Submitted:
08 October 2025
Posted:
09 October 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
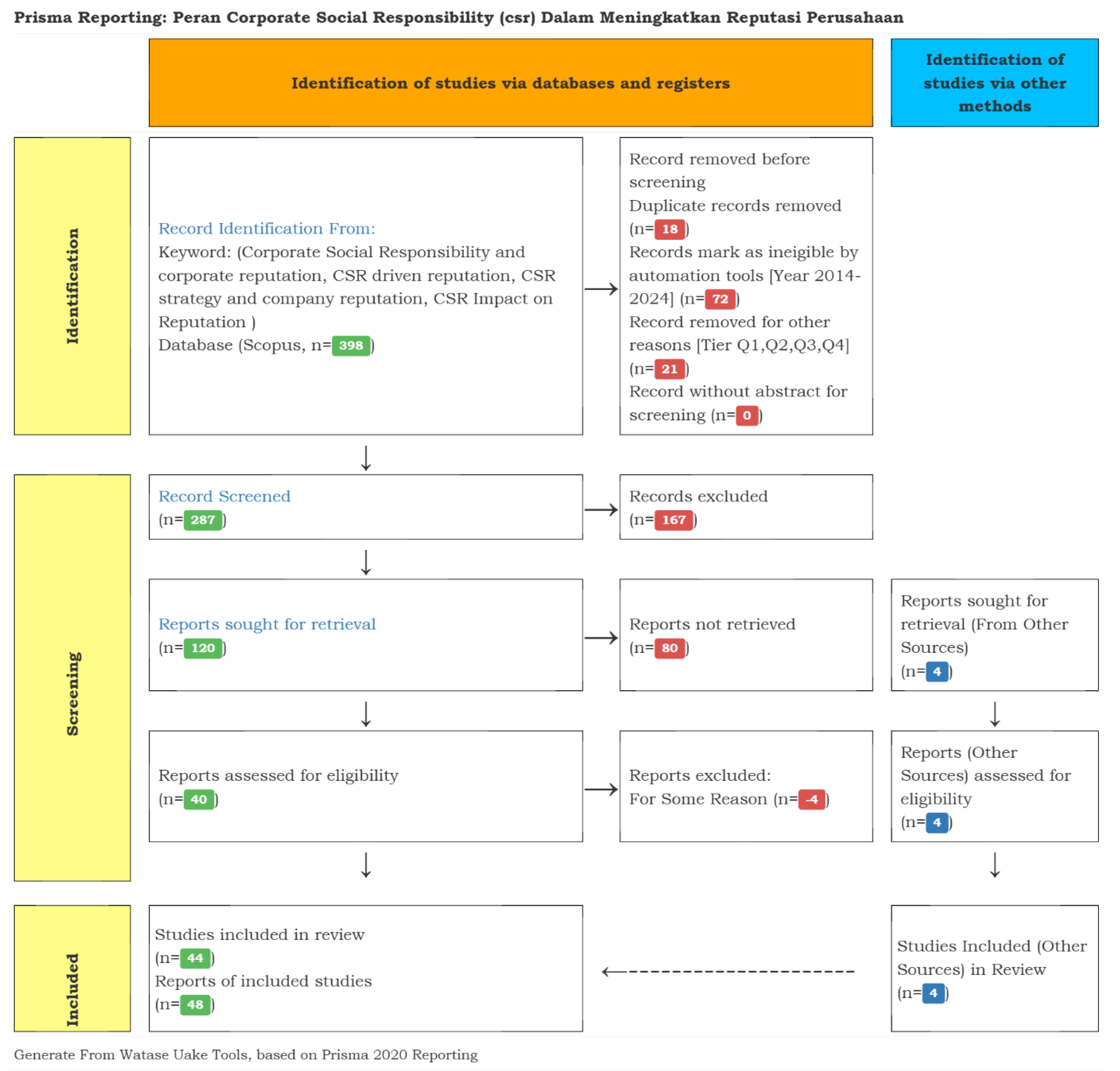
1.1. Identification of Records
2.2. Screening Identification
2.3. Inclusion of Records (Step 3)
3. Results
3.1. Results
| Authors | Title | Journal | Results |
| Park, 2019 | Corporate social responsibility as a determinant of corporate reputation in the airline industry | Journal of Retailing and Consumer | This study found that higher levels of economic responsibility resulted in increased customer attitudes and satisfaction. In addition, although environmental responsibility had a significant effect on customer attitudes and satisfaction, corporate reputation was significantly determined by customer attitudes and satisfaction. |
| Baraibar-Diez & Sotorrío, 2018 | The mediating effect of transparency in the relationship between corporate social responsibility and corporate reputation | Review of Business Management | The proposed model suggests that transparency mediates the path between corporate social responsibility and corporate reputation. |
| Cabrera-Luján et al., 2023 | Impact of Corporate Social Responsibility, Business Ethics and Corporate Reputation on the Retention of Users of Third-Sector Institutions | Sustainability | The results of the study show that CSR has a positive and significant influence on CR, BE on CR, CSR on RT, and CR and BE on RT. |
| Wang et al., 2021 | The Role of Corporate Social Responsibility Perceptions in Brand Equity, Brand Credibility, Brand Reputation, and Purchase Intentions | Sustainability | The results of the study indicate that consumer perceptions of a company’s CSR affect their intention to purchase the company’s brand in the future. Brand equity, brand credibility, and brand reputation mediate the impact of CSR perceptions on purchase intentions. |
| Ali et al., 2024 | Corporate Social Responsibility and Customer Loyalty in Food Chains--Mediating Role of Customer Satisfaction and Corporate Reputation | Sustainability | The results of the study show that CSR perception has a significant positive impact on customer loyalty, corporate reputation, and customer satisfaction. |
| Gálvez-Sánchez et al., 2024 | Exploring the three-dimensional effect of corporate social responsibility on brand equity, corporate reputation, and willingness to pay. A study of the fashion industry | Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services | The results of the study show that each CSR dimension makes a different contribution to the formation of BE, CR and WTP, also highlighting the value of brand credibility as a variable with an important mediating effect. |
| Bianchi et al., 2019 | The impact of perceived CSR on corporate reputation and purchase intention | European Journal of Management and Business | All direct and mediated effects in the model are significant, except for the effect of perceived CSR on affective satisfaction. Thus, the proposed causal chain is essential to understanding how perceived CSR affects purchase intention and perceived reputation. |
| Bashir, 2022 | Corporate social responsibility and financial performance - the role of corporate reputation, advertising and competition | PSU Research Review | Advertising intensity (AI) plays a significant moderating role in the CSR intensity and CR relationship |
| Ajayi & Mmutle, 2020 | Corporate reputation through strategic communication of corporate social responsibility | Corporate Communications: An International Journal | The informing strategy is also more evident in CSR communication materials than the interactive strategy. In terms of communication channels, the study found that organizations mainly use controlled channels for CSR communication. |
| Pérez-Cornejo & de Quevedo-Puente, 2023 | How corporate social responsibility mediates the relationship between corporate reputation and enterprise risk management evidence from Spain | Eurasian Business Review | The results of this study also confirm that the ERM system has a positive impact on corporate reputation through the mediation effect of CSR performance. Therefore, companies should use risk management policies to support their CSR and reputation. |
| Vuong & Bui, 2023 | The role of corporate social responsibility activities in employees’ perception of brand reputation and brand equity | Case Studies in Chemical and Environmental Engineering | The results of the study show that internal and external CSR activities increase employee satisfaction and the implementation of CSR activities supports the improvement of brand reputation and adds brand equity value. |
| Singh & Misra, 2021 | Linking Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) and Organizational Performance the moderating effect of corporate reputation | European Research on Management and Business Economics | The research results show that CSR carried out towards external stakeholders will have an impact on organizational performance. |
| Grover et al., 2019 | Impact of corporate social responsibility on reputation--Insights from tweets on sustainable development goals by CEOs | International Journal of Information Management | The results revealed that social media influential CEOs posted 5.97 times more CSR messages on Twitter than wealthy CEOs, which in turn may result in better CR, in terms of shares and likes based on the social capital they have on Twitter. |
| García-Madariaga & Rodríguez-Rivera, 2017 | Corporate social responsibility, customer satisfaction, corporate reputation, and firm market value Evidence from the automobile industry | Spanish Journal of Marketing - ESIC | The results of the study indicate that certain CSR issues related to the company’s core business and important stakeholders can result in better company financial performance. |
| Gallardo-Vázquez et al., 2019 | Corporate Social Responsibility as an Antecedent of Innovation, Reputation, Performance, and Competitive Success A Multiple Mediation Analysis | Sustainability | The results of this study confirm that companies generally have a good orientation towards CSR and the benefits of this strategy are developing and improving the company’s reputation. |
| Mahmood & Bashir, 2020 | How does corporate social responsibility transform brand reputation into brand equity Economic and noneconomic perspectives of CSR | International Journal of Engineering Business Management | The results show that brand reputation is a significant predictor of brand equity, and its predictive power increases with the presence of CSR activities. |
| Baudot et al., 2020 | Is Corporate Tax Aggressiveness a Reputation Threat Corporate Accountability, Corporate Social Responsibility, and Corporate Tax Behavior | Journal of Business Ethics | Drawing on research on celebrity and strategic silence, the study finds that reputation may not be a well-functioning mechanism for holding companies accountable. |
| Kim, 2019 | The Process Model of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) Communication: CSR Communication and its Relationship with Consumers CSR Knowledge, Trust, and Corporate Reputation Perception | Journal of Business Ethics | The findings of this study indicate that the positive impact of CSR information is continuous and independent of the level of consumer identification with the company, while the positive consequences of personal relevance, transparency, and factual tone of CSR communication increase with increasing levels of identification. |
| Axjonow et al., 2018 | The Impact of Corporate Social Responsibility Disclosure on Corporate Reputation A Non-professional Stakeholder Perspective | Journal of Business Ethics | We find that, contrary to popular belief, stand-alone CSR reports do not impact a company’s reputation among non-professional stakeholders. |
| Zhu et al., 2014 | Corporate social responsibility, firm reputation, and firm performance The role of ethical leadership | Asia Pacific Journal of Management | We have two main findings. First, ethical leadership moderates its own indirect effect on corporate reputation through CSR. Ethical leadership has an indirect and positive effect on corporate reputation through CSR when ethical leadership is strong but not when it is weak. |
| Song et al., 2020 | Toward effective CSR communication in controversial industry sectors | Journal of Marketing Communications | We have two main findings. First, ethical leadership moderates its own indirect effect on corporate reputation through CSR. Ethical leadership has an indirect and positive effect on corporate reputation through CSR when ethical leadership is strong but not when it is weak. |
| Dögl & Holtbrügge, 2014 | Corporate environmental responsibility, employer reputation and employee commitment an empirical study in developing and emerging economies | The International Journal of Human | Our research results show that green strategy and culture, green technology and products, green recruitment and evaluation, and green communication have a positive influence on a company’s environmental reputation as an employer and in turn employee commitment. |
| Burke et al., 2018 | The relative impact of corporate reputation on consumer choice: beyond a halo effect | Journal of Marketing Management | The results show that corporate reputation needs more attention by marketing managers to increase preference for their products through this mechanism. |
| Vlastelica et al., 2018 | How Corporate Social Responsibility Affects Corporate Reputation Evidence from an Emerging Market | Journal of East European Management Studies | The results show that CSR items affect corporate reputation. In addition, the intensity of this relationship varies across items. Significant differences were found between citizens and specific stakeholders, as well as between different stakeholder groups. |
| Liu & Lu, 2021 | Corporate social responsibility, firm performance, and firm risk the role of firm reputation | Asia-Pacific Journal of Accounting & Economics | This study documents a significant positive relationship between CSR and corporate reputation, and finds that corporate reputation is positively related to corporate performance while negatively related to corporate risk. |
| González-Rodríguez et al., 2019 | Hotels corporate social responsibility practices, organizational culture, firm reputation, and performance | Journal of Sustainable Tourism | The proposed model is developed using stakeholder theory and general manager perceptions. According to the research results, organizational culture influences various dimensions of CSR. |
| Khuong et al., 2021 | Stakeholders and Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) program as key sustainable development strategies to promote corporate reputation--evidence from Vietnam | Cogent Business & Management | The results of the study show that stakeholder influence not only has a significant effect on the type of CSR but also has a positive impact on the company’s reputation. |
| Komodromos & Melanthiou, 2014 | Corporate Reputation Through Strategic Corporate Social Responsibility Insights From Service Industry Companies | Journal of Promotion Management | The results reveal that CSR has a positive impact on company employees, the environment, stakeholders and the general public, and highlight that CSR is an important element for the success of organizations in the Cypriot market. |
| Lloyd-Smith & An, 2019 | Are corporate social responsibility and advertising complements or substitutes in producing firm reputation | Applied Economics | Our research results also show that advertising, a company’s own CSR activities, and CSR spillover at the industry level contribute positively to corporate reputation. |
| Rothenhoefer, 2019 | The impact of CSR on corporate reputation perceptions of the public--A configurational multi-time, multi-source perspective | Business Ethics: A European Review | Thus, the current study contributes to CSR research by investigating a powerful but under-researched stakeholder group through the lens of category diagnosticity combined with a configurational approach to analysis. |
| Odriozola & Baraibar-Diez, 2017 | Is Corporate Reputation Associated with Quality of CSR Reporting Evidence from Spain | Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management | This study found that the quality of sustainability reporting increases the likelihood of having a higher corporate reputation. |
| Den Hond et al., 2014 | laying on Two Chessboards Reputation Effects between Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) and Corporate Political Activity (CPA) | Journal of Management Studies | This study argues that there is a potential synergy between CSR and corporate political activity (CPA) that is often overlooked by companies and that recognition of this synergy will stimulate companies to align their CSR and CPA. |
| Wei et al., 2014 | Strategically manipulating social reputation by scheduling corporate social responsibility events | Journal of Public Affairs | This study shows that CSR events significantly affect social reputation in the short period after the first CSR event, and then social reputation grows slowly. |
| Fourati & Dammak, 2021 | Corporate social responsibility and financial performance International evidence of the mediating role of reputation | Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management | This study shows that CR mediates the relationship between CSR and CFP: CSR has a significant and positive impact on CR and that CR has a significant and positive impact on CFP. |
| Aljumah, 2023 | Corporate social responsibility’s influence on firm risk and firm performance the mediating role of firm reputation | Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management | |
| Sánchez-Torné et al., 2020 | The importance of corporate social responsibility in achieving high corporate reputation | Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management | This study identified seven dimensions that influence Corporate Reputation: products and services, innovation, workplace, governance, citizenship, leadership, and performance. |
| Miras-Rodríguez et al., 2020 | Does corporate social responsibility reporting actually destroy firm reputation | Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management | This study highlights that corporate reputation tends to be negatively affected by CSR reporting, which is generally identified by stakeholders as an impression management strategy (especially to obtain ‘appropriate’ levels and assurances), although the relationship between CSR reporting and corporate reputation is contingent on a company’s CSR consistency. |
| Javed et al., 2020 | The effects of corporate social responsibility on corporate reputation and firm financial performance Moderating role of responsible leadership | Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management | The results of the study indicate that social responsibility initiatives for different stakeholders significantly and positively affect corporate reputation and financial performance. In addition, the direct relationship between CSR-reputation and CSR-performance is found to be negatively moderated by responsible leadership. |
| Yang & Stohl, 2020 | The (in)congruence of measures of corporate social responsibility performance and stakeholder measures of corporate social responsibility reputation | Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management | This study highlights the importance of taking a multidimensional approach. Addressing the measurement issue helps to uncover the theoretical and practical relationships between CSR and corporate reputation and provides strategic guidance when planning CSR business and communication strategies. |
| Kowalczyk & Kucharska, 2020 | Corporate social responsibility practices incomes and outcomes Stakeholders pressure, culture, employee commitment, corporate reputation, and brand performance. A Polish-German cross-country study | Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management | Key findings suggest that stakeholder pressure can lead to a consistent CSR-oriented system in a business environment. |
| Dell’Atti et al., 2017 | Corporate Social Responsibility Engagement as a Determinant of Bank Reputation: An Empirical Analysis | Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management | The results of this study found that bank reputation is positively related to accounting performance and negatively related to leverage and risk profiles. |
| Graafland, 2018 | Does Corporate Social Responsibility Put Reputation at Risk by Inviting Activist Targeting An Empirical Test among European SMEs | Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management | This study finds that CSR increases the likelihood that SMEs’ CSR will be monitored in the future by local non-governmental organizations (NGOs) and this reduces criticism of SMEs’ CSR. |
| Forcadell & Aracil, 2017 | European Banks Reputation for Corporate Social Responsibility | Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management | Our research findings show that bank efforts to build CSR reputation benefit performance. However, during times of crisis, these efforts do not contribute to increased profits. |
| Abugre & Anlesinya, 2020 | Corporate social responsibility strategy and economic business value of multinational companies in emerging economies The mediating role of corporate reputation | Business Strategy & Development | This study shows that good corporate reputation significantly influences multinational companies’ strategies in combining economic responsibility and business value. |
| Asmara et al., 2023 | Does CSR affect investment efficiency The moderating role of company reputation | PSU Research Review | This study found that CSR activities focused on customers, employees, and the community have a significant impact on INE, as well as other stakeholders, and corporate reputation moderates this relationship. |
| Javed et al., 2020) | Effects of CSR-Related Media Coverage on Corporate Reputation | Corporate Reputation Review | The results show that the effect on reputation is fully mediated by CSR skepticism, and the effect on brand attitude is partially mediated by CSR skepticism. |
| Craddock et al., 2022 | Do environmental CSR practices promote corporate social performance. The mediating role of green innovation and corporate image | Cleaner and Responsible Consumption | The findings of this study indicate that corporate environmental CSR improves corporate social performance through green innovation and corporate image. |
| Singh & Misra, 2021 | Linking Corporate Social Responsibility to Corporate Reputation A Study on Understanding Behavioral Consequences | Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences | These results confirm not only that as an antecedent, CSR has a strong positive impact on CR but also that CR has a strong positive impact on customer, employee, and investor behavior. |
4. Discussion
4.1. The Implementation of CSR Practices Affects the Reputation of Companies in Various Industries
4.2. Effectiveness of CSR Programs in Improving Corporate Reputation
4.3. CSR Implementation Contribute to Strengthening Corporate Reputation in Sustainable Development?
4.4. Influence on Perception of Social Issues
4.5. Influence on Perception of Environmental Issues
5. Conclusions
References
- Bascompta M, Yousefian M, Vintró C, Sanmiquel L, Rodríguez R, Yubero MT. Sustainability Assessment in Mining: A CSR-Based Analysis Model for Social and Environmental Impact. Fudan Journal of the Humanities and Social Sciences [Internet]. 2024;(0123456789). Available from: . [CrossRef]
- Carroll AB. A Three-Dimensional Conceptual Model of Corporate Performance. [Internet]. 1979. Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/303179257.
- Bianchi E, Bruno JM, Sarabia-Sanchez FJ. The impact of perceived CSR on corporate reputation and purchase intention. European Journal of Management and Business Economics. 2019 Oct 3;28(3):206–21.
- García Lara JM, García Osma B, Gazizova I, Khalilov A. Demand-driven corporate social responsibility: Symbolic versus substantive change after environmental disasters. Journal of Corporate Finance. 2025 Sep 1;94.
- He HW, Balmer JMT. A grounded theory of the corporate identity and corporate strategy dynamic: A corporate marketing perspective. Eur J Mark. 2013 Mar;47(3):401–30.
- Rothenhoefer LM. The impact of CSR on corporate reputation perceptions of the public—A configurational multi-time, multi-source perspective. Business Ethics. 2019 Apr 1;28(2):141–55.
- Almeida J, Gonçalves TC. A systematic literature review of investor behavior in the cryptocurrency markets. Vol. 37, Journal of Behavioral and Experimental Finance. Elsevier B.V.; 2023.
- Januari N. Systematic Literatur Review Dengan Metode Prisma: Dampak Teknologi Blockchain Terhadap Periklanan Digital. Jurnal Ilmiah M-Progress. 2024;14(1):1–11.
- Park E. Corporate social responsibility as a determinant of corporate reputation in the airline industry. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services. 2019 Mar 1;47:215–21.
- Baraibar-Diez E, Sotorrío LL. O efeito mediador da transparência na relação entre responsabilidade social corporativa e reputação corporative. Revista Brasileira de Gestao de Negocios. 2018;20(1):5–21.
- Cabrera-Luján SL, Sánchez-Lima DJ, Guevara-Flores SA, Millones-Liza DY, García-Salirrosas EE, Villar-Guevara M. Impact of Corporate Social Responsibility, Business Ethics and Corporate Reputation on the Retention of Users of Third-Sector Institutions. Sustainability (Switzerland). 2023 Feb 1;15(3).
- Wang S, Liao YK, Wu WY, Lê HBK. Hypothesis the role of corporate social responsibility perceptions in brand equity, brand credibility, brand reputation, and purchase intentions. Sustainability (Switzerland). 2021 Nov 1;13(21).
- Ali W, Mahmood Z, Wilson J, Ismail H. The impact of sustainability governance attributes on comprehensive CSR reporting: A developing country setting. Corp Soc Responsib Environ Manag. 2024;31(3):1802–17.
- Gálvez-Sánchez FJ, Molina-Prados A, Molina-Moreno V, Moral-Cuadra S. Exploring the three-dimensional effect of corporate social responsibility on brand equity, corporate reputation, and willingness to pay. A study of the fashion industry. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services. 2024 Jul 1;79.
- Bashir M. Corporate social responsibility and financial performance – the role of corporate reputation, advertising and competition. PSU Research Review. 2022 Nov 1;
- Ajayi OA, Mmutle T. Corporate reputation through strategic communication of corporate social responsibility. Corporate Communications. 2020 Jul 28;26(5):1–15.
- Pérez-Cornejo C, de Quevedo-Puente E. How corporate social responsibility mediates the relationship between corporate reputation and enterprise risk management: evidence from Spain. Eurasian Business Review. 2023 Jun 1;13(2):363–83.
- Vuong TK, Bui HM. The role of corporate social responsibility activities in employees’ perception of brand reputation and brand equity. Case Studies in Chemical and Environmental Engineering. 2023 Jun 1;7.
- Singh K, Misra M. Linking Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) and Organizational Performance: the moderating effect of corporate reputation. European Research on Management and Business Economics. 2021 Jan 1;27(1).
- Grover P, Kar AK, Ilavarasan PV. Impact of corporate social responsibility on reputation—Insights from tweets on sustainable development goals by CEOs. Int J Inf Manage. 2019 Oct 1;48:39–52.
- García-Madariaga J, Rodríguez-Rivera F. Corporate social responsibility, customer satisfaction, corporate reputation, and firms’ market value: Evidence from the automobile industry. Spanish Journal of Marketing - ESIC. 2017 Jul 1;21:39–53.
- Gallardo-Vázquez D, Valdez-Juárez LE, Castuera-Díaz ÁM. Corporate social responsibility as an antecedent of innovation, reputation, performance, and competitive success: A multiple mediation analysis. Sustainability (Switzerland). 2019 Oct 1;11(20).
- Mahmood A, Bashir J. How does corporate social responsibility transform brand reputation into brand equity? Economic and noneconomic perspectives of CSR. International Journal of Engineering Business Management. 2020;12.
- Baudot L, Johnson JA, Roberts A, Roberts RW. Is Corporate Tax Aggressiveness a Reputation Threat? Corporate Accountability, Corporate Social Responsibility, and Corporate Tax Behavior. Journal of Business Ethics. 2020 May 1;163(2):197–215.
- Kim S. The Process Model of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) Communication: CSR Communication and its Relationship with Consumers’ CSR Knowledge, Trust, and Corporate Reputation Perception. Journal of Business Ethics. 2019 Feb 28;154(4):1143–59.
- Axjonow A, Ernstberger J, Pott C. The Impact of Corporate Social Responsibility Disclosure on Corporate Reputation: A Non-professional Stakeholder Perspective. Journal of Business Ethics. 2018 Aug 1;151(2):429–50.
- Zhu Y, Sun LY, Leung ASM. Corporate social responsibility, firm reputation, and firm performance: The role of ethical leadership. Asia Pacific Journal of Management. 2014 Nov 7;31(4):925–47.
- Song B, Wen J, Ferguson MA. Toward effective CSR communication in controversial industry sectors. Journal of Marketing Communications. 2020 Apr 2;26(3):243–67.
- Dögl C, Holtbrügge D. Corporate environmental responsibility, employer reputation and employee commitment: An empirical study in developed and emerging economies. International Journal of Human Resource Management. 2014 Jul;25(12):1739–62.
- Burke PF, Dowling G, Wei E. The relative impact of corporate reputation on consumer choice: beyond a halo effect. Journal of Marketing Management. 2018 Sep 2;34(13–14):1227–57.
- Vlastelica T, Kostic SC, Okanovic M, Milosavljevic M. How corporate social responsibility affects corporate reputation: Evidence from an emerging market. Journal of East European Management Studies. 2018;23(1):10–29.
- Liu M, Lu W. Corporate social responsibility, firm performance, and firm risk: the role of firm reputation. Asia-Pacific Journal of Accounting and Economics. 2021;28(5):525–45.
- González-Rodríguez MR, Martín-Samper RC, Köseoglu MA, Okumus F. Hotels’ corporate social responsibility practices, organizational culture, firm reputation, and performance. Journal of Sustainable Tourism. 2019 Mar 4;27(3):398–419.
- Khuong MN, Truong an NK, Thanh Hang TT. Stakeholders and Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) programme as key sustainable development strategies to promote corporate reputation—evidence from vietnam. Cogent Business and Management. 2021;8(1).
- Komodromos M, Melanthiou Y. Corporate Reputation Through Strategic Corporate Social Responsibility: Insights From Service Industry Companies. Vol. 20, Journal of Promotion Management. Routledge; 2014. p. 470–80.
- Lloyd-Smith P, An H. Are corporate social responsibility and advertising complements or substitutes in producing firm reputation? Appl Econ. 2019 May 3;51(21):2275–88.
- Odriozola MD, Baraibar-Diez E. Is Corporate Reputation Associated with Quality of CSR Reporting? Evidence from Spain. Corp Soc Responsib Environ Manag. 2017 Mar 1;24(2):121–32.
- Den Hond F, Rehbein KA, de Bakker FGA, Lankveld HK Van. Playing on two chessboards: Reputation Effects between Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) and Corporate Political Activity (CPA). Journal of Management Studies. 2014;51(5):790–813.
- Wei J, Wang Y, Zhu W. Strategically manipulating social reputation by scheduling corporate social responsibility events. J Public Aff. 2014;14(2):116–29.
- Fourati YM, Dammak M. Corporate social responsibility and financial performance: International evidence of the mediating role of reputation. Corp Soc Responsib Environ Manag. 2021 Nov 1;28(6):1749–59.
- Aljumah AI. Investigating the Impact of Blockchain Technology on Social Sustainability and the Mediating Role of Ethics and CSR. Sustainability (Switzerland). 2023;15(21).
- Sánchez-Torné I, Morán-Álvarez JC, Pérez-López JA. The importance of corporate social responsibility in achieving high corporate reputation. Corp Soc Responsib Environ Manag. 2020 Nov 1;27(6):2692–700.
- Miras-Rodríguez M del M, Bravo-Urquiza F, Escobar-Pérez B. Does corporate social responsibility reporting actually destroy firm reputation? Corp Soc Responsib Environ Manag. 2020 Jul 1;27(4):1947–57.
- Javed M, Rashid MA, Hussain G, Ali HY. The effects of corporate social responsibility on corporate reputation and firm financial performance: Moderating role of responsible leadership. Corp Soc Responsib Environ Manag. 2020 May 1;27(3):1395–409.
- Yang Y, Stohl C. The (in)congruence of measures of corporate social responsibility performance and stakeholder measures of corporate social responsibility reputation. Corp Soc Responsib Environ Manag. 2020 Mar 1;27(2):969–81.
- Kowalczyk R, Kucharska W. Corporate social responsibility practices incomes and outcomes: Stakeholders’ pressure, culture, employee commitment, corporate reputation, and brand performance. A Polish–German cross-country study. Corp Soc Responsib Environ Manag. 2020 Mar 1;27(2):595–615.
- Dell’Atti S, Trotta A, Iannuzzi AP, Demaria F. Corporate Social Responsibility Engagement as a Determinant of Bank Reputation: An Empirical Analysis. Corp Soc Responsib Environ Manag. 2017 Nov 1;24(6):589–605.
- Graafland J. Does Corporate Social Responsibility Put Reputation at Risk by Inviting Activist Targeting? An Empirical Test among European SMEs. Corp Soc Responsib Environ Manag. 2018 Jan 1;25(1):1–13.
- Forcadell FJ, Aracil E. European Banks’ Reputation for Corporate Social Responsibility. Vol. 24, Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management. John Wiley and Sons Ltd.; 2017. p. 1–14.
- Abugre JB, Anlesinya A. Corporate social responsibility strategy and economic business value of multinational companies in emerging economies: The mediating role of corporate reputation. Business Strategy and Development. 2020 Mar 1;3(1):4–15.
- Asmara TTP, Murwadji T, Kartikasari, Afriana A. Corporate Social Responsibility and Cooperatives Business Sustainability in Indonesia: Legal Perspective. Sustainability (Switzerland). 2023;15(7).
- Craddock N, Spotswood F, Rumsey N, Diedrichs PC. “We should educate the public that cosmetic procedures are as safe as normal medicine”: Understanding corporate social responsibility from the perspective of the cosmetic procedures industry. Body Image. 2022 Dec 1;43:75–86.
- Ali W, Danni Y, Latif B, Kouser R, Baqader S. Corporate social responsibility and customer loyalty in food chains—mediating role of customer satisfaction and corporate reputation. Sustainability (Switzerland). 2021 Aug 2;13(16).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




