Submitted:
08 October 2025
Posted:
08 October 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
A Brief History of the Active Anaerobic Brain
A Brief History of the Active Aerobic Brain
The Brain on Oxygen
To Breathe or Not to Breathe?
Epilogue
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgement
References
- Schurr, A.; West, C.A.; Rigor, B.M. Lactate-supported synaptic function in the rat hippocampal slice preparation. Science, 1988, 240, 1326–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, P.T.; Raichle, M.E.; Mintun, M.A.; Dence, C. Nonoxidative glucose consumption during focal physiologic neural activity. Science, 1988, 241, 462–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warburg, O. On the origi,n of cancer cells. Science, 1956, 123, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellerin, L.; Magistretti, P.J. (1994). Glutamate uptake into astrocytes stimulates aerobic glycolysis: a mechanism coupling neuronal activity to glucose utilization. Proc Nat Acad Sci. 1994, 91, 10625–10629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schurr, A. The feud over lactate and its role in brain energy metabolism: An unnecessary burden on research and the scientists who practice it. Internat J Mol Sci, 2025, 26, 4429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dienel, G.A.; Rothman, D.L.; Mangia, S. A bird’s-eye view of glycolytic upregulation in activated brain: The major fate of lactate is release from activated tissue, not shuttling to nearby neurons. J Neurochem, 2025, 169, e70111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y. : Wilson, G.S. A temporary local energy pool coupled to neuronal activity: fluctuations of extracellular lactate levels in rat brain monitored with rapid-response enzyme-based sensor. J Neurochem. 1997, 69, 1484–1490. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bolaños, J.P.; Alberini, C.M.; Almeida, A. Barros, L.F.; Bonvento, G.; Bouzier-Sore, A. K.; Dringen, R.; Hardingham, G,E,; Hirrlinger, J.; Magistretti, P.J.; Marsicano, G.; Nave, K.A.; Paolicelli, R.C.; Pellerin, L.; Plaçais, P-Y.; Preat, T.; Rouach, N.; Ruminot, I.; Saab, A.S.; Sandi, C.; Schirmeier, S.; Schurr, A.; Sierralta, J.; Solas, M.; Tepavcevic, V.; BWeber, B.; Zimmer, E.R. Embracing the modern biochemistry of brain metabolism. J. Neurochem, 2025, 169, e70166.
- Hu, Y.; Wilson, G.S. A temporary local energy pool coupled to neuronal activity: fluctuations of extracellular lactate levels in rat brain monitored with rapid-response enzyme-based sensor. J. Neurochem. 1997, 69, 1484–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelli, A.M. : Scholkmann, F. The Significance of Lipids for the Absorption and Release of Oxygen in Biological Organisms. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023, 1438, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vervust, W.; Safaei, S.; Witschas, K.; Leybaert, L.; Myelin sheaths can act as compact temporary oxygen storage units as modeled by an electrical RC circuit model. 2025, 122, e2422437122. [CrossRef]
- Schurr, A. Glycolysis paradigm shift dictates a reevaluation of glucose and oxygen metabolic rates of activated neural tissue. Front Neurosci, 2018, 12, 700. [CrossRef]
- Schurr, A.; Passarella, S. (2022). Aerobic glycolysis: a DeOxymoron of (neuro) biology. Metabolites, 2022, 12, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schurr, A. How the ‘aerobic/anaerobic glycolysis’ meme formed a ‘habit of mind’ which impedes progress in the field of brain energy metabolism. Internat J Mol Sci, 2024, 25, 1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prichard, J.; Rothman, D.; Novotny, E.; Petroff, O.; Kuwabara, T.; Avison, M.; Howseman, A.; Hanstock, C.; Shulman, R. Lactate rise detected by 1H NMR in human visual cortex during physiologic stimulation. Proc Nat Acad Sci, 1991, 88, 5829–5831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raichle, M.E. The metabolic requirements of functional activity in the human brain: A Positron emission tomography study. In: Vranic, M., Efendic, S., Hollenberg, C.H. (eds) Fuel Homeostasis and the Nervous System. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, 1991, vol 291. Springer, Boston, MA. [CrossRef]
- Fellows, L.K.; Boutelle, M.G. : Fillenz, M. Physiological stimulation increases nonoxidative glucose metabolism in the brain of the freely moving rat. J Neurochem 1993, 60, 1258–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shulman, R.G. : Blamire, A.M.: Rothman, D.L.: McCarthy, G. (1993). Nuclear magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy ofhuman brain function. Proc Nat Acad Sci, 1993, 90, 3127–3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, E.G.; Holmes, B.E. Contributions to the Study of Brain Metabolism: Carbohydrate Metabolism. Biochem J. 1925, 19, 836–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, E.G.; Holmes, B.E. Contributions to the study of brain metabolism: carbohydrate metabolism relationship of glycogen and lactic acid. Biochem J. 1926, 20, 1196–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, B.E.; Holmes, E.G. Contributions to the Study of Brain Metabolism. IV: Carbohydrate Metabolism of the Brain Tissue of Depancreatised Cats. Biochem J. 2027, 21, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashford, C.A.; Holmes, E.G. Contributions to the study of brain metabolism: Rôle of phosphates in lactic acid production. Biochem J. 1929, 23, 748–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, E.G.; Ashford, C.A. Lactic acid oxidation in brain with reference to the “Meyerhof cycle. ” Biochem J. 1930, 24, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, E.G. Oxidations in central and peripheral nervous tissue. Biochem J. 1930, 24, 914–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, E.G. The relation between carbohydrate metabolism and the function of the grey matter of the central nervous system. Biochem J. 1933, 27, 523–536. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schurr, A. (2006). Lactate: the ultimate cerebral oxidative energy substrate? J Cereb Blood Flow Metab, 2006, 26, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kety, S.S.; Schmidt, C.F. The nitrous oxide method for the quantitative determination of cerebral blood flow in man: theory, procedure and normal values. J clin invest, 1948, 27, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kety, S.S. The general metabolism of the brain in vivo. In; Metabolism of the nervous system, Derek Richter, Ed. Pergamon Press, London, New York, Paris, Los Angeles, 1957, pp 221-235.
- Ogawa, S.; Lee, T.M.; Kay, A.R.; Tank, D.W. (1990). Brain magnetic resonance imaging with contrast dependent on blood oxygenation. Proc Nat Acad Sci, 1990, 87, 9868-9872. [CrossRef]
- Buxton, R.B.; Frank, L.R. A model of the coupling between cerebral blood flow and oxygen metabolism during neural stimulation. J. Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1997, 17: 64–72. [CrossRef]
- Gjedde, A. The relation between brain function and cerebral blood flow and metabolism. In: Cerebrovascular Disease, edited by H. H Batjer. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott-Raven, 1997, p.23–40.
- Hyder, F.; Shulman, R.G.; Rothman, D.L. A model for the regulation of cerebral oxygen delivery. J Appl Physiol, 1998, 85, 554–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theriault, J.E.; Shaffer, C.; Dienel, G.A.; Sander, C.Y.; Hooker, J.M.; Dickerson, B.C.; Feldman Barrett, L.; Quigley, K.S. A functional account of stimulation-based aerobic glycolysis and its role in interpreting BOLD signal intensity increases in neuroimaging experiments. ” Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2023, 153, 105373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dienel, G.A. Astrocytic energetics during excitatory neurotransmission: what are contributions of glutamate oxidation and glycolysis? Neurochem Internt, 2013, 63, 244-258. [CrossRef]
- Ohno, N.; Kidd, G.J.; Mahad, D.; Kiryu-Seo, S.; Avishai, A.; Komuro, H.; Trapp, B.D. Myelination and axonal electrical activity modulate the distribution and motility of mitochondria at CNS nodes of Ranvier. J Neuroscience, 2011, 31, 7249–7258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perge, J.A.; Koch, K.; Miller, R.; Sterling, P.; Balasubramanian, V. How the optic nerve allocates space, energy capacity, and information. J Neurosci, 2009, 29, 7917–7928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacci, M.K.; Bartlett, C.A.; Huynh, M.; Kilburn, M.R; Dunlop, S.A.; . Fitzgerald, M. Three dimensional electron microscopy reveals changing axonal and myelin morphology along normal and partially injured optic nerves. Sci Rep. 2018, 8, 3979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patsatzis, D.G.; Tingas, E-A.; Sarathy, S.M; Goussis, D.A.; Jolivet, R.B. Elucidating reaction dynamics in a model of human brain energy metabolism. PLoS Comput Biol 2025, 21, e1013504. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koep, J.L.; Duffy, J.S.; Carr, J.M.J.R.; Brewster, M.L.; Bird, J.D.; Monteleone, J.A.; Monaghan, T.D.R.; Islam, H.; Steele, A.R.; Howe, C.A.; MacLeod, D.B.; Ainslie, P.N.; Gibbons, T,D. Preferential lactate metabolism in the human brain during exogenous and endogenous hyperlactataemia. J. Physiol. 2025, 0.0, 1-18. [CrossRef]
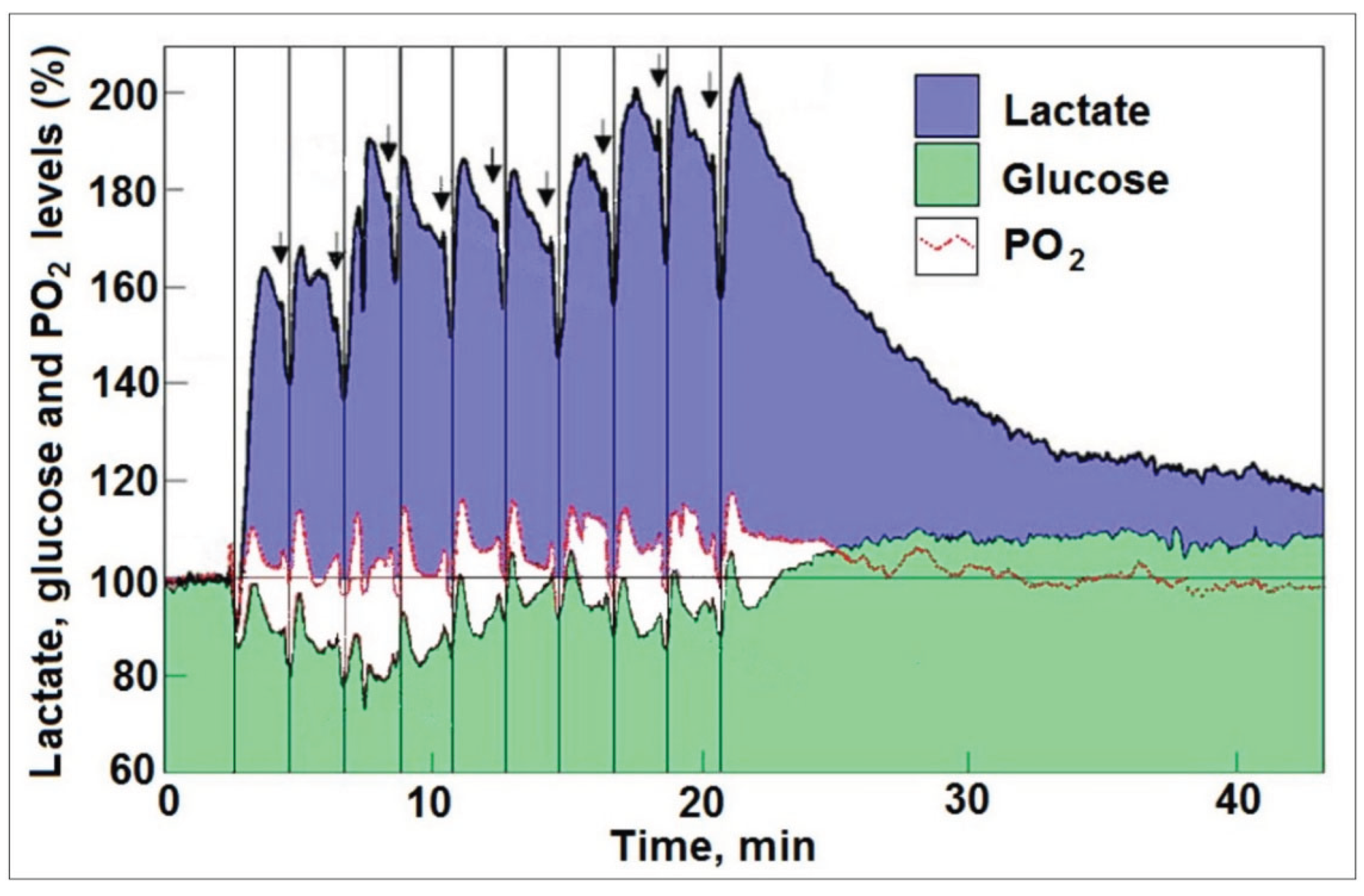
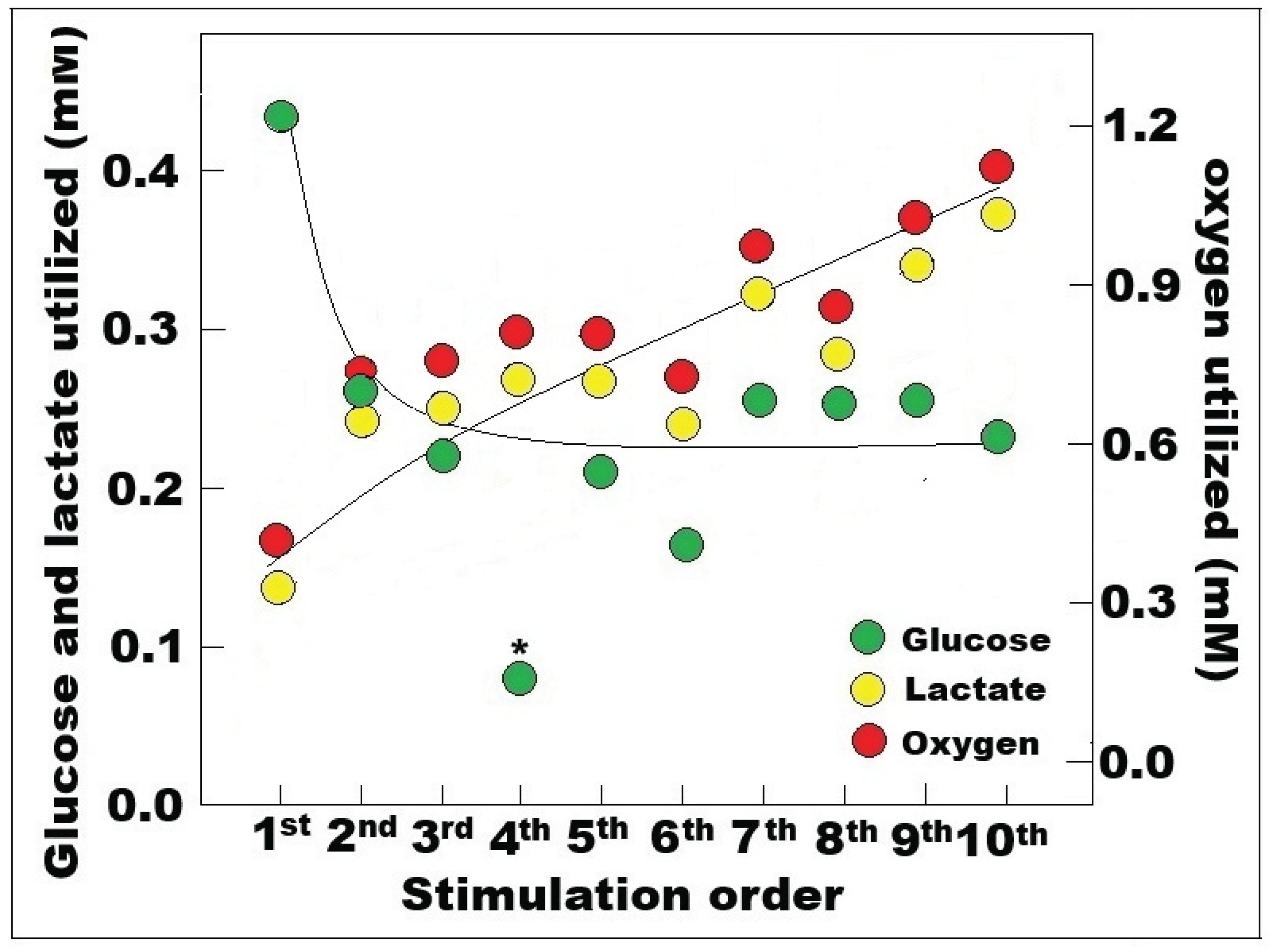
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




