Submitted:
20 November 2025
Posted:
21 November 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
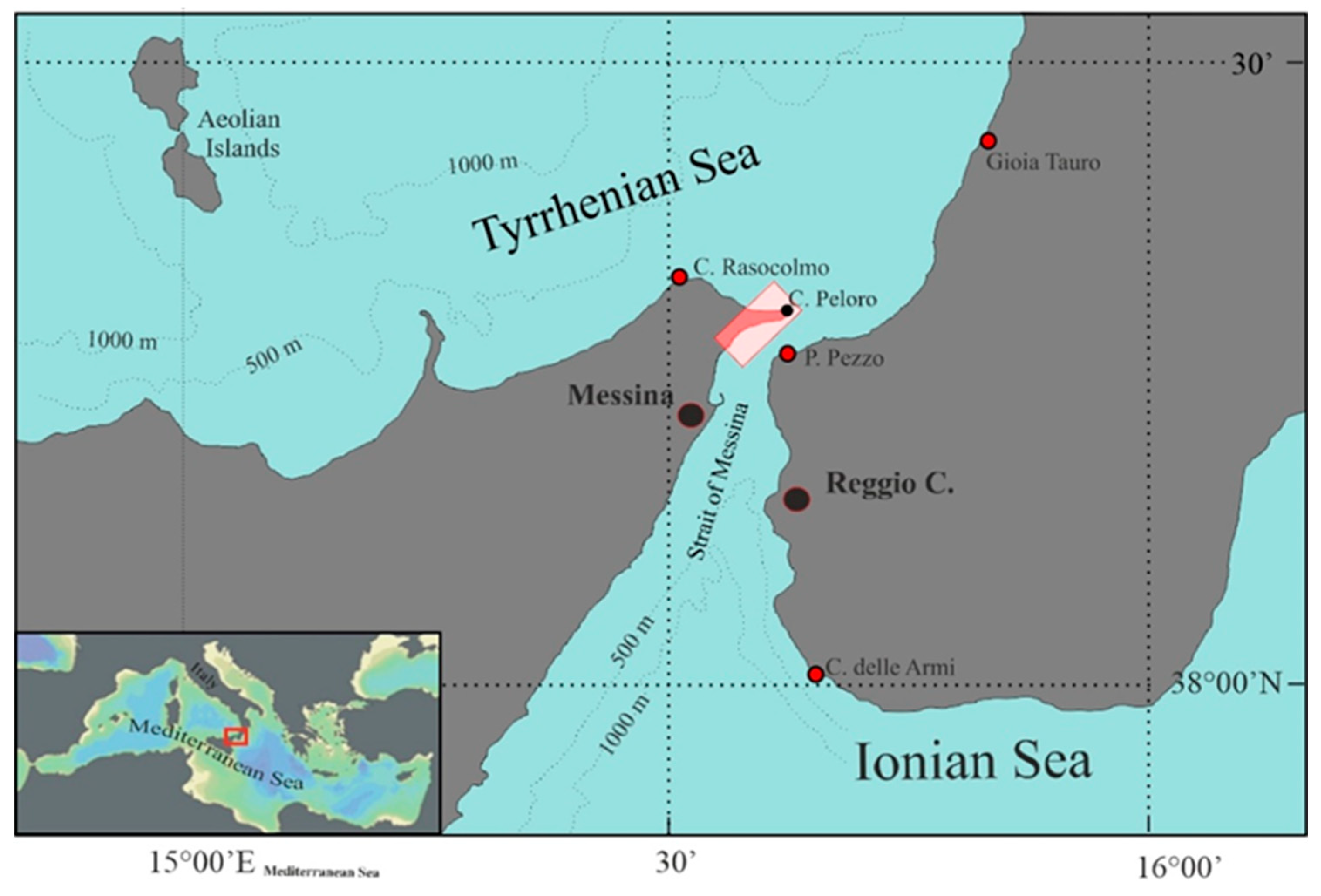
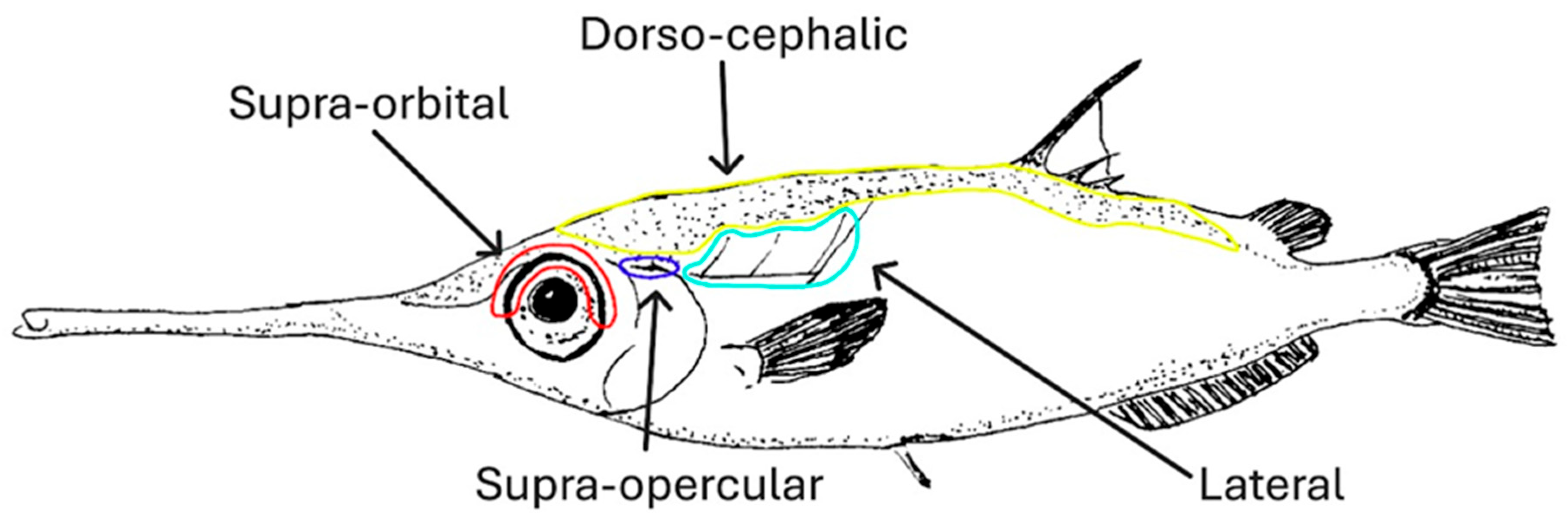
2.1. Study Area
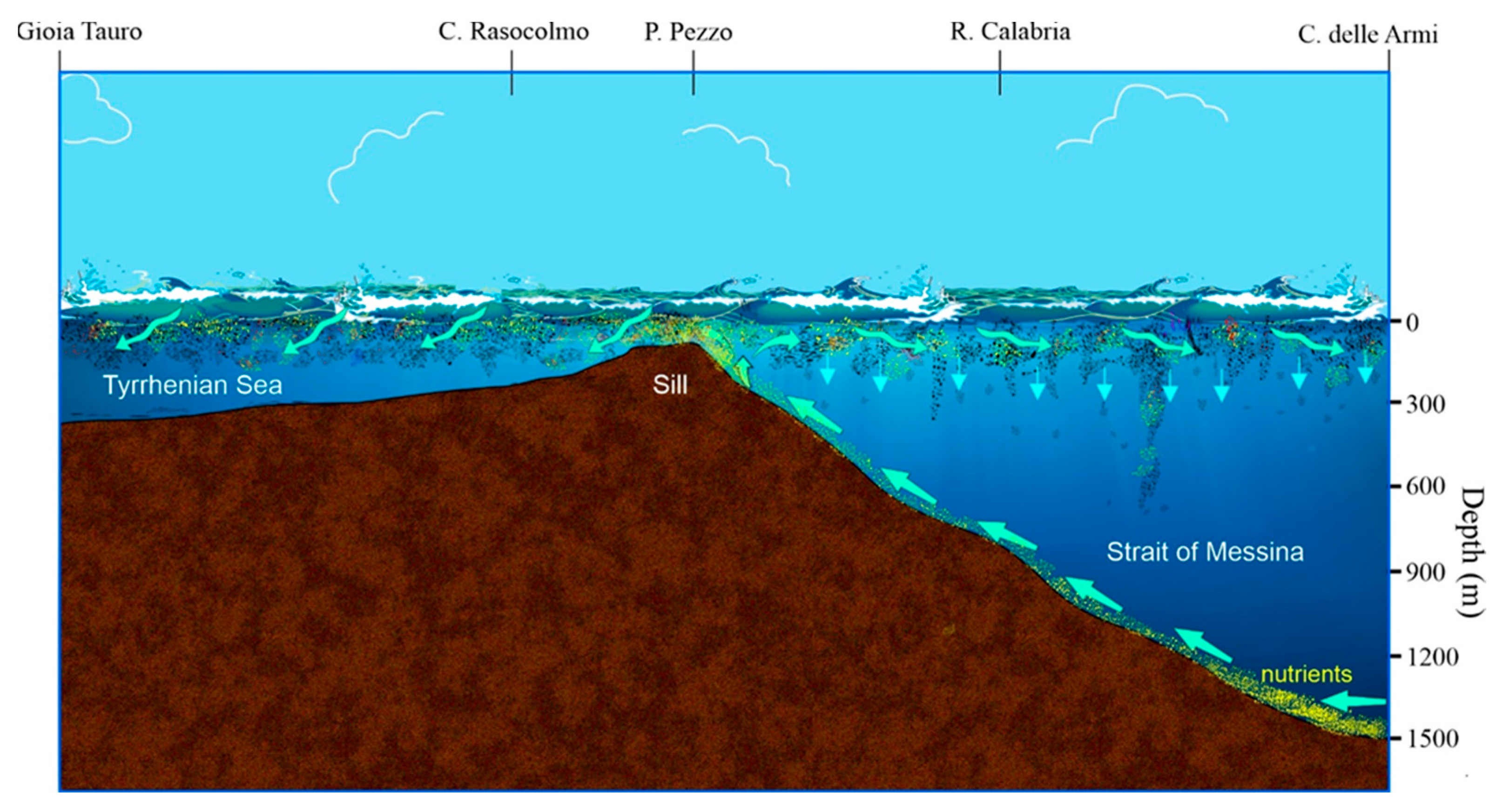
2.1.1. Physical Features
2.1.2. Biological Features
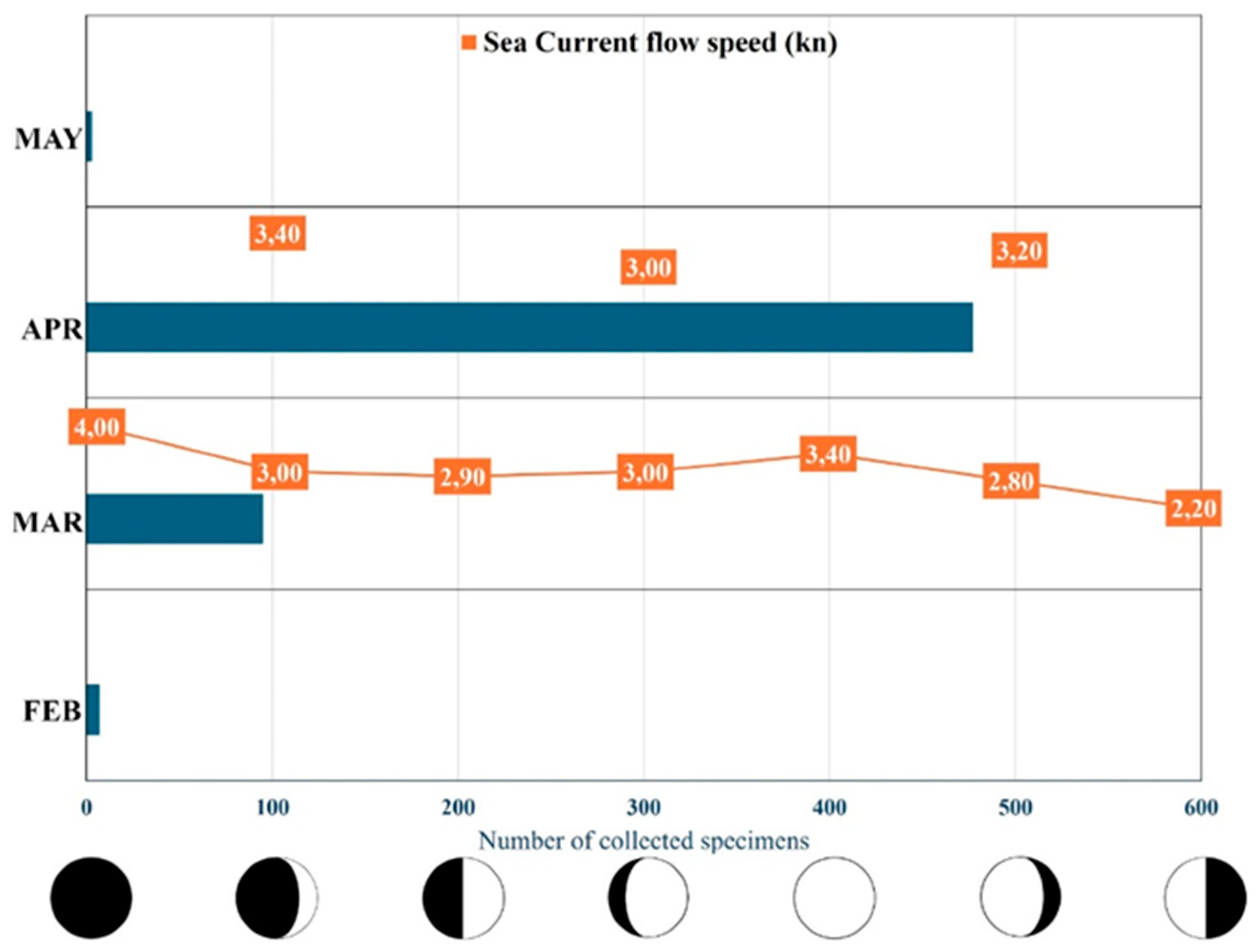
2.2. Samples Collection
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Matthiessen, B.; Fock, H.O.; von Westernhagen, H. Evidence for two sympatric species of snipefishes Macroramphosus spp. (Syngnathiformes, Centriscidae) on Great Meteor Seamount. Helgoland Marine Research 2003, 57, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brêthes, J.-C. Contribution à l'étude des populations de Macrorhamphosus scolopax (L., 1758) et Macrorhamphosus gracilis (Lowe, 1839) des côtes atlantiques marocaines. Bulletin de l'institut des pêches maritimes du Maroc 1979, 24, 1-69.
- Clarke, T.A. Diet and morphological variation in snipefishes, presently recognized as Macrorhamphosus scolopax, from southeast Australia: evidence for two sexually dimorphic species. Copeia 1984, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assis, C.A. On the systematics of Macrorhamphosus scolopax (Linnaeus, 1758) and Macrorhamphosus gracilis (Lowe, 1839). II - Multivariate morphometric analysis. Arquivos do Museu Bocage (new series) 1993, 22, 383–402. [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki, E.; Sasaki, K.; Mitani, T.; Ishida, M.; Uehara, S. The occurrence of two species of Macroramphosus (Gasterosteiformes: Macroramphosidae) in Japan: morphological and ecological observations on larvae, juveniles, and adults. Ichthyological Research 2004, 51, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, L. Age and growth of the snipefish, Macrorhamphosus spp., in the Portuguese continental waters. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom 2000, 80, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farah, I.H.; Kamal, M.; Mahfoud, B.; Najib, C. Snipefish (Macroramphosus spp.) abundance and trophic dynamics in response to upwelling regime in the atlantic region from cape blanc to cape boujdor (20°50 N to 26°00 N). International Journal of Professional Business Review 2024, 9(11):e05136. [CrossRef]
- Matthiessen, B.; Fock, H.O. A null model for the analysis of dietary overlap in Macroramphosus spp. at the Great Meteor Seamount (subtropical North-east Atlantic). Archive of Fishery and Marine Research 2004, 51, 294–304. [Google Scholar]
- Assis, C. On the systematics of Macrorhamphosus scolopax (Linnaeus, 1758) and Macrorhamphosus gracilis (Lowe, 1839). I. A preliminary biometrical approach. Boletim da Sociedade Portuguesa de Ciências Naturais (2nd Sér.) 1992, 25, 5–19. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes, M.; Murta, A.G.; Cabral, H.N. Discrimination of snipefish Macroramphosus species and boarfish Capros aper morphotypes through multivariate analysis of body shape. Helgoland Marine Research 2006, 60, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiansen, B.; Martin, B.; Hirch, S. The benthopelagic fish fauna on the summit of Seine Seamount, NE Atlantic: Composition, population structure and diets. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography 2009, 56, 2705–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D'onghia, G.; Tursi, A.; Maiorano, P.; Matarrese, A.; Panza, M. Demersal fish assemblages from the bathyal grounds of the Ionian Sea (middle-eastern Mediterranean). Italian Journal of Zoology 1998, 65, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaertner, J.-C.; Bertrand, J.A.; Relini, G.; Papaconstantinou, C.; Mazouni, N.; De Sola, L.G; Durbec, J.-P.; Jukic-Peladic, S.; Souplet, A. Spatial pattern in species richness of demersal fish assemblages on the continental shelf of the northern Mediterranean Sea: a multiscale analysis. Marine Ecology Progress Series 2007, 341, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilecenoğlu, M.; Kaya, M.; Cihangir, B.; Çiçek, E. An updated checklist of the marine fishes of Turkey. Turkish Journal of Zoology 2014, 38, 901–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpentieri, P.; Colloca, F.; Ardizzone, G. Day-night variations in the demersal nekton assemblage on the Mediterranean shelf-break. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 2005, 63, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guy-Haim, T.; Stern, N.; Sisma-Ventura, G. Trophic ecology of deep-sea megafauna in the ultra-oligotrophic Southeastern Mediterranean Sea. Frontiers in Marine Science 2022, 9, 857179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauria, V.; Gristina, M.; Fiorentino, F.; Attrill, M.J.; Garofalo, G. Spatial management units as an ecosystem-based approach for managing bottom-towed fisheries in the Central Mediterranean Sea. Frontiers in Marine Science 2020, 7, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovačić, M.; Lipej, L.; Dulčić, J.; Iglesias, S.P.; Goren, M. Evidence-based checklist of the Mediterranean Sea fishes. Zootaxa 2021, 4998, 1–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zorica, B.; Vrgoč, N. Biometry and distribution of snipefish, Macroramphosus scolopax (Linnaeus, 1758), in the Adriatic Sea. Acta adriatica 2005, 46, 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Granata, A.; Cubeta, A.; Minutoli, R.; Bergamasco, A.; Guglielmo, L. Distribution and abundance of fish larvae in the northern Ionian Sea (Eastern Mediterranean). Helgoland Marine Research 2011, 65, 381–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, D.; Profeta, A.; Busalacchi, B.; Minutoli, R.; Guglielmo, L.; Bergamasco, A.; Granata, A. Summer larval fish assemblages in the Southern Tyrrhenian Sea (Western Mediterranean Sea). Marine Ecology 2015, 36, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpentieri, P.; Serpetti. N.; Colloca. F.; Criscoli. A.; Ardizzone. G. Food preferences and rhythms of feeding activity of two co-existing demersal fish, the longspine snipefish, Macroramphosus scolopax (Linnaeus, 1758), and the boarfish Capros aper (Linnaeus, 1758), on the Mediterranean deep shelf. Marine Ecology 2016, 37, 106-118.
- Ben-Tuvia, A. Revised list of the Mediterranean fishes of Israel. Israel Journal of Zoology 1971, 20, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Papaconstantinou, C.; Tsimenidis, N. Some uncommon fishes from the Aegean Sea. Cybium 1979, 3, 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- Demetropoulos, A.; Neocleous, D. The fishes and crustaceans of Cyprus. Fisheries Bulletin of the Ministry of Agriculture and Natural Resources of Cyprus 1969, 1, 3–21. [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Tuvia, A. Collection of fishes from Cyprus. The Bulletin of the Research Council of Israel 1962, 11, 132–145. [Google Scholar]
- Bilecenoglu, M. Status of the genus Macroramphosus (Syngnathiformes: Centriscidae) in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Zootaxa 2006, 1273, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocco, A. Su di alcuni nuovi pesci de’mari di Messina. Giornale di Scienze Lettere e Arti per La Sicilia, 1829, 7, 138–147. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzarelli, G. Gli animali abissali e le correnti sottomarine dello Stretto di Messina. Rivista Mensile di Pesca e Idrobiologia 1909, 11, 177–218. [Google Scholar]
- Genovese, S.; Guglielmo, L. Spiaggiamenti di fauna abissale nello Stretto di Messina. Atti della Società Peloritana di Scienze Fisiche Matematiche e Naturali 1971, 17, 331–370. [Google Scholar]
- Di Carlo, B.S.; Costanzo, G.; Fresi, E.; Guglielmo, L. Feeding ecology and stranding mechanisms in two lanternfishes, Hygophum benoiti and Myctophum punctatum. Marine Ecology Progress Series 1982, 9, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglia, P.; Ammendolia, G.; Cavallaro, M.; Consoli, P.; Esposito, V.; Malara, D.; Rao, I.; Romeo, T.; Andaloro, F. Influence of lunar phases, winds and seasonality on the stranding of mesopelagic fish in the Strait of Messina (Central Mediterranean Sea). Marine Ecology 2017, 38, e12459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglia, P.; Pedà, C.; Malara, D.; Milisenda, G.; MacKenzie, B.R.; Esposito, V.; Consoli, P.; Vicchio, T.M.; Stipa, M.G.; Pagano, L. Importance of the lunar cycle on mesopelagic foraging by Atlantic Bluefin Tuna in the upwelling area of the Strait of Messina (Central Mediterranean Sea). Animals 2022, 12, 2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdar, A.; Cavaliere, A.; Cavallaro, G.; Giuffre, G.; Potoschi, A. Lo studio degli organismi marini spiaggiati nello Stretto di Messina negli ultimi due secoli. Naturalista Siciliano 1983, 7, 3–17. [Google Scholar]
- Berdar, A.; Cavallaro, G.; Giuffre, G.; Potoschi, A. Contributo alla conoscenza dei pesci spiaggiati lungo il litorale siciliano dello Stretto di Messina. Memorie di Biologia Marina e di Oceanografia 1981, 7, 77–87. [Google Scholar]
- Berdar, A.; Berdar, N.; Costa, F. Diminuzione di ittiofauna meso e batipelagica spiaggiata nello Stretto di Messina. Memorie di Biologia Marina e Oceanografia 1988, 17, 43–60. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, F. I pesci del Mediterraneo: stadi larvali e giovanili; Grafo editor: Brescia, Italia, 1999; p. 285. [Google Scholar]
- Cavallaro, M.; Villari, A.; Ammendolia, G.; Spadola, F.; Bonfiglio, L.; Mangano, G.; Panzera, M. Le collezioni di faune ittiche mesopelagiche e malacologica “A. Villari” del Museo della Fauna di Messina. In Atti XXV Congresso Associazione Nazionale Musei Scientifici, Torino, Italia, 11-13 November 2015; Università degli Studi di Torino, 2015; p. 48.
- Cavallaro, M.; Ammendolia, G.; Rao, I.; Villari, A.; Battaglia, P. Variazioni pluriennali del fenomeno dello spiaggiamento di specie ittiche nello Stretto di Messina, con particolare attenzione alle specie mesopelagiche. Annales, Series Historia Naturalis 2021, 31, 69-78.
- Bignami, F.; Salusti, E. Tidal currents and transient phenomena in the Strait of Messina: A review. In The Physical Oceanography of Sea Straits; Pratt, L.J., Ed.; NATO ASI Series: Springer, Dordrecht, 1990; Volume 318, pp. 95–124. [Google Scholar]
- Mosetti, R. Optimal policies in a Bioeconomic model of eutrophication. Applied Mathematics and Computation 1988, 26, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, T.S.; Salusti, E.; Settimi, D. Tidal forcing of the water mass interface in the Strait of Messina. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans 1984, 89, 2013–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercelli, F. Crociere per lo studio dei fenomeni nello Stretto di Messina; Office Grafiche C. Ferrari: Venezia, Italia, 1926.
- Vercelli, F. Il regime delle correnti e delle maree nello Stretto di Messina. Office Grafiche Ferrari: Venezia, Italia, 1925.
- Mosetti, F. Tidal and other currents in the Straits of Messina. In The Straits of Messina ecosystem, Proceedings of the Symposium, Messina, Italia, 4-16 Aprile 1991; Guglielmo, L., Manganaro, A., De Domenico, E., Eds.; Università degli Studi di Messina, Italia, 1995; pp. 15-29.
- Povero, P.; Hopkins, T.; Fabiano, M. Oxygen and nutrient observations in the southern Tyrrhenian Sea. Oceanologica acta 1990, 13, 299–305. [Google Scholar]
- Guglielmo, L.; Crescenti, N.; Costanzo, G.; Zagami, G. Zooplankton and micronekton communities in the Straits of Messina. In The Straits of Messina ecosystem, Proceedings of the Symposium, Messina, Italia, 4-16 Aprile 1991; Guglielmo, L., Manganaro, A., De Domenico, E., Eds.; Università degli Studi di Messina, Italia, 1995; pp. 247-270.
- Guglielmo, L.; Marabello, F.; Vanucci, S. The role of the mesopelagic fishes in the pelagic food web of the Straits of Messina. In The Straits of Messina ecosystem, Proceedings of the Symposium, Messina, Italia, 4-16 Aprile 1991; Guglielmo, L., Manganaro, A., De Domenico, E., Eds.; Università degli Studi di Messina, Italia, 1995; pp. 223-246.
- Decembrini, F.; Hopkins, T.; Azzaro, F. Variability and sustenance of the deep-chlorophyll maximum over a narrow shelf, Augusta Gulf (Sicily). Chemistry and Ecology 2004, 20, 231–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzaro, F.; Decembrini, F.; Raffa, F.; Crisafi, E. Seasonal variability of phytoplankton fluorescence in relation to the Straits of Messina (Sicily) tidal upwelling. Ocean Science 2007, 3, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currieri, G. Sulle cause meccanico biologiche della formazione degli accumuli di plancton. Bollettino della Società zoologica italiana I 1900, 4.
- Zagami, G.; Badalamenti, F.; Guglielmo, L.; Manganaro, A. Short-term variations of the zooplankton community near the Straits of Messina (North-eastern Sicily): relationships with the hydrodynamic regime. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 1996, 42, 667-681.
- Guglielmo, L. Distribuzione dei chetognati nell'area idrografica dello Stretto di Messina. Pubblicazioni della Stazione Zoologica di Napoli 1976, 40, 34–72. [Google Scholar]
- Sparla, M.; Guglielmo, L. Distribuzione del microzooplancton nello Stretto di Messina (estate 1990). In Atti X Congresso AIOL, Alassio, Italia, 4-6 Novembre 1992;1994, pp. 307-325.
- Battaglia, P.; Andaloro, F.; Esposito, V.; Granata, A.; Guglielmo, L.; Guglielmo, R.; Musolino, S.; Romeo, T.; Zagami, G. Diet and trophic ecology of the lanternfish Electrona risso (Cocco 1829) in the Strait of Messina (central Mediterranean Sea) and potential resource utilization from the Deep Scattering Layer (DSL). Journal of Marine Systems 2016, 159, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglia, P.; Andaloro, F.; Consoli, P.; Esposito, V.; Malara, D.; Musolino, S.; Pedà, C.; Romeo, T. Feeding habits of the Atlantic bluefin tuna, Thunnus thynnus (L. 1758), in the central Mediterranean Sea (Strait of Messina). Helgoland Marine Research 2013, 67, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granata, A.; Tringali, L.; Bruno, R.; Guglielmo, L.; Guglielmo, R.; Minutoli, R. Lo Stretto di Messina: via di migrazione per pesci e mammiferi marini. In Sviluppo sostenibile dei trasporti marittimi nel Mediterraneo; Pellegrino, F., Ed.; Edizioni Scientifiche Italiane (ESI): Napoli, Italia, 2013; pp. 691–755. [Google Scholar]
- Ricker, W.E. Computation and interpretation of biological statistics of fish populations. Fisheries Research Board of Canada Bulletin 1975, 191, 1–382. [Google Scholar]
- Hammer, Ø.; Harper, D.A.T. , Ryan P.D. Past: paleontological statistics software package for educaton and data anlysis. Palaeontologia electronica 2001, 4, 1. http://palaeo-electronica.org/2001_1/past/issue1_01.htm.
- Schluter, D. Adaptive radiation in sticklebacks: size, shape, and habitat use efficiency. Ecology 1993, 74, 699–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, S.J.; Goodearly, T.; Wainwright, P.C. Extremely fast feeding strikes are powered by elastic recoil in a seahorse relative, the snipefish, Macroramphosus scolopax. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 2018, 285, 20181078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoro, V.C.; Amore, E.; Cavallaro, L.; Cozzo, G.; Foti, E. Sand waves in the Messina strait, Italy. Journal of Coastal Research 2002, 36, 640–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortier, L. Export production and the production of fish larvae and their prey at hydrodynamic singularities. In The Straits of Messina ecosystem, Proceedings of the Symposium, Messina, Italia, 4-16 Aprile 1991; Guglielmo, L., Manganaro, A., De Domenico, E., Eds.; Università degli Studi di Messina, Italia, 1995; pp. 213-225.
- Brancato, G.; Minutoli, R.; Granata, A.; Sidoti, O.; Guglielmo, L. Diversity and vertical migration of euphausiids across the Straits of Messina area. In Mediterranean ecosystems: structures and processes; Faranda, F.M., Guglielmo, L., Spezie, G., Eds.; Springer: Milano, Italia, 2001; pp. 131–141. [Google Scholar]
- Bergamasco, A.; Cucco, A.; Guglielmo, L.; Minutoli, R.; Quattrocchi, G.; Guglielmo, R.; Palumbo, F.; Pansera, M.; Zagami, G.; Vodopivec, M. Observing and modeling long-term persistence of P. noctiluca in coupled complementary marine systems (Southern Tyrrhenian Sea and Messina Strait). Scientific reports 2022, 12, 14905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arruda, L.; Andrade, J.; Cunha, M. Abundance, diversity, and community structure of the fish population in the Ria de Aveiro (Portugal). Oceanologica Acta 1988, 11, 235–240. [Google Scholar]
- Matallanas, J. Aspectos generales del regimen alimentario de Macroramphosus scolopax (Linnaeus 1758) (Pisces, Macroramphosidae) en las costas catalanas (Mediterrâneo occidental). Cahiers De Biologie Marine 1982, 23, 243–252. [Google Scholar]
- Motta, P.J.; Clifton, K.B.; Hernandez, P.; Eggold, B.T. Ecomorphological correlates in ten species of subtropical seagrass fishes: diet and microhabitat utilization. Environmental biology of fishes 1995, 44, 37–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogland, R.; Morris, D.; Tinbergen, N. The spines of sticklebacks (Gasterosteus and Pygosteus) as means of defence against predators (Perca and Esox). Behaviour 1956, 10, 205–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosher, B.T.; Newton, S.H.; Fine, M.L. The spines of the channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus, as an anti-predator adaptation: an experimental study. Ethology 2006, 112, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domenici, P. Escape responses in fish: kinematics, performance and behavior. In Fish locomotion: An eco-ethological perspective; Domenici, P., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, USA, 2010; pp. 123–170. [Google Scholar]
- Magurran, A.E. The adaptive significance of schooling as an anti-predator defence in fish. Annales Zoologici Fennici, 1990, 27, 51–66. [Google Scholar]
- McFall-Ngai, M.J. Crypsis in the pelagic environment. American Zoologist 1990, 30, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, J. Vision and lack of vision in the ocean. Current biology 2017, 27, R494–R502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granata, A.; Bergamasco, A.; Battaglia, P.; Milisenda, G.; Pansera, M.; Bonanzinga, V.; Arena, G.; Andaloro, F.; Giacobbe, S.; Greco, S. Vertical distribution and diel migration of zooplankton and micronekton in Polcevera submarine canyon of the Ligurian mesopelagic zone (NW Mediterranean Sea). Progress in Oceanography 2020, 183, 102298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A. Feeding habits of John Dory, Zeus faber, off the Portuguese continental coast. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom 1999, 79, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morato, T.; Solà, E.; Grós, M.P.; Menezes, G. Feeding habits of two congener species of seabreams, Pagellus bogaraveo and Pagellus acarne, off the Azores (northeastern Atlantic) during spring of 1996 and 1997. Bulletin of marine science 2001, 69, 1073–1087. [Google Scholar]
- Gravino, F.; Dimech, M.; Schembri, P.J. Feeding habits of the small-spotted catshark Scyliorhinus canicula (L., 1758) in the central Mediterranean. Rapport Commission International de la Mer Mediterranee 2010, 39, 538. [Google Scholar]
- D’Iglio, C.; Porcino, N.; Savoca, S.; Profeta, A.; Perdichizzi, A.; Armeli Minicante, E.; Salvati, D.; Soraci, F.; Rinelli, P.; Giordano, D. Ontogenetic shift and feeding habits of the European hake (Merluccius merluccius L., 1758) in Central and Southern Tyrrhenian Sea (Western Mediterranean Sea): A comparison between past and present data. Ecology and Evolution 2022, 12, e8634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuset, V.M.; Lombarte, A.; Assis, C.A. Otolith atlas for the western Mediterranean, north and central eastern Atlantic. Scientia Marina 2008, 72, 7–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



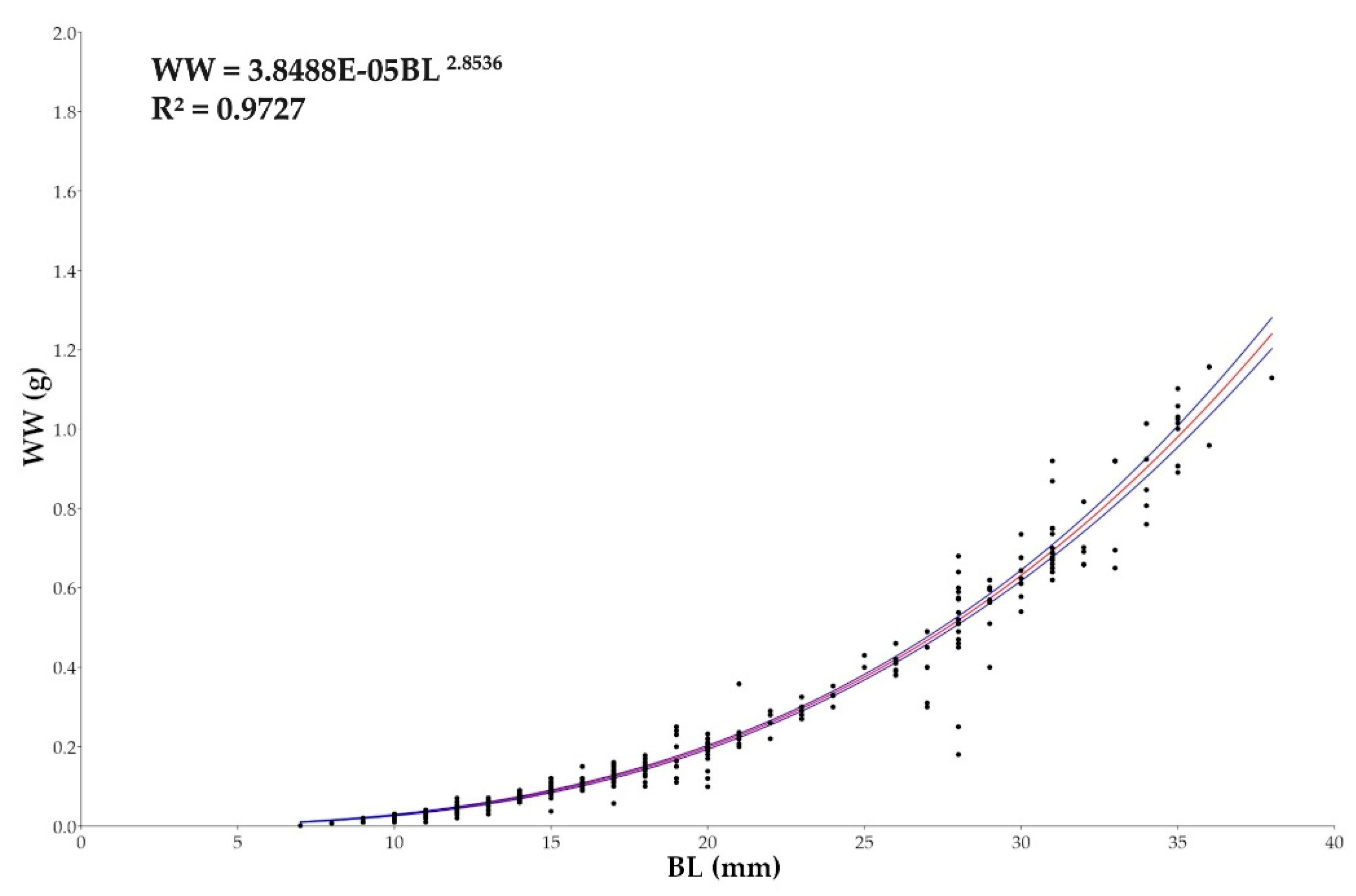
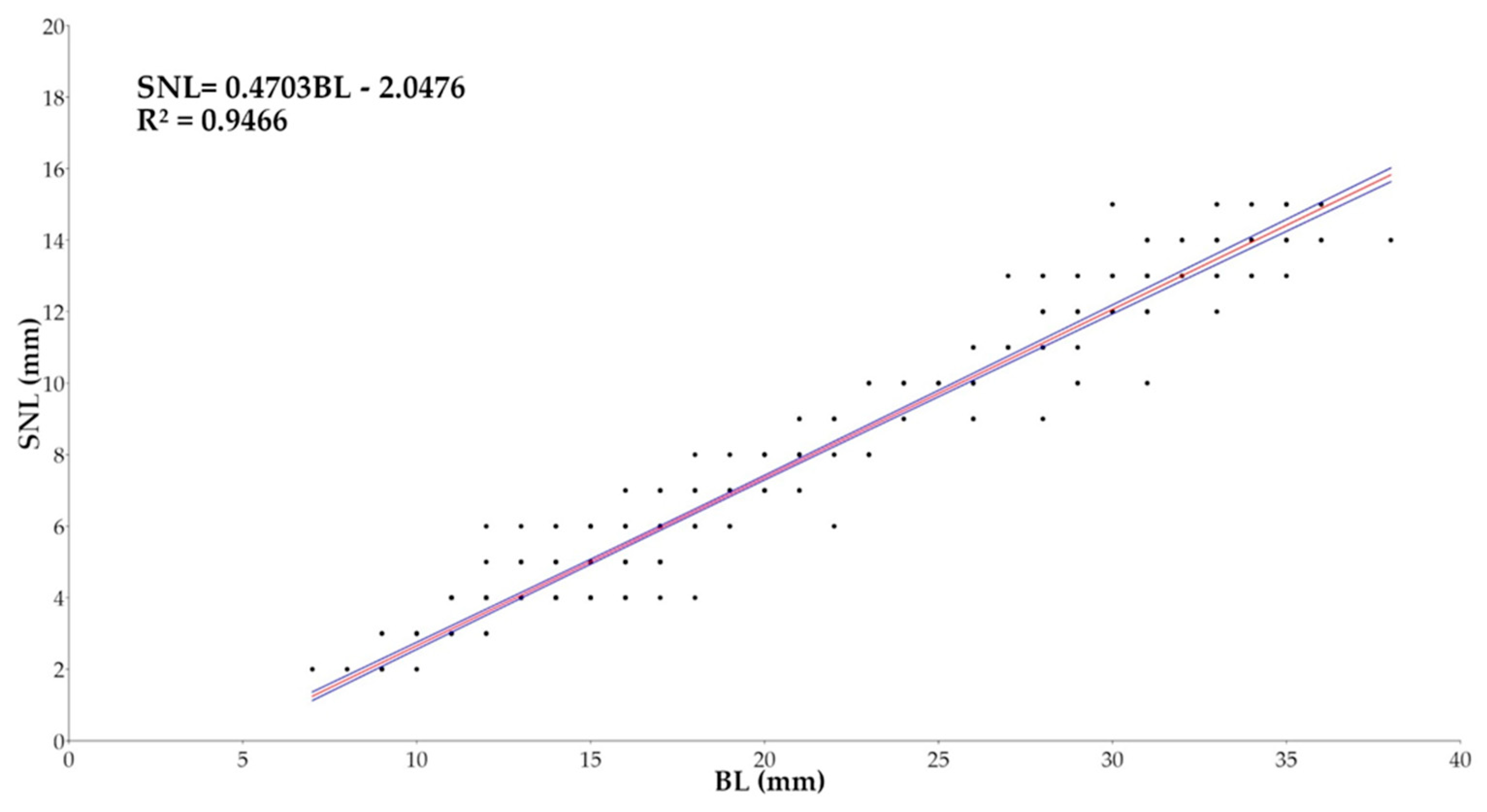
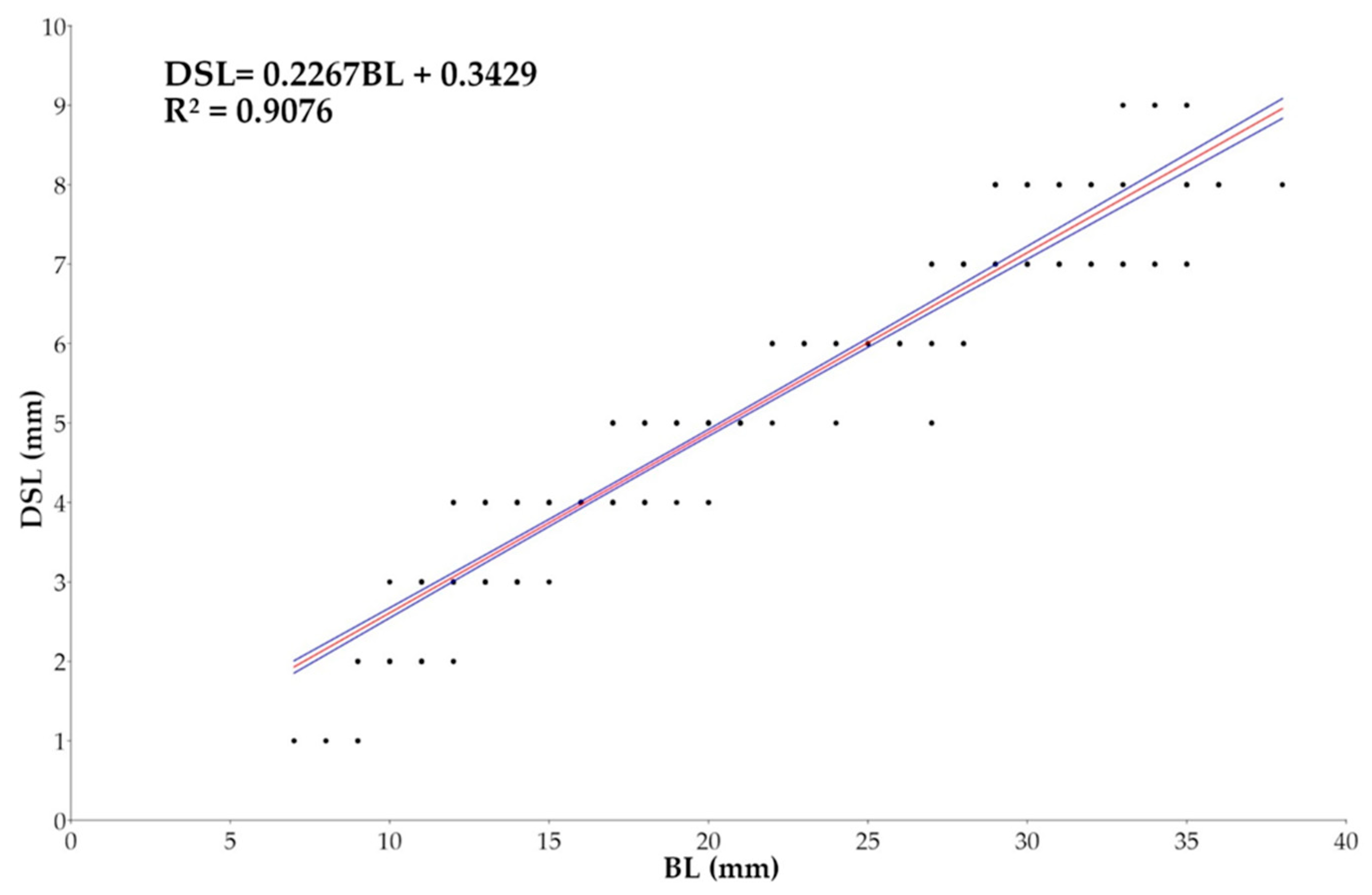
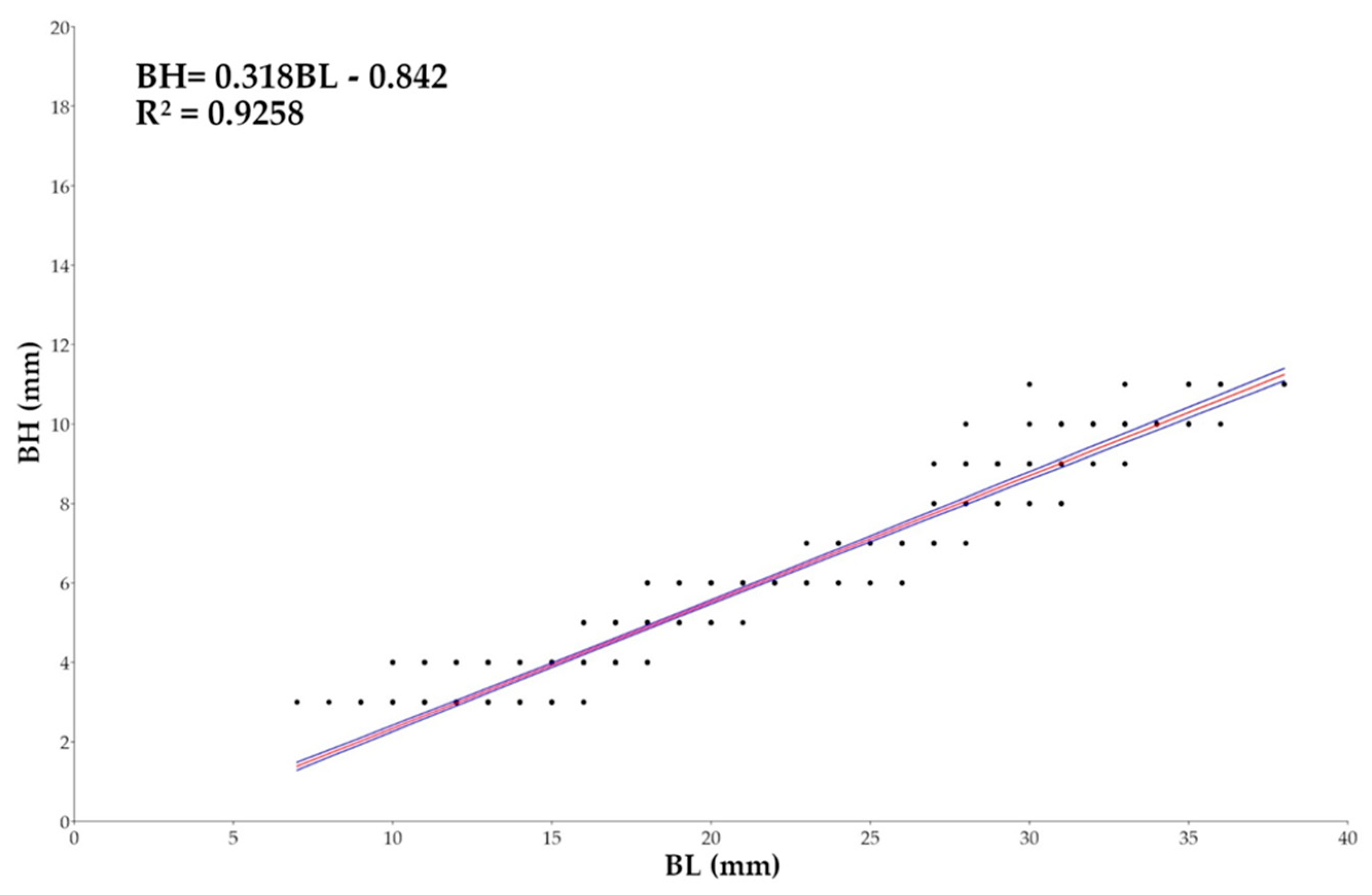
| Species | February | March | April | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Teleosts | Argyropelecus hemigymnus | -- | 11 | -- |
| Argyropelecus hemigymnus juv. | -- | 8 | -- | |
| Conger sp. juv. | -- | 1 | -- | |
| Cyclothone braueri | -- | 6 | -- | |
| Diaphus metopoclampus juv. | -- | 1 | -- | |
| Electrona risso juv. | -- | 2 | -- | |
| Engraulis encrasicolus | -- | 1 | -- | |
| Hygophum benoiti | -- | 25 | 36 | |
| Hygophum hygomii juv. | -- | -- | 2 | |
| Maurolicus muelleri | -- | -- | 1 | |
| Myctophum punctatum | -- | -- | 1 | |
| Microstoma microstoma | -- | 1 | 1 | |
| Microstoma microstoma juv. | -- | -- | 4 | |
| Nansenia oblita | -- | -- | 1 | |
| Nansenia oblita juv. | -- | 1 | -- | |
| Vinciguerria attenuata | -- | 6 | -- | |
| Vinciguerria attenuata juv. | -- | -- | 1 | |
| Amphipods | Lestrigonus schizogeneios | -- | 6 | -- |
| Phronima atlantica | -- | 4 | 1 | |
| Phronima sp. | -- | 11 | 1 | |
| Phrosina semilunata | -- | 2 | -- | |
| Scina crassicornis | -- | 1 | -- | |
| Euphausiids | Euphausia krohni | -- | 1 | -- |
| Thysanoessa gregaria | -- | 45 | -- | |
| Mysids | Siriella sp. | -- | -- | 1 |
| Pteropods | Cymbulia peronii | 1 | -- | 3 |
| M. gracilis | M. scolopax | |
|---|---|---|
|
Ventral body profile in larval and juvenile |
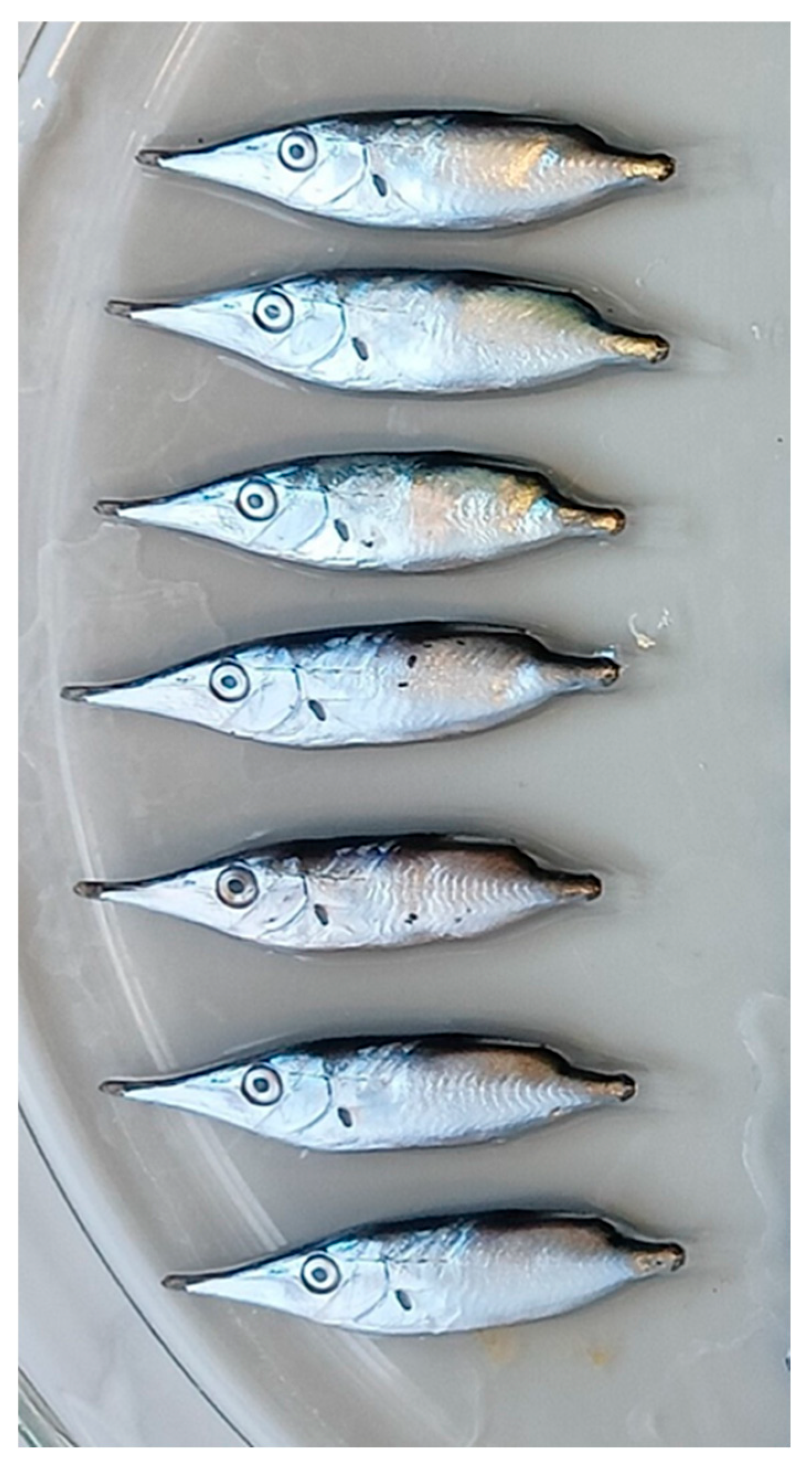
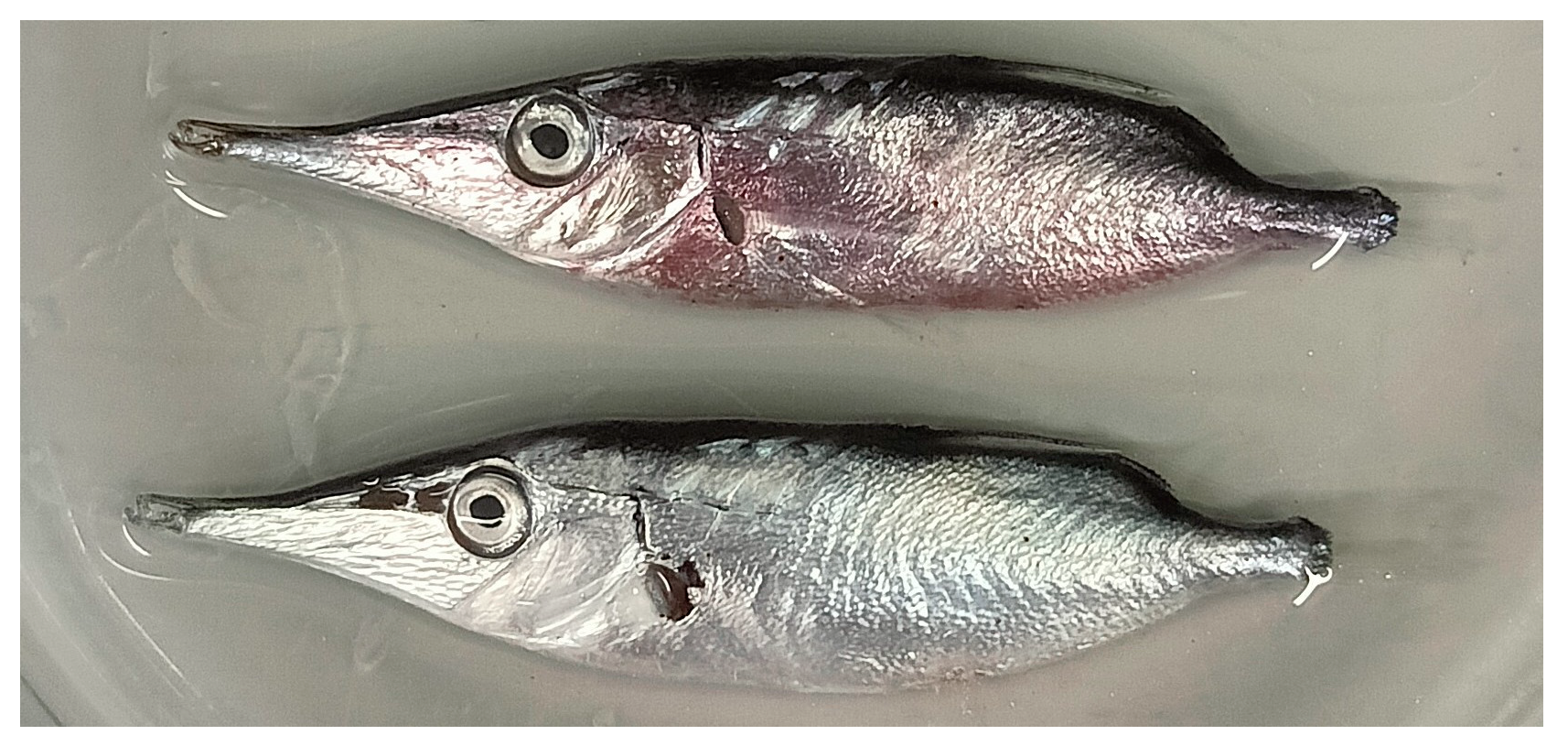
Straight | Notched |
| Body colour | Dark dorsally, with silver sides |
Red-orange with few melanophores dorsally |
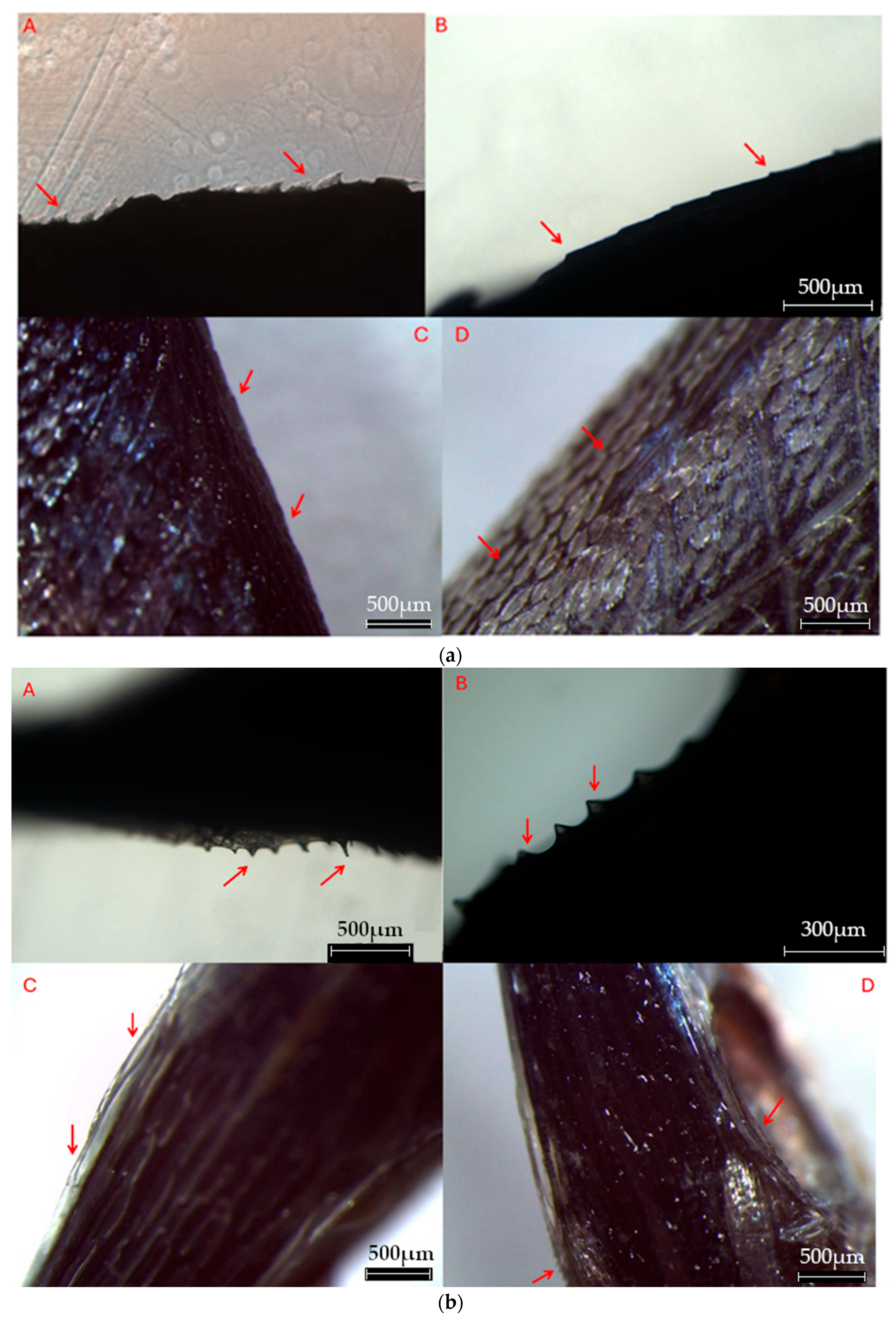
| Posterior margin of dorsal fin spine (spike) in specimens larger than 50 mm SL | Smooth | Serrated with spinules |
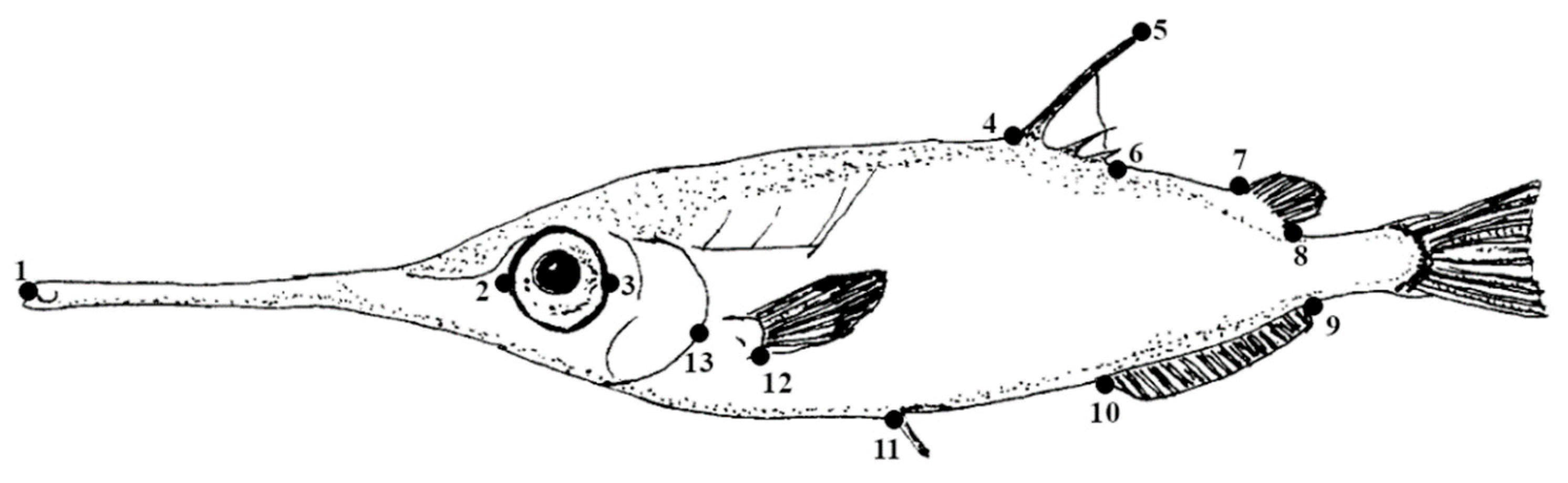
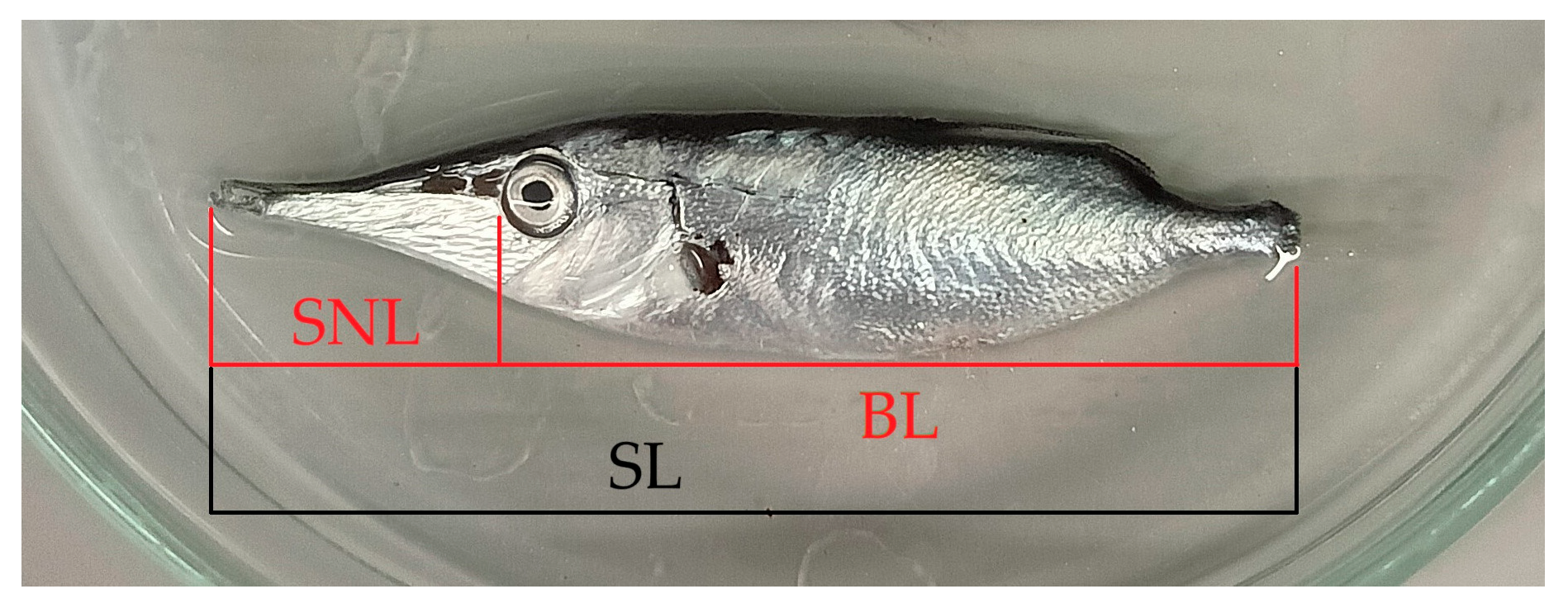
| Lenght of dorsal fin spine (DSL, Dorsal Spine Length; 4-5) | Relatively short: 17.9-32.6% BL. 62.4-138% distance between dorsal spine-second dorsal fin origin (DSFD, Dorsal Spine Fin Distance; 4-7). |
Long: 23.7-46.2% BL. 98.9-231% distance between dorsal spine-second dorsal fin origin (DSFD, Dorsal Spine Fin Distance; 4-7). |
| Body Height (BH; 4-10) | Relatively slender: 20.9-30.8% BL. | Relatively deep: 23.4-36.7% BL. |
| Macroramphosus gracilis features | Macroramphosus scolopax features | Outlier features | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N. | Straight ventral body profile | Silver body, dor-sally dark | DSL/ BL ratio 17.9-32.6% |
DSL/ DSFD ratio 62.4-138% |
BH/BL ratio 20.9- 30.8% |
Notched ventral body profile | Red- orange body | DSL/ BL ratio 23.7-46.2% |
DSL/ DSFD ratio 98.9-231% |
BH/BL ratio 23.4- 36.7% |
Silver body, light red shaded, dorsally dark | DSL/ DSFD ratio <62.4% |
BH/ BL ratio >36.7% |
|
| 490 | x | x | x | x | x | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | |
| 61 | x | x | x | x | / | / | / | / | / | x | / | / | / | |
| 5 | x | x | x | x | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | x | |
| 2 | x | x | x | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | x | x | |
| 4 | x | / | x | x | x | / | / | / | / | / | x | / | / | |
| 3 | x | / | x | x | / | / | / | / | / | x | x | / | / | |
| 2 | x | x | x | / | x | / | / | / | / | / | / | x | / | |
| 1 | x | x | / | x | / | / | / | x | / | x | / | / | / | |
| 3 | x | x | / | x | x | / | / | x | / | / | / | / | / | |
| Tot | 571 | 571 | 564 | 567 | 567 | 499 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 65 | 7 | 4 | 7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





