlated with reduced response to BRAF/MEK inhibitors; TERT overexpression reactivated MAPK pathway independently of telomere maintenance. |
| Sharma S (2022) [28] |
To summarize emerging molecular mechanisms underlying hTERT promoter–driven telomerase reactivation in cancer. | CSIR-Institute of Genomics and Integrative Biology, New Delhi, India. | N/A | Narrative review. | Describes how hTERT promoter mutations, chromatin looping, and G-quadruplex destabilization cooperatively reactivate telomerase across cancers. |
| Baylie T (2025) [29] |
To review telomere and telomerase structure, function, and their role as therapeutic targets in cancer. | Debre Markos U., Ethiopia. | N/A | Narrative review. | Summarizes telomerase biology and emerging therapeutic strategies, including antisense oligonucleotides, G-quadruplex stabilizers, and telomerase-targeted immunotherapies. |
| Kozyra P (2022) [30] Chun-on P (2022)[31] Noureen N (2021) [15] |
To review newly synthesized anti-melanoma agents and their molecular targets (2020–2022). | Medical U. Lublin, Poland. | N/A | Systematic literature review. | Summarizes recent compounds targeting MAPK, PI3K–AKT, and ion-channel pathways; highlights benzimidazole-based telomerase inhibitors among emerging therapeutic candidates. |
| To investigate whether TPP1 promoter mutations cooperate with TERT promoter mutations in melanoma. | U. Pittsburgh & UC Santa Cruz, USA. | 749 melanoma samples. | Genomic and functional analysis. | TPP1 promoter variants co-occur with TERT mutations, enhancing TPP1 expression and synergistically lengthening telomeres in melanoma cells. | |
| To quantify telomerase enzymatic activity and explore its link with cancer stemness and proliferation. | UT Health San Antonio & MD Anderson Cancer Center, USA. | >9,000 tumors from TCGA & multiple validation cell lines. | Computational and experimental validation study. | Developed the EXTEND algorithm; showed telomerase activity strongly correlates with cancer stemness and proliferation, outperforming TERT expression as a biomarker. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





