Submitted:
16 October 2025
Posted:
16 October 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
I. Introduction
II. Related Work
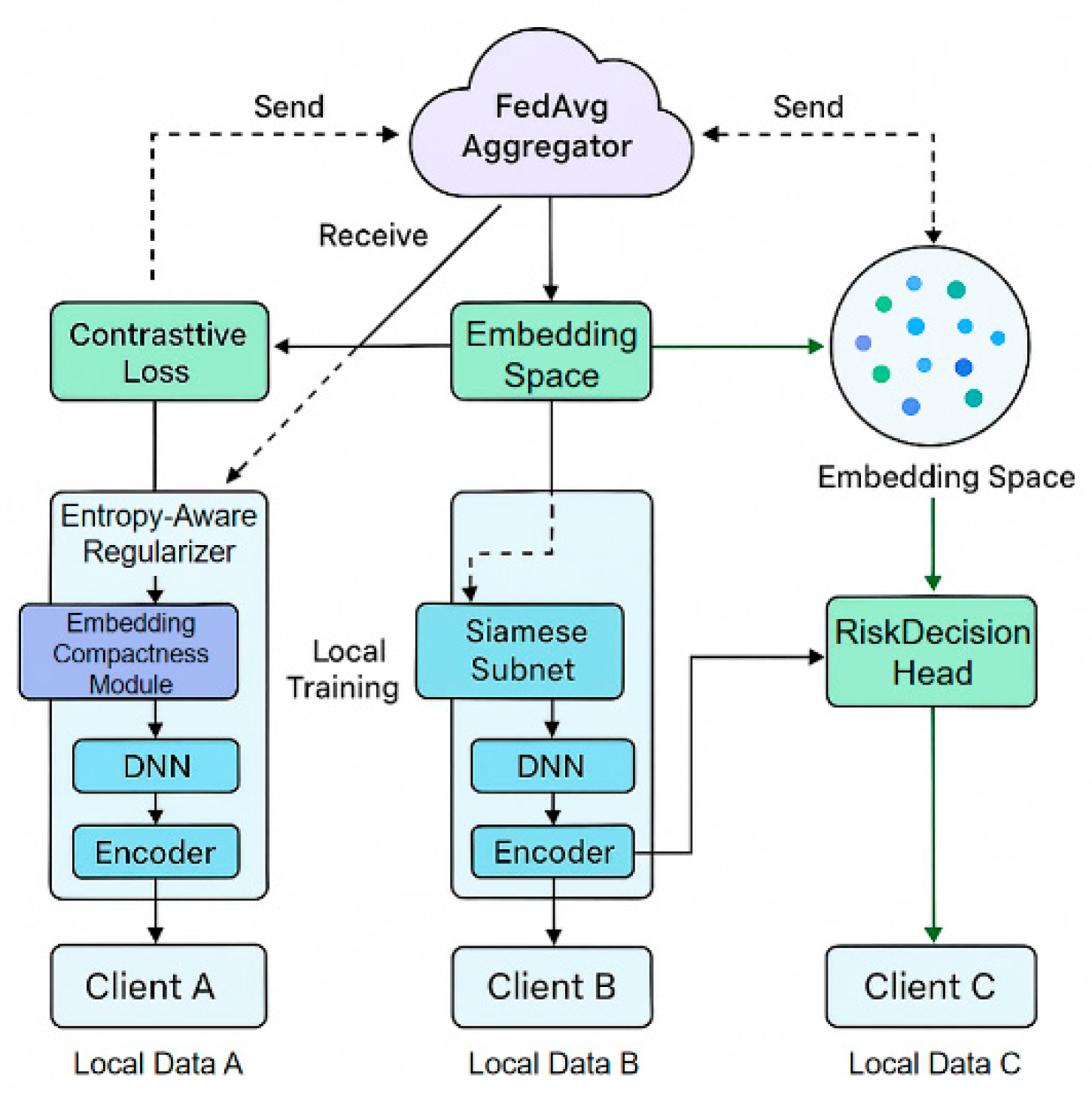
III. Proposed Approach
IV. Performance Evaluation
A. Dataset
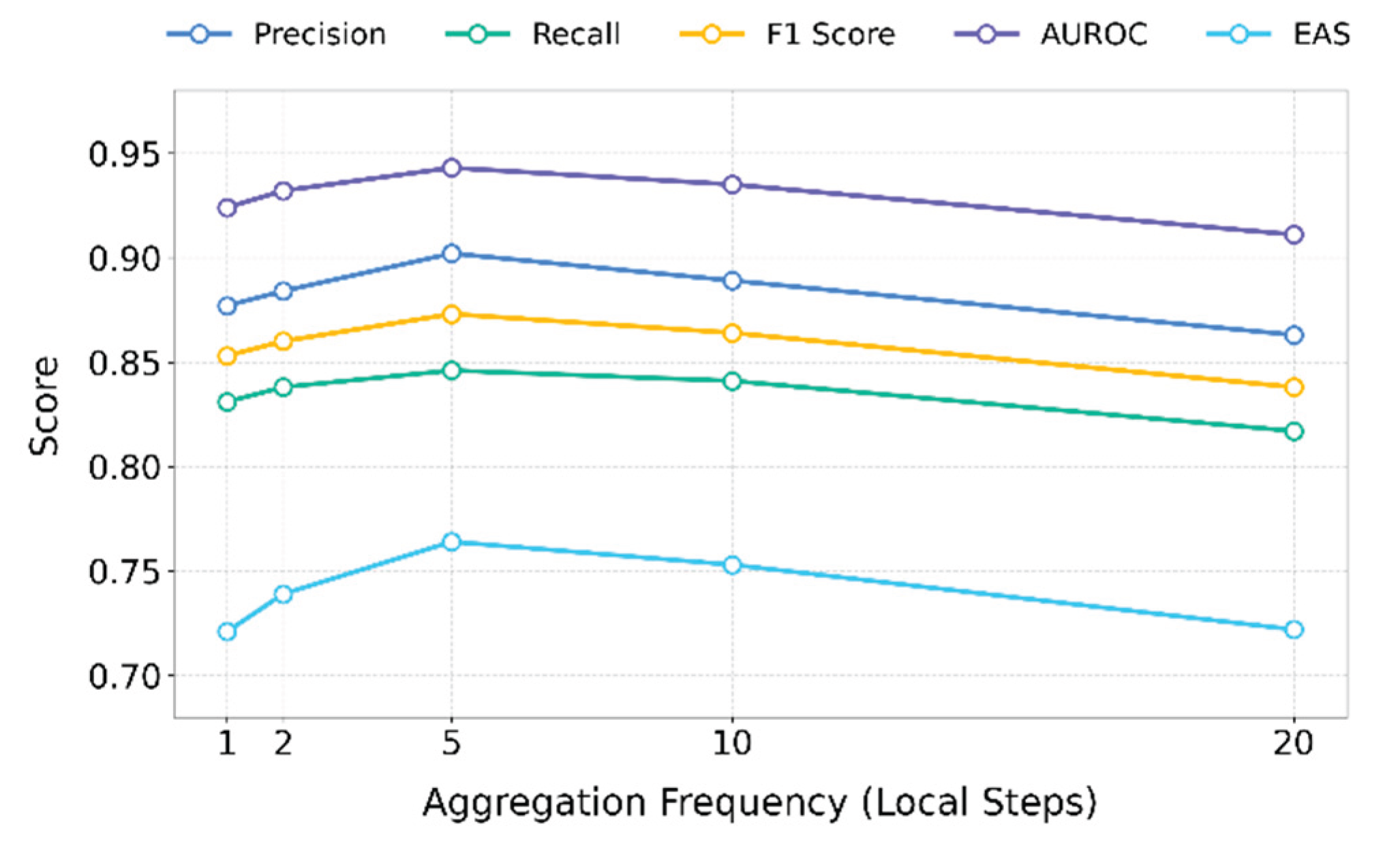
B. Experimental Results
| Model | Precision | Recall | F1 Score | AUROC | EAS |
| MoRF[24] | 0.842 | 0.761 | 0.799 | 0.902 | 0.651 |
| ARFD [25] | 0.868 | 0.779 | 0.821 | 0.918 | 0.684 |
| FRED [26] | 0.889 | 0.812 | 0.849 | 0.931 | 0.703 |
| SAAF [27] | 0.873 | 0.825 | 0.848 | 0.928 | 0.727 |
| Ours (FedSiamRisk) | 0.902 | 0.846 | 0.873 | 0.943 | 0.764 |

V. Conclusions
VI. Future Work
References
- Sharma, N.; Gupta, S.; Mohamed, H.G. , et al. Siamese convolutional neural network-based twin structure model for independent offline signature verification. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanayakkara, S.I.; Pokhrel, S.R.; Li, G. Understanding global aggregation and optimization of federated learning. Future Generation Computer Systems 2024, 159, 114–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Wang, H. ; Graph contrastive pre-training for anti-money laundering. International Journal of Computational Intelligence Systems 2024, 17, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Yao, S. Enterprise financial risk identification and information security management and control in big data environment. Mobile Information Systems 2021, 2021, 7188327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. Entity-aware graph neural modeling for structured information extraction in the financial domain. Transactions on Computational and Scientific Methods 2024, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, M.; Liu, S.; Xu, W.; Long, S.; Yi, Y.; Lin, Y. Function-driven knowledge-enhanced neural modeling for intelligent financial risk identification. 2025.
- Xu, W.; Jiang, M.; Long, S.; Lin, Y.; Ma, K.; Xu, Z. Graph neural network and temporal sequence integration for AI-powered financial compliance detection. 2025.
- Sha, Q.; Tang, T.; Du, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Sheng, Y. Detecting credit card fraud via heterogeneous graph neural networks with graph attention. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2504.08183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, M.; Dai, L.; Wu, Y.; Du, J. Federated graph neural networks for heterogeneous graphs with data privacy and structural consistency. 2025.
- Dai, L. Contrastive learning framework for multimodal knowledge graph construction and data-analytical reasoning. Journal of Computer Technology and Software 2024, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, D. High fidelity text to image generation with contrastive alignment and structural guidance. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2508.10280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Xu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Ma, K.; Lin, Y.; Jiang, M. Integrating feature attention and temporal modeling for collaborative financial risk assessment. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2508.09399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y. Federated distillation with structural perturbation for robust fine-tuning of LLMs. Journal of Computer Technology and Software 2024, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Y. Hierarchical semantic-structural encoding for compliance risk detection with LLMs. Transactions on Computational and Scientific Methods 2024, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, S.; Wu, D. Hierarchical text classification with LLMs via BERT-based semantic modeling and consistency regularization. 2025.
- Hu, X.; Kang, Y.; Yao, G.; Kang, T.; Wang, M.; Liu, H. Dynamic prompt fusion for multi-task and cross-domain adaptation in LLMs. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2509.18113. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, R.; Hu, X.; Zheng, J.; Peng, C.; Lin, J. Fusion of local and global context in large language models for text classification. 2025.
- Xu, Q. Unsupervised temporal encoding for stock price prediction through dual-phase learning. 2025.
- Sha, Q. Hybrid deep learning for financial volatility forecasting: An LSTM-CNN-Transformer model. Transactions on Computational and Scientific Methods 2024, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Su, X. Predictive modeling of volatility using generative time-aware diffusion frameworks. Journal of Computer Technology and Software 2025, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Zheng, J.; Lin, J.; Han, M.; Du, J. Unified representation learning for multi-intent diversity and behavioral uncertainty in recommender systems. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2509.04694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, Z. Modeling audit workflow dynamics with deep Q-learning for intelligent decision-making. Transactions on Computational and Scientific Methods 2024, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Qin, Y.; Su, X.; Lin, Y. Transformer-based risk monitoring for anti-money laundering with transaction graph integration. 2025.
- Gong, J.; Wang, Y.; Xu, W. , et al. A deep fusion framework for financial fraud detection and early warning based on large language models. Journal of Computer Science and Software Applications 2024, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Ma, J.; Chen, G. Attentive statement fraud detection: Distinguishing multimodal financial data with fine-grained attention. Decision Support Systems 2023, 167, 113913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Cao, Y.; Shu, Y. , et al. A dynamic receptive field and improved feature fusion approach for federated learning in financial credit risk assessment. Scientific Reports 2024, 14, 26515. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, B.; Lu, P.; Xu, H. , et al. Health insurance fraud detection based on multi-channel heterogeneous graph structure learning. Heliyon 2024, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




