1. Introduction
Today, e-commerce has evolved into a fast-paced and highly competitive industry where customer retention remains a major business challenge. Customer churn, or the rate at which customers discontinue their interactions with a business, affects profitability, customer lifetime value, and overall business growth [
1]. In the crowded B2C e-commerce market, acquiring new customers is costlier than retaining existing ones, making churn prediction vital to reducing customer loss [
2].
As a result, building effective and stable customer churn prediction models has gained significant attention among companies aiming to enhance targeted retention strategies and improve customer satisfaction. Various machine learning models such as Random Forest, Gradient Boosted Trees, k-Nearest Neighbors, and Decision Trees are effective in identifying customer behaviors and predicting churn [
3,
4]. These models are capable of processing large-scale data, identifying patterns, and delivering accurate predictions. However, challenges such as data imbalance, outliers, and high-dimensional features must be addressed to ensure model reliability [
5,
6].
This study proposes a comprehensive framework that leverages supervised machine learning to generate churn propensity scores in the e-commerce sector. Using the “E-Commerce Customer Churn Analysis and Prediction” dataset from GMI, consisting of 5,630 records and 20 features, we handled missing values, removed 48 outliers, and applied forward feature selection. Among the tested models, Random Forest outperformed others in terms of accuracy, precision, and recall. This research contributes to the existing literature by advancing churn modeling approaches and showcasing the practical application of machine learning in customer retention [
6]. Refer to
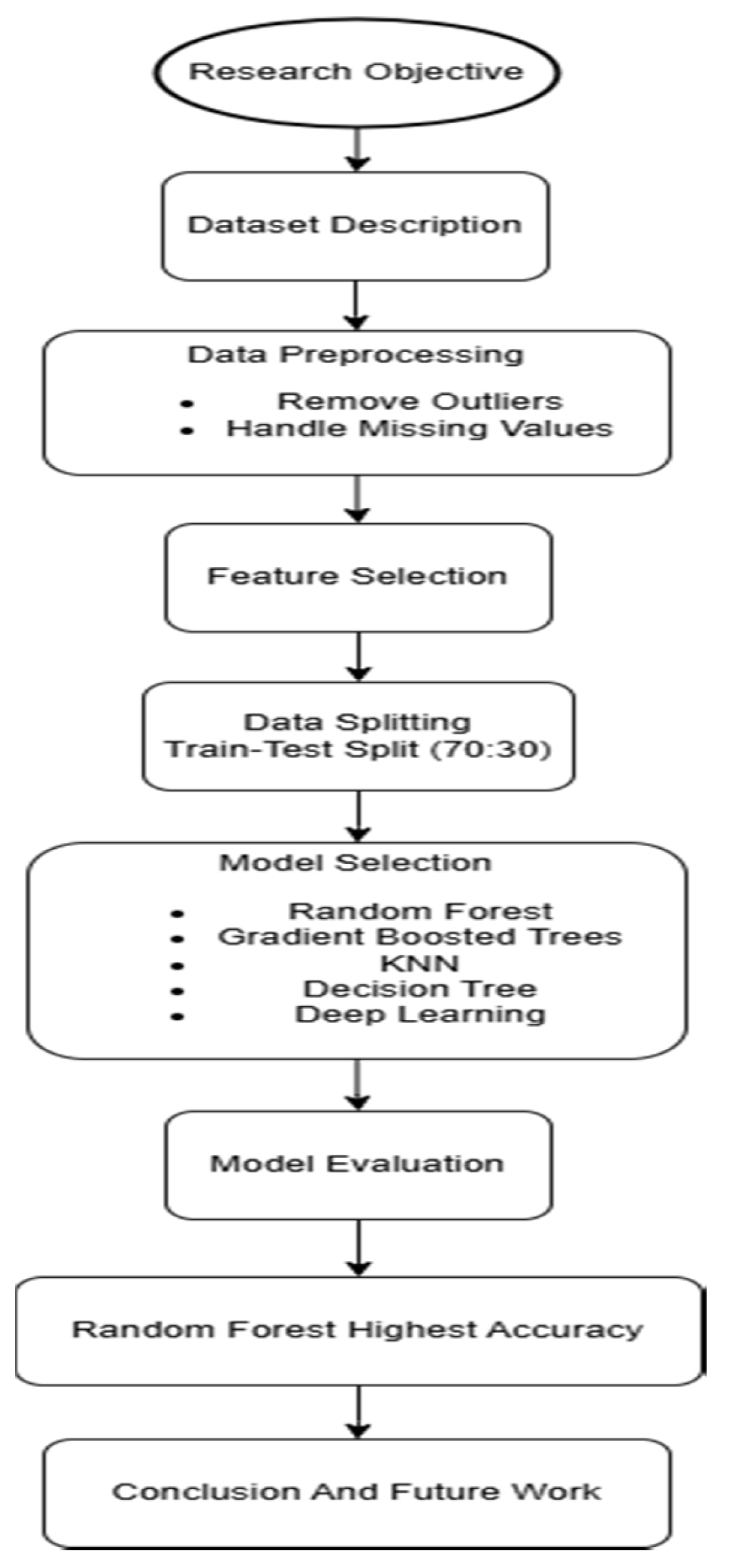
Figure 1. Workflow of Paper, which illustrates the overall methodology and model training process.
Figure 1.
Workflow of Paper.
Figure 1.
Workflow of Paper.
2. Literature Review
Artificial intelligence and its approaches including neural networks, decision trees etc. are majorly used in online buying selling for purposes like recommendation systems, detecting fake or fraudulent account and analyzing customer sentiments. Identifying and addressing such issues and risks as data imbalance and overfitting and improving personalization and user experience remains research priorities necessitating innovation within the field [
1].
Previous studies mostly concentrate on the buyer churn, while the seller churn has been understudied even though it degrades platform performance immensely. In this contribution, we put forward a new model called MCC-StackNet using the Matthews correlation coefficient and StackNet to predict seller churn based on real-world data. The use of such challenges as imbalance of data and the general effectiveness of churn in enhancing its prediction the model outcompetes other traditional methods [
2].
This research aims to develop an improved customer churn prediction model for B2C e-commerce by using a two-step model of k-means clustering followed by the SVM algorithm, which offers better accuracy than the logistic- regression-based models [
12].
This research evidence that segmentation enhances the accuracy in prediction; therefore, argues against homogeneous strategies in customer retention strategies. The work permits certain limitations such as the intrinsic limitations of the datasets used and the kind of segmentation applied and proposes further research to increase external validity and include more variables [
3]. About customer churn and imbalanced data sets across sectors such as telecommunication, e-commerce and banking, this research discusses the following. The presented two-phase resampling approach included clustering and ensemble method and demonstrated higher accuracy in predicting results compared to the previous methods with LSTM.
The study establishes the significance of the proposed technique compared to the existing resampling approaches such as SMOTE and ADASYN, thus presenting a reference for improving churn prediction across various sectors [
4]. In this work, we emphasize the need for customer churn prediction in the highly saturated B2C e-commerce market using state-of-the-art deep learning models. A deep learning model demonstrated 94% accuracy which were higher than the traditional machine learning approach, and it distinguished main drivers of churn, including product quality, price level, and customer care [
13].
The study shows AI’s capability when it comes to increasing value for customer retention and satisfaction, and business profitability [
5]. The purpose of this paper is thus to identify B2C e-commerce customers and, more specifically, to analyze the churn rate of these customers by using k-means clustering and the AdaBoost classification procedures. Hence the model improves accuracy by considering the customer behavior and temporal data. Based on the results, there are learnings that could help enhance the AdaBoost model in the early prediction of churn as a means of supporting a firm’s customer retention or marketing strategies, but the model is not without shortcomings that enable accurate long-term churning prediction [
6]. Recent contributions highlight machine learning’s expanding role in customer churn prediction across various domains including subscription-based platforms, healthcare, and IoT ecosystems. These include frameworks for predicting subscription churn [
9], secure pseudonym anonymization in connected vehicles [
16], and scalable ML architectures for early diagnosis in healthcare settings [
10,
11]. In this research work, customer churn prediction was analyzed using data mining and machine learning approaches[
17,
18,
19,
20]. It was found that the features Monthly Charges and Paperless Billing had a significant impact on the prediction process [
14]. Among the models evaluated, XGBoost proved to be the most accurate in predicting churn. The implications for healthcare service organizations (HSOs) suggest that while this research offers valuable recommendations to improve customer retention, it only focused on online customers. Therefore, future studies are needed to generalize the findings across broader customer segments [
7].
So in this study we compared Logistic Regression, k-Nearest Neighbors (kNN), and Random Forest algorithms for customer churn prediction in the e-commerce context. The kNN model outperformed the others with an accuracy of 94.22%, where Tenure emerged as the most significant predictive variable [
15]. This highlights the importance of preprocessing, feature engineering, and continuous optimization in enhancing customer retention strategies [
8].
3. Methodology
In the current research, different machine learning algorithms and techniques[
21,
22,
23] were applied to classify and analyze the data in the most efficient manner.
3.1. Dataset
The dataset was downloaded from Kaggle. It comprises details such as customer behavior and churn rates, which reflect activities on an e-commerce platform, making it ideal for modeling[
24]. The dataset contains 5,630 samples and 20 features.
| S.No |
Variable |
| 1 |
CustomerID |
| 2 |
Churn |
| 3 |
Durational-tenure |
| 4 |
Device_for_login |
| 5 |
City_Tier |
| 6 |
Distance_fromWarehouse_ToHome |
| 7 |
Payment_Method |
| 8 |
Gender |
| 9 |
App_surfing_inHrs |
| 10 |
Registered_Devices |
| 11 |
OrderCategory |
| 12 |
Satisfaction_Score |
| 13 |
Marital_Status |
| 14 |
Address |
| 15 |
Complaints |
| 16 |
OrderAmountHike_Lastyear |
| 17 |
OrdersCount |
| 18 |
DaySince_LastOrder |
| 19 |
Cashback_Amount |
| 20 |
Coupons_Used |
3.2. Data Preprocessing
During the preprocessing stage, 48 outliers were identified and removed to ensure data quality and improve model performance[
25,
26]. These outliers, likely due to anomalies in customer behavior or data entry errors, could have skewed the results or reduced prediction accuracy. Their removal ensured a dataset more representative of the general population, enhancing model robustness and reliability.
- 2.
Replace Missing Values
Some missing values were observed in the dataset, likely due to data collection biases, system failures, or by design. As machine learning models require complete data, imputation techniques were used to manage these missing values. This step improved the consistency of the dataset and ensured high reliability and accuracy in the predictive models.
- 3.
Forward Feature Selection
The forward selection method was applied to identify the most relevant features affecting churn. This technique helped eliminate less significant variables, thus reducing model complexity and improving both interpretability and efficiency.
- 4.
Data Splitting
The dataset was split into training (70%) and testing (30%) subsets. This ensured that the model was trained on a sufficiently large portion of the data and evaluated on unseen data to test its generalization ability. The split also supported cross-validation for assessing the model’s effectiveness on new data.
-
5.
Tool
The software used for this project was Altair AI Studio Educational 2024.1.0, which supports all stages of machine learning, including preprocessing, modeling, and evaluation. It provides a user-friendly environment to implement models like Random Forest, Gradient Boosted Trees, and Deep Learning techniques. The tool’s enhanced visualization and testing functionalities enabled continuous model improvement.
-
6.
Framework
The machine learning framework employed in this study integrates the end-to-end processes of system development: data acquisition and preprocessing, model selection, training, evaluation, and deployment. This approach enhanced the efficiency of the entire modeling pipeline. We applied Random Forest, along with other algorithms such as k-Nearest Neighbors (kNN), Decision Tree, and Gradient Boosted Trees, to evaluate their performance. Each algorithm was optimized for the given dataset. Random Forest emerged as the best-performing model in terms of accuracy, precision, and recall, outperforming the other techniques tested.
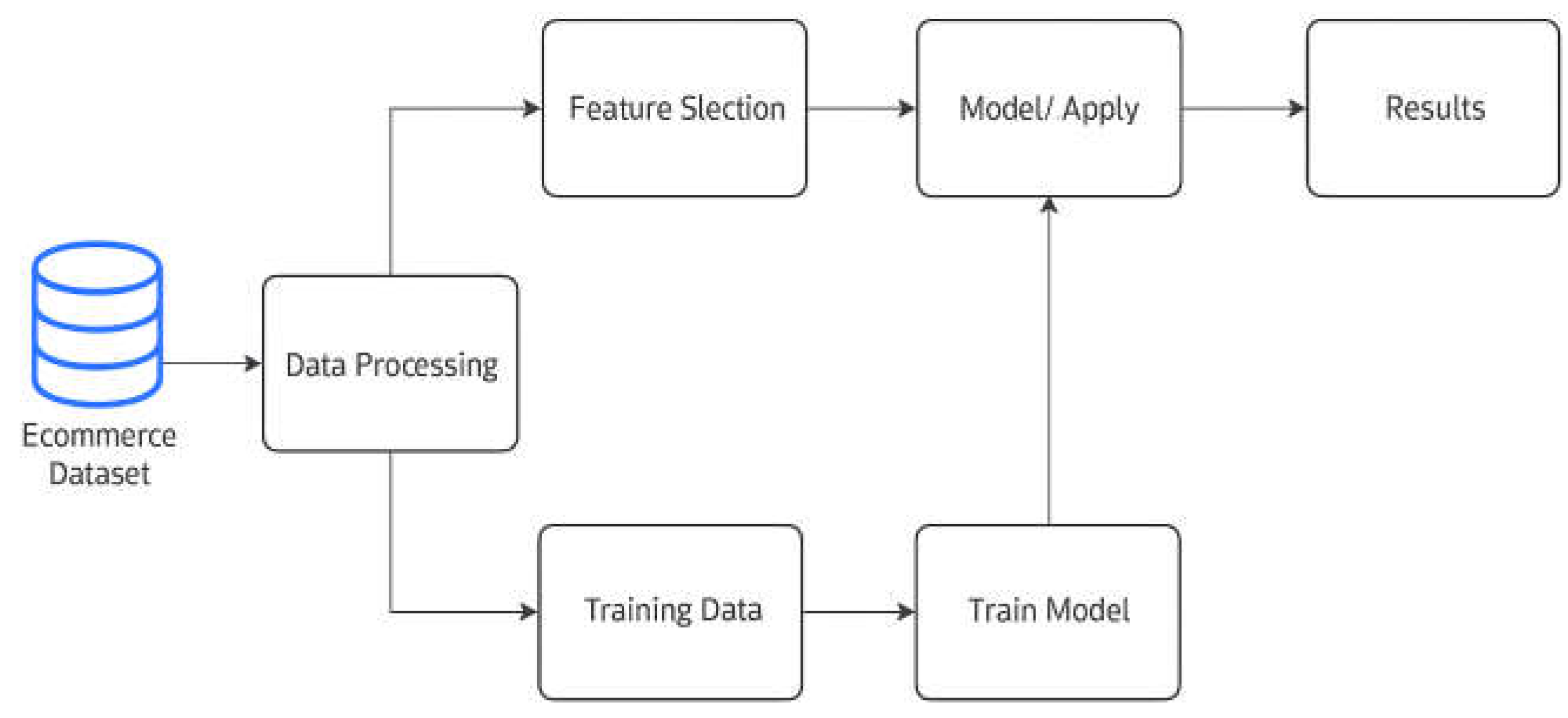
The complete process is illustrated in the flow diagram
Figure 2.
Figure 2.
Framework: E-commerce Customer Churn Analysis and Prediction.
Figure 2.
Framework: E-commerce Customer Churn Analysis and Prediction.
4. Results and Discussions
In this section, we present and analyze the results obtained from the experimental evaluation. The study applied various machine learning algorithms to the dataset and assessed their accuracy using all selected features.
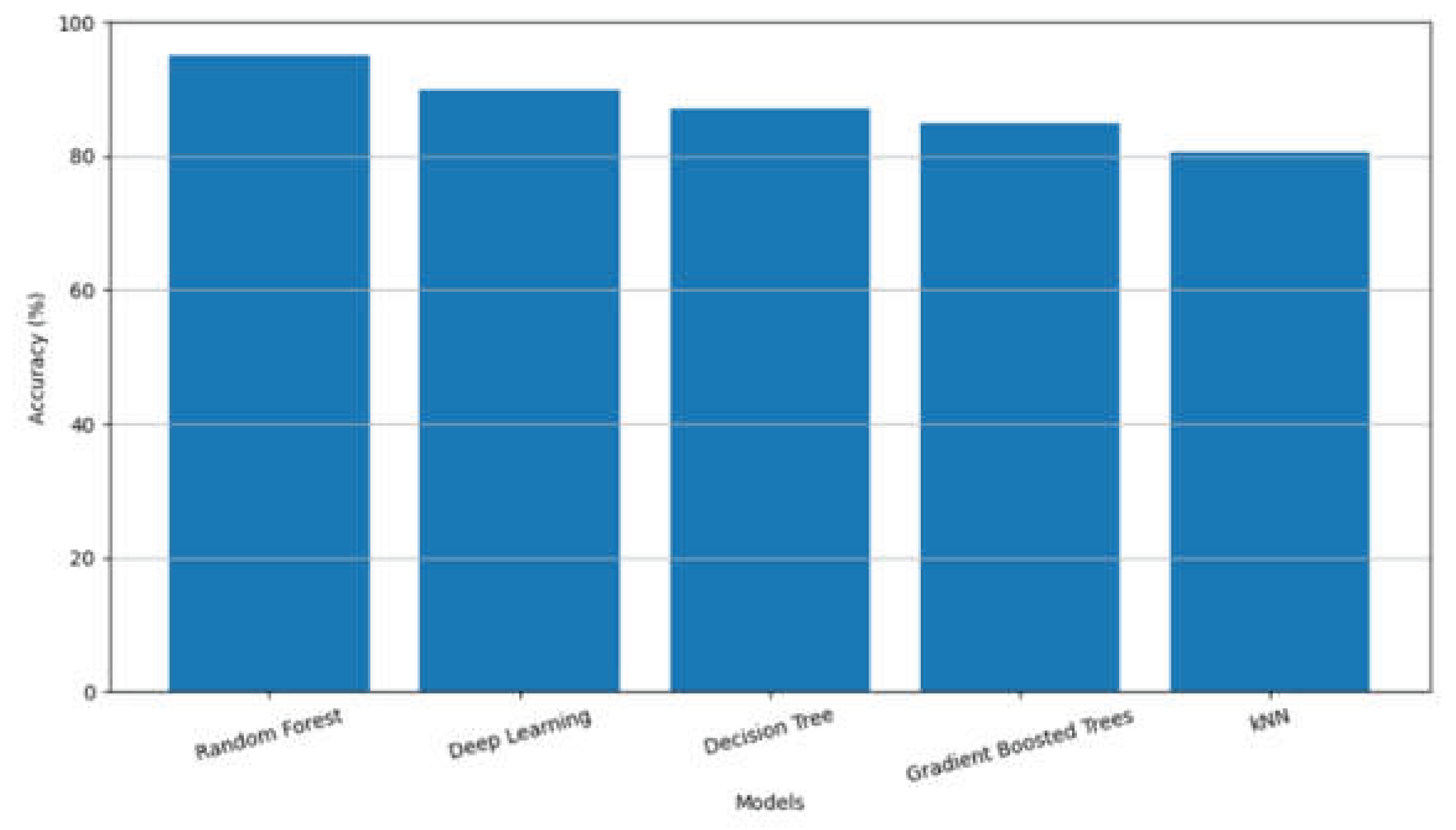
Table 2 presents the accuracy scores of each model.
Table 2.
Model Accuracies.
Table 2.
Model Accuracies.
| Model |
Accuracy |
| Random Forest |
95.15% |
| Deep Learning |
89.91% |
| Decision Tree |
87.08% |
| Gradient Boosted Trees |
85.03% |
| kNN |
80.65% |
As shown in
Table 2, the Random Forest model outperforms all other machine learning algorithms with an accuracy of 95.15%, followed by Deep Learning and Decision Tree. This confirms that ensemble methods like Random Forest are more effective for churn prediction in the given dataset. To provide context,
Table 3 presents a comparison with previous studies from the literature, showing the performance of various models and approaches employed by different authors.
Table 3.
Benchmark Comparison.
Table 3.
Benchmark Comparison.
| Author |
Year |
Model |
Accuracy |
| [5] |
2023 |
Deep Learning |
94% |
| [8] |
2024 |
Random Forest |
92.45% |
| [4] |
2024 |
Random Forest |
82.14% |
These findings (see
Figure 3) demonstrate the effectiveness of the Random Forest model, not only in the current study but also in previous research. The visual comparison further illustrates how the proposed model achieves a higher accuracy than those reported in past studies.
Figure 3.
Visualizations of Accuracy of Different Models.
Figure 3.
Visualizations of Accuracy of Different Models.
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Customer churn prediction for the e-commerce industries is emphasized by using machine learning algorithms in this research. To ensure the validity and accuracy of analysis, the study sample consisted of a large number of subjects, while using complex data preprocessing and analyzing the set of input variables including the outlier treatment, missing values imputation, and forward features selection. Looking at the results of the various algorithms that were implemented, Random Forest was the most accurate, precise, and have the highest recall of the potential churners. The focus of this study is in the importance of the use of predictive analytics to increase the chances of the customer retention planning hence increasing on the profitability and sustainability of the business. As for the future work on this paper, several improvements can be made primarily in terms of methodologies used for different components of the model. First, the proposed integration of deep learning models such as LSTMs and hybrid frameworks may help understand time-variant behaviors of customers. Second, extra boundaries including the exterior customers’ feedback, the social media sentiment analysis, macroeconomic factors may be integrated for model stability. Third, for further improvement of the decision-making performance on imbalanced datasets, other more complex methods, including the Synthetic Major Oversampling Tactic for Enropol (e.g., SMOTE variations), can be applied. Again, the practical viability of the models can be established by implementing the suggested algorithms in concrete e-business settings to investigate the possible performance improvements customer churn rates.
References
- Zhang, X.; Guo, F.; Chen, T.; Pan, L.; Beliakov, G.; Wu, J. , “A Brief Survey of Machine Learning and Deep Learning Techniques for E- Commerce Research,” Dec. 01, 2023, Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute (MDPI). [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Guo, F.; Chen, T.; Pan, L.; Beliakov, G.; Wu, J. , “A Brief Survey of Machine Learning and Deep Learning Techniques for E- Commerce Research,” Dec. 01, 2023, Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute (MDPI). [CrossRef]
- Kwon, G.; Shin, M. , “A study on e-commerce seller churn prediction using MCC-Stakcnet.” [Online]. Available: https://ssrn.com/abstract=4530482.
- Xiahou, X.; Harada, Y. B2C E-Commerce Customer Churn Prediction Based on K-Means and SVM. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Electronic Commerce Research 2022, 17, 458–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddadi, S.J.; Farshidvard, A.; Silva, F.D.S.; Reis, J.C.D.; da Silva Reis, M. Customer churn prediction in imbalanced datasets with resampling methods: A comparative study. Expert Syst Appl 2024, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narina, P. , “Customer churn prediction tool using deep learning: a case of an ecommerce business operating in Kenya.” [Online]. Available: http://hdl.handle.net/11071/13533Followthisandadditionalworksat: http://hdl.handle.net/11071/13533.
- Xiahou, X.; Harada, Y. Customer Churn Prediction Using AdaBoost Classifier and BP Neural Network Techniques in the E- Commerce Industry. American Journal of Industrial and Business Management 2022, 12, 277–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukita, C.; Bakti, L.D.; Rusilowati, U.; Sutarman, A.; Rahardja, U. Predictive and Analytics using Data Mining and Machine Learning for Customer Churn Prediction. Journal of Applied Data Sciences 2023, 4, 454–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljifri, A. Degree Thesis Predicting Customer Churn in a Subscription-Based E-Commerce Platform Using Machine Learning Techniques.
- Rehman, A.U.; et al. A Machine Learning-Based Framework for Accurate and Early Diagnosis of Liver Diseases: A Comprehensive Study on Feature Selection, Data Imbalance, and Algorithmic Performance. International Journal of Intelligent Systems 2024, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, A.; et al. “A novel approach for the effective prediction of cardiovascular disease using applied artificial intelligence“”.
- Zaman, N.; Low, T.J. , Alghamdi T. Energy efficient routing protocol for wireless sensor network. Int. Conf. Adv. Commun. Technol. 2014, 6779072, 808–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashfaq; Jhanjhi; N. Z.; Khan; N. A.; Javaid; Masud; Shorfuzzaman; M. (2025). Enhancing ECG Report Generation With Domain-Specific Tokenization for Improved Medical NLP Accuracy. IEEE Access.
- Mughal; M. A.; Ullah; Jhanjhi; N. Z.; Ray; S. K. A secure and privacy preserved data aggregation scheme in IoMT. Heliyon 2024, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Faisal; Jhanjhi; N. Z.; Ashraf; Ray; S. K.; Ashfaq; F. A Comprehensive Review of Machine Learning Models: Principles, Applications, and Optimal Model Selection. Authorea Preprints 2025.
- Jhanjhi; N. Z. (2024, November). Comparative analysis of frequent pattern mining algorithms on healthcare data. In 2024 IEEE 9th International Conference on Engineering Technologies and Applied Sciences (ICETAS) (pp. 1–10). IEEE.
- Simra; Konatham; Amsaad; Ibrahem; M. I.; Jhanjhi; N. Z. (2024, April). Enhancing anomaly detection of iot using knowledge-based and federated deep learning. In 2024 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Computing and Machine Intelligence (ICMI) (pp. 1–6). IEEE.
- Jhanjhi; N. Z.; Shah; I. A. (Eds.) Cybersecurity Measures for Logistics Industry Framework; Igi Global: 2024.
- Gouda; Sama; N. U.; Al-Waakid; Humayun; Jhanjhi; N. Z. Detection of skin cancer based on skin lesion images using deep learning. Healthcare 2022, 10, 1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeed; Jhanjhi; N. Z.; Naqvi; M. Implementation of donor recognition and selection for bioinformatics blood bank application. In Advanced AI techniques and applications in bioinformatics; CRC Press: 2021; pp. 105–138.
- Das; S. R.; Jhanjhi; N. Z.; Asirvatham; Rizwan; Javed; D. Securing AI-based healthcare systems using blockchain technology. In AI techniques for securing medical and business practices; IGI Global: 2025; pp. 333–356.
- Khan; Jhanjhi; Hamid; D. H. H.; Omar; H. A. H. B. H.; Amsaad; Wassan; S. Future Trends and Challenges in Cybersecurity and Generative AI. Reshaping Cybersecur. Gener. AI Tech. 2025, 491–522.
- Khan; M. R.; Khan; N. R.; Jhanjhi; N. Z. (Eds.). Digital transformation for improved industry and supply chain performance, IGI Global, 2024.
- Ashfaq; Jhanjhi; N. Z.; Khan; N. A.; Muzafar; Das; S. R. CrimeScene2Graph: Generating Scene Graphs from Crime Scene Descriptions Using BERT NER. In International Conference on Computational Intelligence in Pattern Recognition; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2024.
- Gill; S. H.; Razzaq; M. A.; Ahmad; Almansour; F. M.; Haq; I. U.; Jhanjhi; N. Z.; Masud; M. Security and privacy aspects of cloud computing: a smart campus case study. Intelligent Automation & Soft Computing 2022, 31, 117–128.
- Almulhim; Islam; Zaman; N. A lightweight and secure authentication scheme for IoT based e-health applications. International Journal of Computer Science and Network Security 2019, 19, 107–120.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).