Submitted:
26 September 2025
Posted:
30 September 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Methods/Design
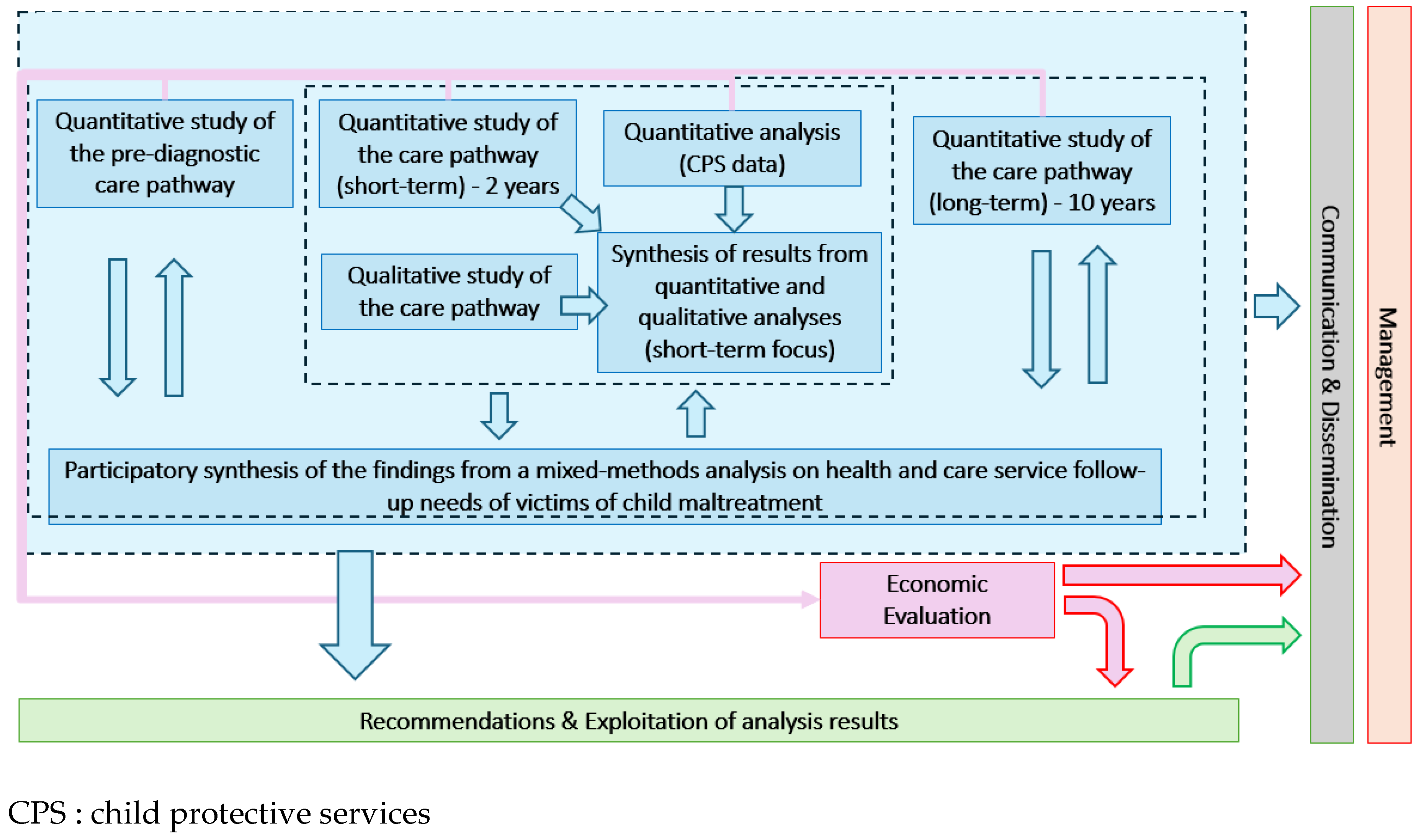
Overall Methodology
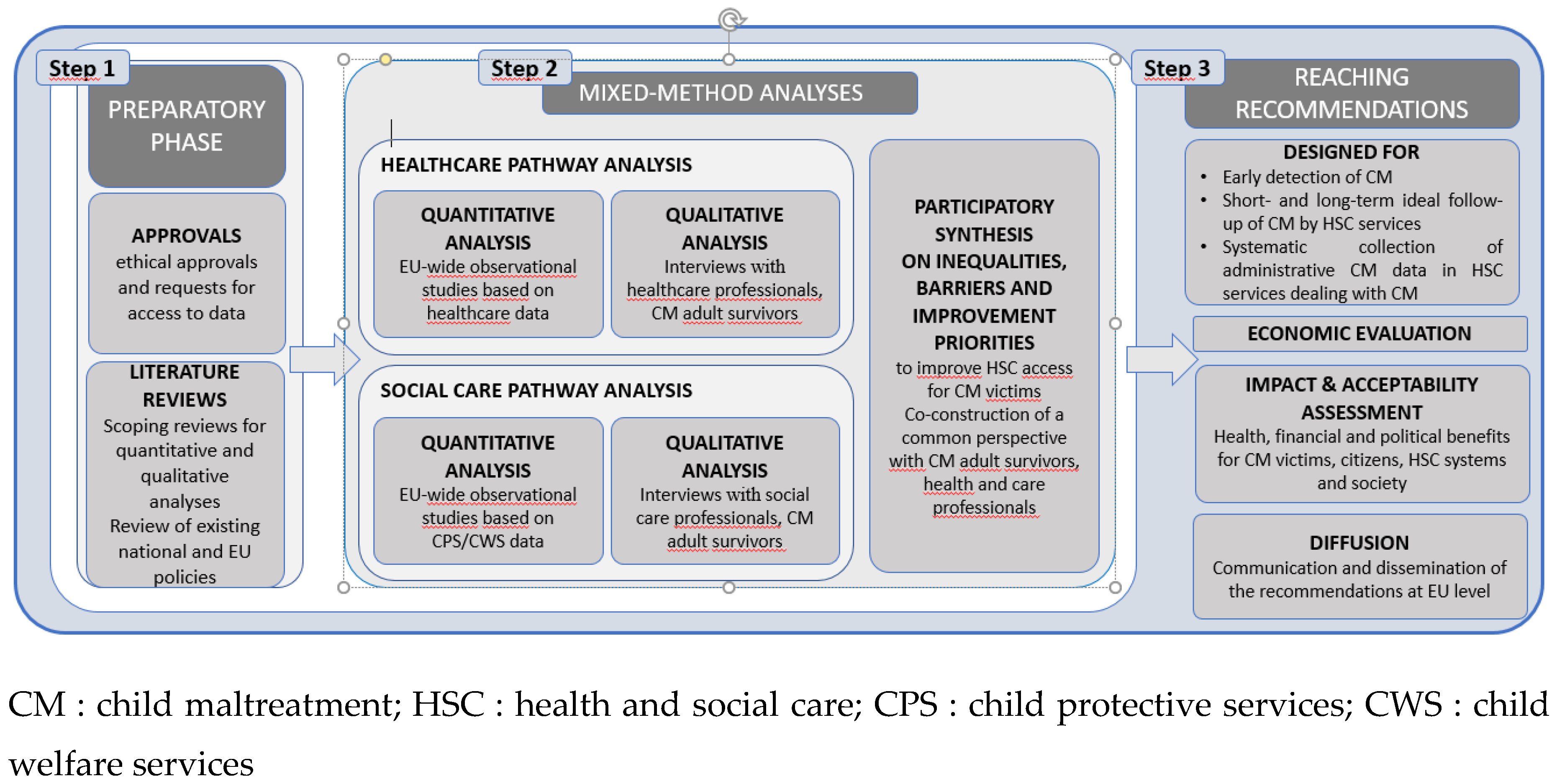
Methodology: A Three-Step Process
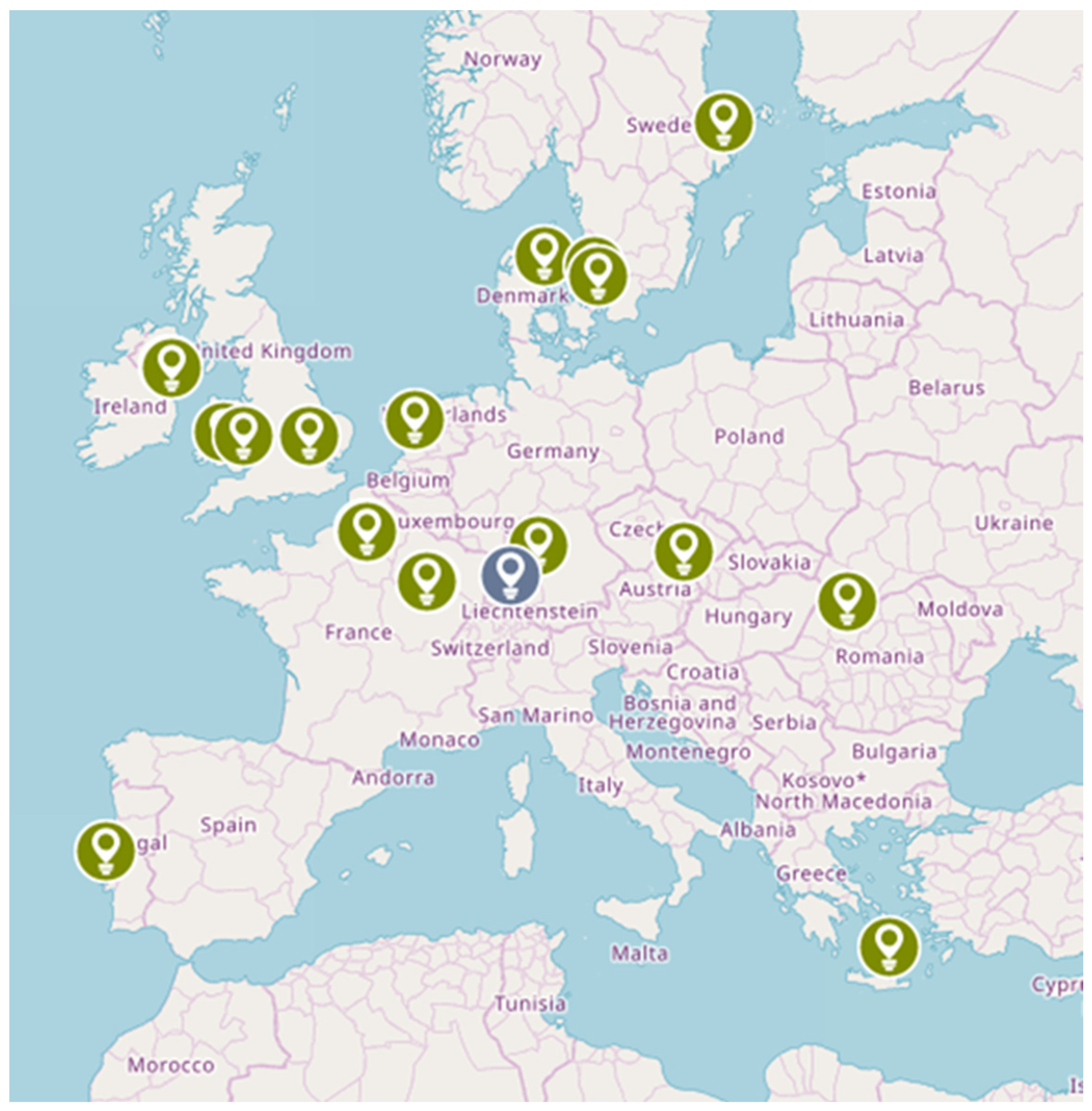
- Step 1: The preparatory phase: country selection and scoping reviews to refine criteria for the subsequent quantitative and qualitative studies.
- Step 2: Mixed-methods analyses involving quantitative and qualitative studies to assess how maltreated children navigate HSC services. A final synthesis of study results will be reviewed by an expert group of ASCM and HSC professionals.
- Step 3: Reaching recommendations
Discussion
Strengths and Limitations
Expected Results
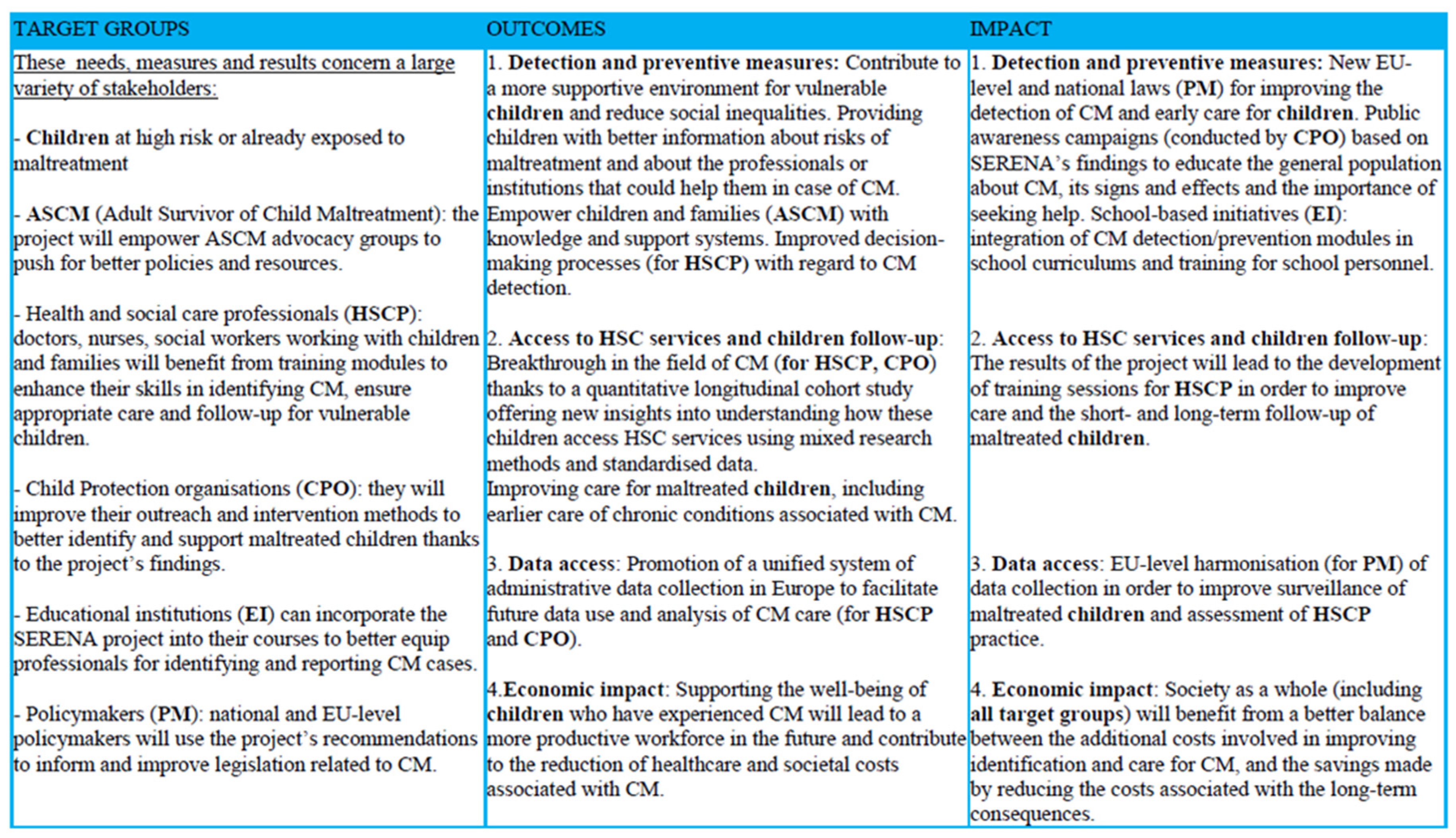
Expected Implications
Project Feasibility
Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Clinical trial number
Consent for publication
Availability of data and materials
Acknowledgements
Competing interests
Ethics approval and consent to participate
List of Abbreviations
References
- Sethi D, Parekh N, Yon Y, Mikkelsen B. Progress in preventing child maltreatment in Europe. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2018 Nov;2(11):774–5.
- Scott KM, Smith DR, Ellis PM. Prospectively ascertained child maltreatment and its association with DSM-IV mental disorders in young adults. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2010 Jul;67(7):712–9. [CrossRef]
- Cagney J, Spencer C, Flor L, Herbert M, Khalil M, O’Connell E, et al. Prevalence of sexual violence against children and age at first exposure: a global analysis by location, age, and sex (1990-2023). Lancet Lond Engl. 2025 May 24;405(10492):1817–36.
- Angelakis I, Gillespie EL, Panagioti M. Childhood maltreatment and adult suicidality: a comprehensive systematic review with meta-analysis. Psychol Med. 2019 May;49(7):1057–78. [CrossRef]
- Vink RM, van Dommelen P, van der Pal SM, Eekhout I, Pannebakker FD, Klein Velderman M, et al. Self-reported adverse childhood experiences and quality of life among children in the two last grades of Dutch elementary education. Child Abuse Negl. 2019 Sep;95:104051. [CrossRef]
- Jud A, Fegert JM, Finkelhor D. On the incidence and prevalence of child maltreatment: a research agenda. Child Adolesc Psychiatry Ment Health. 2016;10:17. [CrossRef]
- Bellis MA, Hughes K, Ford K, Ramos Rodriguez G, Sethi D, Passmore J. Life course health consequences and associated annual costs of adverse childhood experiences across Europe and North America: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Public Health. 2019 Oct;4(10):e517–28.
- WHO, 2020 WHO. Global status report on preventing violence against children. (2020). Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240004191.
- European Union Agency for Fundamental Rights. Mapping Child Protection Systems in the EU – Update 2023. FRA - European Union Agency for Fundamental Rights. 2024. Available online: https://fra.europa.eu/en/publication/2024/mapping-child-protection-systems-eu-update-2023?page=8#read-online.
- Quantin C, Cottenet J, Chambers C, Kennedy N, Whelan S, Debelle G, et al. Hospitalisations for physical abuse in infants and children less than 5 years, 2013-2021: a multinational cohort study using administrative data from five European countries. Lancet Reg Health Eur. 2025 May;52:101270.
- Office for National Statistics. Child physical abuse in England and Wales [Internet]. [cited 2025 Sep 3]. Available online: https://www.ons.gov.uk/peoplepopulationandcommunity/crimeandjustice/articles/childphysicalabuseinenglandandwales/yearendingmarch2019.
- WHO. Child maltreatment [Internet]. 2024 [cited 2025 Sep 3]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/child-maltreatment.
- Habetha S, Bleich S, Weidenhammer J, Fegert JM. A prevalence-based approach to societal costs occurring in consequence of child abuse and neglect. Child Adolesc Psychiatry Ment Health. 2012 Nov 16;6(1):35. [CrossRef]
- Conti G, Pizzo E, Morris S, Melnychuk M. The economic costs of child maltreatment in UK. Health Econ. 2021 Dec;30(12):3087–105.
- Connolly M, Katz I. Typologies of Child Protection Systems: An International Approach. Child Abuse Rev. 2019 Sep 1;28:381–94. [CrossRef]
- Fluke JD, Tonmyr L, Gray J, Bettencourt Rodrigues L, Bolter F, Cash S, et al. Child maltreatment data: A summary of progress, prospects and challenges. Child Abuse Negl. 2021 Sep;119(Pt 1):104650. [CrossRef]
- Cowley LE, Lamela D, Drabarek K, Rodrigues LB, Ntinapogias A, Naughton A, et al. Defining child maltreatment for research and surveillance: an international, multi-sectoral, Delphi consensus study in 34 countries in Europe and surrounding regions. Lancet Reg Health Eur. 2025 Mar;50:101196.
- Otterman G, Nurmatov UB, Akhlaq A, Korhonen L, Kemp AM, Naughton A, et al. Clinical care of childhood sexual abuse: a systematic review and critical appraisal of guidelines from European countries. Lancet Reg Health Eur. 2024 Apr;39:100868.
- Roehrkasse AF, Becker L, Wildeman C, Fallesen P. Introducing a new data resource for comparative child welfare research: The ROCKWOOL-Duke global child welfare database. Child Youth Serv Rev. 2023;152:107075. [CrossRef]
- Mora-Theuer EA, Klomfar S, Ramazanova D, Grylli C, Kletecka-Pulker M, Völkl-Kernstock S, et al. Cohort analysis of child abuse and neglect cases treated during the initial 2 years of a programme to support hospital-based child protection work in Austria. BMJ Open. 2023 Jul 14;13(7):e071536. [CrossRef]
- Bergman JEH, Perraud A, Barišić I, Kinsner-Ovaskainen A, Morris JK, Tucker D, et al. Updated EUROCAT guidelines for classification of cases with congenital anomalies. Birth Defects Res. 2024 Feb;116(2):e2314. [CrossRef]
- Nurmatov U, Cowley LE, Rodrigues LB, Naughton A, Debelle G, Alfandari R, et al. Consensus building on definitions and types of child maltreatment to improve recording and surveillance in Europe: protocol for a multi-sectoral, European, electronic Delphi study. BMJ Open. 2023 Dec 12;13(12):e076517. [CrossRef]
- Pluye P, Hong QN. Combining the power of stories and the power of numbers: mixed methods research and mixed studies reviews. Annu Rev Public Health. 2014;35:29–45. [CrossRef]
- Boyatzis CJ, Baloff P, Durieux C. Effects of perceived attractiveness and academic success on early adolescent peer popularity. J Genet Psychol [Internet]. 1998 Sep [cited 2025 Mar 31];159(3). Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9729839/.
- Braun V, Clarke V. Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qual Res Psychol. 2006;3:77–101.
- Hakkaart-van Roijen l, Peeters S, Kanters T. Costing manual: Methods and Reference Prices for Economic Evaluations in Healthcare [Internet]. 2024. (Commissioned by the National Health Care Institute). Available from: file://///chu-dijon/doc/dl/BAGW1802770/Downloads/Module+-+Costing+manual.pdf.
- Koopmanschap MA, Rutten FF, van Ineveld BM, van Roijen L. The friction cost method for measuring indirect costs of disease. J Health Econ. 1995 Jun;14(2):171–89. [CrossRef]
- Jud A, Fluke J, Alink LRA, Allan K, Fallon B, Kindler H, et al. On the nature and scope of reported child maltreatment in high-income countries: opportunities for improving the evidence base. Paediatr Int Child Health. 2013 Nov;33(4):207–15. [CrossRef]
- Baldwin JR, Reuben A, Newbury JB, Danese A. Agreement Between Prospective and Retrospective Measures of Childhood Maltreatment: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiatry. 2019 Jun 1;76(6):584–93. [CrossRef]
- Pearce LA, Borschmann R, Young JT, Kinner SA. Advancing cross-sectoral data linkage to understand and address the health impacts of social exclusion: Challenges and potential solutions. Int J Popul Data Sci. 2023;8(1):2116. [CrossRef]
- Jud A, Mitrovic T, Portmann R, Gonthier H, Fux E, Koehler J, et al. Multi-sectoral response to child maltreatment in Switzerland for different age groups: Varying rates of reported incidents and gaps in identification. Child Abuse Negl. 2021 Jan;111:104798. [CrossRef]
- Milidou I, Merrild CH, Frost L, Charles AV, Kjeldsen HC, Søndergaard C. Suspicion of child maltreatment: Knowledge and experiences with mandatory reports to social services among general practitioners in Denmark in 2019-20. Child Abuse Negl. 2023 May;139:106132. [CrossRef]
- Kruger, H. “The Discrepancy between the Criminal Capacity and Delictual Accountability of Children: A Children’s Rights Perspective". J Contemp Roman-Dutch Law. 2022;85(1):68–90.
- Herbert JL, Bromfield L. Multi-disciplinary teams responding to child abuse: Common features and assumptions. Child Youth Serv Rev. 2019;106:104467. [CrossRef]
- WHO. Framework to Implement a Life Course Approach in Practice. Geneva: WHO. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO [Internet]. [cited 2025 Sep 3]. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240112575.
- Gilbert R, Widom CS, Browne K, Fergusson D, Webb E, Janson S. Burden and consequences of child maltreatment in high-income countries. Lancet Lond Engl. 2009 Jan 3;373(9657):68–81.
- World Health Organization. INSPIRE: Seven Strategies for Ending Violence against Children. World Health Organization; 2016. Accessed August 25, 2025. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/207717.
- World Health Assembly. Strengthening the role of the health system in addressing violence, in particular against women and girls, and against children. [Internet]. 2014. Report No.: 67. Available online: https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/162855.
- Sethi D, Bellis M, Hughes K, Gilbert R, Mitis F, Galea G. European report on preventing child maltreatment [Internet]. World Health Organization. Regional Office for Europe; 2013 [cited 2025 Apr 1]. Available online: https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/326375.
- Thielen FW, Ten Have M, de Graaf R, Cuijpers P, Beekman A, Evers S, et al. Long-term economic consequences of child maltreatment: a population-based study. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2016 Dec;25(12):1297–305. [CrossRef]
 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





