Submitted:
31 October 2025
Posted:
03 November 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
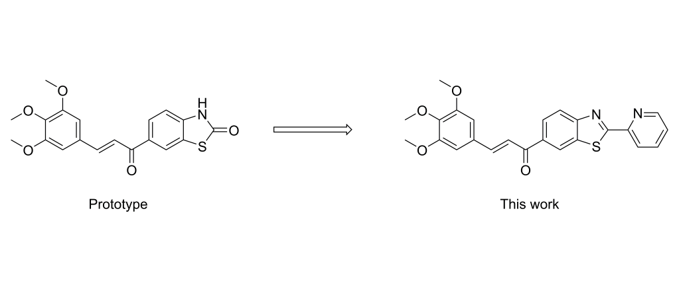
1. Introduction
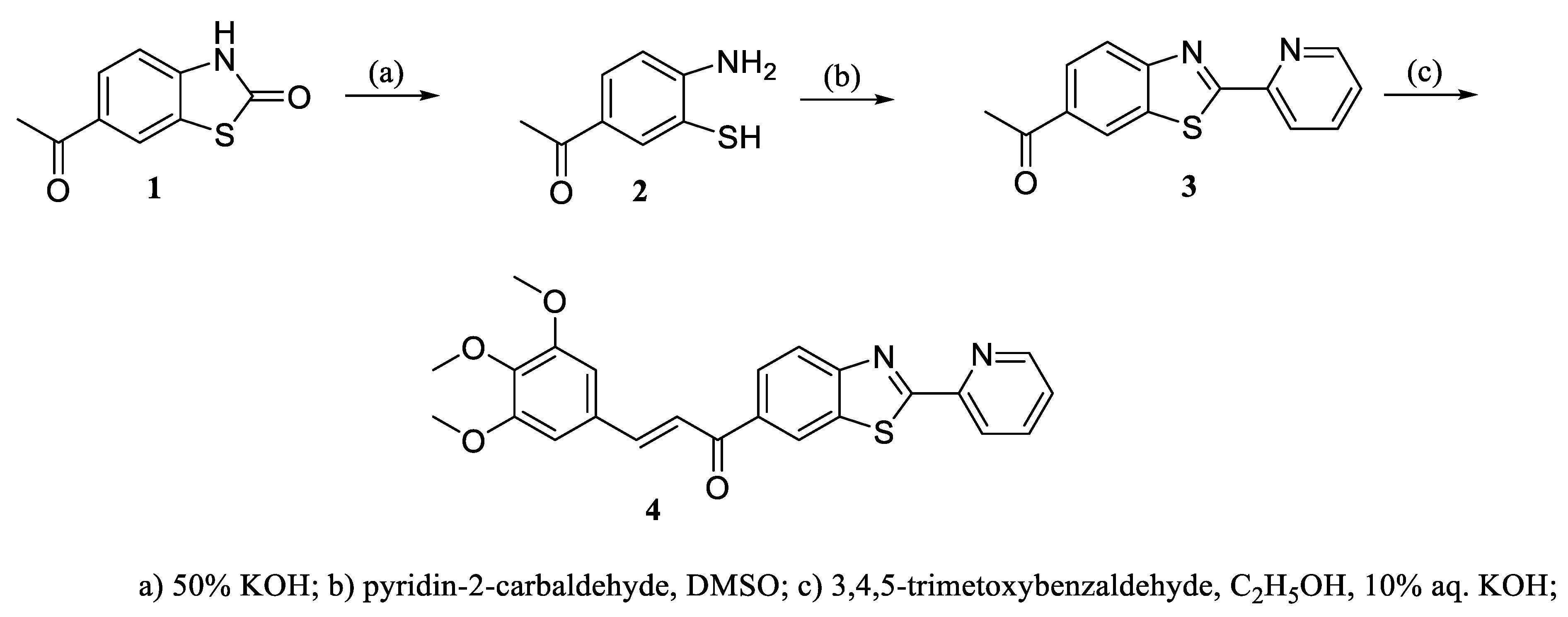
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General
3.2. Synthesis
3.2.1. 1-(2-(Pyridin-2-yl)benzo[d]thiazol-6-yl)ethan-1-one (3)
3.2.2.(. E)-1-(2-(Pyridin-2-yl)benzo[d]thiazol-6-yl)-3-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one (4)
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Almutairi, S.M.; Mehmood, R.; Fatima, A.; Ali, D.; Jamal, M.; Ayyaz, M.; Sarfraz, M. Chalcones from the deep: in silico medicinal chemistry and quantum chemical insights into their anticancer and anti-HIV potency. Comput. Theor. Chem 2025, 115380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Rakesh, K.P.; Bukhari, S.N.; Balakrishna, M.; Manukumar, H.M.; Qin, H.L. Multi-targetable chalcone analogs to treat deadly Alzheimer’s disease: Current view and upcoming advice. Bioorg. Chem., 2018, 80, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, B.; Suresh, J.; Anbazghagan, S.; Paulraj, J.; Krishnan, G.K. Heteroaryl chalcones: Mini review about their therapeutic voyage. Biomed. Prev. Nutr., 2014, 4, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radha, V.P.; Bhavani, G.; Vanaraj, R.; Prabakaran, M. Benzothiazole-imidazoline bearing transition metal complexes of Schiff bases: Synthesis, characterization, chemosensing, antimicrobial, anticancer and DNA cleavage activities. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2025, 122860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, Y.B.; Momekov, G.T.; Petrov, O.I. New heterocyclic chalcones. Part 6. Synthesis and cytotoxic activities of 5-or 6-(3-aryl-2-propenoyl)-2 (3H)-benzoxazolones. Heterocycl. Commun., 2013, 19, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, Y.B.; Gerova, M.S.; Momekov, G.T.; Petrov, O.I. Synthetic chalcones of 2 (3H)-benzothiazolone with potential cytotoxic activity. Comp. Rend. Acad. Bulg. Sci, 2007, 60, 641. [Google Scholar]
- Adhikari, S.; Nath, P.; Das, A.; Datta, A.; Baildya, N.; Duttaroy, A.K.; Pathak, S. A review on metal complexes and its anti-cancer activities: Recent updates from in vivo studies. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 171, 116211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deligeorgiev, T.G. An Improved Method for the Preparation of 2-Aryl-,2-Hetaryl- and 2-Styrylbenzothiazoles. Dye and pigments 1990, 12, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




