Submitted:
16 October 2025
Posted:
16 October 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
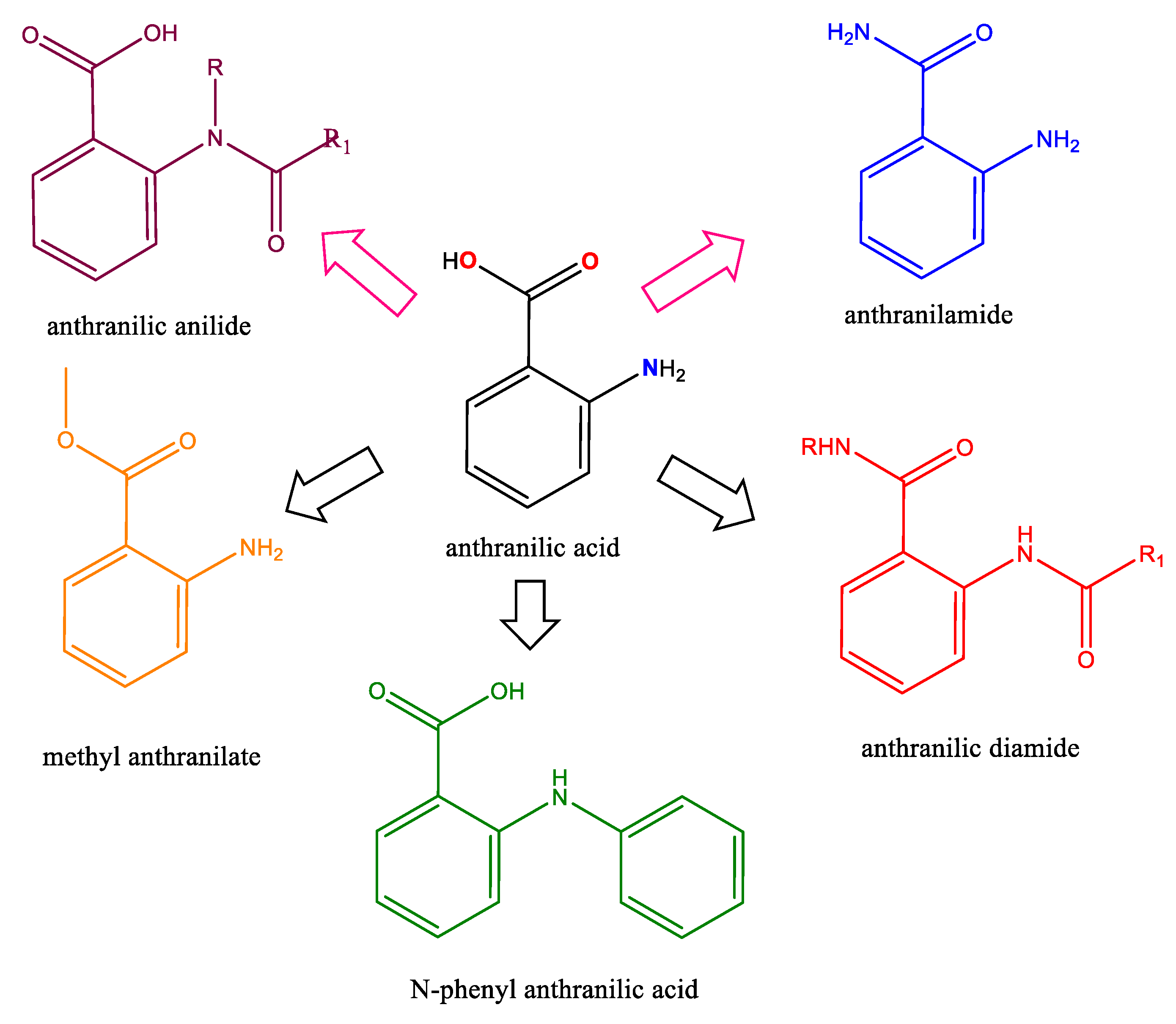
1. Introduction
2. Results
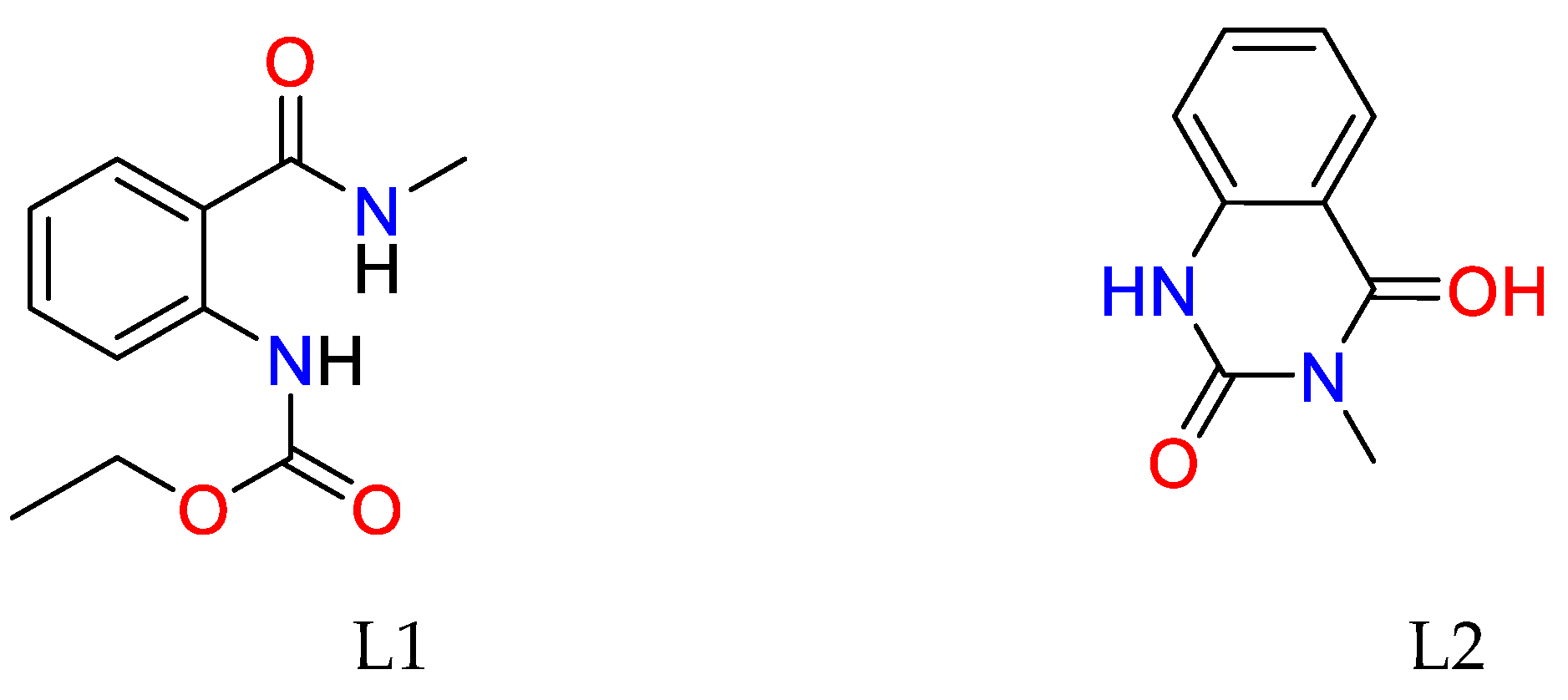
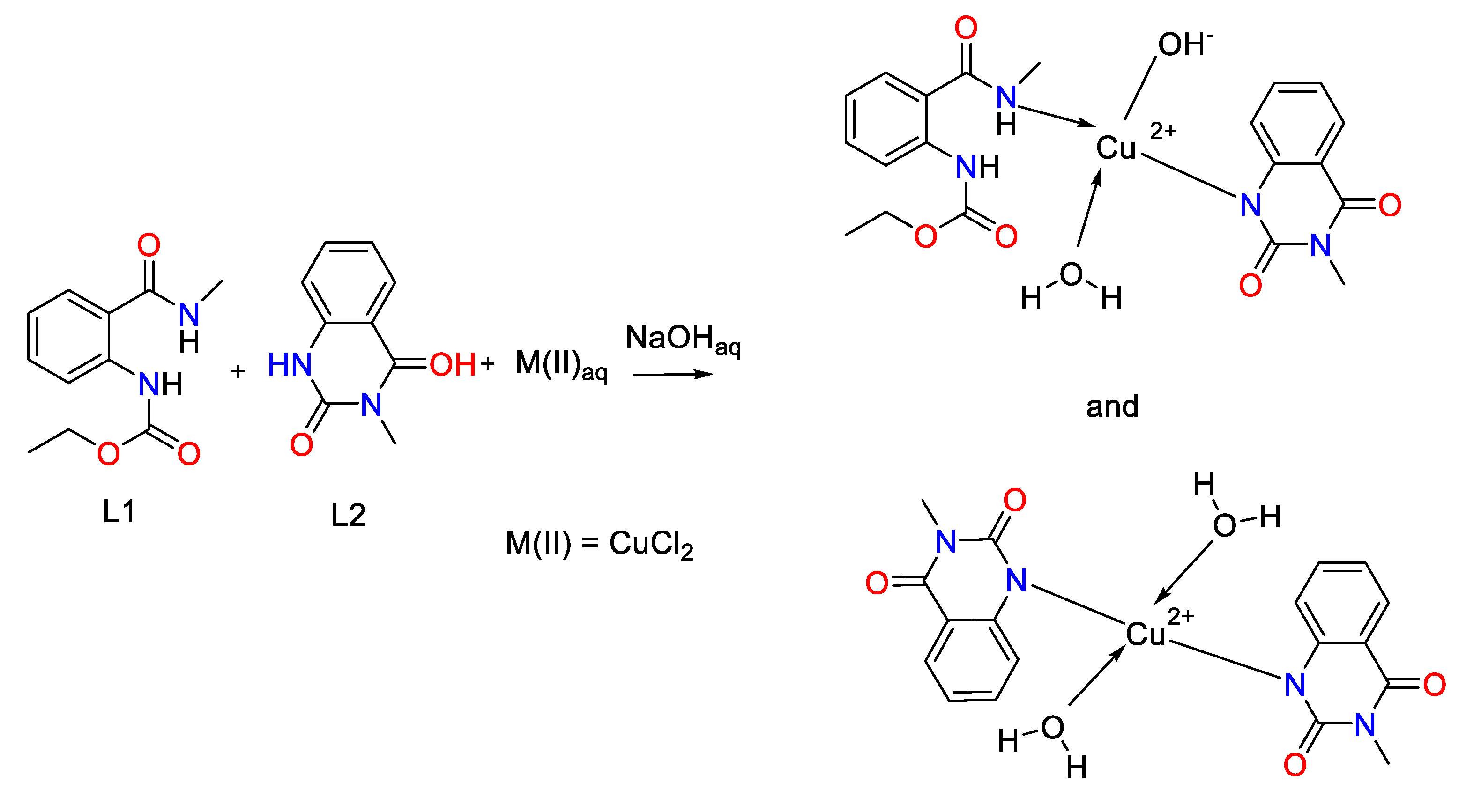
2.1. Synthesis of Cu(II) complex of ethyl (2-(methylcarbamoyl)phenyl)carbamate (L1) and 3-methylquinazoline-2,4(1H,3H)-dione (L2) – general procedure
2.1.1. Spectral Data of the Free Ligand and Its Copper(II) Complex
3. Discussion
| Assignment | L1 | L2 [23] | Cu(II) |
| ν(OH) | - | 3435 | |
| ν(NH, -C(=O)-NH-CH3) | 3345 | 3345 | |
| ν(NH, -NH-C(=O)OCH2CH3) | 3258 | 3165 | 3188 |
| ν(Csp2-H, -Ph) | 3072 | 3058 | |
| ν(C=O) | 1739 | 1715 | 1717 |
| δ(NH) + ν(C=O), -C(=O)-NH-CH3) | 1664 | 1662 | 1665 |
| δ(NH) + ν(C=O), -NH-C(=O)OCH2CH3) | 1633 | 1645 |
| Compound | Solubility, *limited | Melting point (°C) | Yield (%) | Colour |
| L1 | soluble in DMSO and CHCl3 | 136-137 | 80 | colorless |
| CuL | soluble in DMSO* and insoluble in H2O, THF, CH3COCH3, EtOH, EtOAc and cyclohexane | 243-245 ᵒC | 35 | bright blue |
| atom |
δ (1H) ppm L1 |
δ (1H) ppm L2 [25] |
δ (1H) ppm Cu(II) |
| NH(COO) |
10.96 (s) |
11.43 (s) | 10.95* 11.42** |
| NHCH3 |
8.72 (q) |
8.71* | |
| CH |
8.19 (dd) |
7.93 (d) | 8.18* 7.92** |
| CH | 7.70 (dd) | 7.64-7.66 (m) | 7.70* 7.64** |
| CH | 7.48 (ddd) | 7.17-7.21 (m) | 7.48* 7.18** |
| CH | 7.08 (ddd) | 7.17-7.21 (m) | 7.08* 7.18** |
| NHCH3 | 2.78 (d) | 3.26 (s) | 2.78* 3.25** |
| CH2 | 4.12 (q) | 4.12* | |
| CH3 | 1.23 (t) | 1.23* |
| atom |
δ (13C) ppm L1 |
δ (13C) ppm L2 [25] |
δ (13C) ppm Cu(II) |
| NH(C=O) | 169.16 | 162.6 | 169.16* 162.64** |
| NH(COO) | 153.37 | 150.8 | 153.43* 150.82** |
| C | 139.67 | 139.8 | 139.62* 139.76** |
| CH | 132.53 | 135.3 | 132.52* 135.32** |
| CH | 128.40 | 127.7 | 128.40* 127.72** |
| CH | 122.16 | 122.9 | 122.16* 122.89** |
| C | 120.03 | 114.1 | 120.03* 114.14** |
| CH | 119.05 | 115.5 | 119.06* 115.52** |
| CH2CH3 | 61.04 | - | 61.04* |
| NHCH3 | 26.68 | 27.5 | 26.69* 27.46** |
| CH2CH3 | 14.85 | - | 14.86* |
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Spectra Measurements
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Linder, M.C.; Hazegh-Azam, M. Copper biochemistry and molecular biology. Am J Clin Nutr. 1996, 63(5), 797S–811S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalid, H.; Hanif, M.; Hashmi, M.A.; Mahmood, T.; Ayub, K.; Monim-Ul-Mehboob, M. Copper complexes of bioactive ligands with superoxide dismutase activity. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2013, 13, 1944–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Li, Y.; Zhou, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, L.; Wu, M. Copper homeostasis and cuproptosis in atherosclerosis: metabolism, mechanisms and potential therapeutic strategies. Cell Death Discov. 2024, 10(1), 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandmann, O. , Weiss, K.H., Kaler, S.G. Wilson's disease and other neurological copper disorders. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14(1), 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaler, S.G. ATP7A-related copper transport diseases-emerging concepts and future trends. Nat Rev Neurol. 2011, 7(1), 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Xu, K.; Wang, G.; Zhang, F. Copper homeostasis and neurodegenerative diseases. Neural Regen Res. 2025, 20(11), 3124–3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, D.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, M.; Lin, Y.; He, H.; Liu, A.; Shen, S.; Wang, Y.; Han, Z. Mechanisms of copper metabolism and cuproptosis: implications for liver diseases. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1633711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Ji, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Li, C.; Lu, S.; Ge, P. Cuproptosis: Mechanisms, biological significance, and advances in disease treatment—A systematic review. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024, 30, e70039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denoyer, D.; Clatworthy, S.A.S.; Cater, M. A. Copper Complexes in Cancer Therapy. Met Ions Life Sci. 2018, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vo, T.T.T. , Peng, TY., Nguyen, T.H. et al. The crosstalk between copper-induced oxidative stress and cuproptosis: a novel potential anticancer paradigm. Cell Commun Signal 2024, 22, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCormick, R.; Buckley, E.; Donnelly, P.J.; Gilpin, V.; McMath, R.; Smith, R.B.; Papakonstantinou, P.; Davis, J. Anthranilic Acid: A Versatile Monomer for the Design of Functional Conducting Polymer Composites. J. Compos. Sci. 2024, 8, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rio, G. F.; Silva, B. V.; Martinez, S. T.; Pinto, A. C. Anthranilic acids from isatin: an efficient, versatile and environmentally friendly method. An Acad Bras Cienc. 2015, 87(3), 1525–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasher, P.; Sharma, M. Medicinal Chemistry of Anthranilic Acid Derivatives: A Mini Review. Drug Dev. Res. 2021, 82, 945–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganeshpurkar, A.; Gutti, G.; Singh, S.K. Chapter 1 - RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerases and Their Emerging Roles in Antiviral Therapy. Viral Polymerases Structures, Functions and Roles as Antiviral Drug Targets 2019, 1-42. [CrossRef]
- Nasr, T.M.; Aboshanab, A.M.; Abouzid, K.A.M.; Zaghary, W.A. Hands-on Synthetic Approaches and Biological Activities of Anthranilic Acid Derivatives: A Mini-Review. Egypt. J. Chem. 2023, 66, 329–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, M.; Abbasi, M.W.; Tariq, M.; Graham, J.P.; Al-Hagri, A.-R.S.; Elkarim, A.A.; Mohamed, M.E.; Nissapatorn, V.; Taha, M.; Hisaindee, S. Synthesis of Metal Anthranilate Complexes: Catalytic and Antipathogenic Studies. BMC Chem. 2022, 16, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, V.K. Synthesis, characterization, and biological studies of some biometal complexes. Futur J Pharm Sci 2021, 7, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, S. H.; Karem, L. K. A. Synthesis, Spectral and Biochemical Studies of New Complexes of Mixed Ligand Schiff Base and Anthranilic Acid. Orient J Chem 2018, 34. [Google Scholar]
- Abu-Dief, A. M.; Shehata, M. R.; Hassan, A. E.; Alharbi, S.K.; Alzahrani, A. Y.A.; Abo-Dief, H. M.; Ragab M., S. Exploring, anthranilic azomethine complexes: from synthesis, spectroscopic, solution and theoretical studies to DNA interaction and biomedical prospects. J Mol. Str. 2025, 1341, 142571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta B.H.; More P.S. Synthesis, Characterization and X-Ray Diffraction Studies of Co(II), Ni(II), Cu(II) and Zn(II) Complexes with Schiff Base Derived from 5-nitrosalicylaldehyde and Anthranilic Acid. Asian J Chem. 2007, 19(5), 3581-3587. https://svv-research-data.s3.ap-south-1.amazonaws.com/140317-2009-asian%20j%20chem%20Aniket%20Pawanoji.pdf.
- Marinova, P.; Hristov, M. Synthesis and Biological Activity of Novel Complexes with Anthranilic Acid and Its Analogues. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 9426–9429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoneva, S.; Milusheva, M.; Burdzhiev, N.; Marinova, P.; Varbanova, E.; Tumbarski, Y.; Mihaylova, R.; Cherneva, E.; Nikolova, S. Antimicrobial Activity of Ethyl (2-(Methylcarbamoyl)phenyl) carbamate and Its Mixed Ligand Ni(II) and Co(II) Complexes. Inorganics 2025, 13, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizian, J.; Mohammadi, A.A.; Karimi, A.R. An Efficient One-Pot Procedure for Preparation of 2,4(1H,3H)-Quinazolinediones.
- and 2-Thioxoquinazolinone Derivatives Under Microwave Irradiation. Synth. Commun. Int. J. Rapid Commun. Synth. Org. Chem.
- 2003, 33, 415–420. [CrossRef]
- Shirode, P. R. A study of mixed ligand complexes of anthranilic acidsemicarbazone and benzaldehyde with Co(II), Ni(II) and Cu(II). World Journal of Pharmaceutical Research 2018, 7, 1135–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, Q.; Li, L.; Ma, N.; Tian, J.; Sun, H.; Xu, Q.; Yang, Y.; Li, C. Synthesis of N-Unsubstituted and N3-Substituted.
- Quinazoline-2,4(1H,3H)-diones from o-Aminobenzamides and CO2 at Atmospheric Pressure and Room Temperature. Org. Lett. . Org. Lett.
- 2023, 25, 2471–2475. [CrossRef]
- Marinova PE, Tsoneva SH, Nikolova SA, Ivanov II, Novel complexes of n-substituted-4,5-dimethoxy-phenylethyl-2-arylketoamides with metal ions, Bulg. Chem. Commun., 2019; 51, Special issue D: 8-11.
- Oladipupo, O.E.; Ibukun, D.T.; Olalekan, T.E. Synthesis and Characterization of Mixed Ligand Dinuclear Metal(II) Complexes of Anthranilic Acid and Pyridine-2-aldoxime. Niger. J. Chem. Res. 2018, 23, 39–50. [Google Scholar]
- Alwan, A.H.M. Spectroscopic and Magnetic Study of Mixed Ligand Complexes with Divalent Transition Metals Using Azo-Azomethine Ligands. University of Thi-Qar Journal 2025, 20, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Noor, T.H.; AL-Jeboori, A.T.; Ghanim, F.H. Synthesis and characterization of the mixed ligand complexes (L-alanine and anthranilic acid) with some transition Ions. Diyala Journal For Pure Sciences 2010, 6, 103–110. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





