Submitted:
13 October 2025
Posted:
15 October 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Table of Content
1. Introduction
3. Standard Polymer Micelles
4. An Alternative Kind of Polymer Micelle Nanoparticles
5. Polymer Micelle Nanoparticles that Are Acid-Cleavable and pH Sensitive
6. Micelle Nanoparticles of Cross-Linked Polymers
7. Innovative Approaches to Polymer Micelle Nanotechnology
8. C3M Structure-Property Relationships
8.1. Steady-State Properties
8.2. Morphological Transitions
8.3. Sturdy, Long-Lasting, and Stimuli-Sensitive Pharmaceutical Micelles
8.3.1. Longevity
8.3.1.1. Steric Stabilization
- 8.3.1.1.1. Poly(ethylene glycol)
- 8.3.1.1.2. Substitute Coatings
- 8.3.1.1.2.1. Poly(N-vinylpyrrolidone)
- 8.3.1.1.2.2. Polysaccharides
- 8.3.1.1.2.3. Additional Hydrophilic Blocks
8.3.1.2. The Size of Micellar Particles
8.3.1.3. Additional Methods to Enhance Circulation Times
8.3.1.4. Longevity of Polymeric Micelles with Active Targeting
8.3.2. Stability of Micellar Matter
8.3.2.1. Lowering the CMC
8.3.2.2. Physical Interactions
8.3.2.3. Crosslinking of Covalent Bonds
- 8.3.2.3.1. Crosslinking of Shells
- 8.3.2.3.2. The Crosslinking of Interfaces
- 8.3.2.3.3. Crosslinking at the Core
- 8.3.2.3.4. Cleavable Crosslinks
- 8.3.2.3.5. Crosslinking’s Effects on Drug Release and Loading
8.3.2.4. Drug Compatibility with Micellar Core
8.3.3. Sensitivity to Stimuli
8.3.3.1. Polymeric Micelles with Thermosensitivity
8.3.3.2. Polymeric Micelles with pH-Sensitivity
8.3.3.3. Micellar Disintegration Induced by Chemical Hydrolysis
- 8.3.3.3.1. Chemical Hydrolysis of the Polymeric Framework
- 8.3.3.3.2. Cleavable Side Chains
- 8.3.3.3.3. Breakdown of Polymer-Drug Complexes
8.4.3.3. Polymeric Micelle Destabilization Induced by Enzymes
8.5.3.3. Polymeric Micelles Susceptible to Oxidation and Reduction
8.6.3.3. Micellar Deformation Caused by Light
- 8.6.3.3.1. Irreversible Reactions that Occur on Illumination (Photolysis)
- 8.6.3.3.2. Light-Triggered Reversible Alterations
8.7.3.3. Other Physical Triggers that cause Polymeric Micelles to Become Unstable
8.8.3.3. Multi-Trigger-Responsive Polymeric Micelles
- 8.8.3.3.1. Temperature and pH Sensitivity
- 8.8.3.3.2. Temperature-Sensitive Biodegradable Polymers
- 8.8.3.3.2. Diverse
8.9.3.3. Drug Delivery Guided by Imaging
8.4.3. Combining Stability, Longevity, and Stimulus Sensitivity
9. Self-Assembly, Synthesis and Theory of Block Copolymers (BCP) Solution
9.1. Self Assembly
9.1.1. General Aspects
9.1.2. Morphology of Micellar Structures.
9.1.2.1. Spherical, Cylindrical Micelles and Polymersomes
9.1.2.2. Complex Supramolecular Structures
9.1.3. Alternative Self-Assembly Routes
9.1.3.1. Polymerization-Induced and Electrostatic Self-Assembly
9.2. Synthesis and Theory.
9.2.1. Amphiphilic Block Copolymer (AmBC) Synthesis Using a Mixture of Selective Post-Polymerization Functionalization and Anionic Polymerization
9.2.1.1. Amphiphilic Diblock Copolymers
9.2.1.2. Double Hydrophilic Diblock Copolymers
9.2.2. Theory of Nonionic and Ionic Diblock Copolymer Micelles
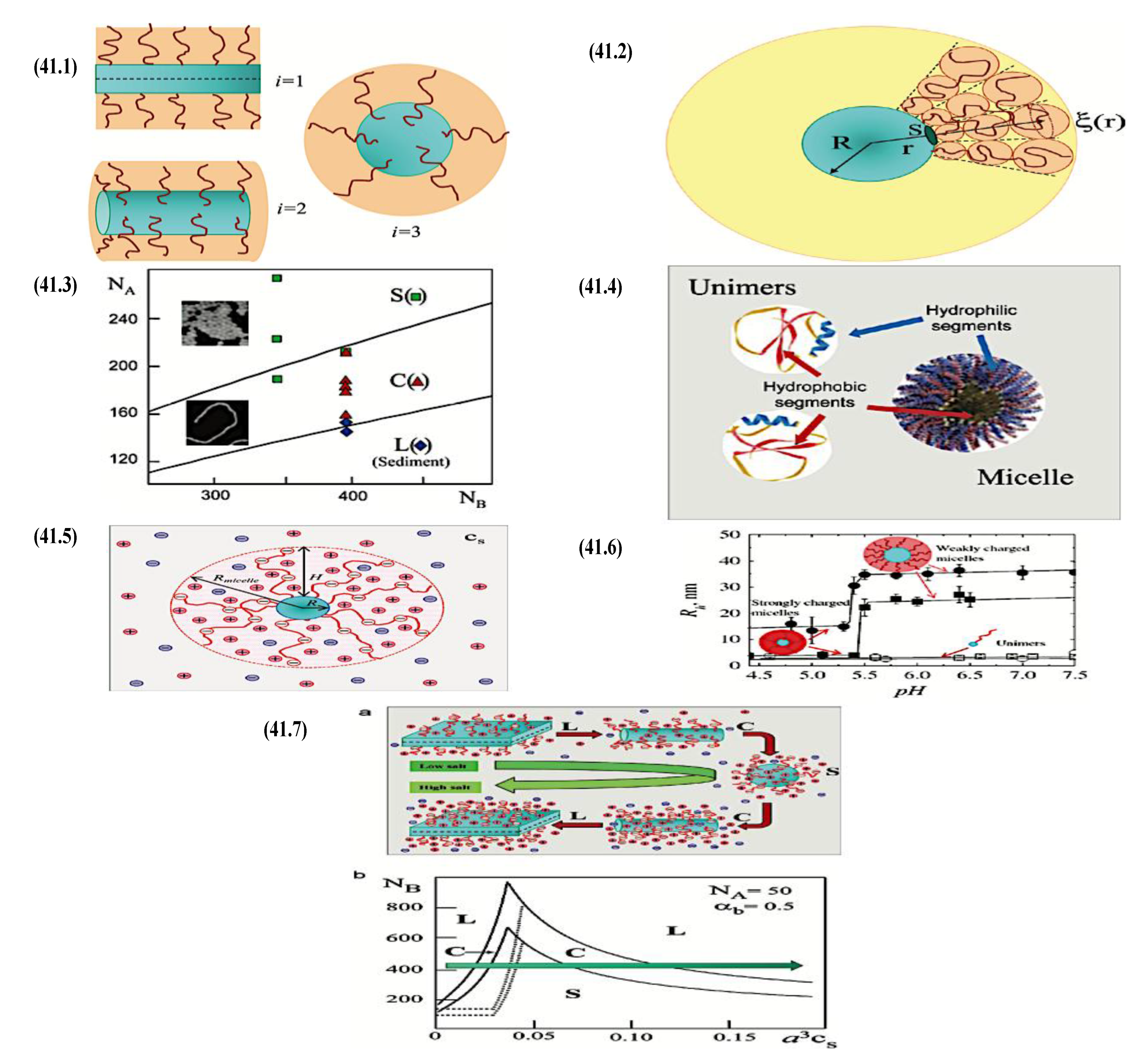
9.2.3. Synthesis of Linear Triblock and Multiblock Copolymers
9.2.3.1. Sequential RAFT and ATRP
9.2.3.2. Sequential AP, AROP and CROP
9.2.3.3. Macroinitiators Available Commercially
9.2.3.4. Combination of Various Methods for Polymerization: To Combine AB and C by Click Reactions
9.2.4. Theory of Triblock Co- and Terpolymer Self-Assembly
9.2.4.1. Soluble C Block ABC Polymers
9.2.4.2. Soluble A and C Blocks in ABC Polymers
9.2.5. Non-Linear Architectures
10. Mechanisms of C3M Formation: Mechanism of Micelle Assembly and Disassembly
10.1. Mechanism of Aggregation: Factors Influencing and Impact of External Factors, Polymer Architecture, the Length of the Core-Forming Block and Charged Functionality’s Structure towards C3M Formation
10.2. Mechanism of Micelle Assembly and Disassembly
11. Kinetics of Micellization and Kinetics of Exchange
11.1. Kinetics of Micellization
11.2. Kinetics of Exchange
11.3. Time-Resolved in situ Polyelectrolyte Complex Micelle Formation Kinetics Uncovered by Small-Angle X-ray Scattering
12. Balance of Micellar Free Energy
13. Complex Coacervate Droplets and Micelles: DNA Dynamics
14. C3M in Dilute Solutions: Interparticle Interactions
15. Methods
15.1. ζ- Potential and Viscosimetry
15.2. Conductometry and Static Light Scattering (SLS)
15.3. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) and Other Methods
16. Applications
16.1. Biomedical Applications
16.1.1. Control of Enzymatic Activity: Optimizing Enzyme Encapsulation Stability and Efficiency in Complicated Coacervate Core Micelles
16.1.2. C3M-Based Biomolecule Delivery
- 16.1.2.1. Nucleic Acid Delivery
16.1.2.2. Brain Delivery
- 16.1.2.2.1. Passing the Brain-Blood Barrier
- 16.1.2.2.2. Potential Applications of C3M in Glioblastoma Treatment.
- 16.1.2.2.2.1. The Importance of Micelle-based Glioblastoma Multiforme (GBM) Therapy Implementation Hindrances
- Due to the CNS’s location of these cells, systemically delivered therapeutic medicines are unable to reach the target malignant tissue without first passing through the BBB. Many therapeutic drugs still do not reach significantly hazardous levels within tumors, despite the existence of a weakened vasculature that may exacerbate the intratumoral EPR impact.[188]
- Necrotic and hypoxic tissue can be found in certain regions of GBM tumors, while neovascularization can be found in other locations. Hypovascularization, fibrosis, and necrotic pockets are the main reasons for reduced intratumoral drug distribution, whereas hypervascularized regions promote accumulation in the surrounding tissue. It's critical to comprehend the distribution of nanoparticles throughout tumors since certain cell populations, such self-renewing GBM cancer stem cells that sustain a tumor, may be restricted to particular vascular habitats.[1435,1436]
- Depending on how it is administered, therapeutic delivery has inherent flaws. Many systemically administered therapeutic drugs produce non-specific organ toxicity and are quickly cleared from circulation by reticuloendothelial cells. Thus, enhancements in the duration of drug circulation and the precision of targeting represent significant advancements for this mode of delivery. The delivery of various dose regimens to a patient and high interstitial pressures that result in poor molecular dispersion limit intratumoral administration of therapeutic medicines.[1437]
- While these clinical micelle formulations improve the potency of the medicine in several solid tumor types, they do not yet have any targeting moieties that could enable increased accumulation in brain tumors or the central nervous system. To increase the effectiveness of currently available formulations, it could be necessary to target alternative receptors expressed on glioma cells molecularly.
- Systemic toxicity may unavoidably be a problem if high dosages of given micelles are required to guarantee sufficient intratumoral accumulation because they lack a controlled-release capability. In order to minimize non-specific release prior to reaching the tumor location, it would be ideal to include stimulus-triggered releasing mechanisms of encapsulated compounds, which would enable release only inside the tumor area.
- 16.1.2.2.2.2. Glioma-Specific Targeting Moieties
- 16.1.2.2.2.3. Therapeutic Micelle Delivery to Brain Tumors
- 16.1.2.3. Drug Delivery
- 16.1.2.3.1. Polymeric Micelles and Vesicles: Their Characteristics
- 16.1.2.3.2. The Building Blocks
- 16.1.2.3.3. Polymeric Micelles: Loading, Retention, and Release of Drugs
- 16.1.2.4. Delivery of Therapeutic Proteins
16.1.3. Diagnostics, Imaging and Theranostics: Combination of Diagnosis and Treatment
16.2. Nanofabrication
16.3. BCP Self-Assembly Applications in Ionic Liquids (ILs)
16.3.1. Soft Actuators
16.3.2. Electrochemical Applications and Devices
16.3.3. Lithium-Ion Batteries
16.3.4. The Electrolyte-Gated Transistors
16.4. Other Applications
17. Micellar Formulations in Clinical Trials
17.1. Genexol-PM and NK105
17.2. SP1049C AND NK911
17.3. NC-6004 AND NC-4016
17.4. NC-6300 and NK102
Conclusion and Perspective
Author Information
Acknowledgments
References
- Mitragotri, S.; Burke, P.; Langer, R. Overcoming the challenges in administering biopharmaceuticals: formulation and delivery strategies. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 655–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muttenthaler, M.; King, G. F.; Adams, D. J.; Alewood, P. F. Trends in peptide drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 309–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, J. A.; Witzigmann, D.; Thomson, S. B.; Chen, S.; Leavitt, B. R.; Cullis, P. R.; van der Meel, R. The current landscape of nucleic acid therapeutics. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2021, 16, 630–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, B. C.; Fletcher, R. B.; Kilchrist, K. V.; Dailing, E. A.; Mukalel, A. J.; Colazo, J. M.; Oliver, M.; Cheung-flynn, J.; Brophy, C. M.; Tierney, J. W.; Isenberg, J. S.; Hankenson, K. D.; Ghimire, K.; Lander, C.; Gersbach, C. A.; Duvall, C. L. An Anionic, Endosome-Escaping Polymer to Potentiate Intracellular Delivery of Cationic Peptides, Biomacromolecules, and Nanoparticles. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, G. Therapeutic insulins and their large-scale manufacture. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2005, 67, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheridan, C. First generic biologics finally approved. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, A. L.; Dhimolea, E.; Reichert, J. M. Development trends for human monoclonal antibody therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, G. Biopharmaceutical benchmarks 2018. Nat. Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 1136–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfram Julie, A.; Donahue, J. K. J. Am. J . Am. Heart Assoc. 2013, 2, e000119. [Google Scholar]
- Lostalé-Seijo, I.; Montenegro, J. Synthetic materials at the forefront of gene delivery. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2018, 2, 258–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainov, N. G. A phase III clinical evaluation of herpes simplex virus type 1 thymidine kinase and ganciclovir gene therapy as an adjuvant to surgical resection and radiation in adults with previously untreated glioblastoma multiforme. Hum. Gene Ther. 2000, 11, 2389–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, W. J. Jr.; Ostrem, J. L.; Verhagen, L.; Starr, P. A.; Larson, P. S.; Bakay, R. A.; Taylor, R.; Cahn-Weiner, D. A.; Stoessl, A. J.; Olanow, C. W.; Bartus, R. T. Safety and tolerability of intraputaminal delivery of CERE-120 (adeno-associated virus serotype 2-neurturin) to patients with idiopathic Parkinson's disease: an open-label, phase I trial. Lancet Neurol. 2008, 7, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartus, R. T.; Baumann, T. L.; Siffert, J.; Herzog, C. D.; Alterman, R.; Boulis, N.; Turner, D. A.; Stacy, M.; Lang, A. E.; Lozano, A. M.; Olanow, C. W. Safety/feasibility of targeting the substantia nigra with AAV2-neurturin in Parkinson patients. Neurology 2013, 80, 1698–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polack, F, P. ; Thomas, S. J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J. L.; P ́erez Marc, G.; Moreira, E. D.; Zerbini, C.; Bailey, R.; Swanson, K. A.; Roychoudhury, S.; Koury, K.; Li, P.; Kalina, W. V.; Cooper, D.; Frenck, R.W.; Hammitt, L. L.; Türeci, ̈ O.; Nell, H.; Schaefer, A.; Ünal, S.; Tresnan, D. B.; Mather, S.; Dormitzer, P. R.; -Sahin, U.; Jansen, K. U.; Gruber, W. C. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2603–2615. [Google Scholar]
- Houseley, J.; Tollervey, D. The many pathways of RNA degradation. Cell 2009, 136, 763–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kisby, T.; Yilmazer, A.; Kostarelos, K. Reasons for success and lessons learnt from nanoscale vaccines against COVID-19. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2021, 16, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crommelin, D. J. A.; Anchordoquy, T. J.; Volkin, D. B.; Jiskoot, W.; Mastrobattista, E. Addressing the Cold Reality of mRNA Vaccine Stability. J Pharm Sci. 2021, 110, 997–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahedifard, F,; Chakravarthy, K. Nanomedicine for COVID-19: the role of nanotechnology in the treatment and diagnosis of COVID-19. Emergent Mater. 2021, 4, 75–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anselmo, A. C.; Mitragotri, S. Nanoparticles in the clinic: An update. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2019, 4, e10143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenton, O. S.; Olafson, K. N.; Pillai, P. S.; Mitchell. M. J.; Langer, R. Advances in Biomaterials for Drug Delivery. Adv Mater. 2018, 30, e1705328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobo, D.; Robinson, K. J.; Islam, J.; Thurecht, K. J.; Corrie, S. R. Nanoparticle-Based Medicines: A Review of FDA-Approved Materials and Clinical Trials to Date. Pharm. Res. 2016, 33, 2373–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Chan, G.; Hu, Y.; Hu, H.; Ouyang, D. A Comprehensive Map of FDA-Approved Pharmaceutical Products. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, K. R.; Maceren, J. P.; Strand, A. I.; He, B.; Overby, C.; Benoit, D. S. W. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 2513–2518. 10.
- Bungenberg de Jong, H. G.; Kruyt, H. R. Coacervation (Partial Miscibility in Colloid Systems). Proc. K. Ned. Akad. Wet. 1929, 32, 849–856. [Google Scholar]
- Hofs, B.; Voets, I. K.; De Keizer, A.; Cohen Stuart, M. A. Comparison of Complex Coacervate Core Micelles from Two Diblock Copolymers or a Single Diblock Copolymer with a Polyelectrolyte. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2006, 8, 4242–4251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, A.; Kataoka, K. Formation of Polyion Complex Micelles in an Aqueous Milieu from a Pair of Oppositely-Charged Block Copolymers with Poly(Ethylene Glycol) Segments. Macromolecules 1995, 28, 5294–5299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voets, I. K.; de Keizer, A.; Cohen Stuart, M. A. Complex Coacervate Core Micelles. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 147–148, 300–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pergushov, D. V.; Müller, A. H. E.; Schacher, F. H. Micellar Interpolyelectrolyte Complexes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 6888–6901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cingil, H. E.; Boz, E. B.; Wang, J.; Cohen Stuart, M. A.; Sprakel, J. Probing Nanoscale Coassembly with Dual Mechanochromic Sensors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 1420–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Burgh, S.; de Keizer, A.; Cohen Stuart, M. A. Complex Coacervation Core Micelles. Colloidal Stability and Aggregation Mechanism. Langmuir 2004, 20, 1073–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Ko, N. R.; Oh, J. K. Recent Advances in Stimuli-Responsive Degradable Block Copolymer Micelles: Synthesis and Controlled Drug Delivery Applications. Chem. Commun. (Camb) 2012, 48, 7542–7552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, C.; Ha, T.-L.; Kim, E.; Jeong, S.W.; Lee, S.G.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, H.-C. Bioreducible Micelles Self-Assembled from Poly(ethylene glycol)-Cholesteryl Conjugate As a Drug Delivery Platform. Polymers 2015, 7, 2245–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Chen, L.; Xiao, C.; Chen, L.; Zhuang, X.; Chen, X. Noncovalent interaction-assisted polymeric micelles for controlled drug delivery. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 11274–11290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.; Kumari, P.; Lakhani, P. M.; Ghosh, B. Recent advances in polymeric micelles for anti-cancer drug delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 83, 184–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, Y.; Fukushima, S.; Harada, A.; Kataoka, K. Design of environment-sensitive supramolecular assemblies for intracellular drug delivery: polymeric micelles that are responsive to intracellular pH change. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2003, 42, 4640–4643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katayose, S.; Kataoka, K. Water-soluble polyion complex associates of DNA and poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(L-lysine) block copolymer. Bioconjug. Chem. 1997, 8, 702–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabral, H.; Miyata, K.; Osada, K.; Kataoka, K. Block Copolymer Micelles in Nanomedicine Applications. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 6844–6892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukerabigwi, J. F.; Ge, Z.; Kataoka, K. Therapeutic nanoreactors as in vivo nanoplatforms for cancer therapy. Chem.-Eur. J. 2018, 24, 15706–15724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facciotti, C.; Saggiomo, V.; Bunschoten, A.; ten Hove, J. B.; Rood, M. T. M.; van Leeuwen, F. W. B.; Velders, A. H. Assembly, Disassembly and Reassembly of Complex Coacervate Core Micelles with Redox-Responsive Supramolecular Cross-Linkers. ChemSystemsChem. 2020, 2, e1900032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orilall, M. C.; Wiesner, U. Block copolymer based composition and morphology control in nanostructured hybrid materials for energy conversion and storage: solar cells, batteries, and fuel cells. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 520–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwars, T.; Paetzold, E.; Oehme, G. Reactions in micellar systems. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2005, 44, 7174–7199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortensen, K. PEO-related block copolymer surfactants oids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2001, 183-185, 277-292.
- Kataoka K, Harada A, Nagasaki Y. Block copolymer micelles for drug delivery: design, characterization and biological significance. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 47, 113–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCullagh, M.; Prytkova, T.; Tonzani, S.; Winter, N. D.; Schatz, G. C. Modeling Self-Assembly Processes Driven by Nonbonded Interactions in Soft Materials. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 10388–10398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haliloglu, T.; Bahar, I.; Erman, B.; Mattice, W. L. Mechanisms of the Exchange of Diblock Copolymers between Micelles at Dynamic Equilibrium. Macromolecules 1996, 29, 4764–4771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Mattice, W. L.; Napper, D. H. Simulation of the Formation of Micelles by Diblock Copolymers under Weak Segregation. Langmuir 1993, 9, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gennes, P. G. Scaling theory of polymer adsorption. J. Phys. (Paris) 1976, 37, 1445–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gennes, P. G. Conformation of Polymers Attached to an Interface. Macromolecules 1980, 13, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halperin, A. Polymeric Micelles: A Star Model. Macromolecules 1987, 20, 2943–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noolandi, J.; Hong, K. M. Theory of Block Copolymer Micelles in Solution. Macromolecules 1983, 16, 1443–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibler, L.; Orland, H.; Wheeler, J. C. Theory of critical micelle concentration for solutions of block copolymers. J. Chem. Phys. 1983, 79, 3550–3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pépin, M. P.; Whitmore, M. D. Monte Carlo and Mean Field Study of Diblock Copolymer Micelles. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 8644–8653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantu, L.; Corti, M.; Salina, P. Direct measurement of the formation time of mixed micelles. J. Phys. Chem. 1991, 95, 5981–5983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, Y.-Y.; Davis, H. T.; Bates, F. S. Molecular Exchange in PEO-PB Micelles in Water. Macromolecules 2003, 36, 953–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, R.; Willner, L.; Richter, D.; Dormidontova, E. E. Equilibrium Chain Exchange Kinetics of Diblock Copolymer Micelles: Tuning and Logarithmic Relaxation. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 4566–4575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sing, C. E.; Perry, S. L. Recent progress in the science of complex coacervation. Soft Matter 2020, 16, 2885–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Schlenoff, J. B. Driving Forces for Oppositely Charged Polyion Association in Aqueous Solutions: Enthalpic, Entropic, but Not Electrostatic. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 980–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marras, A. E.; Ting, J. M.; Stevens, K. C.; Tirrell, M. V. Advances in the Structural Design of Polyelectrolyte Complex Micelles. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2021, 125, 7076–7089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumyantsev, A. M.; Zhulina, E. B.; Borisov, O.V. ; Zhulina, E. B.; Borisov O.V. Scaling Theory of Complex Coacervate Core Micelles. ACS Macro Lett. 2018, 7, 7–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sproncken, C. C. M.; Magana, J. R.; Voets, I. K. 100th Anniversary of Macromolecular Science Viewpoint: Attractive Soft Matter: Association Kinetics, Dynamics, and Pathway Complexity in Electrostatically Coassembled Micelles. ACS Macro Lett. 2021, 10, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magana, J. R.; Sproncken, C. C. M.; Voets, I. K. On Complex Coacervate Core Micelles: Structure-Function Perspectives. Polymers (Basel) 2020, 12, 1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riggleman, R. A.; Kumar, R.; Fredrickson, G. H. Investigation of the interfacial tension of complex coacervates using field-theoretic simulations. J. Chem. Phys. 2012, 136, 024903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabanov, A. V.; Bronich, T. K.; Kabanov, V. A.; Yu, K.; Eisenberg, A. Soluble stoichiometric complexes from poly(N-ethyl-4- vinylpyridinium) cations and poly(ethylene oxide)-block-polymetha- crylate anions. Macromolecules 1996, 29, 6797–6802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; de Keizer, A.; Cohen Stuart, M. A.; Drechsler, M.; Besseling, N. A. M. Stability of complex coacervate core micelles containing metal coordination polymer. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 10908–10914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; de Keizer, A.; Fokkink, R.; Yan, Y.; Cohen Stuart, M. A.; van der Gucht, J. Complex coacervate core micelles from iron-based coordination polymers. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 8313–8319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaucher, G.; Dufresne, M.-H.; Sant, V. P.; Kang, N.; Maysinger, D.; Leroux, J.-C. Block copolymer micelles: preparation, characterization and application in drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2005, 109, 169–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramarenko, E.Y.; Khokhlov, A.R.; Reineker, P. Stoichiometric polyelectrolyte complexes of ionic block copolymers and oppositely charged polyions. J. Chem. Phys. 2006, 125, 194902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Wang, B.; Liu, X.; An, Y.; Li, Y.; He, Z.; Shi, L. Pyranine- induced micellization of poly(ethylene glycol)-block-poly(4-vinyl- pyridine) and pH-triggered release of pyranine from the complex micelles. Langmuir 2007, 23, 7498–7504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemmers, M.; Voets, I. K.; Cohen Stuart, M. A.; van der Gucht, J. Transient network topology of interconnected polyelectrolyte complex micelles. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 1378–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, A.; Kataoka, K. Formation of stable and monodispersive polyion complex micelles in aqueous medium from poly(L-lysine) and poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(aspartic acid) block copolymer. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A. 1997, 34, 2119–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dautzenberg, H.; Rother, G. Response of polyelectrolyte complexes to subsequent addition of sodium chloride: time-dependent static light scattering studies. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2004, 205, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matralis, A.; Sotiropoulou, M.; Bokias, G.; Staikos, G. Water- soluble stoichiometric polyelectrolyte complexes based on cationic comb-type copolymers. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2006, 207, 1018–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-S.; Akiyama, Y.; Yamasaki, Y.; Kataoka, K. Preparation and characterization of polyion complex micelles with a novel thermosensitive poly(2-isopropyl-2-oxazoline) shell via the complexation of oppositely charged block ionomers. Langmuir 2007, 23, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pispas, S. Complexes of polyelectrolyte-neutral double hydrophilic block copolymers with oppositely charged surfactant and polyelectrolyte. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 8351–8359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindhoud, S.; Voorhaar, L.; de Vries, R.; Schweins, R.; Cohen Stuart, M. A.; Norde, W. Salt-induced disintegration of lysozyme- containing polyelectrolyte complex micelles. Langmuir 2009, 25, 11425–11430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soliman, G. M. Polysaccharide-Based Polyion Complex Micelles as New Delivery Systems for Hydrophilic Cationic Drugs. Ph.D. thesis, Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Montreal, 09; pp 1-258. 20 August.
- Brzozowska, A.; Zhang, Q.; de Keizer, A.; Norde, W.; Cohen Stuart, M. Reduction of protein adsorption on silica and polysulfone surfaces coated with complex coacervate core micelles with poly(vinyl alcohol) as a neutral brush forming block. Colloids Surf. A 2010, 368, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzozowska, A.; de Keizer, A.; Christophe, D.; Cohen Stuart, M. A.; Norde, W. Grafted ionomer complexes and their effect on protein adsorption on silica and polysulfone surfaces. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2010, 288, 1621–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danial, M.; Klok, H.-A.; Norde, W.; Cohen Stuart, M. A. Complex coacervate core micelles with a lysozyme-modified corona. Langmuir 2007, 23, 8003–8009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindhoud, S.; de Vries, R.; Schweins, R.; Cohen Stuart, M. A.; Norde, W. Salt-induced release of lipase from polyelectrolyte complex micelles. Soft Matter 2009, 5, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overbeek, J. T.; Voorn, M. J. Phase separation in polyelectrolyte solutions; theory of complex coacervation. J. Cell Physiol. Suppl. 1957, 49 (Suppl. 1), 7–22; discussion, 22-26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, J. N.; Feldman, K. E.; Lynd, N. A.; Deek, J.; Campos, L. M.; Spruell, J. M.; Hernandez, B. M.; Kramer, E. J.; Hawker, C. J. Tunable, high modulus hydrogels driven by ionic coacervation. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 2327–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capito, R. M.; Azevedo, H. S.; Velichko, Y. S.; Mata, A.; Stupp, S. I. Self-assembly of large and small molecules into hierarchically ordered sacs and membranes. Science 2008, 319, 1812–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakizawa, Y.; Kataoka, K. Block copolymer micelles for delivery of gene and related compounds. Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 2002, 54, 203–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, A.; Kataoka, K. Supramolecular assemblies of block copolymers in aqueous media as nanocontainers relevant to biological applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2006, 31, 949–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holappa, S.; Kantonen, L.; Andersson, T.; Winnik, F.; Tenhu, H. Overcharging of polyelectrolyte complexes by the guest polyelectrolyte studied by fluorescence spectroscopy. Langmuir 2005, 21, 11431–11438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolles, A.; Hooiveld, E.; Westphal, A. H.; van Berkel, W. J.; Kleijn, J. M.; Borst, J. W. FRET Reveals the Formation and Exchange Dynamics of Protein-Containing Complex Coacervate Core Micelles. Langmuir 2018, 34, 12083–12092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amann, M.; Diget, J. S.; Lyngsø, J.; Pedersen, J. S.; Narayanan, T.; Lund, R. Kinetic Pathways for Polyelectrolyte Coacervate Micelle Formation Revealed by Time-Resolved Synchrotron SAXS. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 8227–8237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, I.; Sprakel, J. Langevin Dynamics Simulations of the Exchange of Complex Coacervate Core Micelles: The Role of Nonelectrostatic Attraction and Polyelectrolyte Length. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 8923–8931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Ting, J. M.; Tirrell, M. V. Mechanism of Dissociation Kinetics in Polyelectrolyte Complex Micelles. Macromolecules 2020, 53, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berret, J.-F.; Cristobal, G.; Herve,́ P. ; Oberdisse, J.; Grillo, I. Structure of colloidal complexes obtained from neutral/polyelectrolyte copolymers and oppositely charged surfactants. Eur. Phys. J. E Soft Matter 2002, 9, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Ting, J. M.; Werba, O.; Meng, S.; Tirrell, M. V. Non- equilibrium phenomena and kinetic pathways in self-assembled polyelectrolyte complexes. J. Chem. Phys. 2018, 149, 163330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofs, B.; De Keizer, A.; Cohen Stuart, M. A. On the stability of (highly aggregated) polyelectrolyte complexes containing a charged- block-neutral diblock copolymer. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 5621–5627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindhoud, S.; Norde, W.; Cohen Stuart, M. A. Reversibility and relaxation behavior of polyelectrolyte complex micelle formation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 5431–5439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, I.; Terenzi, C.; Sprakel, J. Chemical Feedback in Templated Reaction-Assembly Networks. Macromolecules 2020, 53, 10675–10685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dormidontova, E. E. Micellization kinetics in block copolymer solutions: Scaling model. Macromolecules 1999, 32, 7630–7644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, R.; Willner, L.; Stellbrink, J.; Lindner, P.; Richter, D. Logarithmic chain-exchange kinetics of diblock copolymer micelles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 96, 068302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-H.; Lodge, T. P.; Bates, F. S. Mechanism of molecular exchange in diblock copolymer micelles: hypersensitivity to core chain length. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 104, 047802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinn, T.; Willner, L.; Lund, R.; Pipich, V.; Richter, D. Equilibrium exchange kinetics in n-alkyl-PEO polymeric micelles: single exponential relaxation and chain length dependence. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 623–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Choi, S.; Bates, F.; Lodge, T. Molecular exchange in diblock copolymer micelles: bimodal distribution in core-block molecular weights. ACS Macro Lett. 2012, 1, 982–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Bates, F.; Lodge, T. Chain exchange in binary copolymer micelles at equilibrium: confirmation of the independent chain hypothesis. ACS Macro Lett. 2013, 2, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.; Lu, J.; Bates, F. S.; Lodge, T. P. Effect of corona block length on the structure and chain exchange kinetics of block copolymer micelles. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 3563–3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, I.; Timmerman, M.; Sprakel, J. FRET-Based Determination of the Exchange Dynamics of Complex Coacervate Core Micelles. Macromolecules 2021, 54, 398–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semenov. A. N. Contribution to the theory of microphase layering in block-copolymer melts. Sov. Phys. JETP 1985, 61, 733–742. [Google Scholar]
- Borisov, O. V.; Zhulina, E. B.; Leermakers, F. A. M.; Müller, A. H. E. Self-Assembled Structures of Amphiphilic Ionic Block Copolymers: Theory, Self-Consistent Field Modeling and Experiment. Adv. Polym. Sci. 2011, 241, 57–129. [Google Scholar]
- van der Kooij, H. M.; Spruijt, E.; Voets, I. K.; Fokkink, R.; Cohen Stuart, M. A.; van der Gucht, J. . On the Stability and Morphology of Complex Coacervate Core Micelles: From Spherical to Wormlike Micelles Langmuir 2012, 28 (40), 14180-14191.
- Lueckheide, M. , Vieregg, J. R.; Bologna, A. J.; Leon, L.; Tirrell, M. V. Structure-property relationships of oligonucleotide polyelectrolyte complex micelles. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 7111–7117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakata, M.; Zanchetta, G.; Chapman, B. D.; Jones, C. D.; Cross, J. O.; Pindak, R.; Bellini, T.; Clark, N. A. End-to-end stacking and liquid crystal condensation of 6 to 20 base pair DNA duplexes. Science 2007, 318, 1276–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumyantsev A., M. , de Pablo J. J., Liquid crystalline and isotropic coacervates of semiflexible polyanions and flexible polycations. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 5140–5156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloi, A.; Guibert, C.; Olijve, L. L. C.; Voets, I. K. Morphological Evolution of Complex Coacervate Core Micelles Revealed by iPAINT Microscopy. Polymer 2016, 107, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakya, A.; Girard, M.; King, J. T.; De La Cruz, M. O. Role of Chain Flexibility in Asymmetric Polyelectrolyte Complexation in Salt Solutions. Macromolecules 2020, 53, 1258–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blocher McTigue, W. C.; Perry, S. L. Protein Encapsulation Using Complex Coacervates: What Nature Has to Teach Us. Small 2020, 16, e1907671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, A.; Kataoka, K. Polyion Complex Micelle Formation from Double-Hydrophilic Block Copolymers Composed of Charged and Non-Charged Segments in Aqueous Media. Polym. J. 2018, 50, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, P.S. Complex Coacervate-Based Materials for Biomedicine: Recent Advancements and Future Prospects. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2024, 63, 5414–5487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, J. M.; Kapelner, R. A.; Obermeyer, A. C. Macro- and Microphase Separated Protein-Polyelectrolyte Complexes: Design Parameters and Current Progress. Polymers (Basel, Switz.) 2019, 11, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Stenzel, M. H. Polyion Complex Micelles for Protein Delivery. Aust. J. Chem. 2018, 71, 768–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Batys, P.; O’Neal, J. T.; Li, F.; Sammalkorpi, M.; Lutkenhaus, J. L. Molecular Origin of the Glass Transition in Polyelectrolyte Assemblies. ACS Cent. Sci. 2018, 4, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gineste, S.; Di Cola, E.; Amouroux, B.; Till, U.; Marty, J.-D.; Mingotaud, A.-F.; Mingotaud, C.; Violleau, F.; Berti, D.; Parigi, G.; Luchinat, C.; Balor, S.; Sztucki, M.; Lonetti, B. Mechanistic Insights into Polyion Complex Associations. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 1427–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathee, V. S.; Sidky, H.; Sikora, B. J.; Whitmer, J. K. Role of Associative Charging in the Entropy-Energy Balance of Polyelectrolyte Complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 15319–15328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, P. S.; Samanta, A.; Mukherjee, M.; Roy, B.; Mukherjee, A. Designing Novel pH-Induced Chitosan-Gum Odina Complex Coacervates for Colon Targeting. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 15728–15745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takemoto, H.; Miyata, K.; Hattori, S.; Ishii, T.; Suma, T.; Uchida, S.; Nishiyama, N.; Kataoka, K. Acidic PH-Responsive SiRNA Conjugate for Reversible Carrier Stability and Accelerated Endosomal Escape with Reduced IFNα-Associated Immune Response. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 6218–6221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Gucht, J.; Spruijt, E.; Lemmers, M.; Cohen Stuart, M. A. Polyelectrolyte Complexes: Bulk Phases and Colloidal Systems. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 361, 407–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stapert, H. R.; Nishiyama, N.; Jiang, D. L.; Aida, T.; Kataoka, K. Polyion Complex Micelles Encapsulating Light-Harvesting Ionic Dendrimer Zinc Porphyrins. Langmuir 2000, 16, 8182–8188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadman, K.; Wang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Keshavarz, B.; Jiang, Z.; Shull, K. R. Influence of Hydrophobicity on Polyelectrolyte Complexation. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 9417–9426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Kruif, C. G.; Weinbreck, F.; De Vries, R. Complex Coacervation of Proteins and Anionic Polysaccharides. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 9, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, C. E.; Obermeyer, A.; Dong, X.; Walker, J.; Olsen, B. D. Complex Coacervate Core Micelles for the Dispersion and Stabilization of Organophosphate Hydrolase in Organic Solvents. Langmuir 2016, 32, 13367–13376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, H.; Zhou, J.; Pan, W.; Li, Z.; Liang, D. Assembly and Reassembly of Polyelectrolyte Complex Formed by Poly(Ethylene Glycol)-Block-Poly(Glutamate Sodium) and S5R4 Peptide. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 4627–4633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Chang, H.; Cheng, Y. Surface-Engineered Dendrimers in Gene Delivery. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 5274–5300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.; Shi, L.; Zhang, W.; An, Y.; Zhu, X.-X.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z. Formation of Hybrid Micelles between Poly(Ethylene Glycol)-Block- Poly(4-Vinylpyridinium) Cations and Sulfate Anions in an Aqueous Milieu. Soft Matter 2005, 1, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanson, N.; Bouyer, F.; Destarac, M.; In, M.; Gérardin, C. Hybrid Polyion Complex Micelles Formed from Double Hydrophilic Block Copolymers and Multivalent Metal Ions: Size Control and Nanostructure. Langmuir 2012, 28, 3773–3782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carl, N.; Prévost, S.; Schweins, R.; Houston, J. E.; Morfin, I.; Huber, K. Invertible Micelles Based on Ion-Specific Interactions of Sr2+ and Ba2+ with Double Anionic Block Copolyelectrolytes. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 8759–8770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facciotti, C.; Saggiomo, V.; van Hurne, S.; Bunschoten, A.; Kaup, R.; Velders, A. H. Oxidant-Responsive Ferrocene-Based Cyclodextrin Complex Coacervate Core Micelles. Supramol. Chem. 2020, 32, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.; Dell, E. J.; Freyer, J. L.; Campos, L. M.; Jang, W. D. Polymeric Supramolecular Assemblies Based on Multivalent Ionic Interactions for Biomedical Applications. Polymer 2014, 55, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Holkar, A.; Srivastava, S. Protein-Polyelectrolyte Complexes and Micellar Assemblies. Polymers (Basel, Switz.) 2019, 11, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A. E.; Sizovs, A.; Grandinetti, G.; Xue, L.; Reineke, T. M. Diblock Glycopolymers Promote Colloidal Stability of Polyplexes and Effective PDNA and siRNA Delivery under Physiological Salt and Serum Conditions. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 3015–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Zha, Y.; Feng, B.; Pang, Z.; Zhang, B.; Sun, X.; Ren, J.; Zhang, C.; Shao, X.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, X. PEGylated Poly(2- (Dimethylamino) Ethyl Methacrylate)/DNA Polyplex Micelles Decorated with Phage-Displayed TGN Peptide for Brain-Targeted Gene Delivery. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 2117–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Karls, L.; Lodge, T. P.; Reineke, T. M. Polycation Architecture and Assembly Direct Successful Gene Delivery: Micelleplexes Outperform Polyplexes via Optimal DNA Packaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 15804–15817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Santis, S.; Diociaiuti, M.; Cametti, C.; Masci, G. Hyaluronic Acid and Alginate Covalent Nanogels by Template Cross-Linking in Polyion Complex Micelle Nanoreactors. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 101, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, E.; Lee, S. H.; Lee, S.; Choi, S. H.; Hawker, C. J.; Kim, B. S. Highly Stable Au Nanoparticles with Double Hydrophilic Block Copolymer Templates: Correlation Between Structure and Stability. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 4528–4537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogstad, D. V.; Choi, S. H.; Lynd, N. A.; Audus, D. J.; Perry, S. L.; Gopez, J. D.; Hawker, C. J.; Kramer, E. J.; Tirrell, M. V. Small Angle Neutron Scattering Study of Complex Coacervate Micelles and Hydrogels Formed from Ionic Diblock and Triblock Copolymers. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 13011–13018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortony, J. H.; Choi, S. H.; Spruell, J. M.; Hunt, J. N.; Lynd, N. A.; Krogstad, D. V.; Urban, V. S.; Hawker, C. J.; Kramer, E. J.; Han, S. Fluidity and Water in Nanoscale Domains Define Coacervate Hydrogels. Chem. Sci. 2014, 5, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Fares, H. M.; Schlenoff, J. B. Ion-Pairing Strength in Polyelectrolyte Complexes. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 1066–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cingil, H. E.; Meertens, N. C. H.; Voets, I. K. Temporally Programmed Disassembly and Reassembly of C3Ms. Small 2018, 14, e1802089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Gao, H.; Liu, G.; Ma, R.; An, Y.; Kong, D.; Shi, L. pH/Sugar Dual Responsive Core-Cross-Linked PIC Micelles for Enhanced Intracellular Protein Delivery. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 3434–3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen Stuart, M. A.; Besseling, N. A. M.; Fokkink, R. G. Formation of Micelles with Complex Coacervate Cores. Langmuir 1998, 14, 6846–6849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voets, I. K.; De Vries, R.; Fokkink, R.; Sprakel, J.; May, R. P.; De Keizer, A.; Cohen Stuart, M. A. Towards a Structural Characterization of Charge-Driven Polymer Micelles. Eur. Phys. J. E: Soft Matter Biol. Phys. 2009, 30, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fresnais, J.; Lavelle, C.; Berret, J. F. Nanoparticle Aggregation Controlled by Desalting Kinetics. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 16371–16379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Fresnais, J.; Berret, J. F.; Castaing, J. C.; Destremaut, F.; Salmon, J. B.; Cousin, F.; Chapel, J. P. Influence of the Formulation Process in Electrostatic Assembly of Nanoparticles and Macromolecules in Aqueous Solution: The Interaction Pathway. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 16373–16381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Fresnais, J.; Berret, J. F.; Castaing, J. C.; Grillo, I.; Chapel, J. P. Influence of the Formulation Process in Electrostatic Assembly of Nanoparticles and Macromolecules in Aqueous Solution: The Mixing Pathway. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 12870–12877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blocher McTigue, W. C.; Voke, E.; Chang, L.-W.; Perry, S. L. The Benefit of Poor Mixing: Kinetics of Coacervation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 20643–20657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voets, I. K. Electrostatically Driven Assembly of Polyelectrolytes. In: Fluorescence Studies of Polymer Containing Systems; Procházka, K., Ed.; Springer Series on Fluorescence, Springer International Publishing, Cham, 2016; Vol 16, pp 65-89. [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.; Zheng, M.; Tao, W.; Chung, R.; Jin, D.; Ghaffari, D.; Farokhzad, O. C. Challenges in DNA Delivery and Recent Advances in Multifunctional Polymeric DNA Delivery Systems. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 2231–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, S.; Kataoka, K. Design concepts of polyplex micelles for in vivo therapeutic delivery of plasmid DNA and messenger RNA. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A. 2019, 107, 978–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka K, Harada A, Nagasaki Y: Block copolymer micelles for drug delivery: design, characterization and biological significance. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 37–48. [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, C.; Brohlin, O.; Shahrivarkevishahi, A.; Gassensmith, J. J. Virus like Particles: Fundamental Concepts, Biological Interactions, and Clinical Applications. Chung E. J., Leon L., Rinaldi C., Eds.; Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications; Elsevier Publishing: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Chapter 11, pp. 153-174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tockary, T. A.; Osada, K.; Chen, Q.; Machitani, K.; Dirisala, A.; Uchida, S.; Nomoto, T.; Toh, K.; Matsumoto, Y.; Itaka, K.; Nitta, K.; Nagayama, K.; Kataoka, K. Tethered Peg Crowdedness Determining Shape and Blood Circulation Profile of Polyplex Micelle Gene Carriers. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 6585–6592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanazawa, T.; Sugawara, K.; Tanaka, K.; Horiuchi, S.; Takashima, Y.; Okada, H. Suppression of tumor growth by systemic delivery of anti-VEGF siRNA with cell-penetrating peptide-modified MPEG-PCL nanomicelles. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 81, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J. H.; Kim, S. W.; Park, T. G. A new antisense oligonucleotide delivery system based on self-assembled ODN-PEG hybrid conjugate micelles. J. Control Release 2003, 93, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindhoud, S.; de Vries, R.; Norde, W.; Cohen Stuart, M. A. Structure and stability of complex coacervate core micelles with lysozyme. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 2219–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oishi, M.; Nagasaki, Y.; Itaka, K.; Nishiyama, N.; Kataoka, K. Lactosylated poly(ethylene glycol)-siRNA conjugate through acid- labile β-thiopropionate linkage to construct pH-sensitive polyion complex micelles achieving enhanced gene silencing in hepatoma cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 1624–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Ishii, T.; Kim, H. J.; Nishiyama, N.; Hayakawa, Y.; Itaka, K.; Kataoka, K. Efficient delivery of bioactive antibodies into the cytoplasm of living cells by charge-conversional polyion complex micelles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2010, 49, 2552–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, W.-D.; Nakagishi, Y.; Nishiyama, N.; Kawauchi, S.; Morimoto, Y.; Kikuchi, M.; Kataoka, K. Polyion complex micelles for photodynamic therapy: incorporation of dendritic photosensitizer excitable at long wavelength relevant to improved tissue-penetrating property. J. Controlled Release 2006, 113, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Besseling, N. A. M.; de Keizer, A.; Marcelis, A.; Drechsler, M.; Cohen Stuart, M. A. Hierarchical self-assembly in solutions containing metal ions, ligand, and diblock copolymer. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2007, 46, 1807–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, S.; Dragan, S. Nonstoichiometric interpolyelectrolyte complexes as colloidal dispersions based on NaPAMPS and their interaction with colloidal silica particles. Macromol. Symp. 2004, 210, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Burgh, S.; Fokkink, R.; de Keizer, A.; Cohen Stuart, M. A. Complex coacervation core micelles as anti-fouling agents on silica and polystyrene surfaces. Colloids Surf. A 2004, 242, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzozowska, A.; Hofs, B.; de Keizer, A.; Fokkink, R.; Cohen Stuart, M.; Norde, W. Reduction of protein adsorption on silica and polystyrene surfaces due to coating with complex coacervate core micelles. Colloids Surf. A 2009, 347, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinkle, S.; McNeil, S. E.; Mühlebach, S.; Bawa, R.; Borchard, G.; Barenholz, Y. C.; Tamarkin, L.; Desai, N. Nanomedicines: addressing the scientific and regulatory gap. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2014, 1313, 35–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmento, B. Have nanomedicines progressed as much as we'd hoped for in drug discovery and development? Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2019, 14, 723–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krukemeyer, M. G.; Krenn, V.; Huebner, F.; Wagner, W.; Resch, R. History and Possible Uses of Nanomedicine Based on Nanoparticles and Nanotechnological Progress. J. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 1000336. [Google Scholar]
- Decuzzi, P.; Peer, D.; Mascolo, D. D.; Palange, A. L.; Manghnani, P. N.; Moghimi, S. M.; Farhangrazi, Z. S.; Howard, K. A.; Rosenblum, D.; Liang, T.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, J. J.; Gu, Z.; Korin, N.; Letourneur, D.; Chauvierre, C.; van der Meel, R.; Kiessling, F.; Lammers, T. Roadmap on nanomedicine. Nanotechnology 2021, 32, 012001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicha, I.; Chauvierre, C.; Texier, I.; Cabella, C.; Metselaar, J. M.; Szebeni, J.; Dézsi, L.; Alexiou, C.; Rouzet, F.; Storm, G.; Stroes, E.; Bruce, D.; MacRitchie, N.; Maffia, P.; Letourneur, D. From design to the clinic: practical guidelines for translating cardiovascular nanomedicine. Cardiovasc Res. 2018, 114, 1714–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Shi, Y.; Qi, T.; Qiu, S.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Sun, Q.; Lin, G. Precise design strategies of nanomedicine for improving cancer therapeutic efficacy using subcellular targeting. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020, 5, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhise, K.; Sau, S.; Alsaab, H.; Kashaw, S. K.; Tekade, R. K.; Iyer, A. K. Nanomedicine for cancer diagnosis and therapy: advancement, success and structure-activity relationship. Ther. Deliv. 2017, 8, 1003–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macchione, M. A.; Aristizabal Bedoya, D.; Figueroa, F. N.; Munoz-Fernandez, M. A.; Strumia, M. C. Nanosystems applied to HIV infection: Prevention and treatments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binda, A.; Murano, C.; Rivolta, I. Innovative Therapies and Nanomedicine Applications for the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease: A State-of-the-Art (2017-2020). Int. J. Nanomedicine 2020, 15, 6113–6135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Khang, D. Past, Present, and Future of Anticancer Nanomedicine. Int. J. Nanomedicine. 2020, 15, 5719–5743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desland, F. A.; Hormigo, A. The CNS and the Brain Tumor Microenvironment: Implications for Glioblastoma Immunotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H. S.; Muresanu, D. F.; Castellani, R. J.; Nozari, A.; Lafuente, J. V.; Tian, Z. R.; Sahib, S.; Bryukhovetskiy, I.; Bryukhovetskiy, A.; Buzoianu, A. D.; Patnaik, R; Wiklund, L. ; Sharma, A. Pathophysiology of blood-brain barrier in brain tumor. Novel therapeutic advances using nanomedicine. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2020, 151, 1–66. [Google Scholar]
- Maher, E. A.; Furnari, F. B.; Bachoo, R. M.; Rowitch, D. H.; Louis, D. N.; Cavenee, W. K.; DePinho, R. A. Malignant glioma: genetics and biology of a grave matter. Genes Dev. 2001, 15, 1311–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stupp, R. , Hegi, M. E., Mason, W. P., van den Bent, M. J., Taphoorn, M. JB., Janzer, R. C., Ludwin, S. K., Allgeier, A., Fisher, B., Belanger, K., Hau, P., Brandes, A. A., Gijtenbeek, J., Marosi, C., Vecht, C. J., Mokhtari, K., Wesseling, P., Villa, S., Eisenhauer, E., Gorlia, T.; Weller, M.; Lacombe, D.; Gregory Cairncross, J.; Mirimanoff, R. O. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 459–466. [Google Scholar]
- Hau, P.; Fabel, K.; Baumgart, U.; Rümmele, P.; Grauer, O.; Bock, A.; Dietmaier, C.; Dietmaier, W.; Dietrich, J.; Dudel, C.; Hübner, F.; Jauch, T.; Drechsel, E.; Kleiter, I.; Wismeth, C.; Zellner, A.; Brawanski, A.; Steinbrecher, A.; Marienhagen, J.; Bogdahn, U. Pegylated liposomal doxorubicin-efficacy in patients with recurrent high-grade glioma. Cancer 2004, 100, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, H. S.; Prados, M. D.; Wen, P. Y.; Mikkelsen, T.; Schiff, D.; Abrey, L. E.; Yung, W. K.; Paleologos, N.; Nicholas, M. K.; Jensen, R.; Vredenburgh, J.; Huang, J.; Zheng, M.; Cloughesy, T. Bevacizumab alone and in combination with irinotecan in recurrent glioblastoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 4733–4740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westphal, M.; Ylä-Herttuala, S.; Martin, J.; Warnke, P.; Menei, P.; Eckland, D.; Kinley, J.; Kay, R.; Ram, Z.; ASPECT Study Group. Adenovirus-mediated gene therapy with sitimagene ceradenovec followed by intravenous ganciclovir for patients with operable high-grade glioma (ASPECT): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zustovich, F.; Landi, L.; Lombardi, G.; Porta, C.; Galli, L.; Fontana, A.; Amoroso, D.; Galli, C.; Andreuccetti, M.; Falcone, A.; Zagonel, V. Sorafenib plus daily low-dose temozolomide for relapsed glioblastoma: a phase II study. Anticancer Res. 2013, 33, 3487–3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunwar, S.; Chang, S.; Westphal, M.; Vogelbaum, M.; Sampson, J.; Barnett, G.; Shaffrey, M.; Ram, Z.; Piepmeier, J.; Prados, M.; Croteau, D.; Pedain, C.; Leland, P.; Husain, S. R.; Joshi, B. H.; Puri, R. K.; PRECISE Study Group. Phase III randomized trial of CED of IL13-PE38QQR vs Gliadel wafers for recurrent glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 2010, 12, 871–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, E.; Bienemann, A.; Taylor, H.; Hopkins, K.; Cameron, A.; Gill, S. A phase I trial of carboplatin administered by convection-enhanced delivery to patients with recurrent/progressive glioblastoma multiforme. Contemp. Clin. Trials 2012, 33, 320–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S. B.; Amiji, M. M. A review of nanocarrier-based CNS delivery systems. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2006, 3, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.; Nakamura, H.; Maeda, H. The EPR effect: Unique features of tumor blood vessels for drug delivery, factors involved, and limitations and augmentation of the effect. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 136–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caraglia, M.; Addeo, R.; Costanzo, R.; Montella, L.; Faiola, V.; Marra, M.; Abbruzzese, A.; Palmieri, G.; Budillon, A.; Grillone, F.; Venuta, S.; Tagliaferri, P.; Del Prete, S. Phase II study of temozolomide plus pegylated liposomal doxorubicin in the treatment of brain metastases from solid tumours. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2006, 57, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beier, C. P.; Schmid, C.; Gorlia, T.; Kleinletzenberger, C.; Beier, D.; Grauer, O.; Steinbrecher, A.; Hirschmann, B.; Brawanski, A.; Dietmaier, C.; Jauch-Worley, T.; Kölbl, O.; Pietsch, T.; Proescholdt, M.; Rümmele, P.; Muigg, A.; Stockhammer, G.; Hegi, M.; Bogdahn, U.; Hau, P. RNOP-09: pegylated liposomal doxorubicine and prolonged temozolomide in addition to radiotherapy in newly diagnosed glioblastoma-a phase II study. BMC Cancer 2009, 9, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Northfelt, D. W.; Dezube, B. J.; Thommes, J. A.; Miller, B. J.; Fischl, M. A.; Friedman-Kien, A.; Kaplan, L. D.; Du Mond, C.; Mamelok, R. D.; Henry, D. H. Pegylated-liposomal doxorubicin versus doxorubicin, bleomycin, and vincristine in the treatment of AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma: results of a randomized phase III clinical trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 1998, 16, 2445–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, A. N.; Tonda, M.; Sun, S.; Rackoff, W.; Doxil Study 30-49 Investigators. Long-term survival advantage for women treated with pegylated liposomal doxorubicin compared with topotecan in a phase 3 randomized study of recurrent and refractory epithelial ovarian cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2004, 95, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O'Brien, M. E. R.; Wigler, N.; Inbar, M.; Rosso, R.; Grischke, E.; Santoro, A.; Catane, R.; Kieback, D. G.; Tomczak, P.; Ackland, S. P.; Orlandi, F.; Mellars, L.; Alland, L.; Tendler, C.; CAELYX Breast Cancer Study Group. Reduced cardiotoxicity and comparable efficacy in a phase III trial of pegylated liposomal doxorubicin HCl (CAELYX/Doxil) versus conventional doxorubicin for first-line treatment of metastatic breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2004, 15, 440–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlowski, R. Z.; Nagler, A.; Sonneveld, P.; Bladé, J.; Hajek, R.; Spencer, A.; San Miguel, J.; Robak, T.; Dmoszynska, A.; Horvath, N.; Spicka, I.; Sutherland, H. J.; Suvorov, A. N.; Zhuang, S. H.; Parekh, T.; Xiu, L.; Yuan, Z.; Rackoff, W.; Harousseau, J. L. Randomized phase III study of pegylated liposomal doxorubicin plus bortezomib compared with bortezomib alone in relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma: combination therapy improves time to progression. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 3892–3901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaitan, D.; Reddy, P. L.; Ningaraj, N. Targeting Brain Tumors with Nanomedicines: Overcoming Blood Brain Barrier Challenges. Curr. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 13, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunton, C. J. Management of treatment-related toxicity in advanced ovarian cancer. Oncologist 2002, 7, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yallapu, M. M.; Jaggi, M.; Chauhan, S. C. Scope of nanotechnology in ovarian cancer therapeutics. J. Ovarian Res. 2010, 3, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waite, C. L.; Roth, C. M. Nanoscale drug delivery systems for enhanced drug penetration into solid tumors: current progress and opportunities. Crit. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 40, 21–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peer, D.; Karp, J. M.; Hong, S.; Farokhzad, O. C.; Margalit, R.; Langer, R. Nanocarriers as an emerging platform for cancer therapy. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petros, R. A.; DeSimone, J. M. Strategies in the design of nanoparticles for therapeutic applications. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 615–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L. R.; Lin, M. Z.; Zhong, H. H.; Cai, Y. J.; Li, B.; Xiao, Z. C.; Shuai, X. T. Nanodrug regulates lactic acid metabolism to reprogram the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment for enhanced cancer immunotherapy. Biomater. Sci. 2022, 10, 3892–3900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, B.; Xu, Z. P. MnO2-shelled Doxorubicin/Curcumin nanoformulation for enhanced colorectal cancer chemo-immunotherapy. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 617, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han Y, Wen P, Li J, Kataoka K. Targeted nanomedicine in cisplatin-based cancer therapeutics. J. Control Release 2022, 345, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, S.; Nabi, B.; Javed, A.; Khan, T.; Iqubal, A.; Ansari, M. J.; Baboota, S.; Ali, J. Unraveling enhanced brain delivery of paliperidone-loaded lipid nanoconstructs: pharmacokinetic, behavioral, biochemical, and histological aspects. Drug Deliv. 2022, 29, 1409–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Zhang, T.; Qin, S.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, L.; Shi, J.; Nice, E. C.; Xie, N.; Huang, C.; Shen, Z. Enhancing the therapeutic efficacy of nanoparticles for cancer treatment using versatile targeted strategies. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Ye, Z.; Huang, C.; Qiu, M.; Song, D.; Li, Y.; Xu, Q. Lipid nanoparticle-mediated lymph node-targeting delivery of mRNA cancer vaccine elicits robust CD8+ T cell response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2022, 119, e2207841119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, V. K.; Chau, E.; Mishra, A.; DeAnda, A.; Hegde, V. L.; Sastry, J. K.; Haviland, D.; Jagannath, C.; Godin, B.; Khan, A. CD44 receptor targeted nanoparticles augment immunity against tuberculosis in mice. J. Control Release. 2022, 349, 796–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Yan, H.; Zhang, J.; Thomas, R. K. Binding of sodium dodecyl sulfate with linear and branched polyethyleneimines in aqueous solution at different pH values. Langmuir 2006, 22, 1526–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kimura, K.; Dubin, P. L.; Jaeger, W. Polyelectrolyte−Micelle Coacervation: Effects of Micelle Surface Charge Density, Polymer Molecular Weight, and Polymer/Surfactant Ratio. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 3324–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kimura, K.; Huang, Q.; Dubin P., L.; Jaeger, W. Effects of Salt on Polyelectrolyte−Micelle Coacervation. Macromolecules 1999, 32, 7128–7134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B. S.; Park, S. W.; Hammond, P. T. Hydrogen-bonding layer-by-layer-assembled biodegradable polymeric micelles as drug delivery vehicles from surfaces. ACS Nano 2008, 2, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Wang, G.; Ma, Y.; Cui, Z.; Binks, B. P. Smart worm-like micelles responsive to CO₂/N₂ and light dual stimuli. Soft Matter 2017, 13, 2727–2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.; Shin, E.; Kim, B. S. Light-responsive micelles of spiropyran initiated hyperbranched polyglycerol for smart drug delivery. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 628–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.; Ketner A., M.; Heymann, R.; Kesselman, E.; Danino, D.; Falvey, D. E.; Raghavan, S. R. A Simple Route to Fluids with Photo-Switchable Viscosities Based on a Reversible Transition between Vesicles and Wormlike Micelles. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 5025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, T. S.; Ketner, A. M.; Raghavan, S. R. Self-assembly of surfactant vesicles that transform into viscoelastic wormlike micelles upon heating. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 6669–6675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Han, Y.; Chu, Z.; He, S.; Zhang, J.; Feng, Y. Thermally induced structural transitions from fluids to hydrogels with pH-switchable anionic wormlike micelles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 394, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezei, A.; Meszaros, R.; Varga, I.; Gilanyi, T. Effect of mixing on the formation of complexes of hyperbranched cationic polyelectrolytes and anionic surfactants. Langmuir 2007, 23, 4237–4247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiappisi, L.; Leach, S. D.; Gradzielski, M. Precipitating polyelectrolyte–surfactant systems by admixing a nonionic surfactant – a case of cononsurfactancy. Soft Matter 2017, 13, 4988–4996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Eghtesadi, S. A.; Dawadi, M. B.; Wang, C.; Huang, S; Seymore, A. E.; Vogt, B. D.; Modarelli, D. A.; Liu, T.; Zacharia, N. S. Partitioning of Small Molecules in Hydrogen-Bonding Complex Coacervates of Poly(acrylic acid) and Poly(ethylene glycol) or Pluronic Block Copolymer. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 3818–3830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, K. A.; Priftis, D.; Perry, S. L.; Yip, J.; Byun, W. Y.; Tirrell, M. Protein Encapsulation via Polypeptide Complex Coacervation. ACS Macro Lett. 2014, 3, 1088–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Zacharia, N. S. Sequestration of Methylene Blue into Polyelectrolyte Complex Coacervates. Macromol Rapid Commun. 2016, 37, 1249–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, K.; Perriman, A. W.; Mann, S. Photocatalytic multiphase micro-droplet reactors based on complex coacervation. Chemical Communications 2015, 51, 8600–8602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Liu, X. K.; Yuan, W. C.; Brown, L. J.; Wang, D. Y. Confined flocculation of ionic pollutants by Poly(l-dopa)-based polyelectrolyte complexes in hydrogel beads for three-dimensional, quantitative, efficient water decontamination. Langmuir 2015, 31, 6351–6366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Mazzawi, M.; Chen, K.; Sun, L.; Dubin, P. L. Protein purification by polyelectrolyte coacervation: influence of protein charge anisotropy on selectivity. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 1512–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dora Tang, T. Y.; Rohaida Che Hak, C.; Thompson, A. J.; Kuimova, M. K.; Williams, D. S.; Perriman, A. W.; Mann, S. Fatty acid membrane assembly on coacervate microdroplets as a step towards a hybrid protocell model. Nat. Chem. 2014, 6, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stano, P.; Luisi, P. L. Achievements and open questions in the self-reproduction of vesicles and synthetic minimal cells. Chem. Commun. (Camb) 2010, 46, 3639–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurihara, K.; Tamura, M.; Shohda, K.; Toyota, T.; Suzuki, K.; Sugawara, T. Self-reproduction of supramolecular giant vesicles combined with the amplification of encapsulated DNA. Nat Chem. 2011, 3, 775–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansy, S. S.; Schrum, J. P.; Krishnamurthy, M.; Tobé, S.; Treco, D. A.; Szostak, J. W. Template-directed synthesis of a genetic polymer in a model protocell. Nature 2008, 454, 122–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadler, B.; Price, A. D.; Chandrawati, R.; Hosta-Rigau, L.; Zelikin, A. N.; Caruso, F. Polymer hydrogel capsules: En route toward synthetic cellular systems. Nanoscale 2009, 1, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Bai, S.; Ansorge-Schumacher, M. B.; Wang, D. Nanoparticle cages for enzyme catalysis in organic media. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 5694–5699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramaniam, A. B.; Wan, J.; Gopinath, A.; Stone, H. A. Semi-permeable vesicles composed of natural clay. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 2600–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luisi, P. L.; Ferri, F.; Stano, P. Approaches to semi-synthetic minimal cells: a review. Naturwissenschaften 2006, 93, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzieciol, A. J.; Mann, S. Designs for life: protocell models in the laboratory. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priftis, D.; Farina, R.; Tirrell, M. Interfacial energy of polypeptide complex coacervates measured via capillary adhesion. Langmuir 2012, 28, 8721–8729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Zhao, M.; Dawadi, M. B.; Cai, Y.; Lapitsky, Y.; Modarelli, D. A.; Zacharia, N. S. Effect of small molecules on the phase behavior and coacervation of aqueous solutions of poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride) and poly(sodium 4-styrene sulfonate). J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 518, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapitsky, Y.; Kaler, E. W. Surfactant and polyelectrolyte gel particles for encapsulation and release of aromatic oils. Soft Matter 2006, 2, 779–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehrani-Bagha, A. R.; Holmberg, K. Solubilization of Hydrophobic Dyes in Surfactant Solutions. Materials (Basel) 2013, 6, 580–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehrani-Bagha, A. R.; Singh, R. G.; Holmberg, K. Solubilization of two organic water-insoluble dyes by anionic, cationic and nonionic surfactants. Colloid Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2013, 417, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thalberg, K.; Lindman, B.; Karlstroem, G. Phase-behavior of systems of cationic surfactant and anionic polyelectrolyte: influence of surfactant chain-length and polyelectrolyte molecular-weight. J. Phys. Chem. 1991, 95, 3370–3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, N.; Trabelsi, S.; Guillot, S.; McLoughlin, D.; Langevin, D.; Letellier, A. P.; Turmine, M. Critical Aggregation Concentration in Mixed Solutions of Anionic Polyelectrolytes and Cationic Surfactants. Langmuir 2004, 20, 8496–8503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y. J.; Xia, J. L.; Dubin, P. L. Complex formation between polyelectrolyte and oppositely charged mixed micelles: Static and dynamic light scattering study of the effect of polyelectrolyte molecular weight and concentration. Macromolecules 1994, 27, 7049–7055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubin P., L.; Rigsbee, D. R.; Gan, L.; Fallon, M. A. Equilibrium Binding of Mixed Micelles to Oppositely Charged Polyelectrolytes. Macromolecules 1988, 21, 2555–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comert, F.; Nguyen, D.; Rushanan, M.; Milas, P.; Xu, A. Y.; Dubin, P. L. Precipitate–Coacervate Transformation in Polyelectrolyte–Mixed Micelle Systems. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2017, 121, 4466–4473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubin, P. L.; Oteri, R. Association of polyelectrolytes with oppositely charged micelles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1983, 95, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Zhang, H.; Rigsbee, D. R.; Dubin, P. L.; Shaikh, T. Structural elucidation of soluble polyelectrolyte-micelle complexes: Intra- vs interpolymer association. Macromolecules 1993, 26, 2759–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kimura, K.; Huang, Q.; Dubin, P.L.; Jaeger, W. Effects of Salt on Polyelectrolyte−Micelle Coacervation. Macromolecules 1999, 32, 7128–7134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McQuigg, D. W.; Kaplan, J. I.; Dubin, P. L. Critical conditions for the binding of polyelectrolytes to small oppositely charged micelles. J. Chem. Phy. 1992, 96, 1973–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mészáros, R.; Thompson, L.; Bos, M.; Varga, I.; Gilányi, T. Interaction of Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate with Polyethyleneimine: Surfactant-Induced Polymer Solution Colloid Dispersion Transition. Langmuir 2003, 19, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezei, A.; Ábrahám, Á.; Pojják, K.; Mészáros, R. The impact of electrolyte on the aggregation of the complexes of hyperbranched poly(ethyleneimine) and sodium dodecylsulfate. Langmuir 2009, 25, 7304–7312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petzold, G.; Schwarz, S. Dye removal from solutions and sludges by using polyelectrolytes and polyelectrolyte-surfactant complexes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 51, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Lee, M. W.; Woo, S. H. Adsorption of congo red by chitosan hydrogel beads impregnated with carbon nanotubes. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 1800–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takae, S.; Miyata, K.; Oba, M.; Ishii, T.; Nishiyama, N.; Itaka, K.; Yamasaki, Y.; Koyama, H.; Kataoka, K. PEG-detachable polyplex micelles based on disulfide-linked block catiomers as bioresponsive nonviral gene vectors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 6001–6009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Z.; Liu, S. Functional block copolymer assemblies responsive to tumor and intracellular microenvironments for site-specific drug delivery and enhanced imaging performance. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 7289–7325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Bu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhuang, Y.; Yang, F.; Shen, H.; Wu, D. Facile construction of pH- and redox-responsive micelles from a biodegradable poly(β-hydroxyl amine) for drug delivery. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Zheng, M.; Meng, F.; Mickler, F. M.; Ruthardt, N.; Zhu, X.; Zhong, Z. Reversibly shielded DNA polyplexes based on bioreducible PDMAEMA-SS-PEG-SS-PDMAEMA triblock copolymers mediate markedly enhanced nonviral gene transfection. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Y.; Velders, A. H.; Gianolio, E.; Aime, S.; Vergeldt, F. J.; Van As, H.; Yan, Y.; Drechsler, M.; de Keizer, A.; Stuart, M. A. C.; van der Gucht, J. Controlled Mixing of Lanthanide(III) Ions in Coacervate Core Micelles. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 3736–3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Groeneveld, A.; Oikonomou, M.; Prusova, A.; Van As, H.; van Lent, J.W.; Velders, A.H. Revealing and Tuning the Core, Structure, Properties and Function of Polymer Micelles with Lanthanide-coordination Complexes. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Ding, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yan, Y.; Huang, J.; de Keizer, A.; Cohen Stuart, M. A. Fluorescence enhancement by microphase separation-induced chain extension of Eu3+ coordination polymers: phenomenon and analysis. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 2720–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang. J.; Cohen Stuart, M. A.; Marcelis, A. T. M., Colomb-Delsuc, M.; Otto, S.; van der Gucht, J. Stable polymer micelles formed by metal coordination. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 7179–7185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ten Hove, J. B.; Wang, J.; van Leeuwen, F. W. B.; Velders, A. H. Dendrimer-encapsulated Nanoparticle-core Micelles as a Modular Strategy for Particle-in-a-box-in-a-box Nanostructures. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 18619–18623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Voets, I. K.; Fokkink, R.; van der Gucht, J.; Velders, A. H. Controlling the Number of Dendrimers in Dendrimicelle Nanoconjugates from 1 to More than 100. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 7337–7345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ten Hove, J. B.; van Oosterom, M. N.; van Leeuwen, F. W. B.; Velders, A. H. Nanoparticles Reveal Extreme Size-Sorting and Morphologies in Complex Coacervate Superstructures. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13820–13827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facciotti, C.; Saggiomo, V.; Bunschoten, A.; Fokkink, R.; Hove, J. B. T.; Wang, J.; Velders, A. H. Cyclodextrin-based Complex Coacervate Core Micelles with Tuneable Supramolecular Host-guest, Metal-to-ligand and Charge Interactions. Soft Matter 2018, 14, 9542–9549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.; Leon, L. Structural dynamics, phase behavior, and applications of polyelectrolyte complex micelles. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 53, 101424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen Stuart, M. A.; Hofs, B.; Voets, I. K.; de Keizer, A. Assembly of polyelectrolyte-containing block copolymers in aqueous media. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 10 (1–2), 30-36.
- Hales, K.; Pochan, D. J. Using polyelectrolyte block copolymers to tune nanostructure assembly. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 11, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colfen, H. Double-hydrophilic block copolymers: synthesis and application as novel surfactants and crystal growth modifiers. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2001, 22, 219–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, H. J.; Kang, S. Double-Hydrophilic Block Copolymers and Their Self-Assembly. Prog. Chem. 2005, 17, 854–859. [Google Scholar]
- Gohy, J. F. Block Copolymer Micelles. In Block Copolymers II; Abetz, V., Ed.; Advances in Polymer Science; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2005; Vol. 190, pp 65-136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riess, G. Micellization of block copolymers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2003, 28, 1107–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabanov, V. A.; Kabanov, A. V. Interpolyelectrolyte and block ionomer complexes for gene delivery: physico-chemical aspects. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1998, 30, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bronich, T. K.; Kabanov, A. V.; Eisenberg, A.; Kabanov, V. A. , Block ionomer complexes: Implications for drug delivery. Abstr. Pap. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 223, U438–U438. [Google Scholar]
- Harada, A.; Kataoka, K. Polyion complex micelles with core-shell structure: their physicochemical properties and utilities as functional materials. Macromol. Symp. 2001, 172, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebhart, C. L.; Kabanov, A. V. Perspectives on Polymeric Gene Delivery. J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 2003, 18, 147–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillies, E. R.; Frechet, J. M. J. Development of acid-sensitive copolymer micelles for drug delivery. Pure Appl. Chem. 2004, 76, 1295–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyama, N.; Jang, W-D. ; Kataoka, K. Supramolecular nanocarriers integrated with dendrimers encapsulating photosensitizers for effective photodynamic therapy and photochemical gene delivery. New J. Chem. 2007, 31, 1074–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Alexandridis, P. Physicochemical aspects of drug delivery andrelease from polymer-based colloids. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 5, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, K.; Togawa, H.; Harada, A.; Yagusi, K.; Matsumoto, T.; Katayose, S. Spontaneous formation of polyion complex micelles with narrow distribution from antisense oligonucleotide and cationic block copolymer in physiological saline. Macromolecules 1996, 29, 8556–8557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen Stuart, M. A.; Besseling, N. A. M.; Fokkink, R. G. Formation of Micelles with Complex Coacervate Cores. Langmuir 1998, 14, 6846–6849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, A.; Kataoka, K. Novel Polyion Complex Micelles Entrapping Enzyme Molecules in the Core. 2. Characterization of the Micelles Prepared at Nonstoichiometric Mixing Ratios. Langmuir 1999, 15, 4208–4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, A.; Kataoka, K. Novel Polyion Complex Micelles Entrapping Enzyme Molecules in the Core: Preparation of Narrowly-Distributed Micelles from Lysozyme and Poly(ethylene glycol)−Poly(aspartic acid) Block Copolymer in Aqueous Medium. Macromolecules 1998, 31, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijmans, C. M.; Zhulina, E. B. Polymer brushes at curved surfaces. Macromolecules 1993, 26, 7214–7224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, A.; Kataoka, K. Chain length recognition: core-shell supramolecular assembly from oppositely charged block copolymers. Science (Washington, DC, U. S.) 1999, 283, 65–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, A.; Kataoka, K. On-off Control of Enzymatic Activity Synchronizing With Reversible Formation of Supramolecular Assembly from Enzyme and Charged Block Copolymers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 9241–9242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, H. S.; Kim, H. J.; Naito, M.; Ogura, S.; Toh, K.; Hayashi, K.; Kim, B. S.; Fukushima, S.; Anraku, Y.; Miyata, K.; Kataoka, K. Systemic Brain Delivery of Antisense Oligonucleotides across the Blood-Brain Barrier with a Glucose-Coated Polymeric Nanocarrier. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2020, 59, 8173–8180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammas, S.; Kataoka, K. Site specific drug-carriers: polymeric micelles as high potential vehicles for biologically active molecules. In Solvents and Self-organization of Polymers; Webber, S. E., Ed.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Quémener, D.; Deratani, A.; Lecommandoux, S. Dynamic Assembly of Block-Copolymers; Barboiu, M., Ed.; Constitutional Dynamic Chemistry. Topics in Current Chemistry; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2011; Vol.322, pp 165-192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, D. J. Theory of block copolymers. I. Domain formation in A-B block copolymers. J. Polym. Sci. Part C 1969, 26, 81–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helfand, E.; Tagami, Y. Theory of the Interface between Immiscible Polymers. II. J. Chem. Phys. 1972, 56, 3592–3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helfand, E.; Tagami, Y. Theory of the Interface Between Immiscible Polymers. J. Chem. Phys. 1972, 57, 1812–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helfand, E.; Wasserman, Z. R. Block Copolymer Theory. 4. Narrow Interphase Approximation. Macromolecules 1976, 9, 879–888. [Google Scholar]
- Helfand, E.; Wasserman, Z. R. Block Copolymer Theory. 5. Spherical Domains. Macromolecules 1978, 11, 960–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helfand, E.; Wasserman, Z. R. Block Copolymer Theory. 6. Cylindrical Domains. Macromolecules 1980, 13, 994–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leermakers, F. A. M.; & Scheutjens, J. M. H. M.; Scheutjens, J. M. H. M. Statistical thermodynamics of associated colloids. 1. Lipid bilayer membranes. Journal of Chemical Physics 1988, 89, 3264–3274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X. F.; Masters, A. J.; Price, C. Self-consistent field theory of micelle formation by block copolymers. Macromolecules 1992, 25, 6876–6884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleer, G.; Stuart, M. C.; Scheutjens, J. M.; Cosgrove, T.; Vincent, B. Polymers at interfaces. Chapman and Hall: London, 1993.
- Leermakers, F. A. M.; Eriksson, J. C.; Lyklema, J. Association colloids and their equilibrium modelling. In Fundamentals of Interface and Colloid Science; Lyklema, J., Elsevier Publishing: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; Vol. V: Soft Colloids, pp 4.1-4.123. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, S. F. The statistical mechanics of polymers with excluded volume. Proc. Phys. Soc. 1965, 85, 613–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, R.D.; Flory, P. J. In: Macromolecular Science. Contemporary Topics in Polymer Science; Ulrich, R. D., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, 1978; Vol. 1, pp 69-98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kik, R. A.; Leermakers, F. A.; Kleijn, J. M. Molecular modeling of lipid bilayers and the effect of protein-like inclusions. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2005, 7, 1996–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kik, R. A.; Lermakers, F. A. M.; Kleijn, J. M. Molecular modeling of protein like inclusions in lipid bilayers: Lipid-mediated interactions. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlin. Soft Matter Phys. 2010, 81 (2 Pt 1)), 021915/1-12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, A. C.; Noolandi, J. Theory of inhomogeneous weakly charged polyelectrolytes. Macromol. Theory Simul. 1999, 8, 214–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Taniguchi, T.; Fredrickson, G. H. Self-Consistent Field Theory of Polyelectrolyte Systems. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 6733–6744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gennes, P. G. Scaling Concepts in Polymer Physics; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, AZ, USA; London, UK, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Birshtein, T. M.; Gridnev, V. N.; Gotlib, Y.Y.; Skvortsov, A. M Simulating the dynamic behaviour of polymer chains using the Monte Carlo method. Polymer Sci. USSR. 1977, 19, 1612–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, D. W.; Joanny, J.-F.; Pincus, P. Dynamics of Semiflexible Polymers in Solution. Macromolecules 1980, 13, 1280–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Gennes, P.-G. In Solid State Physics; Liebert, L. (Eds.) ; Academic: New York, 1978; Suppl. 14.
- Zhulina, Y. B.; Birshtein, T. M. Conformations of block-copolymer molecules in selective solvents (micellar structures). Polym. Sci. USSR. 1985, 27, 570–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birshtein, T. M.; Zhulina, E. B. Scaling theory of supermolecular structures in block copolymer-solvent systems: 1. Model of micellar structures. Polymer 1989, 30, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pergushov, D. V.; Remizova, E. V.; Gradzielski, M.; Lindner, P.; Feldthusen, J.; Zezin, A.B.; Müller, A. H. E.; Kabanov, V. A. Micelles of polyisobutylene-block-poly(methacrylicacid) diblock copolymers and their water-soluble interpolyelectrolyte complexes formed with quaternized poly(4 vinylpyridine). Polymer 2004, 45, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lysenko, E. A.; Chelushkin, P. S.; Bronich, T. K.; Eisenberg, A.; Kabanov, V. A.; Kabanov, A. V. Formation of Multilayer Polyelectrolyte Complexes by Using Block Ionomer Micelles as Nucleating Particles. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 12352–12359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W. Q.; Shi, L. Q.; Gao, L. C.; An, Y. L.; Wu, K. Formation of Core-Shell-Corona Micellar Complexes through Adsorption of Double Hydrophilic Diblock Copolymers into Core-Shell Micelles. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2005, 26, 1341–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R. P.; Wang, Y. M.; He, W. D. Multiple morphological micelles formed from the self-assembly of poly(styrene)-b-poly( 4-vinylpyridine) containing cobalt dodecyl benzene sulfonate. Eur. Polym. J. 2005, 41, 2088–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z. J.; Jonas, A. M.; Varshney, S. K.; Gohy, J. F. Dilution-induced spheres-to-vesicles morphological transition in micelles from block copolymer/surfactant complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 6526–6527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W. Q.; Shi, L. Q.; Gao, L. C.; An, Y. L.; Li, G. Y.; Wu, K.; Liu, Z. Comicellization of Poly(ethylene glycol)-block-poly(acrylic acid) and Poly(4-vinylpyridine) in Ethanol. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 899–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H. W.; Kuang, M.; Wang. ; Chen, D. Y.; Jiang, M. Self-assembly of rigid and coil polymersinto hollow spheres in their common solvent. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 550–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, M.; Duan, H. W.; Wang, J.; Jiang, M. Structural factors of rigid-coil polymer pairs influencing their self-assembly in common solvent. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2004, 108, 16023–16029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Moffitt, M. G. Semiconductor quantum dots with environmentally responsive mixed polystyrene/poly (methyl methacrylate) brush layers. Macromolecules 2007, 40, 5868–5878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffitt, M.; Eisenberg, A. Scaling Relations and Size Control of Block Ionomer Microreactors Containing Different Metal Ions. Macromolecules 1997, 30, 4363–4373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrage, S.; Sigel, R.; Schlaad, H. : Formation of amphiphilic polyion complex vesicles from mixtures of oppositely charged block ionomers. Macromolecules 2003, 36, 1417–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topouza, D.; Orfanou, K.; Pispas, S. Thermosensitive Non-covalently Bonded Block Copolymer-like Micelles from Interpolymer Complexes. J. Polym. Sci. Part A: Polym. Chem. 2004, 42, 6230–6237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohy, J. F.; Khousakoun, E.; Willet, N.; Varshney, S. K.; Jerome, R. Segregation of coronal chains in micelles formed by supramolecular interactions. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2004, 25, 1536–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haley, B.; Frenkel, E. Nanoparticles for drug delivery in cancer treatment. Urol. Oncol. 2008, 26, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, C. Y.; Wei, H.; Sun, Y. X.; Cheng, S. X.; Shen, K.; Gu, Z. W.; Zhang, X. Z.; Zhuo, R. X. Polyethyleneimine modified biocompatible poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)- based nanogels for drug delivery. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2008, 8, 2377–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diez, S.; Navarro, G.; de Ilarduya, C. T. In vivo targeted gene delivery by cationic nanoparticles for treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Gene Med. 2008, 11, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sortino, S.; Mazzaglia, A.; Monsu Scolaro, L.; Marino Merlo, F.; Valveri, V.; Sciortino, M. T. Nanoparticles of cationic amphiphilic cyclodextrins entangling anionic porphyrins as carrier-sensitizer system in photodynamic cancer therapy. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 4256–4265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, M. P.; Bae, Y.; Fukushima, S.; Forrest, M. L.; Nishiyama, N.; Kataoka, K.; Kwon, G. S. pH-responsive Multi-PEGylated dual cationic nanoparticles enable charge modulations for safe gene delivery. ChemMedChem. 2007, 2, 1321–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breunig, M.; Bauer, S.; Goepferich, A. Polymers and nanoparticles: intelligent tools for intracellular targeting? Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 68, 112–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y. T.; Cho, M. Y.; Lee, J. M.; Chung, S. J.; Chung, B. H. Simultaneous intracellular delivery of targeting antibodies and functional nanoparticles with engineered protein G system. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 1197–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatakeyama, H.; Akita, H.; Ishida, E.; Hashimoto, K.; Kobayashi, H.; Aoki, T.; Yasuda, J.; Obata, K.; Kikuchi, H.; Ishida, T.; Kiwada, H.; Harashima, H. Tumor targeting of doxorubicin by anti-MT1-MMP antibody-modified PEG liposomes. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 342, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirpotin, D. B.; Drummond, D. C.; Shao, Y.; Shalaby, M. R.; Hong, K.; Nielsen, U. B.; Marks, J. D.; Benz, C. C.; Park, J. W. Antibody targeting of long-circulating lipidic nanoparticles does not increase tumor localization but does increase internalization in animal models. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 6732–6740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Wang, B.; Weili Qiao, J. L. Multi-anticancer drugs encapsulated in the micelle: a novel chemotherapy to cancer. Med. Hypotheses 2008, 71, 379–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, Y. Basic Aspects and Clinical Trials of Micelle Carrier System. MEMS, NANO and Smart Systems, ICMENS 2004: 25-27 Aug. 2004. p 610.
- Hwang, M. J.; Suh, J. M.; Bae, Y. H.; Kim, S. W. ; Jeong B: Caprolactonic poloxamer analog: PEG-PCL-PEG. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 885–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xiao, Y.; Allen, C. Polymer-drug compatibility: a guide to the development of delivery systems for the anticancer agent, ellipticine. J. Pharm. Sci. 2004, 93, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liggins, R. T.; Burt, H. M. Polyether-polyester diblock copolymers for the preparation of paclitaxel loaded polymeric micelle formulations. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2002, 54, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yallapu, M. M.; Jaggi, M.; Chauhan, S. C. beta-Cyclodextrin-curcumin self- assembly enhances curcumin delivery in prostate cancer cells. Colloids Surf. B Biointerf. 2010, 79, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yallapu, M. M.; Jaggi, M.; Chauhan, S. C. Poly(β-cyclodextrin)/curcumin self-assembly: a novel approach to improve curcumin delivery and its therapeutic efficacy in prostate cancer cells. Macromol. Biosci. 2010, 10, 1141–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yallapu, M. M.; Gupta, B. K.; Jaggi, M.; Chauhan, S. C. Fabrication of curcumin encapsulated PLGA nanoparticles for improved therapeutic effects in metastatic cancer cells. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 351, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasugi, K.; Nagasaki, Y.; Kato, M.; Kataoka, K. Preparation and characterization of polymer micelles from poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(D,L-lactide) block copolymers as potential drug carrier. J. Control Release 1999, 62, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, C. H.; Pho, L. N.; Burt, R. W. Current status of genetic testing for colorectal cancer susceptibility. Oncology 2002, 16, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yoo, H. S.; Park, T. G. Biodegradable polymeric micelles composed of doxorubicin conjugated PLGA-PEG block copolymer. J. Control Release 2001, 70, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jette, K. K.; Law, D.; Schmitt, E. A.; Kwon, G. S. Preparation and drug loading of poly(ethylene glycol)-block-poly(epsilon-caprolactone) micelles through the evaporation of a cosolvent azeotrope. Pharm. Res. 2004, 21, 1184–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Yu, C. H.; Cheng, Y. C.; Yu, P. H.; Cheung, M. K. Biodegradable nanoparticles of amphiphilic triblock copolymers based on poly(3- hydroxybutyrate) and poly(ethylene glycol) as drug carriers. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 4804–4814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La, S. B.; Okano, T.; Kataoka, K. Preparation and characterization of the micelle-forming polymeric drug indomethacin-incorporated poly (ethylene oxide)-poly(beta-benzyl L-aspartate) block copolymer micelles. J. Pharm. Sci. 1996, 85, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Yu, C. H.; Cheng, Y. C.; Yu, P. H.; Cheung, M. K. Micelle formation and sol- gel transition behavior of comb-like amphiphilic poly((PLGA-b-PEG)MA) copolymers. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2008, 46, 1954–1963. [Google Scholar]
- Park, I.; Lee, H.; Chang, T.; Kim, S. W.; Lee, D. S. Poly(D,L-lactic acid-co-glycolic acid)-b-poly(ethylene glycol)-b-poly (D,L-lactic acid-co-glycolic acid) triblock copolymer and thermoreversible phase transition in water. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2002, 61, 188–196. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S. J.; Han, B. R.; Park, S. Y.; Han, D. K.; Kim, S. C. Sol-gel transition behavior of biodegradable three-arm and four-arm star-shaped PLGA-PEG block copolymer aqueous solution. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2006, 44, 888–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H. K.; Park, T. G. Surface Stabilization of Diblock PEG-PLGA Micelles by Polymerization of N-Vinyl-2-pyrrolidone. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2002, 23, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Ahn, C. H.; Park, T. G. Poly[lactic-co-(glycolic acid)]-Grafted Hyaluronic Acid Copolymer Micelle Nanoparticles for Target-Specific Delivery of Doxorubicin. Macromol. Biosci. 2009, 9, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S. H.; Jeong, J. H.; Chun, K. W.; Park, T. G. Target-Specific Cellular Uptake of PLGA Nanoparticles Coated with Poly(l-lysine)-Poly(ethylene glycol)- Folate Conjugate. Langmuir 2005, 21, 8852–8857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinogradov, S. V.; Zeman, A. D.; Batrakova, E. V.; Kabanov, A. V. Polyplex Nanogel formulations for drug delivery of cytotoxic nucleoside analogs. J. Control Release 2005, 107, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinogradov, S. V.; Bronich, T. K.; Kabanov, A. V. Nanosized cationic hydrogels for drug delivery: preparation, properties and interactions with cells. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2002, 54, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galmarini, C. M.; Warren, G.; Kohli, E.; Zeman, A.; Mitin, A.; Vinogradov, S. V. Polymeric nanogels containing the triphosphate form of cytotoxic nucleoside analogues show antitumor activity against breast and colorectal cancer cell lines. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 3373–3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahu, A.; Kasoju, N.; Bora, U. Fluorescence Study of the Curcumin-Casein Micelle Complexation and Its Application as a Drug Nanocarrier to Cancer Cells. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 2905–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S. C.; Kim, D. W.; Shim, Y. H.; Bang, J. S.; Oh, H. S.; Wan Kim, S.; Seo, M. H. In vivo evaluation of polymeric micellar paclitaxel formulation: toxicity and efficacy. J. Control Release 2001, 72, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jubo, L.; Yuehua, X.; Christine, A. Polymer-drug compatibility: A guide to the development of delivery systems for the anticancer agent, ellipticine. J. Pharm. Sci. 2004, 93, 132–143. [Google Scholar]
- Shuai, X.; Merdan, T.; Schaper, A. K.; Xi, F.; Kissel, T. Core-Cross-Linked Polymeric Micelles as Paclitaxel Carriers. Bioconj. Chem. 2004, 15, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, X.; Ai, H.; Nasongkla, N.; Kim, S.; Gao, J. Micellar carriers based on block copolymers of poly(epsilon-caprolactone) and poly(ethylene glycol) for doxorubicin delivery. J. Control Release 2004, 98, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y-C. ; Tang, L-Y.; Sun, T-M.; Li, C-H.; Xiong, M-H.; Wang, J. Self-Assembled Micelles of Biodegradable Triblock Copolymers Based on Poly(ethyl ethylene phosphate) and Poly(ε-caprolactone) as Drug Carriers. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Woodcock, S. E.; Buck, S. M.; Chen, C.; Chen, Z. Different Surface- Restructuring Behaviors of Poly(methacrylate)s Detected by SFG in Water. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 9470–9471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licciardi, M.; Craparo E., F.; Giammona, G.; Armes, S. P.; Tang, Y.; Lewis, A. L. in vitro biological evaluation of folate-functionalized block copolymer micelles for selective anti-cancer drug delivery. Macromol. Biosci. 2008, 8, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S. H.; Jeong, J. H.; Lee, S. H.; Kim, S. W.; Park, T. G. LHRH Receptor-Mediated Delivery of siRNA Using Polyelectrolyte Complex Micelles Self- Assembled from siRNA-PEG-LHRH Conjugate and PEI. Bioconj. Chem. 2008, 19, 2156–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Hu, M.; Reilly, R. M. ; Allen, C: Apoptotic Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF)-Conjugated Block Copolymer Micelles as a Nanotechnology Platform for Targeted Combination Therapy. Mol. Pharm. 2007, 4, 769–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, Y.; Nishiyama, N.; Kataoka, K. In vivo antitumor activity of the folate- conjugated pH-sensitive polymeric micelle selectively releasing adriamycin in the intracellular acidic compartments. Bioconjug. Chem. 2007, 18, 1131–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Lee, E. S.; Park, K.; Kwon, I. C.; Bae, Y. H. Doxorubicin loaded pH-sensitive micelle: antitumoral efficacy against ovarian A2780/DOXR tumor. Pharm. Res. 2008, 25, 2074–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyung Taek Oh, E. S. L. Cancer-associated pH-responsive tetracopolymeric micelles composed of poly(ethylene glycol)-b-poly(L-histidine)-b-poly(L- lactic acid)-b-poly(ethylene glycol). Polym. Adv. Technol. 2008, 19, 1907–1913. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, E. S.; Gao, Z.; Kim, D.; Park, D.; Kwon, I. C.; Bae, Y. H. Super pH-sensitive multifunctional polymeric micelle for tumor pHe specific TAT exposure and multidrug resistance. J. Control Release 2008, 129, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, H. S.; Lee, E. A.; Park, T. G. Doxorubicin-conjugated biodegradable polymeric micelles having acid-cleavable linkages. J. Control Release 2002, 82, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Park, S. Y.; Mok, H.; Park, T. G. Synthesis, Characterization, Antitumor Activity of Pluronic Mimicking Copolymer Micelles Conjugated with Doxorubicin via Acid-Cleavable Linkage. Bioconj. Chem. 2008, 19, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burt, H. M.; Zhang, X.; Toleikis, P.; Embree, L.; Hunter, W. L. Development of copolymers of poly(D,L-lactide) and methoxypolyethylene glycol as micellar carriers of paclitaxel. Colloids Surf. B Biointer. 1999, 16, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Kim, S.; He, W.; Wang, H.; Low, P. S.; Park, K.; Cheng, J. X. Fast Release of Lipophilic Agents from Circulating PEG-PDLLA Micelles Revealed by in Vivo Förster Resonance Energy Transfer Imaging. Langmuir 2008, 24, 5213–5217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, R. K.; Hawker, C. J.; Wooley, K. L. Cross-linked block copolymer micelles: functional nanostructures of great potential and versatility. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2006, 35, 1068–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bontha, S.; Kabanov, A. V.; Bronich, T. K. Polymer micelles with cross-linked ionic cores for delivery of anticancer drugs. J Control Release 2006, 114, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.; Wong, T.; Byrne, F.; Kavallaris, M.; Bulmus, V. Acid-Labile Core Cross- Linked Micelles for pH-Triggered Release of Antitumor Drugs. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 1826–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyama, N.; Kataoka, K. Current state, achievements, and future prospects of polymeric micelles as nanocarriers for drug and gene delivery. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 112, 630–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyagi, T.; Sugi, K.; Sakurai, Y.; Okano, T.; Kataoka, K. Peptide drug carrier: studies on incorporation of vasopressin into nano-associates comprising poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(-aspartic acid) block copolymer. Colloids Surf. B Biointerf. 1999, 16, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, M.; Miyauchi, M.; Yamada, N.; Okano, T.; Sakurai, Y.; Kataoka, K. Characterization and anticancer activity of the micelle-forming polymeric anticancer drug adriamycin-conjugated poly(ethylene glycol)- poly(aspartic acid) block copolymer. Cancer Res. 1990, 50, 1693–1700. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z.; Fain, H. D.; Rapoport, N. Ultrasound-enhanced tumor targeting of polymeric micellar drug carriers. Mol. Pharm. 2004, 1, 317–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, A.; Sun, H.; Husseini, G. A.; Pitt, W. G.; Christensen, D. A.; Rapoport, N. Y. Drug delivery in pluronic micelles: effect of high-frequency ultrasound on drug release from micelles and intracellular uptake. J. Control Release 2002, 84, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namdeo, M.; Sutanjay, S.; Tankhiwale, R.; Bajpai, M.; Yallapu, M. M.; Bajpai, S. K. Magnetic Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery Applications. J. Nanosci. Nanotech. 2008, 8, 3247–3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, J. R.; Weissleder, R. Multifunctional magnetic nanoparticles for targeted imaging and therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 1241–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertorelle, F.; Wilhelm, C.; Roger, J.; Gazeau, F.; Menager, C.; Cabuil, V. Fluorescence-modified superparamagnetic nanoparticles: intracellular uptake and use in cellular imaging. Langmuir 2006, 22, 5385–5391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinteza, L. O.; Ohulchanskyy, T. Y.; Sahoo, Y.; Bergey, E. J.; Pandey, R. K.; Prasad, P. N. Diacyllipid micelle-based nanocarrier for magnetically guided delivery of drugs in photodynamic therapy. Mol. Pharm. 2006, 3, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, R.; Zhang, L.; Qian, H.; Li, R.; Jiang, X.; Liu, B. Multifunctional nanocarriers for cell imaging, drug delivery, and near-IR photothermal therapy. Langmuir 2010, 26, 5428–5434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guthi, J. S.; Yang, S. G.; Huang, G.; Li, S.; Khemtong, C.; Kessinger, C. W.; Peyton, M.; Minna, J. D.; Brown, K. C.; Gao, J. MRI-visible micellar nanomedicine for targeted drug delivery to lung cancer cells. Mol. Pharm. 2010, 7, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, P.; Giri, J.; Rieken, F.; Koch, C.; Mykhaylyk, O.; Doblinger, M.; Banerjee, R.; Bahadur, D.; Plank, C. Targeted temperature sensitive magnetic liposomes for thermo-chemotherapy. J. Control Release 2010, 142, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio-Retama, J.; Zafeiropoulos, N. E.; Serafinelli, C.; Rojas-Reyna, R.; Voit, B.; Cabarcos, E. L.; Stamm, M. Synthesis and characterization of thermosensitive PNIPAM microgels covered with superparamagnetic gamma-Fe2O3 nanoparticles. Langmuir 2007, 23, 10280–10285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shubayev, V. I.; Pisanic, T. R.; Jin, S. Magnetic nanoparticles for theragnostics. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L. Biofunctional nanoparticles with magnetization and luminescence. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 3955–3959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, T. K.; Foy, S. P.; Erokwu, B.; Dimitrijevic, S.; Flask, C. A.; Labhasetwar, V. Magnetic resonance imaging of multifunctional pluronic stabilized iron-oxide nanoparticles in tumor-bearing mice. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 6748–6756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridolfo, R.; Tavakoli, S.; Junnuthula, V.; Williams, D. S.; Urtti, A.; van Hest, J. C. Exploring the impact of morphology on the properties of biodegradable nanoparticles and their diffusion in complex biological medium. Biomacromolecules 2021, 22, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, A.; Kataoka, K. Effect of Charged Segment Length on Physicochemical Properties of Core–Shell Type Polyion Complex Micelles from Block Ionomers. Macromolecules 2003, 36, 4995–5001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marras, A. E.; Campagna, T. R.; Vieregg, J. R.; Tirrell, M. V. Physical Property Scaling Relationships for Polyelectrolyte Complex Micelles. Macromolecules 2021, 54, 6585–6594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holley, A. C.; Parsons, K. H.; Wan, W. M.; Lyons, D. F.; Bishop, G. R.; Correia, J. J.; Huang, F. Q.; McCormick, C. L. Block ionomer complexes consisting of siRNA and aRAFT-synthesized hydrophilic-block-cationic copolymers: the influence of cationic block length on gene suppression. Polym. Chem. 2014, 5, 6967–6976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, K. H.; Holley, A. C.; Munn, G. A.; Flynt, A. S.; McCormick, C. L. Block ionomer complexes consisting of siRNA and aRAFT-synthesized hydrophilic-block-cationic copolymers II: The influence of cationic block charge density on gene suppression. Polym. Chem. 2016, 7, 6044–6054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, T. Y.; Kim, I.; Chen, L.; Lee, E.; Lee, S.; Choi, S. H. Effect of Ionic Group on the Complex Coacervate Core Micelle Structure. Polymers (Basel) 2019, 11, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koide, A.; Kishimura, A.; Osada, K.; Jang, W. D.; Yamasaki, Y.; Kataoka, K. Semipermeable polymer vesicle (PICsome) self-assembled in aqueous medium from a pair of oppositely charged block copolymers: physiologically stable micro-/nanocontainers of water-soluble macromolecules. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 5988–5989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuanoi, S.; Anraku, Y.; Hori, M.; Kishimura, A.; Kataoka, K. Fabrication of polyion complex vesicles with enhanced salt and temperature resistance and their potential applications as enzymatic nanoreactors. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 2389–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, S.; Sanada, Y.; Sakashita, M.; Nishina, K.; Nakai, K.; Yusa, S. I.; Sakurai, K. Chain-Length Dependence of Polyion Complex Architecture Bearing Phosphobetaine Block Explored Using SAXS and FFF-MALS. Polym. J. 2014, 46, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voets, I. K.; De Keizer, A.; Cohen Stuart, M. A.; Justynska, J.; Schlaad, H. Irreversible Structural Transitions in Mixed Micelles of Oppositely Charged Diblock Copolymers in Aqueous Solution. Macromolecules 2007, 40, 2158–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anraku, Y.; Kishimura, A.; Oba, M.; Yamasaki, Y.; Kataoka, K. Spontaneous formation of nanosized unilamellar polyion complex vesicles with tunable size and properties. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 1631–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wibowo, A.; Osada, K.; Matsuda, H.; Anraku, Y.; Hirose, H.; Kishimura, A.; Kataoka, K. Morphology Control in Water of Polyion Complex Nanoarchitectures of Double-Hydrophilic Charged Block Copolymers through Composition Tuning and Thermal Treatment. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 3086–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marras, A. E.; Vieregg, J. R.; Ting, J. M.; Rubien, J. D.; Tirrell, M. V. Polyelectrolyte Complexation of Oligonucleotides by Charged Hydrophobic-Neutral Hydrophilic Block Copolymers. Polymers 2019, 11, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, R.; Sato, T.; Terao, K.; Yusa, S. Intermolecular Interactions and Self-Assembly in Aqueous Solution of a Mixture of Anionic-Neutral and Cationic-Neutral Block Copolymers. Macromolecules 2015, 48, 7222–7229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, R.; Sato, T.; Terao, K.; Yusa, S. Reversible Vesicle- Spherical Micelle Transition in a Polyion Complex Micellar System Induced by Changing the Mixing Ratio of Copolymer Components. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 3091–3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, S. L.; Leon, L.; Hoffmann, K. Q.; Kade, M. J.; Priftis, D.; Black, K. A.; Wong, D.; Klein, R. A.; Pierce, C. F., 3rd; Margossian, K. O.; Whitmer, J. K.; Qin, J.; de Pablo, J. J.; Tirrell, M. Chirality-selected phase behaviour in ionic polypeptide complexes. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.; Leon, L. Structural transitions and encapsulation selectivity of thermoresponsive polyelectrolyte complex micelles. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 6438–6448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Hernandez, J.; Lecommandoux, S. Reversible inside- out micellization of pH-responsive and water-soluble vesicles based on polypeptide diblock copolymers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 2026–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holder, S. J.; Sommerdijk, N. A. J. M. New micellar morphologies from amphiphilic block copolymers: disks, toroids and bicontinuous micelles. Polym. Chem. 2011, 2, 1018–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Tirrell, M. V. Polyelectrolyte Complexation. In Advances in Chemical Physics; Rice, S. A., Dinner, A. R., Eds.; Advances in Chemical Physics; Wiley-Blackwell: Malden, 2016; Vol. 161, pp 499-544. [Google Scholar]
- Burke, P. A.; Pun, S. H.; Reineke, T. M. Advancing polymeric delivery systems amidst a nucleic acid therapy renaissance. ACS Macro Lett. 2013, 2, 928–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hays, J. B.; Magar, M. E.; Zimm, B. H. Persistence Length of DNA. Biopolymers 1969, 8, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinland, B.; Pluen, A.; Sturm, J.; Weill, G. Persistence length of single-stranded DNA. Macromolecules 1997, 30, 5763–5765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieregg, J. R.; Lueckheide, M.; Marciel, A. B.; Leon, L.; Bologna, A. J.; Rivera, J. R.; Tirrell, M. V. Oligonucleotide-Peptide Complexes: Phase Control by Hybridization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 1632–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakya, A.; King, J. T. DNA Local-Flexibility-Dependent Assembly of Phase-Separated Liquid Droplets. Biophys. J. 2018, 115, 1840–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, K.; Chaya, H.; Fukushima, S.; Watanabe, S.; Takemoto, H.; Osada, K.; Nishiyama, N.; Miyata, K.; Kataoka, K. Influence of RNA Strand Rigidity on Polyion Complex Formation with Block Catiomers. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2016, 37, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, K. M.; Osada, K.; Tockary, T. A.; Dirisala, A.; Chen, Q.; Kataoka, K. Poly(ethylene glycol) Crowding as Critical Factor To Determine pDNA Packaging Scheme into Polyplex Micelles for Enhanced Gene Expression. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, R.; Narayanan, T.; Yusa, S. I.; Sato, T. Kinetics of Morphological Transition between Cylindrical and Spherical Micelles in a Mixture of Anionic-Neutral and Cationic-Neutral Block Copolymers Studied by Time-Resolved SAXS and USAXS. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 3654–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, S. E.; Eisenberg, A. Kinetics and Mechanisms of the Sphere-to-Rod and Rod-to-Sphere Transitions in the Ternary System PS310-b-PAA52/Dioxane/Water. Langmuir 2001, 17, 6705–6714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voets, I. K.; Moll, P. M.; Aqil, A.; Jeŕôme, C.; Detrembleur, C.; De Waard, P.; De Keizer, A.; Cohen Stuart, M. A. Temperature Responsive Complex Coacervate Core Micelles with a PEO and PNIPAAm Corona. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 10833–10840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crommelin, D. J. A.; Scherphof, G.; Storm, G. Active targeting with particulate carrier systems in the blood compartment. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1995, 17, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gros, L.; Ringsdorf, H.; Schupp, H. Polymeric antitumor agents on a molecular and on a cellular level? Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1981, 20, 305–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, M. A.; Brem, H.; Langer, R. Advancing the field of drug delivery: taking aim at cancer. Cancer Cell 2003, 4, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, M. L.; Lavasanifar, A.; Kwon, G. S. Amphiphilic block copolymers for drug delivery. J. Pharm. Sci. 2003, 92, 1343–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, C.; Maysinger, D.; Eisenberg, A. Nano-engineering block copolymer aggregates for drug delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces. 1999, 16, 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.; Leroux, J. Polymeric micelles - a new generation of colloidal drug carriers. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 1999, 48, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabanov, A. V.; Batrakova, E. V.; Melik-Nubarov, N. S.; Fedoseev, N. A.; Dorodnich, T. Y.; Alakhov, V. Y.; Chekhonin, V. P.; Nazarova, I. R.; Kabanov, V. A. A new class of drug carriers: Micelles of poly (oxyethylene)-poly (oxypropylene) block copolymers as microcontainers for drug targeting from blood in brain. J. Control. Release 1992, 22, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreuter, J. Nanoparticles--a historical perspective. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 2006 331, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, G. S. Polymeric micelles for delivery of poorly water-soluble compounds. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carrier Syst. 2003, 20, 357–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavasanifar, A.; Samuel, J.; Kwon, G. S. Poly(ethylene oxide)-block-poly(L-amino acid) micelles for drug delivery. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2002, 54, 169–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zeng, F.; Allen, C. In vivo fate of unimers and micelles of a poly(ethylene glycol)-block-poly(caprolactone) copolymer in mice following intravenous administration. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2007, 65, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghimi, S. M.; Hunter, A. C.; Murray, J. C. Long-circulating and target-specific nanoparticles: theory to practice. Pharmacol. Rev. 2001, 53, 283–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torchilin, V. P. Structure and design of polymeric surfactant-based drug delivery systems. J. Control Release 2001, 73, 137–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torchilin, V. P. Multifunctional nanocarriers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2006, 58, 1532–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, M.; Kwon, G. S.; Okano, T.; Sakurai, Y.; Seto, T.; Kataoka, K. Preparation of micelle-forming polymer-drug conjugates. Bioconjug. Chem. 1992, 3, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillies, E. R.; Fréchet, J. M. pH-Responsive copolymer assemblies for controlled release of doxorubicin. Bioconjug. Chem. 2005, 16, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrubý, M.; Konák, C.; Ulbrich, K. Polymeric micellar pH-sensitive drug delivery system for doxorubicin. J. Control Release 2005, 103, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabanov, A. V.; Batrakova, E. V.; Alakhov, V. Y. Pluronic block copolymers for overcoming drug resistance in cancer. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2002, 54, 759–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E. S.; Na, K.; Bae, Y. H. Super pH-sensitive multifunctional polymeric micelle. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, T.; Fukushima, S.; Okamoto, K.; Suzuki, M.; Matsumura, Y.; Yokoyama, M.; Okano, T.; Sakurai, Y.; Kataoka, K. Development of the polymer micelle carrier system for doxorubicin. J. Control. Release 2001, 74, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapoport, N. Combined cancer therapy by micellar-encapsulated drug and ultrasound. Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 277, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallaro, G.; Licciardi, M.; Giammona, G.; Caliceti, P.; Semenzato, A.; Salmaso, S. Poly(hydroxyethylaspartamide) derivatives as colloidal drug carrier systems. J. Control. Release 2003, 89, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamaguchi, T.; Matsumura, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Shimizu, K.; Goda, R.; Nakamura, I.; Nakatomi, I.; Yokoyama, M.; Kataoka, K.; Kakizoe, T. NK105, a paclitaxel-incorporating micellar nanoparticle formulation, can extend in vivo antitumour activity and reduce the neurotoxicity of paclitaxel. Br. J. Cancer 2005, 92, 1240–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huh, K. M.; Lee, S. C.; Cho, Y. W.; Lee, J.; Jeong, J. H.; Park, K. Hydrotropic polymer micelle system for delivery of paclitaxel. J. Control. Release 2005, 101, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T-Y. ; Kim, D-W.; Chung, J-Y.; Shin, S. G.; Kim, S-C.; Heo, D. S.; Kim, N. K.; Bang, Y-J. Phase I and pharmacokinetic study of Genexol-PM, a cremophor-free, polymeric micelle-formulated paclitaxel, in patients with advanced malignancies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 3708–3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnadas, A.; Rubinstein, I.; Onyüksel, H. Sterically stabilized phospholipid mixed micelles: in vitro evaluation as a novel carrier for water-insoluble drugs. Pharm. Res. 2003, 20, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torchilin, V. P.; Lukyanov, A. N.; Gao, Z.; Papahadjopoulos-Sternberg, B. Immunomicelles: targeted pharmaceutical carriers for poorly soluble drugs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2003, 100, 6039–6044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavasanifar, A.; Samuel, J.; Sattari, S.; Kwon, G. S. Block copolymer micelles for the encapsulation and delivery of amphotericin B. Pharm. Res. 2002, 19, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Garrec, D.; Gori, S.; Luo, L.; Lessard, D.; Smith, D. C.; Yessine, M-A; Ranger, M. ; Leroux, J. C. Poly(N-vinylpyrrolidone)-block-poly(D,L-lactide) as a new polymeric solubilizer for hydrophobic anticancer drugs: in vitro and in vivo evaluation. J. Control. Release 2004, 99, 83–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Nostrum, C. F. Polymeric micelles to deliver photosensitizers for photodynamic therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2004, 56, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G. D.; Harada, A.; Nishiyama, N.; Jiang, D. L.; Koyama, H.; Aida, T.; Kataoka, K. Polyion complex micelles entrapping cationic dendrimer porphyrin: effective photosensitizer for photodynamic therapy of cancer. J. Control. Release 2003, 93, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barratt, G. M. Therapeutic applications of colloidal drug carriers. Pharm. Sci. Technol. Today 2000, 3, 163–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumura, Y.; Hamaguchi, T.; Ura, T.; Muro, K.; Yamada, Y.; Shimada, Y.; Shirao, K.; Okusaka, T.; Ueno, H.; Ikeda, M.; Watanabe, N. Phase I clinical trial and pharmacokinetic evaluation of NK911, a micelle-encapsulated doxorubicin. Br. J. Cancer. 2004, 91, 1775–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torchilin, V. P. Micellar nanocarriers: pharmaceutical perspectives. Pharm. Res. 2007, 24, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torchilin, V. P. PEG-based micelles as carriers of contrast agents for different imaging modalities. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2002, 54, 235–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, H.; Fang, J.; Inutsuka, T.; Kitamoto, Y. Vascular permeability enhancement in solid tumor: various factors, mechanisms involved and its implications. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2003, 3, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, H.; Wu, J.; Sawa, T.; Matsumura, Y.; Hori, K. Tumor vascular permeability and the EPR effect in macromolecular therapeutics: a review. J. Control. Release 2000, 65, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumura, Y.; Maeda, H. A new concept for macromolecular therapeutics in cancer chemotherapy: mechanism of tumoritropic accumulation of proteins and the antitumor agent smancs. Cancer Res. 1986, 46, 6387–6392. [Google Scholar]
- Illum, L.; Jacobsen, L. O.; Müller, R. H.; Mak, E.; Davis, S. S. Surface characteristics and the interaction of colloidal particles with mouse peritoneal macrophages. Biomaterials 1987, 8, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroux, J. C.; De Jaeghere, F.; Anner, B.; Doelker, E.; Gurny, R. An investigation on the role of plasma and serum opsonins on the internalization of biodegradable poly(D,L-lactic acid) nanoparticles by human monocytes. Life Sci. 1995, 57, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghimi, S. M.; Porter, C. J. H.; Illum, L.; Davis, S. S. The effect of poloxamer-407 on liposome stability and targeting to bone marrow: comparison with polystyrene microspheres. Int. J. Pharm. 1991, 68, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, D. E. , 3rd.; Peppas, N. A. Opsonization, biodistribution, and pharmacokinetics of polymeric nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 307, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolnik, S.; Illum, L.; Davis, S. S. Long circulating microparticulate drug carriers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1995, 16, 195–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodle, M. C.; Lasic, D. D. Sterically stabilized liposomes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1992, 1113, 171–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vonarbourg, A.; Passirani, C.; Saulnier, P.; Benoit, J. P. Parameters influencing the stealthiness of colloidal drug delivery systems. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 4356–4373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Rossin, R.; Turner, J. L.; Becker, M. L.; Joralemon, M. J.; Welch, M. J.; Wooley, K. L. An assessment of the effects of shell cross-linked nanoparticle size, core composition, and surface PEGylation on in vivo biodistribution. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 2541–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carstens, M. G.; Bevernage, J. J. L.; van Nostrum, C. F.; van Steenbergen, M. J.; Flesch, F. M.; Verrijk, R.; de Leede, L. G. J.; Crommelin, D. J. A.; Hennink, W. E. Small Oligomeric Micelles Based on End Group Modified mPEG–Oligocaprolactone with Monodisperse Hydrophobic Blocks. Macromolecules 2007, 40, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagan, S. A.; Coombes, A. G. A.; Garnett, M. C.; Dunn, S. E.; Davies, M. C.; Illum, L.; Davis, S. S.; Harding, S. E.; Purkiss, S.; Gellert, P. R. Polylactide-poly(ethylene glycol) copolymers as drug delivery systems. 1. Characterization of water dispersible micelle-forming systems. Langmuir 1996, 12, 2153–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Tam, J.; Maysinger, D.; Eisenberg, A. Cellular internalization of poly(ethylene oxide)-b-poly(epsilon-caprolactone) diblock copolymer micelles. Bioconjug. Chem. 2002, 13, 1259–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.; Fang, C.; You, M. X.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, S.; Pei, Y. Stealth MePEG-PCL micelles: effects of polymer composition on micelle physicochemical characteristics, in vitro drug release, in vivo pharmacokinetics in rats and biodistribution in S180 tumor bearing mice. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2005, 283, 954–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Nagasaki, Y.; Kato, Y.; Sugiyama, Y.; Kataoka, K. Long-circulating poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(D,L-lactide) block copolymer micelles with modulated surface charge. J. Control. Release 2001, 77, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukyanov, A. N.; Torchilin, V. P. Micelles from lipid derivatives of water-soluble polymers as delivery systems for poorly soluble drugs. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2004, 56, 1273–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissig, V.; Whiteman, K. R.; Torchilin, V. P. Accumulation of protein-loaded long-circulating micelles and liposomes in subcutaneous Lewis lung carcinoma in mice. Pharm. Res. 1998, 15, 1552–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neradovic, D.; Soga, O.; Van Nostrum, C. F.; Hennink, W. E. The effect of the processing and formulation parameters on the size of nanoparticles based on block copolymers of poly(ethylene glycol) and poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) with and without hydrolytically sensitive groups. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 2409–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rijcken, C. J. F.; Veldhuis, T. F. J.; Ramzi, A.; Meeldijk, J. D.; van Nostrum, C. F.; Hennink, W. E. Novel fast degradable thermosensitive polymeric micelles based on PEG-block-poly(N-(2-hydroxyethyl)methacrylamide-oligolactates). Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 2343–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soga, O.; van Nostrum, C. F.; Ramzi, A.; Visser, T.; Soulimani, F.; Frederik, P. M.; Bomans, P. H.; Hennink, W. E. Physicochemical characterization of degradable thermosensitive polymeric micelles. Langmuir 2004, 20, 9388–9395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topp, M. D. C, Dijkstra P. J.; Talsma, H.; Feijen, J. Thermosensitive micelle-forming block copolymers of poly(ethylene glycol) and poly(N-isopropylacrylamide). Macromolecules 1997, 30, 8518–8520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, T. M.; Hansen, C. Pharmacokinetics of stealth versus conventional liposomes: effect of dose. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1991, 1068, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K. Y.; Ha, W. S.; Park, W. H. Blood compatibility and biodegradability of partially N-acylated chitosan derivatives. Biomaterials 1995, 16, 1211–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molineux, G. Pegylation: engineering improved pharmaceuticals for enhanced therapy. Cancer Treat Rev. 2002, 28 (Suppl. A), 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torchilin, V. P.; Trubetskoy, V. S. Which polymers can make nanoparticulate drug carriers long-circulating? Adv. Drug Deliver. Rev. 1995, 16, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klibanov, A. L.; Maruyama, K.; Torchilin, V. P.; Huang, L. Amphipathic polyethyleneglycols effectively prolong the circulation time of liposomes. FEBS Lett. 1990, 268, 235–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soppimath, K. S.; Aminabhavi, T. M.; Kulkarni, A. R.; Rudzinski, W. E. Biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles as drug delivery devices. J. Control. Release 2001, 70, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, R.; Pasche, S.; Textor, M.; Castner, D. G. Influence of PEG architecture on protein adsorption and conformation. Langmuir 2005, 21, 12327–12332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, G. S.; Suwa, S.; Yokoyama, M.; Okano, T.; Sakurai, Y.; Kataoka, K. Enhanced Tumor Accumulation and Prolonged Circulation Times of Micelle-Forming Poly (Ethylene Oxide-Aspartate) Block Copolymer-Adriamycin Conjugates. J. Control. Release 1994, 29, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, G. S.; Yokoyama, M.; Okano, T.; Sakurai, Y.; Kataoka, K. Biodistribution of micelle-forming polymer-drug conjugates. Pharm. Res. 1993, 10, 970–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabanov, A. V.; Batrakova, E. V.; Alakhov, V. Y. Pluronic block copolymers as novel polymer therapeutics for drug and gene delivery. J. Control. Release 2002, 82, 189–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vonarbourg, A.; Passirani, C.; Saulnier, P.; Simard, P.; Leroux, J. C.; Benoit, J. P. Evaluation of pegylated lipid nanocapsules versus complement system activation and macrophage uptake. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2006, 78, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Xie, J.; Tong, Y. W.; Wang, C. H. Effect of PEG conformation and particle size on the cellular uptake efficiency of nanoparticles with the HepG2 cells. J. Control. Release 2007, 118, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peracchia, M. T.; Vauthier, C.; Passirani, C.; Couvreur, P.; Labarre, D. Complement consumption by poly(ethylene glycol) in different conformations chemically coupled to poly(isobutyl 2-cyanoacrylate) nanoparticles. Life Sci. 1997, 61, 749–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghimi, S. M.; Szebeni, J. Stealth liposomes and long circulating nanoparticles: critical issues in pharmacokinetics, opsonization and protein-binding properties. Prog. Lipid Res. 2003, 42, 463–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carstens, M. G.; Romberg, B.; Laverman, P.; Boerman, O. C.; Oussoren, C.; Storm. G. Observations on the disappearance of the stealth property of PEGylated liposomes. Effects of lipid dose and dosing frequency. In Liposome Technology, 3rd ed.; Gregoriadis, G. Ed.; CRC Press: London, 2006; Vol III, pp 79-93.
- Dams, E. T.; Laverman, P.; Oyen, W. J.; Storm, G.; Scherphof, G. L.; van Der Meer, J. W.; Corstens, F. H.; Boerman, O. C. Accelerated blood clearance and altered biodistribution of repeated injections of sterically stabilized liposomes. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2000, 292, 1071–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, T.; Harashima, H.; Kiwada, H. Liposome clearance. Biosci. Rep. 2002, 22, 197–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laverman, P.; Brouwers, A. H.; Dams, E. T.; Oyen, W. J.; Storm, G.; van Rooijen, N.; Corstens, F. H.; Boerman, O. C. Preclinical and clinical evidence for disappearance of long-circulating characteristics of polyethylene glycol liposomes at low lipid dose. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2000, 293, 996–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyama, N.; Okazaki, S.; Cabral, H.; Miyamoto, M.; Kato, Y.; Sugiyama, Y.; Nishio, K.; Matsumura, Y.; Kataoka, K. Novel cisplatin-incorporated polymeric micelles can eradicate solid tumors in mice. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 8977–8983. [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama, M.; Fukushima, S.; Uehara, R.; Okamoto, K.; Kataoka, K.; Sakurai. ; Y, Okano, T. Characterization of physical entrapment and chemical conjugation of adriamycin in polymeric micelles and their design for in vivo delivery to a solid tumor. J. Control. Release 1998, 50, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, M.; Okano, T.; Sakurai, Y; Fukushima, S. ; Okamoto, K.; Kataoka, K. Selective delivery of adriamycin to a solid tumor using a polymeric micelle carrier system. J. Drug Target. 1999, 7, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodle, M. C.; Engbers, C. M.; Zalipsky, S. New amphipatic polymer-lipid conjugates forming long-circulating reticuloendothelial system-evading liposomes. Bioconjug. Chem. 1994, 5, 493–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruyama, K.; Okuizumi, S.; Ishida, O.; Yamauchi, H.; Kikuchi, H.; Iwatsuru, M. Phosphatidyl polyglycerols prolong liposome circulation in vivo. Int. J. Pharm. 1994, 111, 103–107. [CrossRef]
- Torchilin, V. P.; Levchenko, T. S.; Whiteman, K. R.; Yaroslavov, A. A.; Tsatsakis, A. M.; Rizos, A. K.; Michailova, E. V.; Shtilman, M. I. Amphiphilic poly-N-vinylpyrrolidones: synthesis, properties and liposome surface modification. Biomaterials 2001, 22, 3035–3044.
- Torchilin, V. P.; Shtilman, M. I.; Trubetskoy, V. S.; Whiteman, K.; Milstein, A. M. Amphiphilic vinyl polymers effectively prolong liposome circulation time in vivo. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (Bba) Biomembr. 1994, 1195, 181–184. [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, H.; Kojima, H.; Yamamoto, H.; Kawashima, Y. Evaluation of circulation profiles of liposomes coated with hydrophilic polymers having different molecular weights in rats. J. Control Release 2001, 75, 83–91. [CrossRef]
- Whiteman, K. R.; Subr, V.; Ulbrich, K.; Torchilin, V. P. Poly(Hpma)-coated liposomes demonstrate prolonged circulation in mice. J. Liposome Res. 2001, 11, 153–164. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metselaar, J. M.; Bruin, P.; de Boer, L. W.; de Vringer, T.; Snel, C.; Oussoren, C.; Wauben, M. H.; Crommelin, D. J.; Storm, G.; Hennink, W. E. A novel family of L-amino acid-based biodegradable polymer-lipid conjugates for the development of long-circulating liposomes with effective drug-targeting capacity. Bioconjug. Chem. 2003, 14, 1156–1164.
- Romberg, B.; Oussoren, C.; Snel. C. J.; Carstens, M. G.; Hennink, W. E.; Storm, G. Pharmacokinetics of poly(hydroxyethyl-l-asparagine)-coated liposomes is superior over that of PEG-coated liposomes at low lipid dose and upon repeated administration. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2007, 1768, 737–743. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiue, G. H.; Wang, C. H.; Lo, C. L.; Wang, C. H.; Li, J. P.; Yang, J. L. Environmental-sensitive micelles based on poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline)-b-poly(L-lactide) diblock copolymer for application in drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 317, 69–75. [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Lee, S. C.; Shin, J. H.; Kwon, I. C.; Jeong, S. Y. Amphiphilic diblock copolymers based on poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) and poly(1,3-trimethylene carbonate): Synthesis and micellar characteristics. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 7448–7452. [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.C.; Chang, Y. K.; Yoon, J. S.; Kim, C. H.; Kwon, I. C.; Kim, Y. H.; Jeong, S. Y. Synthesis and micellar characterization of amphiphilic diblock copolymers based on poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) and aliphatic polyesters. Macromolecules 1999, 32, 1847–1852. [CrossRef]
- Lee, S. C.; Lee, H. J. pH-controlled, polymer-mediated assembly of polymer micelle nanoparticles. Langmuir 2007, 23, 488–495. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volet, G.; Chanthavong, V.; Wintgens, V.; Amiel, C. Synthesis of Monoalkyl End-Capped Poly(2-Methyl-2-Oxazoline) and Its Micelle Formation in Aqueous Solution. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 5190–5197. [CrossRef]
- Benahmed, A.; Ranger, M.; Leroux, J. C. Novel polymeric micelles based on the amphiphilic diblock copolymer poly(N-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone)-block-poly(D,L-lactide). Pharm. Res. 2001, 18, 323–328. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, T. W.; Cho, K. Y.; Lee, H. C.; Nah, J. W.; Yeo, J. H.; Akaike, T.; Cho, C. S. Novel micelle-forming block copolymer composed of poly(e-caprolactone) and poly(vinyl pyrrolidone). Polymer 2004, 45, 1591–1597. [CrossRef]
- Le Garrec, D.; Taillefer, J.; Van Lier, J. E.; Lenaerts, V.; Leroux J. C. Optimizing pH-responsive polymeric micelles for drug delivery in a cancer photodynamic therapy model. J. Drug Target. 2002, 10, 429–437. [CrossRef]
- Lele, B. S.; Lereux, J. C. Synthesis and Micellar Characterization of Novel Amphiphilic A-B-A Tricopolymers of N-(2-Hydroxypropyl) Methacrylamide or N-Vinyl-2-pyrrolidone with Poly (caprolactone). Macromolecules 2002, 35, 6714–6723. [CrossRef]
- Luo, L. B.; Ranger, M.; Lessard, D. G.; Le Garrec, D.; Gori, S.; Leroux, J. C.; Rimmer, S.; Smith, D. Novel amphiphilic diblock copolymer of low molecular weight poly(N-vinylpyrrolidone)-block-poly(D,L-lactide): Synthesis, characterization, and micellization. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 4008–4013.
- Lemarchand, C.; Gref, R.; Lesieur, S.; Hommel, H.; Vacher, B.; Besheer, A.; Maeder, K.; Couvreur, P. Physico-chemical characterization of polysaccharide-coated nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2005, 108, 97–111. [CrossRef]
- Rouzes, C.; Gref, R.; Leonard, M.; De Sousa Delgado, A.; Dellacherie, E. Surface modification of poly(lactic acid) nanospheres using hydrophobically modified dextrans as stabilizers in an o/w emulsion/evaporation technique. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2000, 50, 557–565. [CrossRef]
- Lemarchand, C.; Gref, R.; Couvreur, P. Polysaccharide-decorated nanoparticles. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2004, 58, 327–341. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passirani, C.; Barratt, G.; Devissaguet, J. P.; Labarre, D. Long-circulating nanoparticles bearing heparin or dextran covalently bound to poly(methyl methacrylate). Pharm. Res. 1998, 15, 1046–1050. [CrossRef]
- Besheer, A.; Hause, G.; Kressler, J.; Mäder, K. Hydrophobically modified hydroxyethyl starch: synthesis, characterization, and aqueous self-assembly into nano-sized polymeric micelles and vesicles. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 359–367. [CrossRef]
- Lemarchand, C.; Gref, R.; Passirani, C.; Garcion, E.; Petri, B.; Müller, R.; Costantini, D.; Couvreur, P. Influence of polysaccharide coating on the interactions of nanoparticles with biological systems. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 108–118. [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, A.; Ishihara, T.; Adachi, N.; Akaike, T. Preparation of nanoparticles bearing high density carbohydrate chains using carbohydrate-carrying polymers as emulsifier. Biomaterials 1994, 15, 1035–1042. [CrossRef]
- Bougard, F.; Jeusette, M.; Mespouille, L.; Dubois, P.; Lazzaroni, R. Synthesis and supramolecular organization of amphiphilic diblock copolymers combining poly(N,N-dimethylamino-2-ethyl methacrylate) and poly(epsilon-caprolactone). Langmuir 2007, 23, 2339–2345. [CrossRef]
- Nam, Y. S.; Kang, H. S.; Park, J. Y.; Park, T. G.; Han, S. H.; Chang, I. S. New micelle-like polymer aggregates made from PEI-PLGA diblock copolymers: micellar characteristics and cellular uptake. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 2053–2059. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, T.; Chen, G.; Nakamae, K.; Hoffman, A. S. An AB block copolymer of oligo(methyl methacrylate) and poly(acrylic acid) for micellar delivery of hydrophobic drugs. J. Control. Release 1998, 51, 221–229. [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J. H.; Kang, H. S.; Yang, S. R.; Park, K.; Kim, J-D. Biodegradable poly(asparagine) grafted with poly(caprolactone) and the effect of substitution on self-aggregation. Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2005, 264, 187–194. [CrossRef]
- Kohori, F.; Sakai, K.; Aoyagi, T.; Yokoyama, M.; Yamato, M.; Sakurai, Y.; Okano, T. Control of adriamycin cytotoxic activity using thermally responsive polymeric micelles composed of poly (N-isopropylacrylamide-co-N,N-dimethylacrylamide)-β-poly (D,L-lactide). Colloid Surf B: Biointerfaces 1999, 16, 195–205.
- Zuccari, G.; Carosio, R.; Fini, A.; Montaldo, P. G.; Orienti, I. Modified polyvinylalcohol for encapsulation of all-trans-retinoic acid in polymeric micelles. J. Control. Release 2005, 103, 369–380. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghimi, S. M.; Porter, C. J.; Muir, I. S.; Illum, L.; Davis, S. S. Non-phagocytic uptake of intravenously injected microspheres in rat spleen: influence of particle size and hydrophilic coating. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1991, 177, 861–866. [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, S. K.; Monsky, W. L.; Yuan, F.; Roberts, W. G.; Griffith, L.; Torchilin, V. P.; Jain, R. K. Regulation of transport pathways in tumor vessels: role of tumor type and microenvironment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 1998, 95, 4607–4612. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, F.; Dellian, M.; Fukumura, D.; Leunig, M.; Berk, D. A.; Torchilin, V. P.; Jain, R. K. Vascular permeability in a human tumor xenograft: molecular size dependence and cutoff size. Cancer Res. 1995, 55, 3752–3756.
- Bae, Y.; Nishiyama, N.; Fukushima, S.; Koyama, H.; Yasuhiro, M.; Kataoka, K. Preparation and biological characterization of polymeric micelle drug carriers with intracellular pH-triggered drug release property: tumor permeability, controlled subcellular drug distribution, and enhanced in vivo antitumor efficacy. Bioconjug. Chem. 2005, 16, 122–130.
- Oku, N.; Namba, Y. Long-circulating liposomes. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carrier Syst. 1994, 11, 231–270.
- Senior, J.; Gregoriadis, G. Stability of small unilamellar liposomes in serum and clearance from the circulation: the effect of the phospholipid and cholesterol components. Life Sci. 1982, 30, 2123–2136. [CrossRef]
- Abra, R. M.; Bosworth, M. E.; Hunt, C. A. Liposome disposition in vivo: effects of pre-dosing with lipsomes. Res. Commun. Chem. Pathol. Pharmacol. 1980, 29, 349–360.
- Gao, Z.; Lukyanov, A. N.; Chakilam, A. R.; Torchilin, V. P. PEG-PE/phosphatidylcholine mixed immunomicelles specifically deliver encapsulated taxol to tumor cells of different origin and promote their efficient killing. J. Drug Target. 2003, 11, 87–92. [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y. I.; Seo, S. J.; Park, I. K.; Lee, H. C.; Kang, I. C.; Akaike, T.; Cho, C. S. Cellular recognition of paclitaxel-loaded polymeric nanoparticles composed of poly(gamma-benzyl L-glutamate) and poly(ethylene glycol) diblock copolymer endcapped with galactose moiety. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 296, 151–161.
- Park, E. K.; Kim, S. Y.; Lee, S. B.; Lee, Y. M. Folate-conjugated methoxy poly(ethylene glycol)/poly(epsilon-caprolactone) amphiphilic block copolymeric micelles for tumor-targeted drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2005, 109, 158–168. [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X. B.; Mahmud, A.; Uludağ, H.; Lavasanifar, A. Conjugation of arginine-glycine-aspartic acid peptides to poly(ethylene oxide)-b-poly(epsilon-caprolactone) micelles for enhanced intracellular drug delivery to metastatic tumor cells. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 874–884. [CrossRef]
- Sethuraman, V. A.; Bae, Y. H. TAT peptide-based micelle system for potential active targeting of anti-cancer agents to acidic solid tumors. J. Control. Release 2007, 118, 216–224. [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Villamarin, M.; Sousa-Herves, A.; Porto, S.; Guldris, N.; Martinez-Costas, J.; Riguera, R.; Fernandez-Megia, E. A dendrimer- hydrophobic interaction synergy improves the stability of polyion complex micelles. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 2528–2537. [CrossRef]
- Izumrudov, V. A.; Zhiryakova, M. V.; Kudaibergenov, S. E. Controllable stability of DNA-containing polyelectrolyte complexes in water-salt solutions. Biopolymers 1999, 52, 94–108. [CrossRef]
- Kim, B. S.; Chuanoi, S.; Suma, T.; Anraku, Y.; Hayashi, K.; Naito, M.; Kim, H. J.; Kwon, I. C.; Miyata, K.; Kishimura, A.; Kataoka K. Self- assembly of siRNA/PEG-b-catiomer at integer molar ratio into 100 nm- sized vesicular polyion complexes (siRNAsomes) for RNAi and codelivery of cargo macromolecules. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 3699–3709.
- Miyata, K.; Kakizawa, Y.; Nishiyama, N.; Harada, A.; Yamasaki, Y.; Koyama, H.; Kataoka, K. Block catiomer polyplexes with regulated densities of charge and disulfide cross-linking directed to enhance gene expression. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 2355–2361. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Ma, B.; Abdeen, A. A.; Chen, G.; Xie, R.; Saha, K.; Gong, S. Versatile Redox-Responsive Polyplexes for the Delivery of Plasmid DNA, Messenger RNA, and CRISPR-Cas9 Genome-Editing Machinery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 31915–31927. [CrossRef]
- Bronich, T. K.; Keifer, P. A.; Shlyakhtenko, L. S.; Kabanov, A. V. Polymer micelle with cross-linked ionic core. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 8236–8237. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, C.; Han, J.; Yu, Y.; Maysinger, D.; Eisenberg, A. Polycaprolactone-b-poly(ethylene oxide) copolymer micelles as a delivery vehicle for dihydrotestosterone. J. Control. Release 2000, 63, 275–286. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Grijpma, D. W.; Feijen, J. Thermo-sensitive transition of monomethoxy poly(ethylene glycol)-block-poly(trimethylene carbonate) films to micellar-like nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2006, 112, 57–63. [CrossRef]
- Kwon, G. S.; Naito, M.; Yokoyama, M.; Okano, T.; Sakurai, Y.; Kataoka, K. Micelles based on AB block copolymers of poly(ethylene oxide) and poly(b-benzyl l-aspartate). Langmuir 1993, 9, 945–949. [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Kawano, K.; Yokoyama, M.; Opanasopit, P.; Okano, T.; Maitani, Y. Preparation of camptothecin-loaded polymeric micelles and evaluation of their incorporation and circulation stability. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 308, 183–189. [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, M.; Opanasopit, P.; Okano, T.; Kawano, K.; Maitani, Y. Polymer design and incorporation methods for polymeric micelle carrier system containing water-insoluble anti-cancer agent camptothecin. J. Drug Target. 2004, 12, 373–384. [CrossRef]
- Neradovic, D.; Van Nostrum, C. F.; Hennink, W. E. Thermoresponsive Polymeric Micelles with Controlled Instability Based on Hydrolytically Sensitive N-Isopropylacrylamide Copolymers. Macromolecules 2001, 34, 7589–7591. [CrossRef]
- Rapoport, N.; Marin, A.; Luo, Y.; Prestwich, G. D.; Muniruzzaman, M. D. Intracellular uptake and trafficking of Pluronic micelles in drug-sensitive and MDR cells: effect on the intracellular drug localization. J. Pharm. Sci. 2002, 91, 157–170. [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Feng, S. S. Methoxy poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(lactide) (MPEG-PLA) nanoparticles for controlled delivery of anticancer drugs. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 2843–2849. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attwood, D.; Florence, A. T. Surfactant Systems. Their Chemistry, Pharmacy and Biology. Chapman and Hall: London, 1983.
- Kwon, G. S.; Okano, T. Polymeric micelles as new drug carriers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1996, 21, 107–116. [CrossRef]
- Kim, S. Y.; Shin, I. G.; Lee, Y. M.; Cho, C. S.; Sung, Y. K. Methoxy poly(ethylene glycol) and epsilon-caprolactone amphiphilic block copolymeric micelle containing indomethacin. II. Micelle formation and drug release behaviours. J Control. Release 1998, 51, 13–22. [CrossRef]
- Forrest, M. L.; Zhao, A.; Won, C. Y.; Malick, A. W.; Kwon, G. S. Lipophilic prodrugs of Hsp90 inhibitor geldanamycin for nanoencapsulation in poly(ethylene glycol)-b-poly(epsilon-caprolactone) micelles. J. Control. Release 2006, 116, 139–149. [CrossRef]
- Lavasanifar, A.; Samuel, J.; Kwon, G. S. The effect of fatty acid substitution on the in vitro release of amphotericin B from micelles composed of poly(ethylene oxide)-block-poly(N-hexyl stearate-L-aspartamide). J. Control. Release 2002, 79, 165–172. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Lee, S. C.; Acharya, G.; Chang, C. J.; Park, K. Hydrotropic solubilization of paclitaxel: analysis of chemical structures for hydrotropic property. Pharm Res. 2003, 20, 1022–1030. [CrossRef]
- Prompruk, K.; Govender, T.; Zhang, S.; Xiong, C. D.; Stolnik, S. Synthesis of a novel PEG-block-poly(aspartic acid-stat-phenylalanine) copolymer shows potential for formation of a micellar drug carrier. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 297, 242–253. [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, M.; Zhao, C.; Wang, Y.; Xu, R.; Winnik, M. A.; Mura, J. L; Riess, G.; Croucher, M. D. Poly(styrene-ethylene oxide) block copolymer micelle formation in water: a fluorescence probe study. Macromolecules 1991, 24, 1033–1040. [CrossRef]
- Konan-Kouakou, Y. N.; Boch, R..; Gurny, R.; Allemann, E. In vitro and in vivo activities of verteporfin-loaded nanoparticles. J. Control Release 2005, 103, 83–91. [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zeng, F.; Allen, C. Influence of serum protein on polycarbonate-based copolymer micelles as a delivery system for a hydrophobic anti-cancer agent. J. Control. Release 2005, 103, 481–497. [CrossRef]
- Lo, C. L.; Huang, C. K.; Lin, K. M.; Hsiue, G. H. Mixed micelles formed from graft and diblock copolymers for application in intracellular drug delivery. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 1225–1235. [CrossRef]
- Opanasopit, P.; Yokoyama, M.; Watanabe, M.; Kawano, K.; Maitani, Y.; Okano, T. Influence of serum and albumins from different species on stability of camptothecin-loaded micelles. J. Control. Release 2005, 104, 313–321. [CrossRef]
- Savić, R.; Azzam, T.; Eisenberg, A.; Maysinger, D. Assessment of the integrity of poly(caprolactone)-b-poly(ethylene oxide) micelles under biological conditions: a fluorogenic-based approach. Langmuir 2006, 22, 3570–3578. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letchford, K.; Zastre, J.; Liggins, R.; Burt H. Synthesis and micellar characterization of short block length methoxy poly(ethylene glycol)-block-poly(caprolactone) diblock copolymers. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2004, 35, 81–91. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmud, A.; Xiong, X.B.; Lavasanifar, A. Novel self-associating poly(ethylene oxide)-block-poly(ε-caprolactone) block copolymers with functional side groups on the polyester block for drug delivery. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 9419–9428. [CrossRef]
- Opanasopit, P.; Yokoyama, M.; Watanabe, M.; Kawano, K.; Maitani, Y.; Okano, T. Block copolymer design for camptothecin incorporation into polymeric micelles for passive tumor targeting. Pharm Res. 2004, 21, 2001–2008. [CrossRef]
- Lavasanifar, A.; Samuel, J.; Kwon, G. S. The effect of alkyl core structure on micellar properties of poly(ethylene oxide)-block-poly(L-aspartamide) derivatives. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2001, 22, 115–126. [CrossRef]
- Kang, N.; Perron, M. E.; Prud'homme, R. E.; Zhang, Y.; Gaucher, G.; Leroux, J. C. Stereocomplex block copolymer micelles: core-shell nanostructures with enhanced stability. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 315–319. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, L. Q.; Wang, H.; Tu, K. Micellization phenomena of amphiphilic block copolymers based on methoxy poly(ethylene glycol) and either crystalline or amorphous poly(caprolactone-b-lactide). Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 2492–2500. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, E.; Kunugi, S. Micelle formation of poly(vinyl phenol)-block-polystyrene by alfa,omega-diamines. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Pol. Chem. 2002, 40, 3063–3067. [CrossRef]
- 577. Rijcken, C. Tuneable & degradable polymeric micelles for drug delivery: from synthesis to feasibility in vivo. Ph.D Thesis, Utrecht University, Sep 17, 2007.
- Rodriguez-Hernandez, J.; Checot, F.; Gnanou, Y.; Lecommandoux, S. Toward ‘smart’ nano- objects by self-assembly of block copolymers in solution. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2005, 30, 691–724. [CrossRef]
- Rösler, A.; Vandermeulen, G. W.; Klok, H. A. Advanced drug delivery devices via self-assembly of amphiphilic block copolymers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 53, 95–108. [CrossRef]
- Iijima, M.; Nagasaki, Y.; Okada, T.; Kato, M.; Kataoka, K. Core-polymerized reactive micelles from heterotelechelic amphiphilic block copolymers. Macromolecules 1999, 32, 1140–1146. [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Emoto, K.; Lijima, M.; Nagasaki, Y.; Aoyagi, T.; Okano, T.; Sakurai, Y.; Kataoka, K. Core-stabilized polymeric micelle as potential drug carrier: Increased solubilization of taxol. Polym. Adv. Technol. 1999, 10, 647–654. [CrossRef]
- Bae, K. H.; Choi, S. H.; Park, S. Y.; Lee, Y.; Park, T. G. Thermosensitive pluronic micelles stabilized by shell cross-linking with gold nanoparticles. Langmuir 2006, 22, 6380–6384. [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Weaver, J. V. M.; Tang, Y.; Billingham, C.; Armes, S. P.; Tribe, K. Synthesis of shell cross-linked micelles with pH-responsive cores using ABC triblock copolymers. Macromolecules 2002, 35, 6121–6131. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Qi, B.; Lepage, M.; Zhao, Y. Polymer micelles stabilization on demand through reversible photo-cross-linking. Macromolecules 2007, 40, 790–792. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Luo, S.; Armes, S. P.; Shi, W.; Liu, S. UV Irradiation-induced shell cross-linked micelles with pH-responsive cores using ABC triblock copolymers. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 5987–5994. [CrossRef]
- Joralemon, M. J.; O'Reilly, R. K.; Hawker, C. J.; Wooley, K. L. Shell click-crosslinked (SCC) nanoparticles: a new methodology for synthesis and orthogonal functionalization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 16892–16899. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Ji, J.; Shen, J. Synthesis of hydroxyl-capped comb-like poly(ethylene glycol) to develop shell cross-linkable micelles. Polymer 2006, 47, 1987–1994. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lokitz, B. S.; Armes, S. P.; McCormick, C. L. Synthesis of reversible shell cross-linked micelles for controlled release of bioactive agents. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 2726–2728. [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Hernández J, Babin J, Zappone B, Lecommandoux S. Preparation of shell cross-linked nano-objects from hybrid-peptide block copolymers. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 2213–2220. [CrossRef]
- 590. Pilon, L. N.; Armes, S. P.; Findlay, P.; Rannard, S. P. Synthesis and characterization of shell cross-linked micelles with hydroxy-functional coronas: a pragmatic alternative to dendrimers? Langmuir 2005, 21, 3808–3813.
- Thurmond, K. B., II.; Huang H, Clark, C. G., Jr.; Kowalewski, T.; Wooley, K. L. Shell cross-linked polymer micelles: stabilized assemblies with great versatility and potential. Colloid Surf. B - Biointerfaces 1999, 16, 45–54. [CrossRef]
- Hu, F. Q.; Ren, G. F.; Yuan, H.; Du, Y. Z.; Zeng, S. Shell cross-linked stearic acid grafted chitosan oligosaccharide self-aggregated micelles for controlled release of paclitaxel. Colloids Surf. B - Biointerfaces 2006, 50, 97–103. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Weaver, J. V. M.; Save, M.; Armes, S. P. Synthesis of pH-responsive shell crosslinked micelles and their use as nanoreactors for the preparation of gold nanoparticles. Langmuir 2002, 18, 8350–8357. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L; Katapodi, K; Davis, T. P; Stenzel, M; Barner-Kowollik, C. W. Using the Reversible Addition-Fragmentation Chain Transfer Process to Synthesize Core-Crosslinked Micelles. J. Polym. Sci., Part A: Polym. Chem. 2006, 44, 2177–2194. [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ding, J.; Day, M.; Tao, Y. Molecularly imprinted polymeric nanospheres by diblock copolymer self-assembly. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 2629–2636. [CrossRef]
- 596. Rheingans, O.; Hugenberg, N.; Harris, J. R.; Fischer, K.; Maskos, M. Nanoparticles built of cross- linked heterotechelic amphiphilic poly(dimethylsiloxane)-b-poly(ethylene oxide) diblock copolymers, Macromolecules 2000, 33, 4780–4790.
- Lee, B. H.; West, B.; McLemore, R.; Pauken, C.; Vernon, B. L. In-situ injectable physically and chemically gelling NIPAAm-based copolymer system for embolization. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 2059–2064. [CrossRef]
- Petrov, P.; Bozukov, M.; Tsvetanov, C. B. Innovative approach for stabilizing poly(ethylen oxide)-b-poly(propylene oxide)-b-poly(ethylen oxide) micelles by forming nano-sized networks in the micelle. J. Mater. Chem. 2005, 15, 1481–1486. [CrossRef]
- Jaturanpinyo, M.; Harada, A.; Yuan, X.; Kataoka, K. Preparation of bionanoreactor based on core-shell structured polyion complex micelles entrapping trypsin in the core cross-linked with glutaraldehyde. Bioconjug. Chem. 2004, 15, 344–348. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakizawa, Y.; Harada, A.; Kataoka, K. Environment-sensitive stabilization of core-shell structured polyion complex micelle by reversible cross-linking of the core through disulfide bond. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 11247–11248. [CrossRef]
- Rijcken, C. J.; Snel, C. J.; Schiffelers, R. M.; van Nostrum, C. F.; Hennink, W. E. Hydrolysable core-crosslinked thermosensitive polymeric micelles: synthesis, characterisation and in vivo studies. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 5581–5593. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourouina, N.; Cohen Stuart, M. A.; Mieke Kleijn, J. Complex coacervate core micelles as diffusional nanoprobes. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 320–331. [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Huang, W.; Shi, C.; Atkinson, S. T.; Luo, J. Reversibly crosslinked nanocarriers for on-demand drug delivery in cancer treatment. Ther. Deliv. 2012, 3, 1409–1427. [CrossRef]
- 604. Hebels, E. R.; van Steenbergen, M. J.; Haegebaert, R.; Cornelis W. Seinen, C. W.; Mesquita, B. S.; van den Dikkenberg, A.; Remaut, K.; Rijcken, C. J. F.; van Ravensteijn, B. G. P.; Hennink, W. E.; Vermonden, T. Mechanistic Study on the Degradation of Hydrolysable Core-Crosslinked Polymeric Micelles. Langmuir 2023, 39, 12132–12143.
- Talelli, M.; Barz, M.; Rijcken, C. J.; Kiessling, F.; Hennink, W. E.; Lammers, T. Core-Crosslinked Polymeric Micelles: Principles, Preparation, Biomedical Applications and Clinical Translation. Nano Today 2015, 10, 93–117. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, M. S.; Kwon. Y. J. Acid-transforming polypeptide micelles for targeted nonviral gene delivery. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 3404–3413. [CrossRef]
- Krishnakumar, G. S.; Sampath, S.; Muthusamy, S.; John, M. A. Importance of crosslinking strategies in designing smart biomaterials for bone tissue engineering: A systematic review. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2019, 96, 941–954. [CrossRef]
- Hennink, W. E.; van Nostrum, C. F. Novel crosslinking methods to design hydrogels. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2002, 54, 13–36. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Nostrum, C. F. Covalently cross-linked amphiphilic block copolymer micelles. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 3246–3259. [CrossRef]
- Tillet, G.; Boutevin, B.; Ameduri. B. Chemical Reactions of Polymer Crosslinking and Post-Crosslinking at Room and Medium Temperature. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 191–217. [CrossRef]
- Ayyub, O. B.; Ibrahim, M. B.; Kofinas, P. Synthesis and characterization of microphase separated primary amine functionalized polystyrene-b-poly(2-vinylpyridine). Polymer 2014, 55, 6227–6231. [CrossRef]
- Kembaren, R.; Mieke Kleijn, J.; Borst, J. W.; Kamperman, M.; Hofman, A. H. Enhanced stability of complex coacervate core micelles following different core-crosslinking strategies. Soft Matter 2022, 18, 3052–3062. [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, G.; Lecolley, F.; Tao, L.; Haddleton, D. M.; Clerx, J.; Cornelissen, J. J.; Velonia, K. Design and synthesis of N-maleimido-functionalized hydrophilic polymers via copper-mediated living radical polymerization: a suitable alternative to PEGylation chemistry. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 2966–2973.
- Ju, M.; Gong, F.; Cheng, S.; Gao, Y. Fast and Convenient Synthesis of Amine-Terminated Polylactide as a Macroinitiator for ω-Benzyloxycarbonyl-L-Lysine-N-Carboxyanhydrides. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2011, 2011, 1–8.
- McMaster, P. D.; Byrnes, E. W.; Block, A. J.; Paul A. Tenthorey, P. A. New antiarrhythmic agents. 5..alpha.-Aminoaceto-2,6-xylidides with functionalized amide alkyl substituents. J. Med. Chem. 1981, 24, 53–58. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Tong, X.; Morris, D.; Zhao, Y. Toward photocontrolled release using light-dissociable block copolymer micelles. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 4633–4640. [CrossRef]
- 617. Liu, D-Z.; Hsieh, J-H.; Fan, X-C.; Yang, J-D.; Chung, T-W. Synthesis, characterization and drug delivery behaviors of new PCP polymeric micelles, Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 68, 544–554.
- Tian, L.; Yam, L.; Wang, J.; Tat, H.; Uhrich, K. Core crosslinkable polymeric micelles from PEG- lipid amphiphiles as drug carriers. J. Mater. Chem. 2004, 14, 2317–2324. [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, M.; Miyauchi, M.; Yamada, N.; Okano, T.; Sakurai, Y.; Shohei, I.; Kataoka, K. Polymeric Micelles as Novel Drug Carrier: Adriamycin-Conjugated Poly(Ethylene Glycol)–Poly(Aspartic Acid) Block Copolymer. J. Control. Release 1990, 11, 269–278. [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, K.; Matsumoto, T.; Yokoyama, M.; Okano, T.; Sakurai, Y.; Fukushima, S.; Okamoto, K.; Kwon, G. S. Doxorubicin-loaded poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(beta-benzyl-L-aspartate) copolymer micelles: their pharmaceutical characteristics and biological significance. J. Control. Release 2000, 64, 143–153.
- Seymour, L. W.; Duncan, R.; Strohalm, J.; Kopecek, J. Effect of molecular weight (Mw) of N-(2-hydroxypropyl)methacrylamide copolymers on body distribution and rate of excretion after subcutaneous, intraperitoneal, and intravenous administration to rats. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1987, 21, 1341–1358. [CrossRef]
- Mart, R. J.; Osborne, R. D.; Stevens, M. M.; Ulijn, R. V. Peptide-based stimuli-responsive biomaterials. Soft Matter 2006, 2, 822–835. [CrossRef]
- Rijcken, C. J.; Soga, O.; Hennink, W. E.; van Nostrum, C. F. Triggered destabilisation of polymeric micelles and vesicles by changing polymers polarity: an attractive tool for drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2007, 120, 131–148. [CrossRef]
- Chilkoti, A.; Dreher, M. R.; Meyer, D. E.; Raucher, D. Targeted drug delivery by thermally responsive polymers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2002, 54, 613–630. [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, A. S.; Stayton, P. S.; Volga, B.; Chen, G.; Chen, J.; Cheung, C.; Chilkoti, A.; Ding, Z.; Dong, L.; Fong, R.; Lackey, C. A.; Long, C. J.; Miura, M.; Morris, J. E.; Murthy, N.; Nabeshima, Y.; Park, T. G.; Press, O. W.; Shimoboji, T.; Shoemaker, S.; Yang, H. J.; Monji, N.; Nowinski, R. C.; Cole, C. A.; Priest, J. H.; Harris, J. M.; Nakamae, K.; Nishino, T.; Miyata, T. Really smart bioconjugates of smart polymers and receptor proteins. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2000, 52, 577–586.
- Jeong, B.; Bae, Y. H.; Lee, D. S.; Kim, S. W. Biodegradable block copolymers as injectable drug-delivery systems. Nature 1997, 388, 860–862. [CrossRef]
- Heskins, M.; Guillet, J. E. Solution properties of poly (N-isopropylacrylamide). J. Macromol. Sci. A Chem. 1968, 2, 1441–1455. [CrossRef]
- Pelton, R. Temperature-sensitive aqueous microgels. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 85, 1–33. [CrossRef]
- Schild, H. G. Poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) experiment, theory and application. Prog. Polym. Sci. 1992, 17, 163–249. [CrossRef]
- Feil, H.; Bae, Y. H.; Feijen J.; Kim, S. W. Effect of comonomer hydrophilicity and ionization on the lower critical solution temperature of N-isopropylacrylamide copolymers. Macromolecules 1993, 26, 2496–2500. [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-S.; Kataoka, K. Precise control of lower critical solution temperature of thermosensitive poly(2-isopropyl-2-oxazoline) via gradient copolymerization with 2-ethyl-2-oxazoline as a hydrophilic comonomer. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 6622–6630. [CrossRef]
- Shibayama, M.; Mizutani, S.; Nomura, S. Thermal properties of copolymer gels containing N- isopropylacrylamide. Macromolecules 1996, 29, 2019–2024. [CrossRef]
- Soga, O.; van Nostrum, C. F.; Hennink, W. E. Poly(N-(2-hydroxypropyl) methacrylamide mono/di lactate): a new class of biodegradable polymers with tuneable thermosensitivity. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 818–821. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, X. P.; Wu, C. Study of the core-shell nanoparticle formed through the "coil-to-globule" transition of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) grafted with poly(ethylene oxide). Macromolecules 1997, 30, 7921–7926. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P. W.; Napper, D. H. Effect of heating rate on nanoparticle formation of poly(N- isopropylacrylamide)-poly(ethylene glycol) block copolymer microgels. Langmuir 2000, 16, 8543–8545. [CrossRef]
- Engin, K.; Leeper, D. B.; Cater, J. R.; Thistlethwaite, A. J.; Tupchong, L.; McFarlane, J. D. Extracellular pH distribution in human tumours. Int. J. Hyperthermia 1995, 11, 211–216.
- Haag, R. Supramolecular drug-delivery systems based on polymeric core-shell architectures. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2004, 43, 278–282. [CrossRef]
- Lee, E. S.; Na, K.; Bae, Y. H. Polymeric micelle for tumor pH and folate-mediated targeting. J Control. Release 2003, 91, 103–113. [CrossRef]
- Lee, E. S.; Shin, H. J.; Na, K.; Bae, Y. H. Poly(L-histidine)-PEG block copolymer micelles and pH-induced destabilization. J. Control. Release 2003, 90, 363–374. [CrossRef]
- Martin, T. J.; Procházka, K.; Munk, P.; Webber, S. E. pH-Dependent Micellization of Poly(2-vinylpyridine)-block-poly(ethylene oxide). Macromolecules 1996, 29, 6071–6073. [CrossRef]
- Lee, A. S.; Gast, A. P.; Bütün, V.; Armes, S. P. Characterizing the structure of pH dependent polyelectrolyte block copolymer micelles. Macromolecules 1999, 32, 4302–4310. [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Liu, S. Y.; Armes, S. P.; Billingham, N. C. Solubilization and controlled release of a hydrophobic drug using novel micelle-forming ABC triblock copolymers. Biomacromolecules 2003, 4, 1636–1645. [CrossRef]
- Na, K.; Bae, Y. H. Self-assembled hydrogel nanoparticles responsive to tumor extracellular pH from pullulan derivative/sulfonamide conjugate: characterization, aggregation, and adriamycin release in vitro. Pharm. Res. 2002, 19, 681–688. [CrossRef]
- Na, K.; Lee, K. H.; Bae, Y. H. pH-sensitivity and pH-dependent interior structural change of self-assembled hydrogel nanoparticles of pullulan acetate/oligo-sulfonamide conjugate. J. Control. Release 2004, 97, 513–525. [CrossRef]
- Giacomelli, C.; Le Men, L.; Borsali, R.; Lai-Kee-Him, J.; Brisson, A.; Armes, S. P.; Lewis, A. L. Phosphorylcholine-based pH-responsive diblock copolymer micelles as drug delivery vehicles: light scattering, electron microscopy, and fluorescence experiments. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 817–828.
- Licciardi, M.; Giammona, G.; Du, J.; Armes, S. P.; Tang, Y.; Lewis, A. L. New folate-functionalized biocompatible block copolymer micelles as potential anti-cancer drug delivery systems. Polymer 2006, 47, 2946–2955. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Ravikumar, M. N.; Domb, A. J. Biodegradable block copolymers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 53, 23–44. [CrossRef]
- Zweers, M. L.; Engbers, G. H.; Grijpma, D. W.; Feijen, J. In vitro degradation of nanoparticles prepared from polymers based on DL-lactide, glycolide and poly(ethylene oxide). J Control. Release 2004, 100, 347–356. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Cao, Y.; Ge, H.; Jiang, X.; Yang, C. Degradation behavior of poly(epsilon-caprolactone)-b-poly(ethylene glycol)-b-poly(epsilon-caprolactone) micelles in aqueous solution. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 1756–1762. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carstens, M. G.; van Nostrum, C. F.; Verrijk, R.; de Leede, L. G.; Crommelin, D. J.; Hennink, W. E. A mechanistic study on the chemical and enzymatic degradation of PEG-Oligo(epsilon-caprolactone) micelles. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 97, 506–518. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, Y.; Discher, D. E. Hydrolytic degradation of poly(ethylene oxide)-block-polycaprolactone worm micelles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 12780–12781. [CrossRef]
- De Jong, S. J.; Arias, E. R.; Rijkers, D. T. S., van Nostrum, C. F.; Kettenes-van den Bosch, J. J.; Hennink, W. E. New insights into the hydrolytic degradation of poly (lactic acid): Participation of the alcohol terminus. Polymer 2001, 42, 2795–2802. [CrossRef]
- Heller, J.; Barr, J. Poly(ortho esters)--from concept to reality. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 1625–1632. [CrossRef]
- Heller J.; Barr, J.; Ng, S. Y, Abdellauoi, K. S, Gurny R. Poly(ortho esters): synthesis, characterization, properties and uses. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2002, 54, 1015–1039. [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Discher, D. E. Visualization of degradable worm micelle breakdown in relation to drug release. Polymer 2006, 47, 2519–2525. [CrossRef]
- Gillies, E. R.; Frechet, J. M. A new approach towards acid sensitive copolymer micelles for drug delivery. Chem. Comm. 2003, 0, 1640–1641.
- Hrubý, M.; Konák, C.; Ulbrich, K. Polymeric micellar pH-sensitive drug delivery system for doxorubicin. J. Control. Release 2005, 103, 137–148. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillies, E. R.; Jonsson, T. B.; Fréchet, J. M. Stimuli-responsive supramolecular assemblies of linear-dendritic copolymers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 11936–11943. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Guan, H,; Chen, X.; Lu, C.; Chen, L.; Hu, X.; Shi, Q.; Jing, X. A novel polymer-paclitaxel conjugate based on amphiphilic triblock copolymer. J. Control. Release 2007, 117, 210–216. [CrossRef]
- Gan, Z.; Jim, T. F.; Li, M.; Yuer, Z.; Wang, S.; Wu, C. Enzymatic Biodegradation of Poly(ethylene oxide-b-ε-caprolactone) Diblock Copolymer and Its Potential Biomedical Applications. Macromolecules 1999, 32, 590–594. [CrossRef]
- Akagi, T.; Higashi, M.; Kaneko, T.; Kida, T.; Akashi, M. Hydrolytic and enzymatic degradation of nanoparticles based on amphiphilic poly(gamma-glutamic acid)-graft-L-phenylalanine copolymers. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 297–303. [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Basu, S.; Thayumanavan, S. Simultaneous and reversible functionalization of copolymers for biological applications. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 5595–5597. [CrossRef]
- Kakizawa, Y.; Harada, A.; Kataoka, K. Glutathione-sensitive stabilization of block copolymer micelles composed of antisense DNA and thiolated poly(ethylene glycol)-block-poly(L-lysine): a potential carrier for systemic delivery of antisense DNA. Biomacromolecules 2001, 2, 491–497. [CrossRef]
- Anton, P.; Heinze, J.; Laschewsky, A. Redox-active monomeric and polymeric surfactants. Langmuir 1993, 9, 77–85. [CrossRef]
- Takeoka, Y.; Aoki, T.; Sanui, K.; Ogata, N.; Yokoyama, M.; Okano, T.; Sakurai, Y.; Watanabe, M. Electrochemical control of drug release from redox-active micelles. J. Control. Release 1995, 33, 79–87. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Tong, X.; Zhao, Y. A new design for light-breakable polymer micelles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 8290–8291. [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, A. P.; Mynar, J. L.; Ma, Y.; Fleming, G. R.; Fréchet, J. M. Synthetic micelle sensitive to IR light via a two-photon process. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 9952–9953. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, X.; Wang, G.; Soldera, A.; Zhao, Y. How can azobenzene block copolymer vesicles be dissociated and reformed by light? J. Phys. Chem. B. 2005, 109, 20281–20287. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konak, C.; Rathi, R. C.; Kopeckova, P.; Kopecek, J. Photoassociation of water-soluble copolymers containing photochromic spirobenzopyran moieties. Polym. Adv. Technol. 1998, 9, 641–648. [CrossRef]
- Kono, K.; Nishihara, Y.; Takagishi, T. Photoresponsive permeability of polyelectrolyte complex capsule membrane containing triphenylmethane leucohydroxide residues. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1995, 56, 707–713. [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z. G.; Fain, H. D.; Rapoport, N. Controlled and targeted tumor chemotherapy by micellar-encapsulated drug and ultrasound. J. Control. Release 2005, 102, 203–222. [CrossRef]
- Rapoport, N.; Pitt, W. G.; Sun, H.; Nelson, J. L. Drug delivery in polymeric micelles: from in vitro to in vivo. J. Control. Release 2003, 91, 85–95. [CrossRef]
- Rapoport, N. Y.; Christensen, D. A.; Fain, H. D.; Barrows, L.; Gao, Z. Ultrasound-triggered drug targeting of tumors in vitro and in vivo. Ultrasonics 2004, 42, 943–950. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecommandoux, S.; Sandre, O.; Checot, F.; Perzynski, R. Smart hybrid magnetic self-assembled micelles and hollow capsules. Prog. Solid State Chem. 2006, 34, 171–179. [CrossRef]
- Lecommandoux, S.; Sandre, O.; Checot, F.; Rodriguez-Hernandez, J.; Perzynski, R. Self- assemblies of magnetic nanoparticles and di-block copolymers: Magnetic micelles and vesicles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2006, 300, 71–74. [CrossRef]
- Liu, S. Q.; Wiradharma, N.; Gao, S. J.; Tong, Y. W.; Yang, Y. Y. Bio-functional micelles self-assembled from a folate-conjugated block copolymer for targeted intracellular delivery of anticancer drugs. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 1423–1433. [CrossRef]
- Soppimath, K. S.; Tan, DC-W.; Yang, Y-Y. pH-triggered thermally responsive polymer core-shell nanoparticles for drug delivery. Adv. Mater. 2005, 17, 318–323. [CrossRef]
- Liu, X-M.; Wang, L-S.; Wang, L.; Huang, J.; He, C. The effect of salt and pH on the phase-transition behaviors of temperature-sensitive copolymers based on N-isopropylacrylamide. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 5659–5666. [CrossRef]
- Mertoglu, M.; Garnier, S.; Laschewsky, A.; Skrabania, K.; Storsberg, J. Stimuli responsive amphiphilic block copolymers for aqueous media synthesised via reversible addition fragmentation chain transfer polymerisation (RAFT). Polymer 2005, 46, 7726–7740. [CrossRef]
- Pişkin E. Molecularly designed water soluble, intelligent, nanosize polymeric carriers. Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 277, 105–118. [CrossRef]
- Salgado-Rodriguez, R.; Licea-Claverie, A.; Arndt, K. F. Random copolymers of N- isopropylacrylamide and methacrylic acid monomers with hydrophobic spacers: pH- tunable temperature sensitive materials. Eur. Polym. J. 2004, 40, 1931–1946. [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Hoffman, A. S.; Stayton, P. S. Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-propylacrylic acid) copolymers that respond sharply to temperature and pH. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 1381–1385. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B. H.; Vernon, B. Copolymers of N-isopropylacrylamide HEMA-lactate and acrylic acid with time-dependent lower critical solution temperature as a bioresorbable carrier. Polym. Int. 2005, 54, 418–422. [CrossRef]
- Neradovic, D.; Hinrichs, W. L. J.; Kettenes-van den Bosch, J. J.; Hennink, W. E. Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) with hydrolyzable lactic acid ester side groups: a new type of thermosensitive polymer. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 1999, 20, 577–581. [CrossRef]
- Shah, S. S.; Wertheim, J.; Wang, C. T.; Pitt, C. G. Polymer-drug conjugates: manipulating drug delivery kinetics using model LCST systems. J. Control. Release 1997, 45, 95–101. [CrossRef]
- Soga, O.; van Nostrum, C. F.; Fens, M.; Rijcken, C. J.; Schiffelers, R. M.; Storm, G.; Hennink, W. E. Thermosensitive and biodegradable polymeric micelles for paclitaxel delivery. J. Control. Release 2005, 103, 341–353.
- Cui, Z.; Lee, B. H.; Vernon, B. L. New hydrolysis-dependent thermosensitive polymer for an injectable degradable system. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 1280–1286. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hruby, M.; Kueka, J.; Lebeda, O.; Mackova, H.; Babie, M.; Kooak, E.; Studenovsky, M.; Sikora, A.; Kozempel, J.; Ulbrich, K. New bioerodable thermoresponsive polymers for possible radiotherapeutic applications. J. Control. Release 2007, 119, 25–33.
- Huang, X.; Rong, F. D.; Li, J. Z. Novel acid-labile, thermoresponsive poly(methacrylamide)s with pendent ortho ester moieties. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2007, 28, 597–603. [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, A. E.; Eremeev, N. L.; Wahlund, P-O.; Galaev, I. Y.; Mattiasson, B. Photosensitive copolymer of N-isopropylacrylamide and methacryloyl derivative of spyrobenzopyran. Polymer 2002, 43, 3819–3823. [CrossRef]
- Laschewsky, A.; Rekai, E. D. Photochemical modification of the lower critical solution temperature of cinnamoylated poly(N-2-hydropropylmethacrylamide) in water. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2000, 21, 937–940. [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, K.; Sono, K. Characterization of photo- and thermoresponsible amphiphilic copolymers having azobenzene moieties as side groups. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2000, 81, 3056–3063.
- Ravi, P.; Sin, S. L.; Gan, L. H.; Gan, Y. Y.; Tam, K. C.; Xia, X. L.; Hu, X. New water soluble azobenzene- containing diblock copolymers: synthesis and aggregation behavior. Polymer 2005, 46, 137–146. [CrossRef]
- 694. Desponds, A.; Freitag, R. Synthesis and characterization of photoresponsive N- isopropylacrylamide cotelomers. Langmuir 2003, 19, 6261–6270.
- 695. Szczubialka, K.; Moczek, L.; Blaskiewicz, S.; Nowakowska, M. Photocrosslinkable smart terpolymers responding to pH, temperature and ionic strength. J. Polym. Sci., Part A: Polym. Chem. 2004, 42, 3879–3886.
- Bütün, V.; Billingham, N. C.; Armes, S. P. Unusual Aggregation Behavior of a Novel Tertiary Amine Methacrylate-Based Diblock Copolymer: Formation of Micelles and Reverse Micelles in Aqueous Solution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 11818–11819. [CrossRef]
- Bütün, V.; Liu, S.; Weaver, J. V. M; Bories-Azeau, X.; Cai, Y.; Armes, S. P. A Brief Review of “Schizophrenic” Block Copolymers React. Funct. Polym. 2006, 66, 157–165.
- Katayama, Y.; Sonoda, T.; Maeda, M. A polymer micelle responding to the protein kinase A signal. Macromolecules 2001, 34, 8569–8573. [CrossRef]
- Wickline, S. A.; Lanza, G. M. Nanotechnology for molecular imaging and targeted therapy. Circulation 2003, 107, 1092–1095. [CrossRef]
- Trubetskoy, V. S.; Frank-Kamenetsky, M. D.; Whiteman, K. R.; Wolf, G. L.; Torchilin, V. P. Stable polymeric micelles: lymphangiographic contrast media for gamma scintigraphy and magnetic resonance imaging. Acad. Radiol. 1996, 3, 232–238. [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, H.; Nagasaki, Y.; Kataoka, K. PEGylated nanoparticles for biological and pharmaceutical applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2003, 55, 403–419. [CrossRef]
- Ai, H.; Flask, C.; Weinberg, B.; Shuai, X.; Pagel, M. D.; Farrell, D.; Duerk, J.; Gao, J. Magnetite-loaded polymeric micelles as ultrasensitive magnetic-resonance probes. Adv. Mater. 2005, 17, 1949–1952. [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, E.; Makino, K.; Okano, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Yokoyama, M. A polymeric micelle MRI contrast agent with changeable relaxivity. J. Control. Release 2006, 114, 325–333. [CrossRef]
- Yoon, T. J.; Kim, J. S.; Kim, B. G.; Yu, K. N.; Cho, M. H.; Lee, J. K. Multifunctional nanoparticles possessing a "magnetic motor effect" for drug or gene delivery. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2005, 44, 1068–1071. [CrossRef]
- Kopelman, R.; Lee Koo, Y. E. L.; Philbert, M.; Moffat, B. A.; Ramachandra Reddy, G.; McConville, P.; Hall, D. E.; Chenevert, T. L.; Bhojani, M. S.; Buck, S. M.; Rehemtulla, A.; Ross, B. D. Multifunctional nanoparticle platforms for in vivo MRI enhancement and photodynamic therapy of a rat brain cancer. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2005, 293, 404–410.
- Reddy, G. R.; Bhojani, M. S.; McConville, P.; Moody, J.; Moffat, B. A.; Hall, D. E.; Kim, G.; Koo, Y. E.; Woolliscroft, M. J.; Sugai, J. V.; Johnson, T. D.; Philbert, M. A.; Kopelman, R.; Rehemtulla, A.; Ross, B. D. Vascular targeted nanoparticles for imaging and treatment of brain tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 6677–6686.
- Sahoo, S. K.; Labhasetwar, V. Nanotech approaches to drug delivery and imaging. Drug Discov. Today 2003, 8, 1112–1120. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 708. Maysinger, D.; Lovrić, J.; Eisenberg, A.; Savić, R. Fate of micelles and quantum dots in cells. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2007, 65, 270–281.
- Dubertret, B.; Skourides, P.; Norris, D. J.; Noireaux, V.; Brivanlou, A. H.; Libchaber, A. In vivo imaging of quantum dots encapsulated in phospholipid micelles. Science 2002, 298, 1759–1762. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Cui, Y.; Levenson, R. M.; Chung, L. W.; Nie, S. In vivo cancer targeting and imaging with semiconductor quantum dots. Nat. Biotechnol. 2004, 22, 969–976. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamaguchi, T.; Kato, K.; Yasui, H.; Morizane, C.; Ikeda, M.; Ueno, H.; Muro, K.; Yamada, Y.; Okusaka, T.; Shirao, K.; Shimada, Y.; Nakahama, H.; Matsumura, Y. A phase I and pharmacokinetic study of NK105, a paclitaxel-incorporating micellar nanoparticle formulation. Br. J. Cancer 2007, 97, 170–176.
- Doncom, K. E. B.; Blackman, L. D.; Wright, D. B.; Gibson, M. I.; O'Reilly, R. K. Dispersity effects in polymer self-assemblies:a matter of hierarchical control. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 4119–4134. [CrossRef]
- Israelachvili, J. N.; Mitchell, D. J.; Ninham, B. W. Theory of self-assembly of lipid bilayers and vesicles. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1977, 470, 185–201. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tritschler, U.; Pearce, S.; Gwyther, J.; Whittell, G. R.; Manners, I. 50th Anniversary Perspective: Functional Nanoparticles from the Solution Self-Assembly of Block Copolymers. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 3439–3463. [CrossRef]
- 715. Wyman, I. W.; Liu, G. Micellar structures of linear triblock terpolymers: Three blocks but many possibilities. Polymer 2013, 54, 54–1950.
- 716. Gröschel, A. H.; Müller, A. H. Self-assembly concepts for multicompartment nanostructures. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 7–11841.
- Mai, Y.; Eisenberg, A. Self-Assembly of Block Copolymers. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 5969–5985. [CrossRef]
- Lin, P. C.; Lin, S.; Wang, P. C.; Sridhar, R. Techniques for physicochemical characterization of nanomaterials. Biotechnol. Adv. 2014, 32, 711–726. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patterson, J. P.; Robin, M. P.; Chassenieux, C.; Colombani, O.; O'Reilly, R. K. The analysis of solution self-assembled polymeric nanomaterials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 2412–2425. [CrossRef]
- Epps, T. H., III; O’Reilly, R. K. Block copolymers: controlling nanostructure to generate functional materials – synthesis, characterization, and engineering. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 1674–1689. [CrossRef]
- 721. Agrahari, V.; Agrahari, V. Advances and applications of block-copolymer-based nanoformulations. Drug. Discov. Today. 2018, 23, 1139–1151.
- Zhulina, E. B.; Borisov, O. V. Theory of Block Polymer Micelles: Recent Advances and Current Challenges. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 4429–4440. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Lin, J. P.; Wang, L. Q.; Xu, Z. W. Theoretical modeling and simulations of self-assembly of copolymers in solution. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2017, 75, 1–30. [CrossRef]
- 724. Voets, I. K.; van der Burgh, S.; Farago, B.; Fokkink, R.; Kovacevic, D.; Hellweg, T.; de Keizer, A.; Cohen Stuart, M. A. Electrostatically driven coassembly of a diblock copolymer and an oppositely charged homopolymer in aqueous solutions. Macromolecules 2007, 40, 8476–8482.
- Zhulina, E. B.; Adam, M.; LaRue, I.; Sheiko, S. S.; Rubinstein, M. Diblock copolymer micelles in a dilute solution. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 5330–5351. [CrossRef]
- Borisov, O.; Zhulina, E. Effect of salt on self-assembly in charged block copolymer micelles. Macromolecules 2002, 35, 4472–4480. [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Liu, S. Emerging trends in solution self-assembly of block copolymers. Polymer 2020, 207, 122914. [CrossRef]
- Jiao, W.; Yang, H.; Wu, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhang, W. Self-assembled block polymer aggregates in selective solution: controllable morphology transitions and their applications in drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2020, 17, 947–961. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangelov, S.; Pispas, S. Polymer and Polymer-Hybrid Nanoparticles: From Synthesis to Biomedical Applications, Ed.; CRC Press: Taylor and Francis Group, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- 730. Crassous, J. J.; Schurtenberger, P.; Ballauff, M.; Mihut, A. M. Design of Block. Copolymer Micelles via Crystallization. Polymer 2015, 62, 62–A1.
- Foster, J. C.; Varlas, S.; Couturaud, B.; Coe, Z.; O'Reilly, R. K. Getting into Shape: Reflections on a New Generation of Cylindrical Nanostructures’ Self-Assembly Using Polymer Building Blocks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 2742–2753. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 732. Ganda, S.; Stenzel, M.H. Concepts, fabrication methods and applications of living crystallization-driven self-assembly of block copolymers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2020, 101, 101195.
- 733. MacFarlane, L.; Zhao, C.; Cai, J.; Qiu, H.; Manners, I. Emerging applications for living crystallization-driven self-assembly. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 4661–4682.
- Qiu, H.; Gao, Y.; Du, V. A.; Harniman, R.; Winnik. M. A.; Manners, I. Branched Micelles by Living Crystallization-Driven Block Copolymer Self-Assembly under Kinetic Control. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 2375–2385. [CrossRef]
- 735. Hayward D. W. Gilroy J. B. Rupar P. A. Chabanne L. Pizzey C. Winnik M. A. Whittell G. R. Manners I. Richardson R. M. Tailored assemblies of block copolymers in solution: it is all about the process. Macromolecules, 2015; 48 (5), 1579-1591.
- Song, S.; Liu, X.; Nikbin, E.; Howe, J. Y.; Yu, Q.; Manners, I.; Winnik, M. A. Uniform 1D Micelles and Patchy & Block Comicelles via Scalable, One-Step Crystallization-Driven Block Copolymer Self-Assembly. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 6266–6280.
- Gwyther, J.; Gilroy, J. B.; Rupar, P. A.; Lunn, D. J.; Kynaston, E.; Patra, S. K.; Whittell, G. R.; Winnik, M. A.; Manners, I. Dimensional Control of Block Copolymer Nanofibers with a π-Conjugated Core: Crystallization-Driven Solution Self-Assembly of Amphiphilic Poly(3-hexylthiophene)-b-poly(2-vinylpyridine). Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 9186–9197.
- Qian, J.; Li, X.; Lunn, D. J.; Gwyther, J.; Hudson, Z. M.; Kynaston, E.; Rupar, P. A.; Winnik, M. A.; Manners, I. Uniform, High Aspect Ratio Fiber-like Micelles and Block Co-micelles with a Crystalline π-Conjugated Polythiophene Core by Self-Seeding. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 4121–4124. [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wolanin, P. J.; MacFarlane, L. R.; Harniman, R. L.; Qian,J.; Gould, O. E. C.; Dane, T. G.; Rudin, J.; Cryan, M. J.; Schmaltz, T.;Frauenrath, H.; Winnik, M. A.; Faul, C. F. J.; Manners, I. Uniform Electroactive Fibre-like Micelle Nanowires for Organic Electronics. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15909/1-8 (Erratum 1).
- Karayianni M.; Pispas S. Block copolymer solution self-assembly: Recent advances, emerging trends, and applications. J. Polym. Sci. 2021, 59, 1874–1898. [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Pitto-Barry, A.; Kirby, N.; Schiller, T. L.; Sanchez, A. M.; Dyson, M. A.; Sloan, J.; Wilson, N. R.; O'Reilly, R. K.; Dove, A. P. Structural reorganization of cylindrical nanoparticles triggered by polylactide stereocomplexation. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5746.
- Pitto-Barry, A.; Kirby, N.; Dove, A. P.; O'Reilly, R. K. Expanding the scope of the crystallization-driven self-assembly of polylactide-containing polymers. Polym. Chem. 2014, 5, 1427–1436. [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Inam, M.; Jones, J. R.; Dove, A.P.; O’Reilly, R. K. Understanding the CDSA of poly(lactide) containing triblock copolymers. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 5504–5512. [CrossRef]
- 744. Coe, Z.; Weems, A.; Dove, A. P.; O’Reilly, R. K. Synthesis of Monodisperse Cylindrical Nanoparticles via Crystallization-driven Self-assembly of Biodegradable Block Copolymers. J. Vis. Exp. 2019, 20, e59772.
- Yu, W.; Foster, J. C.; Dove, A. P.; O’Reilly, R. K. Length Control of Biodegradable Fiber-Like Micelles via Tuning Solubility: A Self-Seeding Crystallization-Driven Self-Assembly of Poly(ε-caprolactone)-Containing Triblock Copolymers. Macromolecules 2020, 53, 1514–1521. [CrossRef]
- Pearce, A. K.; Wilks, T. R.; Arno, M. C.; O'Reilly, R. K. Synthesis and applications of anisotropic nanoparticles with precisely defined dimensions. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2021, 5, 21–45.
- Lefley, J.; Waldron, C.; Becer, C.R. Macromolecular design and preparation of polymersomes. Polym. Chem. 2020, 11, 7124–7136. [CrossRef]
- Palivan, C. G.; Goers, R.; Najer, A.; Zhang, X.; Car, A.; Meier, W. Bioinspired polymer vesicles and membranes for biological and medical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 377–411. [CrossRef]
- Che, H.; van Hest, J. C. M. Stimuli-responsive polymersomes and nanoreactors. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 4632–4647. [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, Z.; Jing, X.; Bellotti, A.; Gu, Z. Stimuli-Responsive Polymersomes for Biomedical Applications. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 649–673. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y. Q.; Yang, B.; Chen, S.; Du, J. Z. Polymer vesicles: Mechanism, preparation, application, and responsive behavior. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2017, 64, 1–22. [CrossRef]
- Leong, J.; Teo, J. Y.; Aakalu, V. K.; Yang, Y. Y.; Kong, H. Engineering Polymersomes for Diagnostics and Therapy. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, e1701276.
- Klermund, L.; Castiglione, K. Polymersomes as nanoreactors for preparative biocatalytic applications: current challenges and future perspectives. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 2018, 41, 1233–1246. [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Xiao, J.; Chen, S.; Sun, H.; Yang, B.; Jiang, J.; Zhou, X.; Du, J. Polymer Vesicles: Modular Platforms for Cancer Theranostics. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1705674. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yorulmaz Avsar, S.; Kyropoulou, M.; Di Leone, S.; Schoenenberger, C.-A.; Meier, W. P.; Palivan, C. G. Biomolecules turn self-assembling amphiphilic block co-polymer platforms into biomimetic interfaces. Front. Chem. 2019, 6, 645. [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, S.; Blenner, M.; Alexander-Bryant, A.; Larsen, J. Polymersomes for Therapeutic Delivery of Protein and Nucleic Acid Macromolecules: From Design to Therapeutic Applications. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 1327–1350. [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Sun, H.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, S.; Cornel, E. J.; Zhu, Y.; Du, J. Design principles, synthesis and biomedical applications of polymer vesicles with inhomogeneous membranes. J. Control. Release 2020, 326, 365–386. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, S.; Voit, B.; Gaitzsch, J. The chemistry of cross-linked polymeric vesicles and their functionalisation towards biocatalytic nanoreactors. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2021, 299, 309–324. [CrossRef]
- 759. Liarou, E.; Varlas, S.; Skoulas, D.; Tsimblouli, C.; Sereti, E.; Dimas, K.; Iatrou, H. Smart polymersomes and hydrogels from polypeptide-based polymer systems through α-amino acid N-carboxyanhydride ring-opening polymerization. From chemistry to biomedical applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2018, 83, 28–78.
- De Oliveira, H.; Thevenot, J.; Lecommandoux, S. Smart polymersomes for therapy and diagnosis: fast progress toward multifunctional biomimetic nanomedicines. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2012, 4, 525–546. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konishcheva E. Daubian D. Gaitzsch J. Meier W. Synthesis of Linear ABC Triblock Copolymers and Their Self-Assembly in Solution. Helv. Chim. Acta. 2018, 101, e1700287. [CrossRef]
- Brendel, J. C.; Schacher, F. H. Block Copolymer Self-Assemblyin Solution-Quo Vadis? Chem. - Asian J. 2018, 13, 230–239. [CrossRef]
- Lunn, D. J.; Finnegan, J. R.; Manners, I. Self-assembly of “patchy” nanoparticles: a versatile approach to functional hierarchical materials. Chem Sci. 2015, 6, 3663–3673. [CrossRef]
- Huang J.; Guo, Y.; Gu, S.; Han, G.; Duan, W.; Gao, C.; Zhang, W. Multicompartment block copolymer nanoparticles: recent advances and future perspectives. Polym. Chem. 2019, 10, 3426–3435. [CrossRef]
- Nghiem, T.-L.; Steinhaus, A., Chakroun, R., Tjaberings, S., Qiang, X., Chen, C., Tjaberings, A., Quintieri, G., Gröschel, A. H. In Comprehensive Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, Eds.; Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2019; Vol. 1-5, p 217. [Google Scholar]
- Hils, C.; Manners, I.; Schöbel, J.; Schmalz, H. Patchy Micelles with a Crystalline Core: Self-Assembly Concepts, Properties, and Applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 1481. [CrossRef]
- Nayanathara, U.; Kermaniyan, S. S.; Such, G. K. Multicompartment Polymeric Nanocarriers for Biomedical Applications. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2020, 41, e2000298. [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Lin, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L.; Cai, C. Self-Assembly of Copolymer Micelles: Higher-Level Assembly for Constructing Hierarchical Structure. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 4111–4140. [CrossRef]
- Gröschel, A. H.; Schacher, F. H.; Schmalz, H.; Borisov, O. V.; Zhulina, E. B.; Walther, A.; Müller, A. H. Precise hierarchical self-assembly of multicompartment micelles. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 710/1-10.
- Gröschel, A. H.; Walther, A.; Löbling, T. I.; Schacher, F. H.; Schmalz, H.; Müller, A. H. Guided hierarchical co-assembly of soft patchy nanoparticles. Nature 2013, 503, 247–251. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Löbling, T. I.; Borisov, O. V.; Haataja, J. S.; Ikkala, O.; Gröschel, A. H.; Müller, A. H. E. Rational design of ABC triblock terpolymer solution nanostructures with controlled patch morphology. Nat Commun 2016, 7, 12097. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Löbling, T. I.; Ikkala, O.; Gröschel, A. H.; Müller, A. H. E. Controlling Multicompartment Morphologies Using Solvent Conditions and Chemical Modification. ACS Macro Lett. 2016, 5, 1044–1048. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nghiem, T.-L.; Löbling, T. I.; Gröschel. A. H. Supracolloidal chains of patchy micelles in water. Polym. Chem. 2018, 9, 1583–1592. [CrossRef]
- Moreno, N.; Sutisna B.; Fried, E. Entropic factors and structural motifs of triblock-terpolymer-based patchy nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 22059–22069. [CrossRef]
- Moughton, A. O.; Hillmyer, M. A.; Lodge. T. P. Multicompartment Block Polymer Micelles. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 2–19. [CrossRef]
- Moughton, A. O.; Sagawa, T.; Yin, L.; Lodge, T. P.; Hillmyer, M. A. Multicompartment Micelles by Aqueous Self-Assembly of μ-A(BC) nMiktobrush Terpolymers. ACS Omega 2016, 1, 1027–1033. [CrossRef]
- Hanisch A.; Gröschel A. H.; Förtsch M.; Drechsler M.; Jinnai H.; Ruhland T. M.; Schacher F. H.; Müller A. H. E. Counterion-Mediated Hierarchical Self-Assembly of an ABC Miktoarm Star Terpolymer. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 4030–4041. [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Wu, D.; Huang, Y.; Wei, H.; Gao, Y.; Feng, X.; Yan, D.; Mai, Y. Multi-Dimensional Self-Assembly of a Dual-Responsive ABC Miktoarm Star Terpolymer. ACS Macro Lett. 2017, 6, 426–430. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, H.; Liu, J.; Kannan, S.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, F. Multicompartment nanoparticles bearing hydrophilic/hydrophobic subdomains by self-assembly of star polymers in aqueous solution. Macromolecules 2020, 54, 35–43.
- Liu, R.; Rong, Z.; Han, G.; Yang, X.; Zhang, W. Synthesis and self-assembly of star multiple block copolymer of poly (4-vinylpyridine)-block-polystyrene. Polymer 2021, 215, 123431. [CrossRef]
- Gädt, T.; Ieong, N. S.; Cambridge, G.; Winnik, M. A.; Manners, I. Complex and hierarchical micelle architectures from diblock copolymers using living, crystallization-driven polymerizations. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 144–150. [CrossRef]
- Schmelz, J.; Schmalz, H.. Corona structure on demand: Tailor-made surface compartmentalization in worm-like micelles via random cocrystallization. Polymer 2012, 53, 4333–4337. [CrossRef]
- Hudson, Z. M.; Boott, C. E.; Robinson, M. E.; Rupar, P. A.; Winnik, M. A.; Manners, I. Tailored hierarchical micelle architectures using living crystallization-driven self-assembly in two dimensions. Nat. Chem. 2014, 6, 893–898. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, H.; Cambridge, G.; Winnik, M. A.; Manners I. Multi-armed micelles and block co-micelles via crystallization-driven self-assembly with homopolymer nanocrystals as initiators. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 12180–12183. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Gao, Y.; Boott, C. E.; Winnik, M. A.; Manners, I. Non-covalent synthesis of supermicelles with complex architectures using spatially confined hydrogen-bonding interactions. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8127. [CrossRef]
- Gegenhuber, T.; Gröschel, A. H.; Löbling, T. I.; Drechsler, M.; Ehlert, S.; Förster, S.; Schmalz, H. Noncovalent Grafting of Carbon Nanotubes with Triblock Terpolymers: Toward Patchy 1D Hybrids. Macromolecules 2015, 48, 1767–1776. [CrossRef]
- Schöbel, J.; Hils, C.; Weckwerth, A.; Schlenk, M.; Bojer, C.; Stuart, M. C. A.; Breu, J.; Förster, S.; Greiner, A.; Karg, M.; Schmalz, H. Strategies for the selective loading of patchy worm-like micelles with functional nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 18257–18268. [CrossRef]
- Oliver, A. M.; Gwyther, J.; Winnik, M. A.; Manners, I. Cylindrical Micelles with “patchy” Coronas from the Crystallization-Driven Self-Assembly of ABC Triblock Terpolymers with a Crystallizable Central Polyferrocenyldimethylsilane Segment. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 222–231. [CrossRef]
- Oliver, A. M.; Spontak, R. J.; Manners, I. Solution self-assembly of ABC triblock terpolymers with a central crystallizable poly(ferrocenyldimethylsilane) core-forming segment. Polymer Chemistry 2019, 10, 2559–2569. [CrossRef]
- Finnegan, J. R.; Lunn, D. J.; Gould, O. E.; Hudson, Z. M.; Whittell, G. R.; Winnik, M. A.; Manners I. Gradient crystallization-driven self-assembly: cylindrical micelles with “patchy” segmented coronas via the coassembly of linear and brush block copolymers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 13835–13844.
- Cruz, M.; Xu, J.; Yu, Q.; Guerin, G.; Manners, I.; Winnik, M. A. Visualizing Nanoscale Coronal Segregation In Rod-Like Micelles Formed By Co-Assembly Of Binary Block Copolymer Blends. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2018, 39, 1800397. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Zhou, H.; Yu, Q.; Manners, I.; Winnik, M. A. Competitive Self-Assembly Kinetics as a Route to Controlling the Morphology of Core-Crystalline Cylindrical Micelles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 2619–2638. [CrossRef]
- Atanase, L. I.; Riess, G. Self-Assembly of Block and Graft Copolymers in Organic Solvents: An Overview of Recent Advances. Polymers (Basel) 2018, 10, 62. [CrossRef]
- Daubian, D.; Gaitzsch, J.; Meier, W. Synthesis and complex self-assembly of amphiphilic block copolymers with a branched hydrophobic poly(2-oxazoline) into multicompartment micelles, pseudo-vesicles and yolk/shell nanoparticles. Polym. Chem. 2020, 11, 1237–1248. [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-L.; Jin, R.-H. Synthesis and self-assembly of amphiphilic comb-copolymers possessing polyethyleneimine and its derivatives: Site-selective formation of loop-cluster covered vesicles and flower micelles. Polymer 2021, 212, 123289. [CrossRef]
- Qiang, X.; Chakroun, R.; Janoszka, N.; Gröschel, A. H. Self-assembly of Multiblock Copolymers. Isr. J. Chem. 2019, 59, 945–958. [CrossRef]
- Haque, F. M.; Grayson, S. M. The synthesis, properties and potential applications of cyclic polymers. Nat Chem. 2020, 12, 433–444. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varlas, S.; Lawrenson, S. B.; Arkinstall, L. A.; O’Reilly, R. K.; Foster, J. C. Self-assembled nanostructures from amphiphilic block copolymers prepared via ring-opening metathesis polymerization (ROMP). Prog. Polym. Sci. 2020, 107, 101278. [CrossRef]
- Nam, J.; Kim, Y. J.; Kim, J. G.; Seo, M. Self-Assembly of Monolayer Vesicles via Backbone-Shiftable Synthesis of Janus Core-Shell Bottlebrush Polymer. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 9484–9494. [CrossRef]
- 800. Shao, F.; Wang, Y.; Tonge, C. M.; Sauvé, E. R.; Hudson, Z. M. Self-assembly of luminescent triblock bottlebrush copolymers in solution Polym. Chem. 2020, 11, 1062–1071.
- Ma, H.; Kim, K.T.. Self-assembly of bottlebrush block copolymers into triply periodic nanostructures in a dilute solution. Macromolecules 2020, 53, 711–718. [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, E.; Tyler Womble, C.; & Weck, M. Synthesis and aqueous self-assembly of ABCD bottlebrush block copolymers. Macromolecules 2020, 53, 9018–9025.
- Kim, S.; Lee, S.; Choi, S.-H.; Char, K. Chain Exchange Kinetics of Bottlebrush Block Copolymer Micelles. Macromolecules 2021, 54, 4739–4746. [CrossRef]
- Kepola, E. J.; Loizou, E.; Patrickios, C. S.; Leontidis, E.; Voutouri, C.; Stylianopoulos, T.; Schweins, R.; Gradzielski, M.; Krumm, C.; Tiller, J. C.; Kushnir, M.; Wesdemiotis, C. Amphiphilic Polymer Conetworks Based on End-linked “Core-first” Star Block Copolymers: Structure Formation with Long-range Order. ACS Macro Lett. 2015, 4, 1163–1168.
- Varnava, C. K.; Patrickios, C. S. Model Amphiphilic Polymer Conetworks in Water: Prediction of Their Ability for Oil Solubilization. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 4721–4738. [CrossRef]
- Gröschel, A. H.; Walther, A. Block copolymer micelles with inverted morphologies. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 10992–10994. [CrossRef]
- Ha, S.; La, Y.; Kim, K. T. Polymer Cubosomes: Infinite Cubic Mazes and Possibilities. Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 620–631. [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Wang, V.; Kim, K. T. Block Copolymers Composed of Main-Chain Cyclic Polymers: Morphology Transition and Covalent Stabilization of Self-Assembled Nanostructures via Intra- and Interchain Cyclization of Styrene-co-isoprene Blocks. Macromolecules 2020, 53, 10725–10733. [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.; Lowe, A. B.; Roth, P. J. Stimulus-Responsive Nanoparticles and Associated (Reversible) Polymorphism via Polymerization Induced Self-assembly (PISA). Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2017, 38, 1600528. [CrossRef]
- Penfold, N. J. W.; Yeow, J.; Boyer, C.; Armes, S. P. Emerging Trends in Polymerization-Induced Self-Assembly. ACS Macro Lett. 2019, 8, 1029–1054. [CrossRef]
- Canning, S. L.; Smith, G. N.; Armes, S. P. A Critical Appraisal of RAFT-Mediated Polymerization-Induced Self-Assembly. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 1985–2001. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Agosto, F.; Rieger, J.; Lansalot, M. RAFT-Mediated Polymerization-Induced Self-Assembly. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2020, 59, 8368–8392. [CrossRef]
- Varlas, S.; Foster, J. C.; O'Reilly, R. K. Ring-opening metathesis polymerization-induced self-assembly (ROMPISA). Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 9066–9071. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Hong, C. Y.; Pan, C. Y. Polymerization techniques in polymerization-induced self-assembly (PISA). Polym. Chem. 2020, 11, 3673–3689. [CrossRef]
- Boott, C. E.; Gwyther, J.; Harniman, R. L.; Hayward, D. W.; Manners, I. Scalable and uniform 1D nanoparticles by synchronous polymerization, crystallization and self-assembly. Nat. Chem. 2017, 9, 785–792. [CrossRef]
- Oliver, A. M.; Gwyther, J.; Boott, C. E.; Davis, S.; Pearce, S.; Manners, I. Scalable Fiber-like Micelles and Block Co-micelles by Polymerization-Induced Crystallization-Driven Self-Assembly. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 18104–18114. [CrossRef]
- Sha, Y.; Rahman, M. A.; Zhu, T.; Cha, Y.; McAlister, C. W.; Tang, C. ROMPI-CDSA: ring-opening metathesis polymerization-induced crystallization-driven self-assembly of metallo-block copolymers. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 9782–9787. [CrossRef]
- Hurst P. J.; Rakowski A. M.; Patterson J. P. Ring-Opening Polymerization-Induced Crystallization-Driven Self-Assembly of Poly-L-Lactide-Block-Polyethylene Glycol Block Copolymers (ROPI-CDSA. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4690. [CrossRef]
- Yeow, J.; Boyer, C. Photoinitiated Polymerization-Induced Self-Assembly (Photo-PISA): New Insights and Opportunities. Adv. Sci. (Weinh) 2017, 4, 1700137. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.-J.; Hong, C.-Y.; Pan, C.-Y. Polymerization-Induced Self-Assembly of Functionalized Block Copolymer Nanoparticles and Their Application in Drug Delivery. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2019, 40, 1800279. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearce S.; Perez-Mercader J. PISA: Construction of Self-Organized and Self-Assembled Functional Vesicular Structures. Polym. Chem. 2021, 12, 29–49. [CrossRef]
- 822. Phan, H.; Taresco, V.; Penelle, J.; Couturaud, B. Polymerisation-induced self-assembly (PISA) as a straightforward formulation strategy for stimuli-responsive drug delivery systems and biomaterials: Recent advances. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 38–50.
- Zhang, W. J.; Kadirkhanov, J.; Wang, C. H.; Ding, S. G.; Hong, C. Y.; Wang, F.; You, Y. Z. Polymerization-induced self-assembly for the fabrication of polymeric nano-objects with enhanced structural stability by cross-linking. Polym. Chem. 2020, 11, 3654–3672. [CrossRef]
- El Jundi, A.; Buwalda, S. J.; Bakkour, Y.; Garric, X.; Nottelet, B. Double hydrophilic block copolymers self-assemblies in biomedical applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 283, 102213. [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.; Eyler, A., Tabandeh, S., Leon, L. Electrostatically driven self-assembled nanoparticles and coatings. In Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications, Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 349–370. [Google Scholar]
- Ku, K. H. Responsive Nanostructured Polymer Particles. Polymers 2021, 13, 273. [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Qiang, X.; Hils, C.; Schmalz, H.; Gröschel, A. H. Frustrated Microparticle Morphologies of a Semicrystalline Triblock Terpolymer in 3D Soft Confinement. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 1111–1120. [CrossRef]
- Qiang, X.; Steinhaus, A.; Chen, C.; Chakroun, R.; Gröschel, A. H. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 7122–7126.
- Steinhaus, A.; Chakroun, R.; Müllner, M.; Nghiem, T. L.; Hildebrandt, M.; Gröschel, A. H. Confinement Assembly of ABC Triblock Terpolymers for the High-Yield Synthesis of Janus Nanorings. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 6269–6278. [CrossRef]
- Tamate, R.; Hashimoto, K.; Ueki, T.; Watanabe, M. Block copolymer self-assembly in ionic liquids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 25123–25139. [CrossRef]
- Ghorbanizamani, F.; Moulahoum, H.; Zihnioglu, F.; Timur, S. Self-assembled block copolymers in ionic liquids: Recent advances and practical applications. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 323, 115076. [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Li, Z.; Simone, P.; Lodge, T. P. Self-assembly of block copolymer micelles in an ionic liquid. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 2745–2750. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Ma, Y.; Lodge, T. P. Exchange Kinetics for a Single Block Copolymer in Micelles of Two Different Sizes. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 2312–2320. [CrossRef]
- Bhushan, V.; Heitz, M. P.; Baker, G. A.; Pandey, S. Ionic Liquid-Controlled Shape Transformation of Spherical to Nonspherical Polymersomes via Hierarchical Self-Assembly of a Diblock Copolymer. Langmuir 2021, 37, 5081–5088. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Ma, Y.; Alexandridis, P. Comparison of ionic liquid and salt effects on the thermodynamics of amphiphile micellization in water. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 559, 159–168. [CrossRef]
- Rideau, E.; Dimova, R.; Schwille, P.; Wurm F. R.; Landfester, K. Liposomes and polymersomes: A comparative review towards cell mimicking. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 8572–8610. [CrossRef]
- Kita-Tokarczyk, K.; Grumelard, J.; Haefele, T.; Meier, W. Block copolymer vesicles-using concepts from polymer chemistry to mimic biomembranes. Polymer 2005, 46, 3540–3563. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhao, H.; Ming, T.; Wang, J.; Wu, C. Nanopore extrusion-induced transition from spherical to cylindrical block copolymer micelles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 16650–16651. [CrossRef]
- Caire da Silva, L.; Cao, S.; Landfester, K. Bursting and Reassembly of Giant Double Emulsion Drops Form Polymer Vesicles. ACS Macro Lett. 2021, 10, 401–405. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chariou, P. L.; Ortega-Rivera, O. A.; Steinmetz, N. F. Nanocarriers for the Delivery of Medical, Veterinary, and Agricultural Active Ingredients. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 2678–2701. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rameez, S.; Alosta, H.; Palmer, A. F. Biocompatible and biodegradable polymersome encapsulated hemoglobin: a potential oxygen carrier. Bioconjug. Chem. 2008, 19, 1025–1032. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishimura, A.; Koide, A.; Osada, K.; Yamasaki, Y.; Kataoka, K. Encapsulation of myoglobin in PEGylated polyion complex vesicles made from a pair of oppositely charged block ionomers: a physiologically available oxygen carrier. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2007, 46, 6085–6088. [CrossRef]
- Forster, S.; Antonietti, M. Amphiphilic block copolymers in structure- controlled nanomaterials hybrids. Adv. Mater. 1998, 10, 195–217. [CrossRef]
- Hadjichristidis, N.; Pispas, S., Ed.; Floudas, G. Block copolymers: synthetic strategies, physical properties, and applications. John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, New Jersey, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Gohy, J. F.; Antoun, S.; Jerome, R. pH-dependent micellization of poly(2- vinylpyridine)-block-((dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate) diblock copolymers. Macromolecules 2001, 34, 7435–7440. [CrossRef]
- Antoun, S.; Gohy, J. F.; Jerome, R. Micellization of quaternized poly(2-(dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate)-block-poly(methyl methacrylate) copolymers in water. Polymer 2001, 42, 3641–3648. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Winnik, A.; Manners, I. Synthesis and self assembly of poly(ferrocenyldimethylsilane-b-dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate): toward water-soluble cylinders with an organometallic core. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 1928–1935. [CrossRef]
- Valint Jr, P. L.; Bock, J. Synthesis and characterization of hydrophobically associating block copolymers. Macromolecules 1988, 21, 175–179. [CrossRef]
- Guenoun, P.; Davis, H. T.; Tirrell, M.; Mays, J. W. Aqueous micellar solutions of hydrophobically modified polyelectrolytes. Macromolecules 1996, 29, 3965–3969. [CrossRef]
- Yang, J. C.; Jablonsky, M. J.; Mays, J. W. NMR and FT-IR studies of sulfonated styrene-based homopolymers and copolymers. Polymer 2002, 43, 5125–5132. [CrossRef]
- Muller, F.; Delsanti, M.; Auvray, L.; Yang, J.; Chen, Y. J.; Mays, J. W.; Demé, Tirrell, M.; Guenoun, P. Ordering of urchin-like charged copolymer micelles: electrostatic, packing and polyelectrolyte correlations. Eur. Phys. J. E 2000, 3, 45–53. [CrossRef]
- Muller, F.; Fontaine, P.; Delsanti, M.; Belloni, L.; Yang, J.; Chen, Y. J.; Mays, J. W.; Lesieur, P.; Tirrell, M.; Guenoun, P. Counterion distribution in a spherical charged sparse brush. Eur. Phys. J. E 2001, 6, 109–115.
- Muller, F.; Guenoun, P.; Delsanti, M.; Demé, B.; Auvray, L.; Yang, J.; Mays, J. W. Spherical polyelectrolyte block copolymer micelles: structural change in presence of monovalent salt. Eur. Phys. J. E Soft Matter 2004, 15, 465–472. [CrossRef]
- Szczubialka, K.; Ishikawa, K.; Morishima, Y. Micelle formationof diblock copolymers of styrene and sulfonated isoprene inaqueous solution. Langmuir 1999, 15, 454–462. [CrossRef]
- Tauer, K.; Zimmermann, A.; Schlaad, H. New reactive block copolymers as stabilizers in emulsion polymerization. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2002, 203, 319–327. [CrossRef]
- Justynska, J.; Hordyjewucz, Z.; Schlaad, H. Toward a toolbox of functional block copolymers via free-radical addition of mercaptans. Polymer 2005, 46, 12057–12064. [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Discher, D.; Justynska, J.; Schladd, H. Grafting short peptides onto polybutadiene-blockpoly(ethylene oxide): a platform for self- assembling hybrid amphiphiles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 118, 7578–7581.
- Uchman, M.; Procházka, K.; Stepánek, M.; Mountrichas, G.; Pispas, S.; Spírková, M.; Walther, A. pH-dependent self-assembly of polystyrene-block-poly((sulfamate-carboxylate)isoprene) copolymer in aqueous media. Langmuir 2008, 24, 12017–12025. [CrossRef]
- Pispas, S.; Siakali-Kioulafa, E.; Hadjichristidis, N.; Mavromoustakos, T. Block copolymers with crystalline/amorphous, crystalline/ polyelectrolyte and amorphous/polyelectrolyte blocks. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2002, 203, 1317–1327. [CrossRef]
- Prochazka, K.; Kiserow, D.; Ramireddy, C.; Tuzar, Z.; Munk, P.; Webber, S. E. Time-resolved fluorescence studies of the chain dynamics of naphthalene-labeled polystyrene-blocks-poly(methacrylic acid) micelles in aqueous media. Macromolecules 1992, 25, 454–460. [CrossRef]
- André X.; Zhang M.; Müller A. H. E. Thermo- and pH-Responsive Micelles of Poly(acrylic acid)-block-Poly(N,N-diethylacrylamide). Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2005, 26, 558–563. [CrossRef]
- Perrin, R.; Elomaa, M.; Jannasch, P. Nanostructured proton conducting polystyrene-poly(vinylphosphonic acid)block copolymers prepared via sequential anionic polymerizations. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 5146–5154. [CrossRef]
- Kuo, S. W.; Tung, P.; Chang, F. Syntheses and the study of strongly hydrogen-bonded poly(vinyphenol-b-vinylpyridine)diblock copolymer through anionic polymerization. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 9388–9395. [CrossRef]
- Kaditi, E.; Pispas, S. β-Lactam functionalized poly(isoprene-b- ethylene oxide) amphiphilic block copolymers. J. Polym. Sci. Part A: Polym. Chem. 2010, 48, 24–33. [CrossRef]
- Hrubý, M.; Koňák, Č.; Ulbrich, K. Poly(allyl glycidyl ether)-Block-Poly(ethylene oxide): A Novel Promising Polymeric Intermediate for the Preparation of Micellar Drug Delivery Systems. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2005, 95, 201–211. [CrossRef]
- Mahltig, B.; Gohy, J. F.; Antoun, S.; Jerome, R.; Stamm, M. Adsorption and structure formation of the weak polyelectrolytic diblock copolymer, PVP-b-PDMAEMA. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2002, 280, 495–502. [CrossRef]
- Fragouli, P. G.; Iatrou, H.; Hadjichristidis, N. Synthesis and characterization of linear diblock and triblock copolymers of 2-vinyl pyridine and ethylene oxide. Polymer 2002, 43, 7141–7144. [CrossRef]
- Pispas, S. Double hydrophilic block copolymer of sodium(2- sulfamate-3-carboxylate)isoprene and ethylene oxide. J. Polym. Sci Part A: Polym. Chem. 2006, 44, 606–613. [CrossRef]
- Mountrichas, G.; Pispas, S. Synthesis and pH responsive self-assembly of new double hydrophilic block copolymers. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 4767–4774. [CrossRef]
- Mountrichas, G.; Pispas, S. Novel double hydrophilic block copolymers based on poly(p-hydroxystyrene) derivatives and poly(ethylene oxide). J. Polym. Sci. Part A: Polym. Chem. 2007, 45, 5790–5799. [CrossRef]
- Kaluzynski, K., Pretula, J., Lapienis, G., Basko, M., Bartczak, Z., Dworak, A., Penczek, S. Dihydrophilic block copolymers with ionic and nonionic blocks. I. poly(ethylene oxide)-b-polyglycidol with OP(O)(OH)2, COOH, OR SO3H functions: synthesis and influence for CaCO3 crystallization. J. Polym. Sci. Part A: Polym. Chem. 2001, 39, 955–963.
- Kaditi, E.; Mountrichas, G.; Pispas, S. Amphiphilic block copolymers by a combination of anionic polymerization and selective post-polymerization functionalization. Eur. Polym. J. 2011, 47, 415–434. [CrossRef]
- 873. Alexander, S. Adsorption of chain molecules with a polar head - a scaling description. J. Phys. (Paris) 1977, 38, 38–983.
- Daoud, M.; Cotton. J. P. Star shaped polymers : a model for the conformation and its concentration dependence. J. Phys. (Paris) 1982, 43, 531–538. [CrossRef]
- Birshtein, T. M.; Zhulina, E. B. Conformations of star-branched macromolecules. Polymer 1984, 25, 1453–1461. [CrossRef]
- Willner, L.; Poppe, A.; Allgaier, J.; Monkenbusch, M.; Lindner, P.; Richter, D. Micellization of amphiphilic diblock copolymers: Corona shape and mean-field to scaling crossover. Europhys. Lett. 2000, 51, 628–634. [CrossRef]
- Jensen, G. V.; Shi, Q.; Hernansanz, M. J.; Oliveira, C. L. P.; Deen, G. R.; Almdal, K.; Pederson, J. S. Structure of PEP-PEO block copolymer micelles: Exploiting the complementarity of small-angle X-ray scattering and static light scattering. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2011, 44, 473–482. [CrossRef]
- Förster, S.; Zisenis, M.; Wenz, E.; Antonietti, M. Micellization of strongly segregated block copolymers. J. Chem. Phys. 1996, 104, 9956–9970. [CrossRef]
- Zhulina, E. B.; Birshtein, T. M.; Borisov, O. V. Curved polymer and polyelectrolyte brushes beyond the Daoud-Cotton model. Eur. Phys. J. E Soft Matter 2006, 20, 243–256. [CrossRef]
- Birshtein, T.; Lyatskaya, Yu. Theory of the Collapse-Stretching Transition of a Polymer Brush in a Mixed Solvent. Macromolecules 1994, 27, 1256–1266. [CrossRef]
- Lai, P.-Y.; Halperin, A. Polymer brushes in mixed solvents: chromatography and collapse. Macromolecules 1992, 25, 6693–6695. [CrossRef]
- Birshtein, T. M.; Zhulina, E. B.; Merkurieva, A. A. Amphiphilic polymer brush in a mixture of incompatible liquids. Macromol. Theory Simul. 2000, 9, 47–55. [CrossRef]
- Merkurieva, A. A.; Leermakers, F. A. M.; Birshtein, T. M.; Fleer, G. L.; Zhulina, E. B. Amphiphilic Polymer Brush in a Mixture of Incompatible Liquids. Numerical Self-Consistent-Field Calculations. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 1072–1081. [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, R.; Ganesh, K. Block copolymer self-assembly in selective solvents: theory of solubilization in spherical micelles. Macromolecules 1989, 22, 4312–4325. [CrossRef]
- Cogan, K. A.; Leermakers, F. A. M.; Gast, A. P. Predictions of copolymer micelle behavior in immiscible solvents. Langmuir 1992, 8, 429–436. [CrossRef]
- MacEwan, S. R.; Chilkoti, A. Elastin-like polypeptides: biomedical applications of tunable biopolymers. Biopolymers 2010, 94, 60–77. [CrossRef]
- Dreher, M. R.; Simnick, A. J.; Fischer, K.; Smith, R. J.; Patel, A.; Schmidt, M.; Chilkoti, A. Temperature triggered self-assembly of polypeptides into multivalent spherical micelles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 687–694. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trent, A.; Marullo, R.; Lin, B.; Black, M.; Tirrell, M. Structural properties of soluble peptide amphiphile micelles. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 9572–9582. [CrossRef]
- 889. Kastantin, M.; Tirrell, M. Helix Formation in the Polymer Brush. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 4977–4987.
- Gervais, M.; Gallot, B. Phase diagram and structural study of polystyrene-poly (ethylene oxide) block copolymers, 1. Systems polystyrene/poly (ethylene oxide)/diethyl phthalate. Makromol. Chem. 1973, 171, 157–178. [CrossRef]
- Lin, E. K.; Gast, A. P. Semicrystalline Diblock Copolymer Platelets in Dilute Solution. Macromolecules 1996, 29, 4432–4441. [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Hillmyer, M. A. Disklike Micelles in Water from Polyethylene-Containing Diblock Copolymers. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 3021–3028. [CrossRef]
- Schmalz, H.; Schmelz, J.; Drechsler, M.; Yuan, J.; Walther, A.; Schweimer, K.; Mihut, A. M. Thermo-Reversible Formation of Wormlike Micelles with a Microphase-Separated Corona from a Semicrystalline Triblock Terpolymer. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 3235–3242. [CrossRef]
- Schmelz, J.; Karg, M.; Hellweg, T.; Schmalz, H. General pathway toward crystalline-core micelles with tunable morphology and corona segregation. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 9523–9534. [CrossRef]
- Yu-Su, S. Y.; Sheiko, S. S.; Lee, H.-I.; Jakubowski, W.; Nese, A.; Matyjaszewski, K.; Anokhin, D.; Ivanov, D. A. Crystallization of molecular brushes with block copolymer side chains. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 9008–9017.
- DiMarzio, E. A.; Guttman, C. M.; Hoffman, J. D. Calculation of lamellar thickness in a diblock copolymer, one of whose components is crystalline. Macromolecules 1980, 13, 1194–1198. [CrossRef]
- Birshtein, T. M.; Zhulina, E. B. Scaling theory of supermolecular structures in block copolymer-solvent systems: 2. Supercrystalline structures. Polymer 1990, 31, 1312–1320. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Eisenberg, A. Multiple Morphologies of “Crew-Cut” Aggregates of Polystyrene-b-poly(acrylic acid) Block Copolymers. Science 1995, 268, 1728–1731. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Eisenberg, A. Multiple morphologies and characteristics of “crew-cut” micelle-like aggregates of polystyrene-b-poly (acrylic acid) diblock copolymers in aqueous solutions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 3168–3181. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Barlow, R. J.; Eisenberg, A. Scaling relations and coronal dimensions in aqueous block polyelectrolyte micelles. Macromolecules 1995, 28, 6055–6066. [CrossRef]
- Manning, G. J. Limiting Laws and Counterion Condensation in Polyelectrolyte Solutions I. Colligative Properties. J. Chem. Phys. 1969, 51, 924–933. [CrossRef]
- 902. Zhulina, E. B.; Borisov, O. V. Structure and interaction of weakly charged polyelectrolyte brushes: Self-consistent field theory. J. Chem. Phys. 1997, 107, 5952–5967.
- Zhulina, E. B.; Borisov, O. V. Poisson-Boltzmann theory of pH-sensitive (annealing) polyelectrolyte brush. Langmuir 2011, 27, 10615–10633. [CrossRef]
- 904. Tamashiro, M. N.; Hernández-Zapata, E.; Schorr, P. A.; Balastre, M.; Tirrell, M.; Pincus, P. Salt dependence of compression normal forces of quenched polyelectrolyte brushes, J. Chem. Phys. 2001, 115, 1960–1969.
- Lauw, Y.; Leermakers, F. A. M.; Cohen Stuart, M. A.; Borisov, O. V.; Zhulina, E. B. Coexistence of crew-cut and starlike spherical micelles composed of copolymers with an annealed polyelectrolyte block. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 3628–3641. [CrossRef]
- Marko, J. F.; Rabin, Y. Microphase separation of charged diblock copolymers: melts and solutions. Macromolecules 1992, 25, 1503–1509. [CrossRef]
- Wittmer, J.; Joanny, J.-F. Charged diblock copolymers at interfaces. Macromolecules 1993, 26, 2691–2697. [CrossRef]
- Pincus, P. Colloid stabilization with grafted polyelectrolytes. Macromolecules 1991, 24, 2912–2919. [CrossRef]
- 909. Borisov, O. V.; Birshtein, T. M.; Zhulina, E. B. Collapse of Grafted Polyelectrolyte Layer. J. Phys. II 1991, 1, 521–526.
- Borisov, O. V.; Zhulina, E. B.; Birshtein, T. M. Diagram of the states of a grafted polyelectrolyte layer. Macromolecules 1994, 27, 4795–4803. [CrossRef]
- Shusharina, N. P.; Nyrkova, I. A.; Khokhlov, A. R. Diblock copolymers with a charged block in a selective solvent: micellar structure. Macromolecules 1996, 29, 3167–3174. [CrossRef]
- Dan, N.; Tirrell, M. Self-assembly of block copolymers with a strongly charged and a hydrophobic block in a selective, polar solvent. Micelles and adsorbed layers. Macromolecules 1993, 26, 4310–4315. [CrossRef]
- Zhulina, E. B.; Borisov, O. V. Self-assembly in solution of block copolymers with annealing polyelectrolyte blocks. Macromolecules 2002, 35, 9191–9203. [CrossRef]
- Borisov, O. V.; Zhulina, E. B. Reentrant morphological transitions in copolymer micelles with pH-sensitive corona. Langmuir 2005, 21, 3229–3231. [CrossRef]
- Zhulina, E. B.; Borisov, O. V. Theory of morphological transitions in weakly dissociating diblock polyelectrolyte micelles. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 6726–6741. [CrossRef]
- Förster, S.; Hermsdorf, N.; Böttcher, C.; Lindner, P. Structure of polyelectrolyte block copolymer micelles. Macromolecules 2002, 35, 4096–4105. [CrossRef]
- Burkhardt, M.; Martinez-Castro, N.; Tea, S.; Drechsler, M.; Babin, I.; Grishagin, I.; Schweins, R.; Pergushov, D. V.; Gradzielski, M.; Zezin, A. B.; Müller, A. H. E. Polyisobutylene-Block-Poly(Methacrylic Acid) Diblock Copolymers: Self-Assembly in Aqueous Media. Langmuir 2007, 23, 12864–12874.
- Xu, L.; Zhu, Z.; Borisov, O. V.; Zhulina, E. B.; Sukhishvili, S. A. pH-Triggered Block Copolymer Micelle-to-Micelle Phase Transition. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 103, 118301. [CrossRef]
- Borisov, O. V.; Zhulina, E. B. Morphology of micelles formed by diblock copolymer with a polyelectrolyte block. Macromolecules 2003, 36, 10029–10036. [CrossRef]
- Victorov, A. I.; Plotnikov, N. V.; Hong, P.-D. Molecular thermodynamic modeling of the morphology transitions in a solution of a diblock copolymer containing a weak polyelectrolyte chain. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 8846–8860. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Netz, R. R. Micellar morphologies of charged diblock-copolymers. Europhys. Lett. 1999, 47, 391–397. [CrossRef]
- Venev, S. V.; Reineker, P.; Potemkin, I. I. Direct and inverse micelles of diblock copolymers with a polyelectrolyte block: Effect of equilibrium distribution of counterions. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 10735–10742. [CrossRef]
- Nyrkova, I.; Semenov, A. N. On the theory of aggregation and micellization: PEO–PVP copolymer in water. Faraday Discuss 2005, 128, 113–127. [CrossRef]
- Munk, P.; Ramieddi, C.; Tian, M.; Webber, S. E.; Prochazka, K.; Tuzar, Z. Block copolymer micelles in aqueous media. Macromol. Chem., Macromol. Symp. 1992, 58, 195–199. [CrossRef]
- Rager T.; Meyer W. H.; Wegner G. Micelle Formation of Poly(acrylic acid)-block-Poly(methyl methacrylate) Block Copolymers in Mixtures of Water with Organic Solvents. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 1999, 200, 1672–1680. [CrossRef]
- Deniau-Lejeune, E.; Drechsler, M.; Jestin, J.; Müller, A. H.; Chassenieux, C.; Colombani, O. Amphiphilic diblock copolymers with a moderately hydrophobic block: Toward dynamic micelles. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 2667–2671. [CrossRef]
- Charbonneau, C.; Chassenieux, C.; Colombani, O.; Nicolai, T. Controlling the Dynamics of Self-Assembled Triblock Copolymer Networks via the pH. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 4487–4495. [CrossRef]
- Borisova, O. V.; Billon, L.; Zaremski, M.; Grassl, B.; Bakaeva, Z.; Lapp, A.; Stepanek, P.; Borisov, O. V. pH-triggered reversible sol–gel transition in aqueous solutions of amphiphilic gradient copolymers. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 10824–10833. [CrossRef]
- Borisova, O.; Billon, L.; Zaremski, M.; Gassl, B.; Bakaeva, Z.; Lapp, A.; Stepanekc, P.; Borisov, O. Synthesis and pH-and salinity-controlled self-assembly of novel amphiphilic block-gradient copolymers of styrene and acrylic acid. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 7649–7659. [CrossRef]
- Carlsen, A.; Lecommandoux, S. Self-assembly of polypeptide-based block copolymer amphiphiles. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 14, 329–339. [CrossRef]
- Checot, F.; Rodriguez-Hernandez, J.; Gnanou, Y.; Lecommandoux, S. pH-responsive micelles and vesicles nanocapsules based on polypeptide diblock copolymers. Biomed. Eng. 2007, 24, 81–85.
- Checot, F.; Brulet, A.; Oberdisse, J.; Gnanou, Y.; Mondain- Monval, O.; Lecommandoux, S. Structure of polypeptide-based diblock copolymers in solution: Stimuli-responsive vesicles and micelles. Langmuir 2005, 21, 4308–4315. [CrossRef]
- Tirrell, M. Modular materials by self-assembly. AIChE J. 2005, 51, 2386–2390. [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, F. Jr.; Rigler, P.; Vebert-Nardin, C. Nucleo-copolymers: oligonucleotide-based amphiphilic diblock copolymers. Chem. Commun. 2007, 11, 1130–1132.
- Halperin, A.; Buhot, A.; Zhulina, E. B. On the hybridization isotherms of DNA microarrays: the Langmuir model and its extensions. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 2006, 18, S463–S490.
- Konradi, R.; Rühe, J. Interaction of poly(methacrylic acid) brushes with metal ions: swelling properties. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 4345–4354. [CrossRef]
- 937. Li, F. Polyelectrolyte Brushes at Interfaces: Properties, Structure and Interactions. Ph.D Thesis, University of California, Santa Barbara, 2005.
- Birshtein, T. M.; Zhulina, E. B. The effect of polyvalent salt ions on the properties of annealed polyelectrolyte brushes. Ber. Bunsen-Ges. Phys. Chem. 1996, 100, 929–935. [CrossRef]
- Zhulina, E. B.; Borisov, O. V.; Birshtein, T. M. Polyelectrolyte Brush Interaction with Multivalent Ions. Macromolecules 1999, 32, 8189–8196. [CrossRef]
- Shusharina, N. A.; Rubinstein, M. Concentration Regimes in Solutions of Polyelectrolyte Stars. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 203–217. [CrossRef]
- Skandalis, A.; Pispas, S. PDMAEMA-b-PLMA-b-POEGMA Tri- block Terpolymers via RAFT Polymerization and Their Self- Assembly in Aqueous Solutions. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 4538–4547. [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Tian, J.; Lian, X.; Sun, P.; Zhao, H. Reactive Triblock Copolymer Micelles Induced by Click Reaction: A Platform for RAFT Polymerization. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 11194–11202. [CrossRef]
- Löbling, T. I.; Hiekkataipale, P.; Hanisch, A.; Bennet, F.; Schmalz, H.; Ikkala, O.; Gröschel, A.; Müller, A. H. Bulk morphologies of polystyrene-block-polybutadiene-block-poly(tert-butyl methacrylate) triblock terpolymers. Polymer 2015, 72, 479–489. [CrossRef]
- Barthel, M. J.; Mansfeld, U.; Hoeppener, S.; Czaplewska, J. A.; Schacher, F. H.; Schubert, U. S. Understanding and tuning the self-assembly of polyether-basedtriblock terpolymers in aqueous solution. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 3509–3520. [CrossRef]
- Kempe, K.; Baumgaertel, A.; Hoogenboom, R.; Schubert, U. S. Design of New Amphiphilic Triblock Copoly(2-oxazoline)s Containing a Fluorinated Segment. J. Polym. Sci., Part A: Polym. Chem. 2010, 48, 5100–5108. [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yao, Y.; Han, L.; Che, S. A. Amphiphilic ABC Triblock Terpolymer Templating for Mesoporous Silica. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2014, 30, 863–867. [CrossRef]
- Petrova, S.; Venturini, C. G.; Jäger, A.; Jäger, E.; Černoch, P.; Kereïche, S.; Kovácik, L.; Raška, I.; Štěpánek, P. Novel Thermo- Responsive Double-Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic MPEO-b- PEtOx-b-PCL Triblock Terpolymers: Synthesis, Characterization and Self-Assembly Studies. Polymer 2015, 59, 215–225.
- Konishcheva, E. V.; Zhumaev, U. E.; Meier, W. P. PEO-b-PCL- b-PMOXA Triblock Copolymers: From Synthesis to Micro- scale Polymersomes with Asymmetric Membrane. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 1512–1520. [CrossRef]
- Stoenescu, R.; Meier W. Vesicles with Asymmetric Membranes from Amphiphilic ABC Triblock Copolymers. Chem Commun (Camb). 2002, (24), 3016–3017.
- Bian, J.; Hao, Y.; He, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, M.; Ni, P. Synthesis and Characterization of a Biodegradable ABC Triblock Terpolymer as Co-Delivery Carrier of Doxorubicin and DNA. J. Polym. Sci., Part A: Polym. Chem. 2014, 52, 3005–3016. [CrossRef]
- Matter, Y.; Enea, R.; Casse, O.; Lee, C. C.; Baryza, J.; Meier, W. Amphiphilic PEG-b-PMCL-b-PDMAEMA Triblock Copolymers : from Synthesis to Physico-Chemistry of Self-Assembled Structures. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2011, 212, 937–949.
- He, X.; Liang, L.; Xie, M.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, S.; Yan, D. Synthesis of Novel Linear PEO-b-PS-b-PCL Triblock Copolymers by the Combination of ATRP, ROP, and a Click Reaction. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2007, 208, 1797–1802. [CrossRef]
- Tsitsilianis, C.; Iliopoulos, I.; Ducouret, G. An associative polyelectrolyte end-capped with short polystyrene chains. Synthesis and reological behavior. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 2936–2943. [CrossRef]
- Tsitsilianis, C.; Iliopoulos, I. Viscoelastic properties of physical gels formed by associative telechelic polyelectrolytes in aqueous media. Macromolecules 2002, 35, 3662–3667. [CrossRef]
- Sfika, V.; Tsitsilianis, C. Association phenomena of poly(acrylic acid)- b-poly(2-vinylpyrine)-b-poly(acrylic acid) triblock polyampholyte in aqueous solution from transient network to compact micelles. Macromolecules 2003, 36, 4983–4988. [CrossRef]
- Sfika, V.; Tsitsilianis, C.; Bossard, F.; Yannopoulos, S.; Petekidis. G. A novel thermothickening phenomenon exhibited by a triblock polyampholyte in aqueous salt-free solutions. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 2883–2888. [CrossRef]
- Stavrouli, N.; Tsitsilianis, C.; Aubry, T. Rheological properties of ABA telechelic polyelectrolyte and ABA polyampholyte reversible hydrogels: a comparative study. Polymer 2008, 49, 1249–1256. [CrossRef]
- Karanikolas, A.; Tsolakis, P.; Bokias, G.; Tsitsilianis, C. Stimuli-responsive poly(ethylene oxide)-b-(2-vinylpyridine)-b-poly(ethylene oxide) triblock copolymers and complexation with poly(acrylic acid) at low pH. Eur. Phys. J. E 2008, 27, 335–343. [CrossRef]
- Angelopoulos, S.; Tsistilianis, C. Thermo-reversible hydrogels based on poly(N,N-diethylamine)-block-poly(acrylicacid)-block-poly(N,N- diethylamine double hydrophilic triblock copolymer. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2006, 207, 2188–2194. [CrossRef]
- Uchman, M.; Stepanek, M.; Prochazka, K.; Mountrichas, G.; Pispas, S.; Voets, I. K.; Walther, A. Multicompartment Nanoparticles Formed by a Heparin-Mimicking Block Terpolymer in Aqueous Solutions. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 5605–5613. [CrossRef]
- Katsampas, I.; Roiter, Y.; Minko, S.; Tsitsilianis, C. Multifunctional stimuli responsive ABC terpolymers: From 3-compartment micelles to 3-dimentional Network. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2005, 26, 1371–1376. [CrossRef]
- Koutalas, G.; Pispas, S.; Hadjichristidis, N. Micelles of poly(isoprene-b-2-vinylpyridine-b-ethylene oxide) terpolymers in aqueous media and their interaction with surfactants. Eur. Phys. J. E Soft Matter 2004, 15, 457–464. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Liu, M.; Mays, J.; Dadmum, M.; Advincula, R. Nano-donuts from pH dependent block restructuring in amphiphilic ABA triblock copolymer vesicles at the air–water interface. Soft Matter 2009, 5, 747–749. [CrossRef]
- Sfika, V.; Tsitsilianis, C.; Kiriy, A.; Gorodyska, G.; Stamm, M. pH responsive heteroarm starlike micelles from double hydrophilic ABC terpolymers with ampholitic A and C blocks. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 9551–9560. [CrossRef]
- 965. Tsitsilianis, C.; Stavrouli, N.; Bocharova, V.; Angelopoulos, S.; Kiriy, A.; Katsampas, I.; Stamm, M. Stimuli responsive associative polyampholytes based on ABCBA pentablock terpolymer architecture. Polymer 2008, 49, 2996–3006.
- Stavrouli, N.; Tsitsilianis, C.; Angelopoulos, A.; Katsampas, I. pH/ thermosensitive hydrogels formed at low pH by a PMMA-PAA- P2VP-PAA-PMMA pentablock terpolymer. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2008, 29, 130–135. [CrossRef]
- Moad, G.; Rizzardo, E.; Thang, S. H. RAFT polymerization and some of its applications. Chem. Asian J. 2013, 8, 1634–1644. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davaran, S.; Ghamkhari, A.; Alizadeh, E.; Massoumi, B.; Jaymand, M. Novel dual stimuli-responsive ABC triblock copolymer: RAFT synthesis, “schizophrenic” micellization, and its performance as an anticancer drug delivery nanosystem. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 488, 282–293. [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lin, L.; Lu, J.; Liang, H.; Feng, H.; Hu, L., Synthesis, self-assembly, and formation of photo-crosslinking-stabilized fluorescent micelles covalently containing zinc(II)-bis(8-hydroxyquinoline) for ABC triblock copolymer bearing cinnamoyl and 8-hydroxyquinoline side groups. J. Polym. Sci., Part A: Polym. Chem. 2016, 54, 1056–1064.
- Hadasha, W.; Klumperman, B. Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization as a Powerful Tool in the Synthesis of Molecular Brushes. Polym. Int. 2014, 63, 824–834. [CrossRef]
- Siegwart, D. J.; Oh, J. K.; Matyjaszewski, K. ATRP in the design of functional materials for biomedical applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 18–37. [CrossRef]
- Gaynor, S.; Qiu, J., Matyjaszewski, K. Using atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) in environmentally benign processes. In Advancing Sustainability Through Green Chemistry and Engineering, Lankey, R. L., Anastas, P. T., Eds.; American Chemistry Society (ACS) Symposium Series, Washington; DC: American Chemical Society, 2002; Vol. 823, Chapter 9, pp. 113-126. [Google Scholar]
- Lomas, H.; Canton, I.; MacNeil, S.; Du, J.; Armes, S. P.; Ryan, A. J.; Lewis, A. L.; Battaglia, G. Biomimetic pH Sensitive Polymersomes for Efficient DNA Encapsulation and Delivery. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 4238–4246. [CrossRef]
- Baskaran, D.; Müller, A. H. E. Anionic Vinyl Polymerization. In Controlled and Living Polymerizations; Müller, A. H. E., Matyjaszewski, K., Eds.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, Germany, 2010; pp 1-56.
- Penczek, S.; Cypryk, M.; Duda, A.; Kubisa, P.; Slomkowski, S. Living Ring-Opening Polymerizations of Heterocyclic Monomers. Progr. Polym. Sci. 2007, 32, 247–282. [CrossRef]
- Lecomte, P.; Jérôme, C. Recent developments in ring-opening polymerization of lactones. In Synthetic biodegradable polymers, Rieger, B., Künkel, A., Coates, G., Reichardt, R., Dinjus, E., Zevaco, T., Eds.; Advances in polymer science; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2011; Vol 245, pp 173-217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbraeken, B.; Monnery, B. D.; Lava, K.; Hoogenboom, R. The Chemistry of Poly(2-oxazoline)s. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 88, 451–469.
- Hoogenboom, R.; Wiesbrock, F.; Huang, H.; Leenen, M. A.; Thijs, H. M.; van Nispen, S. F.; van der Loop, M.; Fustin, C. A.; Jonas, A. M.; Gohy, J. F.; Schubert, U. S. Microwave-assisted cationic ring-opening polymerization of 2-oxazolines: A powerful method for the synthesis of amphiphilic triblock copolymers. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 4719–4725.
- Kempe, K.; Hoogenboom, R.; Hoeppener, S.; Fustin, C.-A.; Gohy, J.-F.; Schubert, U. S. Discovering New Block Terpolymer Micellar Morphologies. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 6455–6457. [CrossRef]
- Fetsch, C.; Luxenhofer, R. Highly defined multiblock copolypeptoids: pushing the limits of living nucleophilic ring-opening polymerization. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2012, 33, 1708–1713. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barthel, M. J.; Schacher, F. H.; Schubert, U. S. Poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO)-Based ABC Triblock Terpolymers – Synthetic Complexity vs. Application Benefits. Polym. Chem. 2014, 5, 2647–2662. [CrossRef]
- 982. Sun, J.; Černoch, P.; Völkel, A.; Wei, Y.; Ruokolainen, J.; Schlaad, H. Aqueous self-assembly of a protein-mimetic ampholytic block copolypeptide. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 5494–5501.
- Stoenescu, R.; Graff, A.; Meier, W. Asymmetric ABC-triblock copolymer membranes induce a directed insertion of membrane proteins. Macromol. Biosci. 2004, 4, 930–935. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konishcheva, E.; Häussinger, D.; Lörcher, S.; Meier, W. Key aspects to yield low dispersity of PEO-b-PCL diblock copolymers and their mesoscale self-assembly. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 83, 300–310. [CrossRef]
- Semenov, A. M.; Joanny, J.-F.; Khokhlov, A. R. Associating Polymers: Equilibrium and Linear Viscoelasticity. Macromolecules 1995, 28, 1066–1075, pp 156-164. [CrossRef]
- Halperin, A. 986. Halperin, A., Zhulina, E. B. Triblock copolymers, mesogels and deformation behavior in poor solvents. In Physics of Polymer Networks; Progress in Colloid & Polymer Science; Steinkopff; 1992; Vol. 90. [CrossRef]
- Erhardt, R.; Zhang, M.; Böker, A.; Zettl, H.; Abetz, C.; Frederik, P.; Krausch, G.; Abetz, V.; Müller, A. H. E. Amphiphilic Janus micelles with polystyrene and poly(methacrylic acid) hemispheres. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 3260–3267. [CrossRef]
- Walther, A.; Müller, A. H. E. Janus particles. Soft Matter 2008, 4, 663–668.
- Walther, A.; Barner-Kowollik, C.; Müller A. H. E. Mixed, multicompartment, or Janus micelles? A systematic study of thermoresponsive bis-hydrophilic block terpolymers. Langmuir 2010, 26, 12237–12246. [CrossRef]
- Charlaganov, M. I.; Borisov, O. V.; Leermakers, F. A. M. Modeling of Triblock Terpolymer Micelles with a Segregated Corona. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 3668–3677. [CrossRef]
- Bütün, V.; Wang, X.-S.; de Paz Báñez, M. V.; Robinson, K. L.; Billingham, N. C.; Armes, S. P.; Tuzar, Z. Synthesis of shell cross-linked micelles at high solids in aqueous media. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 1–3. [CrossRef]
- Laschewsky, A. Polymerized micelles with compartments. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 8, 274–281. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Abetz, V.; Müller, A. H. E. Janus Cylinders. Macromolecules 2003, 36, 7894–7898.
- Stewart, S.; Liu, G. Block Copolymer Nanotubes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000, 39, 340–344. [CrossRef]
- Holmes, R. M.; Williams, D. R. M. Single Chain Asymmetric Block Copolymers in Poor Solvents. Candidates for Patchy Colloids. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 6172–6181. [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Hillmyer, M. A.; Lodge, T. P. Morphologies of multicompartment micelles formed by ABC miktoarm star terpolymers. Langmuir 2006, 22, 9409–9417. [CrossRef]
- Saito, N.; Liu, C.; Lodge, T. P.; Hillmyer, M. A. Multicompartment micelle morphology evolution in degradable miktoarm star terpolymers. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 1907–1912. [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Kesselman, E.; Talmon, Y.; Hillmyer, M. A.; Lodge, T. P. Multicompartment micelles from ABC miktoarm stars in water. Science 2004, 306, 98–101. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Huang, L.; Liang, H.; Pan, C. Self-assembly of star block copolymers by dynamic density functional theory. J. Chem. Phys. 2002, 116, 10508–10513. [CrossRef]
- He, X. H.; Huang, L.; Liong, H. J.; Pan, C. Y. Localizations of junction points of ABC 3-miktoarm star terpolymers. J. Chem. Phys. 2003, 118, 9861–9863. [CrossRef]
- Birshtein, T. M.; Polotsky, A.; Abetz, V. Theory of the Lamellar Superstructure of an ABC 3-Miktoarm Star-Terpolymer. Macromol. Theory Simul. 2004, 13, 512–519. [CrossRef]
- Gemma, T.; Hatono, A.; Dotera, T. Monte Carlo Simulations of the Morphology of ABC Star Polymers Using the Diagonal Bond Method. Macromolecules 2002, 35, 3225–3237. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, R. K. Y.; Jiang, W. A Monte Carlo simulation for the micellization of ABC 3-miktoarm star terpolymers in a selective solvent. Chem. Phys. 2006, 327, 137–143. [CrossRef]
- Zhulina, E. B.; Borisov, O. V. (). Scaling theory of 3-miktoarm ABC copolymer micelles in selective solvent. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 5934–5944. [CrossRef]
- Fang, B.; Walther, A.; Wolf, A.; Xu, Y.; Yuan, J.; Müller, A. H. Undulated multicompartment cylinders by the controlled and directed stacking of polymer micelles with a compartmentalized corona. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2009, 48, 2877–2880. [CrossRef]
- Konishcheva, E. V.; Zhumaev, U. E.; Kratt, M.; Oehri, V.; Meier, W. Complex Self-Assembly Behavior of Bis-hydrophilic PEO-b-PCL-b-PMOXA Triblock Copolymers in Aqueous Solution. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 7155–7168. [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Bates, F. S. On the origins of morphological complexity in block copolymer surfactants. Science 2003, 300, 460–464. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zupancich, J. A.; Bates, F. S.; Hillmyer, M. A. Aqueous dispersions of poly(ethylene oxide)-b-poly(γ-methyl-ε-caprolactone) block copolymers. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 4286–4288. [CrossRef]
- Adams, D. J.; Butler, M. F.; Weaver, A. C. Effect of block length, polydispersity, and salt concentration on PEO-PDEAMA block copolymer structures in dilute solution. Langmuir 2006, 22, 4534–4540. [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Spulber, M.; Itel, F.; Chami, M.; Pfohl, T.; Palivan, C. G.; Meier, W. Effect of Molecular Parameters on the Architec- ture and Membrane Properties of 3D Assemblies of Amphiphilic Copolymers. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 5060–5069. [CrossRef]
- Israelachvili, J. N. Intermolecular and Surface Forces; Academic Press: New York, 2010; 3rd edition.
- Taubert, A.; Furrer, E.; Meier, W. Water-in-water mesophases for templating inorganics. Chem. Commun. (Camb). 2004, (19), 2170–2171.
- Casse, O.; Shkilnyy, A.; Linders, J.; Mayer, C.; Haussinger, D.; Volkel, A.; Thunemann, A. F.; Dimova, R.; Colfen, H.; Meier, W.; Schlaad, H.; Taubert, A. Solution Behavior of Double-Hydrophilic Block Copolymers in Dilute Aqueous Solution. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 4772–4777.
- Liu, F.; Eisenberg, A. Preparation and pH triggered inversion of vesicles from poly(acrylic acid)-block-polystyrene-block-poly(4-vinyl pyridine). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 15059–15064. [CrossRef]
- Wittemann, A.; Azzam, T.; Eisenberg, A. Biocompatible polymer vesicles from biamphiphilic triblock copolymers and their interaction with bovine serum albumin. Langmuir 2007, 23, 2224–2230. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlaad, H.; You, L.; Sigel, R.; Smarsly, B.; Heydenreich, M.; Mantion, A.; Masić, A. Glycopolymer vesicles with an asymmetric membrane. Chem. Commun. (Camb). 2009, (12), 1478–1480.
- Liu, G.; Ma, S.; Li, S.; Cheng, R.; Meng, F.; Liu, H.; Zhong, Z. The highly efficient delivery of exogenous proteins into cells mediated by biodegradable chimaeric polymersomes. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 7575–7585. [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Fan, L.; Liu, Q. pH-Sensitive Block Copolymer Vesicles with Variable Trigger Points for Drug Delivery. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 8275–8283. [CrossRef]
- Mason, A. F.; Thordarson, P. Polymersomes with Asymmetric Membranes Based on Readily Accessible Di- and Triblock Copolymers Synthesized via SET-LRP. ACS Macro Lett. 2016, 5, 1172–1175. [CrossRef]
- Smith, P. K.; Krohn, R. I.; Hermanson, G. T.; Mallia, A. K.; Gartner, F. H.; Provenzano, M. D.; Fujimoto, E. K.; Goeke, N. M.; Olson, B. J.; Klenk, D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal. Biochem. 1985, 150, 76–85.
- Blanazs, A.; Massignani, M.; Battaglia, G.; Armes, S. P.; Ryan, A. J. Tailoring macromolecular expression at polymersome surfaces. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 2906–2914. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Chen, J.; Du, J. Asymmetrical polymer vesicles with a “stealthy” outer corona and an endosomal-escape-accelerating inner corona for efficient intracellular anticancer drug delivery. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 3072–3082. [CrossRef]
- Njikang, G.; Han, D.; Wang, J.; Liu, G. ABC Triblock Copolymer Micelle-Like Aggregates in Selective Solvents for A and C. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 9727–9735. [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Armes, S. P. Patchy multi-compartment micelles are formed by direct dissolution of an ABC triblock copolymer in water. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 4851–4857. [CrossRef]
- Walther, A.; Millard, P.-E.; Goldmann, A. S.; Lovestead, T. M.; Schacher, F.; Barner-Kowollik, C.; Mueller, A. H. E. Bis-Hydrophilic Block Terpolymers via RAFT Polymerization: Toward Dynamic Micelles with Tunable Corona Properties. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 8608–8619. [CrossRef]
- Erhardt, R.; Böker, A.; Zettl, H.; Kaya, H.; Pyckhout-Hintzen, W.; Krausch, G.; Abetz, V.; Müller, A. H. E. Macromolecules 2001, 34, 1069–1075.
- Saito, R.; Fujita, A.; Ichimura, A.; Ishizu, K. Synthesis of microspheres with microphase-separated shells. J. Polym. Sci., Part A: Polym. Chem. 2000, 38, 2091–2097. [CrossRef]
- Hoppenbrouwers, E.; Li, Z.; Liu G. Triblock nanospheres with amphiphilic coronal chains. Macromolecules 2003, 36, 876–881. [CrossRef]
- Dag, A.; Zhao, J.; Stenzel, M. H. Origami with ABC Triblock Terpolymers Based on Glycopolymers: Creation of Virus-Like Morphologies. ACS Macro Lett. 2015, 4, 579–583. [CrossRef]
- Walther, A.; Müller, A. H. Janus particles: synthesis, self-assembly, physical properties, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 5194–5261. [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; O’Reilly, R. K. Anisotropic particles with patchy, multicompartment and Janus architectures: preparation and application. Chem Soc Rev. 2011, 40, 2402–2416. [CrossRef]
- Tsitsilianis, C.; Voulgaris, D.; Stepanek, M.; Podhajecka, K.; Prochazka, K.; Tuzar, Z.; Brown, W. Polystyrene/poly(2-vinylpyridine) heteroarm star copolymer micelles in aqueous media and onion type micelles stabilized by diblock copolymers. Langmuir 2000, 16, 6868–6876. [CrossRef]
- Gorodyska, G.; Kiriy, A.; Minko, S.; Tsitsilianis, C.; Stamm, M. Reconformation and Metallization of Unimolecular Micelles in Controlled Environment. Nano Lett. 2003, 3, 365–368. [CrossRef]
- Voulgaris, D.; Tsitsilianis, C. Aggregation behavior of polystyrene/poly(acrylic acid) heteroarm star copolymers in 1,4-dioxane and aqueous media. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2001, 202, 3284–3292. [CrossRef]
- 1035. Hammond, M.R.; Li, C.; Tsitsilianis, C.; Mezzenga, R. Hierarchical self-organization in polyelectrolyte-surfactant complexes based on heteroarm star block copolyampholytes. Soft Matter 2009, 5, 2371–2377.
- 1036. Stavrouli, N.; Kyriazis, A.; Tsitsilianis, C. Reversible hydrogels from an ampholytic An(B-b-C)n heteroarm star block terpolymer. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2008, 209, 2241–2247.
- Yang, J. C.; Mays J. W. Synthesis and Characterization of Neutral/Ionic Block Copolymers of Various Architectures. Macromolecules 2002, 35, 3433–3438. [CrossRef]
- Nottelet, B.; Vert, M.; Coudane, J. Novel Amphiphilic Degradable Poly(-caprolactone)-graft-poly(4-vinyl pyridine), Poly(-caprolactone)-graft-poly(dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate) and Water-Soluble Derivatives. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2008, 29, 743–750. [CrossRef]
- Cohen Stuart, M. A.; Besseling, N. A. M.; Fokkink, R. G. Formation of Micelles with Complex Coacervate Cores. Langmuir 1998, 14, 6846–6849. [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J. S.; Benoit, H. C. Polymers and Neutron Scattering, Ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Jhaveri, A. M.; Torchilin, V. P. Multifunctional polymeric micelles for delivery of drugs and siRNA. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 5, 77.
- Machtakova, M.; Thérien-Aubin, H.; Landfester, K. Polymer nano-systems for the encapsulation and delivery of active biomacromolecular therapeutic agents. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 128–152. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J. S.; Feijen, J. Polymersomes for drug delivery: design, formation and characterization. J. Control. Release 2012, 161, 473–483. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LoPresti, C.; Lomas, H.; Massignani, M.; Smart, T.; Battaglia, G. Polymersomes: nature inspired nanometer sized compartments. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 3576–3590. [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, M.; Linse, P. Polyelectrolyte–macroion complexation. II. Effect of chain flexibility. J.Chem.Phys. 2001, 115, 10975–10985. [CrossRef]
- Park, J. M.; Muhoberac, B. B.; Dubin, P. L.; Xia, J. Effects of protein charge heterogeneity in protein-polyelectrolyte complexation. Macromolecules 1992, 25, 290–295. [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, A.; Kojima, C.; Iijima, M.; Harada, A.; Kono. K. Polyion complex micelles formed from glucose oxidase and comb-type polyelectrolyte with poly(ethylene glycol) grafts. J. Polym. Sci. Part A: Polym. Chem. 2008, 46, 3842–3852. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Fay, J. M.; Poon, C. D.; Vinod, N.; Zhao, Y.; Bullock, K.; Qin, S.; Manickam, D. S.; Yi, X.; Banks, W. A.; Kabanov, A. V. Nanoformulation of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor with Target Receptor-Triggered-Release in the Central Nervous System. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1703982. [CrossRef]
- De Luca, S.; Chen, F.; Seal, P.; Stenzel, M. H.; & Smith, S. C. Binding and Release between Polymeric Carrier and Protein Drug: pH-Mediated Interplay of Coulomb Forces, Hydrogen Bonding, van der Waals Interactions, and Entropy. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 3665–3677.
- Kaczmarek, D.; Diget, J. S.; Nyström, B.; Gyulai, G.; Mészáros, R.; Gilányi, T.; Imre Varga, T. Response of block copolyelectrolyte complexes to addition of ionic surfactants. Colloids Surf. A 2017, 532, 290–296. [CrossRef]
- Harada, A.; Kataoka, K. Switching by Pulse Electric Field of the Elevated Enzymatic Reaction in the Core of Polyion Complex Micelles. J.Am.Chem.Soc. 2003, 125, 15306–15307. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamura, A.; Yoshioka, Y.; Harada, A.; Kono, K. Acceleration of enzymatic reaction of trypsin through the formation of water-soluble complexes with poly(ethylene glycol)-block-poly(α,β-aspartic acid). Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 627–631. [CrossRef]
- Sotiropoulou, M.; Bokias, G.; Staikos, G. Water-soluble complexes through coulombic interactions between bovine serum albumin and anionic polyelectrolytes grafted with hydrophilic nonionic side chains. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 1835–1838. [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Harada, A.; Yamasaki, Y.; Kataoka, K. Stabilization of lysozyme-incorporated polyion complex micelles by the ω-end derivatization of poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(α,β-aspartic acid) block copolymers with hydrophobic groups. Langmuir 2005, 21, 2668–2674. [CrossRef]
- Harada, A.; Yoshioka, Y.; Kawamura, A.; Kojima, C.; Kono, K. Effect of polycarboxylate blocks on the amidase activity of trypsin through complexation with PEG/polycarboxylate block ionomers. Macromol. Biosci. 2007, 7, 339–343. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Arounleut, P.; Rheiner, S.; Bae, Y.; Kabanov, A. V.; Milligan, C.; Manickam, D. S. SOD1 nanozyme with reduced toxicity and MPS accumulation. J. Control. Release 2016, 231, 38–49. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuwada K., Kurinomaru T., Tomita S., Shiraki K. Noncovalent PEGylation-based enzyme switch in physiological saline conditions using quaternized polyamines. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2016, 294, 1551–1556. [CrossRef]
- Nakai, K.; Nishiuchi, M.; Inoue, M.; Ishihara, K.; Sanada, Y.; Sakurai, K.; Yusa, S. Preparation and characterization of polyion complex micelles with phosphobetaine shells. Langmuir 2013, 29, 9651–9661. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Fukushima, S.; Bae, Y.; Hiki, S.; Ishii, T.; Kataoka, K. A protein nanocarrier from charge-conversion polymer in response to endosomal pH. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 5362–5363. [CrossRef]
- Shetty, J. K.; Kinsella, J. E. Ready separation of proteins from nucleoprotein complexes by reversible modification of lysine residues. Biochem. J. 1980, 191, 269–272. [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ding, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, C.; Zhuang, X.; Chen, X. Polyion complex micelles with gradient pH-sensitivity for adjustable intracellular drug delivery. Polym. Chem. 2015, 6, 397–405. [CrossRef]
- Park, T. G.; Jeong, J. H.; Kim, S. W. Current status of polymeric gene delivery systems. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2006, 58, 467–486. [CrossRef]
- Mundra, V.; Mahato, R. I. Design of nanocarriers for efficient cellular uptake and endosomal release of small molecule and nucleic acid drugs: learning from virus. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2014, 8, 387–404. [CrossRef]
- Van Bruggen, C.; Hexum, J. K.; Tan, Z.; Dalal, R. J.; Reineke, T. M. Nonviral Gene Delivery with Cationic Glycopolymers. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 1347–1358. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Schlenoff, J. B. The polyelectrolyte complex/coacervate continuum. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 3108–3116. [CrossRef]
- Schlenoff, J. B.; Yang, M.; Digby, Z. A.; Wang, Q. Ion Content of Polyelectrolyte Complex Coacervates and the Donnan Equilibrium. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 9149–9159. [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Ting, J. M.; Weiss, T. M.; Tirrell, M. V. Interparticle Interactions in Dilute Solutions of Polyelectrolyte Complex Micelles. ACS Macro Lett. 2019, 8, 819–825. [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Haddou, M.; Grillo, I.; Mana, Z.; Chapel, J. P.; Schatz, C. Early stage kinetics of polyelectrolyte complex coacervation monitored through stopped-flow light scattering. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 9030–9038. [CrossRef]
- Aniansson E. A. G.; Wall S. N. Kinetics of step-wise micelle association. Correction and improvement. J. Phys. Chem. 1975, 79, 857–858. [CrossRef]
- Halperin A.; Alexander S. Polymeric micelles: their relaxation kinetics. Macromolecules 1989, 22, 2403–2412. [CrossRef]
- Esselink F. J., Dormidontova E., Hadziioannou G. Evolution of Block Copolymer Micellar Size and Structure Evidenced with Cryo Electron Microscopy. Macromolecules 1998, 31, 2925–2932. [CrossRef]
- Rharbi, Y. Fusion and Fragmentation Dynamics at Equilibrium in Triblock Copolymer Micelles. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 9823–9826. [CrossRef]
- Zhang J.; Chen S.; Zhu Z.; Liu S. Stopped-Flow Kinetic Studies of the Formation and Disintegration of Polyion Complex Micelles in Aqueous Solution. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 117–127. [CrossRef]
- Ting, J. M.; Wu, H.; Herzog-Arbeitman, A.; Srivastava, S.; Tirrell, M. V. Synthesis and Assembly of Designer Styrenic Diblock Polyelectrolytes. ACS Macro Lett. 2018, 7, 726–733. [CrossRef]
- 1075. Haladjova, E.; Mountrichas, G.; Pispas, S.; Rangelov, S. Poly(vinyl benzyl trimethylammonium chloride) Homo and Block Copolymers Complexation with DNA. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2016, 120, 2586–2595.
- Lou, B.; Beztsinna, N.; van den Dikkenberg, J. B.; Pispas, S.; Hennink, W. E. Small nanosized poly(vinyl benzyl trimethylammonium chloride) based polyplexes for siRNA delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 525, 388–396. [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C. H.; Leon, L.; Chung, E. J.; Huang, R. T.; Sontag, T. J, Reardon, C. A,; Getz, G. S.; Tirrell, M.; Fang, Y. Inhibition of atherosclerosis-promoting microRNAs via targeted polyelectrolyte complex micelles. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 8142–8153. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marciel, A. B.; Chung, E. J.; Brettmann, B. K.; Leon, L. Bulk and nanoscale polypeptide based polyelectrolyte complexes. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 239, 187–198. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramasamy, T.; Kim, H.; Choi, Y.; Tran, H. pH sensitive polyelectrolyte complex micelles for highly effective combination chemotherapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 6324–6333. [CrossRef]
- Aniansson, E. A. G.; Wall, S. N. On the kinetics of step-wise micelle association. J. Phys. Chem. 1974, 78, 1024–1030. [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Ting, J.; Yu, B.; Jackson, N.; Meng, S.; De Pablo, J.; Tirrell, M. Spatiotemporal formation and growth kinetics of polyelectrolyte complex micelles with millisecond resolution. ACS Macro Lett. 2020, 9, 1674–1680. [CrossRef]
- Lynd, N. A.; Meuler, A. J.; Hillmyer, M. A. Polydispersity and block copolymer self-assembly. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2008, 33, 875–893. [CrossRef]
- Ong, G. M. C.; Sing, C. E. Mapping the phase behavior of coacervate-driven self-assembly in diblock copolyelectrolytes. Soft Matter 2019, 15, 5116–5127. [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Levi, A. E.; Goldfeld, D. J.; Tirrell, M. V. Structure, morphology, and rrheology of polyelectrolyte complex hydrogels formed by self-assembly of oppositely charged triblock polyelectrolytes. Macromolecules 2020, 53, 5763–5774. [CrossRef]
- Ohara, Y.; Nakai, K.; Ahmed, S.; Matsumura, K.; Ishihara, K.; Yusa, S. I. pH-Responsive Polyion Complex Vesicle with Polyphosphobetaine Shells. Langmuir 2019, 35, 1249–1256. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, X.; Ma, L.; Yu, K.; Xiong, W.; Lu, X.; Cai, Y. Polymerization-Induced Hierarchical Electrostatic Self-Assembly: Scalable Synthesis of Multicompartment Polyion Complex Micelles and Their Monolayer Colloidal Nanosheets and Nanocages. ACS Macro Lett. 2020, 9, 454–458. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumetz, A. C.; Chockla, A. M.; Kaler, E. W.; Lenhoff, A. M. Protein Phase Behavior in Aqueous Solutions: Crystallization, Liquid- Liquid Phase Separation, Gels, and Aggregates. Biophys. J. 2008, 94, 570–583. [CrossRef]
- Wallace, A. F.; Hedges, L. O.; Fernandez-Martinez, A.; Raiteri, P.; Gale, J. D.; Waychunas, G. A.; Whitelam, S.; Banfield, J. F.; De Yoreo, J. J. Microscopic Evidence for Liquid-Liquid Separation in Supersaturated CaCO3 Solutions. Science (Washington, DC, U. S.) 2013, 341, 885–889.
- Ianiro, A.; Wu, H.; van Rijt, M. M. J.; Vena, M. P.; Keizer, A. D. A.; Esteves, A. C. C.; Tuinier, R.; Friedrich, H.; Sommerdijk, N. A. J. M.; Patterson, J. P. Liquid−Liquid Phase Separation during Amphiphilic Self-Assembly. Nat. Chem. 2019, 11, 320–328.
- Kiriy, A.; Yu, J.; Stamm, M. Interpolyelectrolyte complexes: a single-molecule insight. Langmuir 2006, 22, 1800–1803. [CrossRef]
- Bakeev, K. N.; Izumrudov, V. A.; Kuchanov, S. I.; Zezin, A. B.; Kabanov, V. A. Kinetics and mechanism of interpolyelectrolyte exchange and addition reactions. Macromolecules 1992, 25, 4249–4254. [CrossRef]
- Marras, A. E.; Vieregg, J. R.; Tirrell, M. V. Assembly and Characterization of Polyelectrolyte Complex Micelles. J. Vis. Exp. 2020, 157, e60894.
- Marciel, A. B.; Srivastava, S.; Ting, J. M.; Tirrell, M. V. SAXS methods for investigating macromolecular and self-assembled polyelectrolyte complexes. Methods Enzymol. 2021, 646, 223–259.
- Ting, J. M.; Marras, A. E.; Mitchell, J. D.; Campagna, T. R.; Tirrell, M. V. Comparing Zwitterionic and PEG Exteriors of Polyelectrolyte Complex Micelles. Molecules 2020, 25, 2553. [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, R.; Narayanan, T.; Sato, T. Growth Kinetics of Polyelectrolyte Complexes Formed from Oppositely-Charged Homo- polymers Studied by Time-Resolved Ultra-Small-Angle X-ray Scattering. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 737–741. [CrossRef]
- Smolsky, I. L.; Liu, P.; Niebuhr, M.; Ito, K.; Weiss, T. M.; Tsuruta, H. Biological small-angle X-ray scattering facility at the Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Laboratory. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2007, 40, s453–s458. [CrossRef]
- Bednar, B.; Edwards, K.; Almgren, M.; Tormod, S.; Tuzar, Z. Rates of association and dissociation of block copolymer micelles: Light-scattering stopped-flow measurements. Makromol. Chem.-Rapid Commun. 1988, 9, 785–790. [CrossRef]
- Prochazka K.; Bednar B.; Mukhtar E.; Svoboda P.; Trnena J.; Almgren M. Nonradiative Energy Transfer in Block Copolymer Micelles. J. Phys. Chem. 1991, 95, 4563–4568. [CrossRef]
- Pacovska, M.; Prochazka, K., Tuzar, Z., Eds.; Munk, P. 1993: Formation of block copolymer micelles : a sedimentation study. Polymer (Guildford) 34, 4585-4588. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, M.; Qin, A.; Ramireddy, C.; Webber, S. E.; Munk, P.; Tuzar, Z.; Prochazka, K. Langmuir 1993, 9, 1741–1748.
- Wang, Y.; Kausch, C. M.; Chun, M.; Quirk, R. P.; Mattice, W. L. Exchange of chains between micelles of labeled polystyrene-block-poly (oxyethylene) as monitored by nonradiative singlet energy transfer. Macromolecules 1995, 28, 904–911. [CrossRef]
- Bednar, B.; Karasek, L.; Pokorny, J. Nonradiative energy transfer studies of block copolymers in selective solvents. Polymer 1996, 37, 5261–5268.
- 1103. Honda, C.; Abe, Y.; Nose, T. Relaxation Kinetics of Micellization in Micelle-Forming Block Copolymer in Selective Solvent. Macromolecules 1996, 29, 6778–6785.
- Haliloglu, T.; Mattice, W. L. In Solvent and Self-Assembly of Polymers, Webber, S. E., Eds.; Kluwer: Dortrecht, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Z. In Solvent and Self-Assembly of Polymers; Webber, S. E., Ed.; Kluwer: Dortrecht, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Honda, C.; Hasegawa, Y.; Hirunuma, R.; Nose, T. Micellization Kinetics of Block Copolymers in Selective Solvent. Macromolecules 1994, 27, 7660–7668. [CrossRef]
- Goldmints, I.; Holzwarth, J. F.; Smith, K. A.; Hatton, T. A. Micellar Dynamics in Aqueous Solutions of PEO-PPO-PEO Block Copolymers. Langmuir 1997, 13, 6130–6134. [CrossRef]
- Michels, B.; Waton, G.; Zana, R. Dynamics of micelles of poly(ethyleneoxide)-poly(propyleneoxide)-poly(ethylene oxide) block copolymers in aqueous solutions. Langmuir 1997, 13, 3111–3118. [CrossRef]
- Esselink F. J.; Dormidontova E. E.; Hadziioannou G. Redistribution of Block Copolymer Chains between Mixed Micelles in Solution. Macromolecules 1998, 31, 4873–4878. [CrossRef]
- Aniansson E. A. G.; Wall S. N.; Almgren M.; Hoffmann H.; Kielmann I.; Ulbricht W.; Zana R.; Lang J.; Tondre C. Theory of the kinetics of micellar equilibria and quantitative interpretation of chemical relaxation studies of micellar solutions of ionic surfactants. J. Phys. Chem. 1976, 80, 905–922.
- Lessner, E.; Teubner, M.; Kahlweit, M. Relaxation Experiments in Aqueous Solutions of Ionic Micelles. 1. Theory and Experiments on the System Water-Sodium Tetradecyl Sulfate-Sodium Perchlorate. J. Phys. Chem. 1981, 85, 1529–1536. [CrossRef]
- Kahlweit, M. Kinetics of formation of association colloids. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1982, 90, 92–99. [CrossRef]
- Shusharina, N. P.; Saphonov, M. V.; Nyrkova, I. A; Khalatur, P. G.; Khokhlov. A. R. The Critical Micelle Concentration for the Solution of Polyelectrolyte/Neutral Block-Copolymers. Ber. Bunsenges. Phys. Chem. 1996, 100, 857–862. [CrossRef]
- Denkova, A. G.; Mendes, E.; Coppens, M.-O. Non-equilibrium dynamics of block copolymer micelles in solution: recent insights and open questions. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 2351–2357. [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Dormidontova, E. E. Kinetics of diblock copolymer micellization by dissipative particle dynamics. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 3521–3531. [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Dormidontova, E. E. Equilibrium chain exchange kinetics in block copolymer micelle solutions by dissipative particle dynamics simulations. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 4179–4188. [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.-J.; Wang, T.-Y.; Chen, W. M.; Tsao, H.-K. A- B diblock copolymer micelles: Effects of soluble-block length and component compatibility. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 10938–10945. [CrossRef]
- Prhashanna, A.; Khan, S. A.; Chen, S. B. Kinetics of chain exchange between diblock copolymer micelles. Macromol. Theory Simul. 2016, 25, 383–391. [CrossRef]
- Spruijt, E.; Sprakel, J.; Lemmers, M.; Cohen Stuart, M. A.; Van Der Gucht, J. Relaxation dynamics at different time scales in electrostatic complexes: time-salt superposition. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 105, 208301. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spruijt, E.; Sprakel, J.; Cohen Stuart, M. A.; van der Gucht, J. Interfacial tension between a complex coacervate phase and its coexisting aqueous phase. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 172–178. [CrossRef]
- Spruijt, E.; van den Berg, S. A.; Cohen Stuart, M. A.; van der Gucht, J. Direct measurement of the strength of single ionic bonds between hydrated charges. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 5297–5303. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Srivastava, S.; Andreev, M.; Marciel, A. B.; de Pablo, J. J.; Tirrell, M. V. Phase behavior and salt partitioning in polyelectrolyte complex coacervates. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 2988–2995. [CrossRef]
- Ou, Z.; Muthukumar, M. Entropy and enthalpy of polyelectrolyte complexation: Langevin dynamics simulations. J. Chem. Phys. 2006, 124, 154902. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziebarth, J.; Wang, Y. Coarse-grained molecular dynamics simulations of DNA condensation by block copolymer and formation of core- corona structures. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 6225–6232. [CrossRef]
- Šindelka, K.; Limpouchova,́ Z.;Lísal, M.; Prochaźka, K. Dissipative particle dynamics study of electrostatic self-assembly in aqueous mixtures of copolymers containing one neutral water-soluble block and one either positively or negatively charged polyelectrolyte block. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 6121–6134.
- Šindelka, K.; Limpouchova,́ Z.; Lísal, M.; Prochaźka, K. The electrostatic co-assembly in non-stoichiometric aqueous mixtures of copolymers composed of one neutral water-soluble and one polyelectrolyte (either positively or negatively charged) block: a dissipative particle dynamics study. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 16137–16151.
- Šindelka, K.; Limpouchova,́ Z.; Prochaźka, K. Computer study of the solubilization of polymer chains in polyelectrolyte complex cores of polymeric nanoparticles in aqueous media. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 29876–29888. [CrossRef]
- Lund, R.; Willner, L.; Monkenbusch, M.; Panine, P.; Narayanan, T.; Colmenero, J.; Richter, D. Structural observation and kinetic pathway in the formation of polymeric micelles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 102, 188301. [CrossRef]
- Katayose S, Kataoka K. Remarkable increase in nuclease resistance of plasmid DNA through supramolecular assembly with poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(L-lysine) block copolymer. J. Pharm. Sci. 1998, 87, 160–163. [CrossRef]
- Dautzenberg H.; Konak C.; Reschel T.; Zintchenko A.; Ulbrich K. Cationic graft copolymers as carriers for delivery of antisense-oligonucleotides. Macromol. Biosci. 2003, 3, 425–435. [CrossRef]
- Harada, A.; Kataoka, K. Selection between block- and homo- polyelectrolytes through polyion complex formation in aqueous medium. Soft Matter 2008, 4, 162–167. [CrossRef]
- Carl, N.; Prévost, S.; Schweins, R.; Huber, K. Contrast variation of micelles composed of Ca2+ and block copolymers of two negatively charged polyelectrolytes. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2020, 298, 663–679. [CrossRef]
- Qiang, Z.; Wang, M. 100th Anniversary of Macromolecular Science Viewpoint: Enabling Advances in Fluorescence Microscopy Techniques. ACS Macro Lett. 2020, 9, 1342–1356. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parent, L. R.; Gnanasekaran, K.; Korpanty, J.; Gianneschi, N. C. 100th Anniversary of Macromolecular Science Viewpoint: Polymeric Materials by In Situ Liquid-Phase Transmission Electron Microscopy. ACS Macro Lett. 2021, 10, 14–38. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, B.; Muthukumar, M. Modeling Competitive Substitution in a Polyelectrolyte Complex. J. Chem. Phys. 2015, 143, 243133. [CrossRef]
- Kembaren, R.; Fokkink, R.; Westphal, A. H.; Kamperman, M.; Kleijn, J. M.; Borst, J. W. Balancing Enzyme Encapsulation Efficiency and Stability in Complex Coacervate Core Micelles. Langmuir 2020, 36, 8494–8502. [CrossRef]
- Obermeyer, A. C.; Mills, C. E.; Dong, X. H.; Flores, R. J.; Olsen, B. D. Complex Coacervation of Supercharged Proteins with Polyelectrolytes. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 3570–3581. [CrossRef]
- Kapelner, R. A.; Obermeyer, A. C. Ionic Polypeptide Tags for Protein Phase Separation. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 2700–2707. [CrossRef]
- 1139. Tabandeh, S.; Leon, L. Engineering Peptide-Based Polyelectrolyte Complexes with Increased Hydrophobicity. Molecules 2019, 24, 868.
- Yang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Wang, J.; Fang, Q.; Peng, Z. Enzymatically Disulfide-Crosslinked Chitosan/Hyaluronic Acid Layer-by-Layer Self-Assembled Microcapsules for Redox-Responsive Controlled Release of Protein. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 33493–33506. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cheng, Y. T.; Cao, C.; Oliver, J. D.; Stenzel, M. H.; Chapman, R. Polyion Complex-Templated Synthesis of Cross-Linked Single-Enzyme Nanoparticles. Macromolecules 2020, 53, 5487–5496. [CrossRef]
- Murmiliuk,̌ A.; Matějíček, P.; Filippov, S. K.; Janata, M.; Slouf, M.; Pispas, S.; Štěpánek, M. Formation of Core/CoronaNano- particles with Interpolyelectrolyte Complex Cores in Aqueous Solution: Insight into Chain Dynamics in the Complex from Fluorescence Quenching. Soft Matter 2018, 14, 7578–7585.
- Marciel, A. B.; Srivastava, S.; Tirrell, M. V. Structure and Rheology of Polyelectrolyte Complex Coacervates. Soft Matter 2018, 14, 2454–2464. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Bronich, T. K.; Chelushkin, P. S.; Kabanov, A. V. Dynamic Properties of Block Ionomer Complexes with Polyion Complex Cores. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 5863–5868. [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, J. S.; Hamley, I. W.; Ryu, C. Y.; Lodge, T. P. Contrast Variation Small-Angle Neutron Scattering Study of the Structure of Block Copolymer Micelles in a Slightly Selective Solvent at Semidilute Concentrations. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 542–550. [CrossRef]
- Lund, R.; Willner, L.; Richter, D.; Lindner, P.; Narayanan, T. Kinetic Pathway of the Cylinder-to-Sphere Transition in Block Copolymer Micelles Observed in Situ by Time-Resolved Neutron and Synchrotron Scattering. ACS Macro Lett. 2013, 2, 1082–1087. [CrossRef]
- Cameron, N. S.; Corbierre, M. K.; Eisenberg, A. 1998 E.W.R. Steacie Award Lecture Asymmetric Amphiphilic Block Copolymers in Solution: A Morphological Wonderland. Can. J. Chem. 1999, 77, 1311–1326. [CrossRef]
- Kalkowski, J.; Liu, C.; Leon-Plata, P.; Szymusiak, M.; Zhang, P.; Irving, T.; Shang, W.; Bilsel, O.; Liu, Y. In Situ Measurements of Polymer Micellization Kinetics with Millisecond Temporal Resolution. ACS Macro Lett. 2019, 52, 3151–3157.
- Parent, L. R.; Bakalis, E.; Ramírez-Hernández, A.; Kammeyer, J. K.; Park, C.; de Pablo, J.; Zerbetto, F.; Patterson, J. P.; Gianneschi, N. C. Directly Observing Micelle Fusion and Growth in Solution by Liquid-Cell Transmission Electron Microscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 17140–17151. [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Ahmed, F.; Bhasin, N.; Discher, D. E. Visualizing Worm Micelle Dynamics and Phase Transitions of a Charged Diblock Copolymer in Water. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 3772–3779. [CrossRef]
- Loverde, S. M.; Ortiz, V.; Kamien, R. D.; Klein, M. L.; Discher, D. E. Curvature-Driven Molecular Demixing in the Budding and Breakup of Mixed Component Worm-Like Micelles. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 1419–1425. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yu, K.; Eisenberg, A. Ion-Induced Morphological Changes in “Crew-Cut” Aggregates of Amphiphilic Block Copolymers. Science 1996, 272, 1777–1779. [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Chen, Z.; Zhong, S.; Wooley, K. L.; Pochan, D. J. Block Copolymer Assembly via Kinetic Control. Science 2007, 317, 647–650. [CrossRef]
- Meli, L.; Santiago, J. M.; Lodge, T. P. Path-Dependent Morphology and Relaxation Kinetics of Highly Amphiphilic Diblock Copolymer Micelles in Ionic Liquids. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 2018–2027. [CrossRef]
- Muthukumar, M. 50th Anniversary Perspective: A Perspective on Polyelectrolyte Solutions. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 9528–9560. [CrossRef]
- Krogstad, D. V.; Lynd, N. A.; Miyajima, D.; Gopez, J.; Hawker, C. J.; Kramer, E. J.; Tirrell, M. V. Structural Evolution of Polyelectrolyte Complex Core Micelles and Ordered-Phase Bulk Materials. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 8026–8032. [CrossRef]
- Martel, A.; Liu, P.; Weiss, T. M.; Niebuhr, M.; Tsuruta, H. An Integrated High-Throughput Data Acquisition System for Biological Solution X-Ray Scattering Studies. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 2012, 19 Pt 3, 431–434. [CrossRef]
- de Pablo, J. J.; Jones, B.; Kovacs, C. L.; Ozolins, V.; Ramirez, A. P. The Materials Genome Initiative, the Interplay of Experiment, Theory and Computation. Curr. Opin. Solid. State Mater. Sci. 2014, 18, 99–117. [CrossRef]
- Acar, H.; Ting, J. M.; Srivastava, S.; LaBelle, J. L.; Tirrell, M. V. Molecular Engineering Solutions for Therapeutic Peptide Delivery. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 6553–6569. [CrossRef]
- Odijk, T. Binding of long flexible chains to a rodlike macromolecule. Macromolecules 1980, 13, 13–1542.
- Perico, A.; Penna, G. L; Arcesi, L. Electrostatic interactions with histone tails may bend linker DNA in chromatin. Biopolymers 2006, 81, 20–28. [CrossRef]
- 1162. Arcesi, L.; Penna, G. L.; Perico, A. Generalized electrostatic model of the wrapping of DNA around oppositely charged proteins. Biopolymers, 2007, 86, 127–135.
- Feric, M.; Vaidya, N.; Harmon, T. S.; Mitrea, D. M.; Zhu, L.; Richardson, T. M.; Kriwacki, R. W.; Pappu, R. V.; Brangwynne, C. P. Coexisting Liquid Phases Underlie Nucleolar Subcompartments. Cell 2016, 165, 1686–1697.
- Banani, S. F.; Lee, H. O.; Hyman, A. A.; Rosen, M. K. Biomolecular condensates: organizers of cellular biochemistry. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 285–298. [CrossRef]
- Yewdall, N. A.; André, A. A. M.; Lu, T.; Spruijt, E. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 52, 101416.
- Drobot, B.; Iglesias-Artola, J. M.; Le Vay, K.; Mayr, V.; Kar, M.; Kreysing, M.; Mutschler, H.; Tang, T. D. Compartmentalised RNA catalysis in membrane-free coacervate protocells. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3643.
- Poudyal, R. R., Guth-Metzler, R. M., Veenis, A. J., Frankel, E. A., Keating, C. D., & Bevilacqua, P. C. Template-directed RNA polymerization and enhanced ribozyme catalysis inside membraneless compartments formed by coacervates. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 490.
- Mountain, G. A.; Keating, C. D. Formation of Multiphase Complex Coacervates and Partitioning of Biomolecules within them. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 630–640. [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Spruijt, E. Multiphase Complex Coacervate Droplets. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 2905–2914. [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Kataoka, K. Biosignal-sensitive polyion complex micelles for the delivery of biopharmaceuticals. Soft Matter 2009, 5, 3810–3817. [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y. H., Lee, K., Li, S. Nucleic acids based polyelectrolyte complexes: Their complexation mechanism, morphology, and stability. Chem. Mater. 2021, 33, 7923–7943. [CrossRef]
- Spruijt, E.; Cohen Stuart, M. A.; van der Gucht, J. Linear viscoelasticity of polyelectrolyte complex coacervates. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 1633–1641. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Winter, H. H.; Perry, S. L. Linear viscoelasticity of complex coacervates. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 239, 46–60. [CrossRef]
- Späth, F.; Donau, C.; Bergmann, A. M.; Kränzlein, M.; Synatschke, C. V.; Rieger, B.; Boekhoven, J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 4782–4789.
- Rubinstein, M.; Semenov, A. N. 1175. Rubinstein, M.; Semenov, A. N. Dynamics of entangled solutions of associating polymers. Macromolecules, 1058. [Google Scholar]
- Heo, T-Y; Kim, S; Chen, L; Sokolova, A; Lee, S and Choi, S-H. Molecular Exchange Kinetics in Complex Coacervate Core Micelles: Role of Associative Interaction. ACS Macro Lett. 2021, 10, 1138–1144. [CrossRef]
- Bos, I.; Brink, E.; Michels, L.; Sprakel, J. DNA dynamics in complex coacervate droplets and micelles. Soft Matter 2022, 18, 2012–2027. [CrossRef]
- Krogstad, D. V.; Lynd, N. A.; Choi, S.-H.; Spruell, J. M.; Hawker, C. J.; Kramer, E. J.; Tirrell, M. V. Effects of Polymer and Salt Concentration on the Structure and Properties of Triblock Copolymer Coacervate Hydrogels. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 1512–1518. [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Andreev, M.; Levi, A. E.; Goldfeld, D. J.; Mao, J.; Heller, W. T.; Prabhu, V. M.; De Pablo, J. J.; Tirrell, M. V. Gel Phase Formation in Dilute Triblock Copolyelectrolyte Complexes. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14131.
- Kim, W. J.; Sato, Y.; Akaike, T.; Maruyama, A. Cationic Comb-Type Copolymers For DNA Analysis. Nat. Mater. 2003, 2, 815–820. [CrossRef]
- Kim, W. J.; Akaike, T.; Maruyama, A. DNA Strand Exchange Stimulated by Spontaneous Complex Formation with Cationic Comb- Type Copolymer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 12676–12677. [CrossRef]
- Bronich, T. K.; Nguyen, H. K.; Eisenberg, A.; Kabanov, A. V. Recognition of DNA Topology in Reactions between Plasmid DNA and Cationic Copolymers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 8339–8343. [CrossRef]
- Kanasty, R.; Dorkin, J. R.; Vegas, A.; Anderson, D. Delivery materials for siRNA therapeutics. Nat. Mater. 2013, 12, 967–977. [CrossRef]
- Matsui, A.; Uchida, S.; Ishii, T.; Itaka, K.; Kataoka, K. Messenger RNA-Based Therapeutics for the Treatment of Apoptosis- Associated Diseases. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15810. [CrossRef]
- Kaczmarek, J. C.; Kowalski, P. S.; Anderson, D. G. Advances in the Delivery of RNA Therapeutics: From Concept to Clinical Reality. Genome Med. 2017, 9, 60. [CrossRef]
- Kole, R.; Krainer, A. R.; Altman, S. RNA Therapeutics: Beyond RNA Interference and Antisense Oligonucleotides. Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 2012, 11, 125–140. [CrossRef]
- Bromberg, L.; Deshmukh, S.; Temchenko, M.; Iourtchenko, L.; Alakhov, V.; Alvarez-Lorenzo, C.; Barreiro-Iglesias, R.; Concheiro, A.; Hatton, T. A. Polycationic Block Copolymers of Poly(ethylene oxide) and Poly(propylene oxide) for Cell Transfection. Bioconjugate Chem. 2005, 16, 626–633. [CrossRef]
- Balomenou, I.; Bokias. G. Water-Soluble Complexes between Cationic Surfactants and Comb-Type Copolymers Consisting of an Anionic Backbone and Hydrophilic Nonionic Poly(N,N-dimethylacrylamide) Side Chains. Langmuir 2005, 21, 9038–9043. [CrossRef]
- Kizhakkedathu, J. N.; Nisha, C. K.; Manorama, S. V.; Maiti, S. Water-Soluble Nanoparticles from Random Copolymer and Oppositely Charged Surfactant, 3. Macromolecular Bioscience 2005, 5, 549–558. [CrossRef]
- Nisha, C. K.; Manorama, S. V.; Kizhakkedathu, J. N.; Maiti, S. Water-soluble complexes from random copolymer and oppositely charged surfactant. 2. Complexes of poly (ethylene glycol)-based cationic random copolymer and bile salts. Langmuir 2004, 20, 8468–8475. [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Chen, H. R.; Hu, J. H.; Yang, W. L.; Wang, C. C. Synthesis and characterization of polyion complex micelles between poly (ethylene glycol)-grafted poly (aspartic acid) and cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide. Colloid Surf A: Physicochem Eng Asp. 2006, 278, 60–66. [CrossRef]
- Bronich, T. K.; Cherry, T.; Vinogradov, S. V.; Eisenberg, A.; Kabanov, V. A., Kabanov, A. V. Self-Assembly in Mixtures of Poly (ethylene oxide)-graft-Poly (ethyleneimine) and Alkyl Sulfates. Langmuir 1998, 14, 6101–6106.
- Bronich, T. K.; Nehls, A.; Eisenberg, A.; Kabanov, V. A., & Kabanov, A. V. Novel drug delivery systems based on the complexes of block ionomers and surfactants of opposite charge. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 1999, 16, 243–251.
- Solomatin, S. V.; Bronich, T. K.; Bargar, T. W.; Eisenberg, A.; Kabanov, V. A.; Kabanov, A. V. Environmentally responsive nanoparticles from block ionomer complexes: effects of pH and ionic strength. Langmuir 2003, 19, 8069–8076. [CrossRef]
- Bronich, T. K.; Kabanov, A. V.; Kabanov, V. A.; Yu, K.; Eisenberg, A. Soluble complexes from poly(ethylene oxide)-block-polymethacrylate anions and n-alkylpyridinium cations. Macromolecules 1997, 30, 3519–3525. [CrossRef]
- Nisha, C. K.; Basak, P.; Manorama, S. V.; Maiti, S.; Jayachandran, K. N. Water-soluble complexes from random copolymer and oppositely charged surfactant. 1. Complexes of poly(ethylene glycol)-based cationic random copolymer and sodium dodecyl sulfate. Langmuir 2003, 19, 2947–2955. [CrossRef]
- Dubruel, P.; De Strycker, J.; Westbroek, P.; Bracke, K.; Temmerman, E.; Vandervoort, J.; Ludwig, A.; Schacht, E. Synthetic polyamines as vectors for gene delivery. Polym. Int. 2002, 51, 948–957.
- Holappa, S.; Andersson, T.; Kantonen, L.; Plattner, P.; Tenhu, H. Soluble polyelectrolyte complexes composed of poly(ethylene oxide)-block-poly(sodium methacrylate) and poly(methacryloyloxyethyl trimethylammonium chloride). Polymer 2003, 44, 7907–7916. [CrossRef]
- Winnik, M. A.; Bystryak, S. M.; Chassenieux, C.; Strashko, V.; Macdonald, P. M.; Siddiqui, J. Study of Interaction of Poly(ethylene imine) with Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate in Aqueous Solution by Light Scattering. Langmuir 2000, 16, 4495–4510. [CrossRef]
- Bystryak, S. M.; Winnik, M. A.; Siddiqui, J. Unusual conductivity changes for sodium dodecyl sulfate solutions in the presence of polyethyleneimine and polyvinylamine. Langmuir 1999, 15, 3748–3751. [CrossRef]
- Voets, I. K.; Fokkink, R.; Hellweg, T.; King, S. M.; de Waard, P.; de Keizer, A.; Stuart, M. A. C. Spontaneous symmetry breaking: formation of Janus micelles. Soft Matter 2009, 5, 999–1005.
- Annaka, M.; Morishita, K.; Okabe, S. Electrostatic Self-Assembly of Neutral and Polyelectrolyte Block Copolymers and Oppositely Charged Surfactant. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 11700–11707. [CrossRef]
- Berret J.-F.; Vigolo, B.; Eng, R.; Hervé, P.; Grillo, I.; Yang, L. Electrostatic Self-assembly of Oppositely Charged Copolymers and Surfactants: A Light, Neutron, and X-ray Scattering Study. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 4922–4930. [CrossRef]
- Gohy, J. F.; Mores, S.; Varshney, S. K.; Jérôme, R. Self-Organization of WaterSoluble Complexes of a Poly (2-vinylpyridinium)-block-poly (ethylene oxide) Diblock with Fluorinated Anionic Surfactants. Macromolecules 2003, 36, 2579–2581.
- Laschewsky, A.; Mertoglu, M.; Kubowicz, S.; Thunemann, A. F. Lamellar Structured Nanoparticles Formed by Complexes of a Cationic Block Copolymer and Perfluorodecanoic Acid. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 9337–9345. [CrossRef]
- Elsabahy, M.; Zhang, M.; Gan, S. M.; Waldron, K. C.; Leroux, J. C. Synthesis and enzymatic stability of PEGylated oligonucleotide duplexes and their self-assemblies with polyamidoamine dendrimers. Soft Matter 2008, 4, 294–302. [CrossRef]
- Harada, A.; Togawa, H.; Kataoka, K.; Physicochemical properties and nuclease resistance of antisense-oligodeoxynucleotides entrapped in the core of polyion complex micelles composed of poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(L-Lysine) block copolymers. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 13, 35–42. [CrossRef]
- Kabanov, A. V.; Vinogradov, S. V.; Suzdaltseva, Y. G.; Alakhov, V. Y. Water-Soluble Block Polycations as Carriers for Oligonucleotide Delivery. Bioconjug. Chem. 1995, 6, 639–643. [CrossRef]
- Vinogradov, S. V.; Bronich, T. K.; Kabanov, A. V. Self-assembly of polyamine-poly(ethylene glycol) copolymers with phosphorothioate oligonucleotides. Bioconjug. Chem. 1998, 9, 805–812. [CrossRef]
- Dufresne, M. H.; Gauthier, M. A.; Leroux, J. C. Thiol-functionalized polymeric micelles: from molecular recognition to improved mucoadhesion. Bioconjug. Chem. 2005, 16, 1027–1033. [CrossRef]
- Jo, J. I.; Nagaya, N.; Miyahara, Y.; Kataoka, M.; Harada-Shiba, M.; Kangawa, K.; Tabata, Y. Transplantation of genetically engineered mesenchymal stem cells improves cardiac function in rats with myocardial infarction: benefit of a novel nonviral vector, cationized dextran. Tissue Eng. 2007, 13, 313–322.
- Alvarez-Lorenzo, C.; Barreiro-Iglesias, R.; Concheiro, A; Iourtchenko, L.; Alakhov, V.; Bromberg, L.; Temchenko, M.; Deshmukh, S.; Hatton, T. A. Biophysical characterization of complexation of DNA with block copolymers of poly(2-dimethylaminoethyl) methacrylate, poly(ethylene oxide), and poly(propylene oxide). Langmuir 2005, 21, 5142–5148.
- Wakebayashi, D.; Nishiyama, N.; Yamasaki, Y.; Itaka, K.; Kanayama, N.; Harada, A.; Nagasaki, Y.; Kataoka, K. Lactose-conjugated polyion complex micelles incorporating plasmid DNA as a targetable gene vector system: their preparation and gene transfecting efficiency against cultured HepG2 cells. J. Control. Release 2004, 95, 653–664.
- Wakebayashi, D.; Nishiyama, N.; Itaka, K.; Miyata, K.; Yamasaki, Y.; Harada, A.; Koyama, H.; Nagasaki, Y.; Kataoka, K., Polyion Complex Micelles of pDNA with Acetalpoly(ethylene glycol)-poly(2-(dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate) Block Copolymer as the Gene Carrier System: Physicochemical Properties of Micelles Relevant to Gene Transfection Efficacy. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 2128–2136.
- Kataoka, K.; Harada, A.; Wakebayashi, D.; Nagasaki, Y. Polyion complex micelles with reactive aldehyde groups on their surface from plasmid DNA and end-functionalized charged block copolymers. Macromolecules 1999, 32, 6892–6894. [CrossRef]
- Harada-Shiba, M.; Yamauchi, K.; Harada, A.; Takamisawa, I.; Shimokado, K.; Kataoka, K. Polyion complex micelles as vectors in gene therapy--pharmacokinetics and in vivo gene transfer. Gene Ther. 2002, 9, 407–414. [CrossRef]
- Wolfert, M. A.; Schacht, E. H.; Toncheva, V.; Ulbrich, K.; Nazarova, O.; Seymour, L. W. Characterization of vectors for gene therapy formed by self-assembly of DNA with synthetic block co-polymers. Hum. Gene Ther. 1996, 7, 2123–2133. [CrossRef]
- Itaka, K.; Yamauchi, K.; Harada, A.; Nakamura, K.; Kawaguchi, H.; Kataoka, K. Polyion complex micelles from plasmid DNA and poly (ethylene glycol)–poly (l-lysine) block copolymer as serum-tolerable polyplex system: physicochemical properties of micelles relevant to gene transfection efficiency. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 4495–4506.
- Itaka, K.; Harada, A.; Nakamura, K.; Kawaguchi, H.; Kataoka K. Evaluation by fluorescence resonance energy transfer of the stability of nonviral gene delivery vectors under physiological conditions. Biomacromolecules 2002, 3, 841–845. [CrossRef]
- Choi, J. S., Lee, E. J., Choi, Y. H., Jeong, Y. J., Park, J. S. Poly (ethylene glycol)-block-poly (L-lysine) dendrimer: novel linear polymer/dendrimer block copolymer forming a spherical water-soluble polyionic complex with DNA. Bioconjug. Chem. 1999, 10, 62–65. [CrossRef]
- Oupický, D., Koňák, Č., Dash, P. R., Seymour, L. W., Ulbrich, K. (). Effect of albumin and polyanion on the structure of DNA complexes with polycation containing hydrophilic nonionic block. Bioconjug. Chem. 1999, 10, 764–772. [CrossRef]
- Oupický, D.; Koňák, Č.; Ulbrich, K. Preparation of DNA Complexes with Diblock Copolymers of Poly[N(2-Hydroxypropyl)Methacrylamide] and Polycations. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 1999, 7, 59–65. [CrossRef]
- Oupicky, D.; Konak, C.; Ulbrich, K. DNA complexes with block and graft copolymers of N-(2-hydroxypropyl)methacrylamide and 2-(trimethylammonio)ethyl methacrylate. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 1999, 10, 573–590. [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Jeong, J. H.; Park, T. G. A new gene delivery formulation of polyethylenimine/DNA complexes coated with PEG conjugated fusogenic peptide. J. Control. Release 2001, 76, 183–192. [CrossRef]
- Caputo, A.; Betti, M.; Altavilla, G.; Bonaccorsi, A.; Boarini, C.; Marchisio, M.; Buttò, S.; Sparnacci, K.; Laus, M.; Tondelli, L.; Ensoli, B. Micellar-type complexes of tailor-made synthetic block copolymers containing the HIV-1 tat DNA for vaccine application. Vaccine 2002, 20, 2303–2317.
- Laus, M.; Sparnacci, K.; Ensoli, B.; Buttò, S. O; Caputo, A.; Mantovani, I.; Zuccheri, G.; Samori, B.; Tondelli, L. Complex associates of plasmid DNA and a novel class of block copolymers with PEG and cationic segments as new vectors for gene delivery. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2001, 12, 209–228. [CrossRef]
- Tan, J. F.; Too, H. P.; Hatton, T. A.; Tam, K. C. Aggregation behavior and thermodynamics of binding between poly (ethylene oxide)-block-poly (2-(diethylamino) ethyl methacrylate) and plasmid DNA. Langmuir 2006, 22, 3744–3750. [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Bazan, G. C. Homogeneous fluorescence-based DNA detection with water-soluble conjugated polymers. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 4467–4476. [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Bazan, G. C. Interpolyelectrolyte complexes of conjugated copolymers and DNA: Platforms for multicolor biosensors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 1942–1943. [CrossRef]
- Scales, C. W.; Huang, F. Q.; Li, N.; Vasilieva, Y. A, Ray, J.; Convertine, A. J.; McCormick, C. L. Corona-stabilized interpolyelectrolyte complexes of SiRNA with nonimmunogenic, hydrophilic/cationic block copolymers prepared by aqueous RAFT polymerization. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 6871–6881. [CrossRef]
- Itaka, K.; Kanayama, N.; Nishiyama, N.; Jang, W. D.; Yamasaki, Y.; Nakamura, K.; Kawaguchi, H.; Kataoka, K. Supramolecular nanocarrier of siRNA from PEG-based block catiomer carrying diamine side chain with distinctive pKa directed to enhance intracellular gene silencing. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 13612–13613.
- Bronstein, L. H.; Sidorov, S. N.; Valetsky, P. M.; Hartmann, J.; Colfen, H.; Antonietti, M. Induced micellization by interaction of poly(2-vinylpyridine)-block-poly(ethylene oxide) with metal compounds. Micelle characteristics and metal nanoparticle formation. Langmuir 1999, 15, 6256–6262.
- Vamvakaki, M.; Papoutsakis, L.; Katsamanis, V.; Afchoudia, T.; Fragouli, P. G.; Iatrou, H.; Hadjichristidis, N.; Armes, S. P.; Sidorov, S.; Zhirov, D.; Zhirov, V.; Kostylev, M.; Bronstein, L. M.; Anastasiadis, S. H. Micellization in pH-sensitive amphiphilic block copolymers in aqueous media and the formation of metal nanoparticles. Faraday Discuss. 2005, 128, 129–147.
- Bronstein, L. M.; Sidorov, S. N.; Zhirov, V.; Zhirov, D.; Kabachii, Y. A.; Kochev, S. Y.; Valetsky, P. M.; Stein, B.; Kiseleva, O. I.; Polyakov, S. N.; Shtykova, E. V.; Nikulina, E. V.; Svergun, D. I.; Khokhlov, A. R. Metalated Diblock and Triblock Poly(ethylene oxide)-block-poly(4-vinylpyridine) Copolymers: Understanding of Micelle and Bulk Structure. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 18786–18798.
- Berret, J. F.; Schonbeck, N.; Gazeau, F.; El Kharrat, D.; Sandre, O.; Vacher, A.; Airiau, M. Controlled clustering of superparamagnetic nanoparticles using block copolymers: design of new contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 1755–1761. [CrossRef]
- Berret J-F. Stoichiometry of electrostatic complexes determined by light scattering. Macromolecules 2007, 40, 4260–4266. [CrossRef]
- Dufresne, M. H.; Leroux, J. C. Study of the Micellization Behavior of Different Order Amino Block Copolymers with Heparin. Pharm. Res. 2004, 21, 160–169. [CrossRef]
- Gohy, J. F.; Varshney, S. K.; Antoun, S.; Jerome, R. Water-soluble complexes formed by sodium poly(4-styrenesulfonate) and a poly(2-vinylpyridinium)-block-poly(ethyleneoxide) copolymer. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 9298–9305. [CrossRef]
- Gohy, J. F.; Varshney, S. K.; Jerome, R. Water-Soluble Complexes Formed by Poly (2-vinylpyridinium)-block-poly (ethylene oxide) and Poly (sodium methacrylate)-block-poly (ethylene oxide) Copolymers. Macromolecules 2001, 34, 3361–3366. [CrossRef]
- van der Burgh, S. 1240. van der Burgh, S. Complex Coacervate Core Micelles in Solution and at Interfaces. PhD thesis, Wageningen Universiteit, Wageningen, The Netherlands, ; pp 1-134. https://edepot.wur. 26 April 1935. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Nakashima, K. Fluorescence Studies on the Properties of the Nanoaggregates of Poly(ethylene oxide)-b-polymethacrylate Copolymer Formed by Binding of Cationic Surfactants to Polymethacrylate Block. Langmuir 2003, 19, 548–553. [CrossRef]
- Bronich, T. K.; Ming, O. Y.; Kabanov, V. A.; Eisenberg, A.; Szoka, F. C.; Kabanov, A. V. Synthesis of vesicles on polymer template. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 11872–11873.
- Bronich, T. K., Popov, A. M., Eisenberg, A., Kabanov, V. A., Kabanov, A. V. Effects of block length and structure of surfactant on self-assembly and solution behavior of block ionomer complexes. Langmuir 2000, 16, 481–489. [CrossRef]
- Kabanov, A. V.; Bronich, T. K.; Kabanov, V. A.; Yu, K.; Eisenberg, A. Spontaneous formation of vesicles from complexes of block ionomers and surfactants. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 9941–9942. [CrossRef]
- Solomatin, S. V.; Bronich, T. K.; Eisenberg, A.; Kabanov, V. A.; Kabanov, A. V., Nanomaterials from Ionic Block Copolymers and Single-, Double-, and Triple-Tail Surfactants. Langmuir 2007, 23, 2838–2842.
- Nagata, I.; Morawetz, H. Study of the association of anionic and cationic polymers by nonradiative energy transfer. Macromolecules 1981, 14, 87–91. [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, A.; Katoh, M.; Ishihara, T.; Akaike, T. Comb-type polycations effectively stabilize DNA triplex. Bioconjug. Chem. 1997, 8, 3–6. [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y. H.; Liu, F.; Choi, J. S.; Kim, S. W.; Park, J. S. Characterization of a targeted gene carrier, lactose-polyethylene glycol-grafted poly-L-lysine and its complex with plasmid DNA. Hum. Gene Ther. 1999, 10, 2657–2665. [CrossRef]
- Harada, A.; Kataoka K. Pronounced activity of enzymes through the incorporation into the core of polyion complex micelles made from charged block copolymers. J. Control. Release. 2001, 72, 85–91.
- Weaver, J. V. M.; Armes, S. P.; Liu, S. Y. A “holy trinity” of micellar aggregates in aqueous solution at ambient temperature: unprecedented self-assembly behavior from a binary mixture of a neutral-cationic diblock copolymer and an anionic polyelectrolyte. Macromolecules 2004, 36, 9994–9998.
- Gohy, J. F.; Varshney, S. K.; Jerome, R. Morphology of water-soluble interpolyelectrolyte complexes formed by poly (2-vinylpyridinium) -block-poly (ethylene oxide) diblocks and poly (4-styrenesulfonate) polyanions. Macromolecules 2001, 34, 2745–2747. [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Besseling, N. A. M.; de Keizer, A.; Drechsler, M.; Fokkink, R.; Cohen Stuart, M. A. Wormlike aggregates from a supramolecular coordination polymer and a diblock copolymer. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 11662–11669. [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Besseling, N. A. M.; de Keizer, A.; Cohen Stuart, M. A. Characteristic differences in the formation of complex coacervate core micelles from neodymium and zinc-based coordination polymers. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 5811–5818. [CrossRef]
- Berret, J.-F.; Sehgal, A.; Morvan, M.; Sandre, O.; Vacher, A.; Airiau, M. Stable oxide nanoparticle clusters obtained by complexation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 303, 315–318. [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Chapel, J.-P.; Castaing, J.-P.; Fresnais, J.; Berret, J.-F. Stability and Adsorption Properties of Electrostatic Complexes: Design of Hybrid Nanostructures for Coating Applications. Langmuir 2007, 23, 11996–11998. [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Shi, L. Q.; Zhang, W. Q.; An, Y. L.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z. Y.; Zhu, X. X. Thermoresponsiveness of hybrid micelles from poly(ethylene glycol)-block-poly(4-vinylpyridium) cations annul SO42− anions in aqueous solutions. Langmuir 2006, 22, 1474–1477. [CrossRef]
- Jang, W. D.; Nishiyama, N.; Zhang, G. D.; Harada, A.; Jiang, D. L.; Kawauchi, S.; Morimoto, Y.; Kikuchi, M.; Koyama, H.; Aida, T.; Kataoka, K. Supramolecular Nanocarrier of Anionic Dendrimer Porphyrins with Cationic Block Copolymers Modified with Polyethylene Glycol to Enhance Intracellular Photodynamic Efficacy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2005, 44, 419–423.
- Li, Y.; Jang, W-D.; Nishiyama, N.; Kishimura, A.; Kawauchi, S.; Morimoto, Y.; Miake, S.; Yamashita, T.; Kikuchi, M.; Aida, T.; Kataoka, K. Dendrimer generation effects on photodynamic efficacy of dendrimer porphyrins and dendrimer-loaded supramolecular nanocarriers. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 5557–5562.
- Ideta, R.; Tasaka, F.; Jang, W. D.; Nishiyama, N.; Zhang, G. D.; Harada, A. Nanotechnology-based photodynamic therapy for neovascular disease using a supramolecular nanocarrier loaded with a dendritic photosensitizer. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 2426–2431. [CrossRef]
- Karanikolopoulos, N.; Pitsikalis, M.; Hadjichristidis, N.; Georgikopoulou, K.; Calogeropoulou, T.; Dunlap, J. R. pH-Responsive aggregates from double hydrophilic block copolymers carrying zwitterionic groups. Encapsulation of antiparasitic compounds for the treatment of leishmaniasis. Langmuir 2007, 23, 4214–4224.
- Katakura, H., Harada, A., Kataoka, K., Furusho, M., Tanaka, F., Wada, H., & Ikenaka, K. Improvement of retroviral vectors by coating with poly (ethylene glycol)-poly (L-lysine) block copolymer (PEG-PLL). J. Gene Med. A cross-disciplinary journal for research on the science of gene transfer and its clinical applications. 2004, 6, 471–477.
- Dautzenberg, H. Polyelectrolyte complex formation in highly aggregating systems. 1. Effect of salt: polyelectrolyte complex formation in the presence of NaCl. Macromolecules 1997, 30, 7810–7815. [CrossRef]
- Dautzenberg, H.; Karibyants, N. Polyelectrolyte complex formation in highly aggregating systems. Effect of salt: response to subsequent addition of NaCl. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 1999, 200, 118–125. [CrossRef]
- Dautzenberg, H.; Kriz, J. Response of polyelectrolyte complexes to subsequent addition of salts with different cations. Langmuir 2003, 19, 5204–5211. [CrossRef]
- Ganguli, M.; Jayachandran, K. N.; Maiti, S. Nanoparticles from cationic copolymer and DNA that are soluble and stable in common organic solvents. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 26–27. [CrossRef]
- Nisha, C. K.; Manorama, S. V.; Ganguli, M.; Maiti, S.; Kizhakkedathu, J. N. Complexes of poly (ethylene glycol)-based cationic random copolymer and calf thymus DNA: a complete biophysical characterization. Langmuir 2004, 20, 2386–2396. [CrossRef]
- Asayama, S.; Maruyama, A.; Cho, C. S.; Akaike, T. Design of comb-type polyamine copolymers for a novel pH-sensitive DNA carrier. Bioconjug. Chem. 1997, 8, 833–838. [CrossRef]
- Tsolakis, P.; Bokias, G. Temperature-sensitive water-soluble polyelectrolyte/surfactant complexes formed between dodecyltrimethylammonium bromide and a comb-type copolymer consisting of an anionic backbone and poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) side chains. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 393–398. [CrossRef]
- Khanal, A.; Nakashima, Y.; Li, Y.; Nakashima, K.; Kawasaki, N.; Oishi, Y. Fabrication of nanoaggregates of poly(ethylene oxide)-b-polymethacrylate by complex formation with chitosan or methylglycolchitosan. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 2005, 260, 129–135. [CrossRef]
- Voets, I. K.; de Keizer, A.; Cohen Stuart, M. A.; de Waard, P. Core and corona structure of mixed polymeric micelles. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 5952–5955. [CrossRef]
- Voets, I. K.; de Keizer, A.; de Waard, P.; Frederik, P. M.; Bomans, P. H. H.; Schmalz, H.; Walther, A.; King, S. M.; Leermakers, F. A. M.; Cohen Stuart, M. A. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 6673–6676.
- Voets, I. K.; Fokkink R.; De Keizer A.; May R. P.; De Waard P.; Cohen Stuart M. A. On the Transition between a Heterogeneous and Homogeneous Corona in Mixed Polymeric Micelles. Langmuir 2008, 24, 12221–12227. [CrossRef]
- Serefoglou, E.; Oberdisse, J.; Staikos, G. Characterization of the soluble nanoparticles formed through coulombic interaction of bovine serum albumin with anionic graft copolymers at low pH. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 1195–1199. [CrossRef]
- Bastardo, L. A.; Iruthayaraj, J.; Lundin, M.; Dedinaite, A.; Vareikis, A.; Makuška, R.; van der Wal, A.; Furó, I.; Garamus, V. M.; Claesson, P. M. Soluble Complexes in Aqueous Mixtures of Low Charge Density Comb Polyelectrolyte and Oppositely Charged Surfactant Probed by Scattering and NMR. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 312, 21–33.
- Berret, J-F. Evidence of overcharging in the complexation between oppositely charged polymers and surfactants. J. Chem. Phys. 2005, 123, 164703–164712. [CrossRef]
- Sanson, N.; Bouyer, F.; Gerardin, C.; In, M. Nanoassemblies formed from hydrophilic block copolymers and multivalent ions. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2004, 6, 1463–1466. [CrossRef]
- Sanson, N.; Putaux, J. L.; Destarac, M.; Gerardin, C.; Fajula, F. Hybrid Organic-Inorganic Colloids with a Core-Corona Structure: A Transmission Electron Microscopy Investigation. Macromol. Symp. 2005, 226, 279–288. [CrossRef]
- Gerardin, C.; Sanson, N.; Bouyer, F.; Fajula, F.; Putaux, J. L.; Joanicot, M.; Chopin, T. Highly Stable Metal Hydrous Oxide Colloids by Inorganic Polycondensation in Suspension. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 3681–3685. [CrossRef]
- Bouyer, F.; Gérardin, C.; Fajula, F.; Putaux, J. L.; Chopin, T. Role of doublehydrophilic block copolymers in the synthesis of lanthanum-based nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2003, 217, 179–184. [CrossRef]
- Berret, J-F.; Sandre, O.; Mauger, A. Size distribution of superparamagnetic particles determined by magnetic sedimentation. Langmuir 2007, 23, 2993–2999. [CrossRef]
- Bouyer, F.; Sanson, N.; Destarac, M.; Gerardin, C. Hydrophilic block copolymer-directed growth of lanthanum hydroxidenanoparticles. New J. Chem. 2006, 30, 399–408. [CrossRef]
- Gu, C. F.; Chen, D. Y.; Jiang, M. Short-Life Core-Shell Structured Nanoaggregates Formed by the Self-Assembly of PEO-b-PAA/ETC (1-(3-Dimethylamino- propyl)-3-ethylcarbodiimide Methiodide) and Their Stabilization. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 1666–1669. [CrossRef]
- Khullar, P.; Singh, V.; Mahal, A.; Kumar, H.; Kaur, G.; Bakshi, M. S. Block Copolymer Micelles as Nanoreactors for Self-assembled Morphologies of Gold Nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 3028–3039. [CrossRef]
- Mathot, F.; van Beijsterveldt, L.; Preat, V.; Brewster, M.; Arien, A. Intestinal Uptake and Biodistribution of Novel Polymeric Micelles after Oral Administration. J. Control. Release 2006, 111, 47–55. [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.-G.; Jiang, Y.-W.; Chen, Z.; Yu, Z.-W. Folding Behaviors of Protein (Lysozyme) Confined in Polyelectrolyte Complex Micelle. Langmuir 2016, 32, 3655–3664. [CrossRef]
- Nolles, A.; Westphal, A. H.; de Hoop, J. A.; Fokkink, R. G.; Kleijn, J. M.; van Berkel, W. J. H.; Borst, J. W. Encapsulation of GFP in Complex Coacervate Core Micelles. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 1542–1549.
- Sant, V. P.; Smith, D.; Leroux, J.-C. Enhancement of Oral Bioavailability of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs by Poly(Ethylene Glycol)-block-Poly(Alkyl Acrylate-co-Methacrylic Acid) Self-Assemblies. J. Control. Release 2005, 104, 289–300. [CrossRef]
- Kotz, J.; Kosmella, S.; Beitz, T. Self-assembled Polyelectrolyte Systems. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2001, 26, 1199–1232. [CrossRef]
- Cooper, C. L.; Dubin, P. L.; Kayitmazer, A. B.; Turksen, S. Polyelectrolyte-Protein Complexes. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 10, 52–78.
- Blocher, W. C.; Perry, S. L. Complex Coacervate-Based Materials for Biomedicine. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2017, 9 (4), No. e1442.
- Gapinśki, J.; Szymanśki, J.; Wilk, A.; Kohlbrecher, J.; Patkowski, A.; Hołyst, R. Size and Shape of Micelles Studied by Means of SANS, PCS, and FCS. Langmuir 2010, 26, 9304–9314. [CrossRef]
- Nolles, A.; Westphal, A. H.; Kleijn, J. M.; van Berkel, W. J. H.; Borst, J. W. Colorful Packages: Encapsulation of Fluorescent Proteins in Complex Coacervate Core Micelles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1557–1576. [CrossRef]
- Elson, E. L. Fluorescence Correlation Spectroscopy: Past, Present, Future. Biophys. J. 2011, 101, 2855–2870. [CrossRef]
- Martins, L. O.; Soares, C. M.; Pereira, M. M.; Teixeira, M.; Costa, T.; Jones, G. H.; Henriques, A. O. Molecular and Biochemical Characterization of a Highly Stable Bacterial Laccase that Occurs as a Structural Component of the Bacillus subtilis Endospore Coat. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 18849–18859.
- Guzik, U.; Hupert-Kocurek, K.; Wojcieszynska, D. Immobilization as Strategy for Improving Enzyme Properties-Application to Oxidoreductases. Molecules 2014, 19, 8995–9018. [CrossRef]
- Enguita, F. J.; Martins, L. O.; Henriques, A. O.; Carrondo, M. A. Crystal Structure of a Bacterial Endospore Coat Component. A Laccase with Enhanced Thermostability Properties. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 19416–19425.
- Christopher, L. P.; Yao, B.; Ji, Y. Lignin Biodegradation with Laccase-Mediator Systems. Front. Energy Res. 2014, 2, 1–13.
- Shraddha; Shekher, R.; Sehgal, R.; Kamthania, M.; Kumar, A. Laccase: Microbial Sources, Production, Purification, and Potential Biotechnological Applications. Enzyme Res. 2011, 2011, 217861.
- Fernandes, A. T.; Lopes, C.; Martins, L. O.; Melo, E. P. Unfolding Pathway of CotA-Laccase and the Role of Copper on the Prevention of Refolding through Aggregation of the Unfolded State. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 422, 442–446. [CrossRef]
- Beneyton, T.; Beyl, Y.; Guschin, D. A.; Griffiths, A. D.; Taly, V.; Schuhmann, W. The Thermophilic CotA Laccase from Bacillus subtilis: Bioelectrocatalytic Evaluation of O2 Reduction in the Direct and Mediated Electron Transfer Regime. Electroanalysis 2011, 23, 1781–1789. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Xie, T.; Zhong, Q.; Wang, G. Crystal Structure of CotA Laccase Complexed with 2,2-azinobis-(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonate) at a Novel Binding Site. Acta Crystallogr., Sect. F: Struct. Biol. Commun. 2016, 72, 328–335. [CrossRef]
- Bryjak, J.; Kruczkiewicz, P.; Rekuc, A.; Peczynska-Czoch, W. Laccase Immobilization on Copolymer of Butyl Acrylate and Ethylene Glycol Dimethacrylate. Biochem. Eng. J. 2007, 35, 325–332. [CrossRef]
- Pich, A.; Bhattacharya, S.; Adler, H.-J. P.; Wage, T.; Taubenberger, A.; Li, Z.; van Pee, K.-H.; Böhmer, U.; Bley, T. Composite Magnetic Particles as Carriers for Laccase from Trametes versicolor. Macromol. Biosci. 2006, 6, 301–310. [CrossRef]
- Movassaghian, S.; Merkel, O. M.; Torchilin, V. P. Applications of polymer micelles for imaging and drug delivery. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2015, 7, 691–707. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C. X.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y. Recent advances in self-assembled nano-therapeutics. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2018, 36, 322–346. [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, C.; Pucci, C.; Ciofani, G. Nanostructured carriers as innovative tools for cancer diagnosis and therapy. APL Bioeng. 2019, 3, 011502. [CrossRef]
- Majumder, N.; Das, N. G.; Das, S. K. Polymeric micelles for anticancer drug delivery. Ther. Deliv. 2020, 11, 613–635. [CrossRef]
- Perin, F.; Motta, A.; Maniglio, D. Amphiphilic copolymers in biomedical applications: Synthesis routes and property control. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2021, 123, 111952. [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, B.; Biswas, S. Polymeric micelles in cancer therapy: State of the art. J. Control. Release 2021, 332, 127–147. [CrossRef]
- Shu, J. Y.; Panganiban, B.; Xu, T. Peptide-polymer conjugates: from fundamental science to application. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2013, 64, 631–657. [CrossRef]
- Wilson, P. Synthesis and Applications of Protein/Peptide-Polymer Conjugates. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2017, 218, 1600595. [CrossRef]
- Paik, B. A.; Mane, S. R.; Jia, X.; Kiick, K. L. Responsive Hybrid (Poly)peptide-Polymer Conjugates. J. Mater. Chem. B. 2017, 5, 8274–8288. [CrossRef]
- Stevens, C.A.; Kaur, K.; Klok, H.-A. Self-Assembly of Protein-Polymer Conjugates for Drug Delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 174, 447–460. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, E.; Yang, J.; Cao, Z. Strategies to improve micelle stability for drug delivery. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 4985–4998. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cagel, M.; Tesan, F. C.; Bernabeu, E.; Salgueiro, M. J.; Zubillaga, M. B.; Moretton, M. A.; Chiappetta, D. A. Polymeric mixed micelles as nanomedicines: Achievements and perspectives. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 113, 211–228. [CrossRef]
- Mi, P.; Cabral, H.; Kataoka, K. Ligand-Installed Nanocarriers toward Precision Therapy. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1902604. [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Wang, L. H.; Ding, S. G.; You, Y. Z. Fluorinated PEG-polypeptide polyplex micelles have good serum-resistance and low cytotoxicity for gene delivery. Macromol. Biosci. 2017, 17, 1700114.
- Chen, G.; Wang, K.; Wang, Y.; Wu, P.; Sun, M.; Oupický, D. Fluorination Enhances Serum Stability of Bioreducible Poly(amido amine) Polyplexes and Enables Efficient Intravenous siRNA Delivery. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2018, 7, 1700978. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, T.; Wang, W.; Bell, C. A.; Han, Y.; Fu, C.; Peng, H.; Tan, X.; Král, P.; Gaus, K.; Gooding, J. J.; Whittaker, A. K. Tuning of the Aggregation Behavior of Fluorinated Polymeric Nanoparticles for Improved Therapeutic Efficacy. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 7425–7434. [CrossRef]
- 1320. Zerrillo, L.; Gupta, K.B.S.S.; Lefeber, F.A.W.M.; Da Silva, C.G.; Galli, F.; Chan, A.; Veltien, A.; Dou, W.; Censi, R.; Di Martino, P.; Srinivas, M.; Cruz, L. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 235.
- Yin, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z.-H.; Han, X. Stimuli-Responsive Block Copolymer-Based Assemblies for Cargo Delivery and Theranostic Applications. Polymers 2016, 8, 268. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Zhang, L.; Yang, T.; Wu, H. Stimuli-responsive polymeric micelles for drug delivery and cancer therapy. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018, 13, 2921–2942. [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, J.; Kong, H.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, G. Functional biomimetic nanoparticles for drug delivery and theranostic applications in cancer treatment. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2018, 19, 771–790. [CrossRef]
- Mi, P. Stimuli-responsive nanocarriers for drug delivery, tumor imaging, therapy and theranostics. Theranostics 2020, 10, 4557–4588. [CrossRef]
- Dhara (Ganguly), M. Smart polymeric nanostructures for targeted delivery of therapeutics. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A 2020, 58, 269–284.
- Das, S. S.; Bharadwaj, P.; Bilal, M.; Barani, M.; Rahdar, A.; Taboada, P.; Bungau, S.; Kyzas, G. Z. Stimuli-Responsive Polymeric Nanocarriers for Drug Delivery, Imaging, and Theragnosis. Polymers 2020, 12, 1397. [CrossRef]
- Shahriari, M.; Torchilin, V. P.; Taghdisi, S. M.; Abnous, K.; Ramezani, M.; Alibolandi, M. “Smart” self-assembled structures: Toward intelligent dual responsive drug delivery systems. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 5787–5803. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mane, S. R.; Sathyan, A.; Shunmugam, R. Biomedical applications of pH-responsive amphiphilic polymer nanoassemblies. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 2104–2117. [CrossRef]
- Grimm, O.; Wendler, F.; Schacher, F. H. Micellization of Photo-Responsive Block Copolymers. Polymers 2017, 9, 396. [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q., Fei C., Yin H., Feng Y. Stimuli-responsive polymer wormlike micelles. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2019, 89, 108–132. [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.; Qiang, M.; Ke, W.; Han, Y.; Mukerabigwi, J. F.; Ge, Z. Hypoxia-responsive block copolymer radiosensitizers as anticancer drug nanocarriers for enhanced chemoradiotherapy of bulky solid tumors. Biomaterials 2018, 181, 360–371. [CrossRef]
- Quader, S.; Cabral, H.; Liu, X.; Paraiso, W. K. D.; Kinoh, H.; Kataoka, K. Engineered Nanomedicine Targets Intractable Cancers. Mater. Proc. 2021, 4, 84.
- Cao, Y.; Cao, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, D.; Li, M.; Xu, Y.; He, K.; Chen, G.; Yuan, C.; Dai, L. The research on multi-responsive azobenzene block copolymer and its self-assembly behavior. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2020, 31, 759–771. [CrossRef]
- Razavi, B.; Abdollahi, A.; Roghani-Mamaqani, H.; Salami-Kalajahi M. Light-, temperature-, and pH-responsive micellar assemblies of spiropyran-initiated amphiphilic block copolymers: Kinetics of photochromism, responsiveness, and smart drug delivery. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 2020, 109, 110524. [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Deng, Y.; Yuan, H.; Yuan, W.; Song, Y.; Li, Z. Hypoxia/Temperature/pH Triple Stimuli–Responsive Block Copolymers: Synthesis, Self-Assembly, and Controlled Drug Release. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2021, 306, 2100073. [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Shamul, J. G.; Shah, S. R.; Shin, A.; Lee, B. J.; Quinones-Hinojosa, A.; Green, J. J. Verteporfin-Loaded Poly(ethylene glycol)-Poly(beta-amino ester)-Poly(ethylene glycol) Triblock Micelles for Cancer Therapy. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 3361–3370. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, W.; Su, F.; Li, S. Self-assembled micelles prepared from poly(D, L -lactide-co-glycolide)-poly(ethylene glycol) block copolymers for sustained release of valsartan. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2021, 32, 1262–1271. [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Meng, F.; Deng, C.; Zhong, Z. Robust, Tumor-Homing and Redox-Sensitive Polymersomal Doxorubicin: A Superior Alternative to Doxil and Caelyx? J. Control. Release 2016, 239, 149–158. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Li, J. W.; Zhang, W. J.; Hong, C. Y.; Pan, C. Y. pH- and reductant-responsive polymeric vesicles with robust membrane-cross-linked structures: In situ cross-linking in polymerization-induced self-assembly. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 1140–1149. [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque, L. J. C.; Sincari, V.; Jäger, A.; Kucka, J.; Humajova, J.; Pankrac, J.; Paral, P.; Heizer, T.; Janouškova, O.; Davidovich, I.; Talmon, Y.; Pouckova, P.; Štěpánek, P.; Sefc, L.; Hruby, M.; Giacomelli, F. C.; Jäger, E. pH-responsive polymersome-mediated delivery of doxorubicin into tumor sites enhances the therapeutic efficacy and reduces cardiotoxic effects. J. Control. Release 2021, 332, 529–538.
- Nishida, H., Matsumoto, Y.; Kawana, K.; Christie, R. J.; Naito, M.; Kim, B. S.; Toh, K.; Min, H. S.; Yi, Y.; Matsumoto, Y.; Kim, H. J.; Miyata, K.; Taguchi, A.; Tomio, K.; Yamashita, A.; Inoue, T.; Nakamura, H.; Fujimoto, A.; Sato, M.; Yoshida, M.; Adachi, K.; Arimoto, T.; Wada-Hiraike, O.; Oda, K.; Nagamatsu, T.; Nishiyama, N.; Kataoka, K.; Osuga, Y.; Fujii, T. Systemic delivery of siRNA by actively targeted polyion complex micelles for silencing the E6 and E7 human papillomavirus oncogenes. J. Control. Release 2016, 231, 29–37.
- Feng, G.; Chen, H.; Li, J.; Huang, Q.; Gupte, M. J.; Liu, H.; Song, Y.; Ge, Z. Gene therapy for nucleus pulposus regeneration by heme oxygenase-1 plasmid DNA carried by mixed polyplex micelles with thermo-responsive heterogeneous coronas. Biomaterials 2015, 52, 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Guo, C.; Feng, B.; Liu, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, D.; Teng, L.; Li, Y.; Yin, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y. Triple-Layered pH-Responsive Micelleplexes Loaded with siRNA and Cisplatin Prodrug for NF-Kappa B Targeted Treatment of Metastatic Breast Cancer. Theranostics 2016, 6, 14–27. [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Rao, J.; Yin, S.; Wei, J.; Xia, C.; Li, M.; Mei, L.; Zhang, Z.; He, Q. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 127, 161–174.
- Koji, K.; Yoshinaga, N.; Mochida, Y.; Hong, T.; Miyazaki, T.; Kataoka, K.; Osada, K.; Cabral, H.; Uchida, S. Bundling of mRNA strands inside polyion complexes improves mRNA delivery efficiency in vitro and in vivo. Biomaterials 2020, 261, 120332.
- Miyazaki, T.; Uchida, S.; Nagatoishi, S.; Koji, K.; Hong, T.; Fukushima, S.; Tsumoto, K.; Ishihara, K.; Kataoka, K.; Cabral, H. Polymeric nanocarriers with controlled chain flexibility boost mRNA delivery in vivo through enhanced structural fastening. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2020, 9, 2000538. [CrossRef]
- Kanto R., Yonenuma R., Yamamoto M., Furusawa H., Yano S., Haruki M., Mori H. Mixed Polyplex Micelles with Thermoresponsive and Lysine-Based Zwitterionic Shells Derived from Two Poly(Vinyl Amine)-Based Block Copolymers. Langmuir 2021, 37, 3001–3014. [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Yu, J.; Qian, C.; Lu, Y.; Kahkoska, A. R.; Xie, Z.; Jing, X.; Buse, J. B.; Gu, Z. H2O2-Responsive Vesicles Integrated with Transcutaneous Patches for Glucose-Mediated Insulin Delivery. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 613–620. [CrossRef]
- Kamenova, K.; Haladjova, E.; Grancharov, G.; Kyulavska, M.; Tzankova, V.; Aluani, D.; Yoncheva, K.; Pispas, S.; Petrov, P. Co-assembly of block copolymers as a tool for developing novel micellar carriers of insulin for controlled drug delivery. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 104, 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Kim, D. H.; Seo, Y. K.; Thambi, T.; Moon, G. J.; Son, J. P.; Li, G.; Park, J H.; Lee, J. H.; Kim, H. H.; Lee, D. S.; Bang, O. Y. Enhancing neurogenesis and angiogenesis with target delivery of stromal cell derived factor-1 alpha using a dual ionic pH-sensitive copolymer. Biomaterials. 2015, 61, 115–125.
- Kim, A.; Miura, Y.; Ishii, T.; Mutaf, O. F.; Nishiyama, N.; Cabral, H.; Kataoka, K. Intracellular Delivery of Charge-Converted Monoclonal Antibodies by Combinatorial Design of Block/Homo Polyion Complex Micelles. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 446–453. [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Gonzalez-Carter, D.; Tockary, T. A.; Nakamura, N.; Xue, Y.; Nakakido, M.; Akiba, H.; Dirisala, A.; Liu, X.; Toh, K.; Yang, T.; Wang, Z.; Fukushima, S.; Li, J.; Quader, S.; Tsumoto, K.; Yokota, T.; Anraku, Y.; Kataoka, K. Dual-sensitive nanomicelles enhancing systemic delivery of therapeutically active antibodies specifically into the brain. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 6729–6742.
- Tao, A.; Huang, G. L.; Igarashi, K.; Hong, T.; Liao, S.; Stellacci, F.; Matsumoto, Y.; Yamasoba, T.; Kataoka, K.; Cabral, H. Polymeric micelles loading proteins through concurrent ion complexation and pH-cleavable covalent bonding for in vivo delivery. Macromol. Biosci. 2020, 20, 1900161.
- Bai, T.; Shao, D.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Xu, B. B, Kong, J. pH-responsive dithiomaleimide-amphiphilic block copolymer for drug delivery and cellular imaging. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 552, 439–447. [CrossRef]
- Weng, J.; Huang, Z.; Pu, X.; Chen, X.; Yin, G.; Tian, Y.; Song, Y. Preparation of polyethylene glycol-polyacrylic acid block copolymer micelles with pH/hypoxic dual-responsive for tumor chemoradiotherapy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 191, 110943.
- Xiao, H.; Li, X.; Zheng, C.; Liu, Q.; Sun, C.; Huang, J.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, Y. Intracellular pH-responsive polymeric micelle for simultaneous chemotherapy and MR imaging of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Nanopart Res 2020, 22, 105. [CrossRef]
- Xiong, D.; Zhang, X.; Peng, S.; Gu, H.; Zhang, L. Smart pH-sensitive micelles based on redox degradable polymers as DOX/GNPs carriers for controlled drug release and CT imaging. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 163, 29–40.
- Yan, K.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, K.; Miao, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Jia, X.; Zhao, X. Enzyme-responsive polymeric micelles with fluorescence fabricated through aggregation-induced copolymer self-assembly for anticancer drug delivery. Polym. Chem. 2020, 11, 7704–7713. [CrossRef]
- Lee, S-Y.; Yang, C-Y.; Peng, C-L.; Wei, M-F.; Chen, K-C.; Yao, C-J.; Shieh, M-J. A theranostic micelleplex co-delivering SN-38 and VEGF siRNA for colorectal cancer therapy. Biomaterials 2016, 86, 92–105. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Chen, S.; Chen, J.; Du, J. An asymmetrical polymer vesicle strategy for significantly improving T1 MRI sensitivity and cancer-targeted drug delivery. Macromolecules 2015, 48, 739–749. [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Gao, J.; Xiao, J.; Du, J. Dually gated polymersomes for gene delivery. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 5562–5568. [CrossRef]
- Insua, I.; Wilkinson, A.; Fernandez-Trillo, F. Polyion complex (PIC) particles: Preparation and biomedical applications. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 81, 198–215. [CrossRef]
- Abolmaali, S. S.; Tamaddon, A. M.; Salmanpour, M.; Mohammadi, S.; Dinarvand, R. Block ionomer micellar nanoparticles from double hydrophilic copolymers, classifications and promises for delivery of cancer chemotherapeutics. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 104, 393–405. [CrossRef]
- Pachioni-Vasconcelos, J. D. A.; Lopes, A. M.; Apolinário, A. C.; Valenzuela-Oses, J. K.; Costa, J. S. R.; Nascimento, L. D. O.; Pessoa, A.; Barbosa, L. R. S.; Rangel-Yagui, C. O. Nanostructures for protein drug delivery. Biomater. Sci. 2016, 4, 205–218.
- Liu, X.; Wu, F.; Ji, Y.; Yin, L. Recent Advances in Anti-cancer Protein/Peptide Delivery. Bioconjugate Chem. 2019, 30, 305–324. [CrossRef]
- Yousefpour Marzbali, M.; Yari Khosroushahi, A. Polymeric micelles as mighty nanocarriers for cancer gene therapy: a review. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2017, 79, 637–649. [CrossRef]
- Amjad, M.W.; Kesharwani, P.; Mohd Amin, M. C. I.; Iyer, A. K. Recent advances in the design, development, and targeting mechanisms of polymeric micelles for delivery of siRNA in cancer therapy. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2017, 64, 154–181. [CrossRef]
- Pereira-Silva, M.; Jarak, I.; Alvarez-Lorenzo, C.; Concheiro, A.; Santos, A. C.; Veiga, F.; Figueiras, A. Micelleplexes as nucleic acid delivery systems for cancer-targeted therapies. J. Control. Release. 2020, 323, 442–462. [CrossRef]
- Banik, B. L.; Fattahi, P.; Brown, J. L. Polymeric Nanoparticles: The Future of Nanomedicine: Polymeric Nanoparticles. WIREs Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2016, 8, 271–299. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshmukh, A. S.; Chauhan, P. N.; Noolvi, M. N.; Chaturvedi, K.; Ganguly, K.; Shukla, S. S.; Nadagouda, M. N.; Aminabhavi, T. M. Polymeric micelles: Basic research to clinical practice. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 532, 249–268.
- Hwang, D.; Ramsey, J. D.; Kabanov, A. V. Polymeric micelles for the delivery of poorly soluble drugs: From nanoformulation to clinical approval. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 156, 80–118. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osorno, L. L.; Brandley, A. N.; Maldonado, D. E.; Yiantsos, A.; Mosley, R. J.; Byrne, M. E. Review of Contemporary Self-Assembled Systems for the Controlled Delivery of Therapeutics in Medicine. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 278. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K. Controlled drug delivery systems: Past forward and future back. J. Control. Release 2014, 190, 3–8. [CrossRef]
- Leroux J.-C. Editorial: Drug Delivery: Too Much Complexity, Not Enough Reproducibility? Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 15170–15171. [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y. W.; Luther, D. C.; Kretzmann, J. A.; Burden, A.; Jeon, T.; Zhai, S.; Rotello, V. M. Protein Delivery into the Cell Cytosol using Non-Viral Nanocarriers. Theranostics 2019, 9, 3280–3292. [CrossRef]
- Acar, H.; Srivastava, S.; Chung, E. J.; Schnorenberg, M. R.; Barrett, J. C.; LaBelle, J. L.; Tirrell, M. Self-assembling peptide-based building blocks in medical applications. Adv. Drug Delivery Rev.
- Lorenzer, C.; Dirin, M.; Winkler, A. M.; Baumann, V.; Winkler, J. Going beyond the liver: progress and challenges of targeted delivery of siRNA therapeutics. J. Control. Release 2015, 203, 1–15. [CrossRef]
- Mukalel, A. J.; Riley, R. S.; Zhang, R.; Mitchell, M. J. Nanoparticles for nucleic acid delivery: applications in cancer immunotherapy. Canc. Lett. 2019, 458, 102–112. [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Wagner, E. Polymeric Carriers for Nucleic Acid Delivery: Current Designs and Future Directions. Biomacromolecules 2019, 20, 3613–3626. [CrossRef]
- Kauffman, K. J.; Webber, M. J.; Anderson, D. G. Materials for non-viral intracellular delivery of messenger RNA therapeutics. J. Control. Release 2016, 240, 227–234. [CrossRef]
- Stewart, M. P.; Sharei, A.; Ding, X. Y.; Sahay, G.; Langer, R.; Jensen, K. F. In vitro and ex vivo strategies for intracellular delivery. Nature 2016, 538, 183–192.
- Kim, S. H.; Jeong, J. H.; Mok, H.; Lee, S. H.; Kim, S. W.; Park, T. G. Folate receptor targeted delivery of polyelectrolyte complex micelles prepared from ODN-PEG-folate conjugate and cationic lipids. Biotechnol. Prog. 2007, 23, 232–237. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J. H.; Ramasamy, T.; Tran, T. H.; Choi, J. Y.; Cho, H. J.; Yong, C. S.; Kim, J. O. Polyelectrolyte complex micelles by self-assembly of polypeptide-based triblock copolymer for doxorubicin delivery. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 9, 191–198.
- Oishi, M.; Nagatsugi, F.; Sasaki, S.; Nagasaki, Y.; Kataoka, K. Smart polyion complex micelles for targeted intracellular delivery of PEGylated antisense oligonucleotides containing acid-labile linkages. ChemBioChem 2005, 6, 718–725. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, B.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y. A self-assembled peptide nucleic acid-microRNA nanocomplex for dual modulation of cancer-related microRNAs. Chem. Commun. (Cambridge, U. K.) 2019, 55, 2106–2109. [CrossRef]
- Konate, K.; Dussot, M.; Aldrian, G.; Vaissière, A.; Viguier, V.; Neira, I. F.; Couillaud, F.; Vivès, E.; Boisguerin, P.; Deshayes, S. Peptide-based nanoparticles to rapidly and efficiently “Wrap’n Roll” siRNA into cells. Bioconjugate Chem. 2019, 30, 592–603.
- Christie, R. J.; Matsumoto, Y.; Miyata, K.; Nomoto, T.; Fukushima, S.; Osada, K.; Halnaut, J.; Pittella, F.; Kim, H. J.; Nishiyama, N.; Kataoka, K. Targeted polymeric micelles for siRNA treatment of experimental cancer by intravenous injection. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 5174–5189. [CrossRef]
- Uchida, S.; Kinoh, H.; Ishii, T.; Matsui, A.; Tockary, T. A.; Takeda, K. M.; Uchida, H.; Osada, K.; Itaka, K.; Kataoka, K. Systemic delivery of messenger RNA for the treatment of pancreatic cancer using polyplex nanomicelles with a cholesterol moiety. Biomaterials 2016, 82, 221–228. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprouse, D.; Reineke, T. M. Investigating the Effects of Block versus Statistical Glycopolycations Containing Primary and Tertiary Amines for Plasmid DNA Delivery. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 2616–2628. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukushima, S.; Miyata, K.; Nishiyama, N.; Kanayama, N.; Yamasaki, Y.; Kataoka, K. PEGylated polyplex micelles from triblock catiomers with spatially ordered layering of condensed pDNA and buffering units for enhanced intracellular gene delivery. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 2810–2811. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dirisala, A.; Uchida, S.; Tockary, T. A.; Yoshinaga, N.; Li, J.; Osawa, S.; Gorantla, L.; Fukushima, S.; Osada, K.; Kataoka, K. Precise tuning of disulphide crosslinking in mRNA polyplex micelles for optimising extracellular and intracellular nuclease tolerability. J. Drug Target. 2019, 27, 670–680.
- Tockary, T. A.; Foo, W.; Dirisala, A.; Chen, Q.; Uchida, S.; Osawa, S.; Mochida, Y.; Liu, X.; Kinoh, H.; Cabral, H.; Osada, K.; Kataoka, K. Single-stranded DNA-packaged polyplex micelle as adeno- associated-virus-iinspired compact vector to ssystemically target stroma-rich pancreatic cancer. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 12732–12742.
- Jiang, Y.; Lodge, T. P.; Reineke, T. M. Packaging pDNA by polymeric ABC micelles simultaneously achieves colloidal stability and structural control. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 11101–11111. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osada, K. Structural ppolymorphism of single pDNA ccondensates elicited by cationic block polyelectrolytes. Polymers 2020, 12, 1603. [CrossRef]
- Hagerman, P. J. Flexibility of DNA. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biophys. Chem. 1988, 17, 265–286. [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, B.; Jayandharan, G. Basic biology of adeno- associated virus (AAV) vectors used in gene therapy. Curr. Gene Ther. 2014, 14, 86–100. [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.; Hou, J.; Yong, X.; Gong, G.; Muddassir, M.; Tang, T.; Xie, J.; Fan, W.; Chen, X. Targeted Dual Small Interfering Ribonucleic Acid Delivery via Non-Viral Polymeric Vectors for Pulmonary Fibrosis Therapy. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2007798. [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-Y.; Perche, F.; Ikegami, M.; Uchida, S.; Kataoka, K.; Itaka, K. Messenger RNA-based therapeutics for brain diseases: An animal study for augmenting clearance of beta-amyloid by intracerebral administration of neprilysin mRNA loaded in polyplex nanomicelles. J. Control. Release 2016, 235, 268–275.
- Jiang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Meng, F.; Zhong, Z. Apolipoprotein E Peptide-Directed Chimeric Polymersomes Mediate an Ultrahigh-Efficiency Targeted Protein Therapy for Glioblastoma. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 11070–11079. [CrossRef]
- Lam, J. H.; Khan, A. K.; Cornell, T. A.; Chia, T. W.; Dress, R. J.; Yeow, W. W. W.; Mohd-Ismail, N. K.; Venkataraman, S.; Ng, K. T.; Tan, Y. J.; Anderson, D. E.; Ginhoux, F.; Nallani, M. Polymersomes as Stable Nanocarriers for a Highly Immunogenic and Durable SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Subunit Vaccine. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 15754–15770.
- Wang, F., Gao, J., Xiao, J., & Du, J. Dually gated polymersomes for gene delivery. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 5562–5568.
- Lomora, M.; Itel, F.; Dinu, I.A.; Palivan, C.G. Selective ion-permeable membranes by insertion of biopores into polymersomes. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 15538–15546. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Grzelakowski, M.; Zilles, J.; Clark, M.; Meier, W. Highly permeable polymeric membranes based on the incorporation of the functional water channel protein Aquaporin Z. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2007, 104, 20719–20724. [CrossRef]
- Einfalt, T.; Goers, R.; Dinu, I. A.; Najer, A.; Spulber, M.; Onaca-Fischer, O.; Palivan, C. G. Stimuli-triggered activity of nanoreactors by biomimetic engineering polymer membranes. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 7596–7603. [CrossRef]
- Burns, J. R.; Stulz, E.; Howorka, S. Self-assembled DNA nanopores that span lipid bilayers. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 2351–2356. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messager, L.; Burns, J. R.; Kim, J.; Cecchin, D.; Hindley, J.; Pyne, A. L. B.; Gaitzsch, J.; Battaglia, G.; Howorka, S. Biomimetic Hybrid Nanocontainers with Selective Permeability. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 11106–11109.
- Xiao, F.-X.; Pagliaro, M.; Xu, Y.-J.; Liu, B. Layer-by-layer Assembly of Versatile Nanoarchitectures with Diverse Dimensionality: A New Perspective for Rational Construction of Multilayer Assemblies. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 3088–3121. [CrossRef]
- Bacskai, B.J.; Kajdasz, S.T.; McLellan, M.E.; Games, D.; Seubert, P.; Schenk, D.; Hyman, B.T. Non-Fc-mediated mechanisms are involved in clearance of amyloid-beta in vivo by immunotherapy. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 7873–7878. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehlin, D.; Fang, X. T.; Cato, L.; Antoni, G.; Lannfelt, L.; and Syvanen, S. Antibody-based PET imaging of amyloid beta in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10759. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevigny, J.; Chiao, P.; Bussière, T.; Weinreb, P. H.; Williams, L.; Maier, M.; Dunstan, R.; Salloway, S.; Chen, T.; Ling, Y.; O’Gorman, J.; Qian, F.; Arastu, M.; Li, M.; Chollate, S.; Brennan, M. S.; Quintero-Monzon, O.; Scannevin, R. H.; Arnold, H. M.; Engber, T.; Rhodes, K.; Ferrero, J.; Hang, Y.; Mikulskis, A.; Grimm, J.; Hock, C.; Nitsch, R. M.; Sandrock, A. The antibody aducanumab reduces Aβ plaques in Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 2016, 537, 50–56.
- Bard, F.; Cannon, C.; Barbour, R.; Burke, R. L.; Games, D.; Grajeda, H.; Guido, T.; Hu, K.; Huang, J.; Johnson-Wood, K.; Khan, K.; Kholodenko, D.; Lee, M.; Lieberburg, I.; Motter, R.; Nguyen, M.; Soriano, F.; Vasquez, N.; Weiss, K.; Welch, B.; Seubert, P.; Schenk, D.; Yednock, T. Peripherally administered antibodies against amyloid beta-peptide enter the central nervous system and reduce pathology in a mouse model of Alzheimer disease. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 916–919.
- Habicht, G.; Haupt, C.; Friedrich, R. P.; Hortschansky, P.; Sachse, C.; Meinhardt, J.; Wieligmann, K.; Gellermann, G. P.; Brodhun, M.; Gotz, J.; Halbhuber, K.; Rocken, C.; Horn, U.; Fandrich, M. Directed Selection of a Conformational Antibody Domain That Prevents Mature Amyloid Fibril Formation by Stabilizing Aβ Protofibrils. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2007, 104, 19232–19237.
- Perche, F.; Uchida, S.; Akiba, H.; Lin, C.; Ikegami, M.; Dirisala, A.; Nakashima, T.; Itaka, K.; Tsumoto, K.; Kataoka, K. Improved Brain Expression of Anti-Amyloid β scFv by Complexation of mRNA Including a Secretion Sequence With PEG-based Block Catiomer. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2017, 14, 295–302. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pul, R.; Dodel, R.; Stangel, M. Antibody-Based Therapy in Alzheimer’s Disease. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2011, 11, 343–357. [CrossRef]
- Montoliu-Gaya, L.; Mulder, S. D.; Veerhuis, R.; Villegas, S.Effects of an Aβ Antibody Fragment on Aβ Aggregation and Astrocytic Uptake Are Modulated by Apolipoprotein E and J MimeticPeptides. PLoS One 2017, 12, e0188191. [CrossRef]
- Marín-Argany, M.; Rivera-Hernández, G.; Martí, J.; Villegas, S. An Anti-aβ (Amyloid β) Single-Chain Variable Fragment Prevents Amyloid Fibril Formation and Cytotoxicity by Withdrawing Aβ Oligomers from the Amyloid Pathway. Biochem. J. 2011, 437, 25–34. [CrossRef]
- Nelson, A. L.; Reichert, J. M. Development Trends for Therapeutic Antibody Fragments. Nat. Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 331–337. [CrossRef]
- Abbott, N. J.; Patabendige, A. A.; Dolman, D. E.; Yusof, S. R.; Begley, D. J. Structure and Function of the Blood-Brain Barrier. Neurobiol. Dis. 2010, 37, 13–25.
- Lemere, C. A.; Masliah, E. Can Alzheimer Disease Be Prevented by Amyloid-Beta Immunotherapy? Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2010, 6, 108–119. [CrossRef]
- Arbel, M.; Solomon, B. Immunotherapy for Alzheimer’s Disease: Attacking Amyloid-β From the Inside. Trends Immunol. 2007, 28, 511–513. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Dyck, C. H. Anti-Amyloid-β Monoclonal Antibodies for Alzheimer’s Disease: Pitfalls and Promise. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 83, 311–319. [CrossRef]
- Neves, V.; Aires-Da-Silva, F.; Corte-Real, S.; Castanho, M. A. R. B. Antibody Approaches to Treat Brain Diseases. Trends Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 36–48. [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Gonzalez-Carter, D.; Tockary, T. A.; Nakamura, N.; Xue, Y.; Nakakido, M.; Akiba, H.; Dirisala, A.; Liu, X.; Toh, K.; Yang, T.; Wang, Z.; Fukushima, S.; Li, J.; Quader, S.; Tsumoto, K.; Yokota, T.; Anraku, Y.; Kataoka, K. Dual-Sensitive Nanomicelles Enhancing Systemic Delivery of Therapeutically Active Antibodies Specifically into the Brain. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 6729–6742.
- Stupp, R.; Mason, W. P.; van den Bent, M. J.; Weller, M.; Fisher, B.; Taphoorn, M. J.; Belanger, K.; Brandes, A. A.; Marosi, C.; Bogdahn, U.; Curschmann, J.; Janzer, R. C.; Ludwin, S. K.; Gorlia, T.; Allgeier, A.; Lacombe, D.; Cairncross, J. G.; Eisenhauer, E.; Mirimanoff, R. O. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 987–996.
- Gong, J.; Chen, M.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y. Polymeric micelles drug delivery system in oncology. J. Control Release 2012, 159, 312–323. [CrossRef]
- Oba, M.; Fukushima, S.; Kanayama, N.; Aoyagi, K.; Nishiyama, N.; Koyama, H.; Kataoka, K. Cyclic RGD peptide-conjugated polyplex micelles as a targetable gene delivery system directed to cells possessing αvβ3 and αvβ5 integrins. Bioconjug. Chem. 2007, 18, 1415–1423. [CrossRef]
- Heffernan, M. J., Murthy, N. Disulfide-crosslinked polyion micelles for delivery of protein therapeutics. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2009, 37, 1993–2002. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, Y-C.; Chang, S-F.; Kao, W. W-Y.; Liu, C-Y.; Liaw, J. Polymeric micelle gene delivery of bcl-xL via eye drop reduced corneal apoptosis following epithelial debridement. J. Control. Release 2010, 147, 76–83. [CrossRef]
- Zhan, C.; Gu, B.; Xie, C.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Lu, W. Cyclic RGD conjugated poly(ethylene glycol)-co-poly(lactic acid) micelle enhances paclitaxel anti-glioblastoma effect. J. Control. Release 2010, 143, 136–142. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, C.; Meng, Q.; Li, Q.; Feng, L.; Zhu, J.; Lu, W. Cyclic RGD- polyethylene glycol-polyethylenimine for intracranial glioblastoma-targeted gene delivery. Chem. Asian J. 2012, 7, 91–96. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, C.; Wei, X.; Qian, J.; Feng, L.; Zhu, J.; Lu, W. Co-delivery of TRAIL gene enhances the anti-glioblastoma effect of paclitaxel in vitro and in vivo. J. Control. Release 2012, 160, 630–636. [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Qian, J.; Yang, Z.; Pang, Z.; Xi, Z.; Cao, S.; Wang, Y.; Pan, S.; Zhang, S.; Wang, W.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, Q. Whole-cell SELEX aptamer-functionalised poly(ethyleneglycol)-poly(ε-caprolactone) nanoparticles for enhanced targeted glioblastoma therapy. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 6264–6272. [CrossRef]
- Yin, T.; Wang, P.; Li, J.; Zheng, R.; Zheng, B.; Cheng, D.; Li, R.; Lai, J.; Shuai, X. Ultrasound- sensitive siRNA-loaded nanobubbles formed by hetero-assembly of polymeric micelles and liposomes and their therapeutic effect in gliomas. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 4532–4543. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, C.; Zheng, M.; Gong, P.; Deng, J.; Yi, H.; Zhang, P., Zhang, Y.; Liu, P.; Ma, Y.; Cai, L. Polypeptide cationic micelles mediated co-delivery of docetaxel and siRNA for synergistic tumor therapy. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 3431–3438. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabrese, C.; Poppleton, H.; Kocak, M.; Hogg, T. L.; Fuller, C.; Hamner, B.; Oh, E. Y.; Gaber, M. W.; Finklestein, D.; Allen, M.; Frank, A.; Bayazitov, I. T.; Zakharenko, S. S.; Gajjar, A.; Davidoff, A.; Gilbertson, R. J. A perivascular niche for brain tumor stem cells. Cancer Cell 2007, 11, 69–82.
- Gilbertson, R. J.; Rich, J. N. Making a tumour’s bed: glioblastoma stem cells and the vascular niche. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 733–736. [CrossRef]
- Jain, R. K. Delivery of novel therapeutic agents in tumors: physiological barriers and strategies. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1989, 81, 570–576.
- Bello, L.; Francolini, M.; Marthyn, P.; Zhang, J.; Carroll, R.S.; Nikas, D.C.; Strasser, J. F.; Villani, R.; Cheresh, D. A.; Black P. M. αvβ3 and αvβ5 integrin expression in glioma periphery. Neurosurgery 2001, 49, 380–389.
- Arap, W.; Pasqualini, R.; Ruoslahti, E. Cancer treatment by targeted drug delivery to tumor vasculature in a mouse model. Science 1998, 279, 377–380. [CrossRef]
- Nasongkla, N.; Bey, E.; Ren, J.; Ai, H.; Khemtong, C.; Guthi, J. S.; Chin, S-F.; Sherry, A. D.; Boothman, D. A.; Gao, J. Multifunctional polymeric micelles as cancer-targeted, MRI-ultrasensitive drug delivery systems. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 2427–2430. [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Luo, F.; Pan, Y.; Hou, C.; Ren, L.; Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y. Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) peptide conjugated poly(lactic acid)–poly(ethylene oxide) micelle for targeted drug delivery. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2008, 85A, 797–807. [CrossRef]
- Kessinger, C. W.; Togao, O.; Khemtong, C.; Huang, G.; Takahashi, M.; and Gao, J. Investigation of in vivo targeting kinetics of αvβ3-specific super- paramagnetic nanoprobes by time-resolved MRI. Theranostics 2011, 1, 263–273. [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Cui, W.; Li, B.; Hong, Z. Targeted therapy for glioma using cyclic RGD-entrapped polyionic complex nanomicelles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 2853–2862.
- Xiao, Y.; Hong, H.; Javadi, A.; Engle, J. W.; Xu, W.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Barnhart, T. E.; Cai, W.; Gong, S. Multifunctional unimolecular micelles for cancer-targeted drug delivery and positron emission tomography imaging. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 3071–3082. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Hu, L.; Yin, Q.; Feng, L.; Li, Y. Transferrin-modified c[RGDfK]-paclitaxel loaded hybrid micelle for sequential blood-brain barrier penetration and glioma targeting therapy. Mol. Pharm. 2012, 9, 1590–1598. [CrossRef]
- Simberg, D.; Duza, T.; Park, J. H.; Essler, M.; Pilch, J.; Zhang, L.; Derfus, A. M.; Yang, M.; Hoffman, R. M.; Bhatia, S.; Sailor, M. J.; Ruoslahti, E. Biomimetic Amplification of Nanoparticle Homing to Tumors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2007, 104, 932–936.
- Bárdos, H., Molnár, P., Csécsei, G., and Adány, R. Fibrin deposition in primary and metastatic human brain tumours. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 1996, 7, 536–548. [CrossRef]
- Chung, E. J.; Cheng, Y.; Morshed, R.; Nord, K.; Han, Y.; Wegscheid, M. L.; Auffinger, B.; Wainwright, D. A.; Lesniak, M. S.; Tirrel, M. V. Fibrin-binding, peptide amphiphile micelles for targeting glioblastoma. Biomaterials 2013, 35, 1249–1256.
- Peters, D.; Kastantin, M.; Kotamraju, V. R.; Karmali, P. P.; Gujraty, K.; Tirrell, M.; Ruoslahti, E. Targeting atherosclerosis by using modular, multifunctional micelles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2009, 106, 9815–9819. [CrossRef]
- Pasqualini, R.; Koivunen, E.; Kain, R.; Lahdenranta, J.; Sakamoto, M.; Stryhn, A.; Ashmun, R. A.; Shapiro, L. H.; Arap, W.; Ruoslahti, E. Aminopeptidase N is a receptor for tumor-homing peptides and a target for inhibiting angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 722–727.
- Ellerby, H. M.; Arap, W.; Ellerby, L. M.; Kain, R.; Andrusiak, R.; Rio, G. D.; Krajewski, S.; Lombardo, C. R.; Rao, R.; Ruoslahti, E.; Bredesen, D. E. Anti-cancer activity of targeted pro-apoptotic peptides. Nat. Med. 1999, 5, 1032–1038.
- Zhao, B-J.; Ke, X-Y.; Huang, Y.; Chen, X-M.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, B-X.; Lu, W-L.; Lou, J-N.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q. The antiangiogenic efficacy of NGR-modified PEG–DSPE micelles containing paclitaxel (NGR-M-PTX) for the treatment of glioma in rats. J. Drug Target. 2011, 19, 382–390. [CrossRef]
- Fishman, J. B.; Rubin, J. B.; Handrahan, J. V.; Connor, J. R.; Fine, R. E. Receptor-mediated transcytosis of transferrin across the blood-brain barrier. J. Neurosci. Res. 1987, 18, 299–304. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Jiang, M.; Kang, T.; Miao, D.; Gu, G.; Song, Q.; Yao, L.; Hu, Q.; Tu, Y.; Pang, Z.; Chen, H.; Jiang, X.; Gao, X.; Chen, J. Lactoferrin-modified PEG-co-PCL nanoparticles for enhanced brain delivery of NAP peptide following intranasal administration. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 3870–3881. [CrossRef]
- Mu, C.; Dave N.; Hu, J.; Desai, P.; Pauletti, G.; Bai, S.; Hao, J. Solubilization of flurbiprofen into aptamer-modified PEG-PLA micelles for targeted delivery to brain-derived endothelial cells In Vitro. J. Microencapsul. 2013, 30, 701–708. [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.-h.; Chang, J.; Yan, C.-h.; Qian, X.-m.; Long, L.-x.; He, B.; Yuan, X.-b.; Kang, C.-s.; Betbeder, D.; Sheng, J.; Pu, P.-y Development of transferrin functionalized poly (ethylene glycol)/poly (lactic acid) amphiphilic block copolymeric micelles as a potential delivery system targeting brain glioma. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2010, 21, 2673–2681.
- Zhang, P.; Hu, L.; Yin, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, L.; Li, Y. Transferrin-conjugated polyphosphoester hybrid micelle loading paclitaxel for brain-targeting delivery: Synthesis, preparation and in vivo evaluation. J. Control. Rel. 2012, 159, 429–434. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalaria, R. N.; Homayoun, P.; Whitehouse, P. J. Nicotinic choliner- gic receptors associated with mammalian cerebral vessels. J. Auton. Nerv. Syst. 1994, 49, S3–S7. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacKlin, K. D., Maus, A. D., Pereira, E. F., Albuquerque, E. X., and Conti-Fine, B. M. Human vascular endothelial cells express functional nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1998, 287, 435–439. [CrossRef]
- Zhan, C.; Li, B.; Hu, L.; Wei, X.; Feng, L.; Fu, W.; Lu, W. Micelle-based brain-targeted drug delivery enabled by a nicotine acetylcholine receptor ligand. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2011, 50, 5482–5485. [CrossRef]
- Wong, A. J.; Bigner, S. H.; Bigner, D. D.; Kinzler, K. W.; Hamilton, S. R.; Vogelstein, B. Increased expression of the epidermal growth factor receptor gene in malignant gliomas is invariably associated with gene amplifi- cation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 1987, 84, 6899–6903. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, Y-C.; Liang, C-T. Inhibition of human brain malignant glioblas toma cells using carmustine-loaded catanionic solid lipid nanoparticles with surface anti-epithelial growth factor receptor. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 3340–3350. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, S.; Schiffelers, R. M.; van der Veeken, J.; van der Meel, R.; Vongpromek, R.; van Bergen en Henegouwen, P. M. P.; Storm, G.; Roovers, R.C. Downregulation of EGFR by a novel multivalent nanobody-liposome platform. J. Control. Release 2010, 145, 165–175.
- Talelli, M.; Rijcken, C. J. F.; Oliveira, S.; van der Meel, R.; van Bergen en Henegouwen, P. M. P.; Lammers, T.; van Nostrum, C. F.; Storm, G.; Hennink, W. E. Nanobody-shell functionalized thermosensitive core-crosslinked polymeric micelles for active drug targeting. J. Control. Release 2011, 151, 183–192.
- Bu, G.; Maksymovitch, E. A.; Geuze, H.; Schwartz, A. L. Subcellular localization and endocytic function of low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein in human glioblastoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 29874–29882. [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; Ikeda, K.; Ohshima, K.; Tsugu, H.; Kimura, H.; Tomonaga, M. Increased expression of low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein/α2-macroglobulin receptor in human malignant astrocytomas. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 2799–2805.
- Herz, J.; Bock, H. H. Lipoprotein receptors in the nervous system. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2002, 71, 405–434. [CrossRef]
- Demeule, M.; Currie, J. C.; Bertrand, Y.; Ché, C.; Nguyen, T.; Régina, A.; Gabathuler, R.; Castaigne, J.-P.; Béliveau, R. Involvement of the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein in the transcytosis of the brain delivery vector Angiopep-2. J. Neurochem. 2008, 106, 1534–1544. [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Zhan, C.; Xie, C.; Meng, Q.; Gu, B.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, W. Poly(ethylene glycol)-block-poly(D,L-lactide acid) micelles anchored with angiopep-2 for brain-targeting delivery. J. Drug Target. 2011, 19, 197–203. [CrossRef]
- Bayrac, A. T.; Sefah, K.; Parekh, P.; Bayrac, C.; Gulbakan, B.; Oktem, H. A.; Tan, W. In vitro selection of DNA aptamers to glioblastoma multiforme. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2011, 2, 175–181. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Sha, X.; Xin, H.; Xu, X.; Gu, J.; Xia, W.; Chen, S.; Xie, Y.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y.; Fang, X. Integrin-facilitated transcytosis for enhanced penetration of advanced gliomas by poly(trimethylene carbonate)-based nanoparticles encapsulating paclitaxel. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 2969–2979.
- Shangguan, D.; Li, Y.; Tang, Z.; Cao, Z. C.; Chen, H. W.; Mallikaratchy, P.; Sefah, K.; Yang, C. J.; Tan, W. Aptamers evolved from live cells as effective molecular probes for cancer study. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2006, 103, 11838–11843. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardridge, W. M. Recent developments in peptide drug delivery to the brain. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1992, 71, 3–10. [CrossRef]
- Calvo, P.; Gouritin, B.; Chacun, H.; Desmaele, D.; D’Angelo, J.; Noel, J.; Georgin, D.; Fattal, E.; Andreux, J.; Couvreur, P. Long-circulating PEGylated polycyanoacrylate nanoparticles as new drug carrier for brain delivery. Pharm. Res. 2001, 18, 1157–1166. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brigger, I.; Morizet, J.; Aubert, G.; Chacun, H.; Terrier-Lacombe, M. J.; Couvreur, P.; Vassal G. Poly(ethylene glycol)-coated hexadecylcyanoacrylate nanospheres display a combined effect for brain tumor targeting. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2002, 303, 928–936. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelperina, S.; Maksimenko, O.; Khalansky, A.; Vanchugova, L.; Shipulo, E.; Abbasova, K.; Berdiev, R.; Wohlfart, S.; Chepurnova, N.; Kreuter, J. Drug delivery to the brain using surfactant-coated poly(lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles: Influence of the formulation parameters. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2010, 74, 157–163.
- Kanazawa, T.; Taki, H.; Tanaka, K.; Takashima, Y.; Okada, H. Cell-Penetrating Peptide-Modified Block Copolymer Micelles Promote Direct Brain Delivery via Intranasal Administration. Pharm. Res. 2011, 28, 2130–2139. [CrossRef]
- Bobo, R. H.; Laske, D. W.; Akbasak, A.; Morrison, P. F.; Dedrick, R. L.; and Oldfield, E. H. Convection-enhanced delivery of macromolecules in the brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 1994, 91, 2076–2080.
- Allard, E.; Passirani, C.; Benoit, J. P. Convection-enhanced delivery of nanocarriers for the treatment of brain tumors. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 2302–2318. [CrossRef]
- Lesniak, M. S. Novel advances in drug delivery to brain cancer. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2005, 4, 417–428. [CrossRef]
- Sampson, J. H., Akabani, G., Archer, G. E., Bigner, D. D., Berger, M. S., Friedman, A. H., Friedman, H. S.; Herndon II, J. E.; Kunwar, S.; Marcus, S.; Mclendon, R. E.; Paolino, A.; Penne, K.; Provenzale, J.; Quinn, J.; Reardon, D. A.; Rich, J.; Stenzel, T.; Tourt-Uhlig, S.; Wikstrand, C.; Wong, T.; Williams, R.; Yuan, F.; Zalutsky, M. R.; Pastan, I. Progress report of a phase I study of the intracerebral microinfu- sion of a recombinant chimeric protein composed of transforming growth factor (TGF)-alpha and a mutated form of the Pseudomonas exotoxin termed PE-38 (TP-38) for the treatment of malignant brain tumors. J. Neurooncol. 2003, 65, 27–35.
- Weaver, M.; Laske, D. W. Transferrin receptor ligand-targeted toxin conjugate (Tf-CRM107) for therapy of malignant gliomas. J. Neurooncol. 2003, 65, 3–14. [CrossRef]
- Vinchon-Petit, S.; Jarnet, D.; Paillard, A.; Benoit, J. P.; Garcion, E.; Menei, P. In vivo evaluation of intracellular drug-nanocarriers infused into intracranial tumours by convection-enhanced delivery: distribution and radiosensitisation efficacy. J. Neurooncol. 2010, 97, 195–205. [CrossRef]
- Thaci, B.; Ahmed, A. U.; Ulasov, I. V.; Tobias, A. L.; Han, Y.; Aboody, K. S.; Lesniak, M. S. Pharmacokinetic study of neural stem cell-based cell carrier for oncolytic virotherapy: targeted delivery of the therapeutic payload in an orthotopic brain tumor model. Cancer Gene Ther. 2012, 19, 431–442.
- Huang, X.; Zhang, F.; Wang, H.; Niu, G.; Choi, K. Y.; Swierczewska, M.; Zhang, G.; Gao, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, L. Mesenchymal stem cell-based cell engineering with multifunctional mesoporous silica nanoparticles for tumor delivery. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 1772–1780. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roger, M.; Clavreul, A.; Venier-Julienne, M.-C.; Passirani, C.; Sindji, L.; Schiller, P.; Montero-Menei, C.; Menei, P. Mesenchymal stem cells as cellular vehicles for delivery of nanoparticles to brain tumors. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 8393–8401. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Guan, Y.; Liu, H.; Hao, N.; Liu, T.; Meng, X.; Fu, C.; Li, Y.; Qu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, S.; Chen, L.; Chen, D.; Tang, F. Silica Nanorattle-Doxorubicin-Anchored Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Tumor-Tropic Therapy. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 7462–7470. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Morshed, R.; Cheng, S-H.; Tobias, A.; Auffinger, B.; Wainwright, D. A.; Zhang, L.; Yunis, C.; Han, Y.; Chen, C-T.; Lo, L-W.; Aboody, K. S.; Ahmed, A. U.; Lesniak, M. S. Nanoparticle-programmed self-destructive neural stem cells for glioblastoma targeting and therapy. Small 2013, 9, 4123–4129.
- Morshed, R. A.; Cheng, Y.; Auffinger, B.; Wegscheid, M. L.; Lesniak, M. S. The potential of polymeric micelles in the context of glioblastoma therapy. Front. Pharmacol. 2013, 4, 157.
- Duncan, R. The dawning era of polymer therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 2003, 2, 347–360. [CrossRef]
- Crommelin, D. J. A.; Storm, G.; Jiskoot, W.; Stenekes, R.; Mastrobattista, E.; Hennink, W. E. Nanotechnological approaches for the delivery of macromolecules. J. Control. Release 2003, 87, 81–88.
- Crommelin, D.J.A.; Storm, G. Liposomes: from the bench to the bed. J. Liposome Res. 2003, 13, 33–36. [CrossRef]
- Drummond, D.C.; Meyer, O.; Hong, K.; Kirpotin. D.B.; Papahadjopoulos, D. Optimizing liposomes for delivery of chemotherapeutic agents to solid tumors. Pharmacol. Rev. 1999, 51, 691–743. [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Mizushima, Y. Lipid microspheres for drug delivery from the pharmaceutical viewpoint. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carr. Syst. 1994, 11, 215–229.
- Tamilvanan, S. Oil-in-water lipid emulsions: implications for parenteral and ocular delivering systems. Prog. Lipid Res. 2004, 43, 489–533. [CrossRef]
- Bala, I.; Hariharan, S.; Ravi Kumar, M. N. V. PLGA nanoparticles in drug delivery: the state of the art. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carr. Syst. 2004, 21, 387–422. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panyam, J.; Labhasetwar, V. Biodegradable nanoparticles for drug and gene delivery to cells and tissue. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2003, 55, 329–347. [CrossRef]
- Discher, D. E.; Eisenberg, A. Polymer vesicles. Science 2002, 297, 967–973. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, F.; Discher, D. E. Self-porating polymersomes of PEG-PLA and PEG-PCL: hydrolysis-triggered controlled release vesicles. J. Control. Release 2004, 96, 37–53. [CrossRef]
- Nori, A.; Kopecek, J. Intracellular targeting of polymer-bound drugs for cancer chemotherapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2005, 57, 609–636. [CrossRef]
- Satchi-Fainaro, R.; Puder, M.; Davies, J. W.; Tran, H. T.; Sampson, D. A.; Greene, A. K.; Corfas, G.; Folkman, J. Targeting angiogenesis with a conjugate of HPMA copolymer and TNP-470. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 255–261. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillies, E. R.; Fréchet, J. M. J. Dendrimers and dendritic polymers in drug delivery. Drug Discov. Today 2005, 10, 35–43. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aulenta, F.; Hayes, W.; Rannard, S. Dendrimers: a new class of nanoscopic containers and delivery devices. Eur. Polym. J. 2003, 39, 1741–1771. [CrossRef]
- Zamboni, W. C. Liposomal, nanoparticle and conjugated formulations of anticancer agents. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 8230–8234. [CrossRef]
- Forster, S.; Plantenberg, T. From self-organizing polymers to nanohybrid and biomaterials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2002, 41, 689–714.
- 1506. Bader, H.; Ringsdorf, H.; Schmidt, B. Water soluble polymers in medicine. Angew. Makromol. Chem. 1984, 123, 457–485.
- Kabanov, A. V.; Chekhonin, V. P.; Alakhov VYu; Batrakova, E. V.; Lebedev, A. S.; Melik-Nubarov, N. S.; Arzhakov, S. A.; Levashov, A. V.; Morozov, G. V.; Severin, E. S.; Kabanov, V. A. The neuroleptic activity of haloperidol increases after its solubilization in surfactant micelles. Micelles as microcontainers for drug targeting. FEBS Lett. 1989, 258, 343–345.
- Avgoustakis, K.; Beletsi, A.; Panagi, Z.; Klepetsanis, P.; Livaniou, E.; Evangelatos, G.; Ithakissios, D. S. Effect of Copolymer Composition on the Physicochemical Characteristics, in Vitro Stability, and Biodistribution of PLGA-mPEG Nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2003, 259, 115–127. [CrossRef]
- Neradovic, D.; van Nostrum, C. F.; Hennink, W. E. Thermoresponsive polymeric micelles with controlled instability based on hydrolytically sensitive N-Isopropylacrylamide copolymers. Macromolecules 2001, 34, 7589–7591. [CrossRef]
- Savic, R.; Luo, L.; Eisenberg, A.; Maysinger, D. Micellar nanocontainers distribute to defined cytoplasmic organelles. Science 2003, 300, 615–618. [CrossRef]
- Allen, T. M. Ligand-targeted therapeutics in anticancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 750–763. [CrossRef]
- Kabanov, A. V.; Lemieux, P.; Vinogradov, S.; Alakhov, V. Pluronic block copolymers: novel functional molecules for gene therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2002, 54, 223–233. [CrossRef]
- Francis, M. F.; Lavoie, L.; Winnik, F. M.; Leroux, J. C. Solubilization of cyclosporin A in dextran-g-polyethyleneglycolalkyl ether polymeric micelles. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2003, 56, 337–346. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J. H.; Lee, H. B.; Andrade, J. D. Blood compatibility of polyethylene oxide surfaces. Prog. Polym. Sci. 1995, 20, 1043–1079. [CrossRef]
- Kwon, G. S.; Naito, M.; Yokoyama, M.; Okano, T.; Sakurai, Y.; Kataoka, K. Physical entrapment of Adriamycin in AB block copolymer micelles. Pharm. Res. 1995, 12, 192–195. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrubý, M.; Konák, C.; Ulbrich, K. Polymeric micellar pH-sensitive drug delivery system for doxorubicin. J. Control. Release 2005, 103, 137–148. [CrossRef]
- Kim, S. C.; Kim, D. W.; Shim, Y. H.; Bang, J. S.; Oh, H. S.; Wan Kim, S.; Seo, M. H. In Vivo Evaluation of Polymeric Micellar Paclitaxel Formulation: Toxicity and Efficacy. J. Control. Release 2001, 72, 191–202. [CrossRef]
- Nishiyama, N.; Kato, Y.; Sugiyama, Y.; Kataoka, K. Cisplatin-loaded polymer–metal complex micelle with time-modulated decaying property as a novel drug delivery system. Pharm. Res. 2001, 18, 1035–1041. [CrossRef]
- Lin, W-J.; Juang, L-W.; Lin, C-C. Stability and release performance of a series of pegylated copolymeric micelles. Pharm Res 2003, 20, 668–673. [CrossRef]
- Djordjevic, J.; Barch, M.; Uhrich, K. E. Polymeric micelles based on amphiphilic scorpion-like macromolecules: novel carriers for water- insoluble drugs. Pharm. Res. 2005, 22, 24–32. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoyama, M.; Satoh, A.; Sakurai, Y.; Okano, T.; Matsumura, Y.; Kakizoe, T.; Kataoka, K. Incorporation of water-insoluble anticancer drug into polymeric micelles and control of their particle size. J. Control. Release 1998, 55, 219–229. [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, Y.; Yokoyama, M.; Kataoka, K.; Okano, T.; Sakurai, Y.; Kawaguchi, T.; Kakizoe, T. Reduction of the side effects of an antitumor agent, KRN5500, by incorporation of the drug into polymeric micelles. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 1999, 90, 122–128. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taillefer, J.; Jones, M. C.; Brasseur, N.; van Lier, J. E.; Leroux, J. C. Preparation and characterization of pH-responsive polymeric micelles for the delivery of photosensitizing anticancer drugs. J. Pharm. Sci. 2000, 89, 52–62. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. C.; Jackson, J. K.; Burt, H. M. Development of amphiphilic diblock copolymers as micellar carriers of taxol. Int. J. Pharm. 1996, 132, 195–206. [CrossRef]
- Teng, Y.; Morrison, M. E.; Munk, P.; Webber, S. E.; Procházka, K. Release Kinetics Studies of Aromatic Molecules into Water from Block Polymer Micelles. Macromolecules 1998, 31, 3578–3587. [CrossRef]
- Kabanov, A. V.; Nazarova, I. R.; Astafieva, I. V.; Batrakova, E. V.; Alakhov, V. Y.; Yaroslavov, A. A.; Kabanov, V. A. Micelle Formation and Solubilization of Fluorescent Probes in Poly(oxyethylene-b-oxypropylene-b-oxyethylene) Solutions. Macromolecules 1995, 28, 2303–2314. [CrossRef]
- Kwon, G. S.; Naito, M.; Kataoka, K.; Yokoyama, M.; Sakurai, Y.; Okano, T. Block copolymer micelles as vehicles for hydrophobic drugs. Colloids Surf. B Biointerface 1994, 2, 429–434. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J. X.; Allen, C.; Eisenberg, A. Partitioning of pyrene between “crew cut” block copolymer micelles and H2O/DMF solvent mixtures. Macromolecules 1997, 30, 7143–7150. [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, M.; Okano, T.; Sakurai, Y.; Kataoka, K. Improved synthesis of adriamycin-conjugated poly (ethylene oxide)-poly (aspartic acid) block copolymer and formation of unimodal micellar structure with controlled amount of physically entrapped adriamycin. J. Control. Release 1994, 32, 269–277. [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Chen, F.; Wang, Y.; Stenzel, M. H.; Chapman, R. Polyion complex micelles for protein delivery benefit from flexible hydrophobic spacers in the binding group. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2020, 41, e2000208. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Lu, C.; Xia, W.; Quan, G.; Huang, Y.; Bai, X.; Yu, F.; Xu, Q.; Qin, W.; Liu, D.; Pan, X. Poly (L-glutamic acid)-based brush co- polymers : fabrication, self-assembly, and evaluation as efficient nnanocarriers for cationic protein drug delivery. AAPS PharmSciTech 2020, 21, 78. [CrossRef]
- Raveendran, R.; Chen, F.; Kent, B.; Stenzel, M. H. Estrone-decorated polyion complex micelles for targeted melittin delivery to hormone-responsive breast cancer cells. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 1222–1233. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Lu, H.; Chen, F.; Callari, M.; Pourgholami, M.; Morris, D. L.; Stenzel, M. H. PEGylated albumin-based polyion complex micelles for protein delivery. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 808–817. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, N. M.; Ritzel, R.; Mancini, N. S.; Jiang, Y.; Yi, X.; Manickam, D. S.; Banks, W. A.; Kabanov, A. V.; McCullough, L. D.; Verma, R. Nano-particle delivery of brain derived neurotrophic factor after focal cerebral ischemia reduces tissue injury and enhances behavioral recovery. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2016, 150–151, 48–56.
- Batrakova, E. V.; Li, S.; Reynolds, A. D.; Mosley, R. L.; Bronich, T. K.; Kabanov, A. V.; Gendelman, H. E. A macrophage-nanozyme delivery system for Parkinson’s disease. Bioconjugate Chemistry 2007, 18, 1498–1506.
- Brynskikh, A. M.; Zhao, Y.; Mosley, R. L.; Li, S.; Boska, M. D.; Klyachko, N. L.; Kabanov, A. V.; Gendelman, H. E.; Batrakova, E. V. Macrophage Delivery of Therapeutic Nanozymes in A Murine Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Nanomedicine 2010, 5, 379–396.
- Haney, M. J.; Zhao, Y.; Li, S.; Higginbotham, S. M.; Booth, S. L.; Han, H. Y.; Vetro, J. A.; Mosley, R. L.; Kabanov, A. V.; Gendelman, H. E.; Batrakova, E. V. Cell-mediated transfer of catalase nanoparticles from macrophages to brain endothelial, glial and neuronal cells. Nanomedicine 2011, 6, 1215–1230.
- Klyachko, N. L.; Haney, M. J.; Zhao, Y.; Manickam, D. S.; Mahajan, V.; Suresh, P.; Hingtgen, S. D.; Mosley, R. L.; Gendelman, H. E.; Kabanov, A. V.; Batrakova, E. V. Macrophages offer a paradigm switch for CNS delivery of therapeutic proteins. Nanomedicine 2014, 9, 1403–1422.
- Rosenbaugh, E. G.; Roat, J. W.; Gao, L.; Yang, R.-F.; Manickam, D. S.; Yin, J.-X.; Schultz, H.D.; Bronich, T. K.; Batrakova, E. V.; Kabanov, A. V.; Zucker, I. H.; Zimmerman, M. C. The attenuation of central angiotensin II-dependent pressor response and intra-neuronal signaling by intracarotid injection of nanoformulated copper/zinc superoxide dismutase. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 5218–5226.
- 1540. Manickam, D. S.; Brynskikh, A. M.; Kopanic, J. L.; Sorgen, P. L.; Klyachko, N. L.; Batrakova, E. V.; Bronich, T. K.; Kabanov, A. V. Well-defined cross-linked antioxidant nanozymes for treatment of ischemic brain injury. J. Control. Release 2012, 162, 636–645.
- Jiang, Y.; Brynskikh, A. M.; Devika, S.; Kabanov, A. V. SOD1 nanozyme salvages ischemic brain by locally protecting cerebral vasculature. J. Control. Release 2015, 213, 36–44. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Li, K.; Hart-Smith, G.; Xu, Y. D.; Jiang, Y.; Lu, H.; Fok, S.; Macmillian, A.; Pandzic, E.; Stenzel M. Light-sheet microscopy as a tool to understanding the behaviour of Polyion complex micelles for drug delivery. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 12618–12621. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Ding, P.; Zhou, W.; Li, Y.; Drechsler, M.; Guo, X.; Cohen Stuart, M. A. A supramolecular crosslinker to give salt- resistant polyion complex micelles and improved MRI contrast agents. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed Engl. 2018, 57, 12680–12684. [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Besseling, N. A. M.; de Keizer, A.; Marcelis, A. T. M.; Drechsler, M.; Cohen Stuart, M. A. Hierarchical self-assembly in solutions containing metal ions, ligand, and diblock copolymer. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2007, 46, 1807–1809. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V. T. A.; De Pauw-Gillet M. C.; Gauthier, M.; Sandre, O. Magnetic polyion complex micelles for cell toxicity induced by radiofrequency magnetic field hyperthermia. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 1014. [CrossRef]
- Mi, P.; Wang, F.; Nishiyama, N.; Cabral, H. Molecular Cancer Imaging with Polymeric Nanoassemblies: From Tumor Detection to Theranostics. Macromol. Biosci. 2017, 17, 1600305.
- Silva, C. O.; Pinho, J. O.; Lopes, J. M.; Almeida, A. J.; Gaspar, M. M.; Reis, C. Current Trends in Cancer Nanotheranostics: Metallic, Polymeric, and Lipid-Based Systems. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 22. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Indoria, S.; Singh, V.; Hsieh, M. F. Recent advances in theranostic polymeric nanoparticles for cancer treatment: A review. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 582, 119314. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Z.; Chan, L.; Zhang, D.; Huang, C.; Mei, C.; Gao, P.; Huang, Y.; Liang, J.; He, L.; Shi, C.; Chen, T.; Luo, L. Precise delivery of a multifunctional nanosystem for MRI-guided cancer therapy and monitoring of tumor response by functional diffusion-weighted MRI. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 2926–2937.
- Deng, K.; Zhao, X.; Liu, F.; Peng, J.; Meng, C.; Huang, Y.; Ma, L.; Chang, C.; Wei, H. Synthesis of Thermosensitive Conjugated Triblock Copolymers by Sequential Click Couplings for Drug Delivery and Cell Imaging. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 3419–3428. [CrossRef]
- Ke, W.; Li, J.; Mohammed, F.; Wang, Y.; Tou, K.; Liu, X.; Wen, P.; Kinoh, H.; Anraku, Y.; Chen, H.; Kataoka, K.; Ge, Z. Therapeutic Polymersome Nanoreactors with Tumor-Specific Activable Cascade Reactions for Cooperative Cancer Therapy. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 2357–2369.
- Hood, M. A.; Mari, M.; Muñoz-Espí, R. Synthetic Strategies in the Preparation of Polymer/Inorganic Hybrid Nanoparticles. Materials (Basel) 2014, 7, 4057–4087. [CrossRef]
- 1553. Tharmavaram, M.; Rawtani, D.; Pandey, G. Fabrication routes for one-dimensional nanostructures via block copolymers. Nano Converg. 2017, 4, 12.
- Li, X.; Iocozzia, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, S.; Cui, X.; Wang, W.; Yu, H.; Lin, S.; Lin, Z. From Precision Synthesis of Block Copolymers to Properties and Applications of Nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2018, 57, 2046–2070. [CrossRef]
- Scaravelli, R. C.; Dazzi, R. L.; Giacomelli, F. C.; Machado, G.; Giacomelli, C.; Schmidt, V. Direct synthesis of coated gold nanoparticles mediated by polymers with amino groups. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 397, 114–121. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 1556. Podhorska, L.; Delcassian, D.; Goode, A. E.; Agyei, M.; McComb, D. W.; Ryan, M. P.; Dunlop, I. E. Mechanisms of Polymer-Templated Nanoparticle Synthesis: Contrasting ZnS and Au. Langmuir 2016, 32, 9216–9222.
- Zhang, G.; Tang, S.; Li, A. Thermally Stable Metallic Nanoparticles Prepared via Core-Cross-linked Block Copolymer Micellar Nanoreactors. Langmuir 2017, 33, 6353–6362. [CrossRef]
- Jang, J. D.; Jeon, S.-W.; Yoon, Y.-J.; Bang, J.; Han, Y. S.; Kim, T.-H. Self-assembly of gold nanoparticles in a block copolymer aggregate template driven by hydrophobic interactions. Polym. Chem. 2019, 10, 6269–6277. [CrossRef]
- Sohn, H.; Shin, H. W.; Lee, S. M. Metal-Mediated Morphology Regulation of Self-Assembled Double-Hydrophilic Block Copolymers. ACS Macro Lett. 2020, 9, 600–605. [CrossRef]
- Constantinou, A. P.; Marie-Sainte, U.; Peng, L.; Carroll, D. R.; McGilvery, C. M.; Dunlop, I. E.; Georgiou, T. K. Effect of block copolymer architecture and composition on gold nanoparticle fabrication. Polymer Chemistry 2019, 10, 4637–4642. [CrossRef]
- Yao, N.; Lin, W.; Zhang, X.; Gu, H.; Zhang, L. Amphiphilic β-cyclodextrin-based star-like block copolymer unimolecular micelles for facile in situ preparation of gold nanoparticles. J. Polym. Sci., Part A: Polym. Chem. 2016, 54, 186–196. [CrossRef]
- 1562. Li, C.; Li, Q.; Kaneti Y. V.; Hou, D.; Yamauchi, Y.; Mai, Y. Self-assembly of block copolymers towards mesoporous materials for energy storage and conversion systems. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 4681–4736.
- 1563. Kumar, L.; Singh, S.; Horechyy, A.; Fery, A.; Nandan B. Block copolymer template-directed catalytic systems: Recent progress and perspectives. Membranes 2021, 11, 318.
- Hara, S.; Zama, T.; Takashima, W.; Kaneto, K. Artificial muscles based on polypyrrole actuators with large strain and stress induced electrically. Polym. J. 2004, 36, 151–161. [CrossRef]
- O’Halloran, A.; O’Malley, F.; McHugh, P. A review on dielectric elastomer actuators, technology, applications, and challenges. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 104, 071101. [CrossRef]
- Imaizumi, S.; Kokubo, H.; Watanabe M. Polymer actuators using ion-gel electrolytes prepared by self-assembly of ABA-triblock copolymers. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 401–409. [CrossRef]
- Imaizumi, S.; Kato, Y.; Kokubo, H.; Watanabe, M. Driving mechanisms of ionic polymer actuators having electric double layer capacitor structures. J. Phys. Chem. B 2012, 116, 5080–5089. [CrossRef]
- Margaretta, E.; Fahs, G. B.; Inglefield Jr., D. L.; Jangu, C.; Wang, D.; Heflin, J. R.; Moore, R. B.; Long, T. E. Imidazolium-containing ABA Triblock copolymers as Electroactive devices. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 1280–1288. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Wang, D.; Zhang, M.; Heflin, J. R.; Moore, R. B.; Long, T. E. RAFT synthesis of ABA triblock copolymers as ionic liquid-containing electroactive membranes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 6552–6559. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, O.; Kim, H.; Choi, U. H.; Park, M. J. One-volt-driven superfast polymer actuators based on single-ion conductors. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13576. [CrossRef]
- Park, M. J.; Choi, I.; Hong, J.; Kim, O. Polymer electrolytes integrated with ionic liquids for future electrochemical devices. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 129, 2363–2376. [CrossRef]
- Seki, S.; Kobayashi, Y.; Miyashiro, H.; Ohno, Y.; Usami, A.; Mita, Y.; Kihira, N.; Watanabe, M.; Terada, N. Lithium secondary batteries using modified-imidazolium room-temperature ionic liquid. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 10228–10230. [CrossRef]
- Zakeeruddin S. M.; Gratzel, M. Solvent-free ionic liquid electrolytes for Mesoscopic dye-sensitized solar cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 2187–2202. [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Fadeev, A. G.; Qi, B.; Smela, E.; Mattes, B. R.; Ding, J.; Spinks, G. M.; Mazurkiewicz, J.; Zhou, D.; Wallace, G. G.; MacFarlane, D. R.; Forsyth, S. A.; Forsyth, M. Use of ionic liquids for pi-conjugated polymer electrochemical devices. Science 2002, 297, 983–987.
- Ding, J.; Zhou, D.; Spinks, G.; Wallace, G.; Forsyth, S.; Forsyth, M.; MacFarlane, D. Use of Ionic Liquids as Electrolytes in Electromechanical Actuator Systems Based on Inherently Conducting Polymers. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 2392–2398. [CrossRef]
- Cho, J. H.; Lee, J.; Xia, Y.; Kim, B.; He, Y.; Renn, M. J.; Lodge, T. P.; Frisbie, C. D. Printable ion- gel gate dielectrics for low-voltage polymer thin-film transistors on plastic. Nat. Mater. 2008, 7, 900–906. [CrossRef]
- Cho, J. H.; Lee, J.; He, Y.; Kim, B.; Lodge, T. P.; Frisbie, C. D. High-capacitance ion gel gate dielectrics with faster polarization response times for organic thin film transistors. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 686–690. [CrossRef]
- Virgili, J. M.; Hexemer, A.; Pople, J. A.; Balsara, N. P.; Segalman, R. A. Phase behavior of polystyrene-block-poly(2-vinylpyridine) copolymers in a selective ionic liquid solvent. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 4604–4613. [CrossRef]
- 1579. Xie, R.; López-Barrón, C. R.; Wagner, N. J. Self-assembly of block copolymers in ionic liquids. ACS Symp. Ser. 2017, 1250, 83–142.
- Yoshida, K.; Nakamura, M.; Kazue, Y.; Tachikawa, N.; Tsuzuki, S.; Seki, S.; Dokko, K.; Watanabe, M. Oxidative-stability enhancement and charge transport mechanism in glyme-lithium salt equimolar complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 13121–13129. [CrossRef]
- Ueno, K.; Yoshida, K.; Tsuchiya, M.; Tachikawa, N.; Dokko, K.; Watanabe, M. Glyme-Lithium Salt Equimolar Molten Mixtures: Concentrated Solutions or Solvate Ionic Liquids? J. Phys. Chem. B 2012, 116, 11323–11331. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitazawa, Y.; Iwata, K.; Imaizumi, S.; Ahn, H.; Kim, S.Y.; Ueno, K.; Park, M.J.; Watanabe, M. Gelation of solvate ionic liquid by self-assembly of block copolymer and characterization as polymer electrolyte. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 6009–6016. [CrossRef]
- Kitazawa, Y.; Iwata, K.; Kido, R.; Imaizumi, S.; Tsuzuki, S.; Shinoda, W.; Ueno, K.; Mandai, T.; Kokubo, H.; Dokko, K.; Watanabe, M. Polymer electrolytes containing solvate ionic liquids: a new approach to achieve high ionic conductivity, thermal stability, and a wide potential window. Chem. Mater. 2017, 30, 252–261.
- 1584. Kawazoe, T.; Hashimoto, K.; Kitazawa, Y.; Kokubo, H.; Watanabe, M. A polymer electrolyte containing solvate ionic liquid with increased mechanical strength formed by self-assembly of ABA-type Ionomer triblock copolymer, Electrochim. Acta 2017, 235, 287–294.
- Lee, J.; Panzer, M. J.; He, Y. Y.; Lodge, T. P.; Frisbie, C. D. Ion gel gated polymer thin-film transistors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 4532–4533. [CrossRef]
- Lee, K. H.; Zhang, S.; Gu, Y.; Lodge, T. P.; Frisbie, C. D. Transfer printing of thermoreversible ion gels for flexible electronics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 9522–9527. [CrossRef]
- Lee, K. H.; Zhang, S.; Lodge, T. P.; Frisbie, C. D. Electrical impedance of spin-coatable ion gel films. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 3315–3321. [CrossRef]
- Yomogida, Y.; Pu, J.; Shimotani, H.; Ono, S.; Hotta, S.; Iwasa, Y.; Takenobu, T. Ambipolar organic single-crystal transistors based on ion gels. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 4392–4397. [CrossRef]
- Pu, J.; Yomogida, Y.; Liu, K. K.; Li, L. J.; Iwasa, Y.; Takenobu, T. Highly flexible MoS2 thin-film transistors with ion gel dielectrics. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 4013–4017. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Yu, M.; Li, F.; Zhu, M.; Li, M.; Gao, Y.; Li, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, D.; Yi, T.; Huang, C. A highly selective fluorescence turn- on sensor for cysteine/homocysteine and its application in bioimaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 10322–10323. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hu, X.; Tian, S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, G.; Liu, S. Polyion complex micellar nanoparticles for integrated fluorometric detection and bacteria inhibition in aqueous media. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 1618–1626. [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Liu. G.; Wang, X.; Wu, T.; Yang, J.; Ye, X.; Zhang, G.; Hu, J.; Liu, S. pH-Regulated Reversible Transition Between Polyion Complexes (PIC) and Hydrogen-Bonding Complexes (HBC) with Tunable Aggregation-Induced Emission. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 3693–3702. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sureka, H.V.; Obermeyer, A.C.; Flores, R.J.; Olsen, B.D. Catalytic Biosensors from Complex Coacervate Core Micelles (C3M) Thin Films. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 32354–32365. [CrossRef]
- Molina, E.; Mathonnat, M.; Richard, J.; Lacroix-Desmazes, P.; In, M.; Dieudonné, P.; Cacciaguerra, T.; Gérardin, C.; Marcotte, N. pH-Mediated Control over the Mesostructure of Ordered Mesoporous Materials Templated by Polyion Complex Micelles. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 144–156. [CrossRef]
- Lim, W. T.; Tan, E. H.; Toh, C. K.; Hee, S. W.; Leong, S. S.; Ang, P. C. S.; Wong, N. S.; Chowbay, B. Phase I pharmacokinetic study of a weekly liposomal paclitaxel formulation (Genexol-PM) in patients with solid tumors. Ann. Oncol. 2010, 21, 382–388. [CrossRef]
- Lee, K. S.; Chung, H. C.; Im, S. A.; Park, Y. H.; Kim, C. S.; Kim, S.-B.; Rha, S. Y.; Lee, M. Y.; Ro, J. Multicenter phase II trial of genexol-PM, a cremophor-free, polymeric micelle formulation of paclitaxel, in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2008, 108, 241–250. [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.- W.; Kim, S.- Y.; Kim, H.- K.; Kim, S.- W., Shin, S. W.; Kim, J. S.; Park, K.; Lee, M. Y.; Heo, D. S. Multicenter phase II trial of genexol-PM, a novel cremophor-free, polymeric micelle formulation of paclitaxel, with cisplatin in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2007, 18, 2009–2014.
- Saif, M. W.; Podoltsev, N. A.; Rubin, M. S.; Figueroa, J. A.; Lee, M. Y.; Kwon, J.; Rowen, E.; Yu, J.; Kerr, R. O. Phase II clinical trial of paclitaxel loaded polymeric micelle in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer. Cancer Invest. 2010, 28, 186–194.
- Kato, K.; Chin, K.; Yoshikawa, T.; Yamaguchi, K.; Tsuji, Y.; Esaki, T.; Sakai, K.; Kimura, M.; Hamaguchi, T.; Shimada, Y.; Matsumura, Y.; Ikeda, R. Phase II study of NK105, a paclitaxel-incorporating micellar nanoparticle, for previously treated advanced or recurrent gastric cancer. Investig. New Drugs 2012, 30, 1621–1627.
- Danson, S.; Ferry, D.; Alakhov, V.; Margison, J.; Kerr, D.; Jowle, D.; Brampton, M.; Halbert, G.; Ranson, M. Phase I dose escalation and pharmacokinetic study of pluronic polymer-bound doxorubicin (SP1049C) in patients with advanced cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2004, 90, 2085–2091. [CrossRef]
- 1601. Valle, J. W.; Armstrong, A.; Newman, C.; Alakhov, V.; Pietrzynski, G.; Brewer, J.; Campbell, S.; Corrie, P.; Rowinsky, E. K.; Ranson, M. A phase 2 study of SP1049C, doxorubicin in P-glycoprotein-targeting pluronics, in patients with advanced adenocarcinoma of the esophagus and gastroesophageal junction. Investig. New Drugs 2010, 29, 1029–1037.
- Uchino, H.; Matsumura, Y.; Negishi, T.; Koizumi, F.; Hayashi, T.; Honda, T.; Nishiyama, N.; Kataoka, K.; Naito, S.; Kakizoe, T. Cisplatin-incorporating polymeric micelles (NC-6004) can reduce nephrotoxicity and neurotoxicity of cisplatin in rats. Br. J. Cancer 2005, 93, 678–687. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alami, N.; Banerjee, K.; Juste, S.; Page, V.; Brossard, M.; Hayashi, T.; Igarashi, E.; Jones, B. L. NC-6004, a novel cisplatin-incorporated polymeric micelle, is highly effective against oxaliplatin-resistant tumor models. AACR Meet. Abstr. 2006, 133.
- Plummer, R.; Wilson, R. H.; Calvert, H.; Boddy, A. V.; Griffin, M.; Sludden, J.; Tilby, M. J.; Eatock, M.; Pearson, D. G.; Ottley, C. J.; Matsumura, Y.; Kataoka, K.; Nishiya, T. A Phase I clinical study of cisplatin-incorporated polymeric micelles (NC-6004) in patients with solid tumours. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 104, 593–598.
- 1605. Takahashi, A.; Yamamoto, Y.; Yasunaga, M.; Koga, Y.; Kuroda, J.; Takigahira, M.; Harada, M.; Saito, H.; Hayashi, T.; Kato, Y.; Kinoshita, T.; Ohkohchi, N.; Hyodo, I.; Matsumura, Y. NC-6300, an epirubicin-incorporating micelle, extends the antitumor effect and reduces the cardiotoxicity of epirubicin. Cancer Sci. 2013, 104, 920–925.
- Hsiang, Y. H.; Liu, L. F. Identification of mammalian DNA topoisomerase I as an intracellular target of the anticancer drug camptothecin. Cancer Res. 1988, 48, 1722–1726.
- Kawato, Y.; Aonuma, M.; Hirota, Y.; Kuga, H.; Sato, K. Intracellular roles of SN-38, a metabolite of the camptothecin derivative CPT-11, in the antitumor effect of CPT-11. Cancer Res. 1991, 51, 4187–4191.
- Kuroda, J.; Kuratsu, J.; Yasunaga, M.; Koga, Y.; Saito, Y.; Matsumura, Y. Potent antitumor effect of SN-38-incorporating polymeric micelle, NK012, against malignant glioma. Int. J. Cancer. 2009, 124, 2505–2511. [CrossRef]
- Kuroda, J.; Kuratsu, J.; Yasunaga, M.; Koga, Y.; Kenmotsu, H.; Sugino, T.; Matsumura, Y. Antitumor effect of NK012, a 7-ethyl-10-hydroxycamptothecin-incorporating polymeric micelle, on U87MG orthotopic glioblastoma in mice compared with irinotecan hydrochloride in combination with bevacizumab. Clin Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 521–529.
- Hamaguchi, T.; Doi, T.; Eguchi-Nakajima, T.; Kato, K.; Yamada, Y.; Shimada, Y.; Fuse, N.; Ohtsu, A.; Matsumoto, S.; Takanashi, M.; Matsumura, Y. Phase I study of NK012, a novel SN-38-incorporating micellar nanoparticle, in adult patients with solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 5058–5066. [CrossRef]
- Burris, H. A., III.; Infante, J. R.; Spigel, D. R.; Greco, F. A.; Thompson, D. S.; Matsumoto, S.; Kawamura, S.; Jones, S. F. A phase I dose-escalation study of NK012. Proc. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2008, Abstract No. 2538.
- Sudimack, J.; Lee, R. J. Targeted drug delivery via the folate receptor. Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 2000, 41, 147–162. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Low, P. S.; Henne, W. A.; Doorneweerd, D. D. Discovery and development of folic-acid-based receptor targeting for imaging and therapy of cancer and inflammatory diseases. Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 120–129. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruoslahti, E. RGD and other recognition sequences for integrins. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 1996, 12, 697–715. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Z.; Chen, Q.; Osada, K.; Liu, X.; Tockary, T. A.; Uchida, S.; Dirisala, A.; Ishii, T.; Nomoto, T.; Toh, K.; Matsumoto, Y.; Oba, M.; Kano, M. R.; Itaka, K.; Kataoka, K. Targeted gene delivery by polyplex micelles with crowded PEG palisade and cRGD moiety for systemic treatment of pancreatic tumors. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 3416–3426.
- Wang, F.; Li, Y.; Shen, Y.; Wang, A.; Wang, S.; Xie, T. The functions and applications of RGD in tumor therapy and tissue engineering. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 13447–13462. [CrossRef]
- Varkouhi, A. K.; Scholte, M.; Storm, G.; Haisma, H. J. Endosomal escape pathways for delivery of biologicals. J. Control. Release 2011, 151, 220–228. [CrossRef]
- Pittella, F.; Zhang, M.; Lee, Y.; Kim, H. J.; Tockary, T.; Osada, K.; Ishii, T.; Miyata, K.; Nishiyama, N.; Kataoka, K. Enhanced endosomal escape of siRNA-incorporating hybrid nanoparticles from calcium phosphate and PEG-block charge-conversional polymer for efficient gene knockdown with negligible cytotoxicity. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 3106–3114.
- Monnery, B. D.; Wright, M.; Cavill, R.; Hoogenboom, R.; Shaunak, S.; Steinke, J. H. G.; Thanou, M. Cytotoxicity of polycations: Relationship of molecular weight and the hydrolytic theory of the mechanism of toxicity. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 521, 249–258. [CrossRef]
- Breunig, M.; Lungwitz, U.; Liebl, R.; Goepferich, A. Breaking up the correlation between efficacy and toxicity for nonviral gene delivery. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2007, 104, 14454–14459. [CrossRef]
- Fischer, D.; Li, Y.; Ahlemeyer, B.; Krieglstein, J.; Kissel, T. In vitro cytotoxicity testing of polycations: influence of polymer structure on cell viability and hemolysis. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 1121–1131. [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, K. Revolutionary advances in 2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine polymers as biomaterials. J. Biomed. Mater. Res., Part A 2019, 107, 933–943. [CrossRef]
- Blanco, E.; Shen, H.; Ferrari, M. Principles of nanoparticle design for overcoming biological barriers to drug delivery. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 941–951. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y. A.; Ni, C. H.; Shi, G.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Li, W. The polyion complex nano-prodrug of doxorubicin (DOX) with poly(lactic acid-co-malic acid)-block-polyethylene glycol: preparation and drug controlled release. Med. Chem. Res. 2015, 24, 1189–1195. [CrossRef]
- Feiner-Gracia, N.; Olea, R. A.; Fitzner, R.; El Boujnouni, N.; van Asbeck, A. H.; Brock, R.; Albertazzi, L. Super-Resolution Imaging of Structure, Molecular Composition, and Stability of Single Oligonucleotide Polyplexes. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 2784–2792. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riera, R.; Feiner-Gracia, N.; Fornaguera, C.; Cascante, A.; Borroś, S.; Albertazzi, L. Tracking the DNA Complexation State of PBAE Polyplexes in Cells with Super Resolution Microscopy. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 17869–17877. [CrossRef]
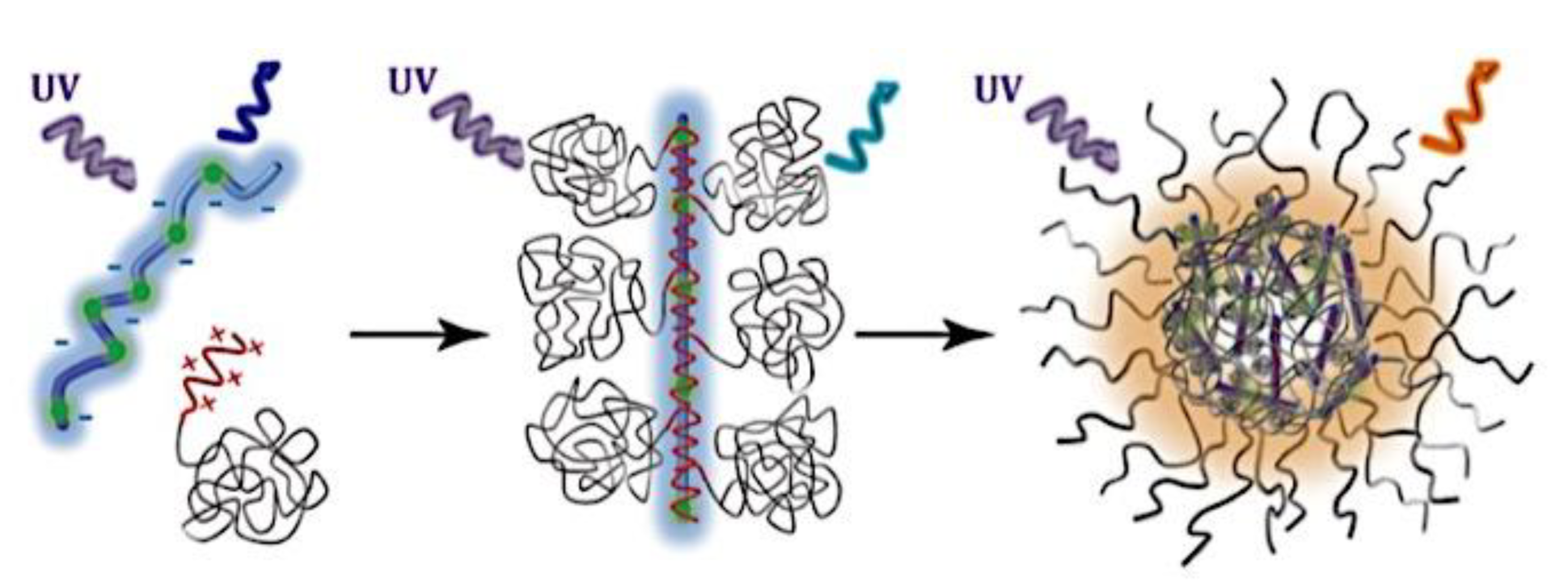
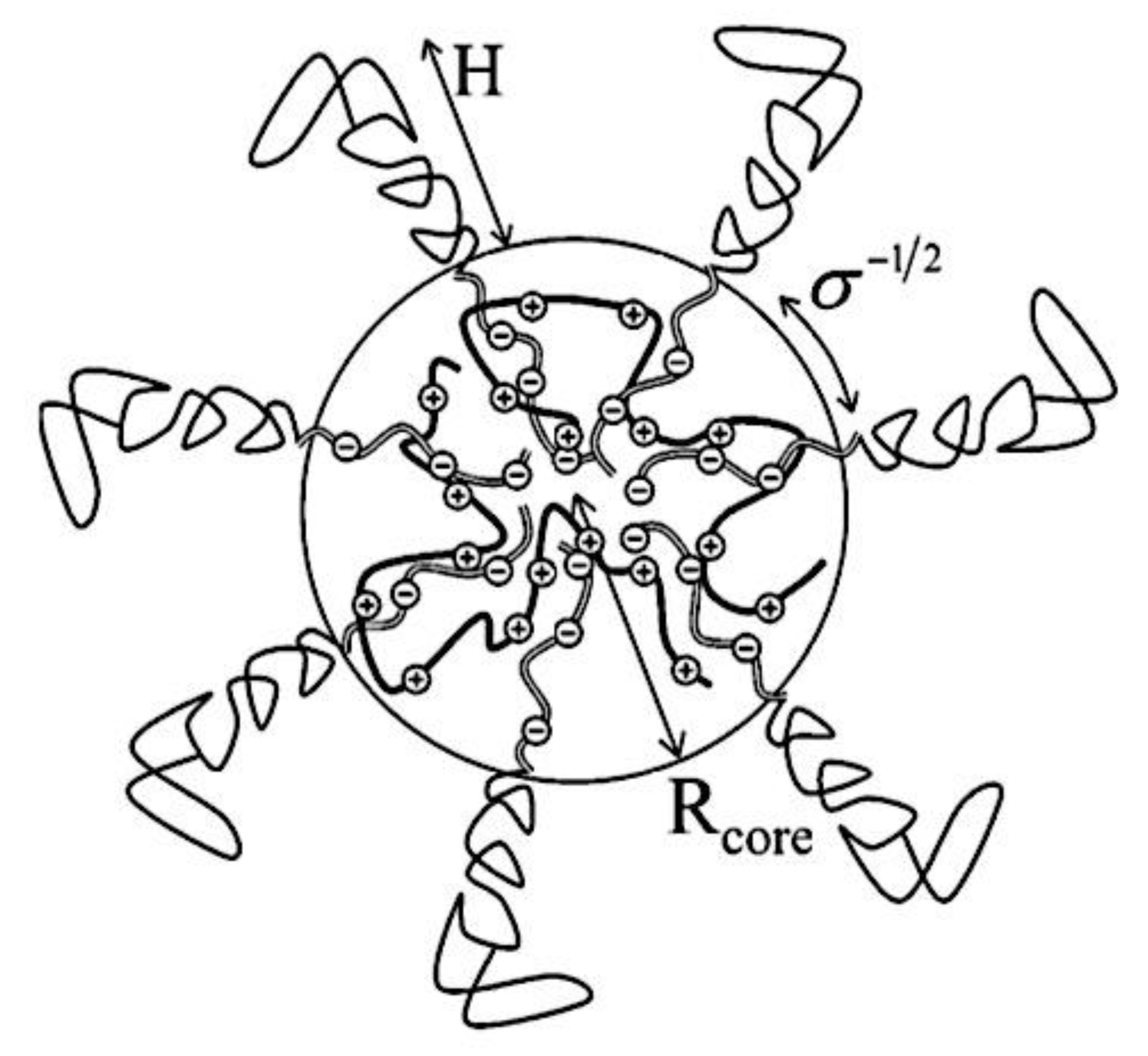
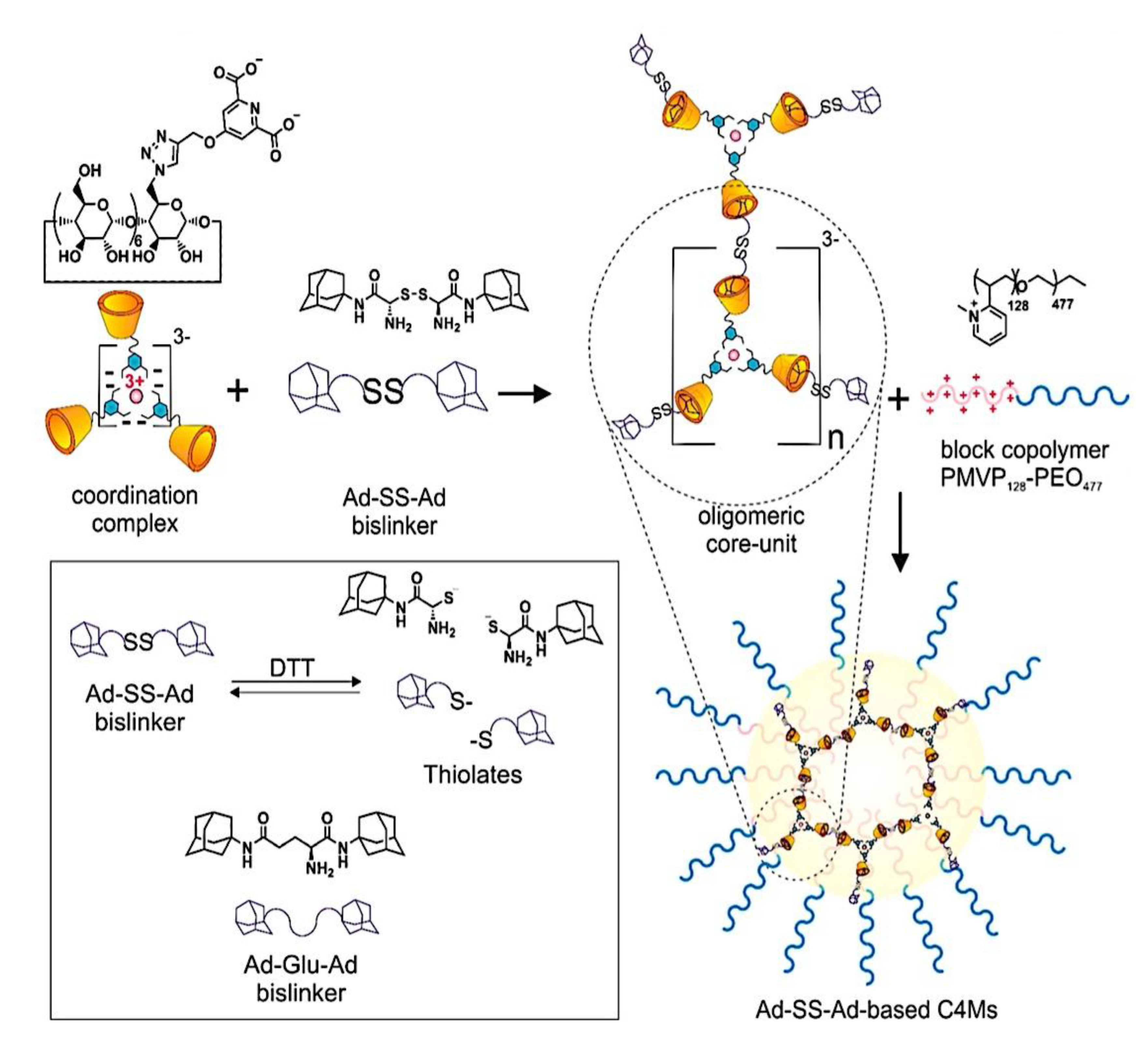
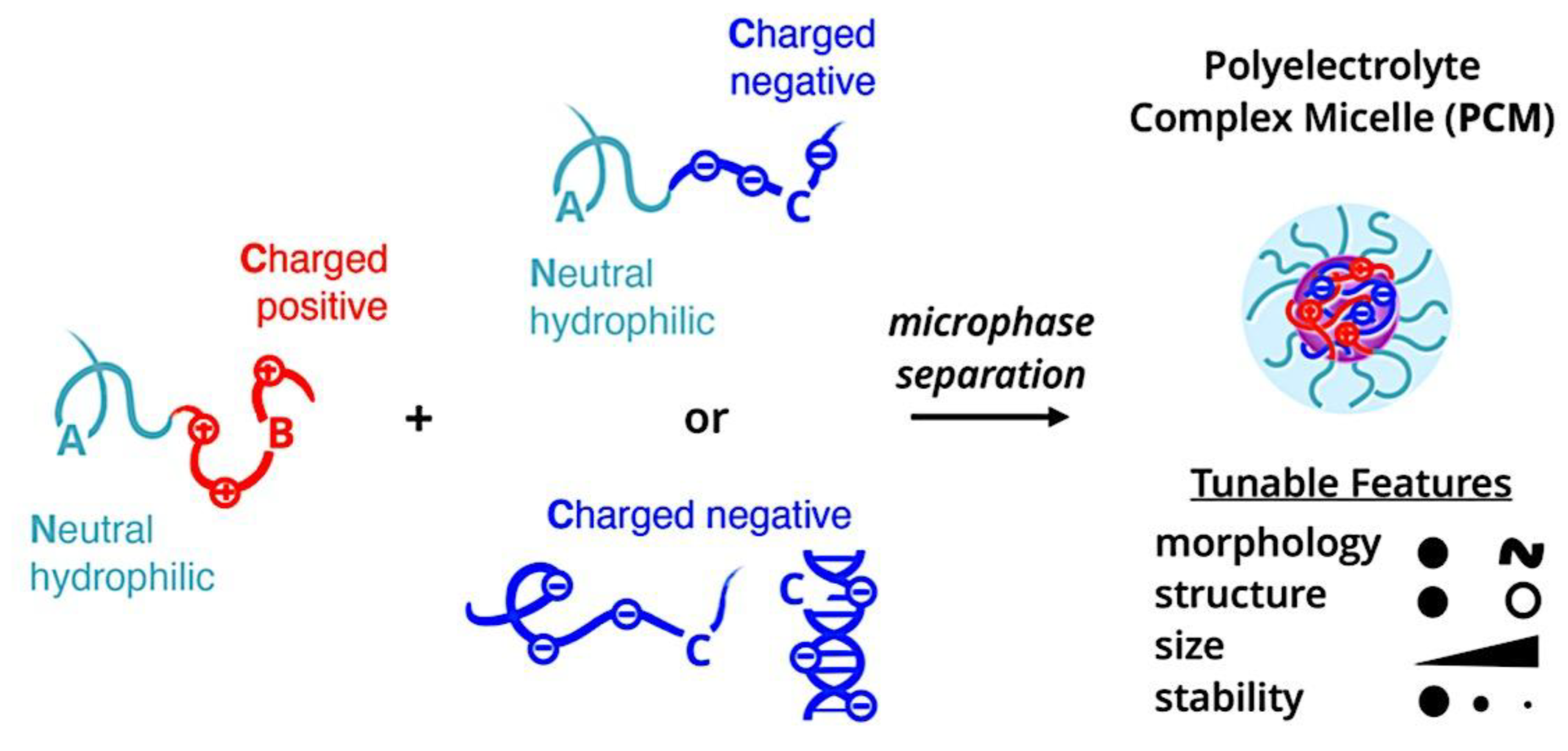
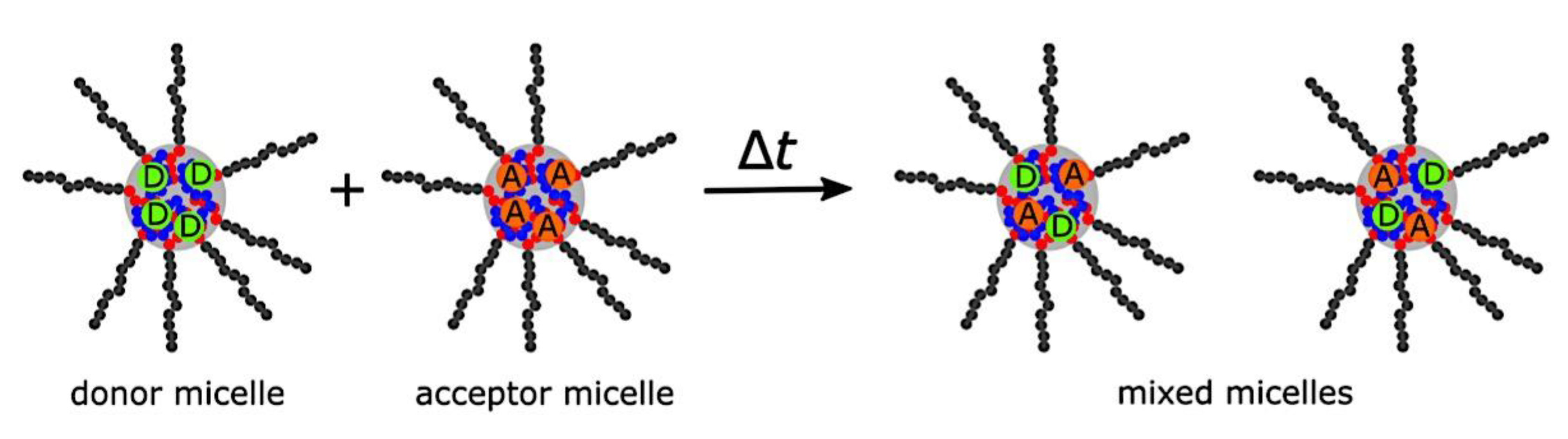
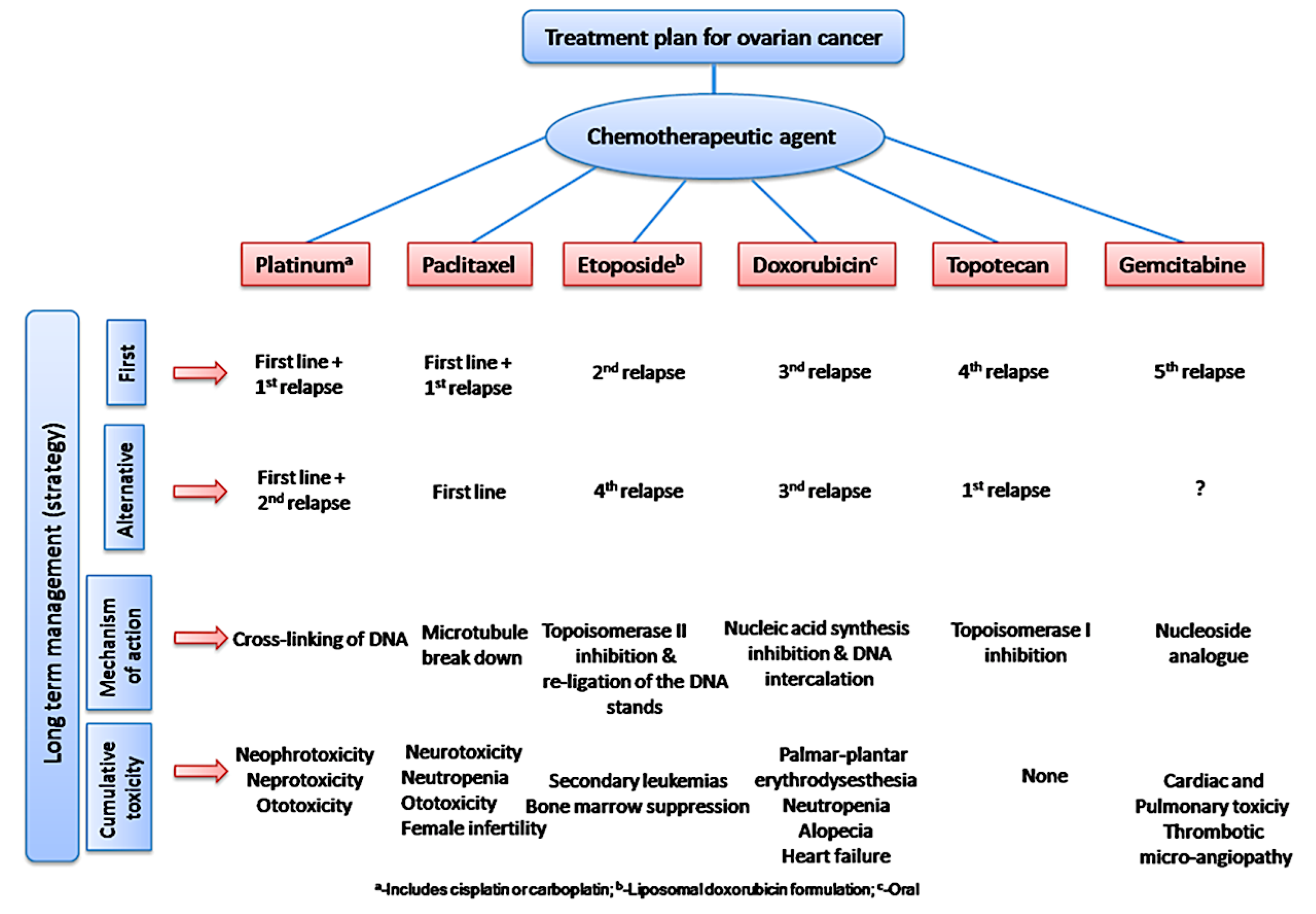
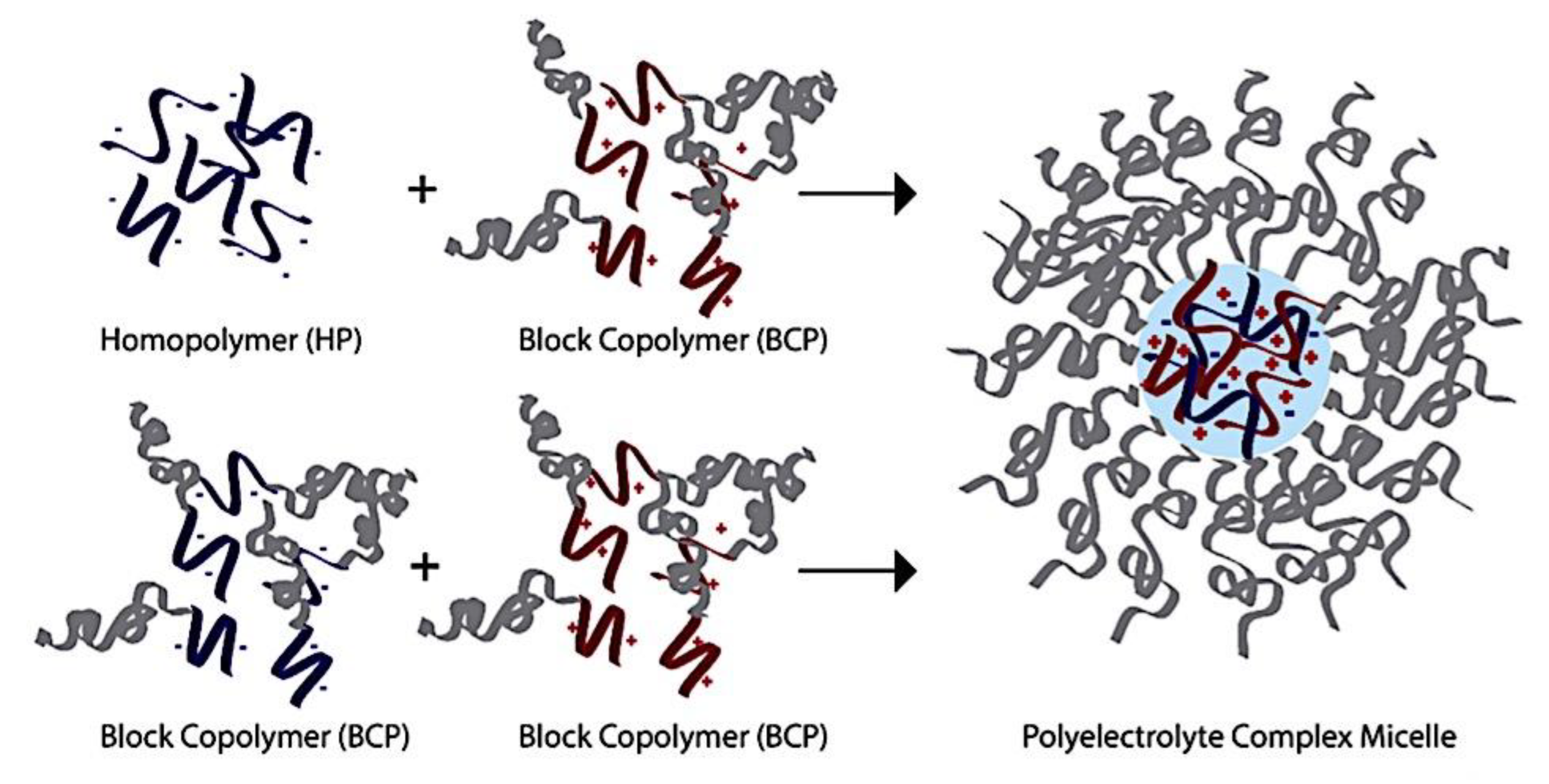
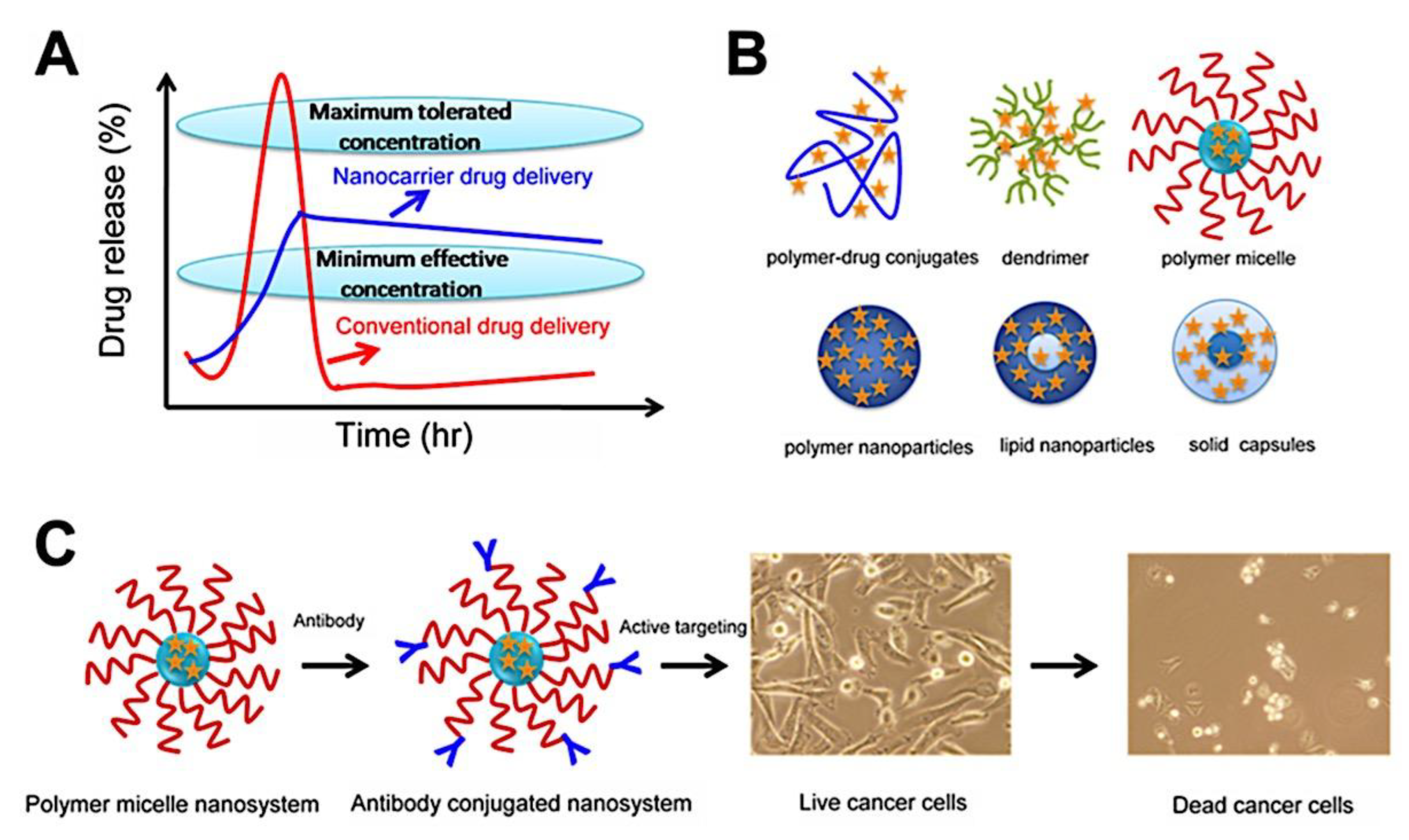
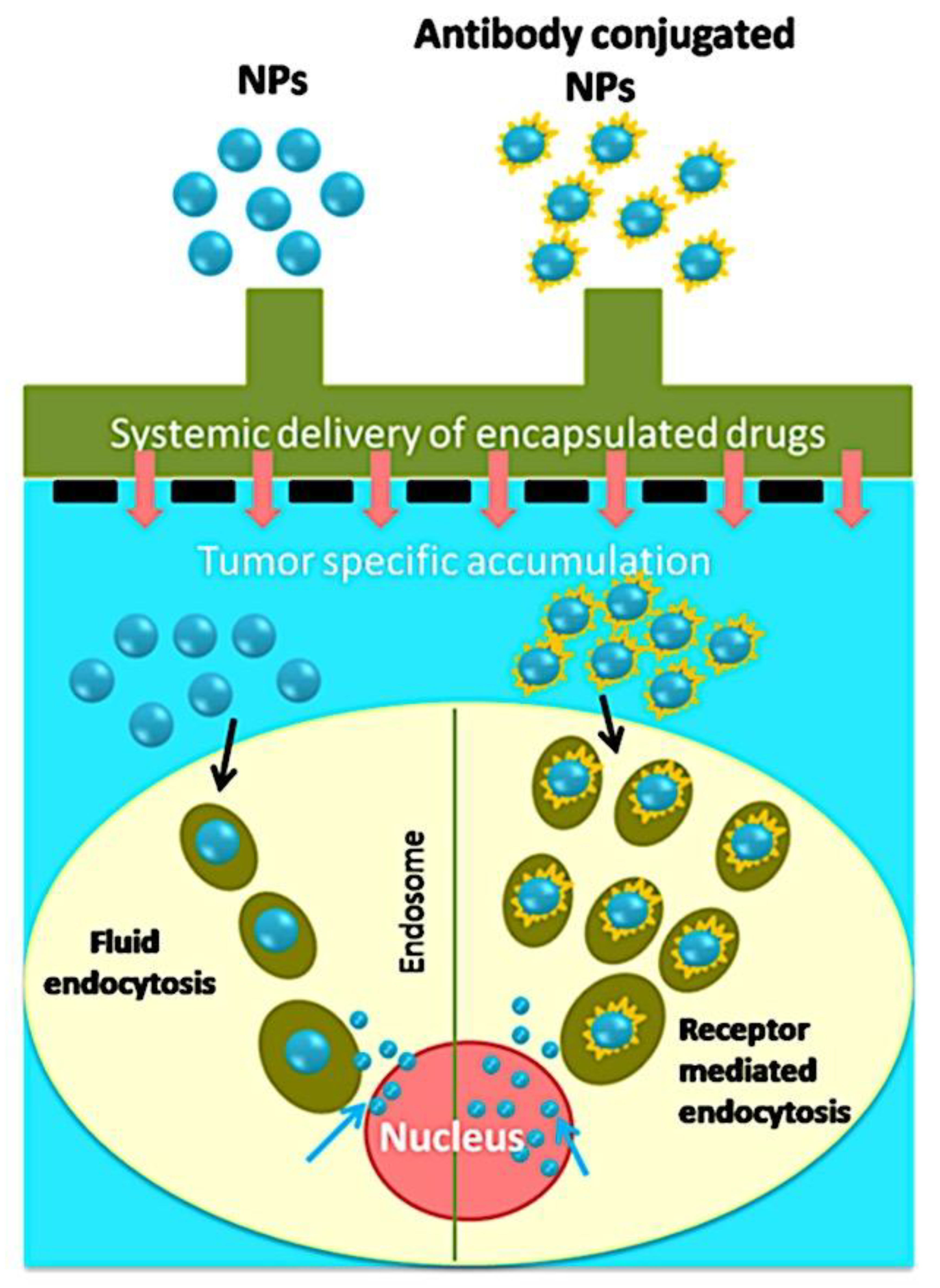
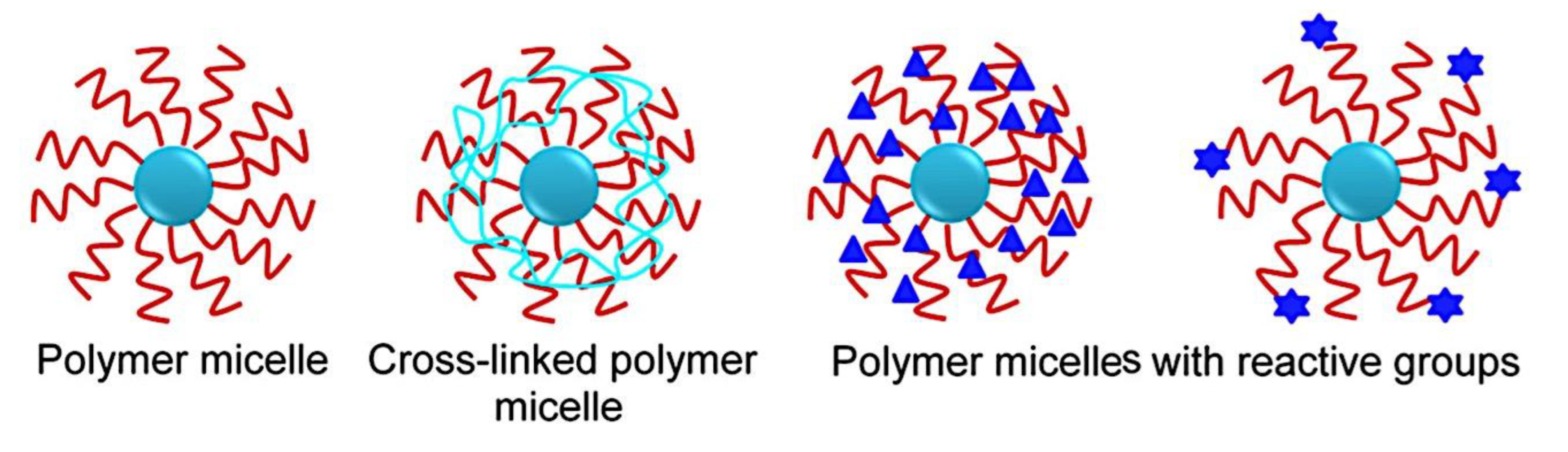
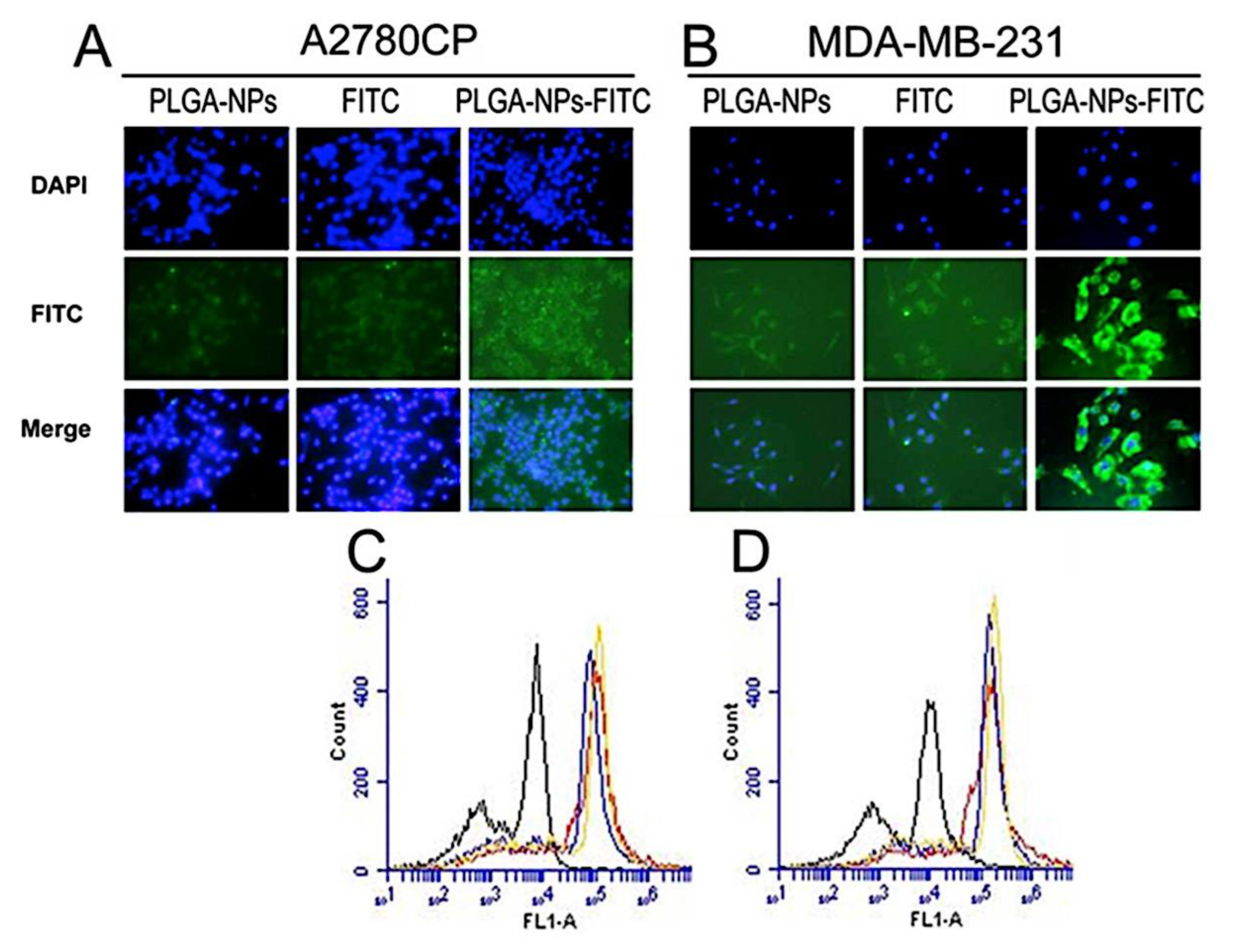
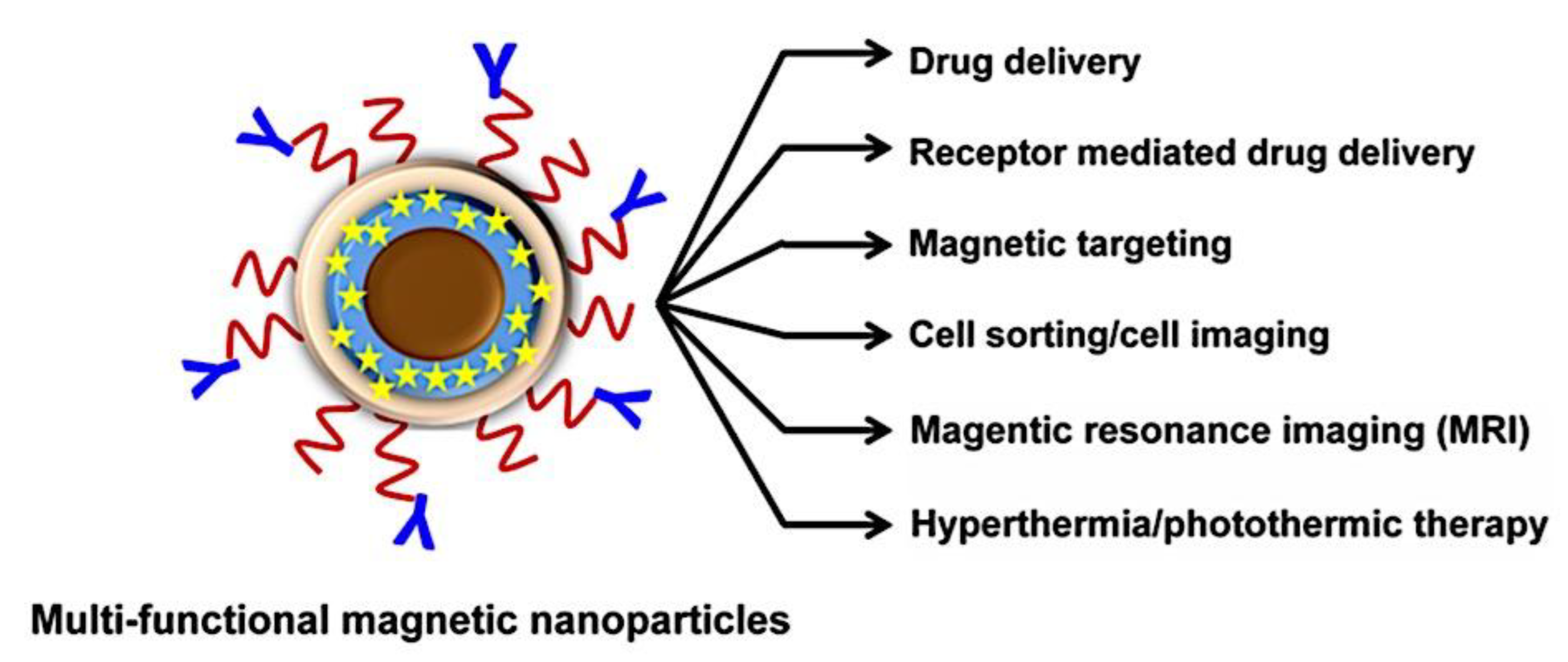
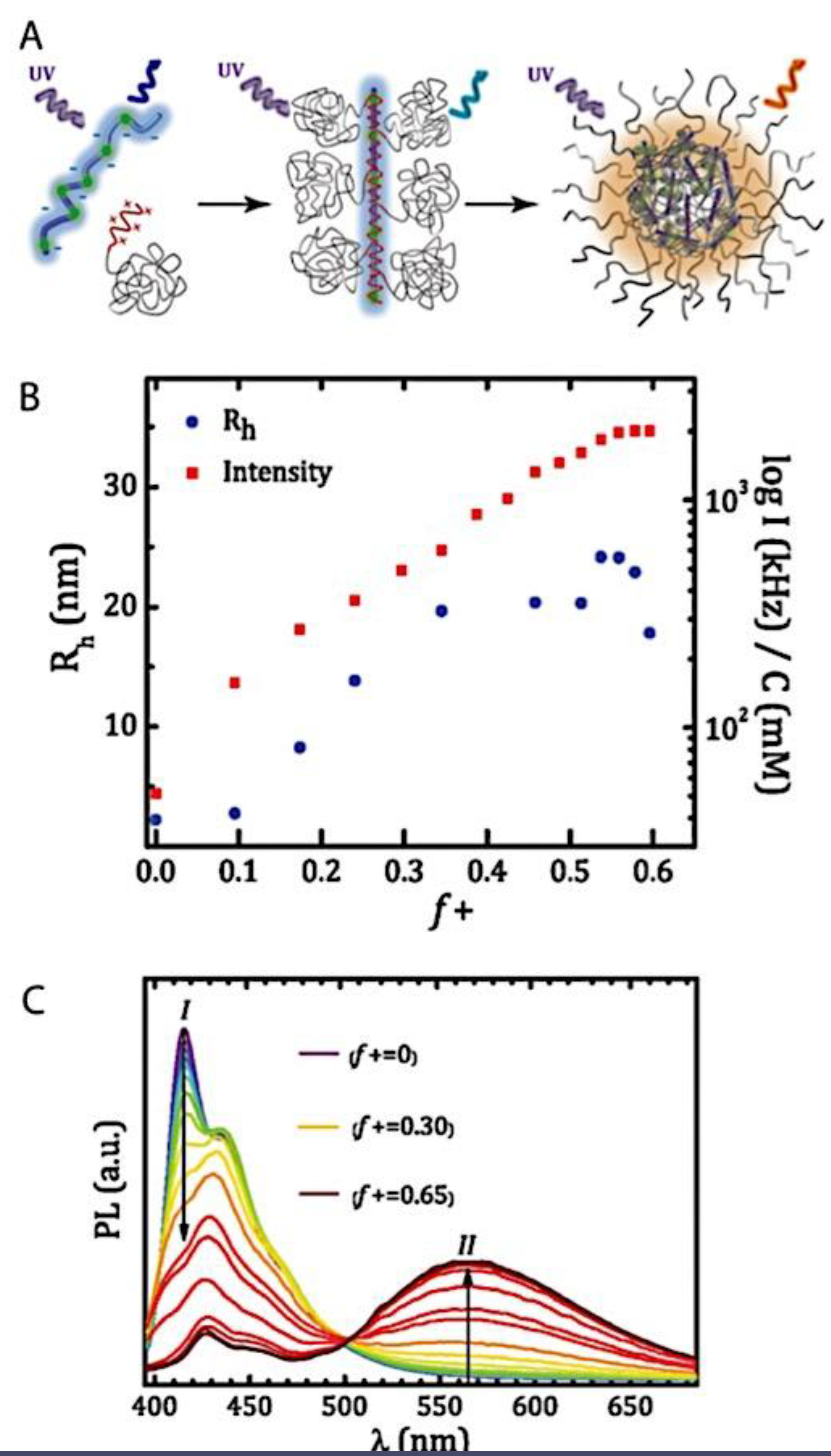
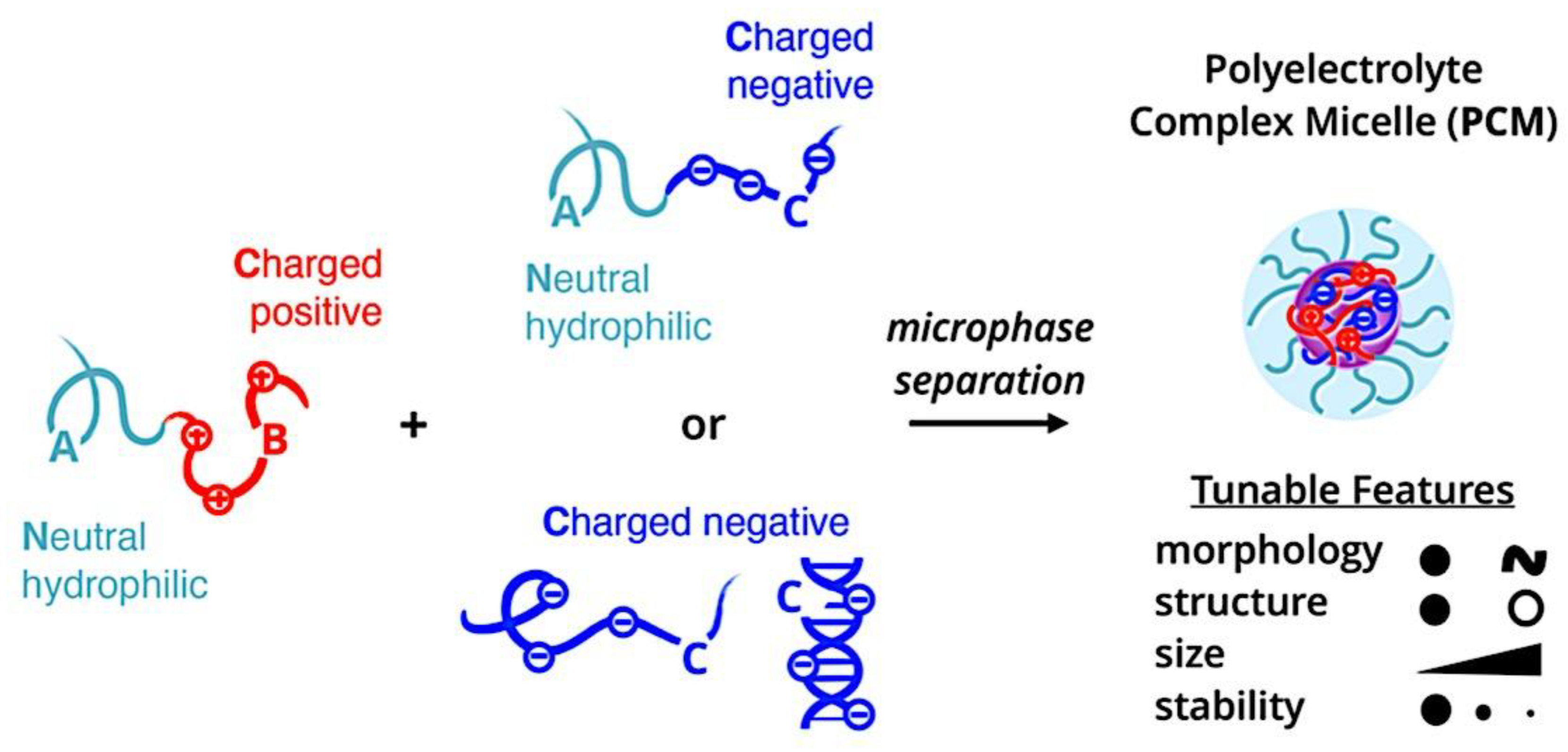
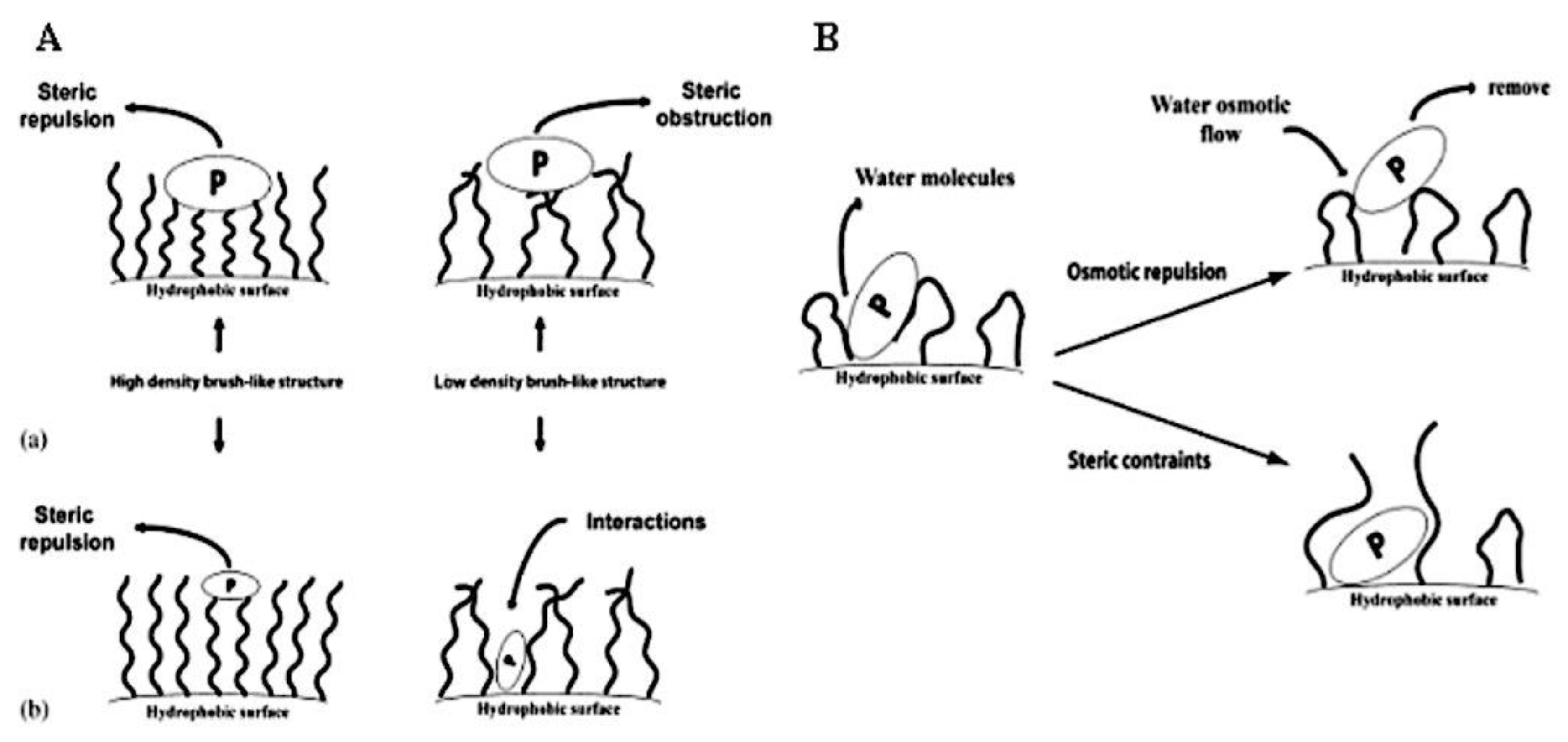
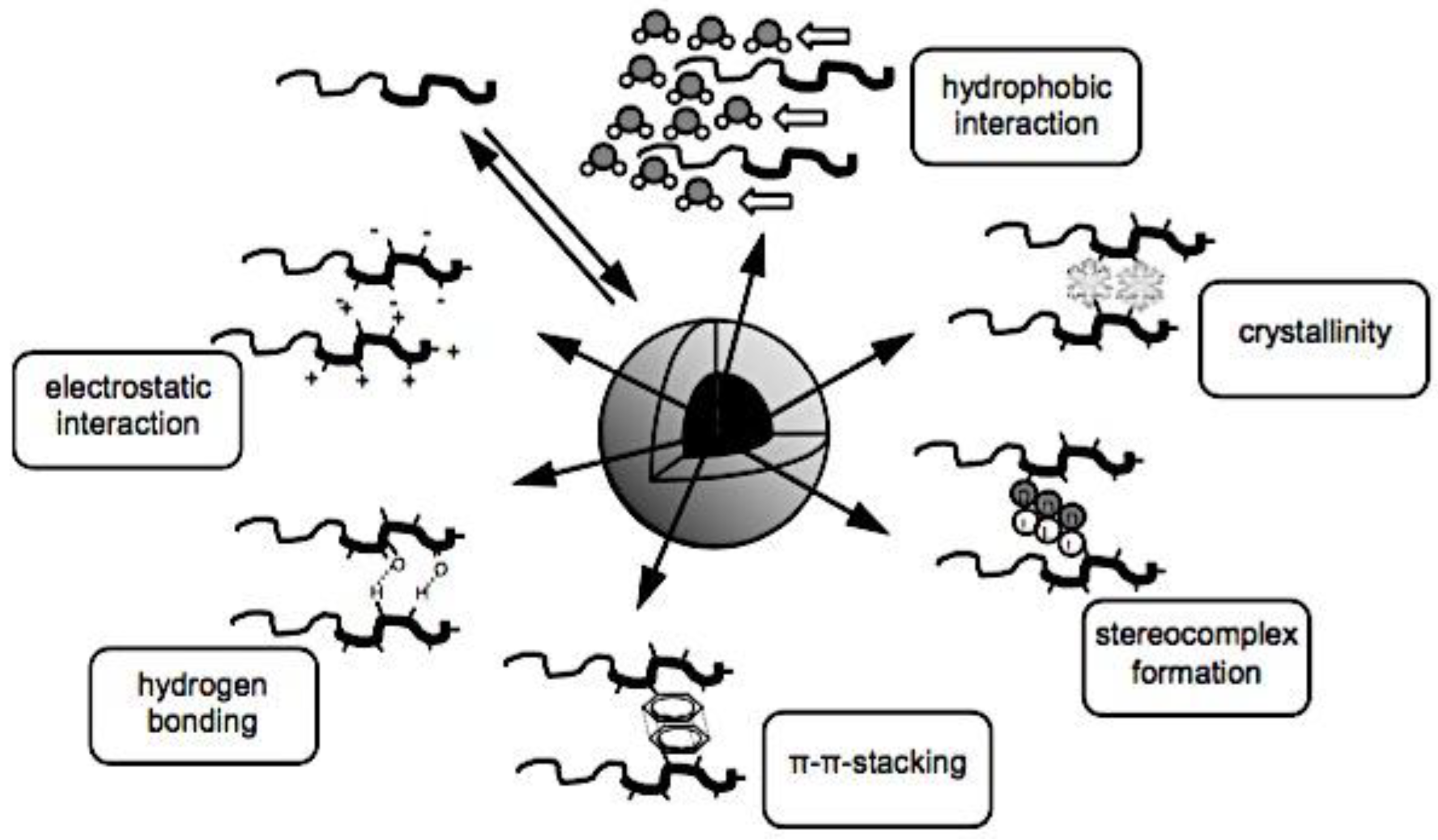
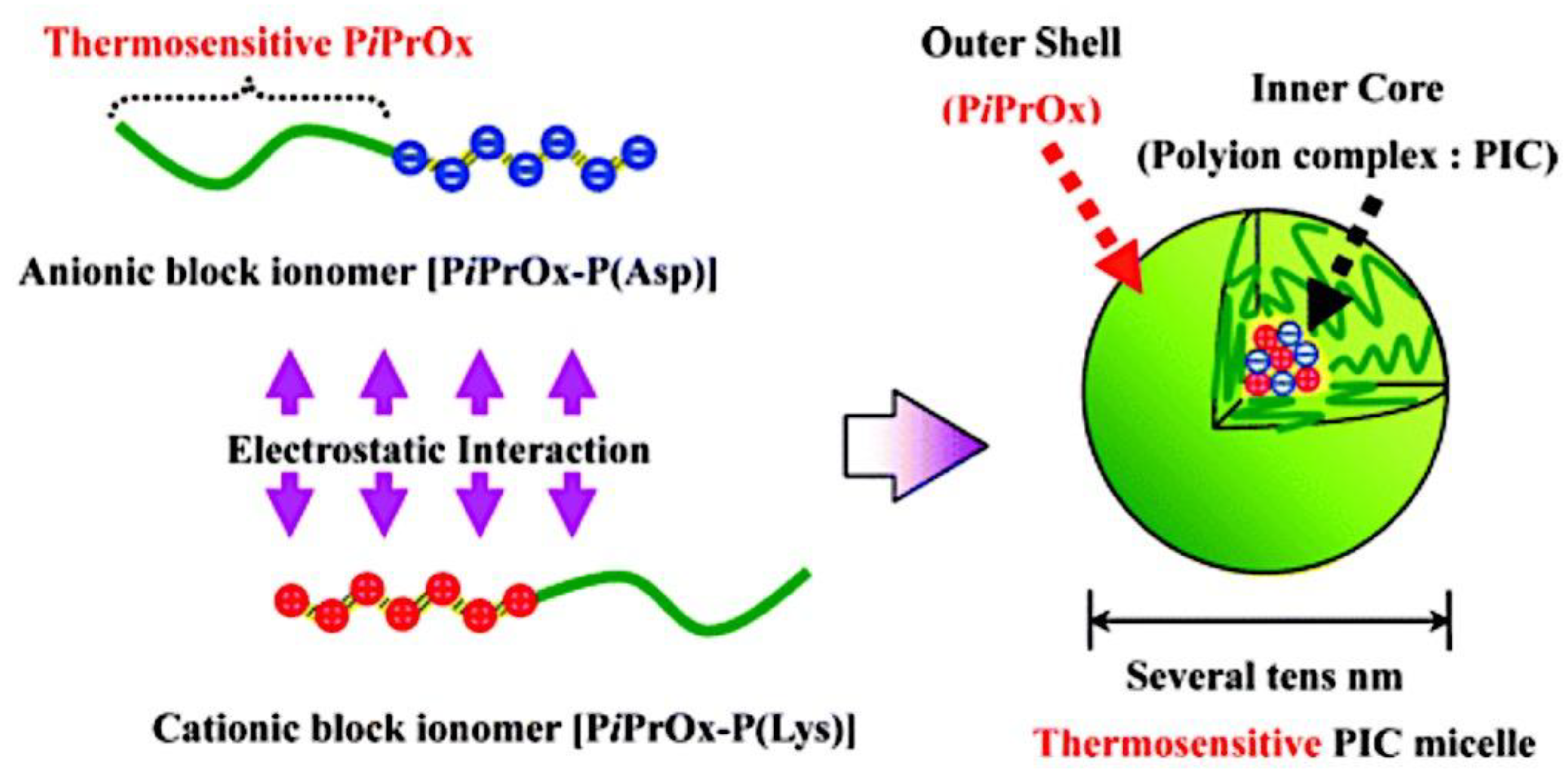
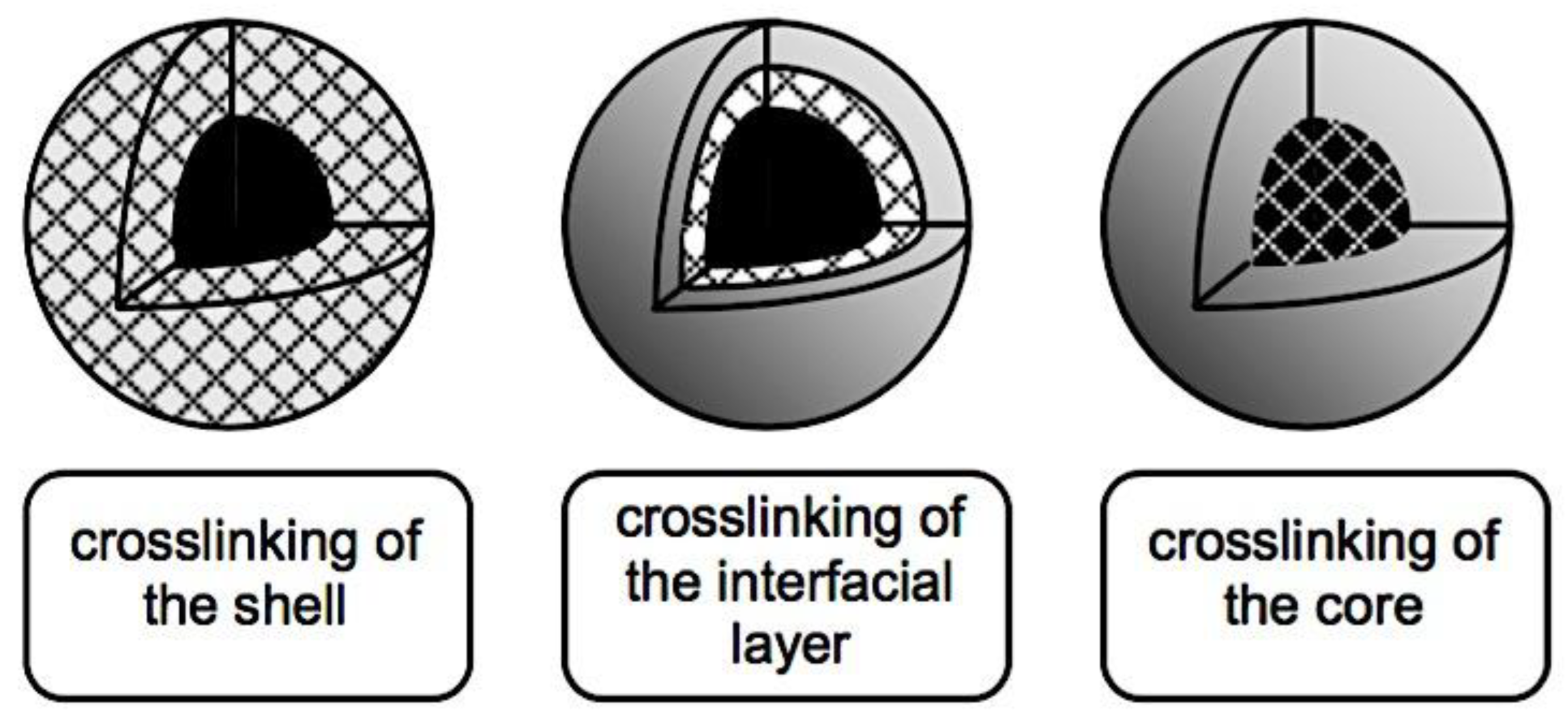
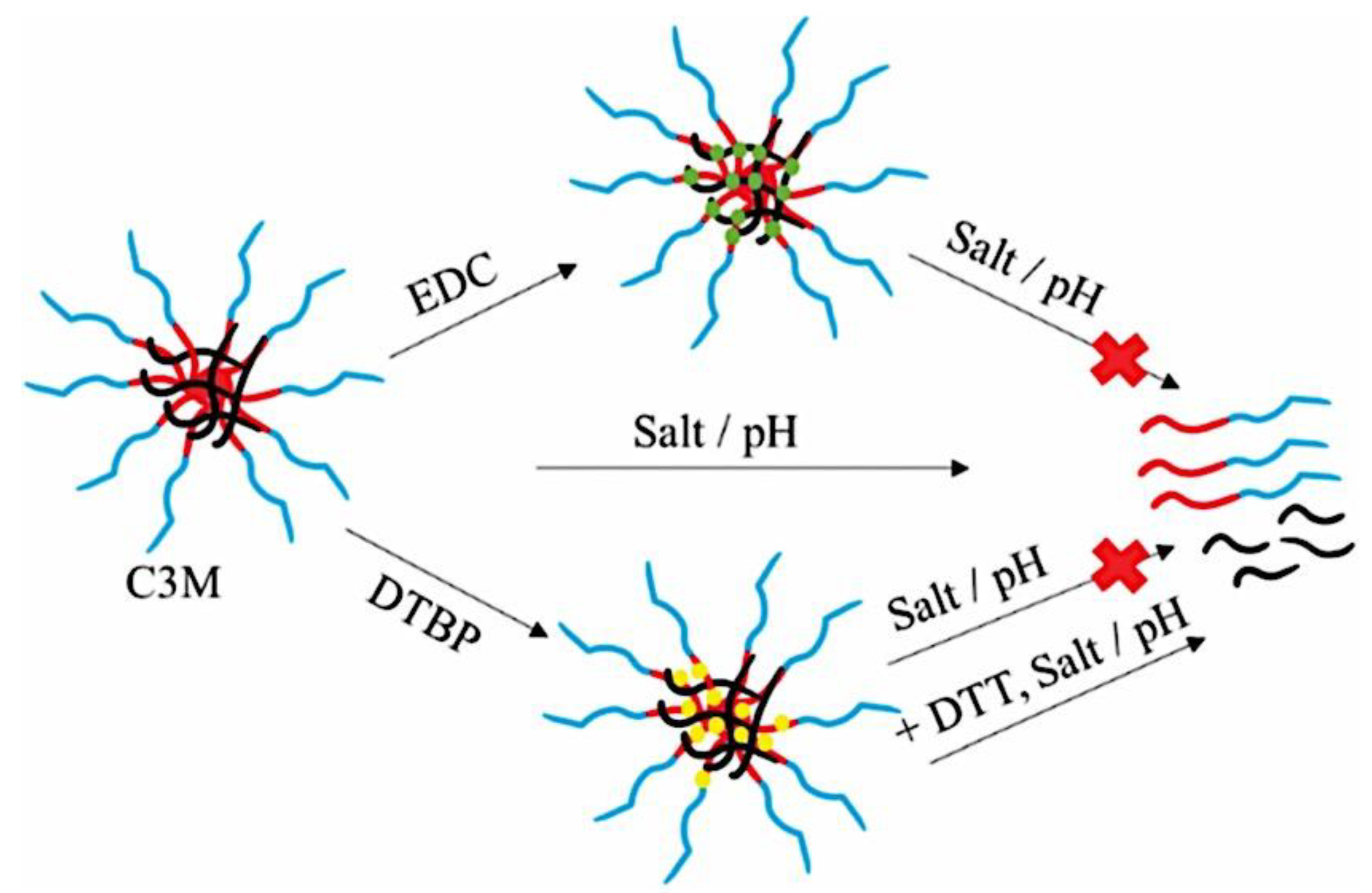
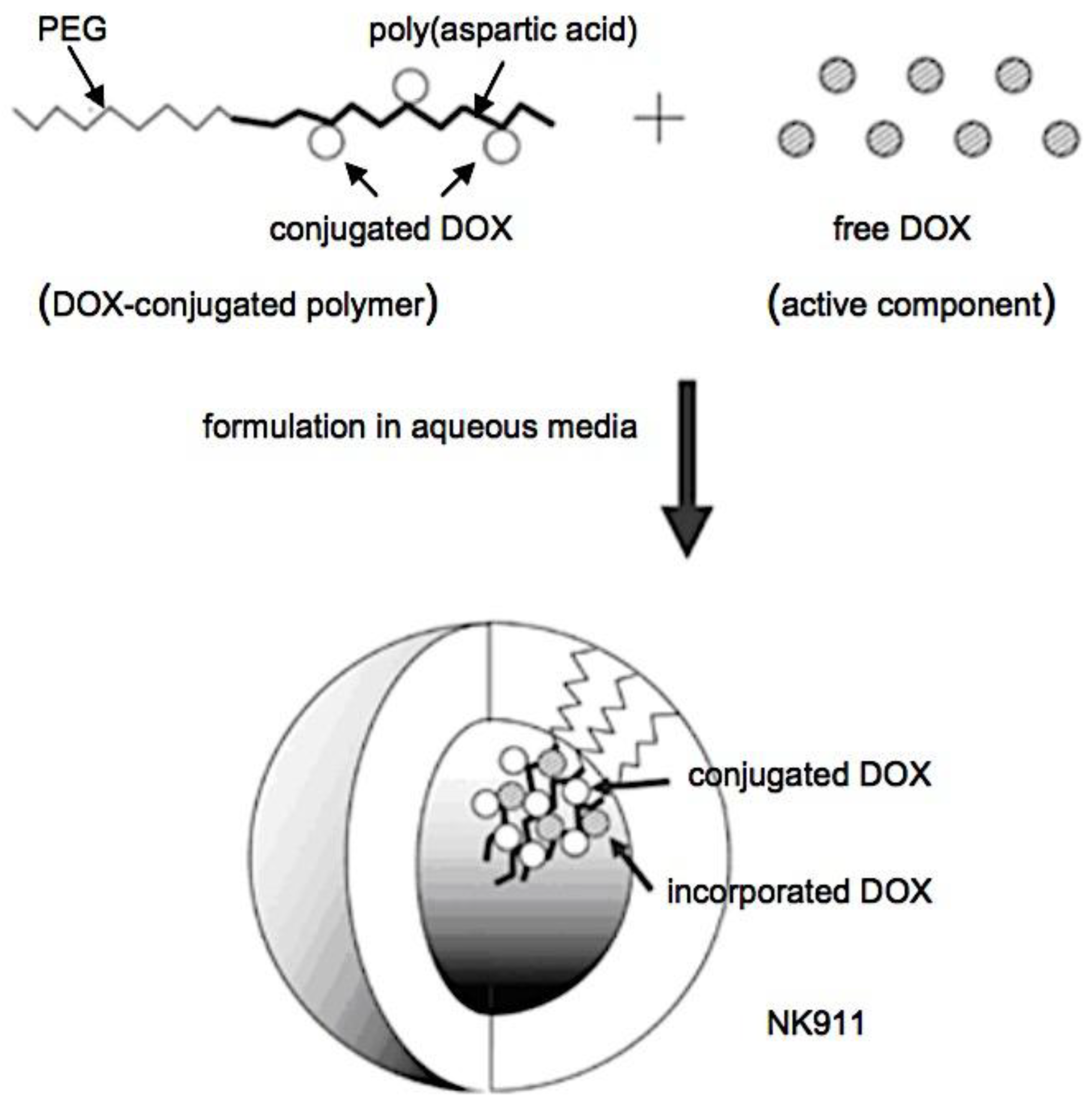
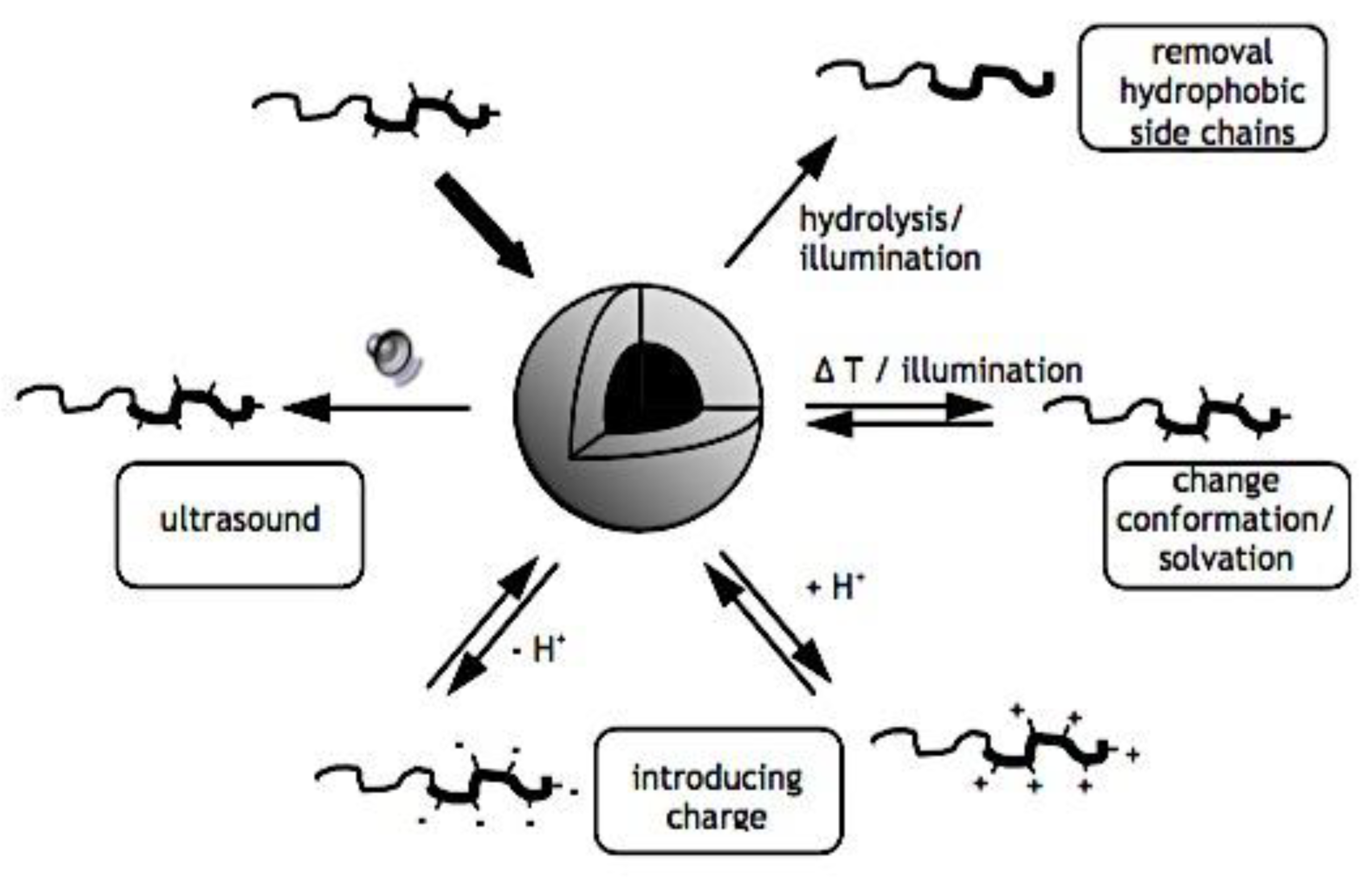
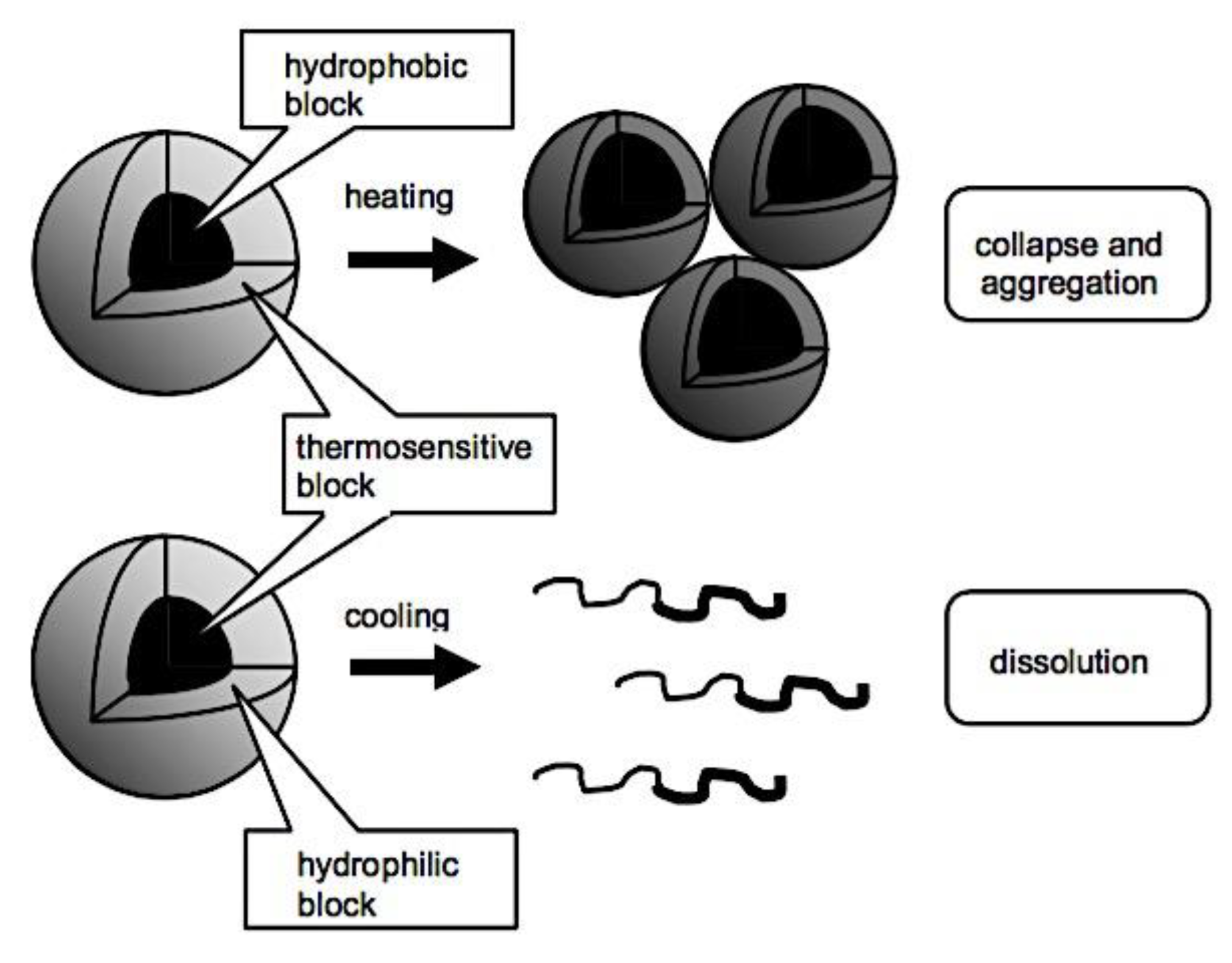
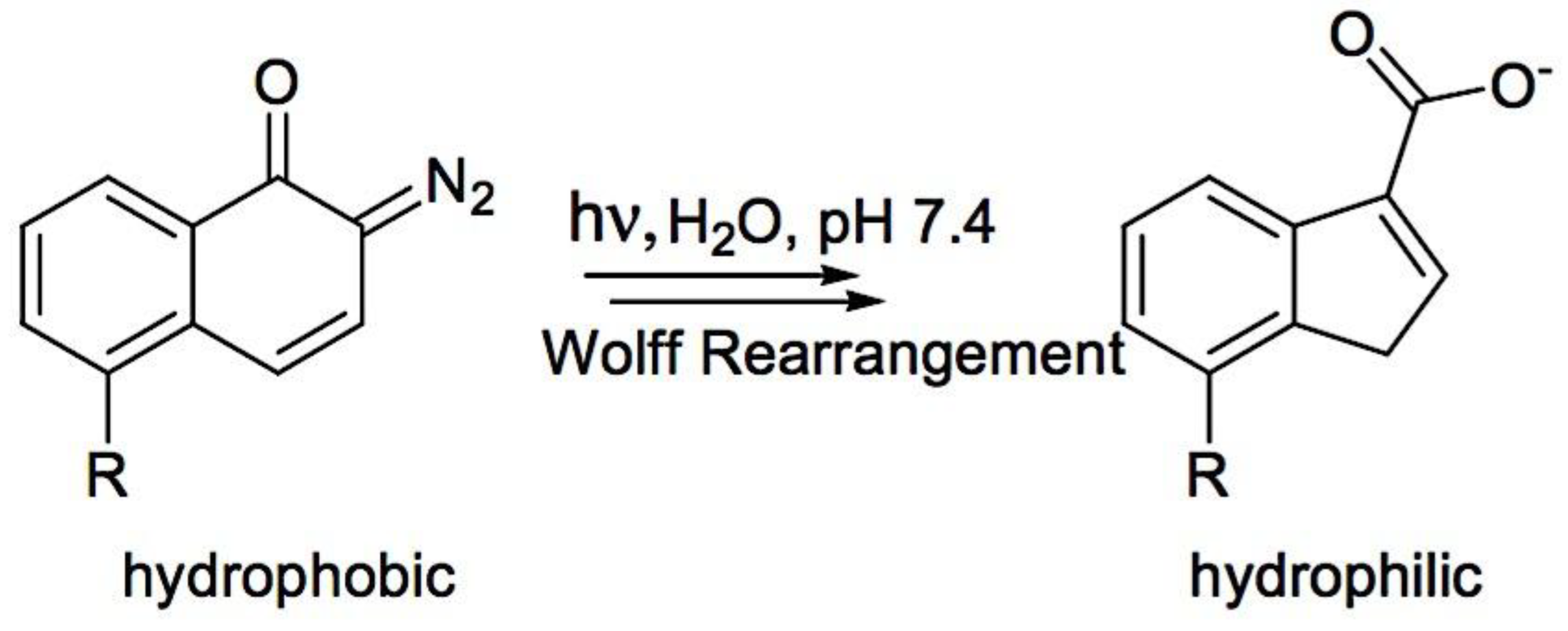
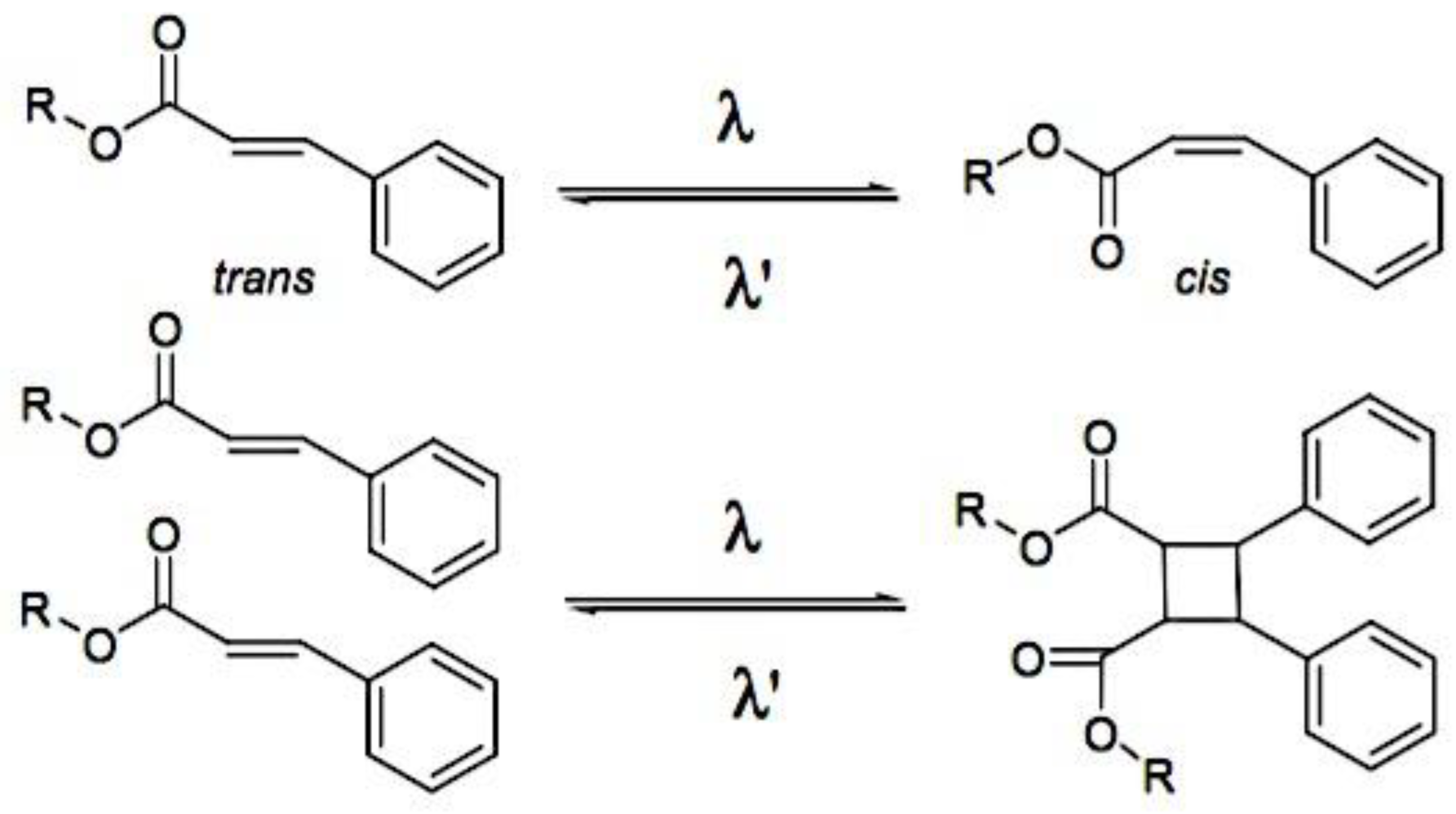
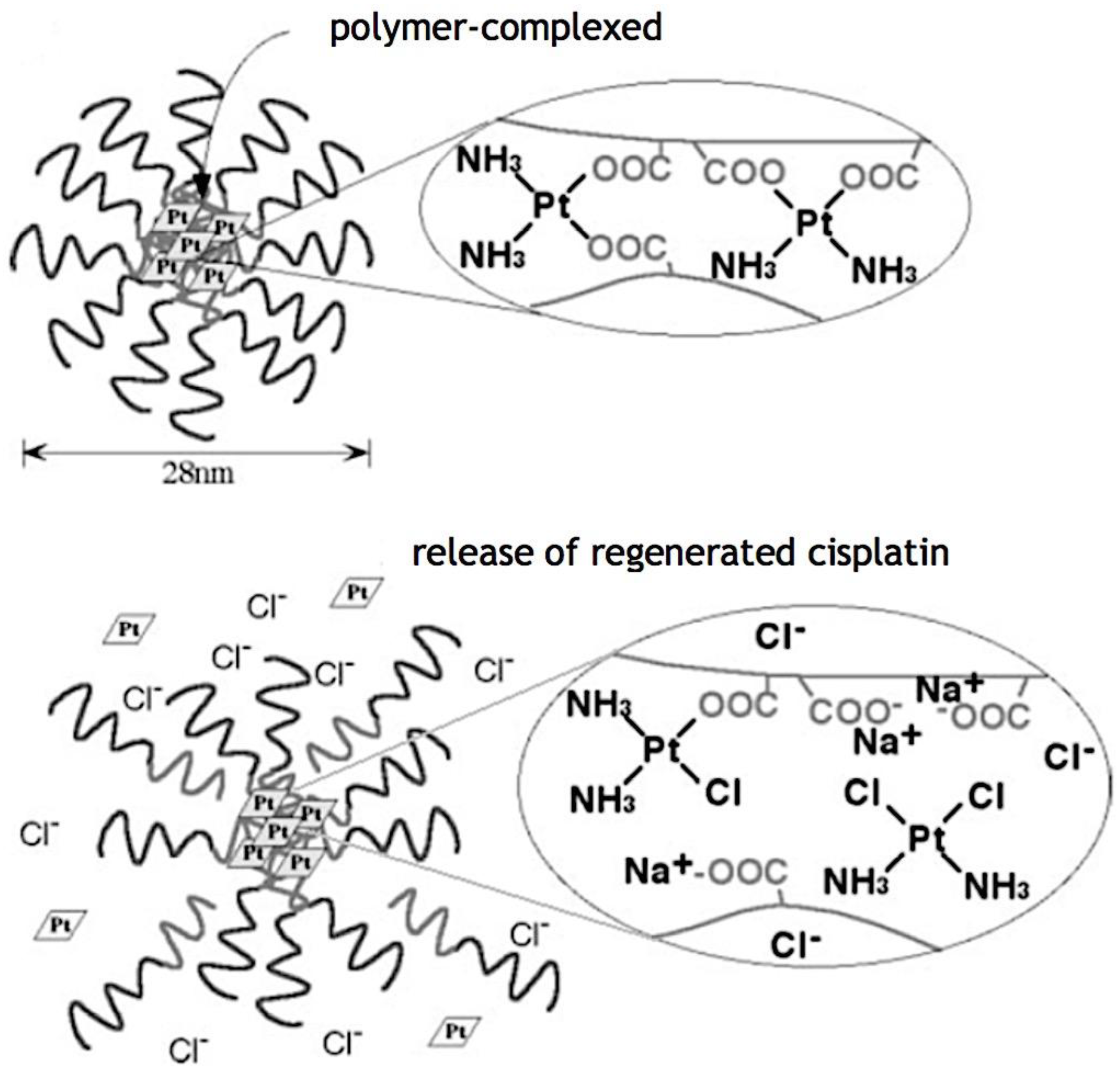
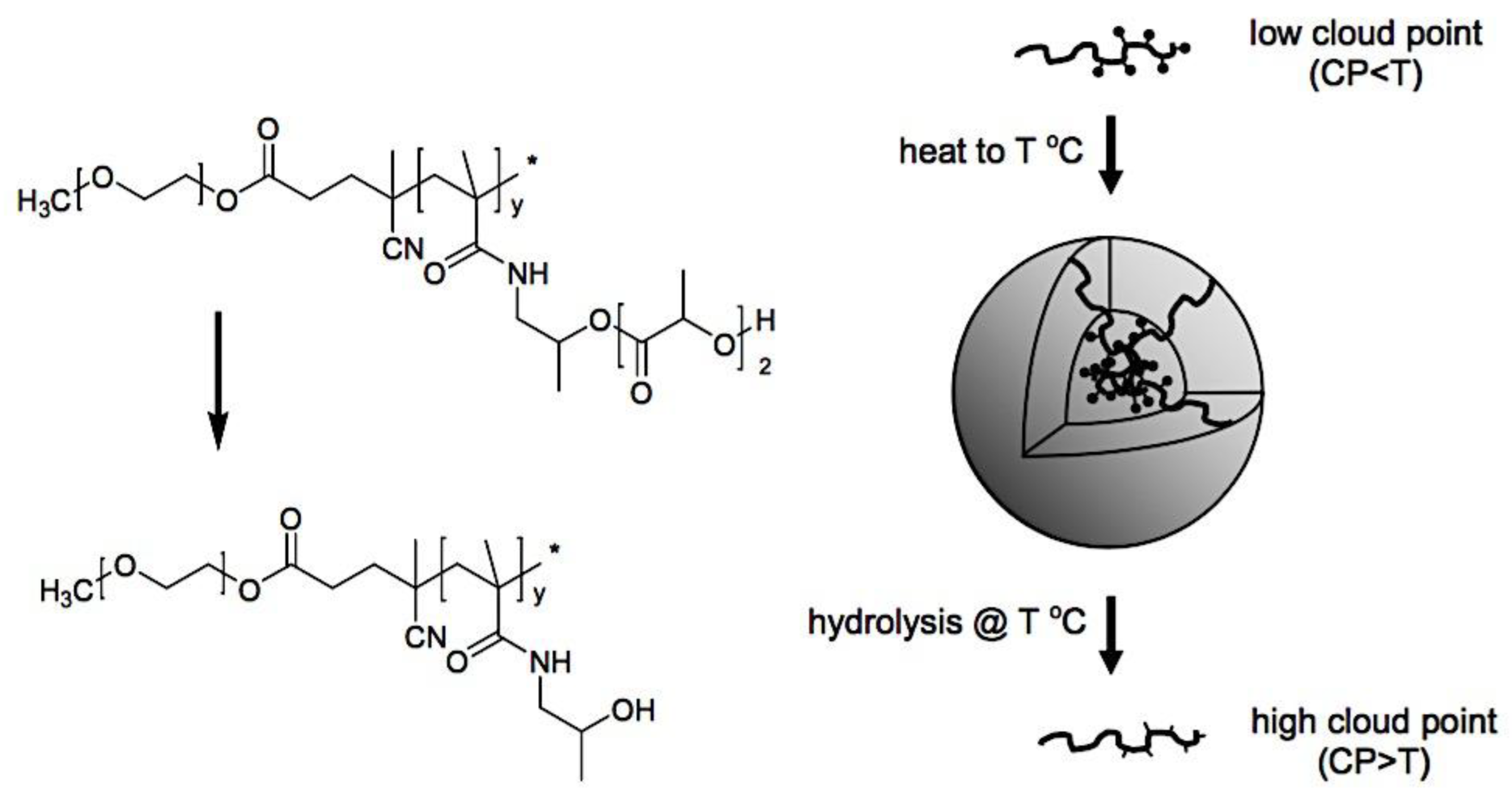
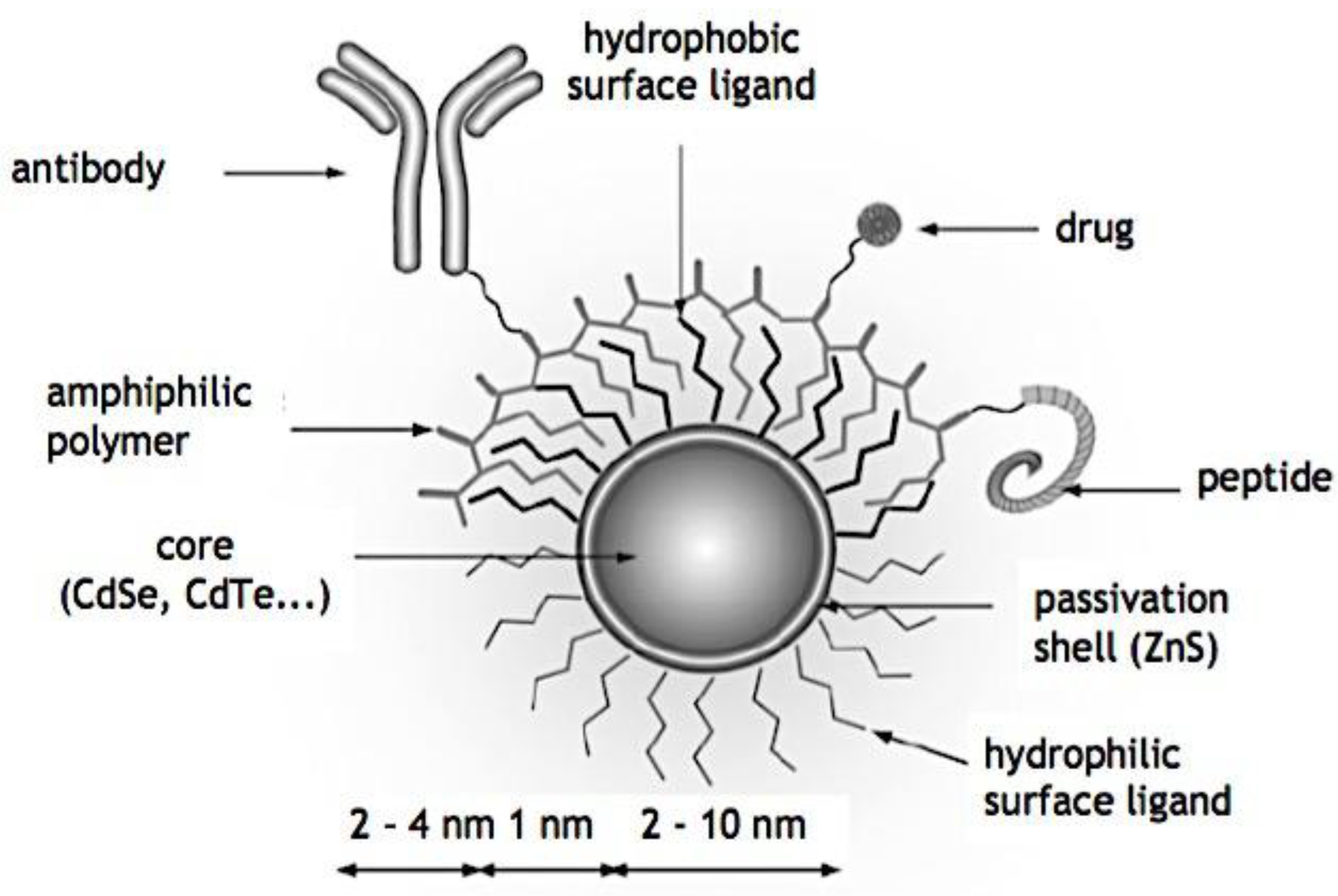
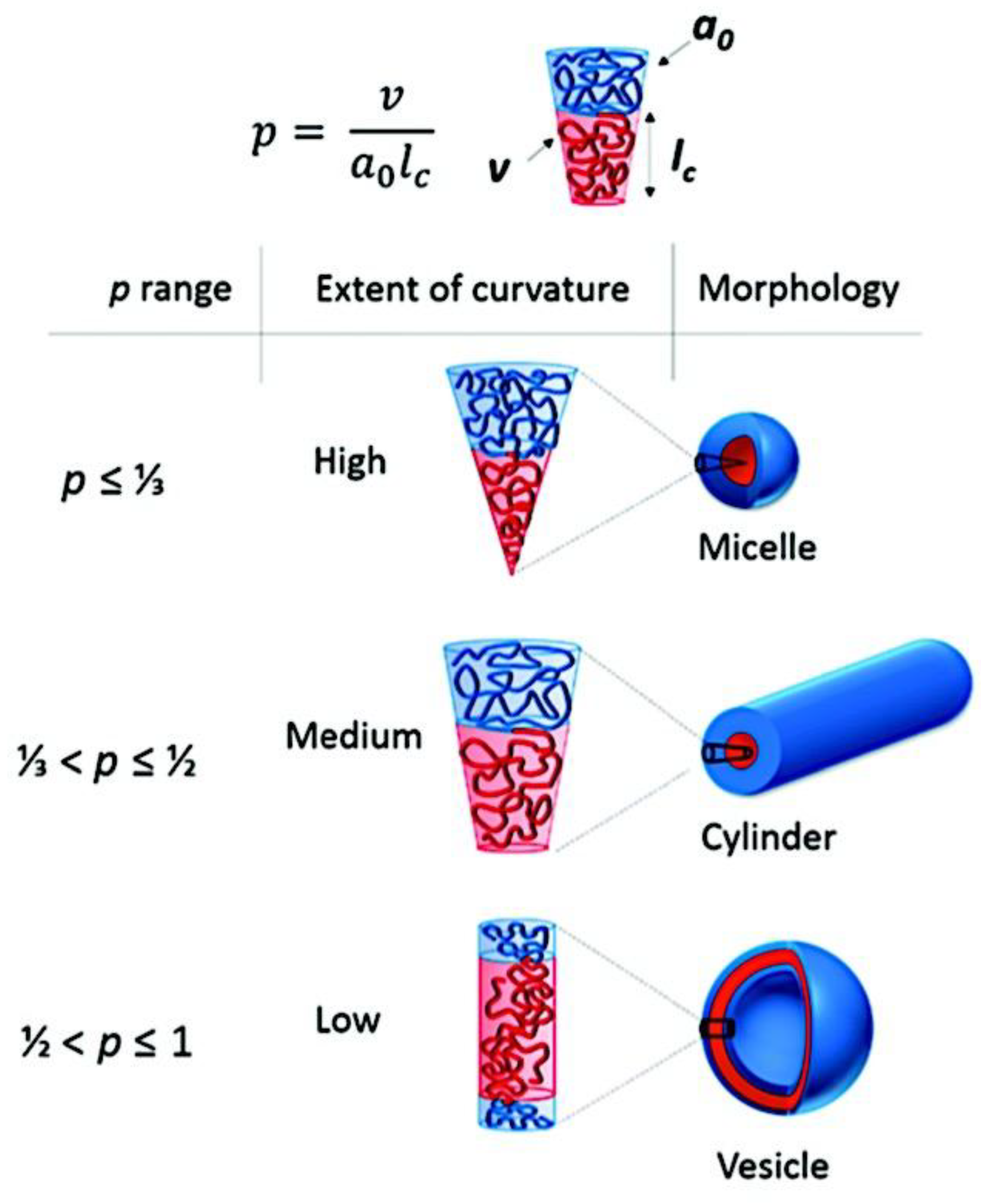
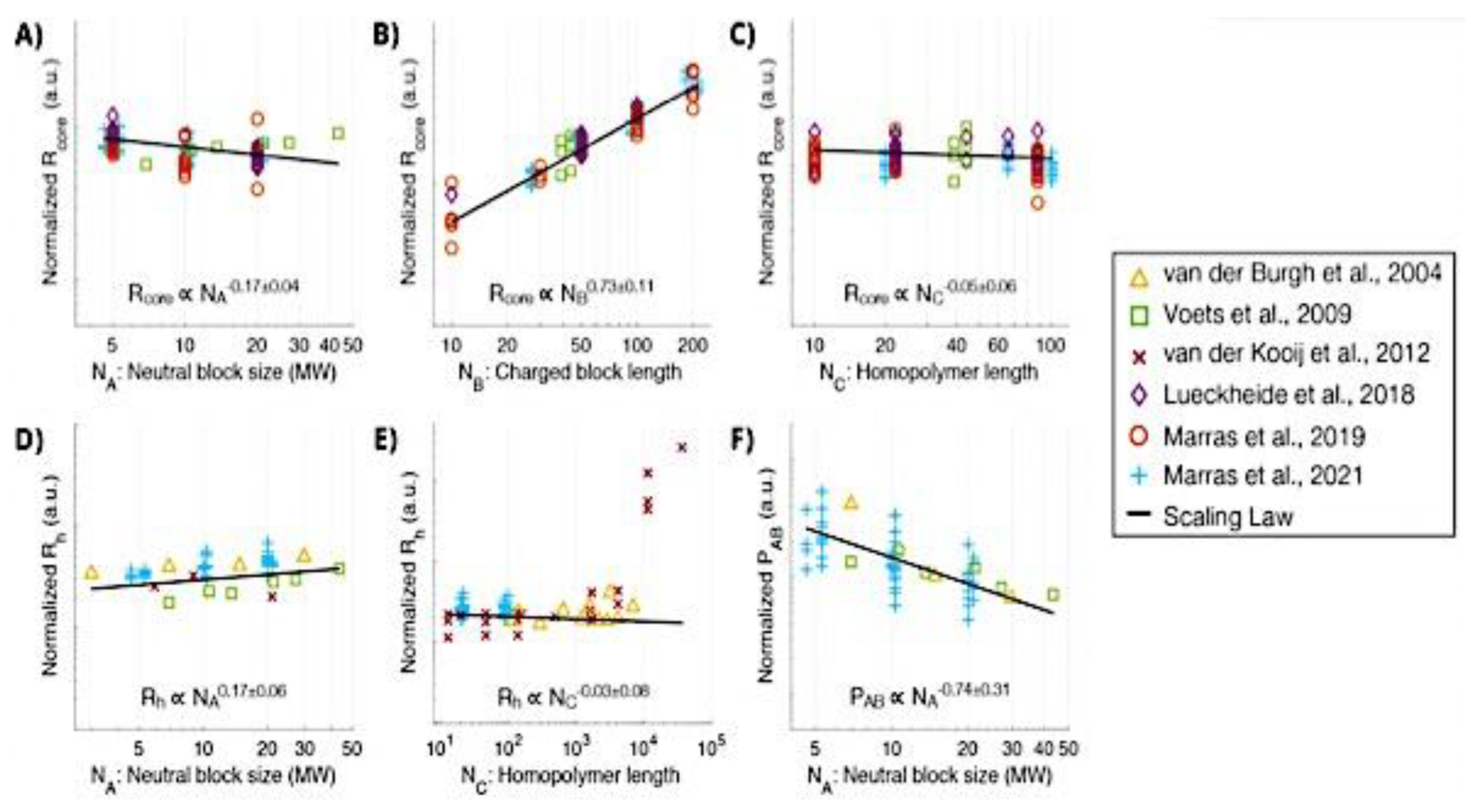
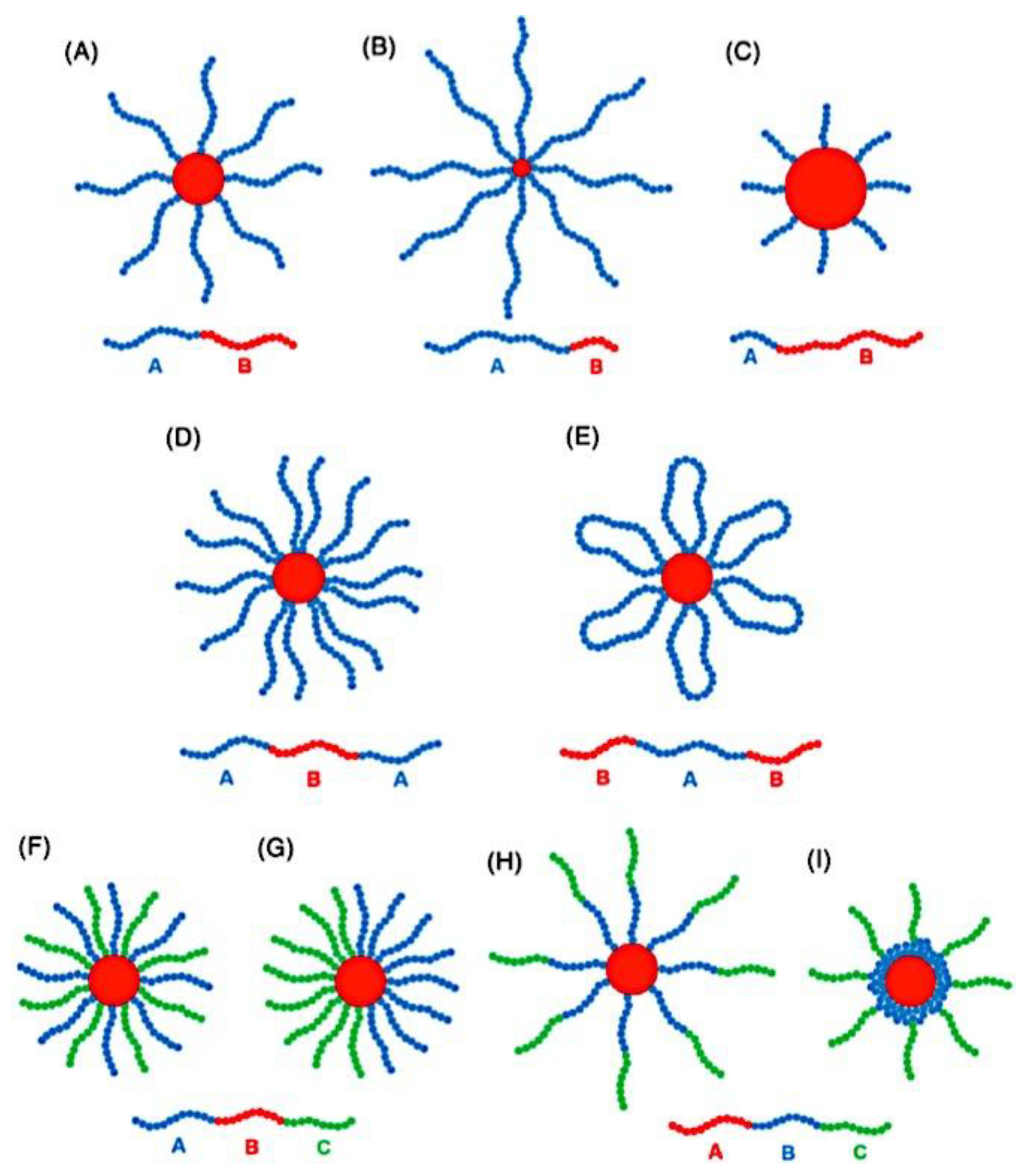
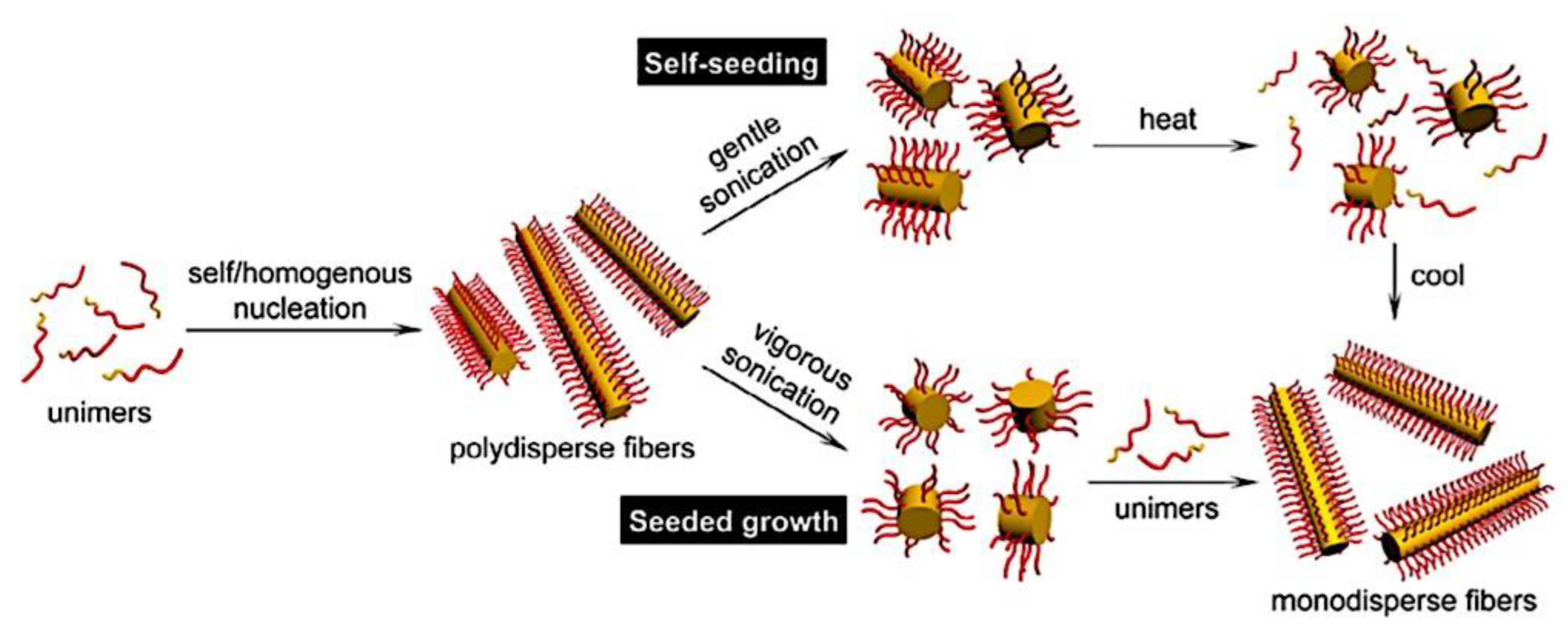
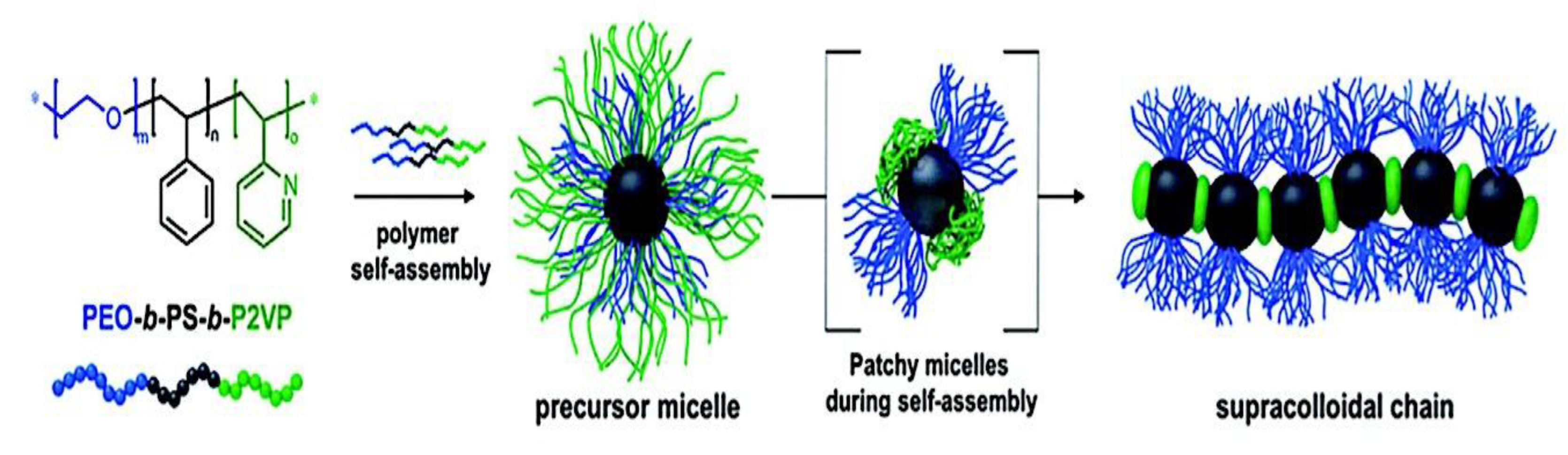
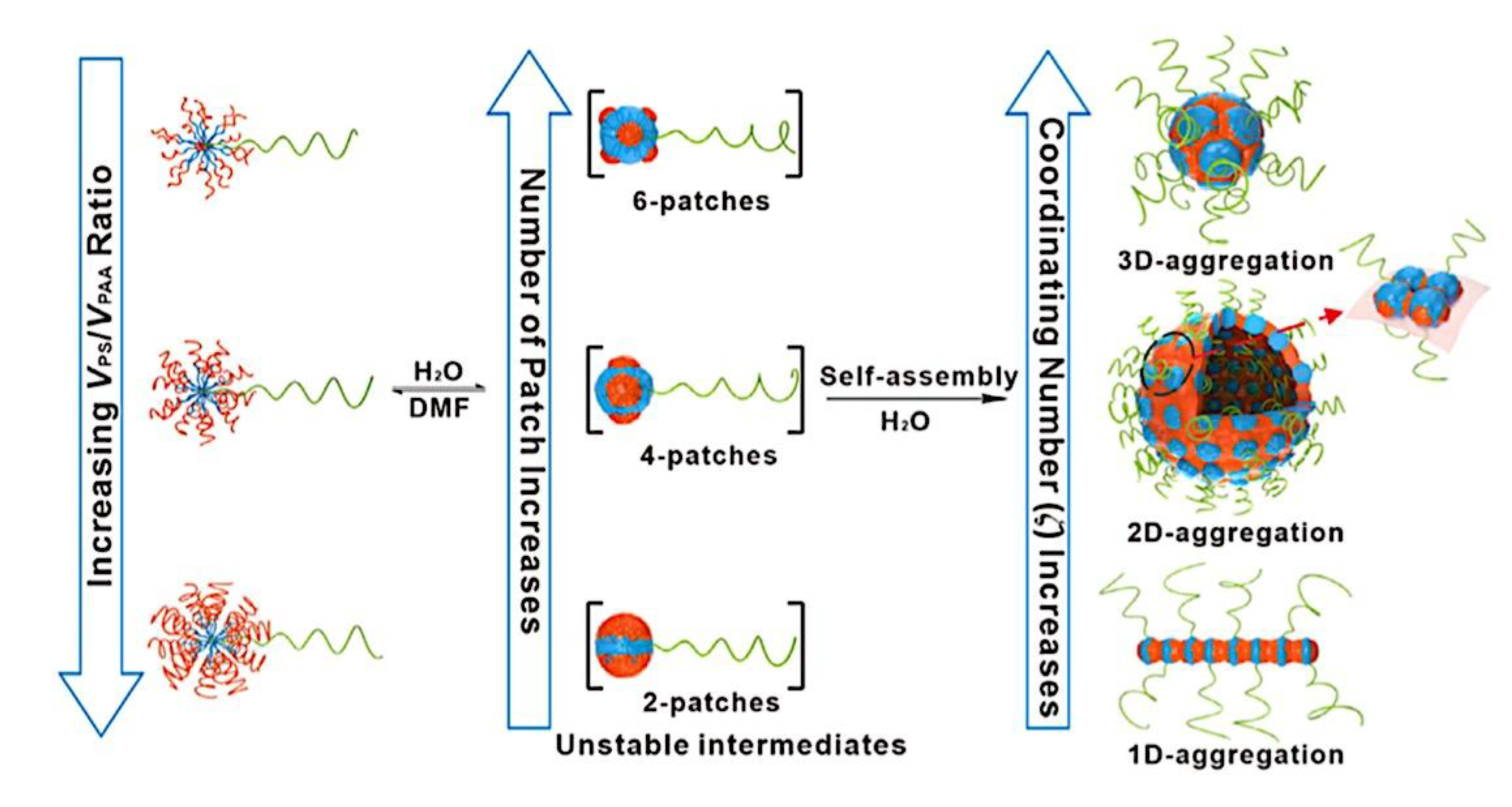
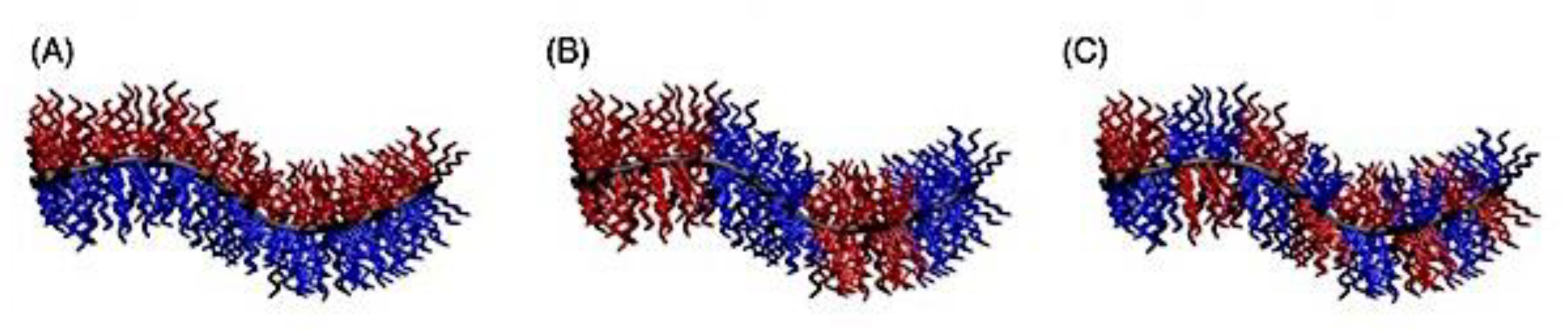
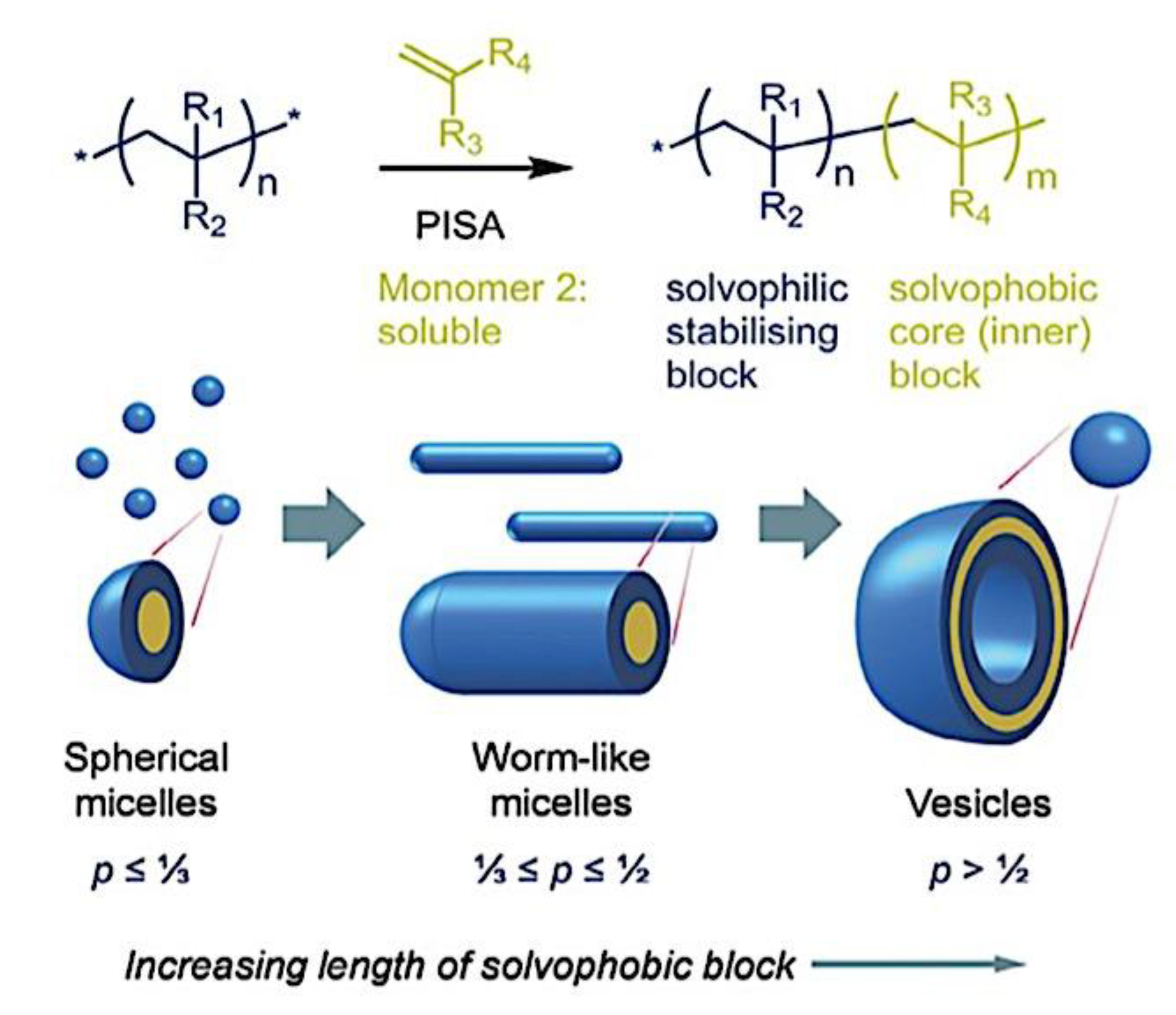
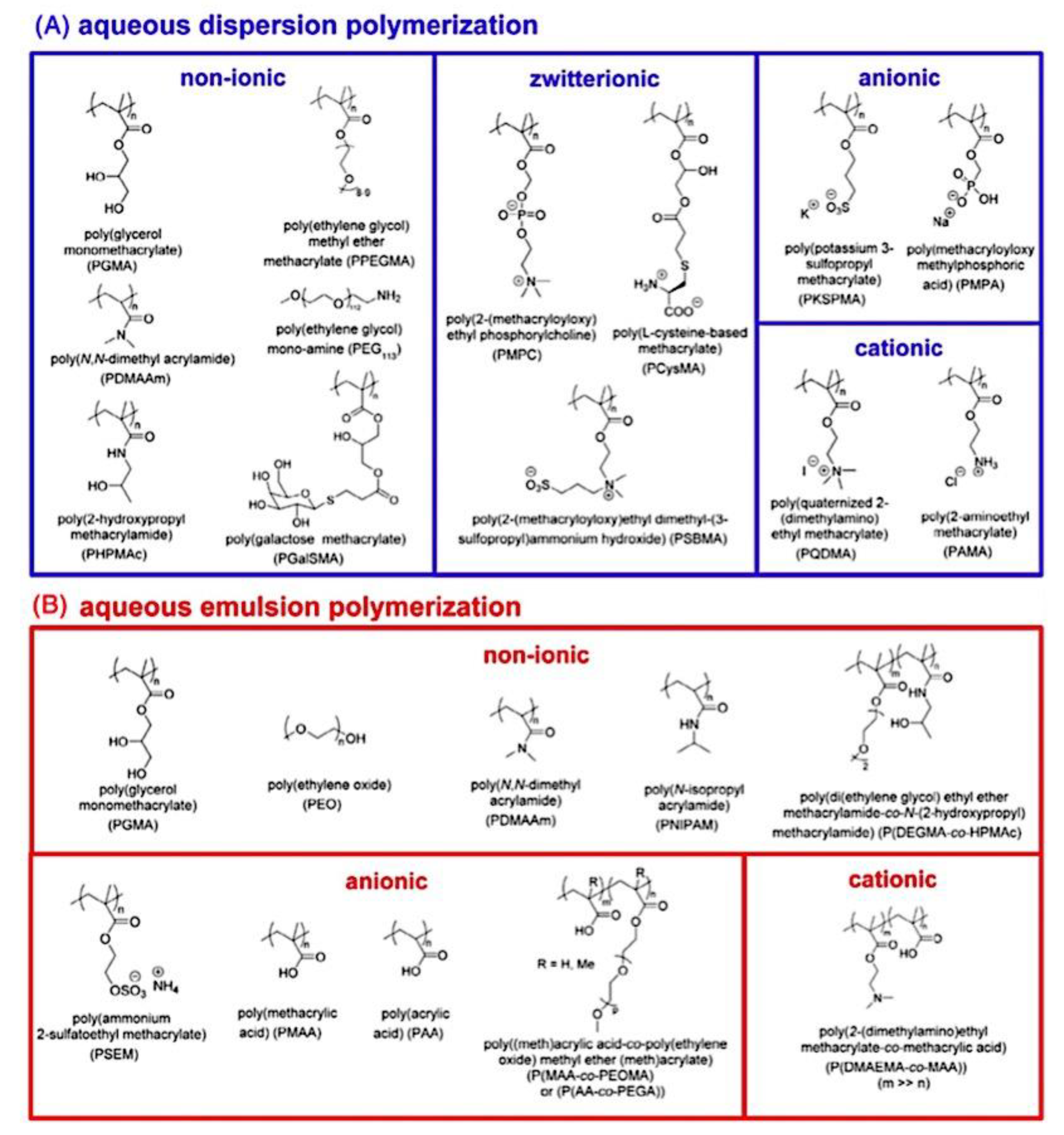
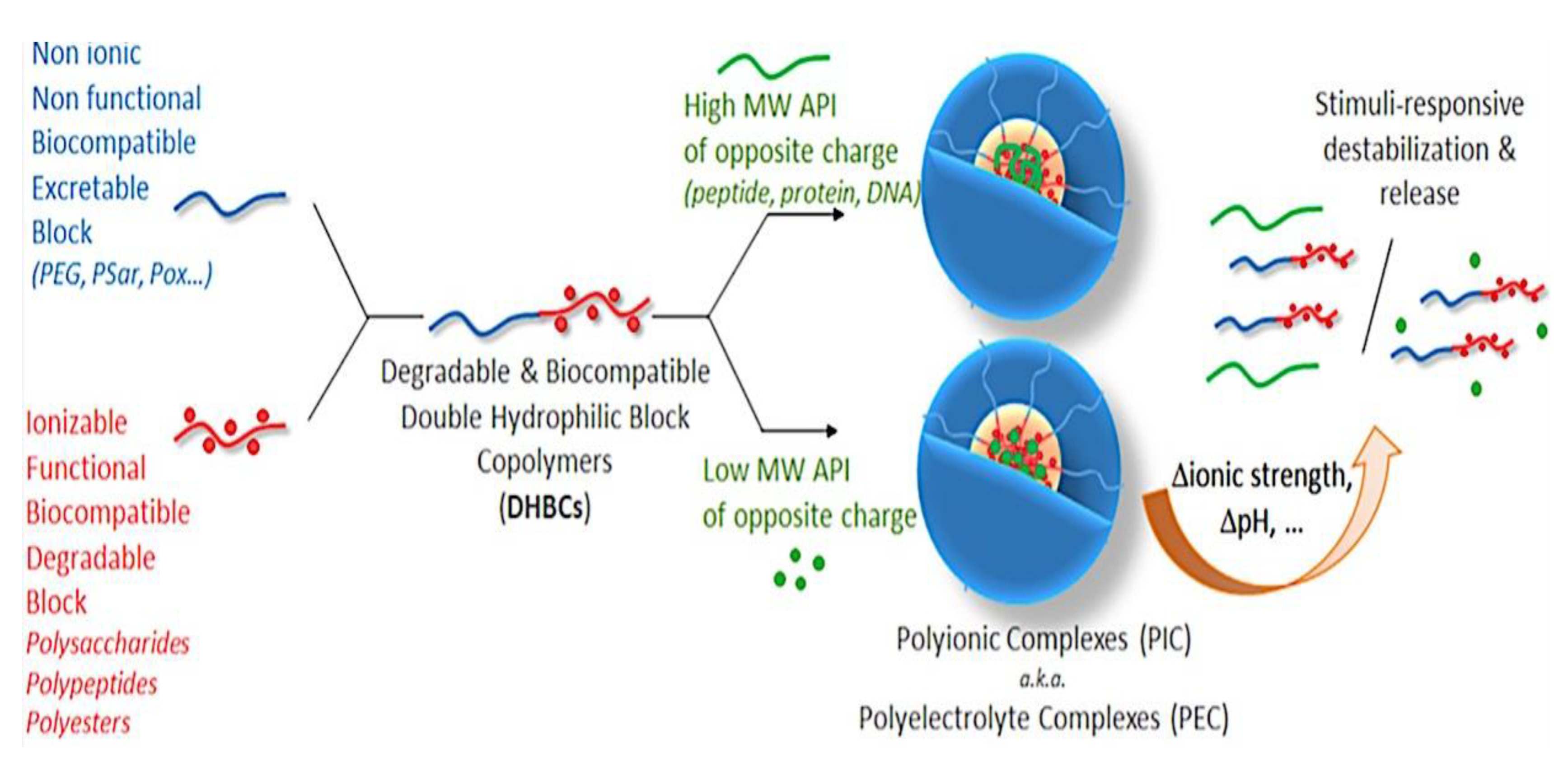
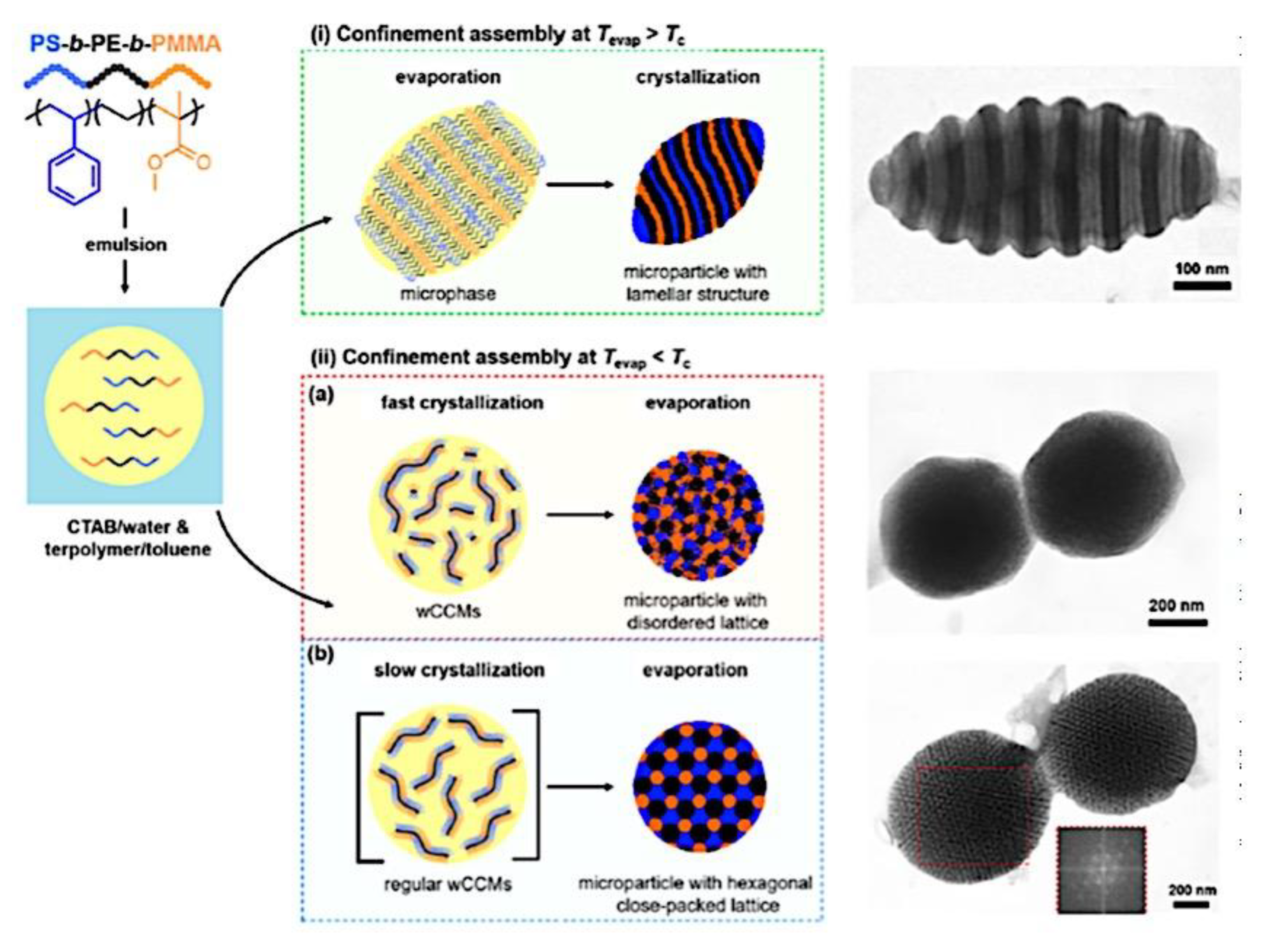
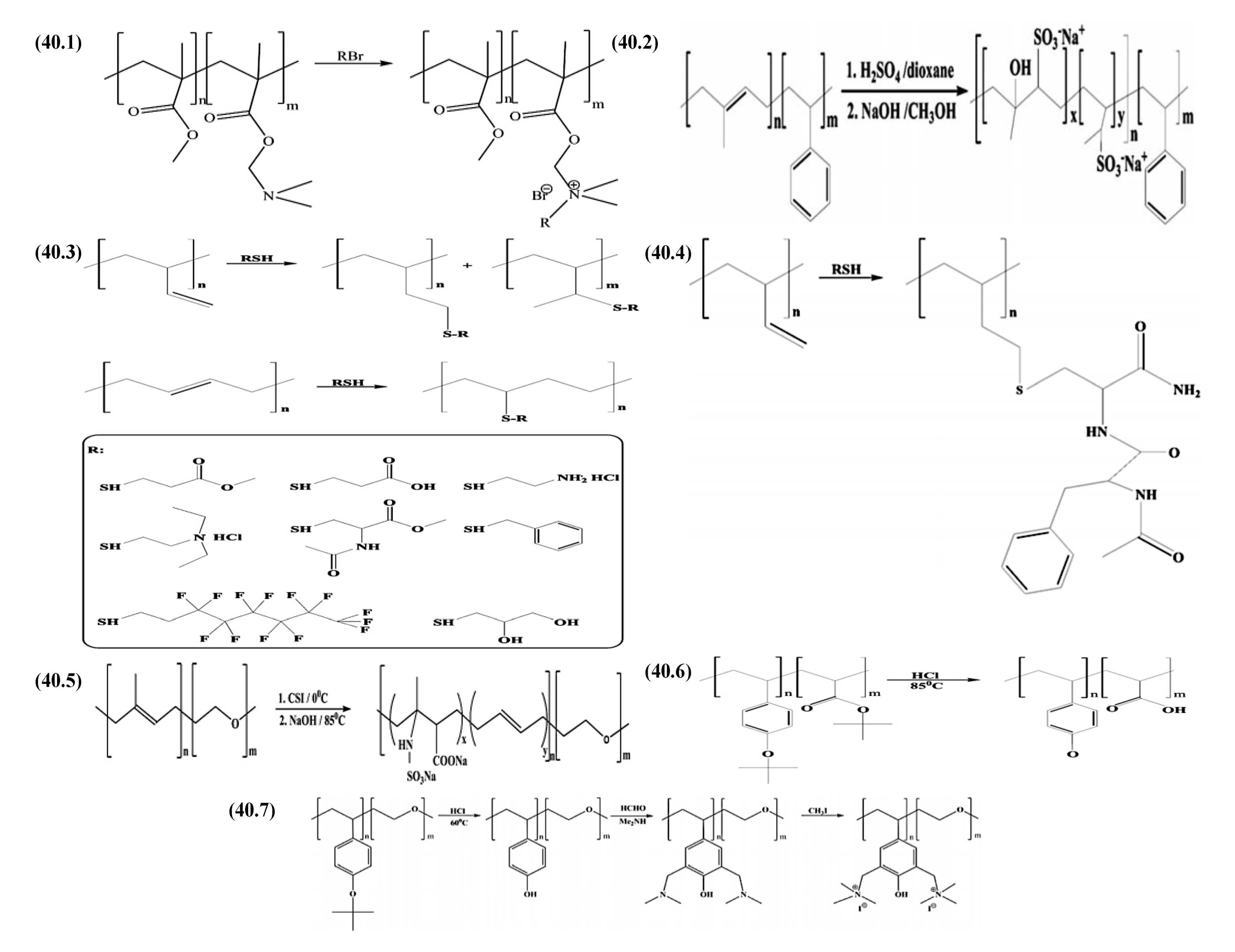
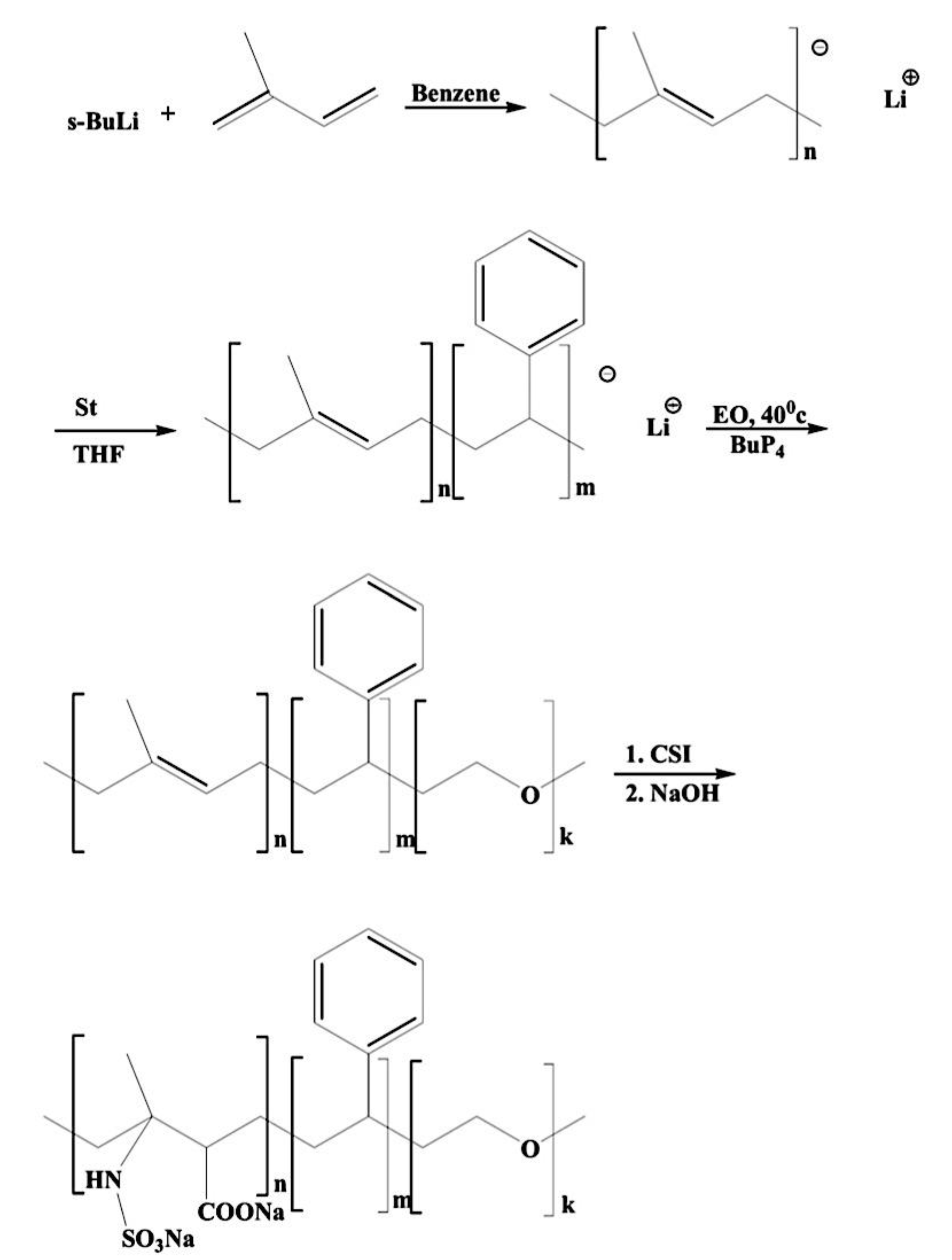
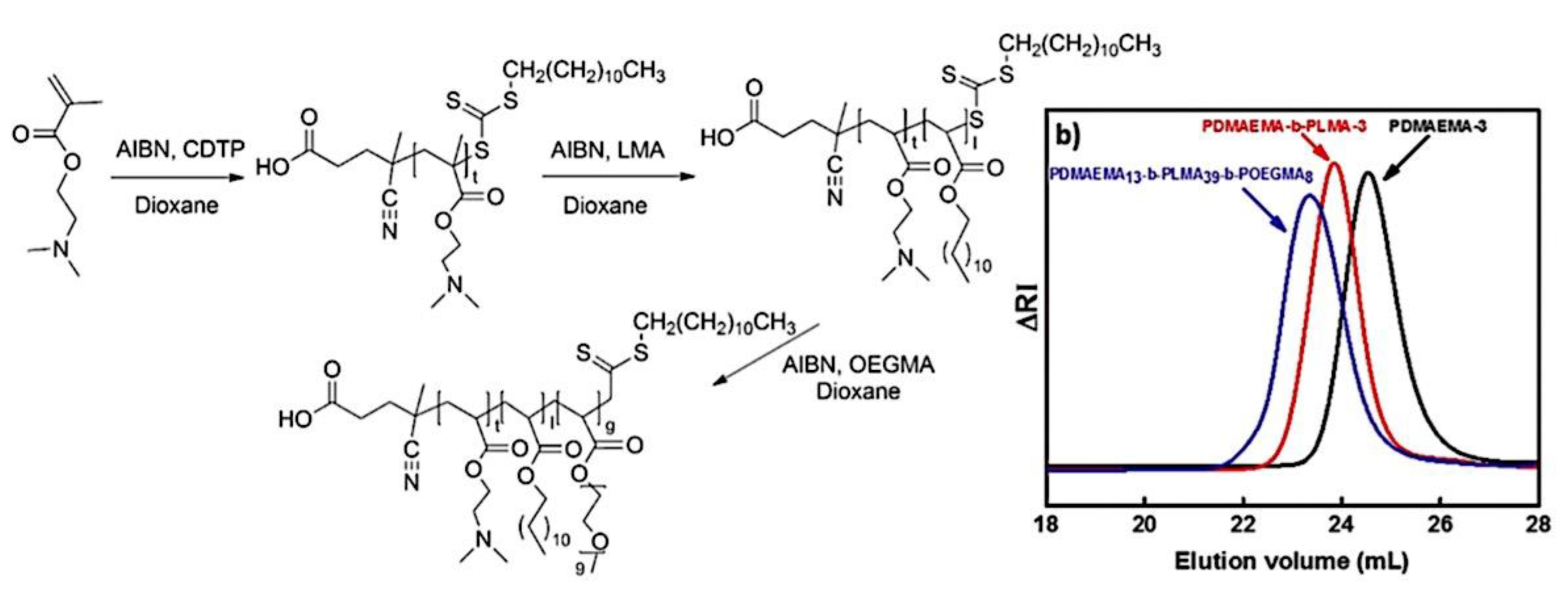
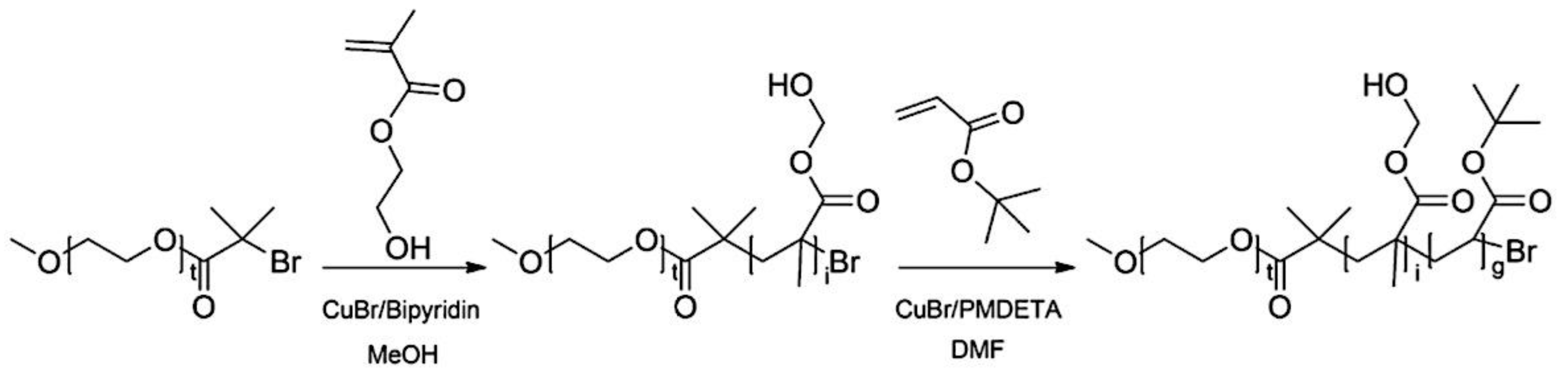
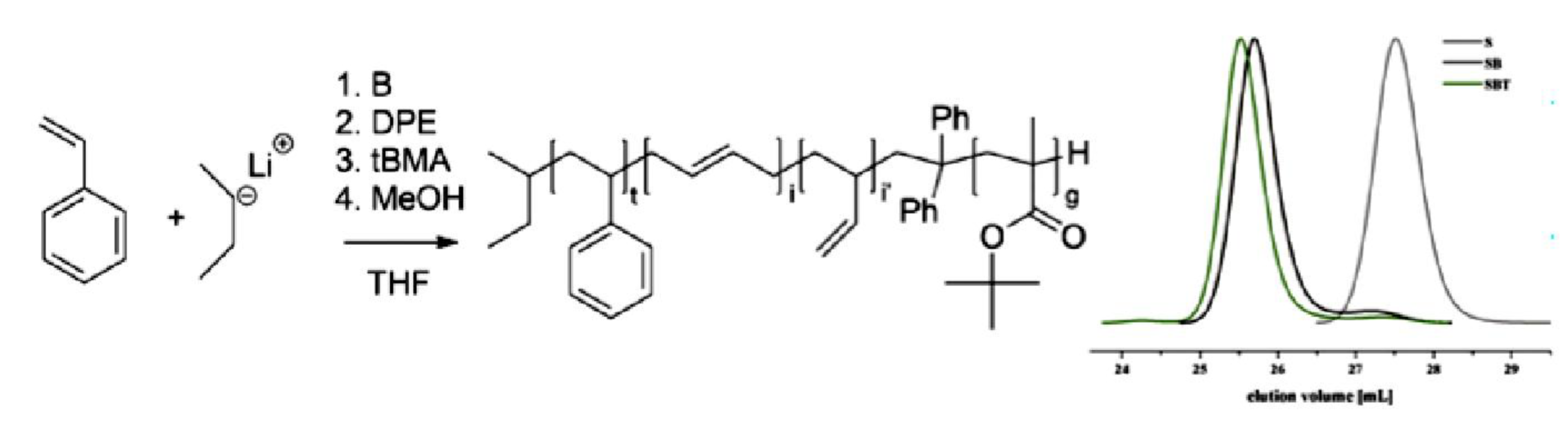
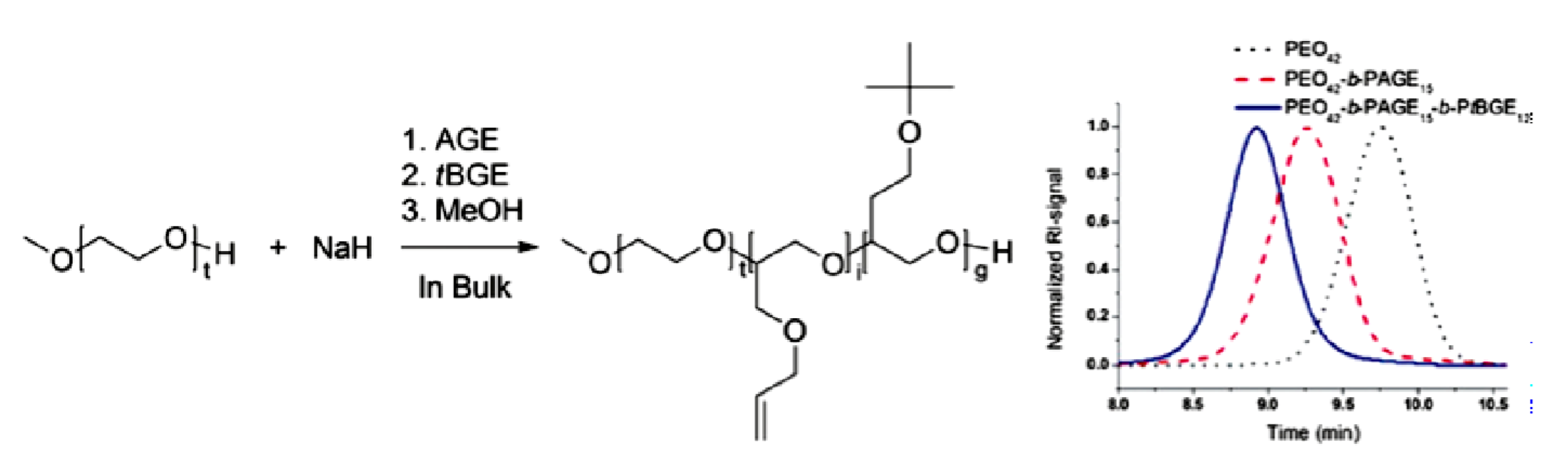
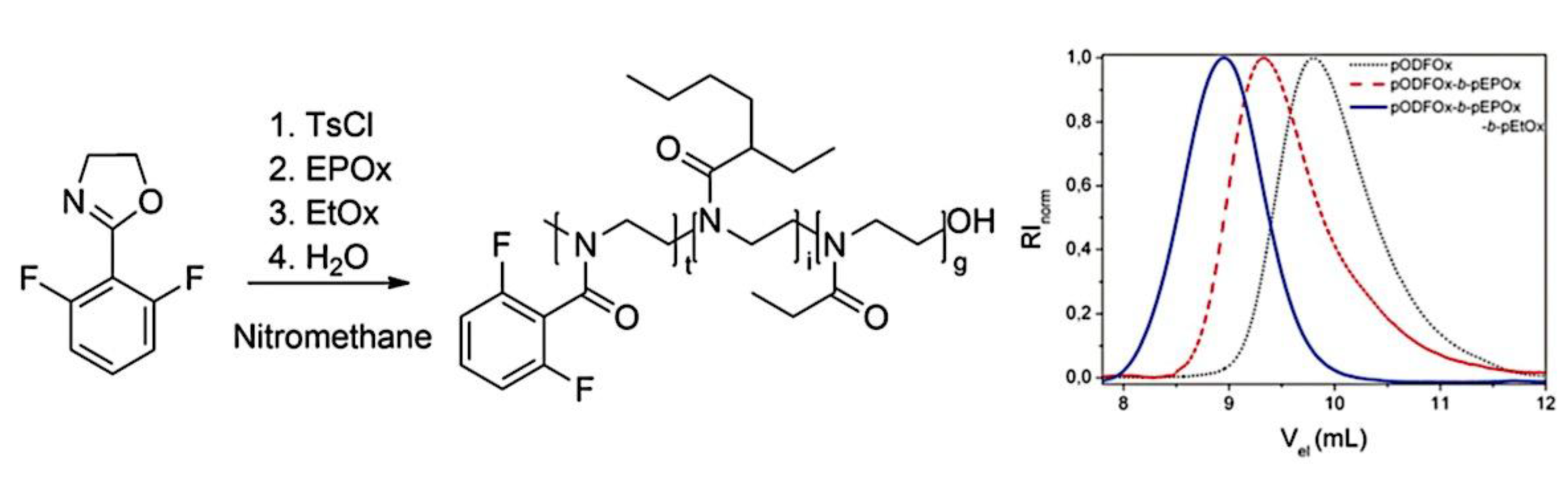
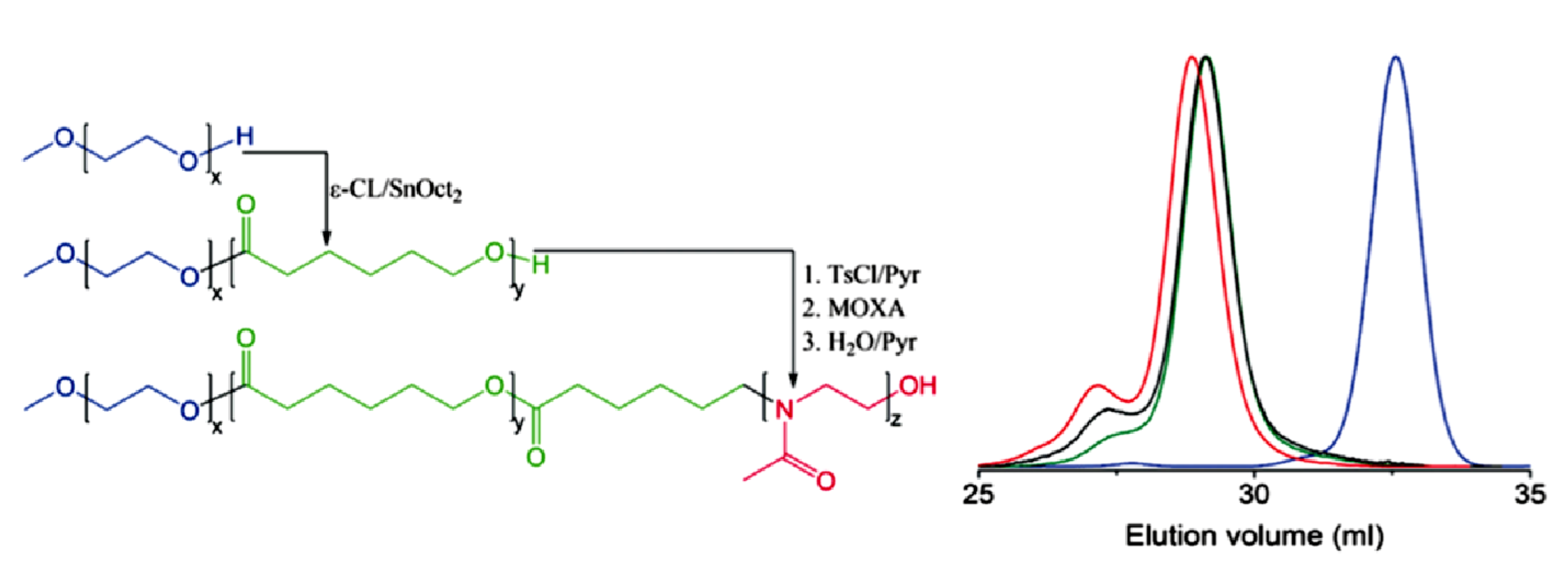
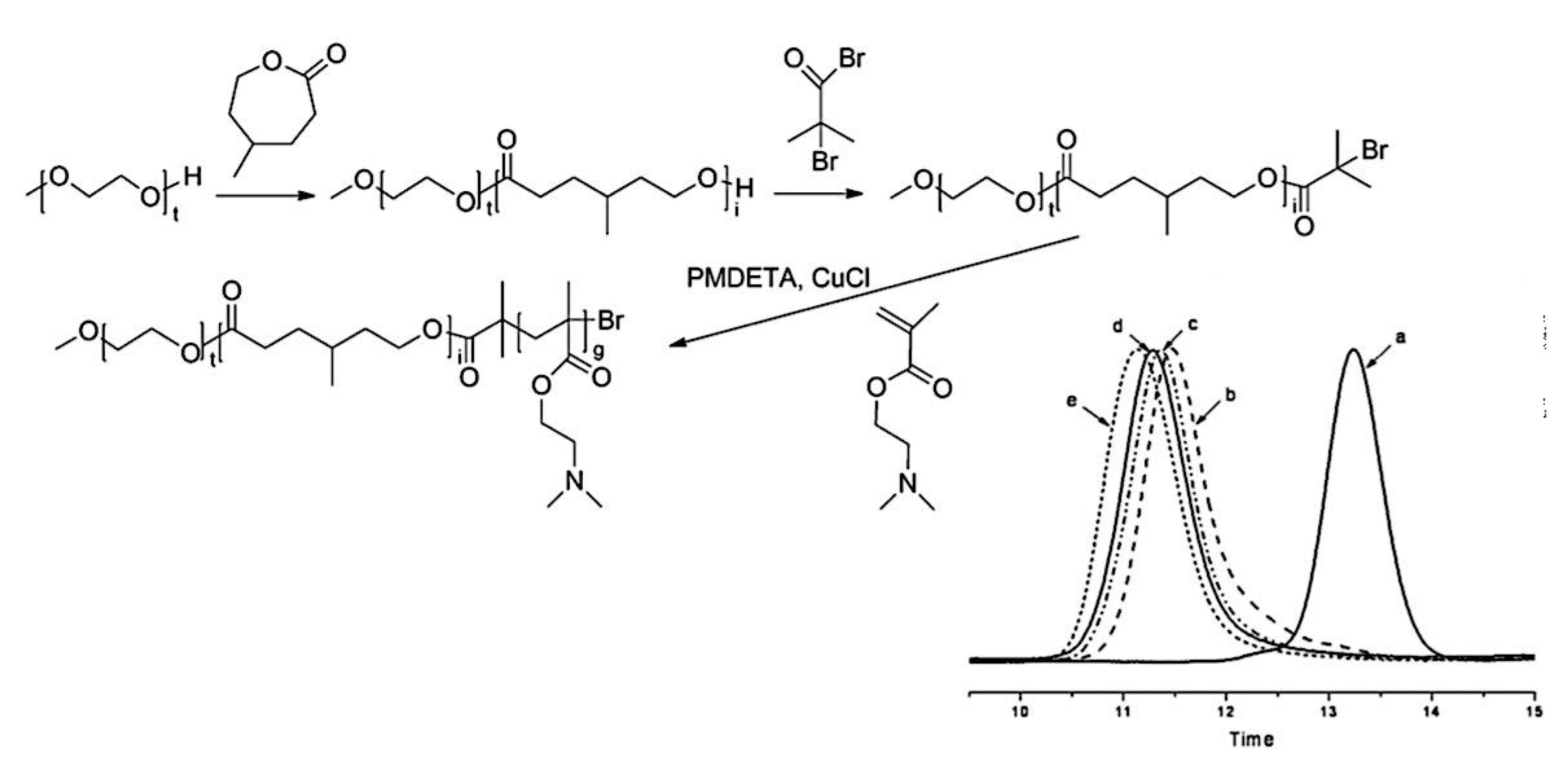
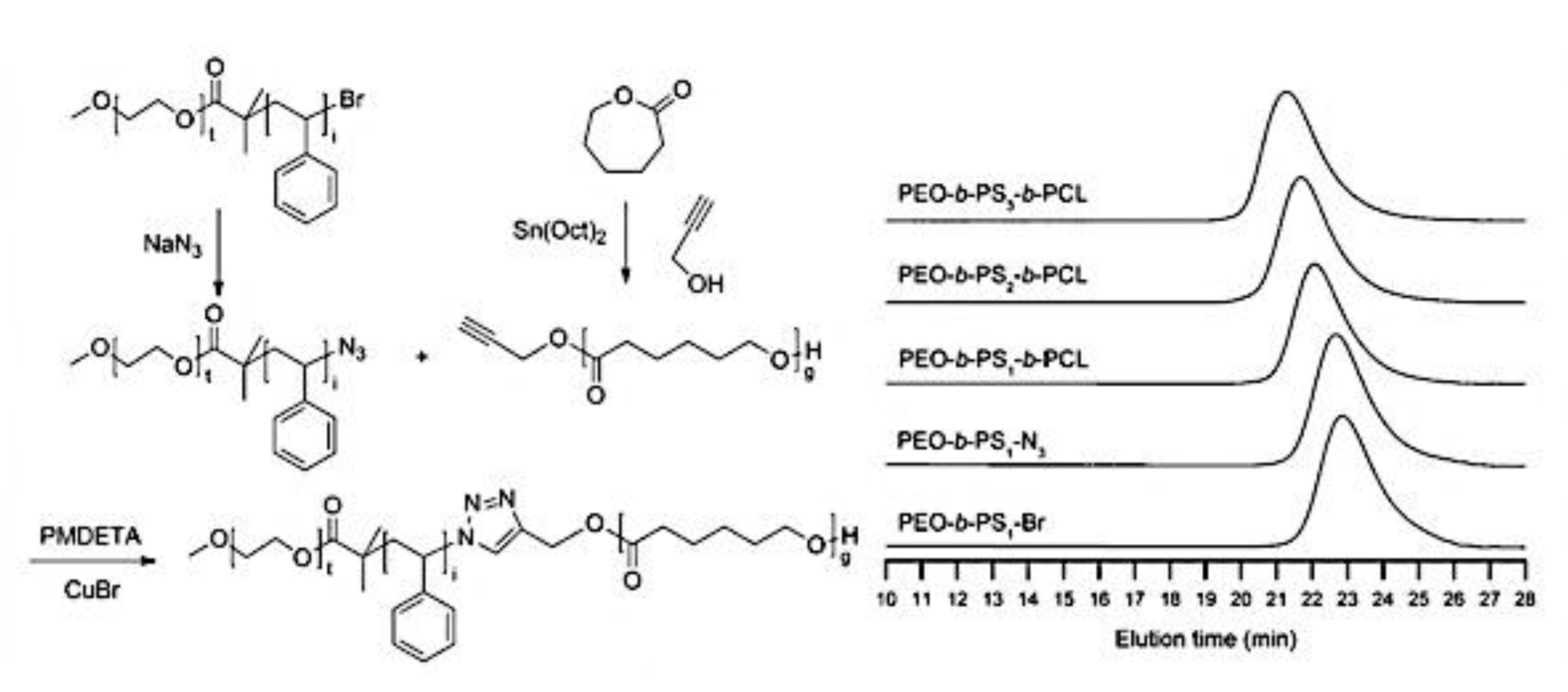
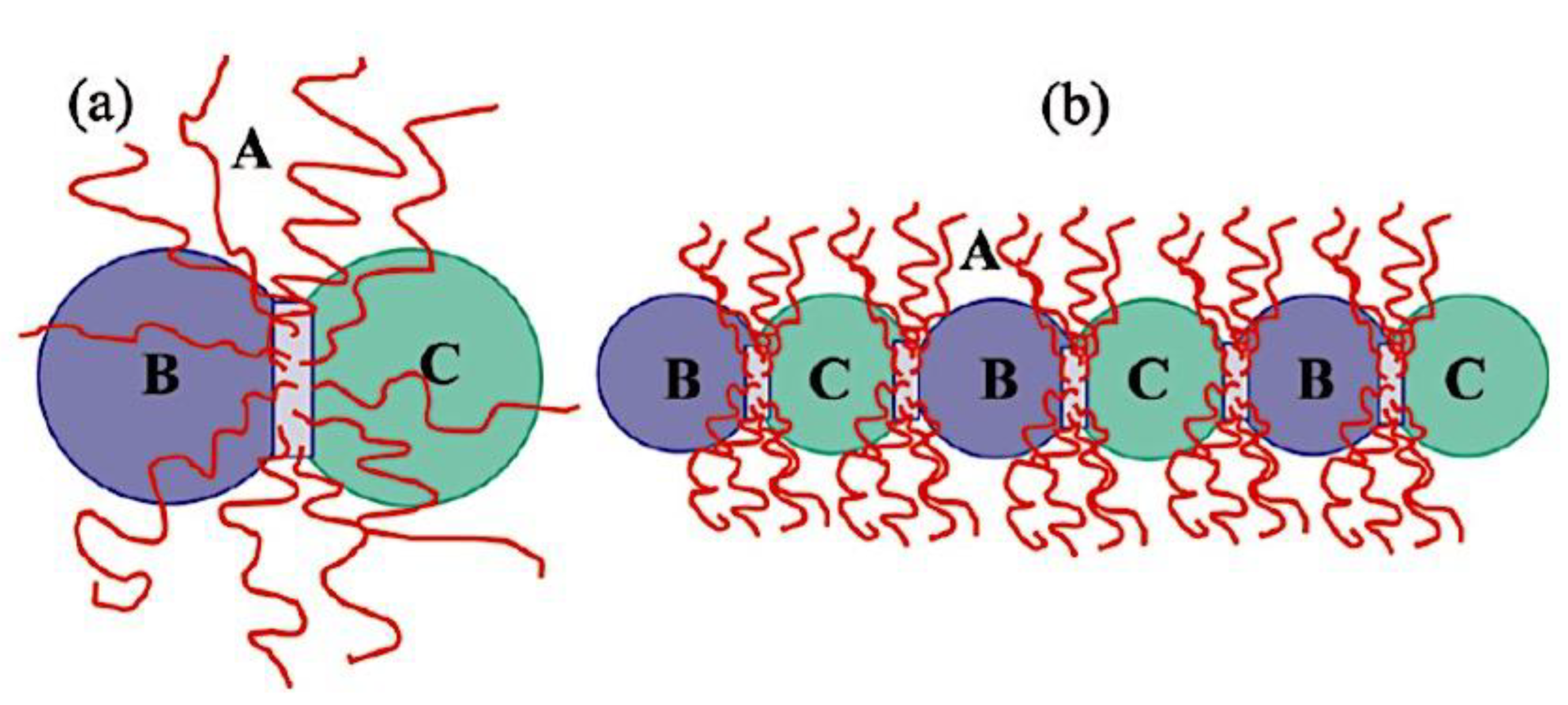
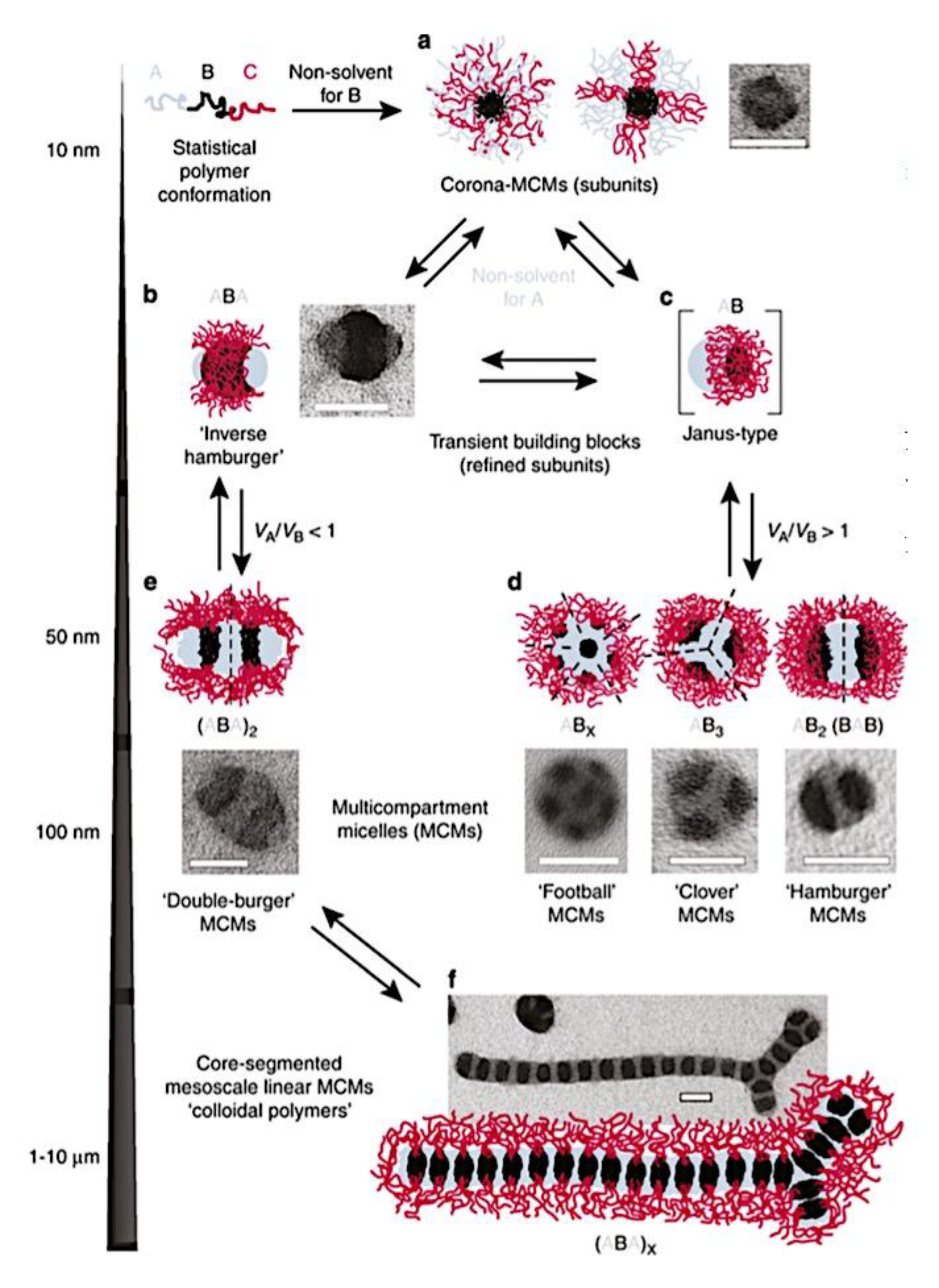
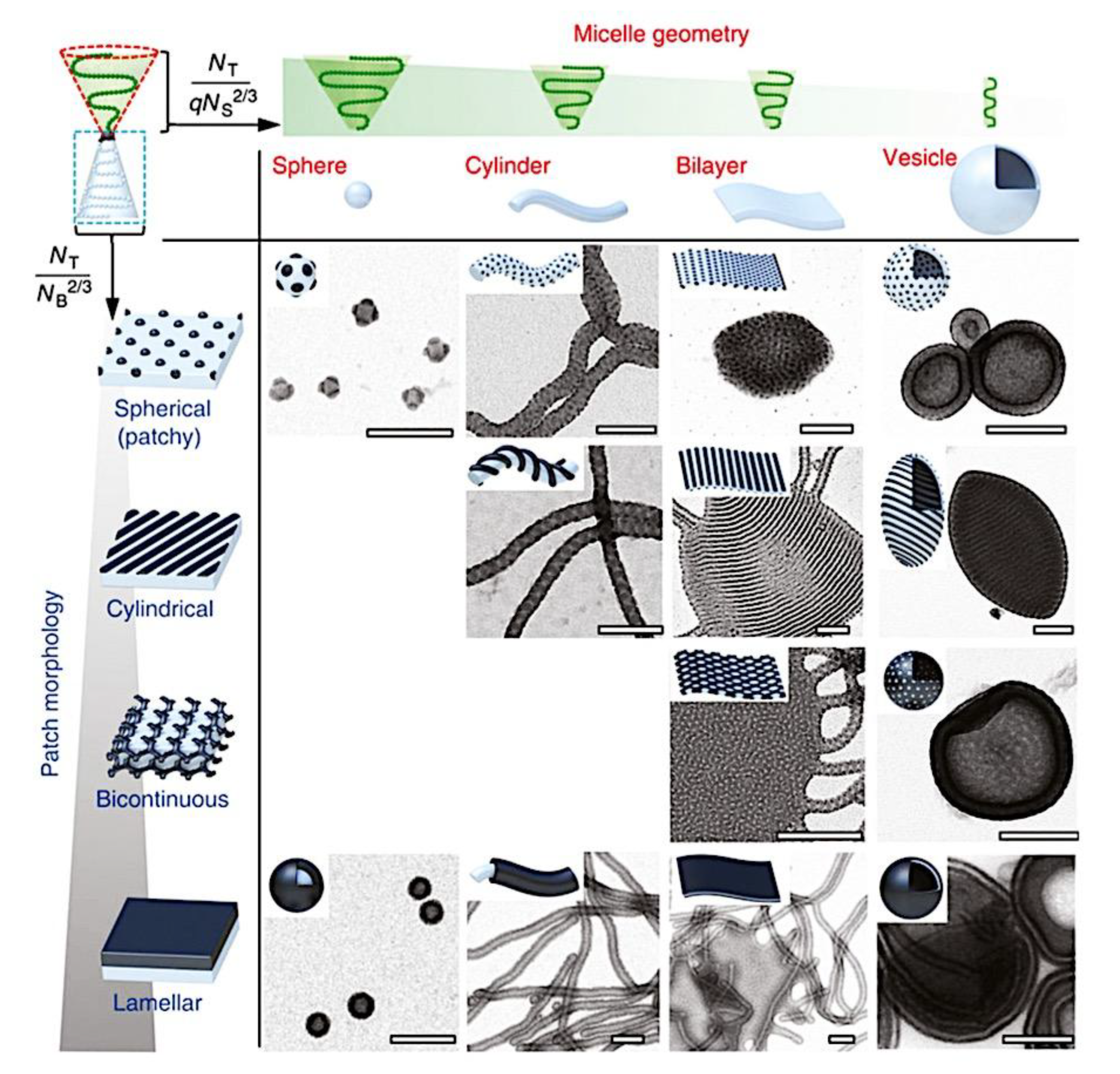
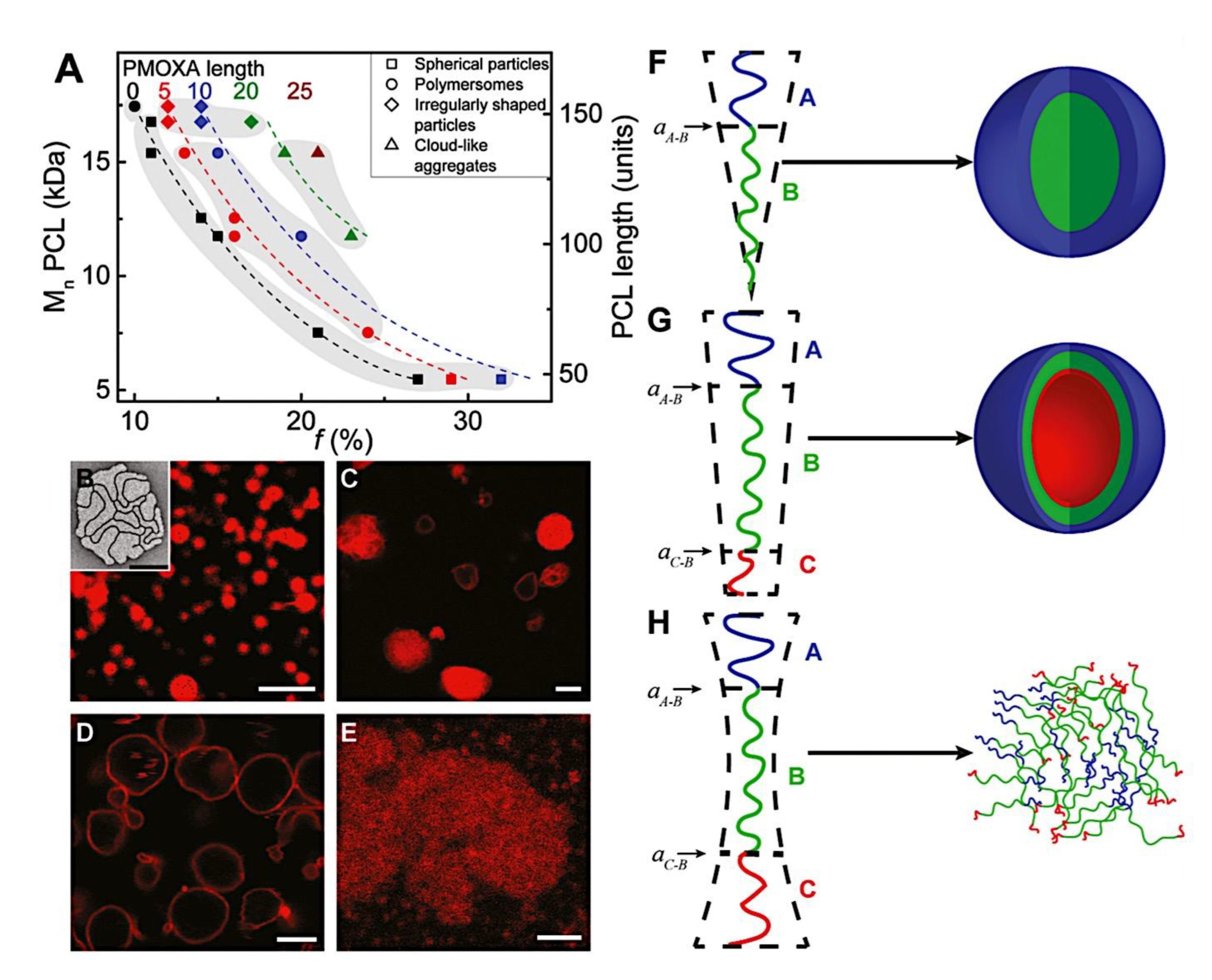
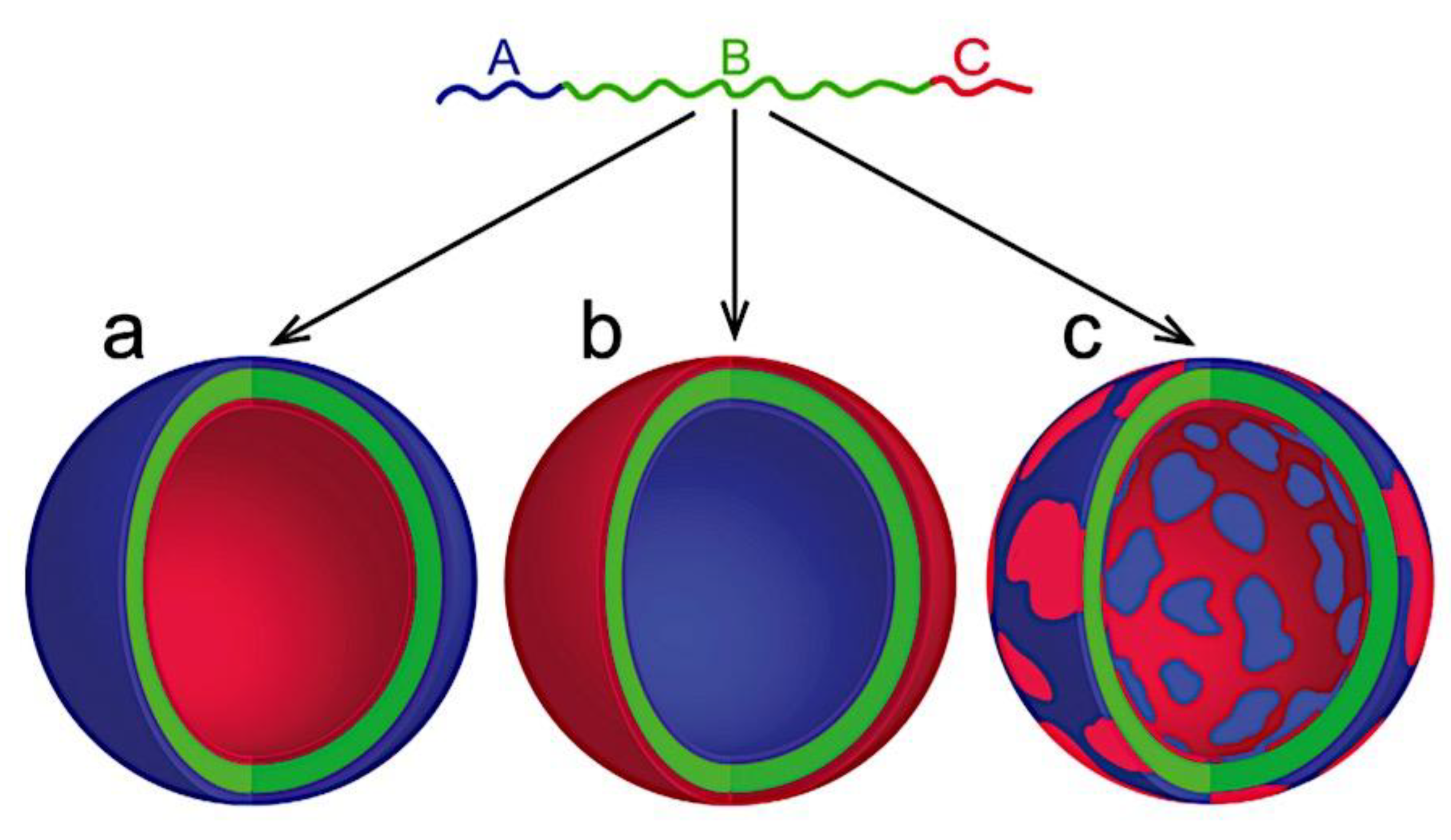
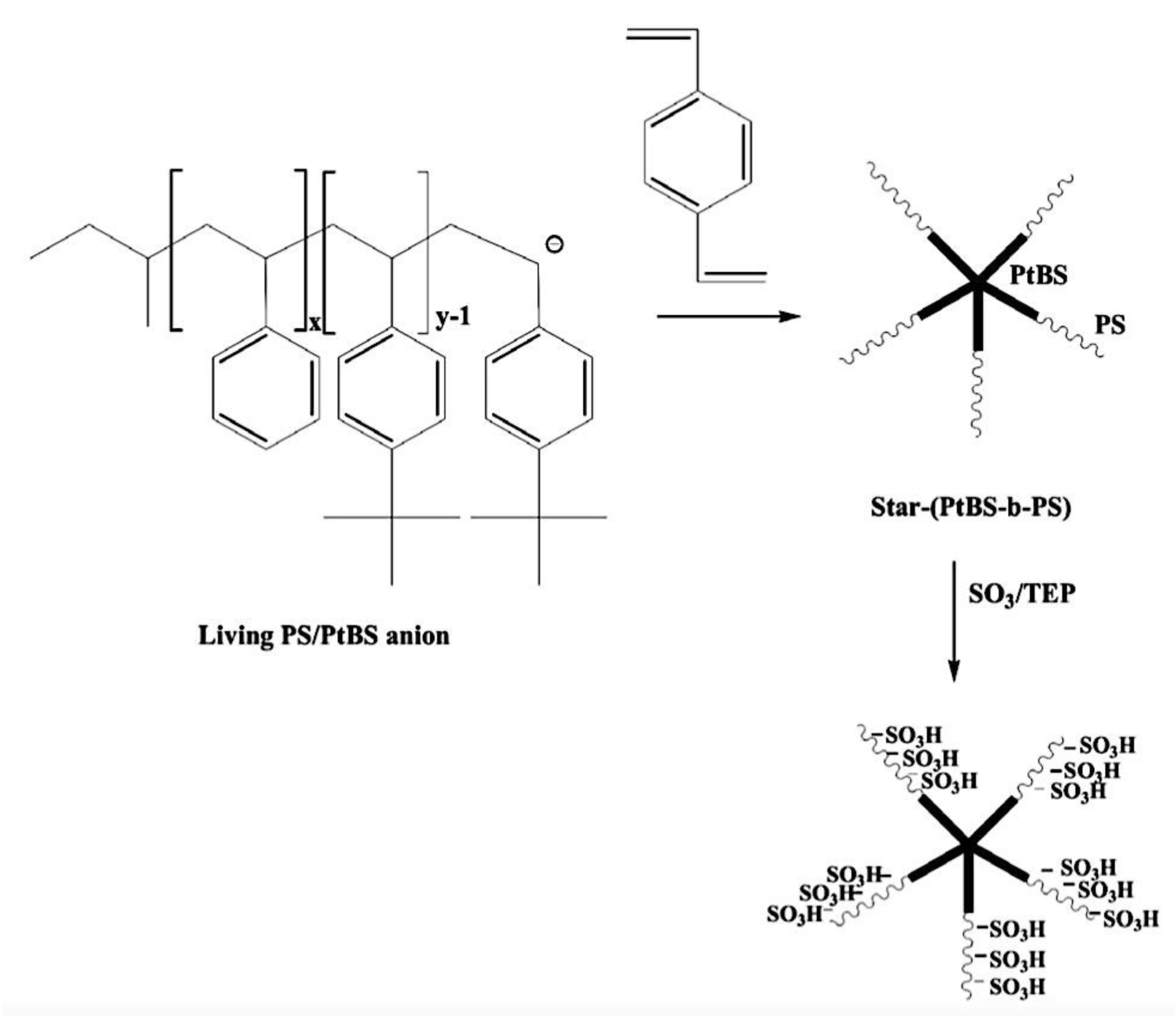
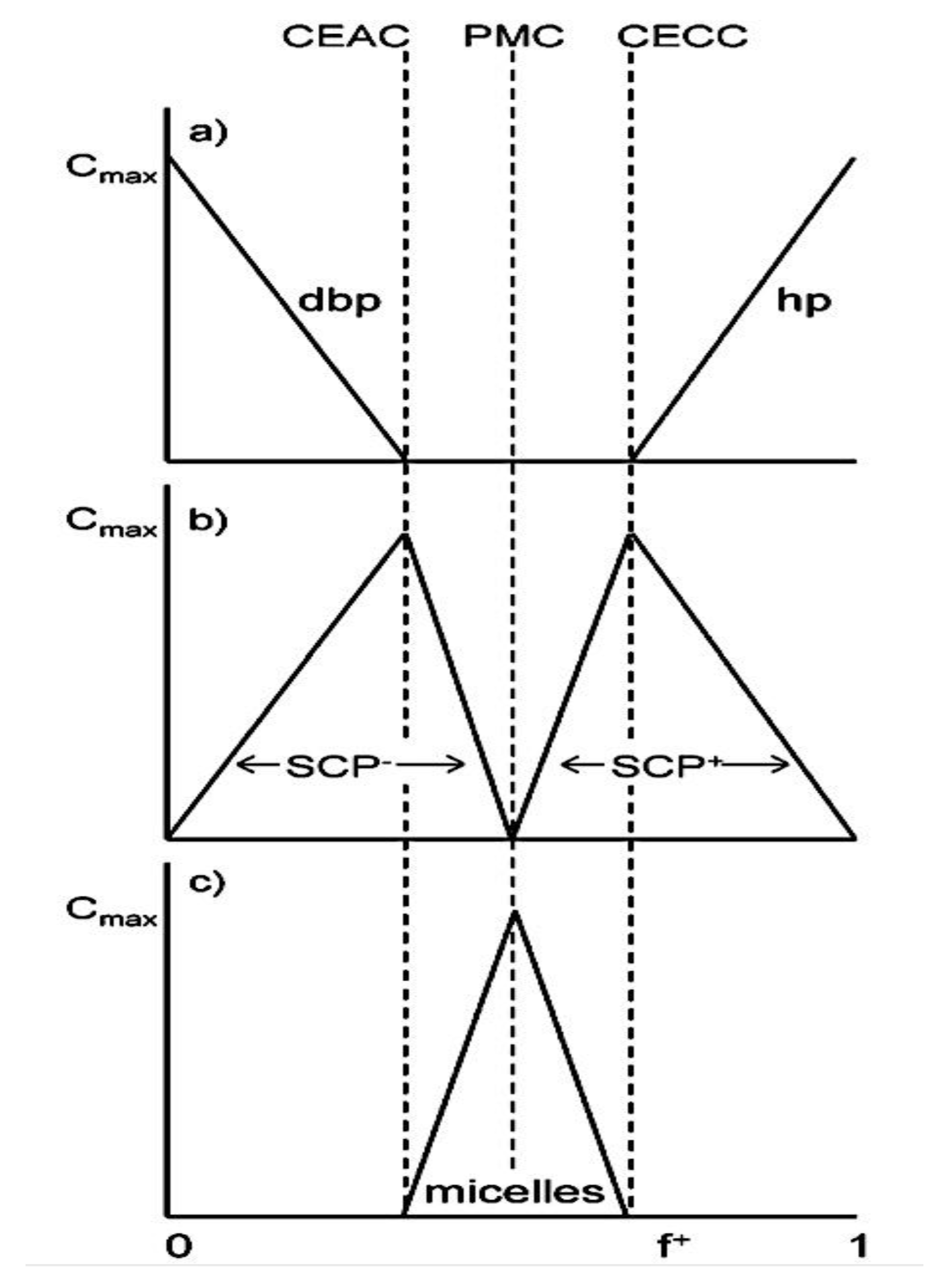
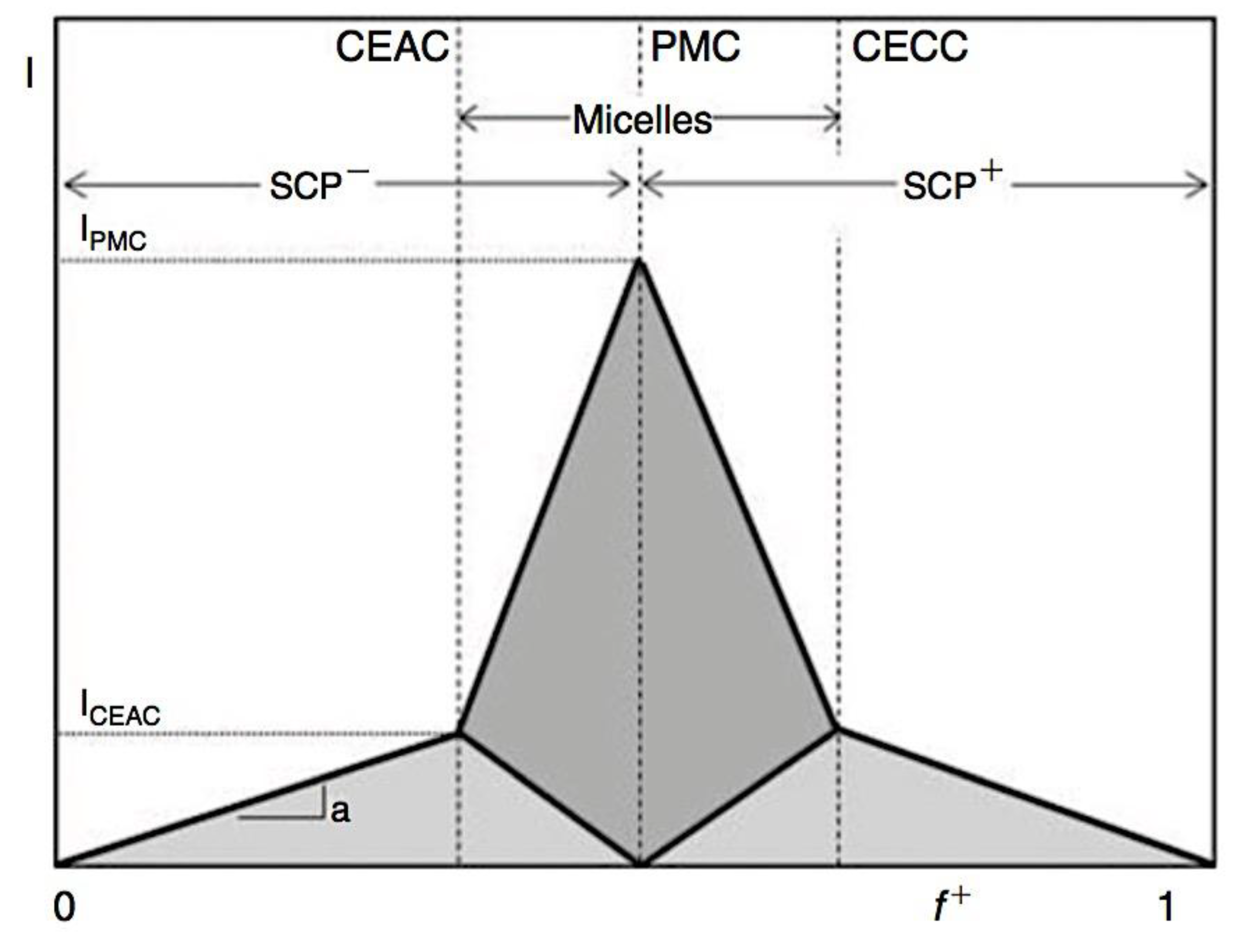
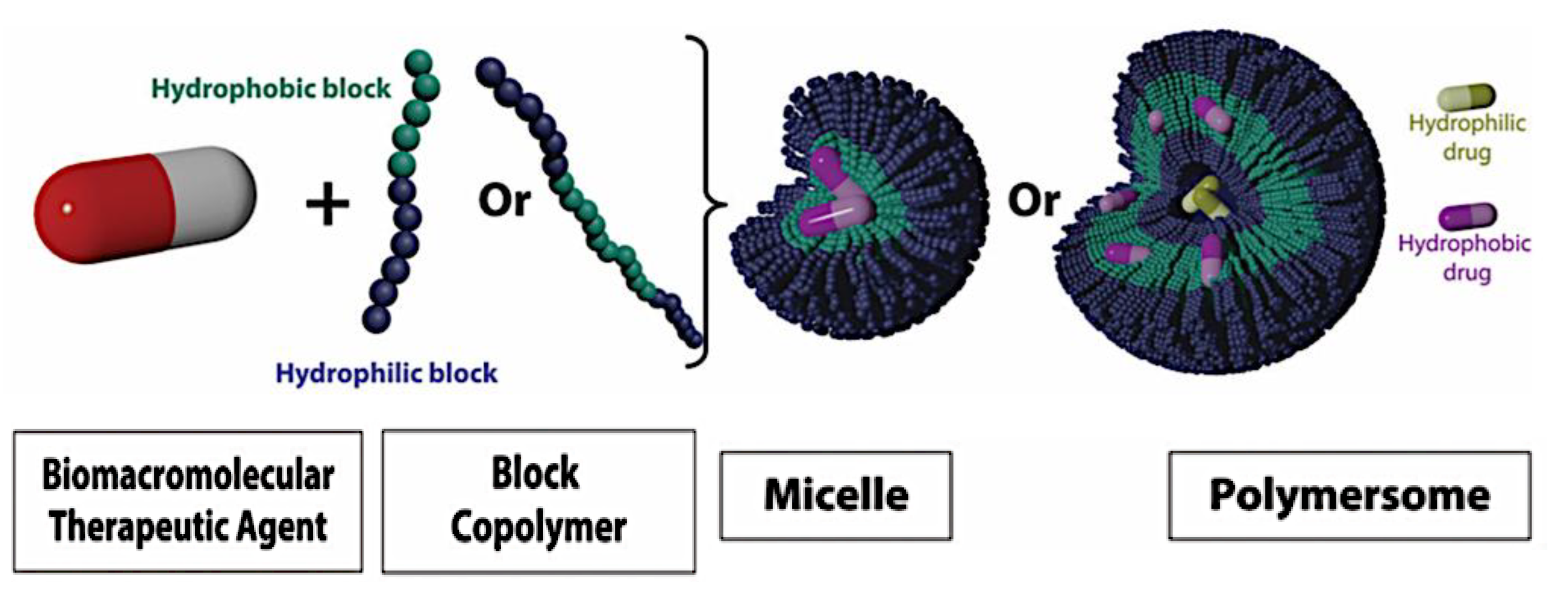
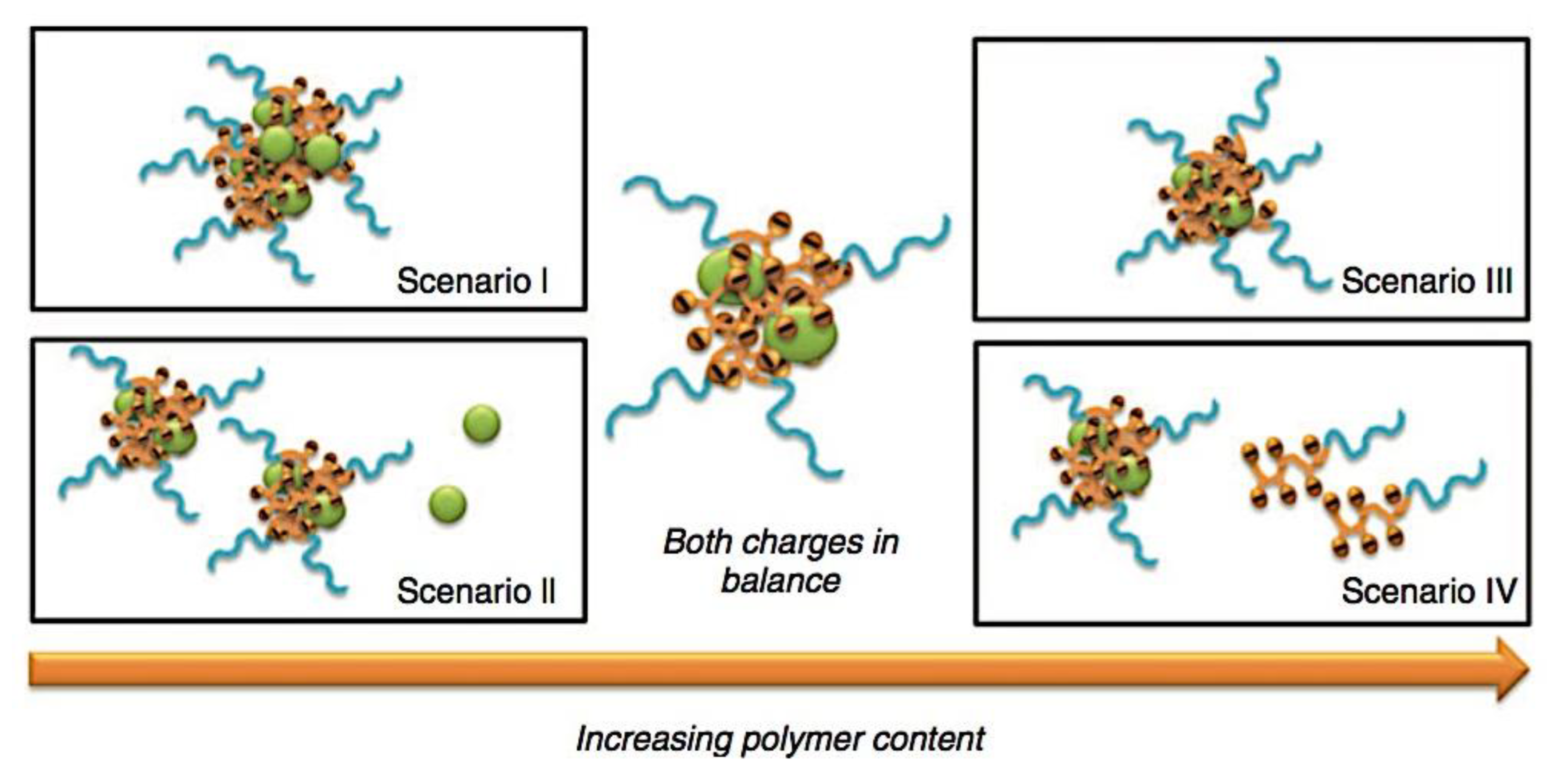
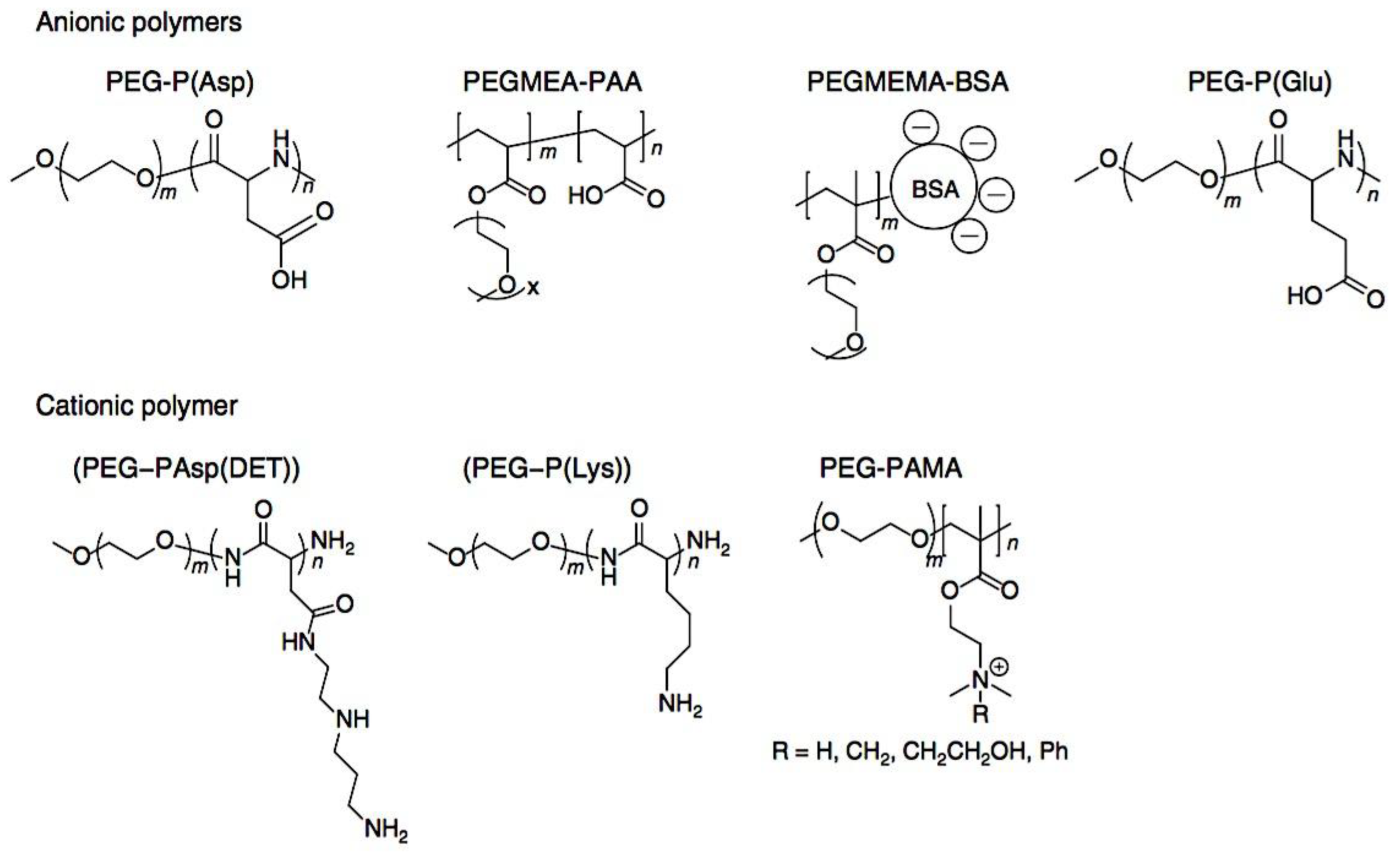
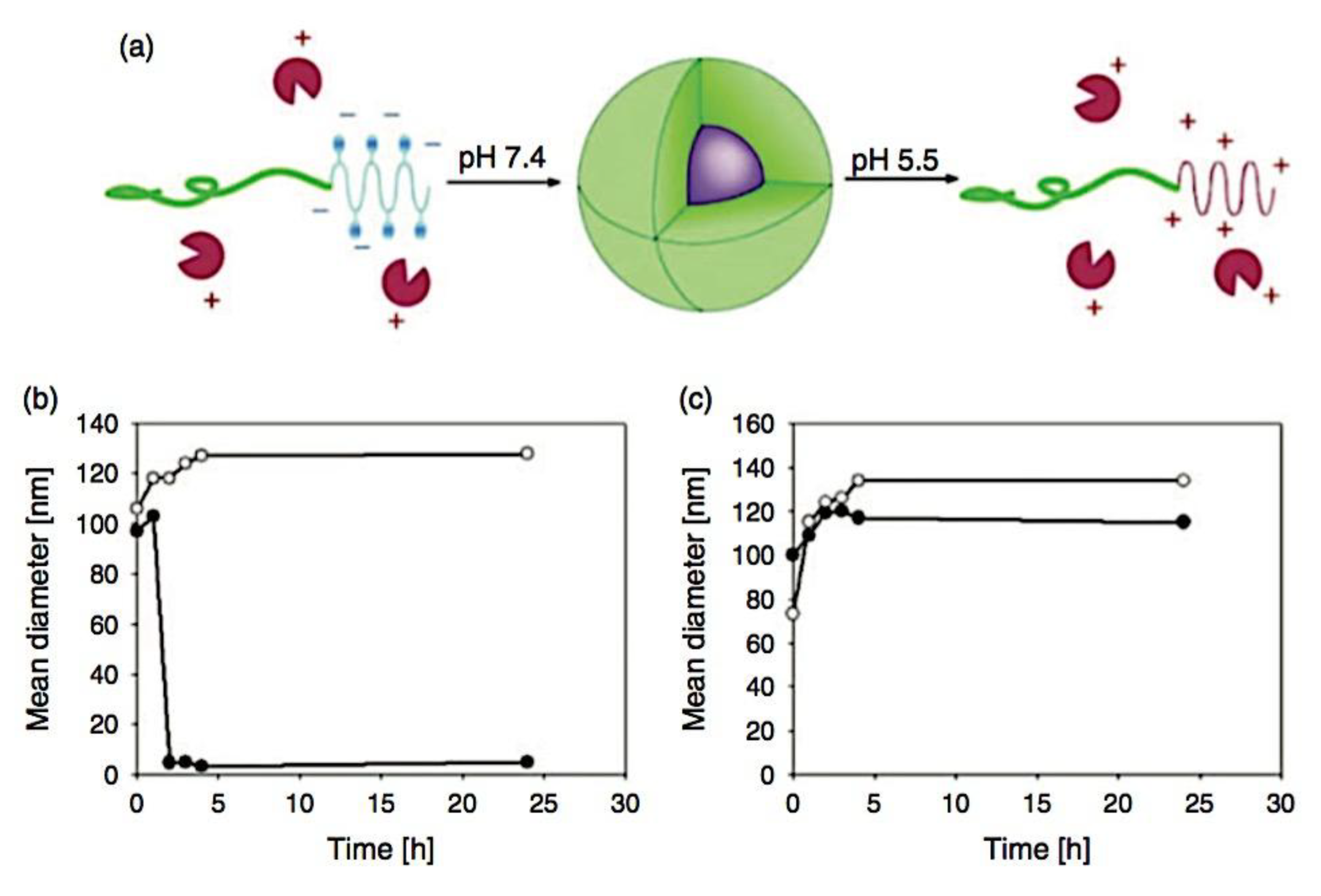
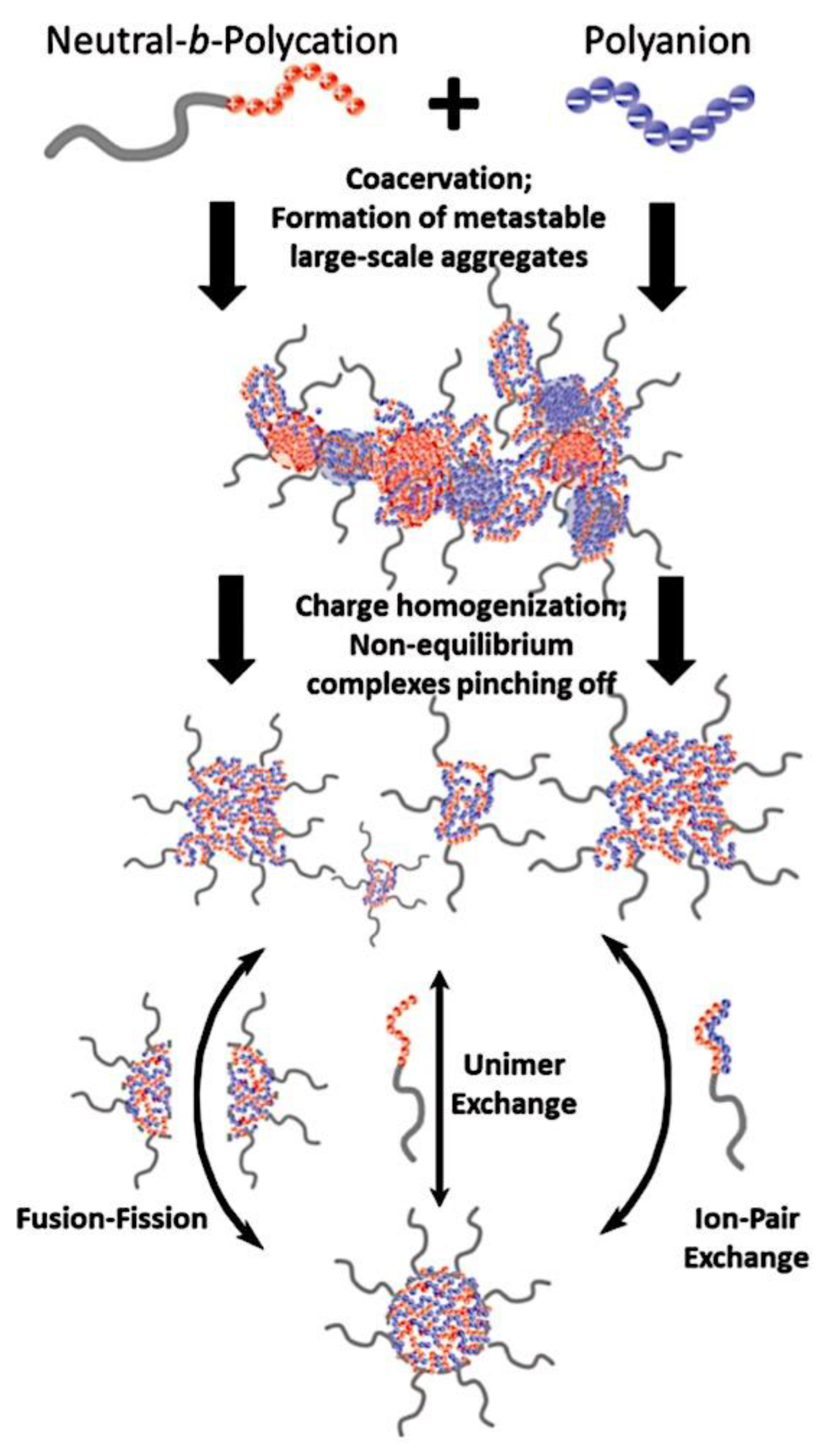
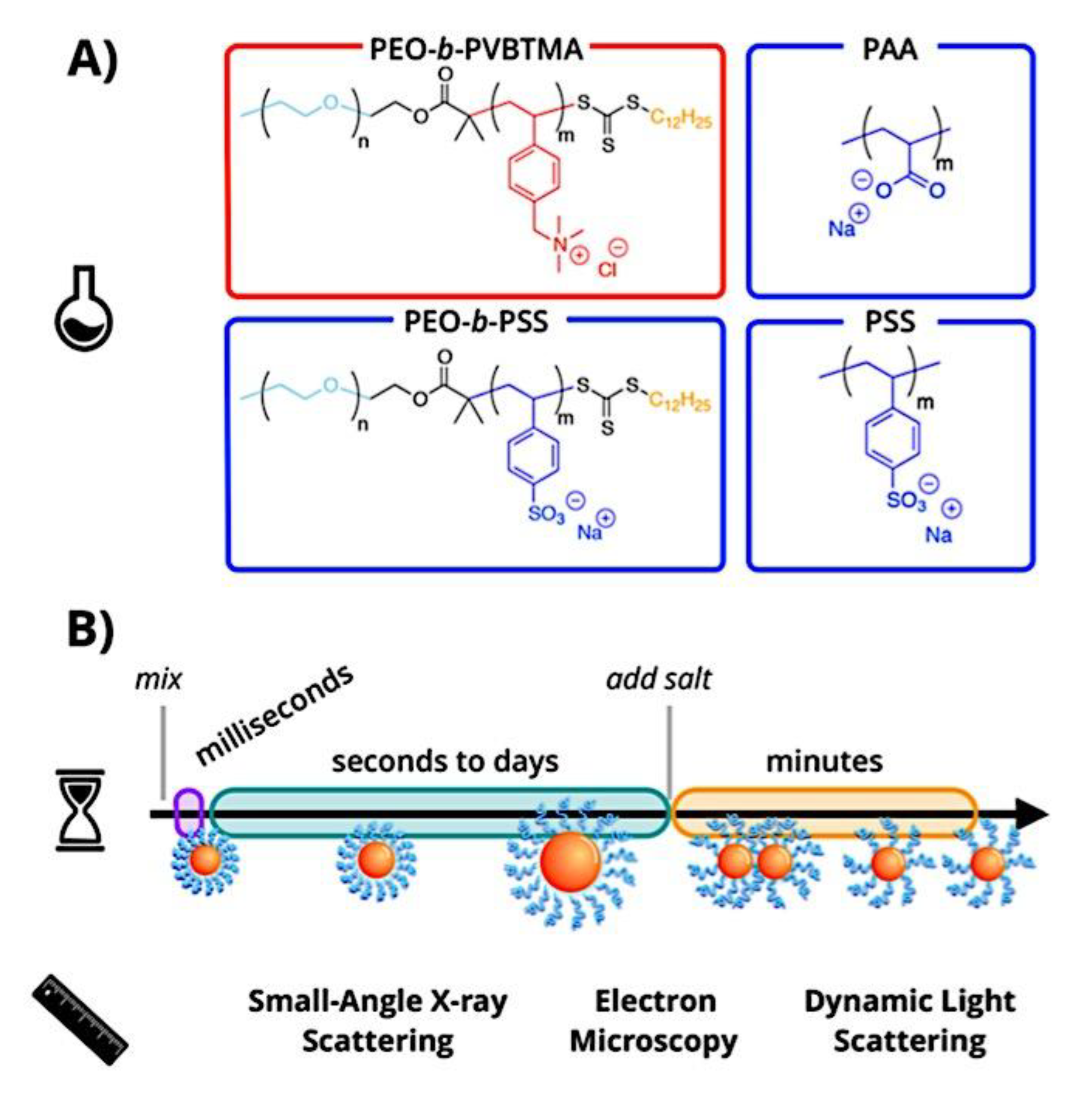
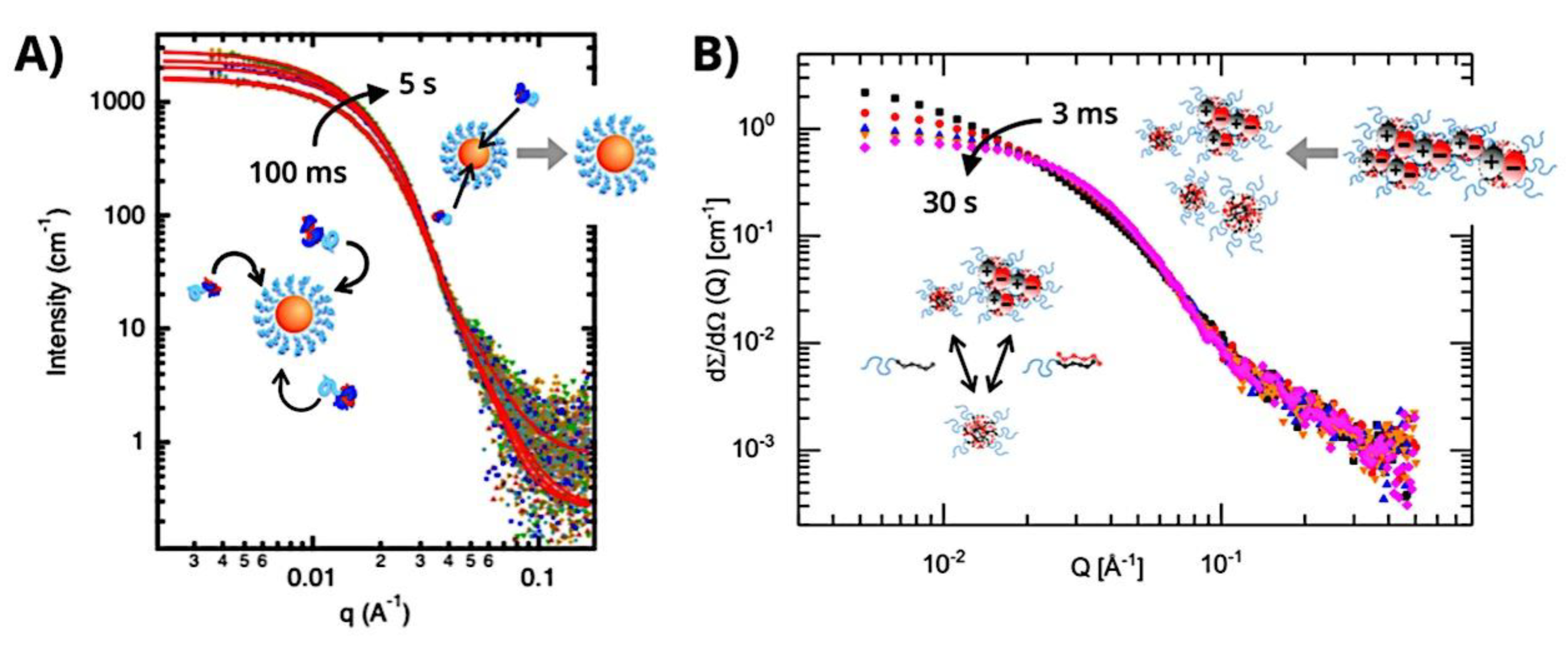
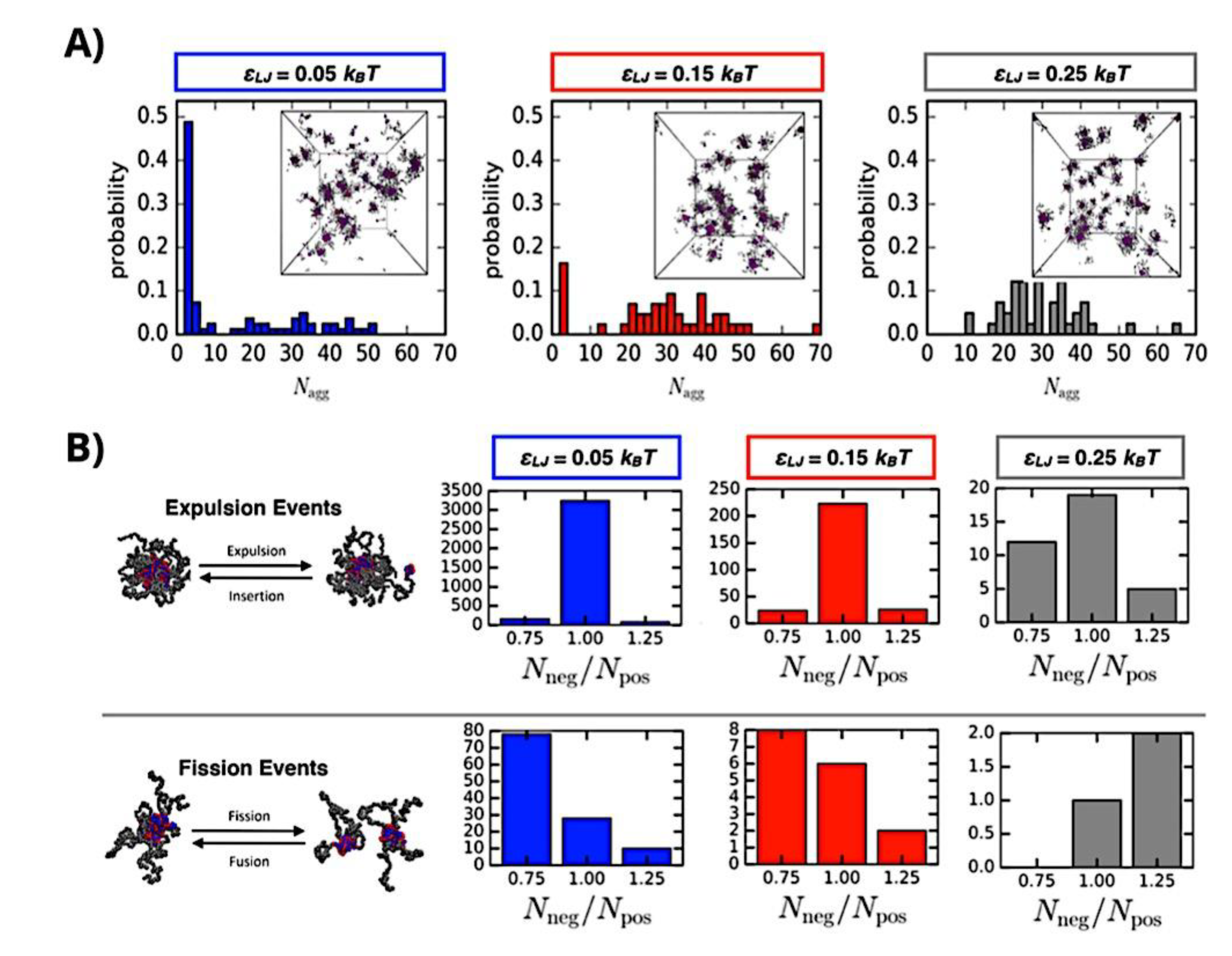
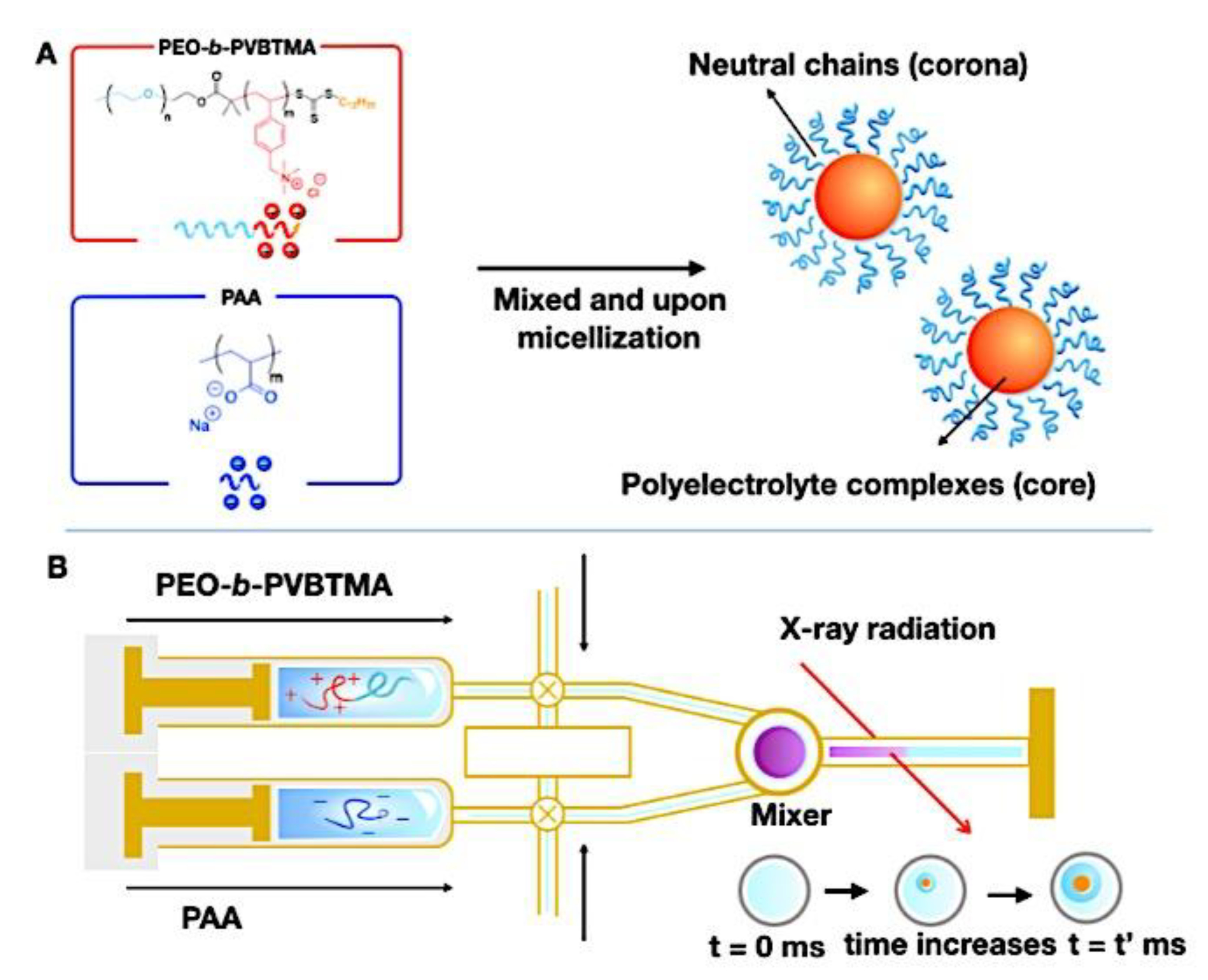
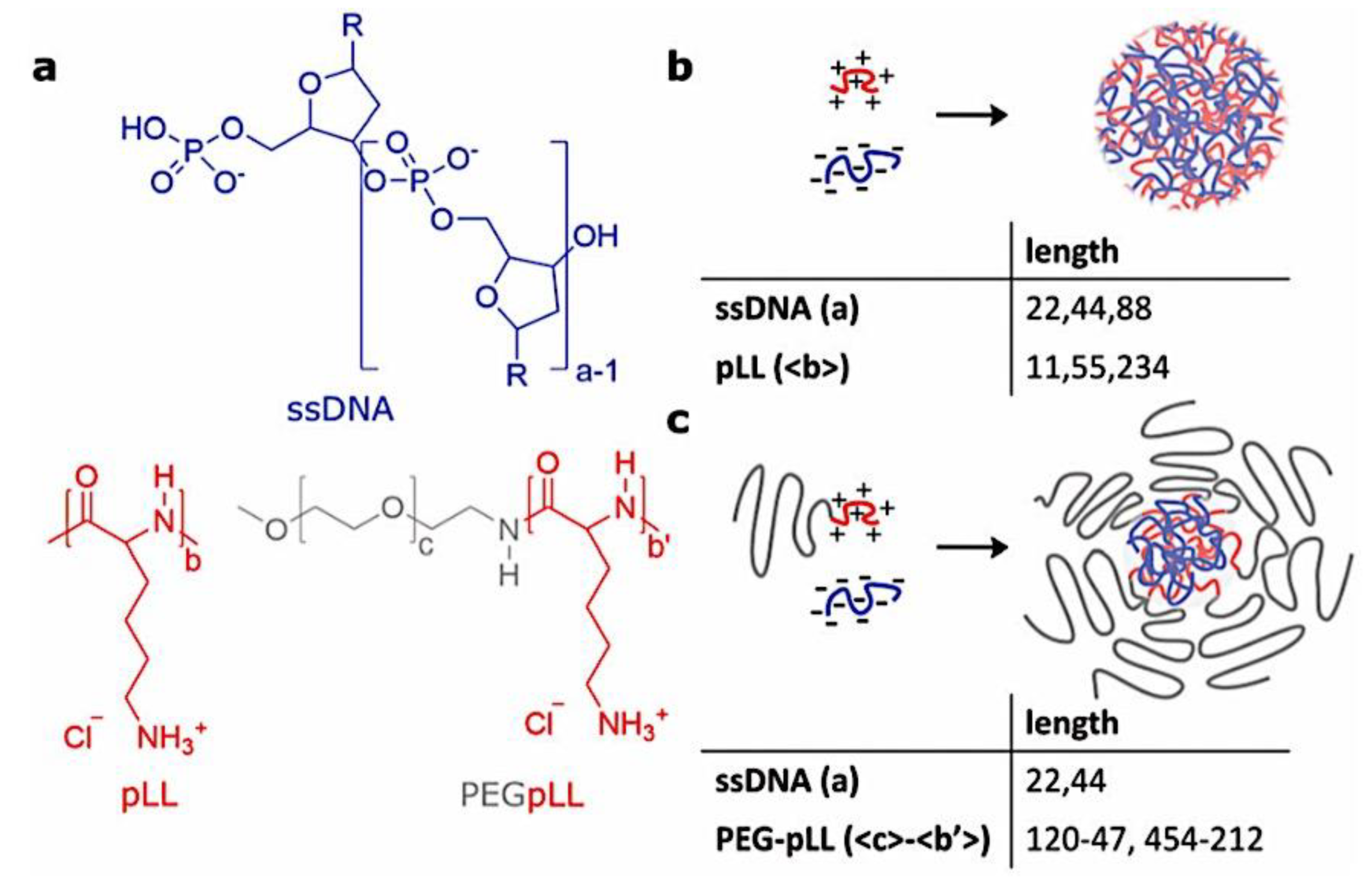
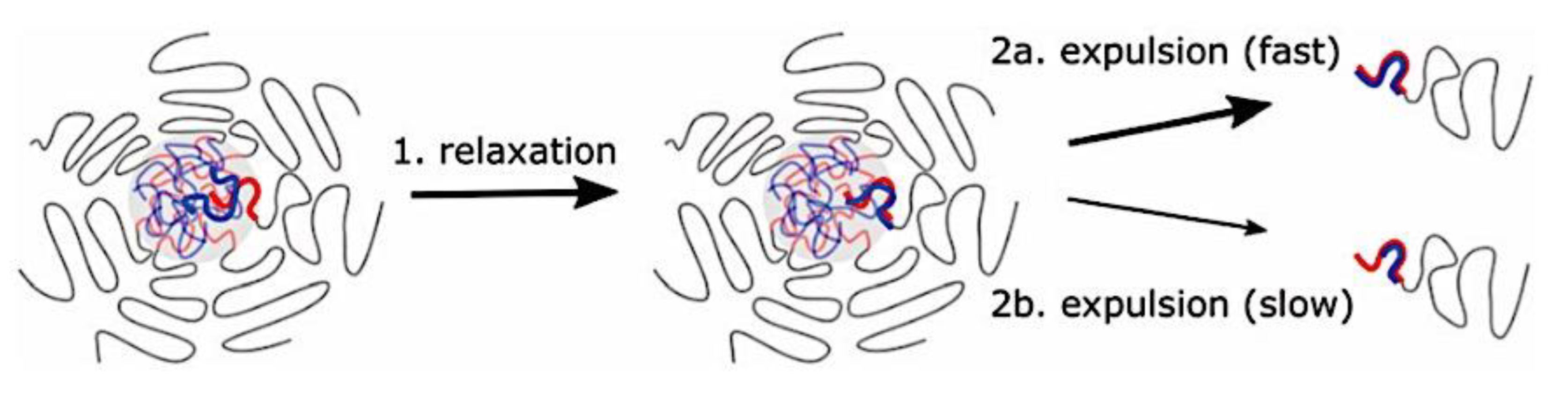
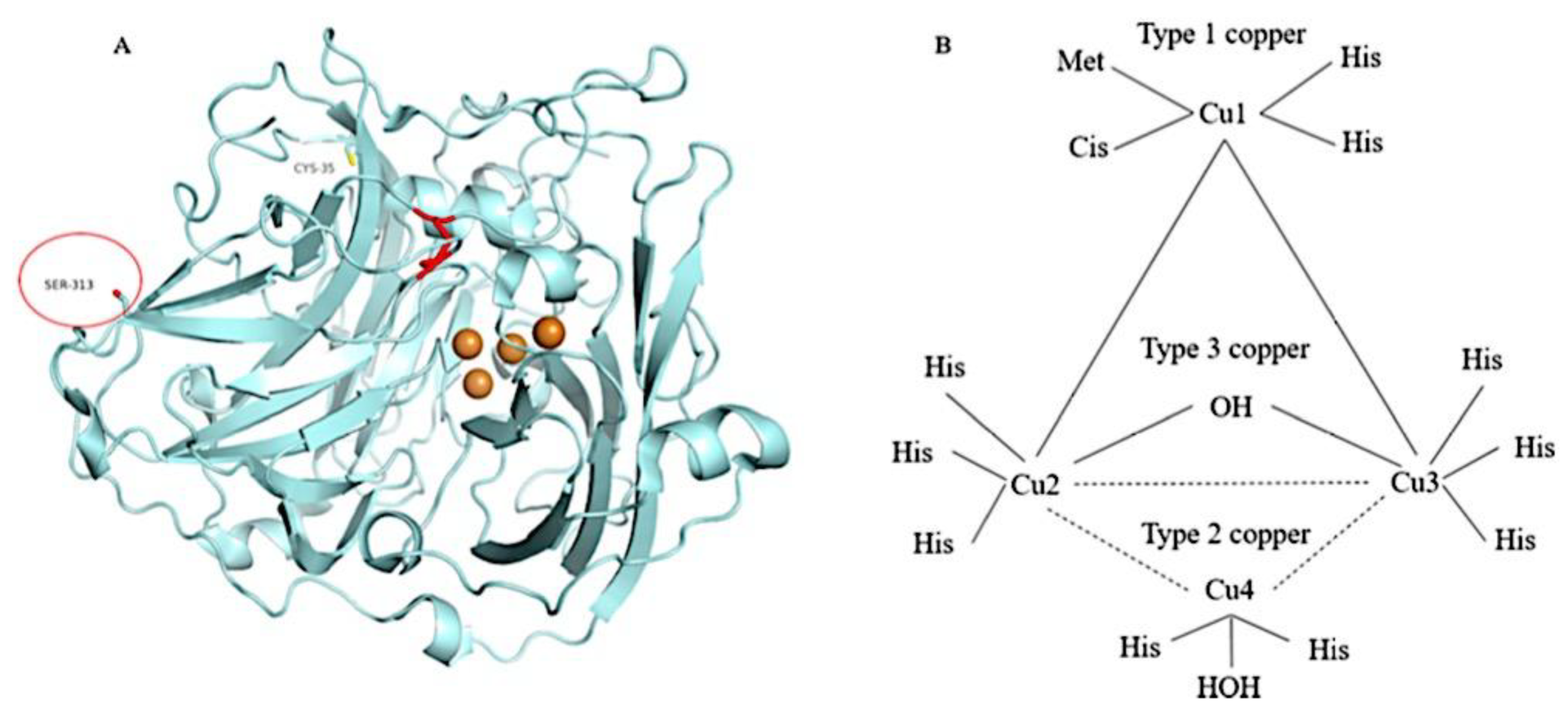
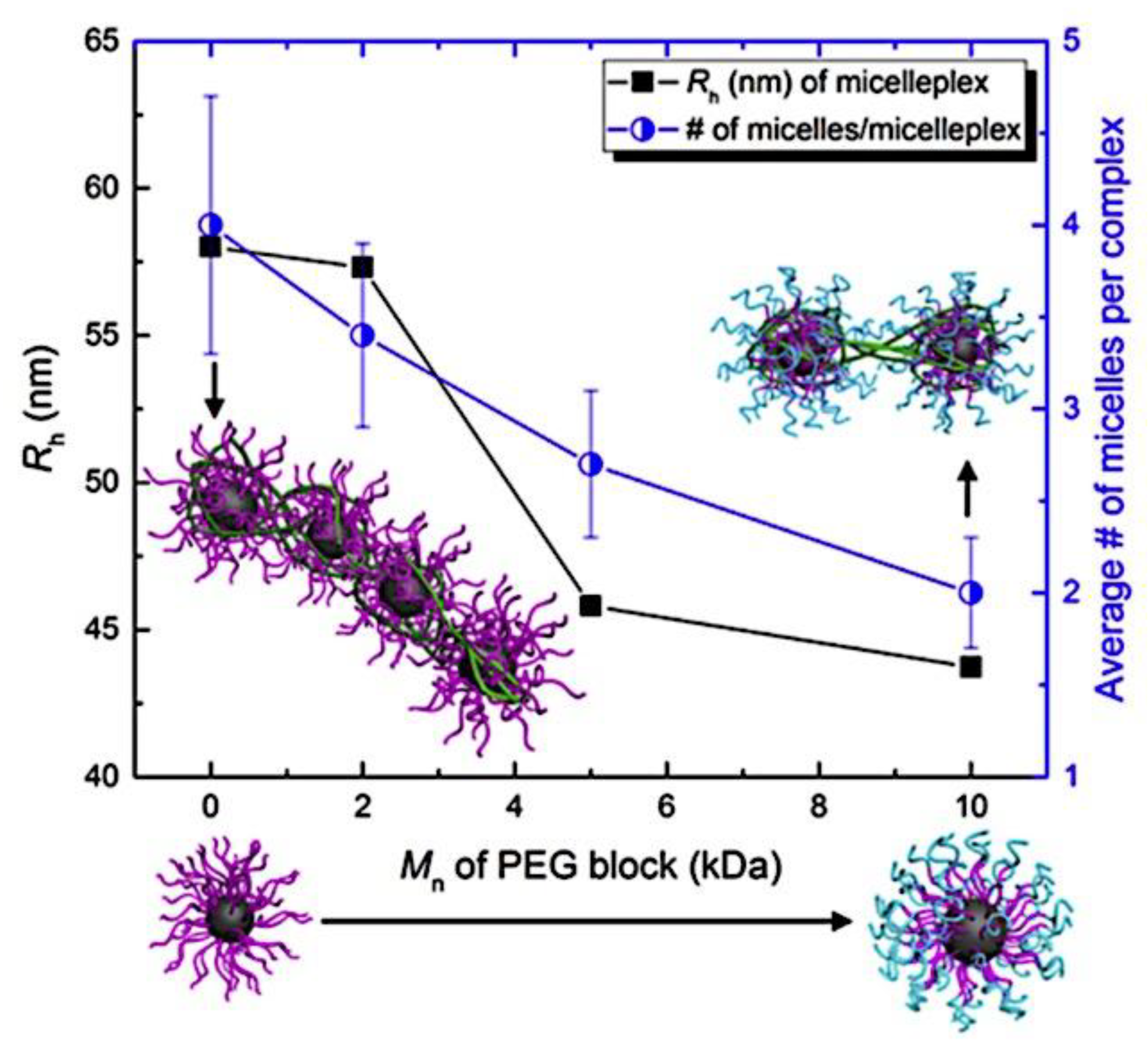
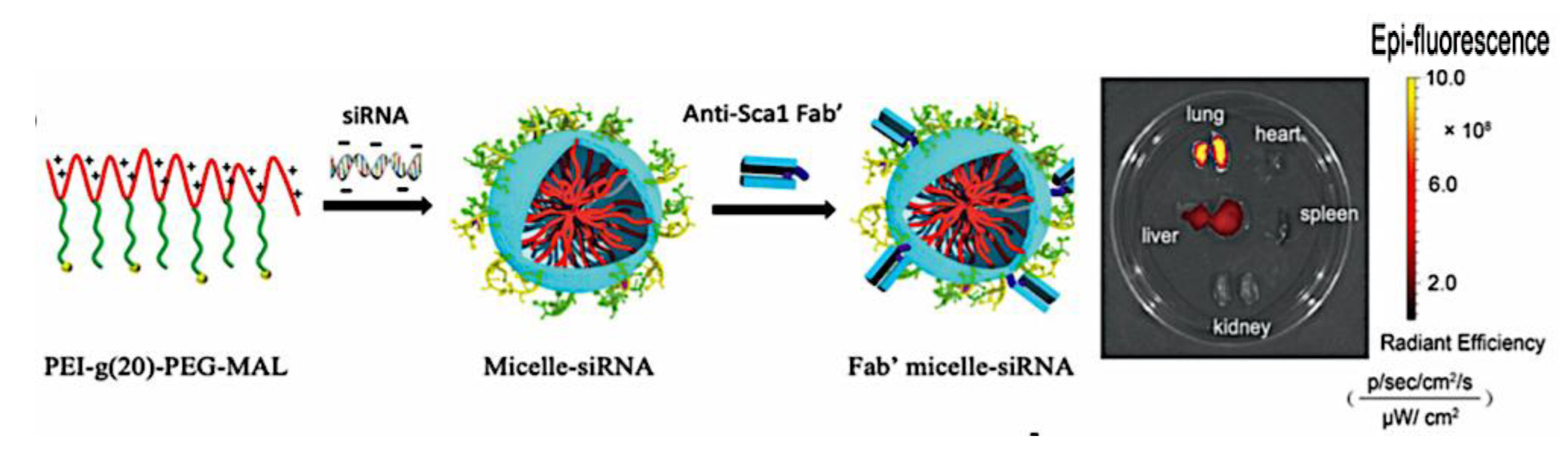
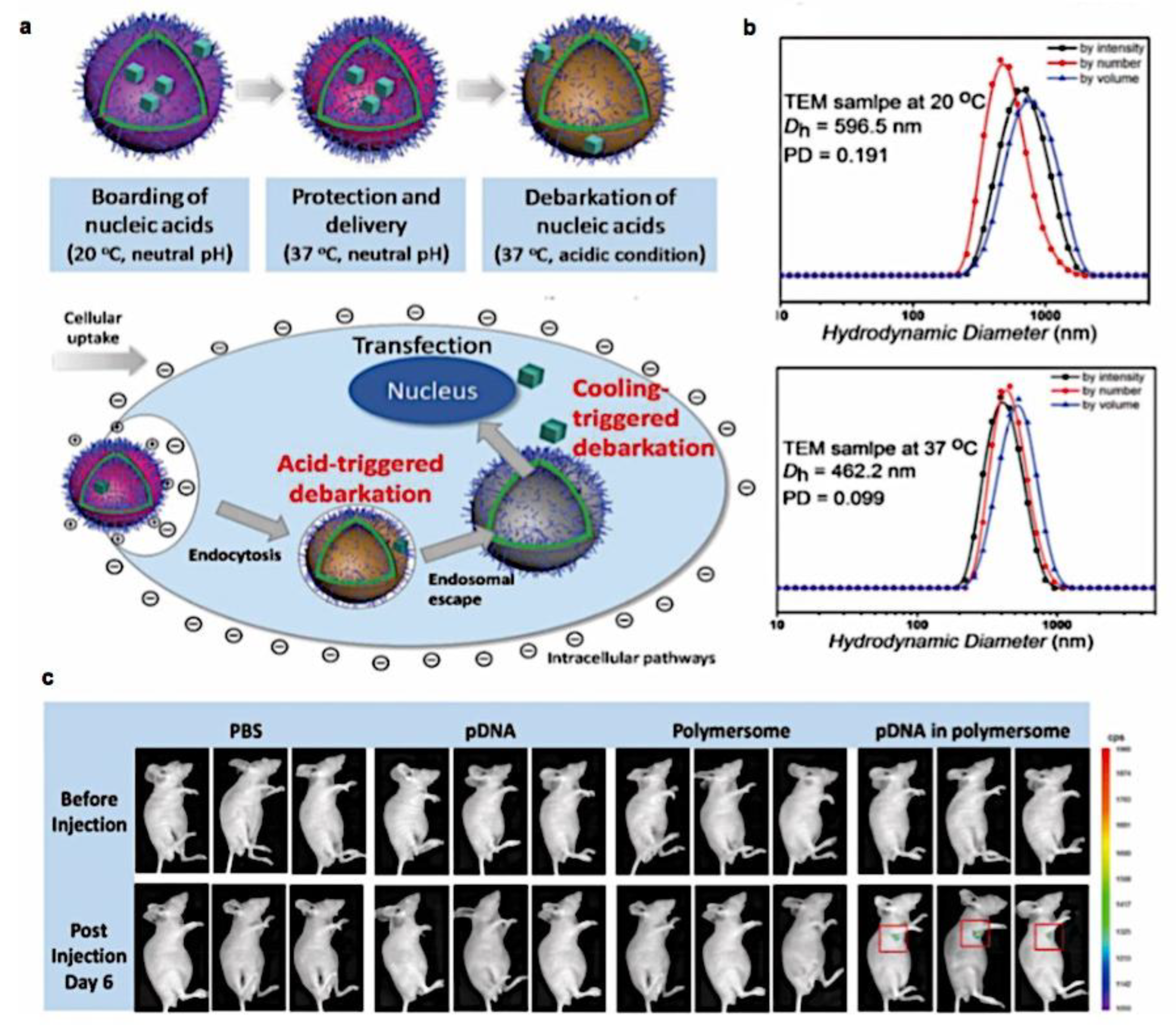
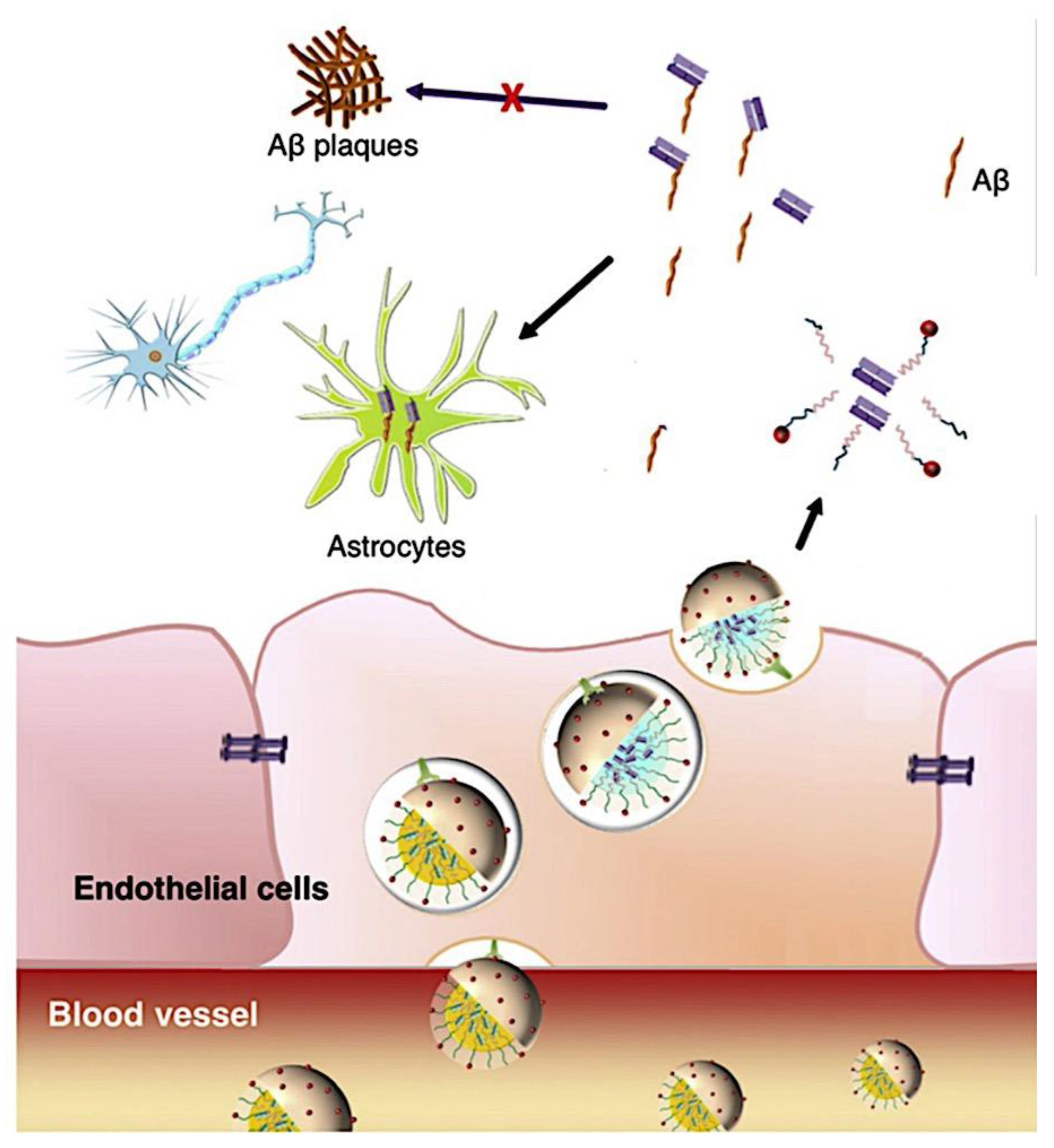
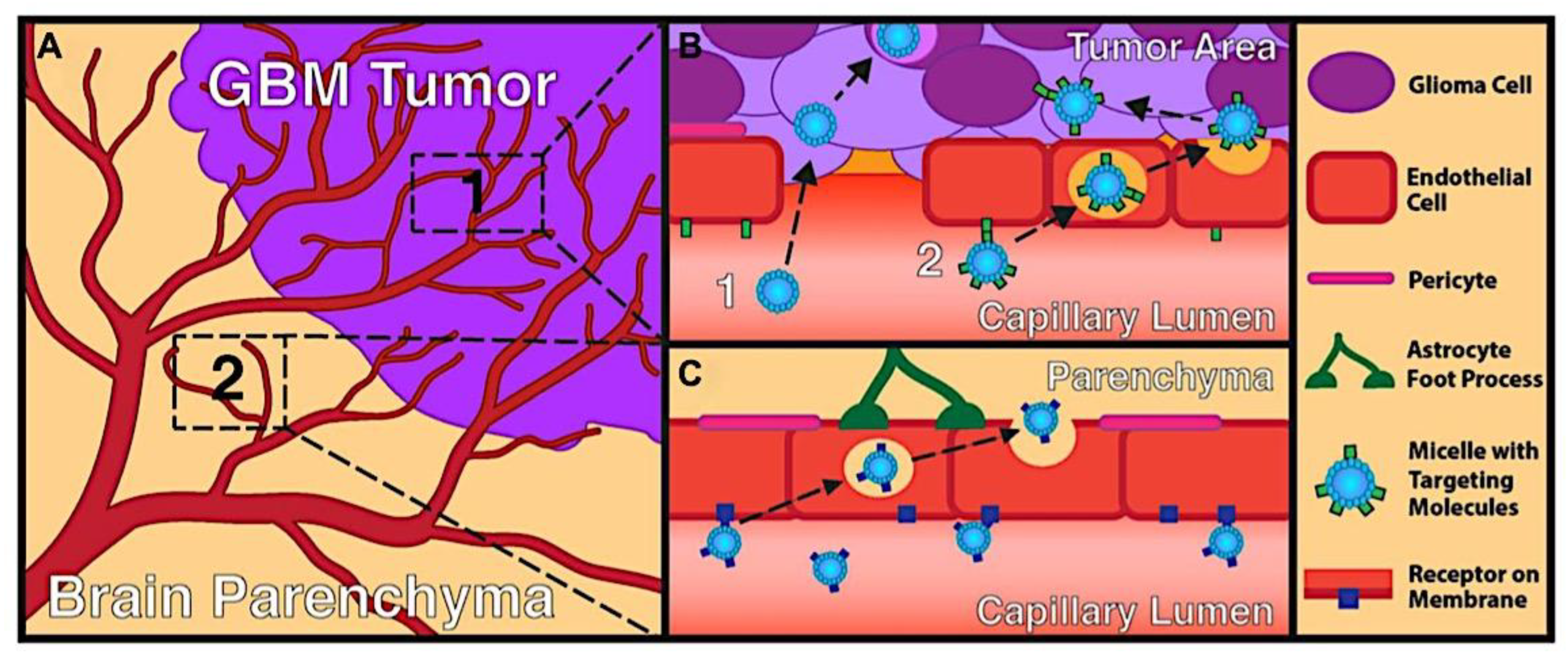
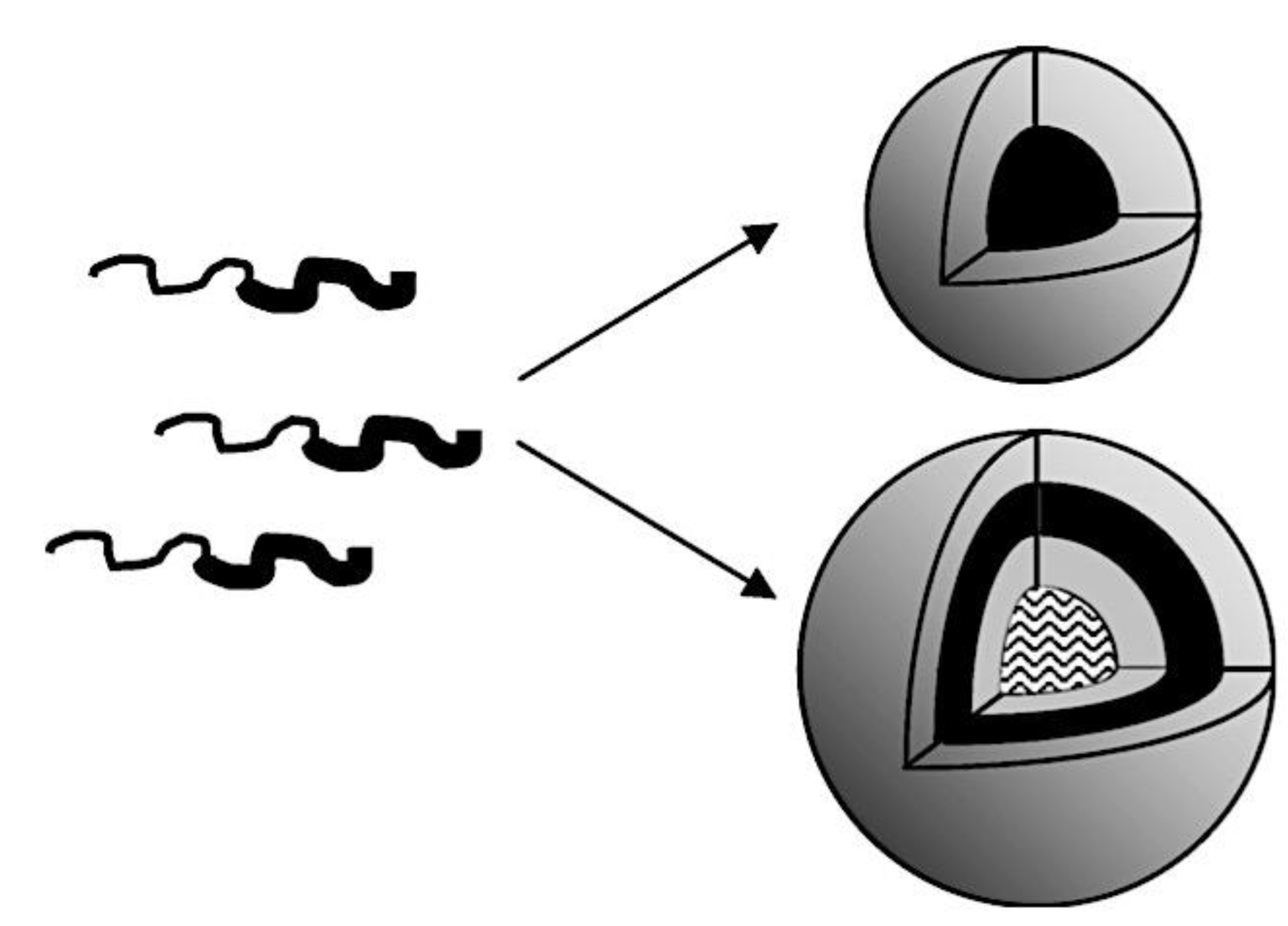
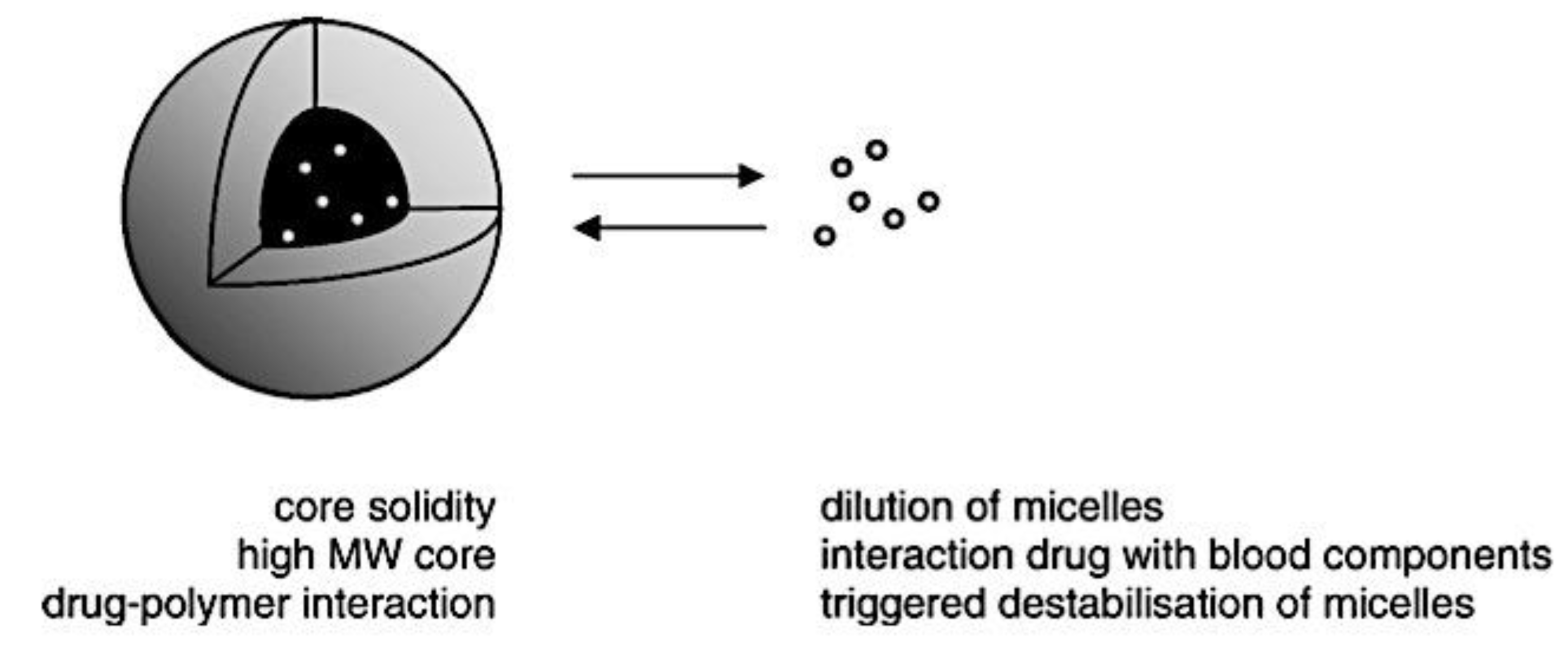
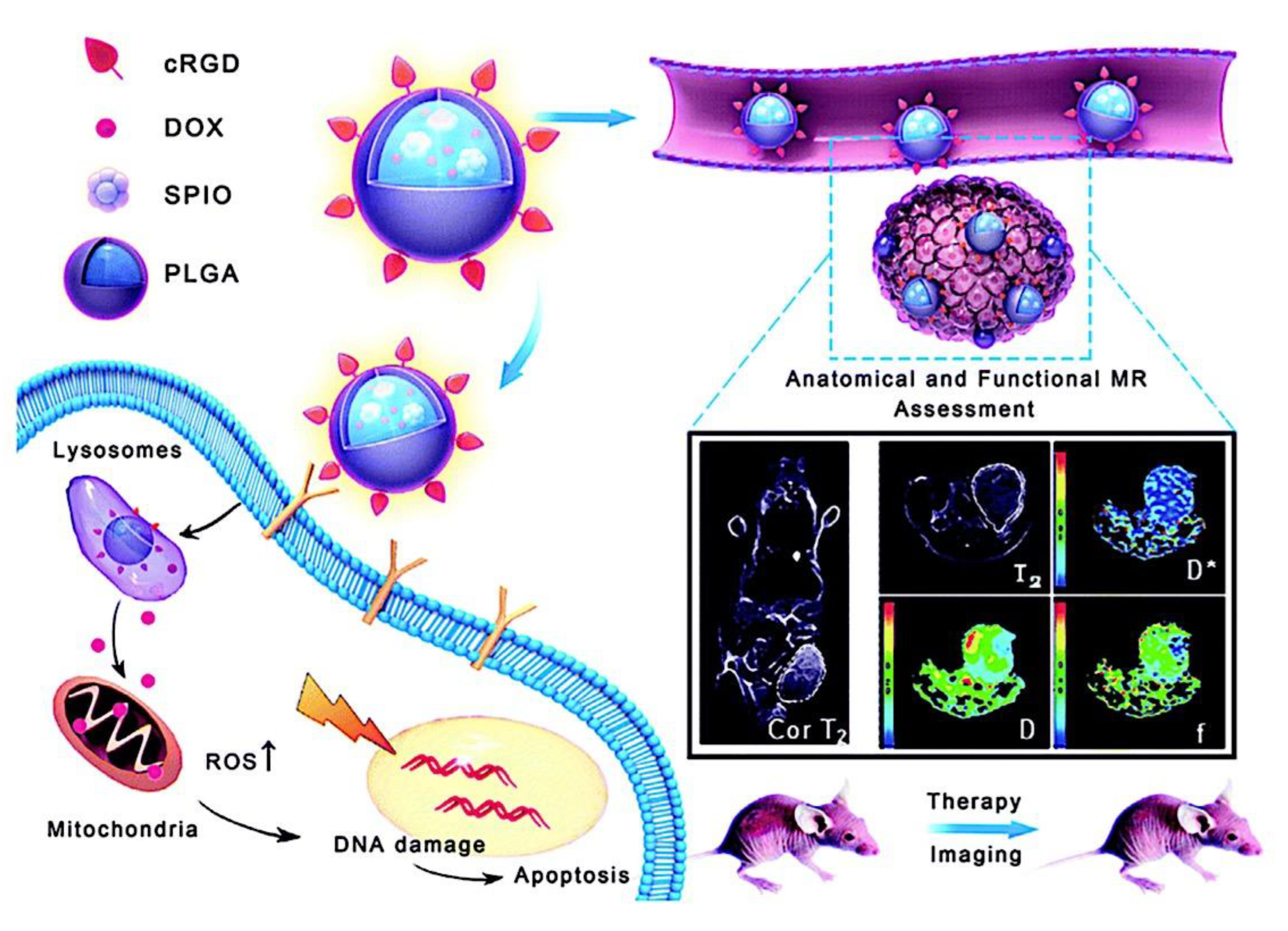
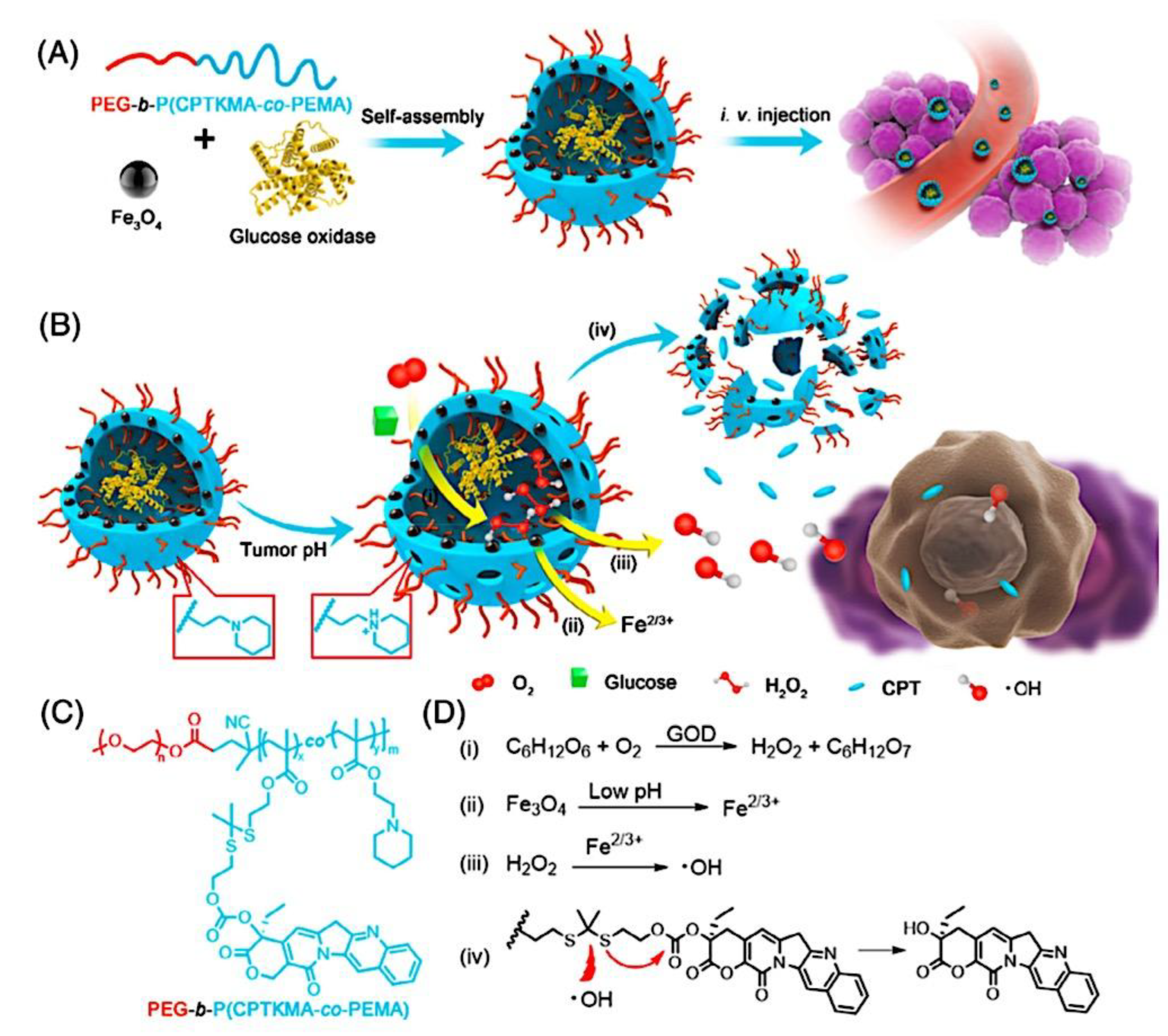
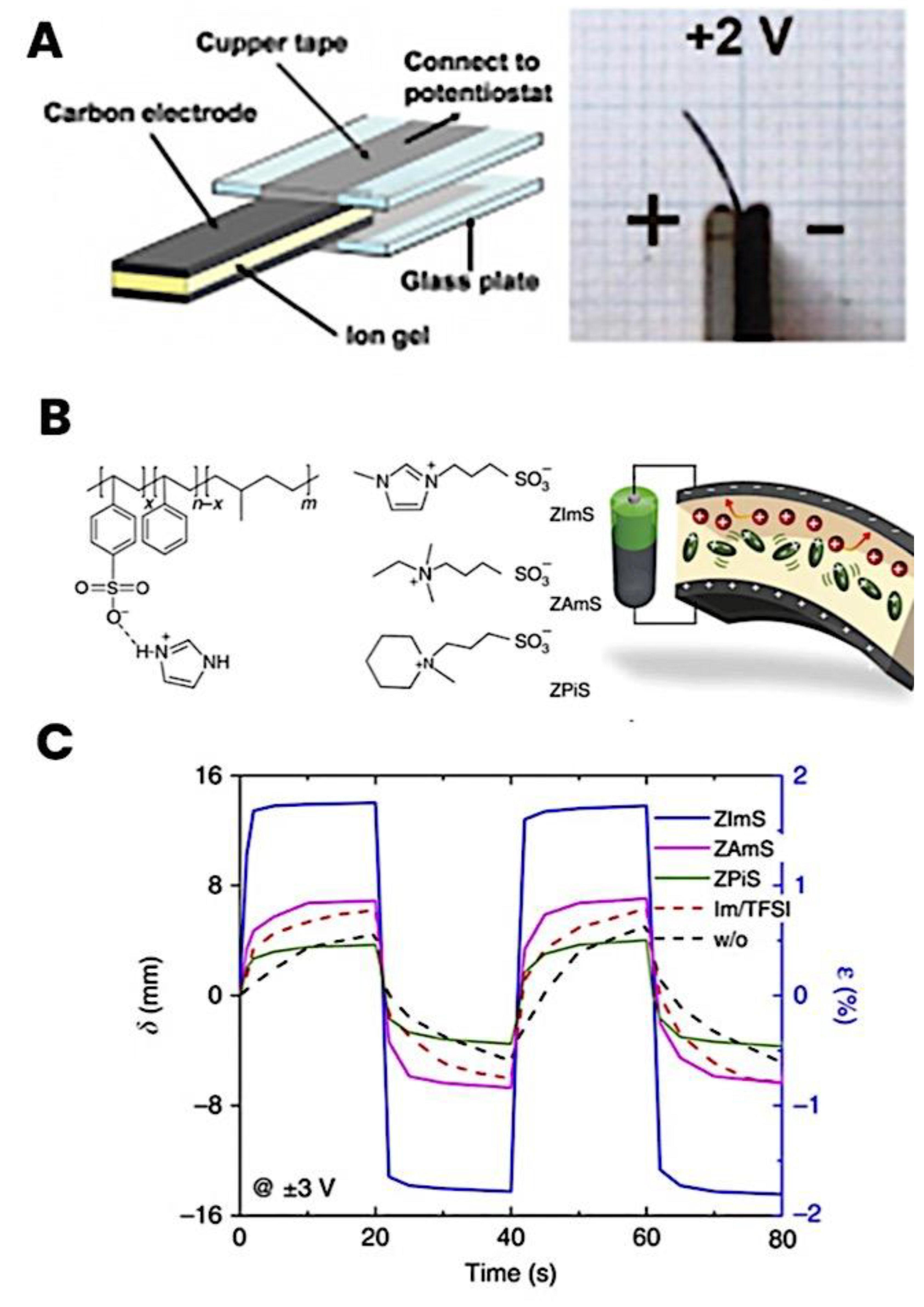

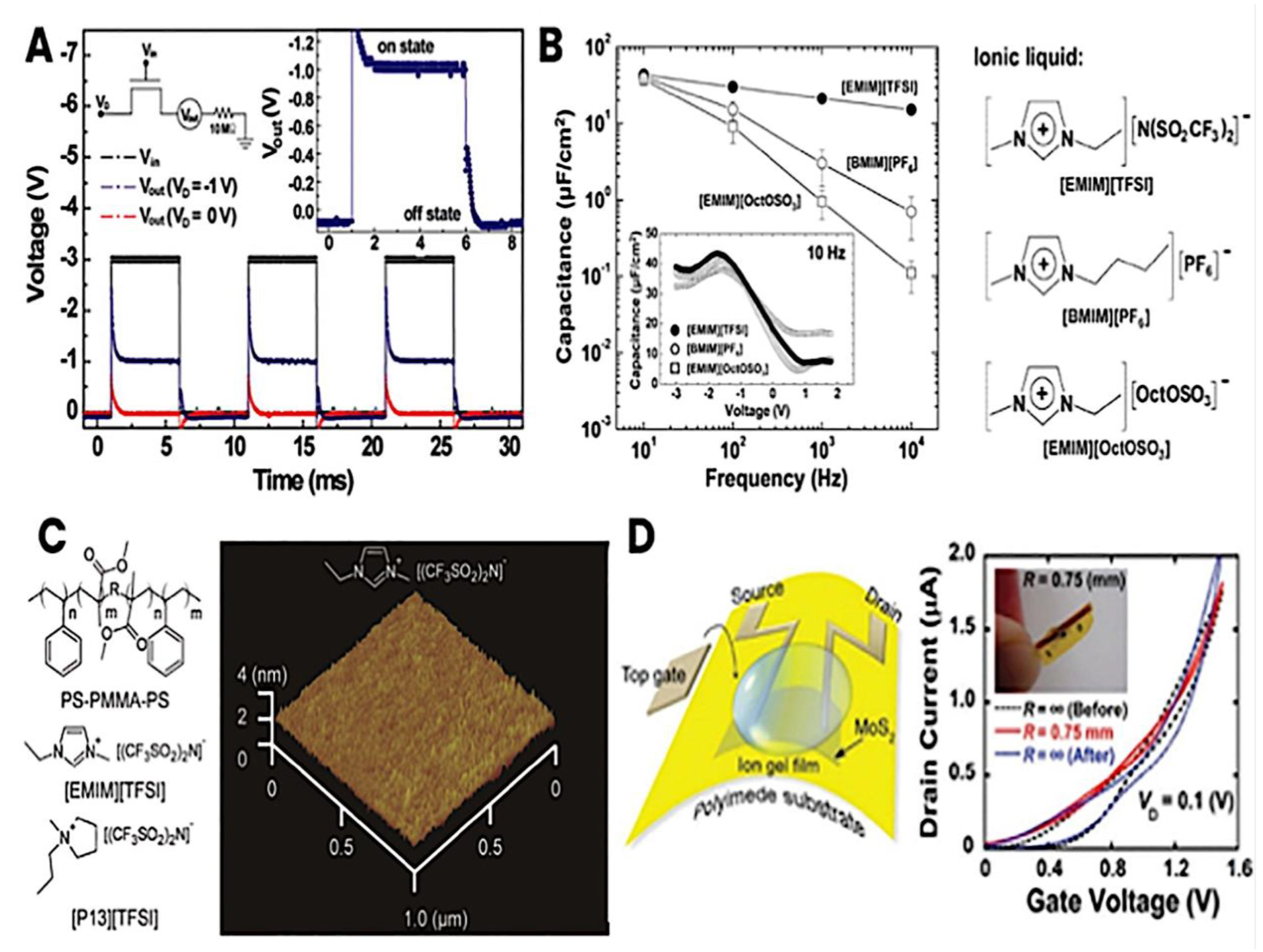
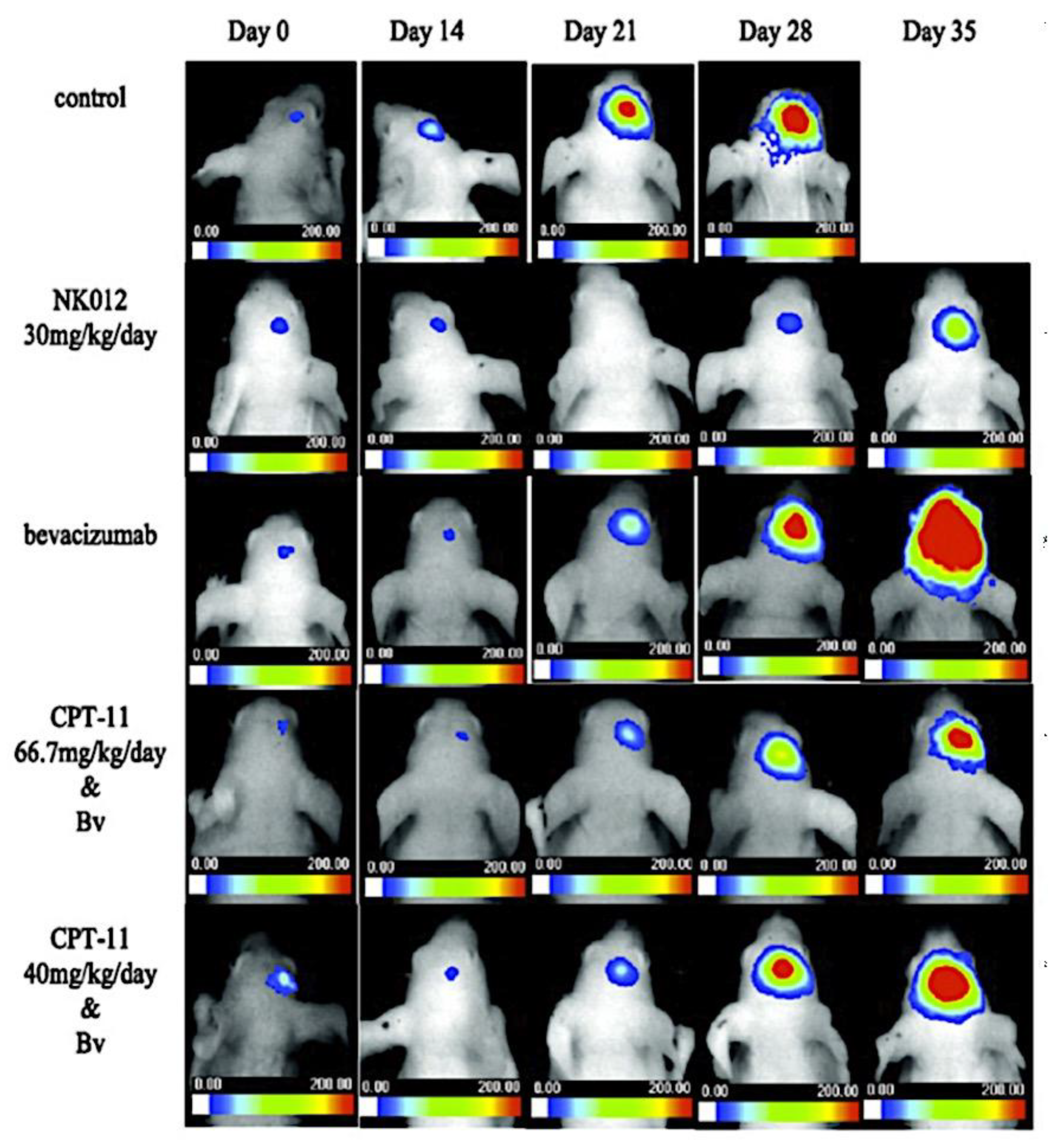
| Polymer | Abbreviation | Chemical Structure | References |
| Poly(vinyl alcohol) | PVA | 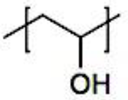 |
[508] |
| Poly(ethylene) glycol | PEG | 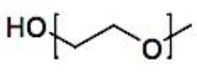 |
[428,468,469,470,471,472,473,474,475,476,477,478,487,498] |
| Poly(2-ethyl-2- oxazoline) | PEOx |  |
[508,509,510,511,512] |
| Poly(N- vinylpyrrolidone) | PVP | 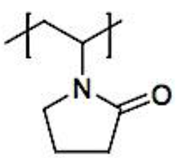 |
[450,511,513,514,515,516,517] |
| Poly(acrylamide) | pAAm | 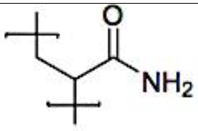 |
[426,482] |
| Poly(N-(2- hydroxypropyl) methacrylamide) | pHPMAm | 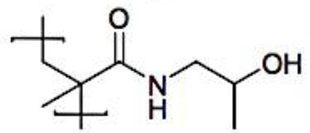 |
[516] |
| Dextran | Dex | 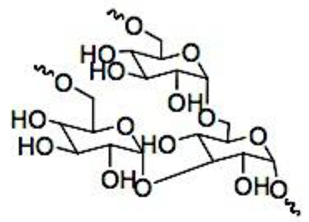 |
[518,519] |
| Polymer | Abbreviation | Chemical Structure | Reference |
| poly(methacryl- amide- oligolactates) | p(HEMAm- Lacn)or p(HPMAm- Lacn) | 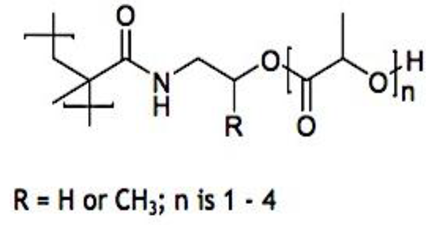 |
[476,477] |
| poly( -benzyl L- glutamate) or poly( -benzyl L- aspartate) | PBLG or PBLA |  |
[539,551,552,553] |
| poly(N- isopropylacryl- amide) | pNIPAAm |  |
[478,554] |
| poly(propylene oxide) | PPO |  |
[428,439,555] |
| poly(lactic acid) | PLA |  |
[450,556] |
| poly( - caprolactone) | PCL |  |
[417,468,517] |
| Degradable group | Structure | Degradation products | Reference |
| Acetal |  |
 |
[656] |
| Ester |  |
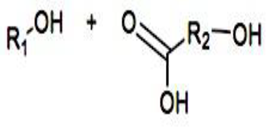 |
[476,650] |
| Hydrazone | 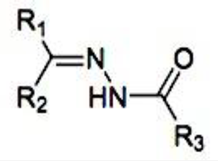 |
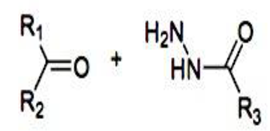 |
[35,534,657] |
| Orthoester | 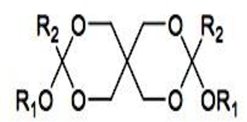 |
 |
[653] |
| Example Triblock | Mn [g mol-1] | ĐM [a] | Synthetic Route | Refs |
| PDMAEMA8-b-PLMA39-b-POEGMA8 | 15,600 [b] | 1.19 | Sequential RAFT | [941] |
| PEO120-b-PHEMA11-b-PtBA46 | 17600 [b] | 1.3 | Sequential ATRP | [942] |
| PS51-b-PB28-b-PtBMA21 | 104,000 [b] | 1.07 | Sequential AP | [943] |
| PEO42-b-PAGE15-b-PtBGE12 | 3400 [b] | 1.07 | Sequential AROP | [944] |
| PODFOx20-b-PEPOx20-b-PEtOx40 | 7900 [c] | 1.12 | Sequential CROP | [945] |
| PE20-b-PEO20-b-PCL10 | 2540 [b] | 1.23 | ROP | [946] |
| PEO44-b-PEtOx263-b-PCL175 | 46,600 [b] | 1.31 | CROP + ROP | [947] |
| PEO45-b-PCL103-b-PMOXA4 | 14,000 [b] | 1.14 | ROP + CROP | [948] |
| PEO45-b-PDMS40-b-PMOXA67 | 13,070 [b] | Not recorded | AROP + CROP | [949] |
| PEEP135-b-PCL50-b-PDMAEMA118 | 44,900 [b] | 1.31 | AROP + ROP + ATRP | [950] |
| PEO45-b-PMCL47-b-PDMAEMA31 | 12,890 [b] | 1.25 | ROP + ATRP | [951] |
| PEO30-b-PS90-b-PCL62 | 19,600 [b] | 1.09 | ATRP + ROP + Click | [952] |
| Particle | CEAC | PMC | CECC |
| SCP- | maximum | 0 | 0 |
| CCCM | 0 | maximum | 0 |
| SCP+ | 0 | 0 | maximum |
| temp. (°C) | [salt] (mM) | τ (min) | β |
| 20 | 500 | 61.5 | 2.00 |
| 37 | 500 | 52.2 | 2.00 |
| 57 | 500 | 39.2 | 2.00 |
| 20 | 300 | 51.9 | 0.82 |
| 20 | 400 | 35.2 | 1.43 |
| 20 | 500 | 27.4 | 2.03 |
| 20 | 600 | 10.9 | 1.94 |
| Formulation | Stimulas/Ligand | Bioactive Compound | Block Copolymer | Intended Target/Function | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug Delivery | |||||
| Micelle | Hypoxia | DOX | PEG-b-P(LG-g-MN) | Tumor chemoradiotherapy | [1331] |
| Micelle | pH | DAVBNH | Functionalized PEG-PAA | Glioblastoma | [1332] |
| Micelle | pH, light, and redox | Nile red | PAA-b-P (AzoMA-co- PEGMA) | Multi-responsiveness | [1333] |
| Micelle | Light, temperature, and pH | DOX | PDMAEMA-PMMA (with spiropyran chain end groups) | Multi-responsiveness | [1334] |
| Micelle | Hypoxia, temperature, and pH | DOX | P(MAA-co-NIMA)-b- PDMAEMA | Multi-responsiveness | [1335] |
| Spherical and filamentous micelles | pH | Verteporfin | PEG-PBAE-PEG | Breast and lung cancer | [1336] |
| Spherical and worm-like micelles | Valsartan | PLGA-PEG | Hypertension | [1337] | |
| Polymersome | Redox/ cNGQGEQc peptide | DOX | PEG-P(TMC-DTC) | Lung cancer | [1338] |
| Polymersome | pH and redox | Rhodamine B | PEG-P(DIPEMA-co-CBMA) | Drug delivery | [1339] |
| Polymersome | pH | DOX | PHPMA-b-PDPA | Lymphoma | [1340] |
| Gene Delivery | |||||
| PIC micelle | cRGD peptide | siRNA | PEG-PLL | Cervical cancer | [1341] |
| Mixed polyplex micelle | Temperature | pDNA | PEG- and PNIPAM-b-PAsp (DET) | Disc degeneration-associated diseases | [1342] |
| Core-shell- corona micelle | pH | siRNA and cisplatin | PEG-b-PAGA-b-PDPA | Breast cancer | [1343] |
| Mixed micelleplex | PD-L1 | siRNA and PTX | PCL-PEG and PCL-PEI | Melanoma | [1344] |
| Polyplex micelle | bundled mRNA | PEG-PLys | Improved mRNA delivery | [1345] | |
| PIC micelle | mRNA | PEG-PGBA or PEG-PLL | Improved mRNA delivery | [1346] | |
| Mixed polyplex micelles | pH and temperature | DNA | PVAm-b-PALysOH and PVAm-b-PNIPAM | DNA delivery | [1347] |
| Protein/Enzyme Delivery | |||||
| Vesicle | H2O2 and glucose | Glucose oxidase and insulin | mPEG-b-P(Ser-PBE) | Glucose regulation | [1348] |
| Mixed micelle | Insulin | PEO-b-PCL-b-PEO and PDMAEMA-b-PCL-b- PDMAEMA | Insulin delivery | [1349] | |
| PIC micelle | pH | SDF-1α | PEG-PUASM | Neuro-restoration | [1350] |
| PIC micelle | IgG (charge-converted | PEG-PAsp(DET) | Antibody delivery | [1351] | |
| PIC micelle | BDNF | PEG-PLE | Brain delivery and neuroprotection | [1048] | |
| PIC micelle | pH and redox | 3D6-Fab antibody | PEG-PLL | Brain delivery and amyloid b peptide inhibition | [1352] |
| PIC micelle | pH | Myoglobin | PEG-P(Lys-CDM) | Protein delivery | [1353] |
| Therapy and Diagnosis | |||||
| Micelle | pH | DOX | PEG-b-P(DPA/DBA-co- DTM) | Tumor chemotherapy and fluorescence imaging |
[1354] |
| Micelle | pH and hypoxia | DOX | PEG-PAA linked with metronidazole | Tumor chemoradiotherapy and fluorescence imaging |
[1355] |
| Micelle | pH | PTX and SPIONs | mPEG-b-PAsp(DIP)-co- PLLeu | Hepatocellular carcinoma treatment and MRI | [1356] |
| Micelle | pH and GSH | DOX and Au NPs | PCL-SS-PDMAEMA (SS: disulfide bond) | Cancer chemotherapy and CT imaging | [1357] |
| Micelle | Enzyme | DOX | mPEG-b-P(AA-g-TPE) | Tumor chemotherapy and fluorescence imaging | [1358] |
| Mixed micelleplex | SN-38, USPIO and VEGF siRNA | PDMA-b-PCL | Colorectal cancer gene silencing, chemotherapy and MRI | [1359] | |
| Vesicle | Folic acid | Gd and DOX | FA/DTPA-PGA-PCL | Cancer chemotherapy and MRI | [1360] |
| Polymersome | Temperature and pH | siRNA and pDNA | PEO-b-P(NIPAM-stat-CMA-stat-DEA) | Gene delivery and fluorescence imaging | [1361] |
| Target | Target location | Targeting molecule | Examples of incorporation onto micelles |
|---|---|---|---|
| αv β3 integrin | Tumor vasculature[1438] Glioma cells[1438] | RGD peptide[1439] | [1426,1429,1430,1431,1440,1441,1442,1443,1444,1445] |
| Fibrin deposits | Tumor vasculature [1446] Tumor stroma[1446,1447] | CREKA Peptide[1446] | [1448,1449] |
| Aminopeptidase N | Tumor vasculature[1450] | NGR peptide [1450,1451] | [1452] |
| Transferrin receptor | CNS vasculature[1453] | Transferrin[1453] Lactoferrin[1454] Aptamer[1455] | [1445,1454,1455,1456,1457] |
| nAchR | CNS vasculature[1458,1459] | Candoxin-derived peptide[1460] | [1431,1460] |
| EGFR | Glioma cells[1461] | Anti-EGFR Antibody[1462] EGa1[1463] | [1462,1464] |
| LRP1 | Glioma cells,[1465,1466] Neurons[1467] | Angiopep2[1468] | [1469] |
| Unknown | Glioma cells[1470] | GMT8 aptamer[1432,1470] | [1432] |
| Representative BCPs | Representative IL Cations | Applications | Working principle |
|---|---|---|---|
| PEO-based polymer (PS-PEO, PEO-PMMA) | AILs with cations and anions of alkyl pyrrolidinium, alkyl imidazolium, and alkyl sulfonium can differ. | Lithium batteries | By acting as a plasticizer, ILs can quicken the relaxation of polymer chains, which lowers the polymers' glass transition temperature (Tg). |
| PVDF-PHFP | |||
| NafionTM | AILs are made up of short alkyl chains of heterocyclic diazonium or alkyl imidazolium. Different cations and anions exist. | Fuel cell | One easy way to achieve high conductivity at high temperatures and without water is to incorporate nonvolatile, highly conductive ILs into polymer matrices. |
| PBI | |||
| PVDF-HFP | |||
| PMMA (and PMMA based copolymers | |||
| P2VP (and P2VP based copolymers) | |||
| PSS (and PSS based copolymers) | |||
| PVDF-PHFP | Electroactive Actuators | By lowering Young's modulus, promoting ion transport, and strengthening electrochemical stability, adding IL to the actuator's ionic polymer layer can enhance performance. | |
| NafionTM | |||
| Bi or triblock ABCs that can form micelles or vesicles in ILs | PILs as well as AILs. | Nanoreactor | In ILs, BCPs have the ability to self-assemble into vesicles or micelles, which can be employed as nanodelivery vehicles. |
| Triblock copolymers (PS-PEO-PS,PPO-PEO-PPO, PEO-PPO-PEO) | AILs containing cations and anions of alkyl imidazolium can differ. EAN is the PIL reported. | Wearable electronics | Wearable electronics applications can benefit from the ultra-stretchability and high ion conductivity of iono-elastomers made of self-assembled BCPs in ILs. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




