Submitted:
07 November 2025
Posted:
07 November 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
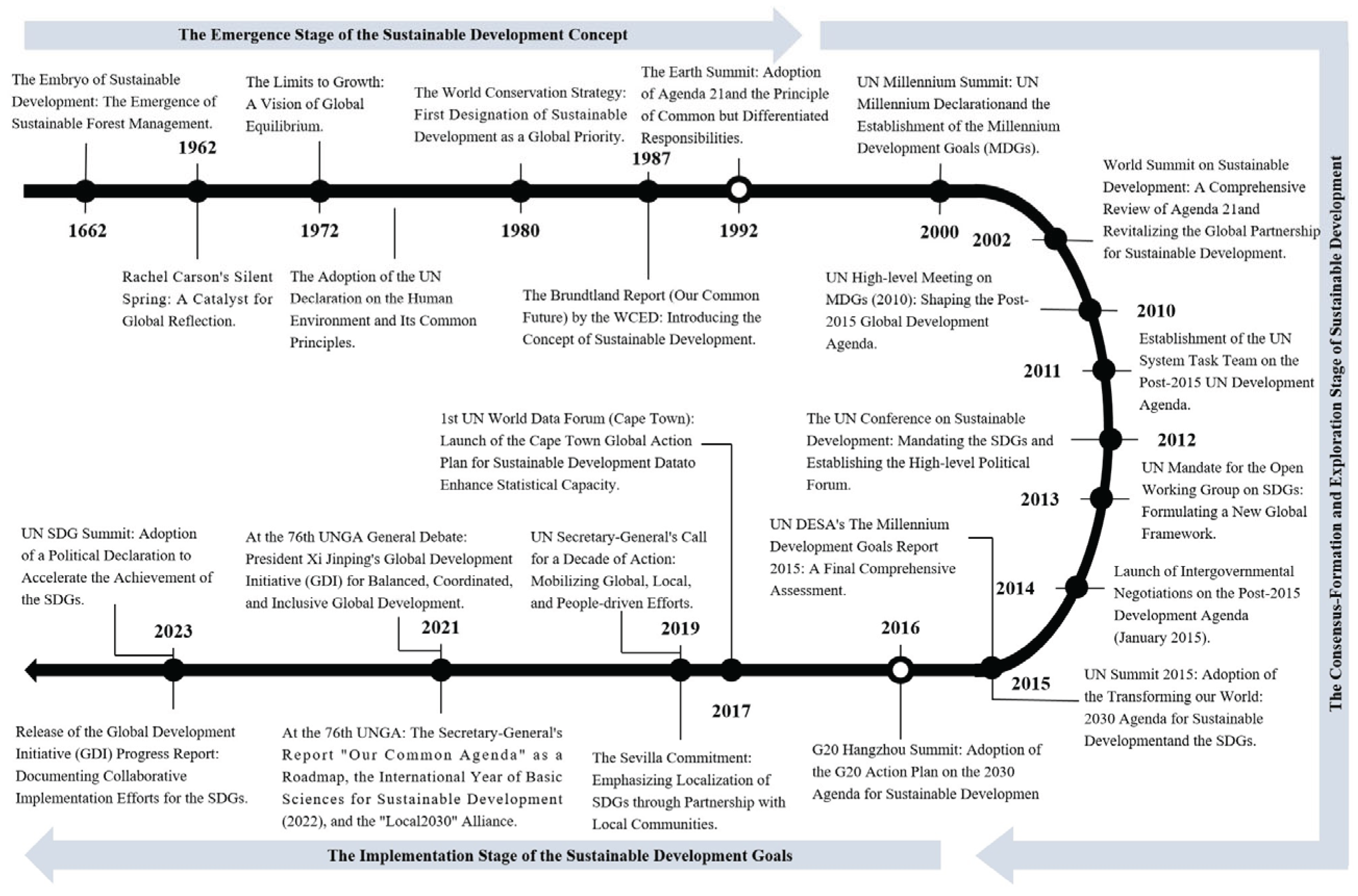
2. Process and History of Reaching Global Consensus on Sustainable Development
2.1. The Formation Stage of the Sustainable Development Concept (From the Early 17th Century to 1991): From Perception to Concept, Accompanied by the Rise of Environmental Protection Awareness in the Context of Economic Development
2.2. The Stage of Consensus Formation and Exploration on Sustainable Development (From 1992 to 2015): From Concept to Action, the Systematic Coordination Concept of Economy, Society and Environment Was Formally Established
2.3. The Stage of Establishing and Implementing the Sustainable Development Goals (From 2016 to the Present): Global and National Development Actions Centered Around the SDGs Have Continued to Deepen
3. Review and Progress of Sustainable Development Goals
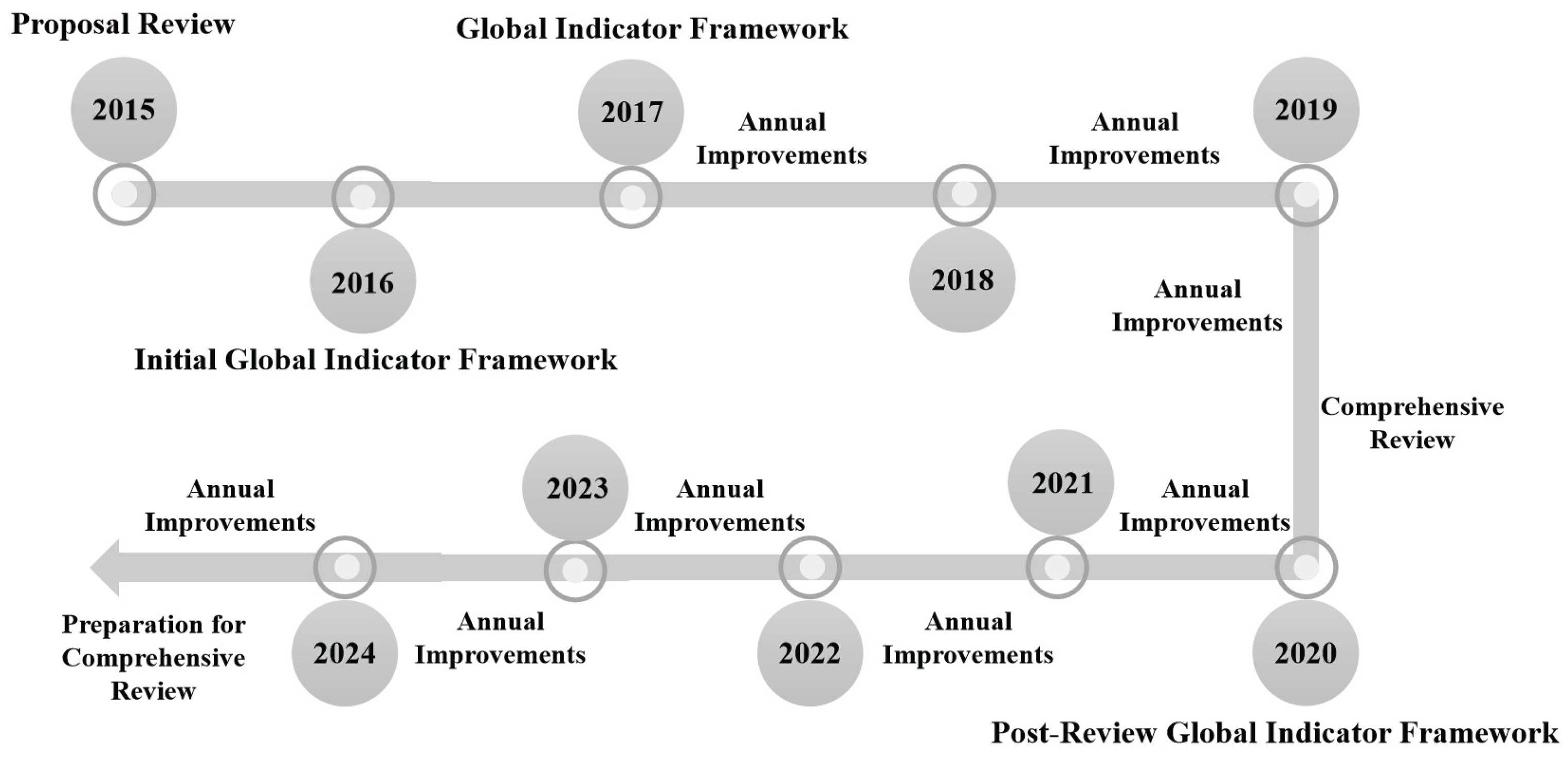
3.1. Global Framework for Sustainable Development Goals
3.2. Review and Assessment for Sustainable Development Goals
3.2.1. The High-Level Political Forum (HLPF)
- Promoting coherence and coordination of system-wide policies on sustainable development;
- Ensuring the 2030 Agenda remains relevant and ambitious, with a focus on assessing progress, achievements, and challenges encountered by both developed and developing countries, as well as emerging issues;
- Establishing effective linkages with the follow-up and review mechanisms of all relevant UN conferences and processes, including those pertaining to Least Developed Countries (LDCs), Small Island Developing States (SIDS), and Landlocked Developing Countries (LLDCs).
- An 8-day session hosted by the Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC), including a 3-day ministerial segment;
- A 2-day summit at the Head of State/Government level every four years, hosted by the UNGA.
3.2.2. The SDG Summits (HLPF Under the UNGA)
3.2.3. SDG Progress Assessment (Since 2016)
- The Sustainable Development Goals Report (issued by the UN Economic and Social Council): This report provides a comprehensive assessment of the global implementation progress of the 17 SDGs outlined in the 2030 Agenda, while also presenting the most recent data, analytical findings, and the current global status of the SDGs and selected indicators.
- The Global Sustainable Development Report (produced by the Independent Group of Scientists appointed by the UN Secretary-General): This report provides a comprehensive assessment of the global situation, taking into account regional disparities across the five United Nations regions. It documents and analyzes key issues related to sustainable development and policy implementation. Drawing on extensive consultations with the United Nations system—including regional commissions—as well as scientists, government officials, and stakeholders at all levels, and grounded in the latest scientific literature, the report identifies critical intervention measures aimed at advancing structural transformation and accelerating progress toward the achievement of sustainable development goals.
- The Sustainable Development Report (co-published by the UN Sustainable Development Solutions Network and Bertelsmann Stiftung): This report analyzes the specific progress and trends in the implementation of the 17 SDGs at the national level and conducts a comparative assessment across countries. It serves as a complementary tool to the official United Nations SDG indicators and country-specific voluntary national reviews. Given the complexity of the SDG indicator framework and the challenges associated with data availability, the Sustainable Development Solutions Network (SDSN) and the Bertelsmann Stiftung pioneered the development of a national-level measurement framework based on the global indicator system, comprising SDG indices and SDG dashboards. Aligned with the dynamic updates to indicators and data by the IAEG-SDGs, this framework supports countries in assessing their current performance, identifying priority areas requiring urgent action, and enabling cross-country and regional comparisons toward the achievement of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
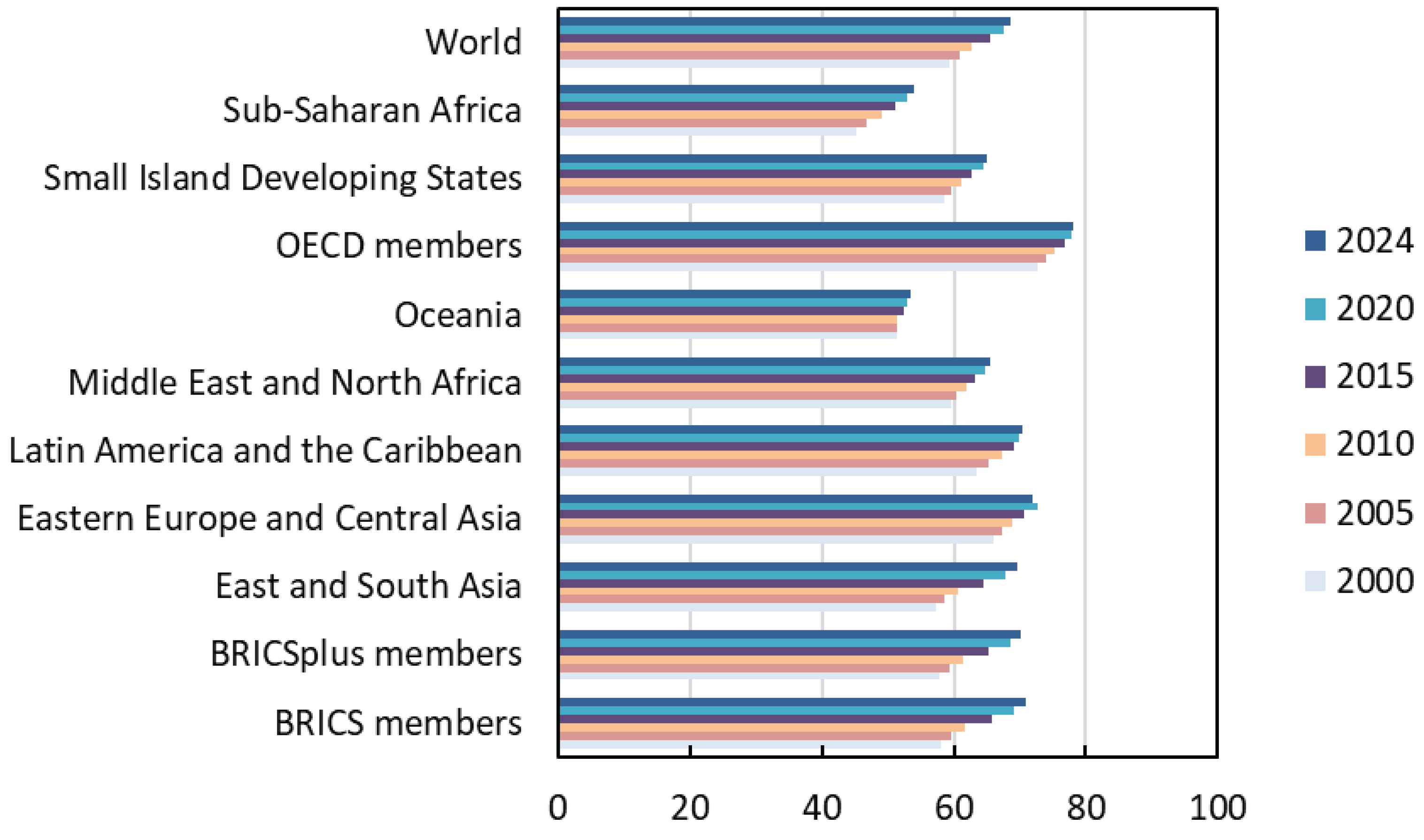
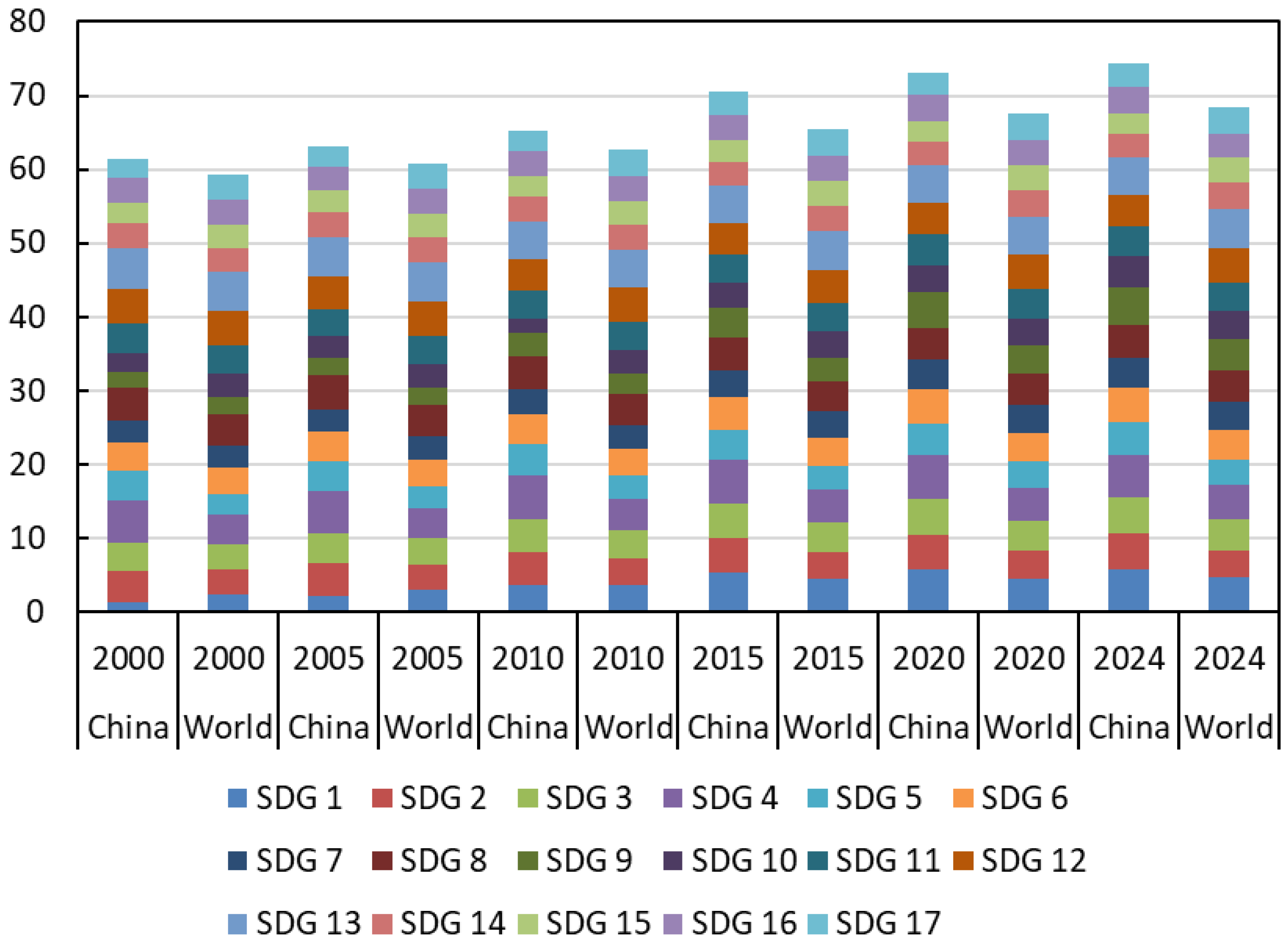
3.3. Global Progress Towards SDGs
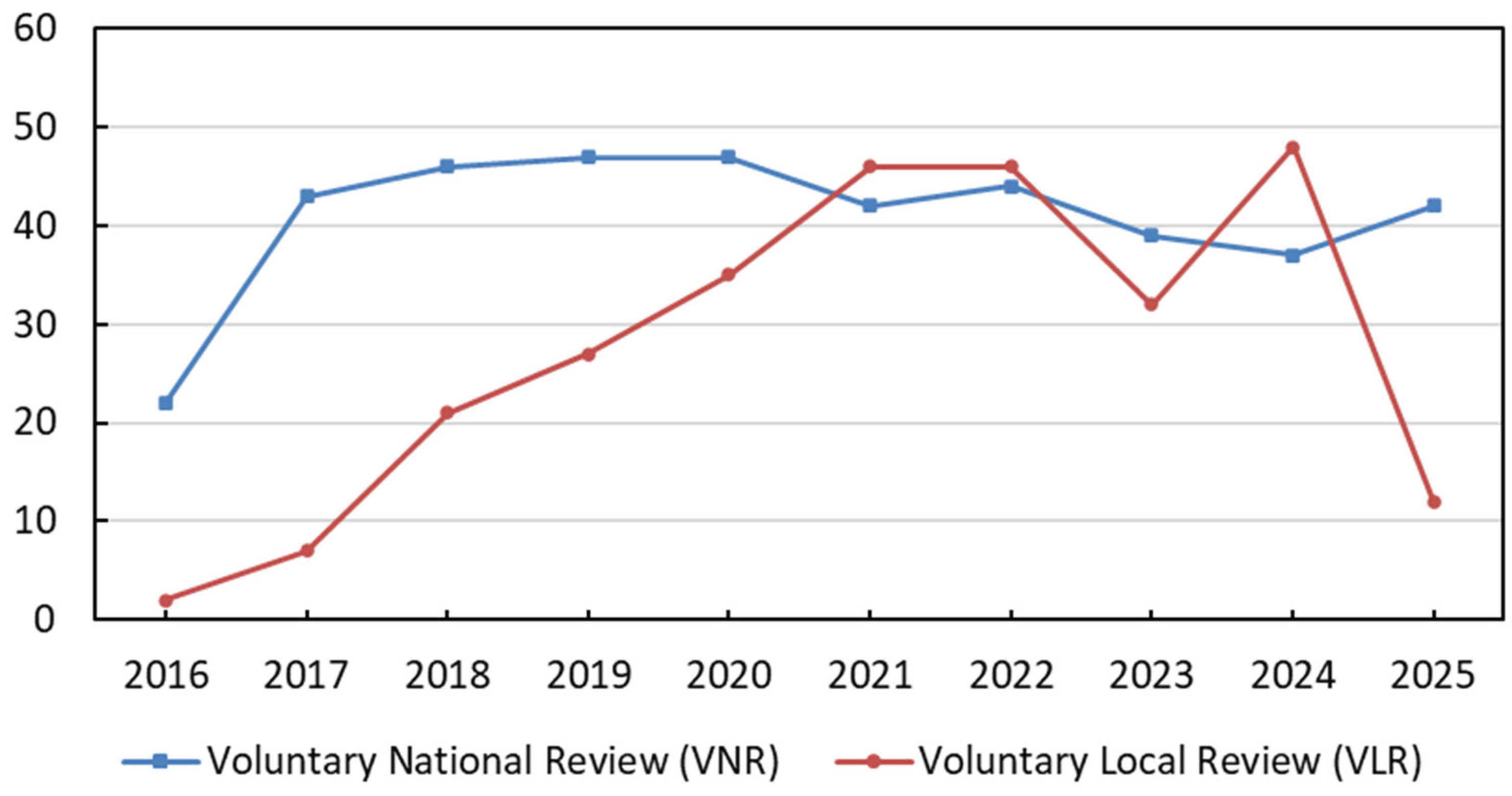
3.4. SDGs Localization Practices at the National and Subnational Levels
4. Global Outlook for Sustainable Development in the Future
4.1. New Challenges in Achieving the Sustainable Development Goals
4.2. Strategies and Suggestions for Enhancing Sustainable Development Goals
4.2.1. By 2050 and Beyond, SDGs Should Remain Central to Global Cooperation
4.2.2. To Strengthen Data Governance, Each Country or Region Should Accelerate the Development of Localized, Quantifiable, and Monitorable SDGs Indicator Systems
4.2.3. The Transformation Driven by Emerging Technologies Will Shape New Engines for Global Sustainable Development
4.2.4. Deepen the Implementation of International Scientific Programs for Sustainable Development Cooperation and Strengthen Collaboration in SDG Implementation
5. Conclusions
- Human-nature relationship: Ensuring humanity’s demands for natural resources are balanced by its contributions to safeguarding nature—i.e., the growth of human-made capital must not come at the expense of destroying or depleting natural capital.
- Interpersonal dimension: During economic development, fostering mutually beneficial harmony, co-creation, and benefit-sharing in interpersonal interactions, intergenerational relationships, interregional cooperation, and interest group engagements so as to advance global governance.
- Resource-environment constraint and development transformation dimension: Achieving a fundamental transition in economic activities—from an unsustainable paradigm characterized by high resource intensity, severe environmental pollution, and significant ecological degradation to a sustainable one that minimizes resource input, environmental impact, and ecological damage. Ultimately, this aims to realize the coordinated and sustainable development of the economy, society, and ecological environment.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, Y.; Shao, C.; Zhou, H. An analysis of the transition of "scarcity types" from the perspective of sustainable development. China population, resources and environment. 2020, 30(12), 38-44.
- Costanza, R.; d’Arge, R.; de Groot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; O’Neill, R.V.; Paruelo, J.; et al. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Wildlife Fund. Living Planet Report 2024. Gland, Switzerland: WWF, 2024. Available online: https://livingplanet.panda.org/ (accessed on 4 November 2025).
- Brundtland, G. Our common future—Call for action. Environmental conservation, 1987, 14(4), 291-294.
- OECD; United Nations Development Programme. G20 Contribution to the 2030 Agenda; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. Transforming our world: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. New York: United Nations; 2015. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/2030agenda (accessed on Day Month Year).
- Steffen, W.; Smith, M.S. Planetary boundaries, equity and global sustainability: why wealthy countries could benefit from more equity. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2013, 5, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, R. Silent Spring; Houghton Mifflin: New York, NY, USA, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Su, M.; Fath, B.D.; Yang, Z. Urban ecosystem health assessment: A review. Sci. Total. Environ. 2010, 408, 2425–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNDP; World Bank. Transitioning from the MDGs to the SDGs; United Nations Development Programme: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Griggs, D.; Smith, M.S.; Rockström, J.; Öhman, M.C.; Gaffney, O.; Glaser, G.; Kanie, N.; Noble, I.; Steffen, W.; Shyamsundar, P. An integrated framework for sustainable development goals. Ecol. Soc. 2014, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, P.; Costa, L.; Rybski, D.; Lucht, W.; Kropp, J.P. A Systematic Study of Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) Interactions. Earth's Futur. 2017, 5, 1169–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z; Chau, S. ; Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Dietz, T.; Wang, J.; Winkler, J.; Fan, F.; Huang, B.; Li, S.; Wu, S.; Herzberger, A.; Tang, Y.; Hong, D.; Li, Y.; Liu, J. Assessing progress towards sustainable development over space and time. Nature. 2020, 577, (7788), 74–+.
- Independent Group of Scientists Appointed by the Secretary-General. Global Sustainable Development Report 2023: Times of Crisis, Times of Change: Science for Accelerating Transformations to Sustainable Development; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Sachs, J.D.; Schmidt-Traub, G.; Mazzucato, M.; Messner, D.; Nakicenovic, N.; Rockström, J. Six Transformations to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals. Nat. Sustain. 2019, 2, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, W. The theoretical connotation of sustainable development: The 20th Anniversary of UN Conference on Environ-ment and Development in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2012, 22, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Cui, C.; Dong, J.; Qu, A.; Shao, C. Implementation of the sustainable development goals in urban agglomeration: Progress and synergies. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2025, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. The sustainable development goals report 2025; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- World Bank. Poverty, Prosperity, and Planet Report 2024: Pathways Out of the Polycrisis; World Bank: Washington, DC, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Sachs, J.D. , Lafortune, G., Fuller, G., Iablonovski, G. Financing Sustainable Development to 2030 and Mid-Century. Sustainable Development Report 2025; Dublin University Press: Dublin, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Chen, X.; Jiang, Q.; Wu, X.; Bhattarai, N.; Mullen, J.; Li, Z.B.; Gurney, G.G.; Li, S.; Li, C.; et al. Assessing global sustainability performance, imbalance, and coordination over space and time. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, S.; Li, J.; Lo, K.; Guo, H.; Li, C. China’s rapidly evolving practice of poverty resettlement: Moving millions to eliminate poverty. Dev. Policy Rev. 2019, 38, 541–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Q.; Krey, V.; Byers, E.; Rafaj, P.; Nguyen, B.; Awais, M.; Riahi, K. Targeting net-zero emissions while advancing other sustainable development goals in China. Nat. Sustain. 2024, 7, 1107–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Ping, Z.-B.; Dong, Z.-F.; Chen, K.-L.; Zhu, X.-D.; Li, B.L.; Tan, X.-Y.; Zhu, B.-K.; Liu, X.; Zhou, C.-C.; et al. Resources and environmental costs of China's rapid economic growth: From the latest theoretic SEEA framework to modeling practice. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Q.; Wu, C.; Chen, F.; Liu, J.; Pradhan, P.; Bryan, B.A.; Schaubroeck, T.; Carrasco, L.R.; Gonsamo, A.; Li, Y.; et al. Intranational synergies and trade-offs reveal common and differentiated priorities of sustainable development goals in China. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, T.; Yun, H. Is it possible to determine an internationally applicable optimal Sustainable Development Goal using a priority-based evaluation. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2025, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afjal, M. Bridging the financial divide: a bibliometric analysis on the role of digital financial services within FinTech in enhancing financial inclusion and economic development. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2023, 10, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, W.L.; Wall, T.; Barbir, J.; Alverio, G.N.; Dinis, M.A.P.; Ramirez, J. Relevance of international partnerships in the implementation of the UN Sustainable Development Goals. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, X.; Lenharo, M.; Basu, M.; Castelvecchi, D.; Tollefson, J. How to fight climate change without the US: a guide to global action. Nature 2025, 647, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malekpour, S.; Raven, R.; Allen, C.; Moallemi, E.A.; Ningrum, D.; Cuesta-Claros, A.; Grainger-Brown, J.; Trundle, A.; Kestin, T.; Coy, D.; et al. Transformative localization to accelerate the 2030 Agenda. Nat. Sustain. 2024, 7, 516–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. The sustainable development goals report 2024; United Nations: 2024.
- Masuda, H.; Kawakubo, S.; Okitasari, M.; Morita, K. Exploring the role of local governments as intermediaries to facilitate partnerships for the Sustainable Development Goals. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sever, S.D.; Tok, E.; Sellami, A.L. Sustainable Development Goals in a Transforming World: Understanding the Dynamics of Localization. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Moya, F.; Yang, Y. Cities’ review of the sustainable development goals and insights from voluntary local reviews. npj Urban Sustain. 2025, 5, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhao, G.; Koh, K.P.; Xu, Z.; Yue, M.; Wang, W.; Tan, Y.; Wu, L. Impact of China’s financial development on the sustainable development goals of the Belt and Road Initiative participating countries. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2024, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, S.; Dong, R.; Cui, C.; Yang, T.; Zhan, X.; Wang, F.; Shao, C. Bibliometric Analysis of Research Hotspots and Frontiers in Progress towards the Sustainable Development Goals. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. Global Sustainable Development Report (GSDR) 2023; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. The Sustainable Development Goals Report 2023; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Chancel, L.; Piketty, T. Global Income Inequality, 1820–2020: the Persistence and Mutation of Extreme Inequality. J. Eur. Econ. Assoc. 2021, 19, 3025–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chancel, L.; Mohren, C.; Bothe, P.; Muti, S.; Villaverde, P. Climate Inequality Report 2025. Climate Change: A Capital Challenge. Why Climate Policy Must Tackle Ownership. World Inequality Lab Key Report. 2025.
- Hao, N.; Li, J. Technological progress, "erosion effect" of human capital and international technology gap: Empirical analysis based on multinational panel data from 2001 to 2015. Economist. 2018, 7, 55–62. [Google Scholar]
- Steffen, W.; Richardson, K.; Rockström, J.; Cornell, S.E.; Fetzer, I.; Bennett, E.M.; Biggs, R.; Carpenter, S.R.; De Vries, W.; De Wit, C.A.; et al. Planetary boundaries: Guiding human development on a changing planet. Science 2015, 347, 1259855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachs, J.; Schmidt-Traub, G.; Lafortune, G. Speaking truth to power about the SDGs. Sustainable Development Solutions Network. 2022. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, B.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Zhao, W. Classification–coordination–collaboration: a systems approach for advancing Sustainable Development Goals. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020, 7, 838–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, Y. New Technological Changes and New Driving Forces for Global Sustainable Development. People' s Tribune Frontiers. 2023, 22, 79–85. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Chau, S.N.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Dietz, T.; Wang, J.; Winkler, J.A.; Fan, F.; Huang, B.; et al. Assessing progress towards sustainable development over space and time. Nature 2020, 577, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Key organizations | The publicly released report |
|---|---|
| United Nations Economic and Social Council | "Sustainable Development Goals Report" (released every July since 2016) |
| United Nations Independent Scientific Group for Sustainable Development | Global Sustainable Development Report (released every four years, with two editions having been published since 2016 - in 2019 and 2023) |
| The UN Sustainable Development Solutions Network | "The Global Sustainable Development Goals Index and Dashboard Report" (released in June each year since 2016; since 2019, it has been renamed as "Sustainable Development Report") |
| United Nations Development Program | The Localization of ASEAN SDGs: Experience in Policy Formulation and Implementation Pathways |
| The contribution of the G20 to the 2030 Agenda | |
| United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific | "Progress Report on Sustainable Development Goals in Asia and the Pacific" (released annually) |
| United Nations Economic Commission for Europe | "Facing Increasingly Severe Challenges in Sustainable Development: Can the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe Region Turn the Situation Around by 2023? " "With Half the Time Left until 2030: How Many Goals Will the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe Region Achieve?" and other series of progress reports (released annually) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





