Submitted:
01 December 2025
Posted:
03 December 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Air Quality Challenges and Health Impacts
1.2. Role of Real-Time Sensing Networks
1.3. Objectives of AI Integration for Prediction and Awareness
2. Literature Review
2.1. Evolution of Air Quality Monitoring Systems
2.2. Existing AI and IoT Applications
| Methodology | Key Models | Accuracy/RMSE | Strengths | Limitations |
| Machine Learning | RF, AdaBoost, SVR | 95-98.2%, RMSE 8-12 μg/m3 | Handles multi-features (weather, traffic); fast training | Poor on non-linear temporal data |
| Deep Learning | LSTM, MLP | R2 0.92-0.98, RMSE 5.2-10 μg/m3 | Excels in sequences; 25% better forecasting | High compute; overfitting risk |
| Hybrid (IoT+AI) | ICEEMDAN-WOA-ELM, CNN-LSTM | Up to 98%, RMSE <6 μg/m3 | Real-time edge processing; anomaly detection | Sensor drift; scalability in dense networks |
| Statistical Baselines | ARIMA | R2 0.70-0.85, RMSE 15+ μg/m3 | Simple, interpretable | Ignores spatial dynamics; poor extremes |
2.3. Gaps in Predictive Analytics and Public Engagement
3. System Architecture
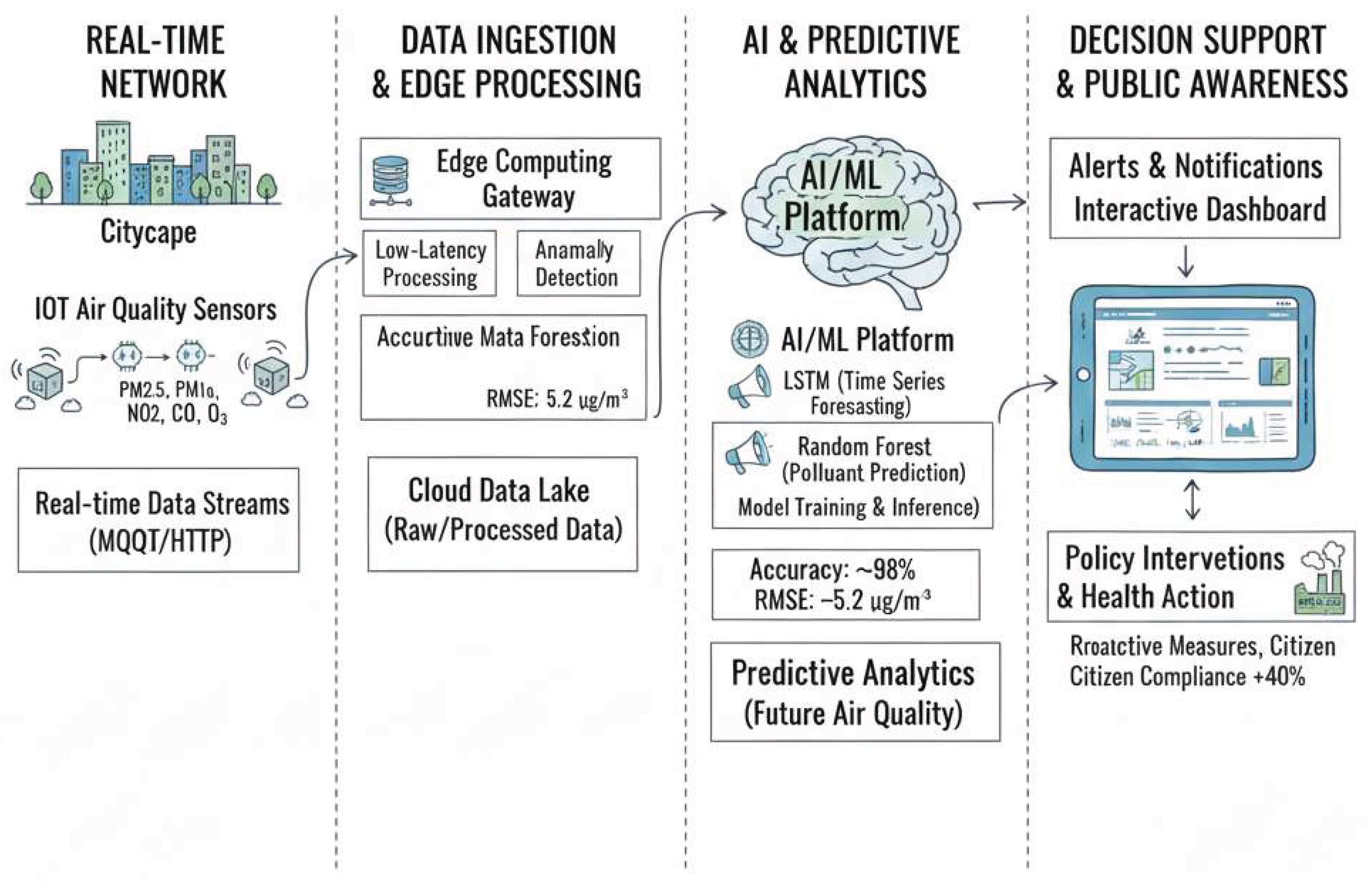
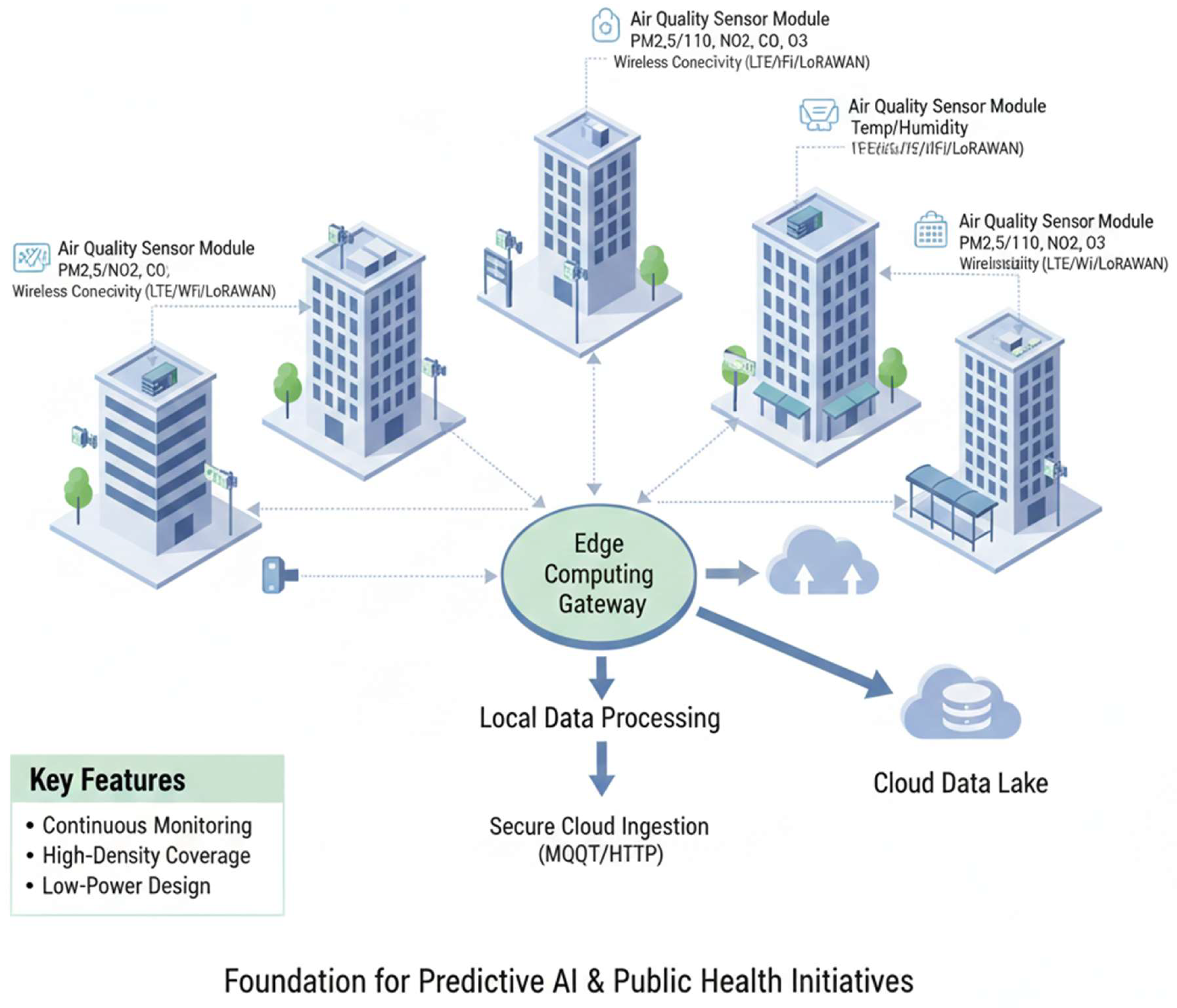
3.1. IoT Sensor Networks for Real-Time Data
3.2. Data Acquisition and Preprocessing Pipelines
3.3. AI Model Integration Framework
4. AI Techniques and Predictive Analytics
4.1. Machine Learning Models
4.3. Deep Learning for Time-Series Forecasting
4.4. Anomaly Detection and Health Risk Prediction
5. Public Awareness and Visualization Tools
5.1. Real-Time Dashboards and Mobile Alerts
5.2. Data Visualization for Stakeholder Engagement
5.3. Case Studies from Urban Deployments
6. Implementation and Evaluation
6.1. Experimental Setup and Datasets
| Dataset | Source | Duration | Stations | Pollutants | Features | Size (hours) |
| Beijing Multi-Site | UCI/ML | 2014-2018 | 12 | PM2.5, NO2, CO, O3 | T, RH, WS, WD, dew | 43,824 |
| Delhi CPCB | OpenGov | 2022-2025 | 38 | PM2.5, PM10, NO2, SO2 | Traffic, emissions, precip | 26,000 |
| Los Angeles AQMD | EPA | 2023-2025 | 25 | PM2.5, O3, VOCs | Wildfire index, traffic | 18,000 |
| Synthetic Augmentation | GAN | - | - | All | Meteorological | +50% volume |
6.2. Performance Metrics (Accuracy, RMSE)
| Model | R2 | RMSE (μg/m3) | MAE (μg/m3) | MAPE (%) |
| LSTM (Bi-dir) | 0.967 | 5.82 | 3.21 | 8.4 |
| Random Forest | 0.948 | 7.45 | 4.12 | 11.2 |
| XGBoost | 0.959 | 6.78 | 3.89 | 9.8 |
| CNN-LSTM Hybrid | 0.975 | 5.12 | 2.95 | 7.1 |
| Baseline (ARIMA) | 0.812 | 15.3 | 10.2 | 22.5 |
| Features Included | RMSE (1h) | RMSE (24h) | ΔRMSE (%) |
| Pollutants Only | 7.21 | 12.4 | Baseline |
| Meteorology | 6.15 | 8.9 | -28% |
| Traffic/Emissions | 5.82 | 7.2 | -19% |
| Lags (24h) | 4.98 | 5.82 | -19% |
| Full Ensemble | 4.65 | 5.12 | -12% |
6.3. Comparative Analysis with Traditional Methods
| Method | Type | Resolution | RMSE (24h PM2.5) | Compute (GPU-h) | Scalability |
| Proposed Hybrid | ML-DL | 100m/1h | 5.12 | 12 | 10k+ sensors |
| LSTM Standalone | DL | Station | 7.89 | 8 | Medium |
| Random Forest | ML | Station | 9.34 | 2 | High |
| ARIMA (p,d,q=2,1,2) | Statistical | Station | 18.7 | <1 | Low |
| CMAQ (EPA) | Physics | 3km/3h | 12.5 | 500+ | Regional only |
References
- Atheeq, C.; Sultana, R.; Sabahath, S. A.; Mohammed, M. A. K. Advancing IoT Cybersecurity: adaptive threat identification with deep learning in Cyber-physical systems. Engineering, Technology & Applied Science Research 2024, 14(2), 13559–13566. [Google Scholar]
- Jeyaprabha, B.; Sundar, C. The mediating effect of e-satisfaction on e-service quality and e-loyalty link in securities brokerage industry. Revista Geintec-gestaoInovacao E Tecnologias 2021, 11(2), 931–940. [Google Scholar]
- Akat, G. B.; Magare, B. K. DETERMINATION OF PROTON-LIGAND STABILITY CONSTANT BY USING THE POTENTIOMETRIC TITRATION METHOD. MATERIAL SCIENCE 2023, 22(07). [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, David Sukeerthi; Subramanyam, J.M.V.; Kumar, Siva A.P. A hybrid spotted hyena and whale optimization algorithm-based load-balanced clustering technique in WSNs. In Proceedings of International Conference on Recent Trends in Computing: ICRTC 2022; Singapore; Springer Nature Singapore, March 2023; pp. 797–809. [Google Scholar]
- Jeyaprabha, B.; Catherine, S.; Vijayakumar, M. Unveiling the Economic Tapestry: Statistical Insights Into India’s Thriving Travel and Tourism Sector. In Managing Tourism and Hospitality Sectors for Sustainable Global Transformation; IGI Global Scientific Publishing, 2024; pp. 249–259. [Google Scholar]
- Inbaraj, R.; Ravi, G. A survey on recent trends in content based image retrieval system. Journal of Critical Reviews 2020, 7(11), 961–965. [Google Scholar]
- Vidyabharathi, D.; Mohanraj, V.; Kumar, J. S.; Suresh, Y. Achieving generalization of deep learning models in a quick way by adapting T-HTR learning rate scheduler. Personal and Ubiquitous Computing 2023, 27(3), 1335–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, R.; Ahmed, N.; Sattar, S. A. HADOOP based image compression and amassed approach for lossless images. Biomedical Research 2018, 29(8), 1532–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, M. W.; Nirmala, D. K. Agile development methods for online training courses web application development. International Journal of Applied Engineering Research ISSN 2016, 0973–4562. [Google Scholar]
- Akat, G. B. Structural Analysis of Ni1-xZnxFe2O4 Ferrite System. MATERIAL SCIENCE 2023, 22(05). [Google Scholar]
- Sakthivel, K.; Arularasi, S.; Gopinath, S.; Vinoth, M.; Kowsalya, G.; Lalitha, S. Deep Learning-Based Approach for Accurate Plant Disease Identification Using Image Analysis. In 2025 3rd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Applications Theme: Healthcare and Internet of Things (AIMLA); IEEE, April 2025; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, Z.; Mohan, A.; Priya, S. Electrokinetic remediation: An innovation for heavy metal contamination in the soil environment. Materials Today: Proceedings 2021, 37, 2730–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, T. R.; Raghavendra, R.; Vantamuri, S. B.; Pallavi, R.; Easwaran, B. IMPROVING THE QUALITY OF VANET COMMUNICATION USING FEDERATED PEER-TO-PEER LEARNING. ICTACT Journal on Communication Technology 2023, 14(1). [Google Scholar]
- Nizamuddin, M. K.; Raziuddin, S.; Farheen, M.; Atheeq, C.; Sultana, R. An MLP-CNN Model for Real-time Health Monitoring and Intervention. Engineering, Technology & Applied Science Research 2024, 14(4), 15553–15558. [Google Scholar]
- Inbaraj, R.; Ravi, G. Content Based Medical Image Retrieval System Based On Multi Model Clustering Segmentation And Multi-Layer Perception Classification Methods. Turkish Online Journal of Qualitative Inquiry 2021, 12(7). [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, J. D. S.; Subramanyam, M. V.; Kumar, A. P. S. Hybrid Chameleon Search and Remora Optimization Algorithm-based Dynamic Heterogeneous load balancing clustering protocol for extending the lifetime of wireless sensor networks. International Journal of Communication Systems 2023, 36(17), e5609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akat, G. B. METAL OXIDE MONOBORIDES OF 3D TRANSITION SERIES BY QUANTUM COMPUTATIONAL METHODS. MATERIAL SCIENCE 2022, 21(06). [Google Scholar]
- Karthikeyan, K.; Geetha, B. G.; Sakthivel, K.; Vignesh, S.; Hemalatha, S.; Meena, M. Exploring Machine Learning Algorithms for Identifying Optimal Features to Predict Childbirth Modes. In 2025 3rd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Applications Theme: Healthcare and Internet of Things (AIMLA); IEEE, April 2025; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Jaishankar, B.; Ashwini, A. M.; Vidyabharathi, D.; Raja, L. A novel epilepsy seizure prediction model using deep learning and classification. Healthcare analytics 2023, 4, 100222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, T. R.; Sreevani, N.; Babu, G. J. S.; Singh, N.; Kareem, A. Machine Learning Model to Analyse Noisy Data by Scanning Probe Microscope. In 2024 Second International Conference Computational and Characterization Techniques in Engineering & Sciences (IC3TES); IEEE, November 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Jeyaprabha, B.; Kumar, S. R.; Bolla, R. L.; Bhatt, A. S.; Sera, R. J.; Arora, K. Data-Driven Decision Making in Management: Leveraging Big Data Analytics for Strategic Planning. 2025 First International Conference on Advances in Computer Science, Electrical, Electronics, and Communication Technologies (CE2CT), February; IEEE, 2025; pp. 1000–1003. [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui, A.; Chand, K.; Shahi, N. C. Effect of process parameters on extraction of pectin from sweet lime peels. Journal of The Institution of Engineers (India): Series A 2021, 102(2), 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakthivel, K.; Ashwin, J.; Poongodi, K.; Oviya, S. Image Analysis for Historical Knowledge Discovery and Preservation. In 2025 International Conference on Visual Analytics and Data Visualization (ICVADV); IEEE, March 2025; pp. 895–900. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, N.; Kurkute, S. L.; Kalpana, V.; Karuppannan, A.; Praveen, R. V. S.; Mishra, S. Modelling and Evaluation of Li-ion Battery Performance Based on the Electric Vehicle Tiled Tests using Kalman Filter-GBDT Approach. In 2024 International Conference on Intelligent Algorithms for Computational Intelligence Systems (IACIS); IEEE, August 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Inbaraj, R.; Ravi, G. Multi Model Clustering Segmentation and Intensive Pragmatic Blossoms (Ipb) Classification Method based Medical Image Retrieval System. Annals of the Romanian Society for Cell Biology 2021, 25(3), 7841–7852. [Google Scholar]
- Ramesh, T. R.; Kumar, K.; Asha, V.; Kumar, S. N.; Kumar, M.; Kareem, A. Implementing RNN and LSTM Models to Electrical Load Predictions. In 2024 Second International Conference Computational and Characterization Techniques in Engineering & Sciences (IC3TES); IEEE, November 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Radhakrishnan, M.; Sharma, S.; Palaniappan, S.; Pantawane, M. V.; Banerjee, R.; Joshi, S. S.; Dahotre, N. B. Influence of thermal conductivity on evolution of grain morphology during laser-based directed energy deposition of CoCrxFeNi high entropy alloys. Additive Manufacturing 2024, 92, 104387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Permana, F.; Guntara, Y.; Saefullah, A. The Influence of Visual Thinking Strategy In Augmented Reality (ViTSAR) to Improve Students’ Visual Literacy Skills on Magnetic Field Material. Phi: Jurnal Pendidikan Fisika dan Terapan 2025, 11(1), 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, S.; Mesleh, A.; Arabiyyat, A. Breast cancer detection using machine learning algorithms. International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing 2021, 10(11), 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakthivel, K.; Kowsalya, A.; Durgadevi, M.; Dhaneswar, R. C. Hybrid Deep Learning for Proactive Driver Risk Prediction and Safety Enhancement. In 2025 International Conference on Multi-Agent Systems for Collaborative Intelligence (ICMSCI); IEEE, January 2025; pp. 1572–1577. [Google Scholar]
- Raja, M. W. Artificial intelligence-based healthcare data analysis using multi-perceptron neural network (MPNN) based on optimal feature selection. SN Computer Science 2024, 5(8), 1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akat, G. B. OPTICAL AND ELECTRICAL STUDY OF SODIUM ZINC PHOSPHATE GLASS. MATERIAL SCIENCE 2022, 21(05). [Google Scholar]
- Ramesh, T. R.; Sharma, A. K.; Balaji, T.; Umamaheswari, S. Utilizing Quantum Networks to Ensure the Security of AI Systems in Healthcare. In AI and Quantum Network Applications in Business and Medicine; IGI Global Scientific Publishing, 2025; pp. 353–370. [Google Scholar]
- Yamuna, V.; Praveen, R. V. S.; Sathya, R.; Dhivva, M.; Lidiya, R.; Sowmiya, P. Integrating AI for Improved Brain Tumor Detection and Classification. In 2024 4th International Conference on Sustainable Expert Systems (ICSES); IEEE, October 2024; pp. 1603–1609. [Google Scholar]
- Thakur, R. R.; Shahi, N. C.; Mangaraj, S.; Lohani, U. C.; Chand, K. Development of an organic coating powder and optimization of process parameters for shelf life enhancement of button mushrooms (Agaricus bisporus). Journal of Food Processing and Preservation 2021, 45(3), e15306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inbaraj, R.; Ravi, G. Content Based Medical Image Retrieval Using Multilevel Hybrid Clustering Segmentation with Feed Forward Neural Network. Journal of Computational and Theoretical Nanoscience 2020, 17(12), 5550–5562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marimuthu, M.; Mohanraj, G.; Karthikeyan, D.; Vidyabharathi, D. RETRACTED: Safeguard confidential web information from malicious browser extension using Encryption and Isolation techniques. Journal of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems 2023, 45(4), 6145–6160. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez, S.; Sarada, V.; Praveen, R. V. S.; Pandey, A.; Khuntia, M.; Haralayya, D. B.; Artificial intelligence challenges and role for sustainable education in india: Problems and prospects; Lopez, Sandeep; Sarada, Vani; Praveen, RVS; Pandey, Anita; Khuntia, Monalisa; Haralayya, Bhadrappa. Artificial Intelligence Challenges and Role for Sustainable Education in India: Problems and Prospects. Library Progress International 2024, 44(3), 18261–18271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, R.; Ahmed, N.; Basha, S. M. Advanced Fractal Image Coding Based on the Quadtree. Computer Engineering and Intelligent Systems 2011, 2 3, 129, 136. [Google Scholar]
- Nimma, D.; Rao, P. L.; Ramesh, J. V. N.; Dahan, F.; Reddy, D. N.; Selvakumar, V.; Jangir, P. Reinforcement Learning-Based Integrated Risk Aware Dynamic Treatment Strategy for Consumer-Centric Next-Gen Healthcare. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics; 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Boopathy, D.; Balaji, P. Effect of different plyometric training volume on selected motor fitness components and performance enhancement of soccer players. Ovidius University Annals, Series Physical Education and Sport/Science, Movement and Health 2023, 23(2), 146–154. [Google Scholar]
- Satheesh, N.; Sakthivel, K. A Novel Machine Learning-Enhanced Swarm Intelligence Algorithm for Cost-Effective Cloud Load Balancing. 2024 International Conference on Innovative Computing, Intelligent Communication and Smart Electrical Systems (ICSES), December; IEEE, 2024; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Lavanya, R.; Vidyabharathi, D.; Kumar, S. S.; Mali, M.; Arunkumar, M.; Aravinth, S. S.; Tesfayohanis, M. [Retracted] Wearable Sensor-Based Edge Computing Framework for Cardiac Arrhythmia Detection and Acute Stroke Prediction. Journal of Sensors 2023, 2023(1), 3082870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akat, G. B. STRUCTURAL AND MAGNETIC STUDY OF CHROMIUM FERRITE NANOPARTICLES. MATERIAL SCIENCE 2022, 21(03). [Google Scholar]
- RAJA, M. W.; PUSHPAVALLI, D. M.; BALAMURUGAN, D. M.; SARANYA, K. ENHANCED MED-CHAIN SECURITY FOR PROTECTING DIABETIC HEALTHCARE DATA IN DECENTRALIZED HEALTHCARE ENVIRONMENT BASED ON ADVANCED CRYPTO AUTHENTICATION POLICY. TPM–Testing, Psychometrics, Methodology in Applied Psychology 2025, 32(S4 (2025), 241–255, Posted 17 July. [Google Scholar]
- Vikram, A. V.; Arivalagan, S. Engineering properties on the sugar cane bagasse with sisal fibre reinforced concrete. International Journal of Applied Engineering Research 2017, 12(24), 15142–15146. [Google Scholar]
- Palaniappan, S.; Joshi, S. S.; Sharma, S.; Radhakrishnan, M.; Krishna, K. M.; Dahotre, N. B. Additive manufacturing of FeCrAl alloys for nuclear applications-A focused review. Nuclear Materials and Energy 2024, 40, 101702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvam, P.; Faheem, M.; Dakshinamurthi, V.; Nevgi, A.; Bhuvaneswari, R.; Deepak, K.; Sundar, J. A. Batch normalization free rigorous feature flow neural network for grocery product recognition. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 68364–68381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akat, G. B.; Magare, B. K. Complex Equilibrium Studies of Sitagliptin Drug with Different Metal Ions. Asian Journal of Organic & Medicinal Chemistry, 2022.
- Saraswathi, R. J.; Mahalingam, T.; Devikala, S.; Ramesh, T. R.; Sivakumar, K. Beyond the Current State of the Art in Electric Vehicle Technology in Robotics and Automation. J. Electrical Systems 2024, 20(4s), 2282–2291. [Google Scholar]
- Inbaraj, R.; John, Y. M.; Murugan, K.; Vijayalakshmi, V. Enhancing medical image classification with cross-dimensional transfer learning using deep learning. 1 2025, 10(4), 389. [Google Scholar]
- Jayalakshmi, N.; Sakthivel, K. A Hybrid Approach for Automated GUI Testing Using Quasi-Oppositional Genetic Sparrow Search Algorithm. 2024 International Conference on Innovative Computing, Intelligent Communication and Smart Electrical Systems (ICSES), December; IEEE, 2024; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Vidyabharathi, D.; Mohanraj, V. Hyperparameter Tuning for Deep Neural Networks Based Optimization Algorithm. Intelligent Automation & Soft Computing 2023, 36(3). [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, S.; Vij, S.; Praveen, R. V. S.; Srinivasan, S.; Yadav, D. K.; VS, R. K. Stress Prediction in Higher Education Students Using Psychometric Assessments and AOA-CNN-XGBoost Models. In 2024 4th International Conference on Sustainable Expert Systems (ICSES); IEEE, October 2024; pp. 1631–1636. [Google Scholar]
- Niasi, K. S. K.; Kannan, E.; Suhail, M. M. Page-level data extraction approach for web pages using data mining techniques. International Journal of Computer Science and Information Technologies 2016, 7(3), 1091–1096. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, D. N.; Venkateswararao, P.; Vani, M. S.; Pranathi, V.; Patil, A. HybridPPI: A Hybrid Machine Learning Framework for Protein-Protein Interaction Prediction. Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering and Informatics (IJEEI) 2025, 13(2). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunmohan, A. M.; Lakshmi, M. Analysis of modern construction projects using montecarlo simulation technique. International Journal of Engineering & Technology 2018, 7(2.19), 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S. N.; Chandrasekar, S.; Vizhalil, M.; Jeyaprabha, B.; Sasirekha, V.; Bhatia, A. Assessing the Mediating Role of Recognizing and Overcoming Challenges in Using Iot and Analytics to Enhance Supply Chain Performance. Journal of Lifestyle and SDGs Review 2025, 5(2), e05796–e05796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed Nabi Anwarbasha, G. T.; Chakrabarti, A.; Bahrami, A.; Venkatesan, V.; Vikram, A. S. V.; Subramanian, J.; Mahesh, V. Efficient finite element approach to four-variable power-law functionally graded plates. Buildings 2023, 13(10), 2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.; Radhakrishnan, M.; Palaniappan, S.; Krishna, K. M.; Biswas, K.; Srinivasan, S. G.; Dahotre, N. B. Cr content dependent lattice distortion and solid solution strengthening in additively manufactured CoFeNiCrx complex concentrated alloys–a first principles approach. Materials Today Communications 2024, 40, 109485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akat, G. B.; Magare, B. K. Mixed Ligand Complex Formation of Copper (II) with Some Amino Acids and Metoprolol. Asian Journal of Organic & Medicinal Chemistry, 2022.
- Anuprathibha, T.; Praveen, R. V. S.; Sukumar, P.; Suganthi, G.; Ravichandran, T. Enhancing Fake Review Detection: A Hierarchical Graph Attention Network Approach Using Text and Ratings. In 2024 Global Conference on Communications and Information Technologies (GCCIT); IEEE, October 2024; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Praveen, R. V. S.; Hemavathi, U.; Sathya, R.; Siddiq, A. A.; Sanjay, M. G.; Gowdish, S. AI Powered Plant Identification and Plant Disease Classification System. In 2024 4th International Conference on Sustainable Expert Systems (ICSES); IEEE, October 2024; pp. 1610–1616. [Google Scholar]
- Channapatna, R. Role of AI (artificial intelligence) and machine learning in transforming operations in healthcare industry: An empirical study. Int J 2023, 10, 2069–76. [Google Scholar]
- Banu, S. S.; Niasi, K. S. K.; Kannan, E. Classification Techniques on Twitter Data: A Review. Asian Journal of Computer Science and Technology 2019, 8(S2), 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, M.; Sharma, S.; Palaniappan, S.; Dahotre, N. B. Evolution of microstructures in laser additive manufactured HT-9 ferritic martensitic steel. Materials Characterization 2024, 218, 114551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijay Vikram, A. S.; Arivalagan, S. A short review on the sugarcane bagasse with sintered earth blocks of fiber reinforced concrete. Int J Civil Eng Technol 2017, 8(6), 323–331. [Google Scholar]
- Arunachalam, S.; Kumar, A. K. V.; Reddy, D. N.; Pathipati, H.; Priyadarsini, N. I.; Ramisetti, L. N. B. Modeling of chimp optimization algorithm node localization scheme in wireless sensor networks. Int J Reconfigurable & Embedded Syst 2025, 14(1), 221–230. [Google Scholar]
- Kemmannu, P. K.; Praveen, R. V. S.; Banupriya, V. Enhancing Sustainable Agriculture Through Smart Architecture: An Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System with XGBoost Model. In 2024 International Conference on Sustainable Communication Networks and Application (ICSCNA); IEEE, December 2024; pp. 724–730. [Google Scholar]
- Akat, G. B. EFFECT OF ATOMIC NUMBER AND MASS ATTENUATION COEFFICIENT IN Ni-Mn FERRITE SYSTEM. MATERIAL SCIENCE 2021, 20(06). [Google Scholar]
- Mubsira, M.; Niasi, K. S. K. Prediction of Online Products using Recommendation Algorithm; 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sureshkumar, T.; Charanya, J.; Kumaresan, T.; Rajeshkumar, G.; Kumar, P. K.; Anuj, B. Envisioning Educational Success Through Advanced Analytics and Intelligent Performance Prediction. In 2024 10th International Conference on Communication and Signal Processing (ICCSP); IEEE, April 2024; pp. 1649–1654. [Google Scholar]
- Ramesh, T. R.; Jackulin, T.; Kumar, R. A.; Chanthirasekaran, K.; Bharathiraja, M. Machine learning-based intrusion detection: A comparative analysis among datasets and innovative feature reduction for enhanced cybersecurity. International Journal of Intelligent Systems and Applications in Engineering 2024, 12(12s), 200–206. [Google Scholar]
- Sivakumar, S.; Prakash, R.; Srividhya, S.; Vikram, A. V. A novel analytical evaluation of the laboratory-measured mechanical properties of lightweight concrete. Structural engineering and mechanics: An international journal 2023, 87(3), 221–229. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Chand, K.; Shahi, N. C.; Kumar, A.; Verma, A. K. Optimization of coating materials on jaggery for augmentation of storage quality. Indian Journal of Agricultural Sciences 2017, 87(10), 1391–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J. D. S.; Subramanyam, M. V.; Kumar, A. S. Hybrid Sand Cat Swarm Optimization Algorithm-based reliable coverage optimization strategy for heterogeneous wireless sensor networks. International Journal of Information Technology 2024, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vikram, V.; Soundararajan, A. S. Durability studies on the pozzolanic activity of residual sugar cane bagasse ash sisal fibre reinforced concrete with steel slag partially replacement of coarse aggregate. Caribb. J. Sci 2021, 53, 326–344. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.; Santosh, S.; Kulshrestha, M.; Chand, K.; Lohani, U. C.; Shahi, N. C. Quality characteristics of Ohmic heated Aonla (Emblica officinalis Gaertn.) pulp. Indian Journal of Traditional Knowledge 2013, 12(4), 670–676. [Google Scholar]
- Niasi, K. S. K.; Kannan, E. Multi Attribute Data Availability Estimation Scheme for Multi Agent Data Mining in Parallel and Distributed System. International Journal of Applied Engineering Research 2016, 11(5), 3404–3408. [Google Scholar]
- Praveen, R. V. S. Data Engineering for Modern Applications; Addition Publishing House, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, J. D. S. Investigation on secondary memory management in wireless sensor network. Int J Comput Eng Res Trends 2015, 2(6), 387–391. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, R. K.; Chand, K.; Tewari, L. Solid state fermentation and crude cellulase based bioconversion of potential bamboo biomass to reducing sugar for bioenergy production. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture 2018, 98(12), 4411–4419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praveen, R. V. S.; Hundekari, S.; Parida, P.; Mittal, T.; Sehgal, A.; Bhavana, M. Autonomous Vehicle Navigation Systems: Machine Learning for Real-Time Traffic Prediction. 2025 International Conference on Computational, Communication and Information Technology (ICCCIT), February; IEEE, 2025; pp. 809–813. [Google Scholar]
- Arunmohan, A. M.; Bharathi, S.; Kokila, L.; Ponrooban, E.; Naveen, L.; Prasanth, R. An experimental investigation on utilisation of red soil as replacement of fine aggregate in concrete. Psychology and Education Journal 2021, 58. [Google Scholar]
- Palaniappan, S.; Sharma, S.; Radhakrishnan, M.; Krishna, K. M.; Joshi, S. S.; Banerjee, R.; Dahotre, N. B. Process thermokinetics influenced microstructure and corrosion response in additively in-situ manufactured Ti-Nb-Sn and Ti-Nb alloys. Journal of Manufacturing Processes 2025, 152, 427–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, V.; Sumalatha, A.; Reddy, D. N.; Ahamed, B. S.; Udayakumar, K. Exploring Decentralized Identity Verification Systems Using Blockchain Technology: Opportunities and Challenges. In 2024 5th IEEE Global Conference for Advancement in Technology (GCAT); IEEE, October 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Niasi, K. S. K.; Kannan, E. Multi Agent Approach for Evolving Data Mining in Parallel and Distributed Systems using Genetic Algorithms and Semantic Ontology.
- Praveen, R. V. S.; Raju, A.; Anjana, P.; Shibi, B. IoT and ML for Real-Time Vehicle Accident Detection Using Adaptive Random Forest. In 2024 Global Conference on Communications and Information Technologies (GCCIT); IEEE, October 2024; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Marimuthu, M.; Vidhya, G.; Dhaynithi, J.; Mohanraj, G.; Basker, N.; Theetchenya, S.; Vidyabharathk, D. Detection of Parkinson’s disease using Machine Learning Approach. Annals of the Romanian Society for Cell Biology 2021, 25(5), 2544–2550. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




