Submitted:
22 September 2025
Posted:
23 September 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Flame Types
1.2. Turbulent Non-Premixed Flames
1.3. Instability of Turbulent Non-Premixed Flames
1.4. Stabilizing Turbulent Non-Premixed Flames
1.5. HM1 Flame
1.6. Some Computational Studies About the HM1 Flame
2. Experimental Geometry of the HM1 Flame
3. Computational reactingFoam Model
3.1. Overview of OpenFOAM and reactingFoam
3.2. Main Governing Equations
3.3. Turbulence-Chemistry Interaction
3.4. Pressure-Velocity Coupling
- First, the elliptic pressure equation, Equation (8), is solved to give a pressure field.
- Second, the mass fluxes at the cell faces are updated using the obtained pressure field.
- Third, the temporary velocity vector field obtained during the predictor stage is corrected using the explicit expression in Equation (9). This takes into account the newly resolved pressure field.
- Momentum equation
- Species mass-fraction equations
- Energy equation
- Elliptic pressure equation
- Explicit velocity vector correction equation
- 4.
- The momentum equation, Equation (2), is solved.
- 5.
- The species equations, Equations (5), are solved.
- 6.
- The energy equation, Equation (6), is solved.
- 7.
- The PISO correction “inner” loop is performed.
3.5. Computational Domain and Mesh
3.6. Mesh and Boundaries Script
4. Results
4.1. Selected Data
- radial profiles of the axial velocity component
- radial profiles of the radial velocity components
- radial profiles and axial profiles of the reactant methane (mass fraction)
- radial profiles and axial profiles of the product water vapor (mass fraction)
- axial profile of the temperature
4.2. Reynolds Averaging Versus Favre Averaging
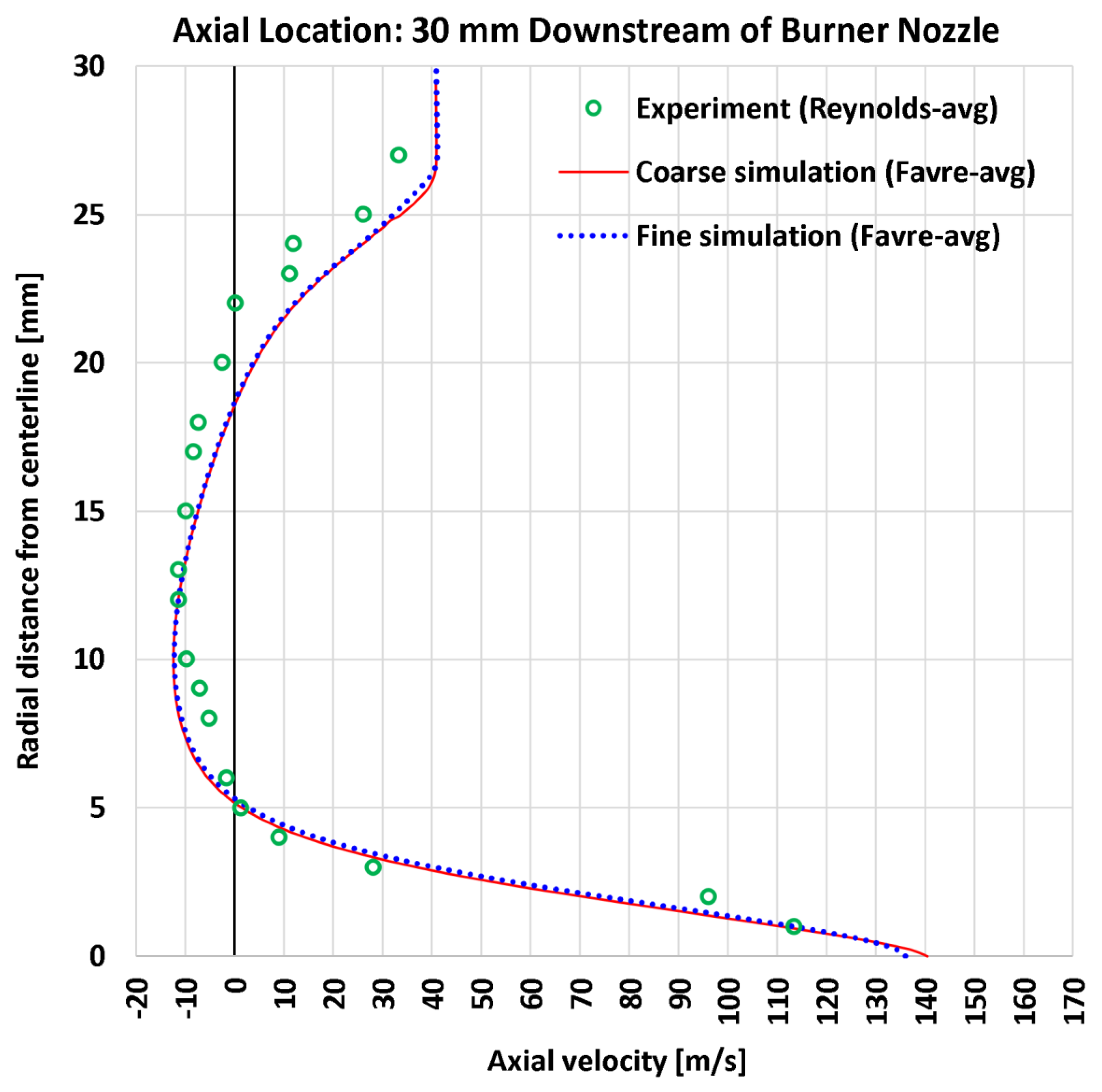
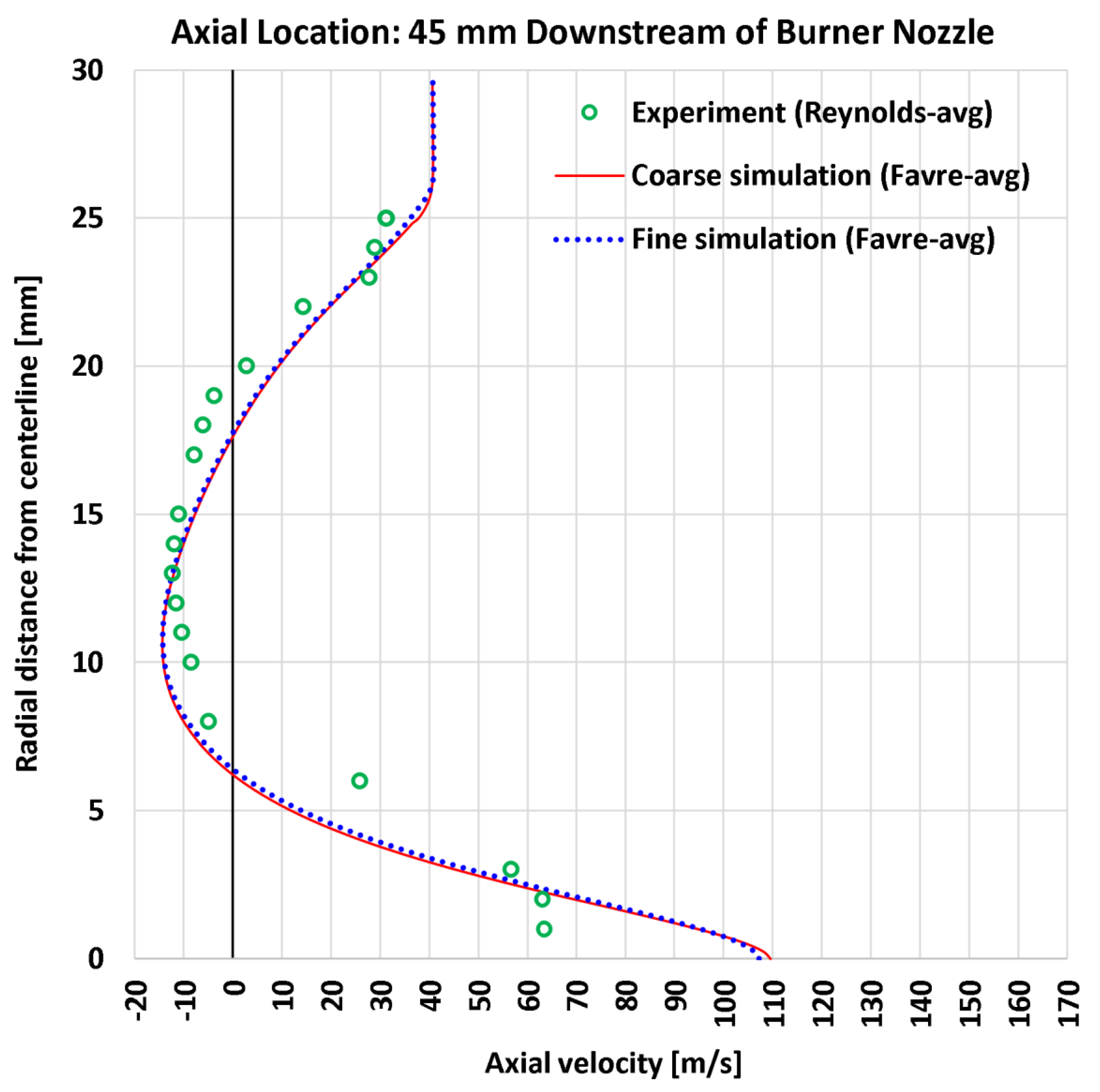
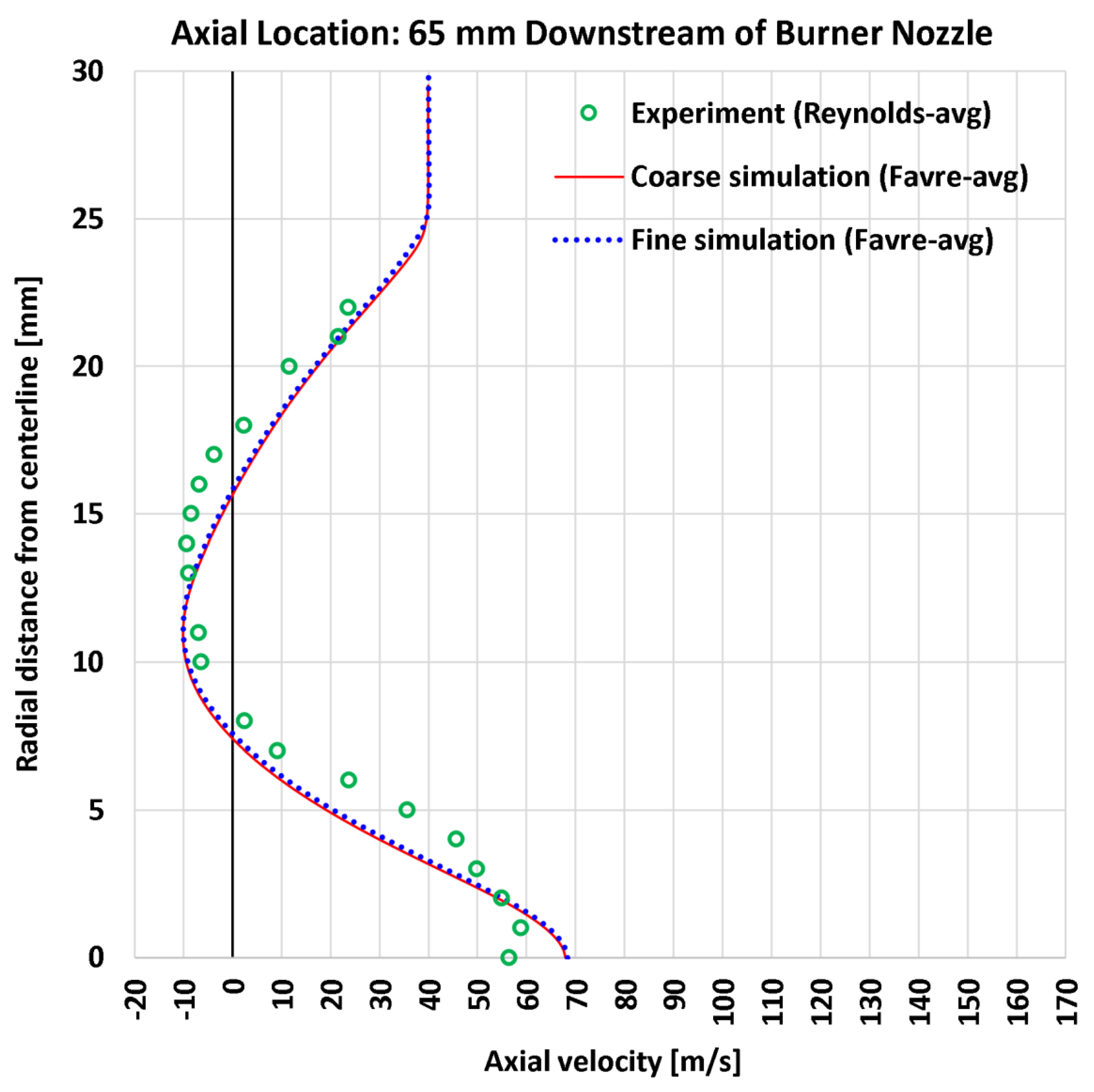
4.3. Radial Profiles of the Axial Velocity
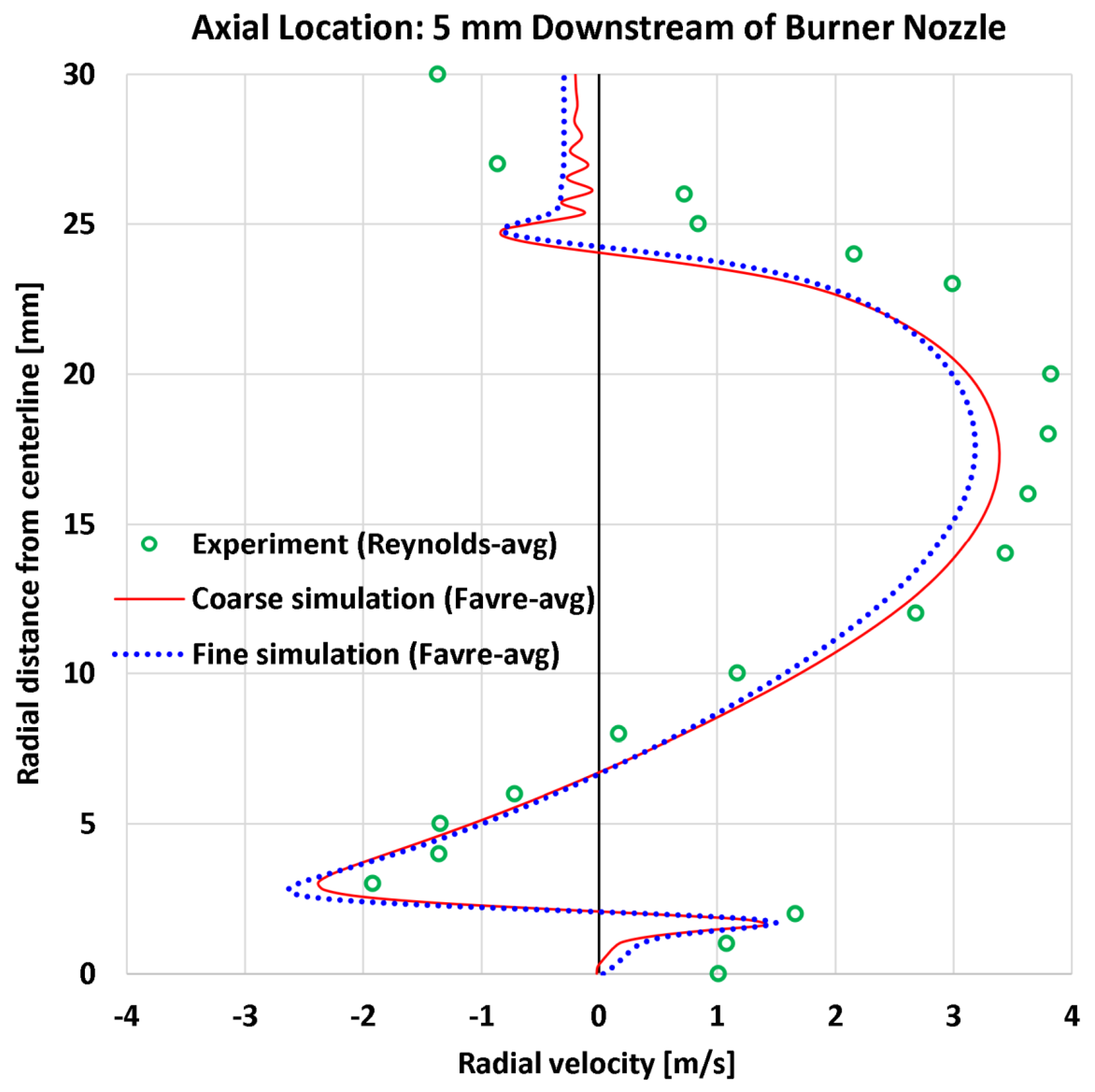
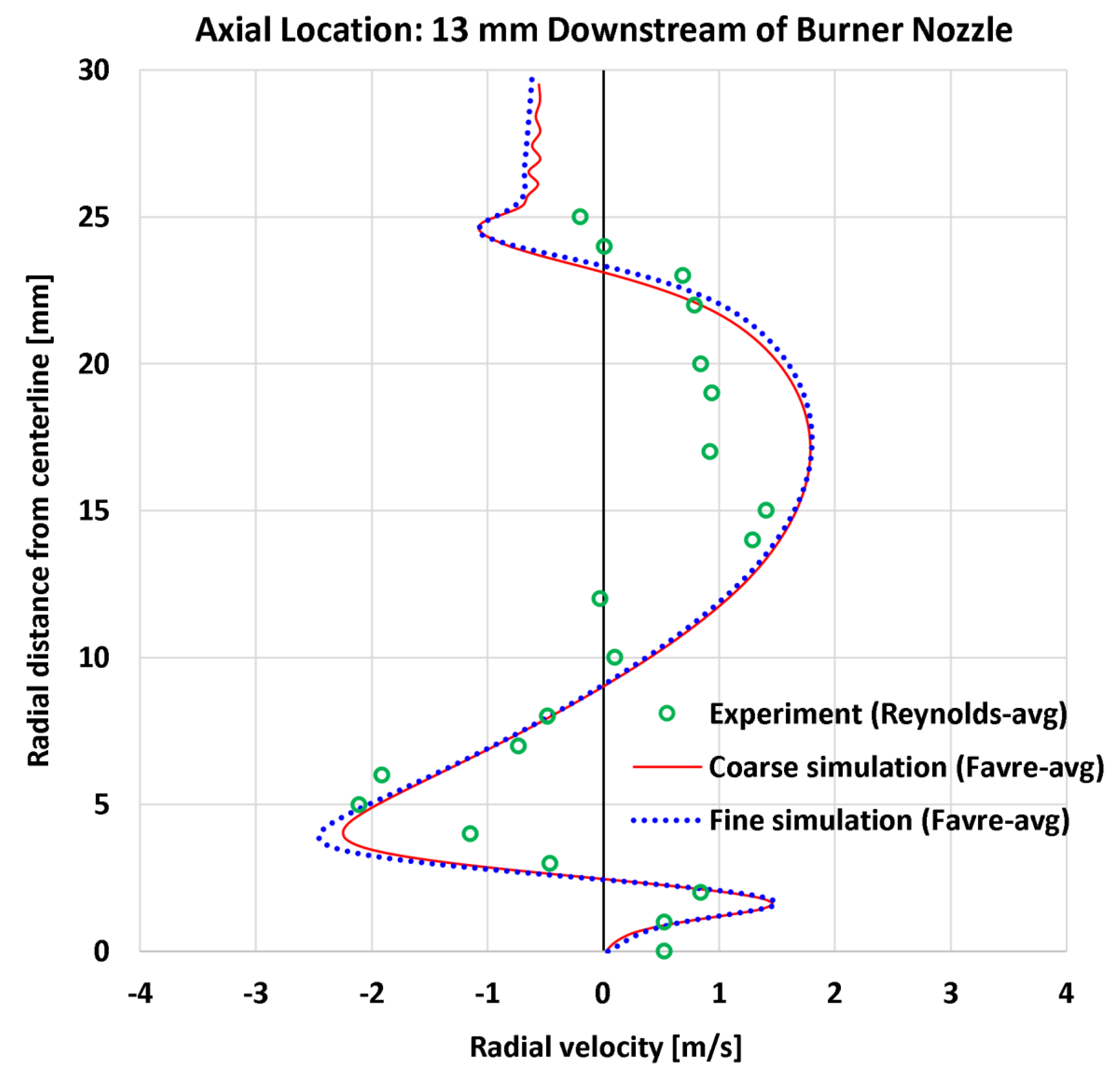
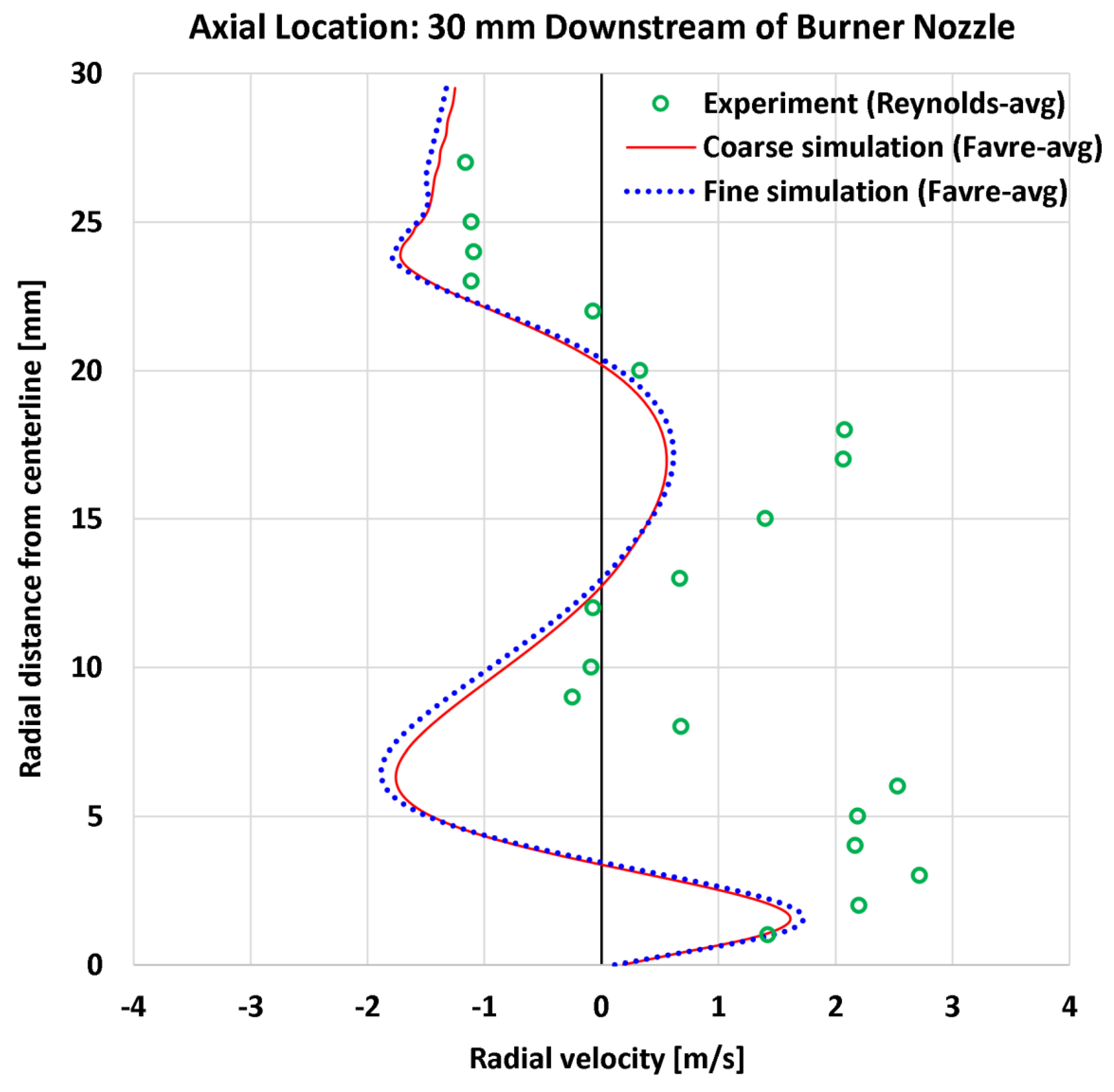
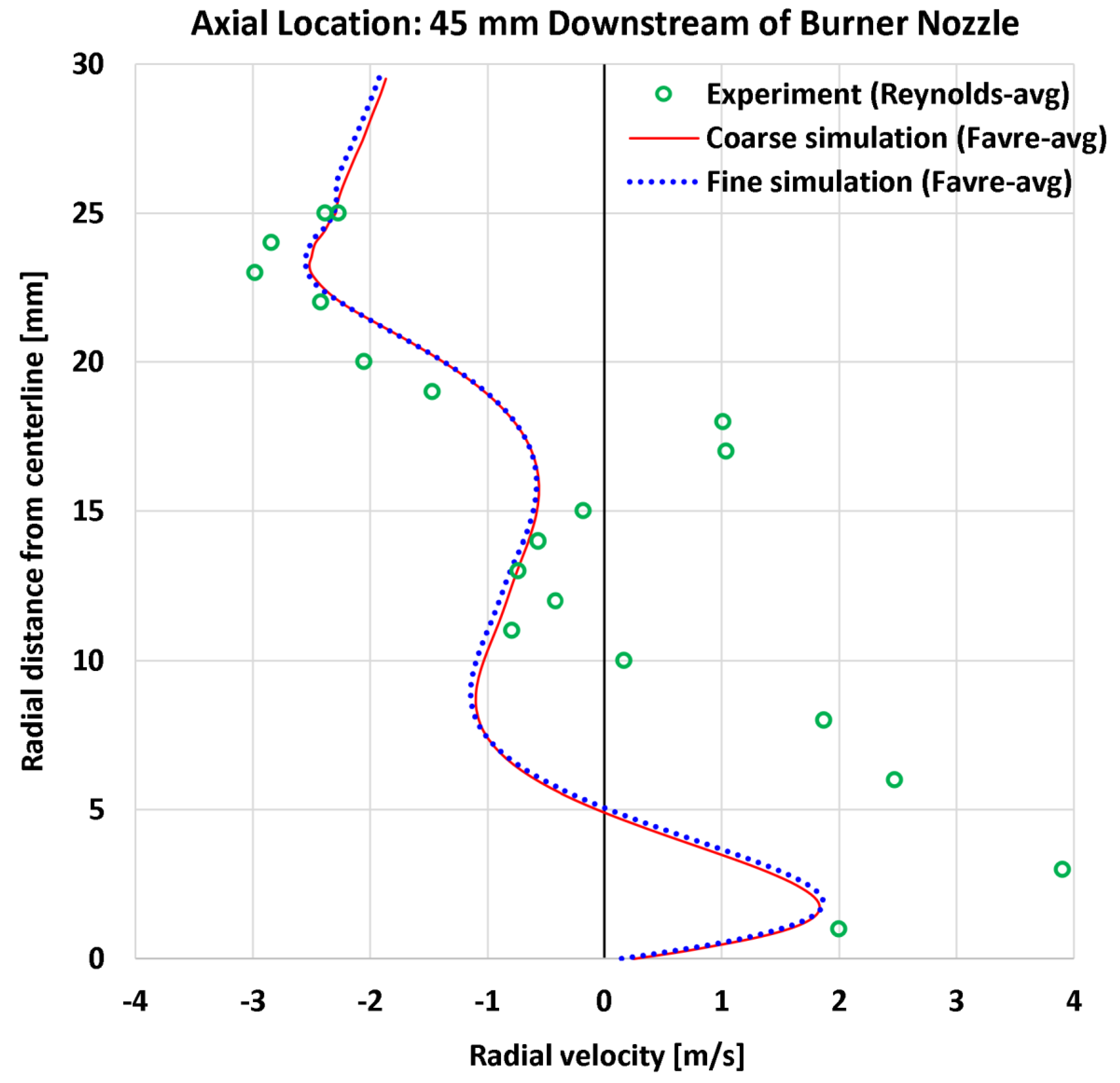
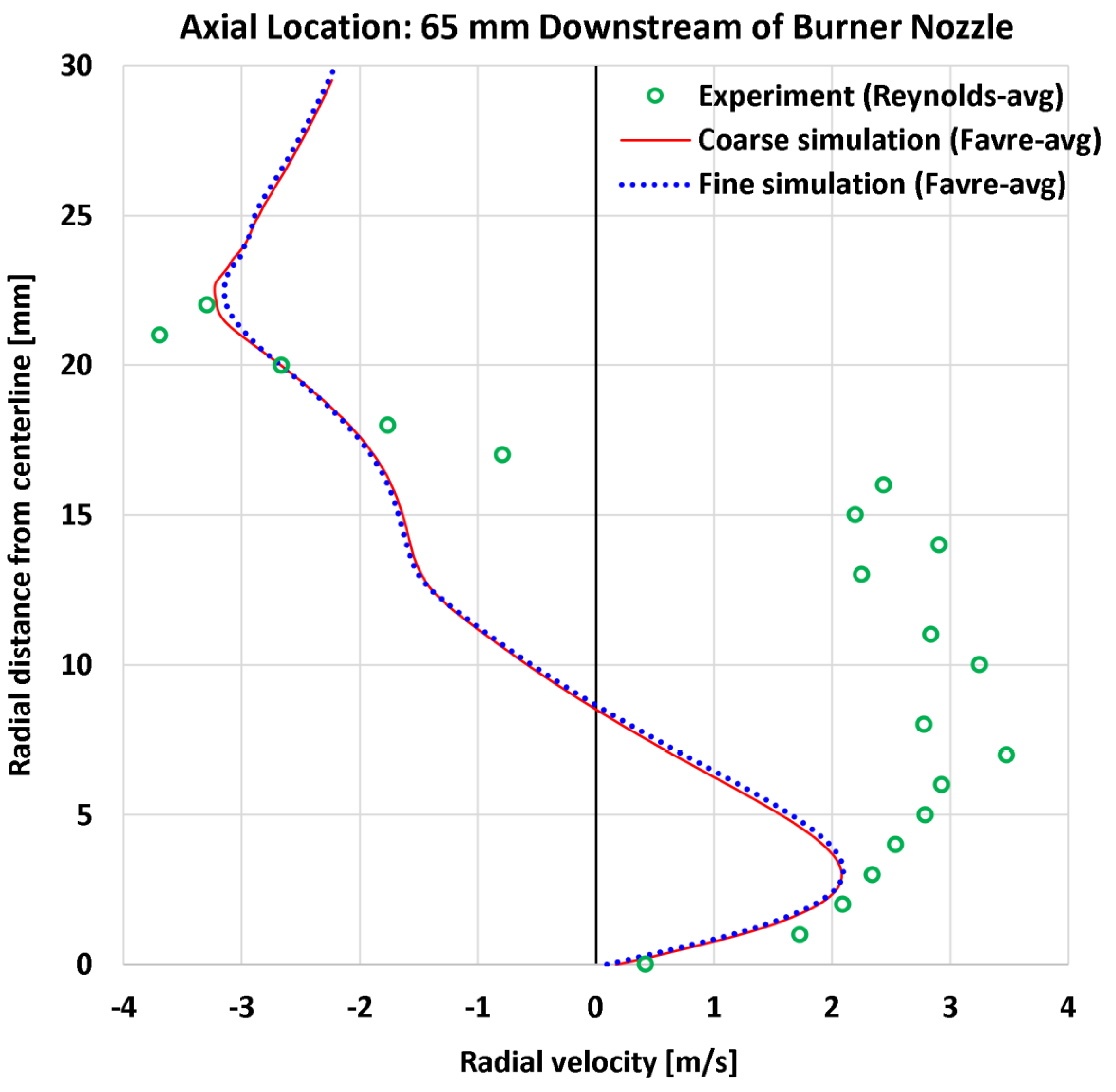
4.4. Radial Profiles of the Radial Velocity
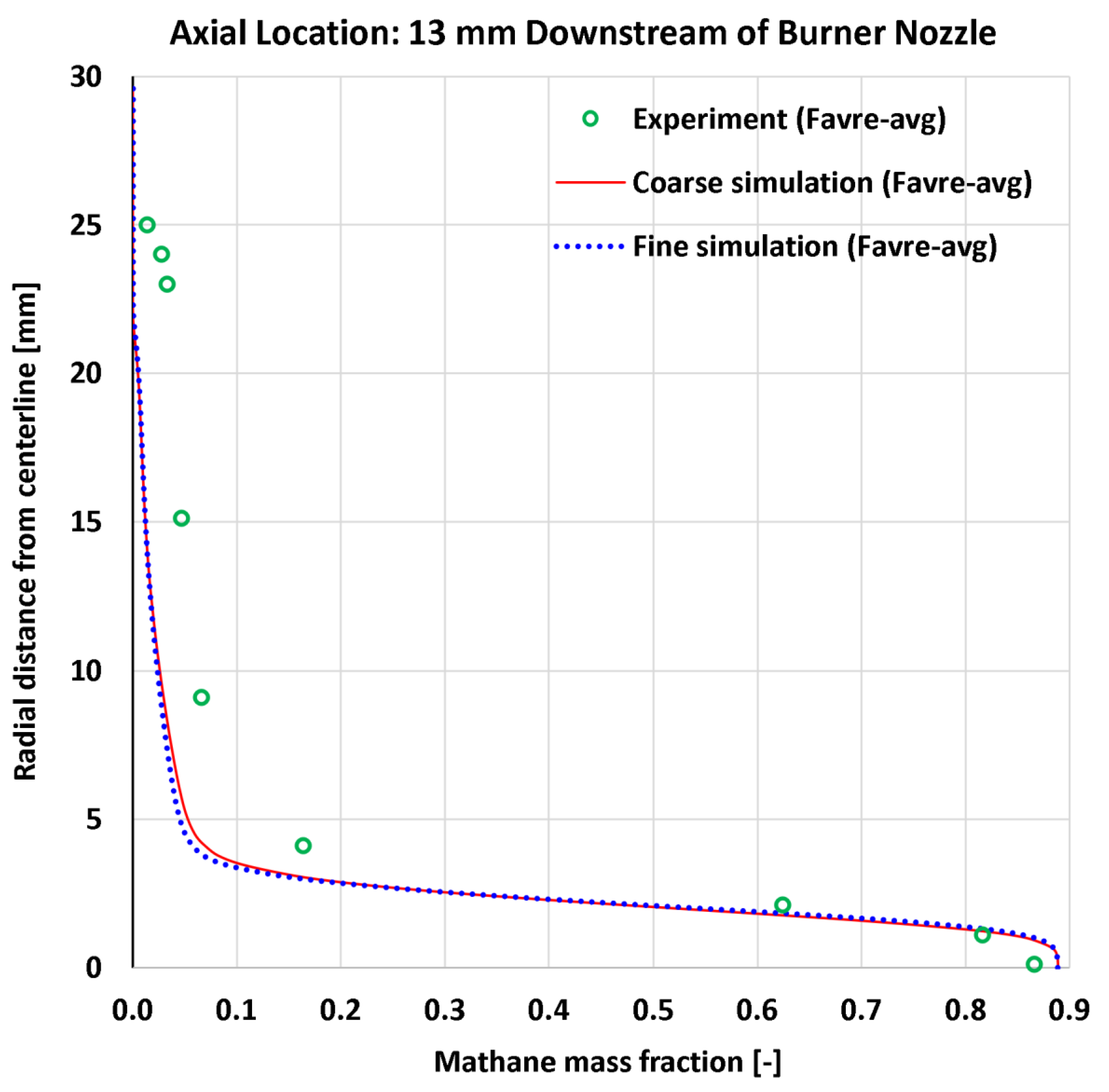
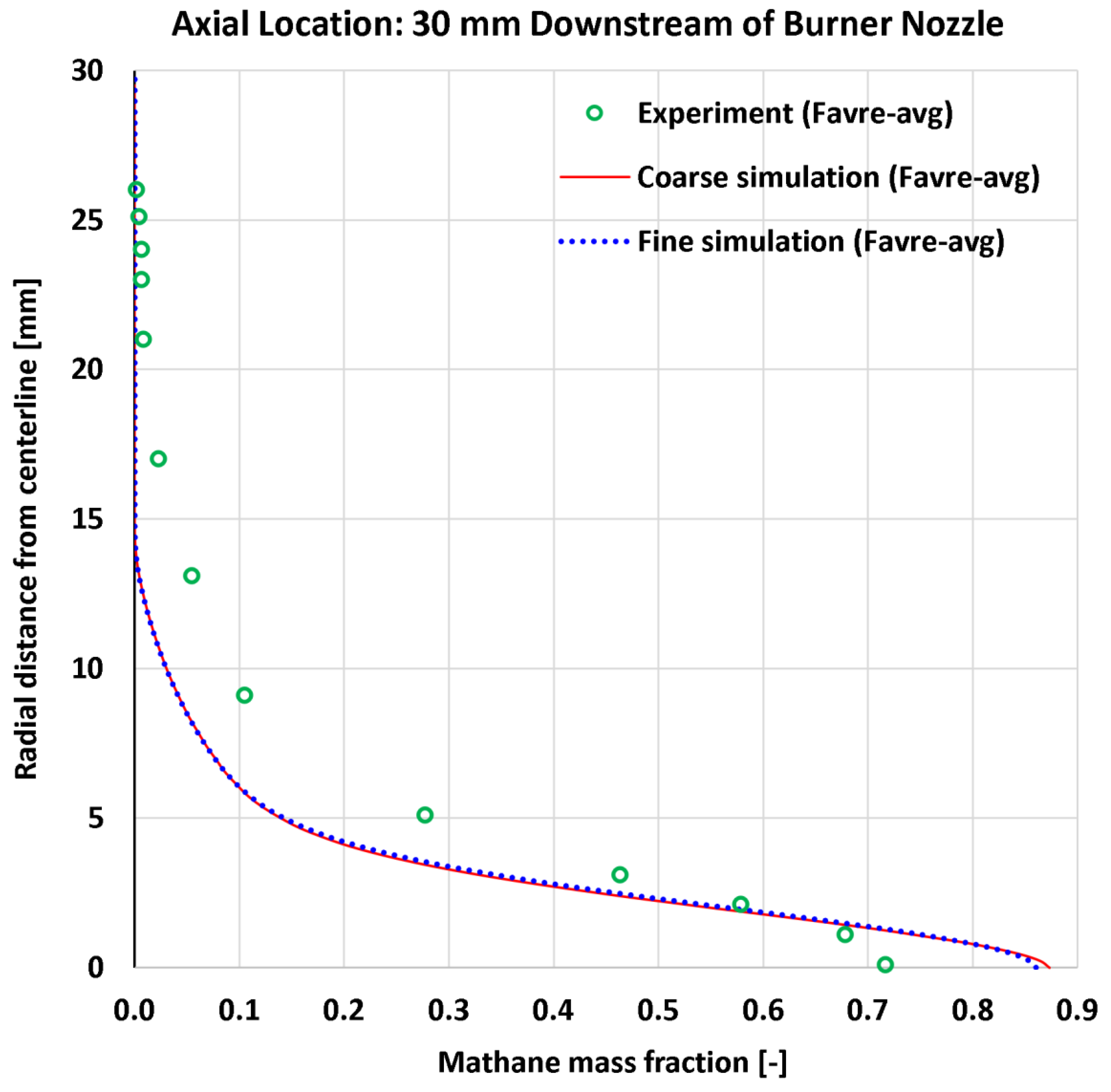
4.5. Radial Profiles of the Methane Mass Fraction
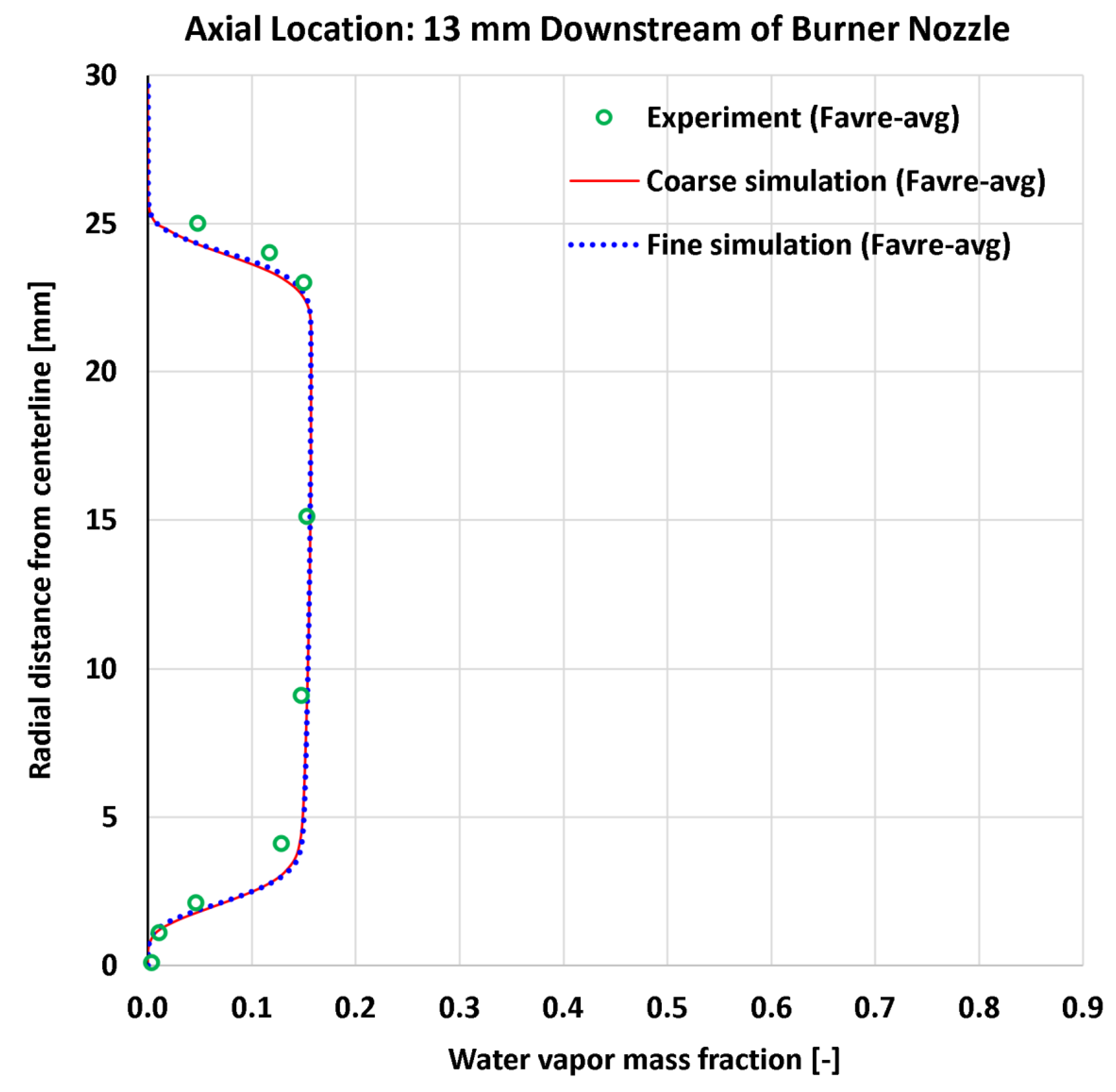
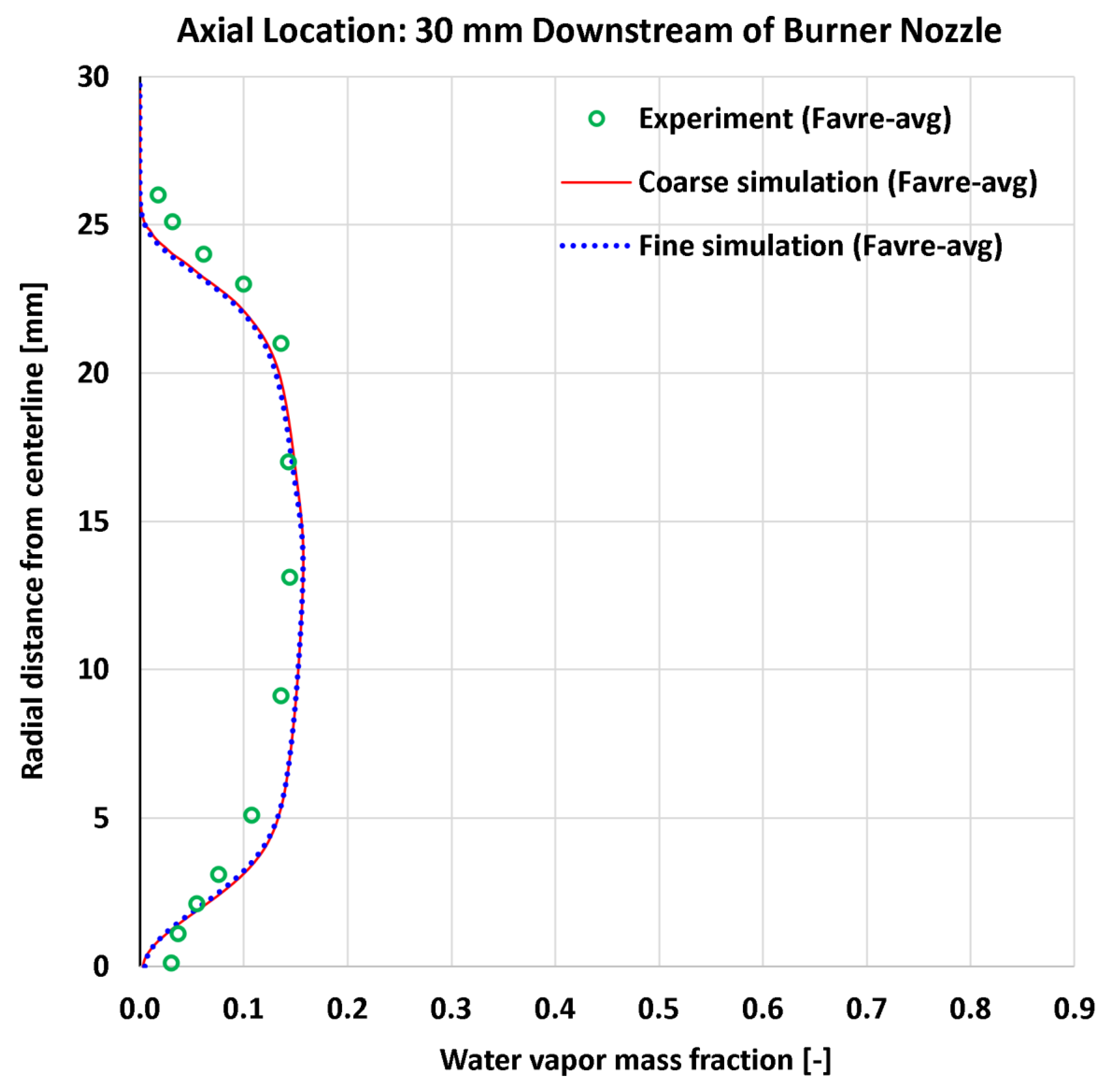
4.6. Radial Profiles of Water Vapor Mass Fraction
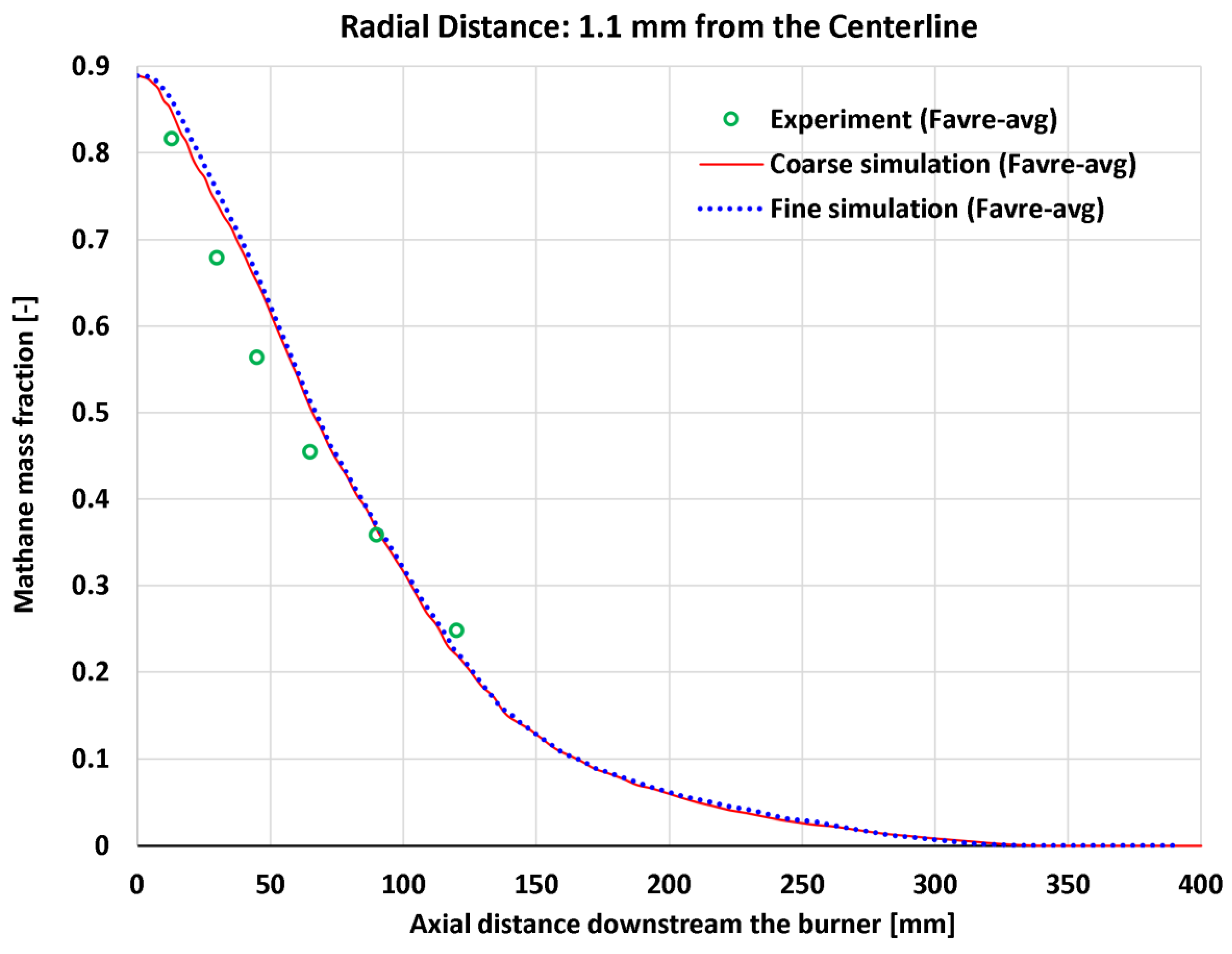
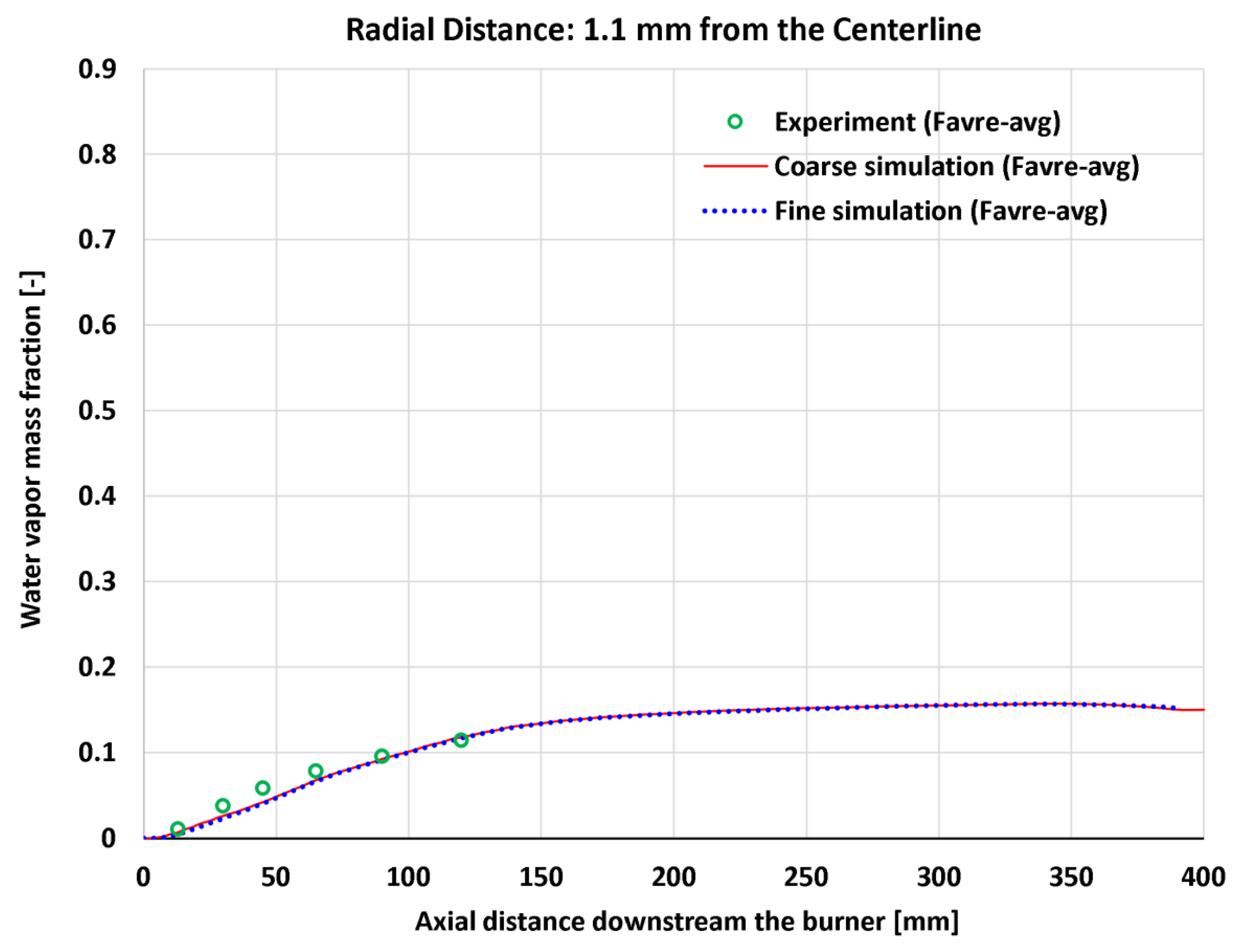
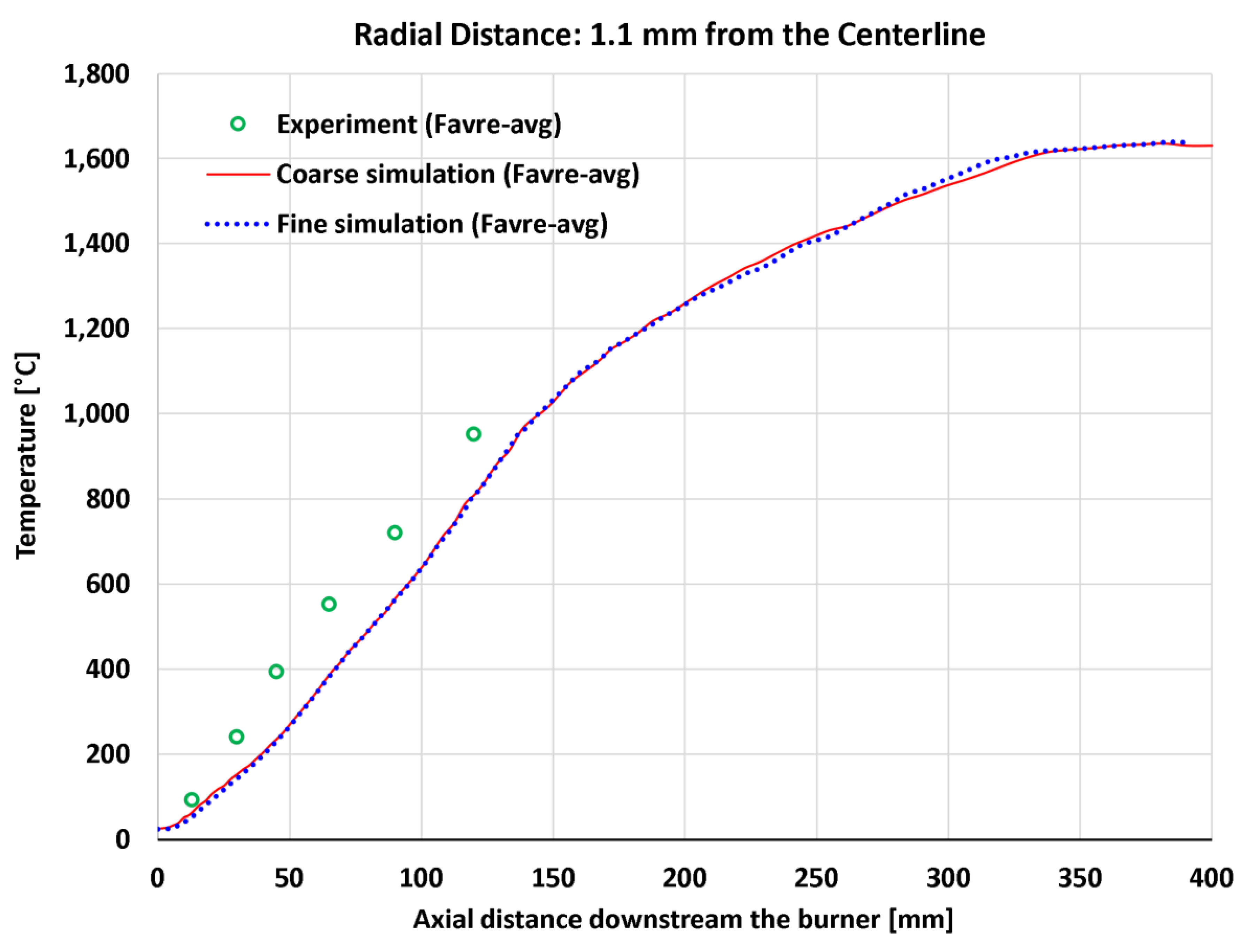
4.7. Near-Centerline Axial Profiles
4.8. Quantified Deviations
5. Conclusion
Funding
Declaration of Competing Interests Statement
Data Availability Statement
References
- Zhou:, L. Chapter 3 - Fundamentals of Combustion Theory. In Theory and Modeling of Dispersed Multiphase Turbulent Reacting Flows; Zhou, L., Ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann, 2018; pp. 15–70 ISBN 978-0-12-813465-8.
- Lo Jacono, D.; Bergeon, A.; Knobloch, E. Spatially Localized Radiating Diffusion Flames. Combustion and Flame 2017, 176, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BEE, [Indian Bureau of Energy Efficiency] BEE │ 1. Fuels and Combustion; BEE [Indian Bureau of Energy Efficiency]: New Delhi, India, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Lackner, M.; Palotás, Á.; Winter, F. Combustion: From Basics to Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Weinheim, Germany, 2013; ISBN 978-3-527-66720-8. [Google Scholar]
- Mailybaev, A.A.; Bruining, J.; Marchesin, D. Analysis of in Situ Combustion of Oil with Pyrolysis and Vaporization. Combustion and Flame 2011, 158, 1097–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansys Ansys │ What Is Combustion? Available online: https://www.ansys.com/simulation-topics/what-is-combustion (accessed on 9 September 2025).
- Karim, G.A. Fuels, Energy, and the Environment; CRC Press: Boca Raton, Florida, USA, 2012; ISBN 978-1-4665-1017-3. [Google Scholar]
- Marzouk, O.A. Adiabatic Flame Temperatures for Oxy-Methane, Oxy-Hydrogen, Air-Methane, and Air-Hydrogen Stoichiometric Combustion Using the NASA CEARUN Tool, GRI-Mech 3.0 Reaction Mechanism, and Cantera Python Package. Engineering, Technology & Applied Science Research 2023, 13, 11437–11444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.; Jung, J.; Bae, C.; Johansson, B. Combustion Process and PM Emission Characteristics in a Stratified DISI Engine under Low Load Condition. In Internal Combustion Engines: Performance, Fuel Economy and Emissions; Woodhead Publishing, 2013; pp. 179–192 ISBN 978-1-78242-183-2.
- Ohkubo, M.; Nakagawa, Y.; Yamagata, T.; Fujisawa, N. Quantitative Visualization of Temperature Field in Non-Luminous Flame by Flame Reaction Technique. J Vis 2012, 15, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quay, B.; Lee, T.-W.; Ni, T.; Santoro, R.J. Spatially Resolved Measurements of Soot Volume Fraction Using Laser-Induced Incandescence. Combustion and Flame 1994, 97, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaddix, C.R.; Williams, T.C. The Effect of Oxygen Enrichment on Soot Formation and Thermal Radiation in Turbulent, Non-Premixed Methane Flames. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute 2017, 36, 4051–4059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marr, K.C.; Clemens, N.T.; Ezekoye, O.A. Mixing Characteristics and Emissions of Strongly-Forced Non-Premixed and Partially-Premixed Jet Flames in Crossflow. Combustion and Flame 2012, 159, 707–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriyama, T.; Yamamoto, K. Numerical Simulation of Methane-Hydrogen Premixed Flames on a Bunsen Burner. Journal of Thermal Science and Technology 2022, 17, 22–00129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winterbone, D.E.; Turan, A. Chapter 15 - Combustion and Flames. In Advanced Thermodynamics for Engineers (Second Edition); Winterbone, D.E., Turan, A., Eds.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Boston, 2015; ISBN 978-0-444-63373-6. [Google Scholar]
- Houldcroft, P. List C - Principles and Basic Characteristics of Welding and Related Processes. In Which Process?; Houldcroft, P., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Welding and Other Joining Technologies; Woodhead Publishing, 1990; pp. 37–93 ISBN 978-1-85573-008-3.
- Lee, M.J.; Kim, N.I. Flame Structures and Behaviors of Opposed Flow Non-Premixed Flames in Mesoscale Channels. Combustion and Flame 2014, 161, 2361–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzouk, O.A. Performance Analysis of Shell-and-Tube Dehydrogenation Module. International Journal of Energy Research 2017, 41, 604–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Lignell, D.O.; Hawkes, E.R.; Chen, J.H.; Wang, H. Examination of the Effect of Differential Molecular Diffusion in DNS of Turbulent Non-Premixed Flames. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 11879–11892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glassman, I.; Yetter, R.A. Chapter 6 - Diffusion Flames. In Combustion (Fourth Edition); Glassman, I., Yetter, R.A., Eds.; Academic Press: Burlington, 2008; ISBN 978-0-12-088573-2. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, N. Laminar Diffusion Flamelet Models in Non-Premixed Turbulent Combustion. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science 1984, 10, 319–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanganeh, J.; Moghtaderi, B.; Ishida, H. Combustion and Flame Spread on Fuel-Soaked Porous Solids. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science 2013, 39, 320–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzouk, O.A. Radiant Heat Transfer in Nitrogen-Free Combustion Environments. International Journal of Nonlinear Sciences and Numerical Simulation 2018, 19, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcanti, M.H.C.; Pappalardo, J.R.; Barbosa, L.T.; Brasileiro, P.P.F.; Roque, B.A.C.; da Rocha e Silva, N.M.P.; Silva, M.F. da; Converti, A.; Barbosa, C.M.B. de M.; Sarubbo, L.A. Hydrogen in Burners: Economic and Environmental Implications. Processes 2024, 12, 2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzouk, O.A. Detailed Derivation of the Scalar Explicit Expressions Governing the Electric Field, Current Density, and Volumetric Power Density in the Four Types of Linear Divergent MHD Channels Under a Unidirectional Applied Magnetic Field. Contemporary Mathematics 2025, 6, 4060–4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAllister, S.; Chen, J.-Y.; Fernandez-Pello, A.C. Non-Premixed Flames (Diffusion Flames). In Fundamentals of Combustion Processes; McAllister, S., Chen, J.-Y., Fernandez-Pello, A.C., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, 2011; ISBN 978-1-4419-7943-8. [Google Scholar]
- Rangwala, A.S.; Raghavan, V. Mechanism of Fires: Chemistry and Physical Aspects; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; ISBN 978-3-030-75498-3. [Google Scholar]
- Eyres, D.J.; Bruce, G.J. 9 - Welding and Cutting Processes Used in Shipbuilding. In Ship Construction (Seventh Edition); Eyres, D.J., Bruce, G.J., Eds.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, 2012; ISBN 978-0-08-097239-8. [Google Scholar]
- Marzouk, O.A. Characteristics of the Flow-Induced Vibration and Forces With 1- and 2-DOF Vibrations and Limiting Solid-to-Fluid Density Ratios. Journal of Vibration and Acoustics 2010, 132, 041013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsopoulos, E.P.; Souflas, K.; Paterakis, G.; Koutmos, P.; Egolfopoulos, F.N. Estimation of Laminar Flame Speeds Using Axisymmetric Bunsen Flames: Molecular Transport Effects. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute 2023, 39, 1861–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Hu, L.; Palacios, A.; Chung, S.H. Burning Characteristics of Candle Flames in Sub-Atmospheric Pressures: An Experimental Study and Scaling Analysis. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute 2019, 37, 2065–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bychkov, V.V.; Liberman, M.A. Dynamics and Stability of Premixed Flames. Physics Reports 2000, 325, 115–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzouk, O.A. Subcritical and Supercritical Rankine Steam Cycles, under Elevated Temperatures up to 900°C and Absolute Pressures up to 400 Bara. Advances in Mechanical Engineering 2024, 16, 16878132231221065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masri, A.R. Challenges for Turbulent Combustion. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute 2021, 38, 121–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzouk, O.A. Hydrogen Utilization as a Plasma Source for Magnetohydrodynamic Direct Power Extraction (MHD-DPE). IEEE Access 2024, 12, 167088–167107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzouk, O.A. Detailed and Simplified Plasma Models in Combined-Cycle Magnetohydrodynamic Power Systems. International Journal of Advanced and Applied Sciences 2023, 10, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annamalai, K.; Puri, I.K. Combustion Science and Engineering; CRC Press: Boca Raton, Florida, USA, 2006; ISBN 978-0-429-11787-9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Delichatsios, M. Numerical Soot Modelling and Radiation in Fires. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the Sixth International Seminar on Fire and Explosion Hazards (FEH6); Research Publishing Service: London, UK; 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Swaminathan, N.; Bai, X.-S.; Haugen, N.E.L.; Fureby, C.; Brethouwer, G. Advanced Turbulent Combustion Physics and Applications; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2022; ISBN 978-1-108-49796-1. [Google Scholar]
- Marzouk, O.A. Reduced-Order Modeling (ROM) of a Segmented Plug-Flow Reactor (PFR) for Hydrogen Separation in Integrated Gasification Combined Cycles (IGCC). Processes 2025, 13, 1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzouk, O.A. Power Density and Thermochemical Properties of Hydrogen Magnetohydrodynamic (H2MHD) Generators at Different Pressures, Seed Types, Seed Levels, and Oxidizers. Hydrogen 2025, 6, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadravec, M.; Rajh, B.; Samec, N.; Hriberšek, M. Numerical Analysis of Oil Combustion in a Small Combustion Device. Anali PAZU 2014, 4, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadanandan, R.; Chakraborty, A.; Arumugam, V.K.; Chakravarthy, S.R. Partially Premixed Flame Stabilization in the Presence of a Combined Swirl and Bluff Body Influenced Flowfield: An Experimental Investigation. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 2020, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pers, H.; Aniello, A.; Morisseau, F.; Schuller, T. Autoignition-Induced Flashback in Hydrogen-Enriched Laminar Premixed Burners. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 10235–10249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catlin, C.A.; Lindstedt, R.P. Premixed Turbulent Burning Velocities Derived from Mixing Controlled Reaction Models with Cold Front Quenching. Combustion and Flame 1991, 85, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoropad, D.; Gelowitz, D.; Idem, R.; Stobbs, B.; Barrie, J. Challenges of Recommissioning a CO2 Capture Pilot Plant in Saskatchewan, Canada. In Greenhouse Gas Control Technologies - 6th International Conference; Gale, J., Kaya, Y., Eds.; Pergamon: Oxford, 2003; ISBN 978-0-08-044276-1. [Google Scholar]
- Lawn, C.J. Lifted Flames on Fuel Jets in Co-Flowing Air. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science 2009, 35, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzouk, O.A. A Two-Step Computational Aeroacoustics Method Applied to High-Speed Flows. Noise Control Engineering Journal 2008, 56, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariuki, J.; Dawson, J.R.; Mastorakos, E. Measurements in Turbulent Premixed Bluff Body Flames Close to Blow-Off. Combustion and Flame 2012, 159, 2589–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedia, K.S.; Ghoniem, A.F. The Blow-off Mechanism of a Bluff-Body Stabilized Laminar Premixed Flame. Combustion and Flame 2015, 162, 1304–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzouk, O.A. Zero Carbon Ready Metrics for a Single-Family Home in the Sultanate of Oman Based on EDGE Certification System for Green Buildings. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turns, S.R. Understanding NOx Formation in Nonpremixed Flames: Experiments and Modeling. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science 1995, 21, 361–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newby, J.N. 21 Years of Real-World Low NOx Injection (“LNI”). In Proceedings of the American Flame Research Committee (AFRC) Industrial Combustion Symposium; Kauai, Hawaii, USA; 2013; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- CORREA, S.M. A Review of NOx Formation Under Gas-Turbine Combustion Conditions. Combustion Science and Technology 1993, 87, 329–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzouk, O.A. Temperature-Dependent Functions of the Electron–Neutral Momentum Transfer Collision Cross Sections of Selected Combustion Plasma Species. Applied Sciences 2023, 13, 11282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BWE, [Babcock & Wilcox Enterprises] BWE │ Nitrogen Oxides (NOx) Primer Available online:. Available online: https://www.babcock.com/home/about/resources/learning-center/nitrogen-oxides-nox-primer (accessed on 9 September 2025).
- The Coen & Hamworthy Combustion Handbook: Fundamentals for Power, Marine & Industrial Applications; Londerville, S.B., Baukal, C.E., Eds. Industrial combustion series; CRC Press/Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, Florida, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-1-4398-7333-5.
- Marzouk, O.A. Compilation of Smart Cities Attributes and Quantitative Identification of Mismatch in Rankings. Journal of Engineering 2022, 2022, 5981551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, G.G.; Dharmadhikari, H.M. Methods for Reducing NOX and PM Emissions in Compression Ignition Engine: A Review. Materials Today: Proceedings 2023, 72, 1406–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutrone, M.B. Low NOx Heavy Fuel Combustor Concept Program, Phase 1; NASA [United States National Aeronautics and Space Administration]: Cleveland, Ohio, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, W.; Mungal, M.; Cappelli, M. Flame Stabilization Using a Plasma Discharge in a Lifted Jet Flame. In Proceedings of the 43rd AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit; AIAA [American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics]: Reno, Nevada, USA, January 2005; p. AIAA 2005-931. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, S.; Patty, A.; Chen, S. Advances in Energy Science and Equipment Engineering: Proceedings of the International Conference on Energy Equipment Science and Engineering, (ICEESE 2015), May 30-31, 2015, Guangzhou, China; CRC Press: London, UK, 2015; ISBN 978-1-315-66798-0. [Google Scholar]
- Barlow, R.; Frank, J. SNL │ Piloted CH4/Air Flames C, D, E, and F – Release 2.1; SNL [Sandia National Laboratories]: Livermore, California, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Marzouk, O.A. Flow Control Using Bifrequency Motion. Theoretical and Computational Fluid Dynamics 2011, 25, 381–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HII, [Honeywell International Inc.] Honeywell │ Pilot Burners Available online:. Available online: https://process.honeywell.com/us/en/products/thermal-solutions/burners-and-heat-exchangers/pilot-burners (accessed on 7 September 2025).
- KES, [Koch Engineered Solutions] John Zink │ Process Burners Available online:. Available online: https://www.johnzink.com/products/process-burners (accessed on 7 September 2025).
- Poinsot, T.; Veynante, D. Theoretical and Numerical Combustion; 2nd ed.; Edwards: Philadelphia, 2005; ISBN 978-1-930217-10-2.
- Fu, X.; Yang, F.; Guo, Z. Combustion Instability of Pilot Flame in a Pilot Bluff Body Stabilized Combustor. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics 2015, 28, 1606–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MVHP, [Mountain View Hearth Products] MVHP │ Standing Pilot Troubleshooting Tips - Mountain View Hearth Products. Available online: https://help.stove-parts-unlimited.com/kb/gas-stove-troubleshooting-and-tips/standing-pilot-troubleshooting-tips (accessed on 7 September 2025).
- SCGC, [Southern California Gas Company] SCGC │ Gas Boilers - Advanced Design Guideline Series; SCGC [Southern California Gas Company]: Los Angeles, California, USA, 1998.
- Marzouk, O.A.; Huckaby, E.D. Simulation of a Swirling Gas-Particle Flow Using Different k-Epsilon Models and Particle-Parcel Relationships. Engineering Letters 2010, 18. [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll, J.; Temme, J. Role of Swirl in Flame Stabilization. In Proceedings of the 49th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting including the New Horizons Forum and Aerospace Exposition; AIAA [American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics]: Orlando, Florida, USA, January 2011; p. AIAA 2011-108. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Fan, Y.; Han, Q. Experimental Investigation of Thermal Protection Performance of Bluff-Body Flameholder in Augmented Combustor under Air Jet Cooling. Energy 2022, 254, 124236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namazian, M.; Kelly, J.; Schefer, R.W.; Johnston, S.C.; Long, M.B. Nonpremixed Bluff-Body Burner Flow and Flame Imaging Study. Experiments in Fluids 1989, 8, 216–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Yang, D.; Zhang, T.; Zhu, M. Characteristics of Flame Modes for a Conical Bluff Body Burner With a Central Fuel Jet. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 2013, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åkerblom, A.; Fureby, C. Large Eddy Simulations of Turbulent Premixed Bluff Body Flames Operated with Ethanol, n-Heptane, and Jet Fuels. Combustion and Flame 2025, 272, 113895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proch, F.; Domingo, P.; Vervisch, L.; Kempf, A.M. Flame Resolved Simulation of a Turbulent Premixed Bluff-Body Burner Experiment. Part I: Analysis of the Reaction Zone Dynamics with Tabulated Chemistry. Combustion and Flame 2017, 180, 321–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caetano, N.R.; Laan, F.T. van der Turbulent Flowfield Analysis in a Bluff-Body Burner Using PIV. World Journal of Mechanics 2013, 3, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzouk, O.A. Benchmarks for the Omani Higher Education Students-Faculty Ratio (SFR) Based on World Bank Data, QS Rankings, and THE Rankings. Cogent Education 2024, 11, 2317117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UoS, [University of Sydney] UoS │ AMME [School of Aerospace, Mechanical and Mechatronic Engineering] - Bluff-Body Flows and Flames. Available online: https://web.aeromech.usyd.edu.au/thermofluids/bluff.php (accessed on 7 September 2025).
- TNF Workshop, [International Workshop on Measurement and Computation of Turbulent Flames] TNF3 Workshop; TNF Workshop [International Workshop on Measurement and Computation of Turbulent Flames]: Boulder, Colorado, USA, 1998; pp. 1–164;
- TNF Workshop, [International Workshop on Measurement and Computation of Turbulent Flames] TNF6 Workshop; TNF Workshop [International Workshop on Measurement and Computation of Turbulent Flames]: Sapporo, Japan, 2002; pp. 1–307;
- TNF Workshop, [International Workshop on Measurement and Computation of Turbulent Flames] TNF7 Workshop; TNF Workshop [International Workshop on Measurement and Computation of Turbulent Flames]: Chicago, Illinois, USA, 2004; pp. 1–273;
- TNF Workshop, [International Workshop on Measurement and Computation of Turbulent Flames] TNF8 Workshop; TNF Workshop [International Workshop on Measurement and Computation of Turbulent Flames]: Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 1–349;
- TNF Workshop, [International Workshop on Measurement and Computation of Turbulent Flames] TNF9 Workshop; TNF Workshop [International Workshop on Measurement and Computation of Turbulent Flames]: Montreal, Canada, 2008; pp. 1–300;
- TNF Workshop, [International Workshop on Measurement and Computation of Turbulent Flames] TNF Workshop │ Bluff Body Flames. Available online: https://tnfworkshop.org/data-archives/bluffbod/ (accessed on 7 September 2025).
- Dally, B.B.; Masri, A.R.; Barlow, R.S.; Fiechtner, G.J. Instantaneous and Mean Compositional Structure of Bluff-Body Stabilized Nonpremixed Flames. Combustion and Flame 1998, 114, 119–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzouk, O.A. Estimated Electric Conductivities of Thermal Plasma for Air-Fuel Combustion and Oxy-Fuel Combustion with Potassium or Cesium Seeding. Heliyon 2024, 10, e31697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, I.; Schmidt, J.H. Methane Oxidation, Biogenic Carbon, and the IPCC’s Emission Metrics. Proposal for a Consistent Greenhouse-Gas Accounting. Int J Life Cycle Assess 2016, 21, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.-Y.; Byeon, S.-H. Specific Process Conditions for Non-Hazardous Classification of Hydrogen Handling Facilities. Safety and Health at Work 2021, 12, 416–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UoS, [University of Sydney] UoS │ AMME [School of Aerospace, Mechanical and Mechatronic Engineering] - Clean Combustion Research Group. Available online: https://web.aeromech.usyd.edu.au/thermofluids/database.php (accessed on 10 September 2025).
- Yan, J.; Thiele, F.; Buffat, M. A Turbulence Model Sensitivity Study for CH4/H2 Bluff-Body Stabilized Flames. Flow, Turbulence and Combustion 2004, 73, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzouk, O.A. The Sod Gasdynamics Problem as a Tool for Benchmarking Face Flux Construction in the Finite Volume Method. Scientific African 2020, 10, e00573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, N. Turbulent Combustion; Cambridge monographs on mechanics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000; ISBN 978-0-521-66082-2. [Google Scholar]
- Rung, T.; Lübcke, H.; Franke, M.; Xue, L.; Thiele, F.; Fu, S. Assessment of Explicit Algebraic Stress Models in Transonic Flows. In Engineering Turbulence Modelling and Experiments 4; Rodi, W., Laurence, D., Eds.; Elsevier Science Ltd.: Oxford, 1999; ISBN 978-0-08-043328-8. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.; Cheng, J.; Li, X.; Yang, C.; Mao, Z.-S. Numerical Simulation of Turbulent Flow in a Baffled Stirred Tank with an Explicit Algebraic Stress Model. Chemical Engineering Science 2012, 69, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Launder, B.E.; Spalding, D.B. The Numerical Computation of Turbulent Flows. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering 1974, 3, 269–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Pope, S.B.; Caughey, D.A. Calculations of Bluff-Body Stabilized Flames Using a Joint Probability Density Function Model with Detailed Chemistry. Combustion and Flame 2005, 141, 89–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, S.B. PDF Methods for Turbulent Reactive Flows. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science 1985, 11, 119–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuurmans, J.H.A.; Peeters, M.; Dorbec, M.; Kuijpers, K.P.L. Determination of Micromixing Times in Commercially Available Continuous-Flow Mixers: Evaluation of the Incorporation and Interaction by Exchange with the Mean Model. Journal of Flow Chemistry 2024, 14, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldyga, J.; Bourne, J.R. Comparison of the Engulfment and the Interaction-by-Exchange-with-the-Mean Micromixing Models. The Chemical Engineering Journal 1990, 45, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, S.; Mount, D.M. A Fast and Simple Algorithm for Computing Approximate Euclidean Minimum Spanning Trees. In Proceedings of the 2016 Annual ACM-SIAM Symposium on Discrete Algorithms (SODA); Proceedings; Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics; 2015; pp. 1220–1233. [Google Scholar]
- Odedra, A.; Malalasekera, W. Eulerian Particle Flamelet Modeling of a Bluff-Body CH4/H2 Flame. Combustion and Flame 2007, 151, 512–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-K.; Kim, Y. Assessment of the Eulerian Particle Flamelet Model for Nonpremixed Turbulent Jet Flames. Combustion and Flame 2008, 154, 232–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansys Fluent Ansys Fluent │ Fluid Simulation Software. Available online: https://www.ansys.com/products/fluids/ansys-fluent (accessed on 7 September 2025).
- Kitamura, O.; Yamamoto, M. Proposal of a Reynolds Stress Model for Gas-Particle Turbulent Flows and Its Application to Cylone Separators. In Engineering Turbulence Modelling and Experiments 4; Rodi, W., Laurence, D., Eds.; Elsevier Science Ltd.: Oxford, 1999; ISBN 978-0-08-043328-8. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Zhou, H.; Ren, Z.; Law, C.K. Transported PDF Simulation of Turbulent CH4/H2 Flames under MILD Conditions with Particle-Level Sensitivity Analysis. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute 2019, 37, 4487–4495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farokhi, M.; Birouk, M. Assessment of Fractal/Wrinkling Theories for Describing Turbulent Reacting Fine Structures under MILD Combustion Regimes. Combustion Science and Technology 2021, 193, 1798–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzouk, O.A. Portrait of the Decarbonization and Renewables Penetration in Oman’s Energy Mix, Motivated by Oman’s National Green Hydrogen Plan. Energies 2024, 17, 4769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medwell, P.R.; Kalt, P.A.M.; Dally, B.B. Simultaneous Imaging of OH, Formaldehyde, and Temperature of Turbulent Nonpremixed Jet Flames in a Heated and Diluted Coflow. Combustion and Flame 2007, 148, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dally, B.B.; Karpetis, A.N.; Barlow, R.S. Structure of Turbulent Non-Premixed Jet Flames in a Diluted Hot Coflow. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute 2002, 29, 1147–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, V.; Pitsch, H. Large-Eddy Simulation of a Bluff-Body-Stabilized Non-Premixed Flame Using a Recursive Filter-Refinement Procedure. Combustion and Flame 2005, 142, 329–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempf, A.; Lindstedt, R.P.; Janicka, J. Large-Eddy Simulation of a Bluff-Body Stabilized Nonpremixed Flame. Combustion and Flame 2006, 144, 170–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, S.; Zhu, J.; Anand, M.; Sekar, B. Large Eddy Simulations of Bluff-Body Stabilized Turbulent Flames and Gas Turbine Combustors. In Proceedings of the 2007 DoD High Performance Computing Modernization Program Users Group Conference; June 2007; pp. 133–138. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Zhou, H.; Ren, Z. A Numerical Study on Flame and Large-Scale Flow Structures in Bluff-Body Stabilized Flames. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics 2019, 32, 1646–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzouk, O.A. Direct Numerical Simulations of the Flow Past a Cylinder Moving With Sinusoidal and Nonsinusoidal Profiles. Journal of Fluids Engineering 2009, 131, 121201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhiyin, Y. Large-Eddy Simulation: Past, Present and the Future. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics 2015, 28, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OpenCFD OpenFOAM. Available online: https://www.openfoam.com (accessed on 7 September 2025).
- Suzuki, K.; Ogata, K.; Morishita, T.; Nagahama, H.; Sat0, T. Stability of a Confined Gaseous Diffusion Flame. Bulletin of JSME 1975, 18, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UoS, [University of Sydney] UoS │ AMME [School of Aerospace, Mechanical and Mechatronic Engineering] - Axisymmetric Bluff Body Turbulent Flow (Flame Code B4F3). Available online: https://web.aeromech.usyd.edu.au/thermofluids/bluff_files/b4f3.htm (accessed on 7 September 2025).
- UoS, [University of Sydney] UoS │ AMME [School of Aerospace, Mechanical and Mechatronic Engineering] - HM Flame Photo. Available online: https://web.aeromech.usyd.edu.au/thermofluids/bluff_files/bluff_flame_big.jpg (accessed on 5 September 2025).
- Liu, F.; Ai, Y.; Kong, W. Effect of Hydrogen and Helium Addition to Fuel on Soot Formation in an Axisymmetric Coflow Laminar Methane/Air Diffusion Flame. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 3936–3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzouk, O.A. Urban Air Mobility and Flying Cars: Overview, Examples, Prospects, Drawbacks, and Solutions. Open Engineering 2022, 12, 662–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-H.; Lee, K.-M.; Hwang, C.-H. Effects of Hydrogen Addition on Soot Formation and Oxidation in Laminar Premixed C2H2/Air Flames. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 9304–9311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gülder, Ö.L.; Snelling, D.R.; Sawchuk, R.A. Influence of Hydrogen Addition to Fuel on Temperature Field and Soot Formation in Diffusion Flames. Symposium (International) on Combustion 1996, 26, 2351–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Liu, J.; Guo, G.; Li, S. The Effects of Hydrogen Addition on Soot Particle Size Distribution Functions in Laminar Premixed Flame. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 6162–6169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzouk, O.A. Energy Generation Intensity (EGI) of Solar Updraft Tower (SUT) Power Plants Relative to CSP Plants and PV Power Plants Using the New Energy Simulator “Aladdin. ” Energies 2024, 17, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauvais, R. Laser-Doppler Velocimetry (LDV). In Optical Measurements: Techniques and Applications; Mayinger, F., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, 1994; ISBN 978-3-662-02967-1. [Google Scholar]
- Clark Brelje, T.; Wessendorf, M.W.; Sorenson, R.L. Chapter 5 - Multicolor Laser Scanning Confocal Immunofluorescence Microscopy: Practical Application and Limitations. In Methods in Cell Biology; Matsumoto, B., Ed.; Cell Biological Applications of Confocal Microscopy; Academic Press, 2002; Vol. 70, pp. 165–249e.
- Post, M.E.; Trump, D.D.; Goss, L.P.; Hancock, R.D. Two-Color Particle-Imaging Velocimetry Using a Single Argon-Ion Laser. Experiments in Fluids 1994, 16, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzouk, O.A. Dataset of Total Emissivity for CO2, H2O, and H2O-CO2 Mixtures; over a Temperature Range of 300-2900 K and a Pressure-Pathlength Range of 0.01-50 Atm.m. Data in Brief 2025, 59, 111428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepman, A.V.; Toro, V.V.; Mokhov, A.V.; Levinsky, H.B. Determination of Temperature and Concentrations of Main Components in Flames by Fitting Measured Raman Spectra. Appl. Phys. B 2013, 112, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcenally, C.S.; Pfefferle, L.D.; Schaffer, A.M.; Long, M.B.; Mohammed, R.K.; Smooke, M.D.; Colkei, M.B. Characterization of a Coflowing Methane/Air Non-Premixed Flame with Computer Modeling, Rayleigh-Raman Imaging, and on-Line Mass Spectrometry. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute 2000, 28, 2063–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daily, J.W. Laser Induced Fluorescence Spectroscopy in Flames. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science 1997, 23, 133–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Zhao, P.; Ge, H. reactingFoam-SCI: An Open Source CFD Platform for Reacting Flow Simulation. Computers & Fluids 2019, 190, 114–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Zhang, H.; Yang, S. A Robust Reacting Flow Solver with Computational Diagnostics Based on OpenFOAM and Cantera. Aerospace 2022, 9, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegner, P. Concepts and Paradigms of Object-Oriented Programming. SIGPLAN OOPS Mess. 1990, 1, 7–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzouk, O.A. Lookup Tables for Power Generation Performance of Photovoltaic Systems Covering 40 Geographic Locations (Wilayats) in the Sultanate of Oman, with and without Solar Tracking, and General Perspectives about Solar Irradiation. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evdokimov, I.; Haensch, S.; Schlegel, F. Scalable Workflows for OpenFOAM Evaluation. In Proceedings of the 2020 Ivannikov Ispras Open Conference (ISPRAS); December 2020; pp. 137–141. [Google Scholar]
- Rosner, D.E. Transport Processes in Chemically Reacting Flow Systems; Dover Publications: Mineola, New York, USA, 2012; ISBN 978-0-486-15063-5. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, K.K. Principles of Combustion; 2nd ed.; John Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, 2005; ISBN 978-0-471-04689-9.
- Bissaï Nkaa, S.J.; Chelem Mayigué, C.; Bomba, V.; Mboumeu, V.; Ekobena Fouda, H. Finite-Rate Chemistry Favre-Averaged Navier–Stokes Based Simulation of a Non-Premixed SynGas/AirFlame. J. Energy Resour. Technol 2024, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gieseking, D.A.; Choi, J.-I.; Edwards, J.R.; Hassan, H.A. Compressible-Flow Simulations Using a New Large-Eddy Simulation/Reynolds-Averaged Navier-Stokes Model. AIAA Journal 2011, 49, 2194–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatski, T.B.; Jongen, T. Nonlinear Eddy Viscosity and Algebraic Stress Models for Solving Complex Turbulent Flows. Progress in Aerospace Sciences 2000, 36, 655–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, N.; Zeng, D.; Meredith, K.V.; Wang, Y.; Dorofeev, S.B. Modeling of Flame Extinction/Re-Ignition in Oxygen-Reduced Environments. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute 2019, 37, 3951–3958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, C.; Wang, B. CRK-PINN: A Physics-Informed Neural Network for Solving Combustion Reaction Kinetics Ordinary Differential Equations. Combustion and Flame 2024, 269, 113647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, E.A.; Vilchevskaya, E.N.; Müller, W.H. Time Derivatives in Material and Spatial Description—What Are the Differences and Why Do They Concern Us? In Advanced Methods of Continuum Mechanics for Materials and Structures; Springer, Singapore, 2016; pp. 3–28 ISBN 978-981-10-0959-4.
- Cloney, C.T.; Ripley, R.C.; Pegg, M.J.; Amyotte, P.R. Laminar Burning Velocity and Structure of Coal Dust Flames Using a Unity Lewis Number CFD Model. Combustion and Flame 2018, 190, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspden, A.J.; Day, M.S.; Bell, J.B. Lewis Number Effects in Distributed Flames. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute 2011, 33, 1473–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haworth, D.C. Progress in Probability Density Function Methods for Turbulent Reacting Flows. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science 2010, 36, 168–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perić, M.; Kessler, R.; Scheuerer, G. Comparison of Finite-Volume Numerical Methods with Staggered and Colocated Grids. Computers & Fluids 1988, 16, 389–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felten, F.N.; Lund, T.S. Kinetic Energy Conservation Issues Associated with the Collocated Mesh Scheme for Incompressible Flow. Journal of Computational Physics 2006, 215, 465–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, H.F.; Alves, J.J.N.; Mori, M. Comparison between Staggered and Collocated Grids in the Finite-Volume Method Performance for Single and Multi-Phase Flows. Computers & Chemical Engineering 1999, 23, 247–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chomiak, J.; Karlsson, A. Flame Liftoff in Diesel Sprays. Symposium (International) on Combustion 1996, 26, 2557–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuirk, J.J.; Rodi, W. The Calculation of Three-Dimensional Turbulent Free Jets. In Proceedings of the Turbulent Shear Flows I; Durst, F., Launder, B.E., Schmidt, F.W., Whitelaw, J.H., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, Germany, 1979; pp. 71–83. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, M.; Jones, J.C.; Malalasekera, W. Modelling of a Bluff-Body Nonpremixed Flame Using a Coupled Radiation/Flamelet Combustion Model. Flow, Turbulence and Combustion 2001, 67, 217–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, W.P.; Lindstedt, R.P. Global Reaction Schemes for Hydrocarbon Combustion. Combustion and Flame 1988, 73, 233–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, H.; Gupta, A.K.; Hasegawa, T.; Katsuki, M.; Kishimoto, K.; Morita, M. High Temperature Air Combustion: From Energy Conservation to Pollution Reduction; CRC Press: Boca Raton, Florida, USA, 2002; ISBN 978-1-4200-4103-3. [Google Scholar]
- Andersen, J.; Rasmussen, C.L.; Giselsson, T.; Glarborg, P. Global Combustion Mechanisms for Use in CFD Modeling under Oxy-Fuel Conditions. Energy Fuels 2009, 23, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y. Some Approaches to Novel Molten Salt Electrochemical Processes. Electrochemistry 2000, 68, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S. Transport Phenomena In Combustion; 1st ed.; Routledge: New York, USA, 2024; ISBN 978-0-203-73513-8.
- Bressloff, N.W. A Parallel Pressure Implicit Splitting of Operators Algorithm Applied to Flows at All Speeds. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids 2001, 36, 497–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzouk, O.A. Contrasting the Cartesian and Polar Forms of the Shedding-Induced Force Vector in Response to 12 Subharmonic and Superharmonic Mechanical Excitations. Fluid Dynamics Research 2010, 42, 035507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasak, H. Error analysis and estimation in the Finite Volume method with applications to fluid flows. Doctoral Thesis, Imperial College London: London, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Marzouk, O.A.; Nayfeh, A.H. A Study of the Forces on an Oscillating Cylinder. In Proceedings of the ASME 2007 26th International Conference on Offshore Mechanics and Arctic Engineering (OMAE 2007); ASME [American Society of Mechanical Engineers]: San Diego, California, USA, May 20 2009; pp. 741–752.
- Lin, H.; Rosenberger, F.; Alexander, J.I.D.; Nadarajah, A. Convective-Diffusive Transport in Protein Crystal Growth. Journal of Crystal Growth 1995, 151, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolukisa, D.C.; Ozbulut, M.; Yildiz, M. The Effect of Iterative Procedures on the Robustness and Fidelity of Augmented Lagrangian SPH. Symmetry 2021, 13, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møyner, O.; Lie, K.-A. A Data-Driven Approach to Select Optimal Time Steps for Complex Reservoir Models.; OnePetro, March 18 2025.
- Marzouk, O.A. Coupled Differential-Algebraic Equations Framework for Modeling Six-Degree-of-Freedom Flight Dynamics of Asymmetric Fixed-Wing Aircraft. International Journal of Applied and Advanced Sciences 2025, 12, 30–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OpenCFD OpenFOAM │ User Guide - Preconditioned Bi-Conjugate Gradient (PBiCG). Available online: https://www.openfoam.com/documentation/guides/latest/doc/guide-solvers-cg-pbicg.html (accessed on 19 September 2025).
- Grylonakis, E.-N.G.; Filelis-Papadopoulos, C.K.; Gravvanis, G.A. Higher Order Finite Difference Scheme for Solving 3D Black-Scholes Equation Based on Generic Factored Approximate Sparse Inverse Preconditioning Using Reordering Schemes. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 18th Panhellenic Conference on Informatics; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, October 2, 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- OpenCFD OpenFOAM │ User Guide - DILU Preconditioner. Available online: https://www.openfoam.com/documentation/guides/v2112/doc/guide-solvers-cg-preconditioner-dilu.html (accessed on 14 June 2025).
- Li, W.-D.; Hong, W.; Zhou, H.-X. An IE-ODDM-MLFMA Scheme With DILU Preconditioner for Analysis of Electromagnetic Scattering From Large Complex Objects. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation 2008, 56, 1368–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekgül, B.; Peltonen, P.; Kahila, H.; Kaario, O.; Vuorinen, V. DLBFoam: An Open-Source Dynamic Load Balancing Model for Fast Reacting Flow Simulations in OpenFOAM. Computer Physics Communications 2021, 267, 108073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzouk, O.A. InvSim Algorithm for Pre-Computing Airplane Flight Controls in Limited-Range Autonomous Missions, and Demonstration via Double-Roll Maneuver of Mirage III Fighters. Scientific Reports 2025, 15, 23382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishna, R.; Méheust, Y.; Neuweiler, I. A Two-Dimensional Depth-Integrated Model for Immiscible Two-Phase Flow in Open Rough Fractures. Journal of Fluid Mechanics 2025, 1011, A43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, N.; Srinadhi, K.; T., K.B. Comparative Studies of Solvers on Compressible Axisymmetric Jet Using OpenFOAM®. AIP Conf. Proc. 2022, 2516, 030006. [CrossRef]
- Rettenmaier, D.; Deising, D.; Ouedraogo, Y.; Gjonaj, E.; De Gersem, H.; Bothe, D.; Tropea, C.; Marschall, H. Load Balanced 2D and 3D Adaptive Mesh Refinement in OpenFOAM. SoftwareX 2019, 10, 100317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorina, C.; Clifford, I.; Aufiero, M.; Mikityuk, K. GeN-Foam: A Novel OpenFOAM® Based Multi-Physics Solver for 2D/3D Transient Analysis of Nuclear Reactors. Nuclear Engineering and Design 2015, 294, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Ma, X.; Bai, W.; Lin, Z.; Li, Y. Numerical Simulation of Water Entry of a Symmetric/Asymmetric Wedge into Waves Using OpenFOAM. Ocean Engineering 2021, 227, 108923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, B.K.; Verma, H.K.; Abraham, B. Investigation of Flow Profile in Open Channels Using CFD.; IIT Roorkee [Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee], India, October 2010; pp. 243–251.
- Worth Longest, P.; Vinchurkar, S. Validating CFD Predictions of Respiratory Aerosol Deposition: Effects of Upstream Transition and Turbulence. Journal of Biomechanics 2007, 40, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, D.; Sharma, S.D.; Roy, S. GPU Optimized Multi-Block-Multi-Mesh Immersed Boundary Method for Flows in Complex Arterial Models. Computers & Fluids 2024, 281, 106367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, Y.S.; Noviani, E. Application of Open FOAM CFD Software for Hydrodynamics Problems. AIP Conf. Proc. 2024, 2891, 030008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eça, L.; Saraiva, G.; Vaz, G.; Abreu, H. The Pros and Cons of Wall Functions.; American Society of Mechanical Engineers Digital Collection, October 21 2015.
- UoS, [University of Sydney] UoS │ AMME [School of Aerospace, Mechanical and Mechatronic Engineering] - Data File for the B4F3 (HM) Flame 2025.
- Bremhorst, K.; Harch, W.H. The Mechanism of Jet Entrainment. AIAA Journal 1978, 16, 1104–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, H. c.; Torczynski, J. r.; Morton, S. a.; Visbal, M. r.; Sweby, P. k. On Spurious Behavior of CFD Simulations. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids 1999, 30, 675–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allgower, E.L.; Böhmer, K. Application of the Mesh Independence Principle to Mesh Refinement Strategies. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 1987, 24, 1335–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alegria, F.A.C. Estimation of the Root Mean Square of the Residuals of Sine Fitting in the Presence of Phase Noise or Jitter. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 150028–150036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yager, R.R.; Alajlan, N. A Note on Mean Absolute Deviation. Information Sciences 2014, 279, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarella, C.; Fanelli, V.; Musti, S. Modelling the Evolution of Credit Spreads Using the Cox Process within the HJM Framework: A CDS Option Pricing Model. European Journal of Operational Research 2011, 208, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.K.; Chatterjee, M.; Kaur, G.; Vavilala, S. 3 - Deep Learning Applications for Disease Diagnosis. In Deep Learning for Medical Applications with Unique Data; Gupta, D., Kose, U., Khanna, A., Balas, V.E., Eds.; Academic Press, 2022; pp. 31–51 ISBN 978-0-12-824145-5.
- Kong, Q.; Siauw, T.; Bayen, A.M. Chapter 17 - Interpolation. In Python Programming and Numerical Methods; Kong, Q., Siauw, T., Bayen, A.M., Eds.; Academic Press, 2021; pp. 295–313 ISBN 978-0-12-819549-9.
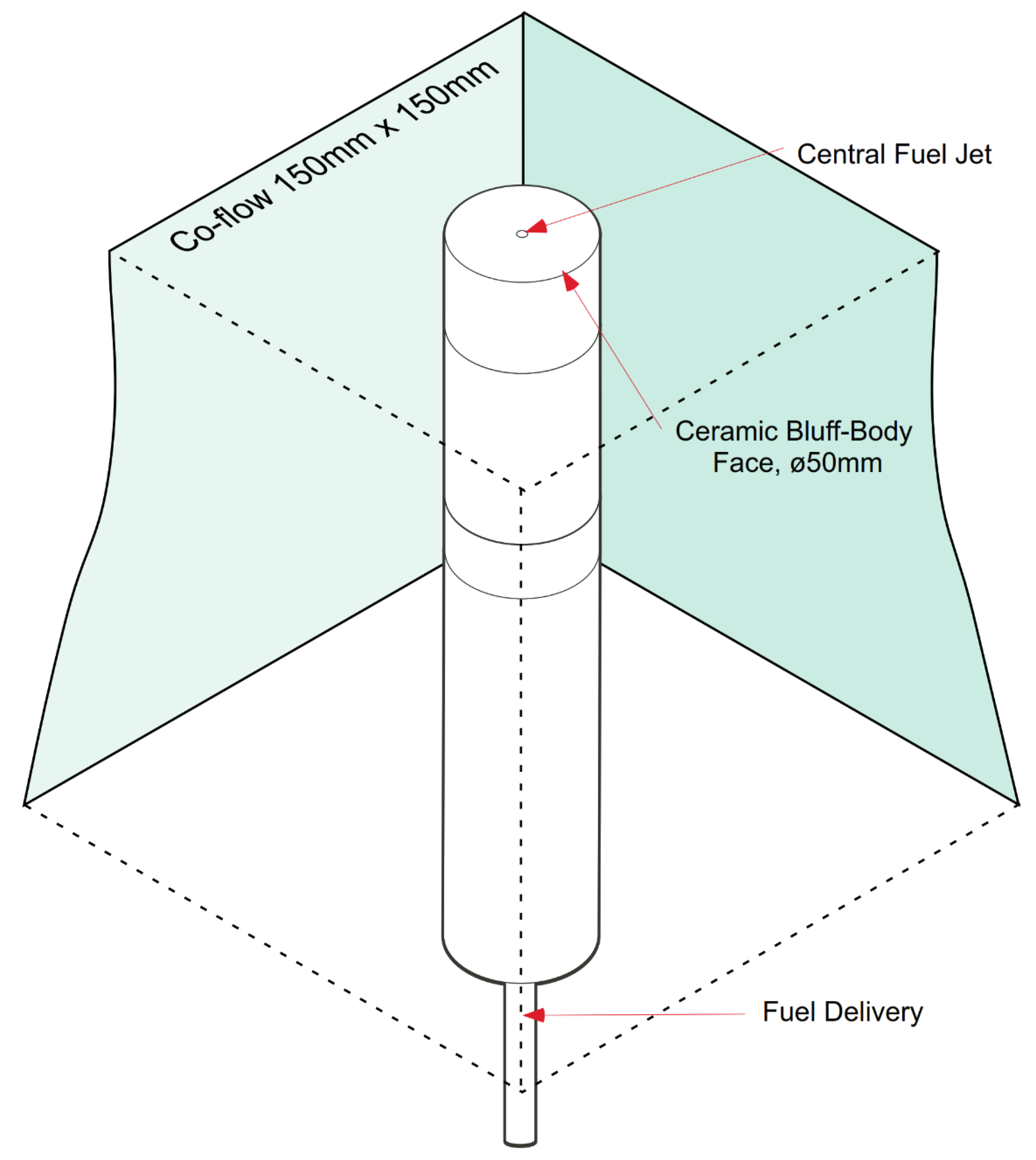

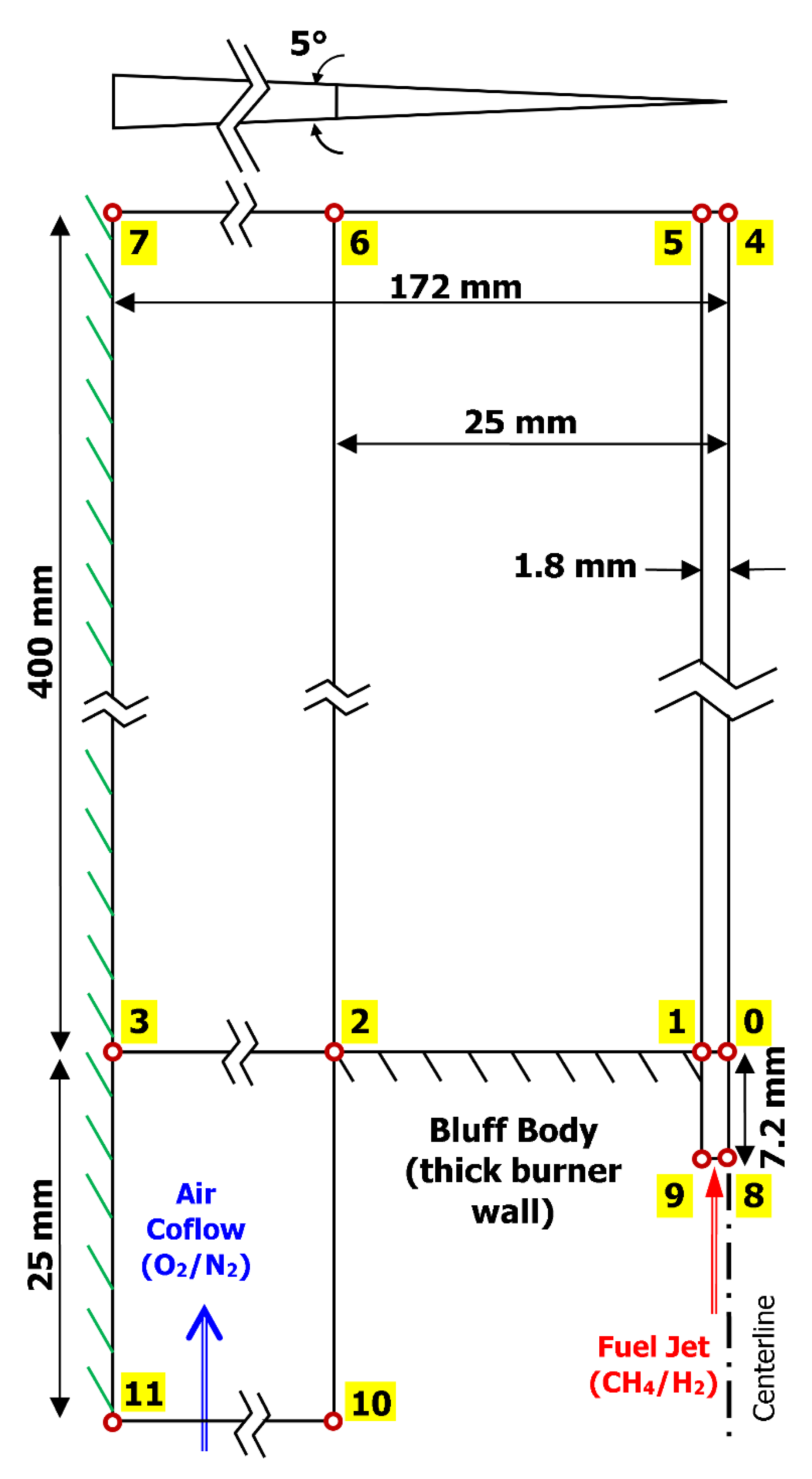
| Wind tunnel dimensions | 305 × 305 mm |
| Fuel jet diameter | 3.6 mm |
| Bluff-body diameter | 50 mm |
| Fuel jet mixture | CH4/H2 (1:1 or 50/50% by mole) |
| Fuel jet speed | 118.0 m/s |
| Blow-off speed | 235.0 m/s |
| %Blow-off (fuel jet speed ÷ blow-off speed) | 50.2% |
| Coflow air velocity | 40 m/s |
| Coflow turbulence intensity | 2% |
| Mass fraction of O2 in the coflow | 0.233 (21% by mole) |
| Mass fraction of N2 in the coflow | 0.767 (79% by mole) |
| Reynolds number of the fuel jet | 15,800 |
| Temperature of the fuel jet at the exit nozzle | 298 K |
| Momentum flux of the fuel jet | 0.03370 N |
| Adiabatic flame temperature | 2,265 K |
| Year of the experiment | 1995 |
| Index | Profile Type | HM1 Variable | Number of Points | Unit | MAD | RMS | ||
| Coarse | Fine | Coarse | Fine | |||||
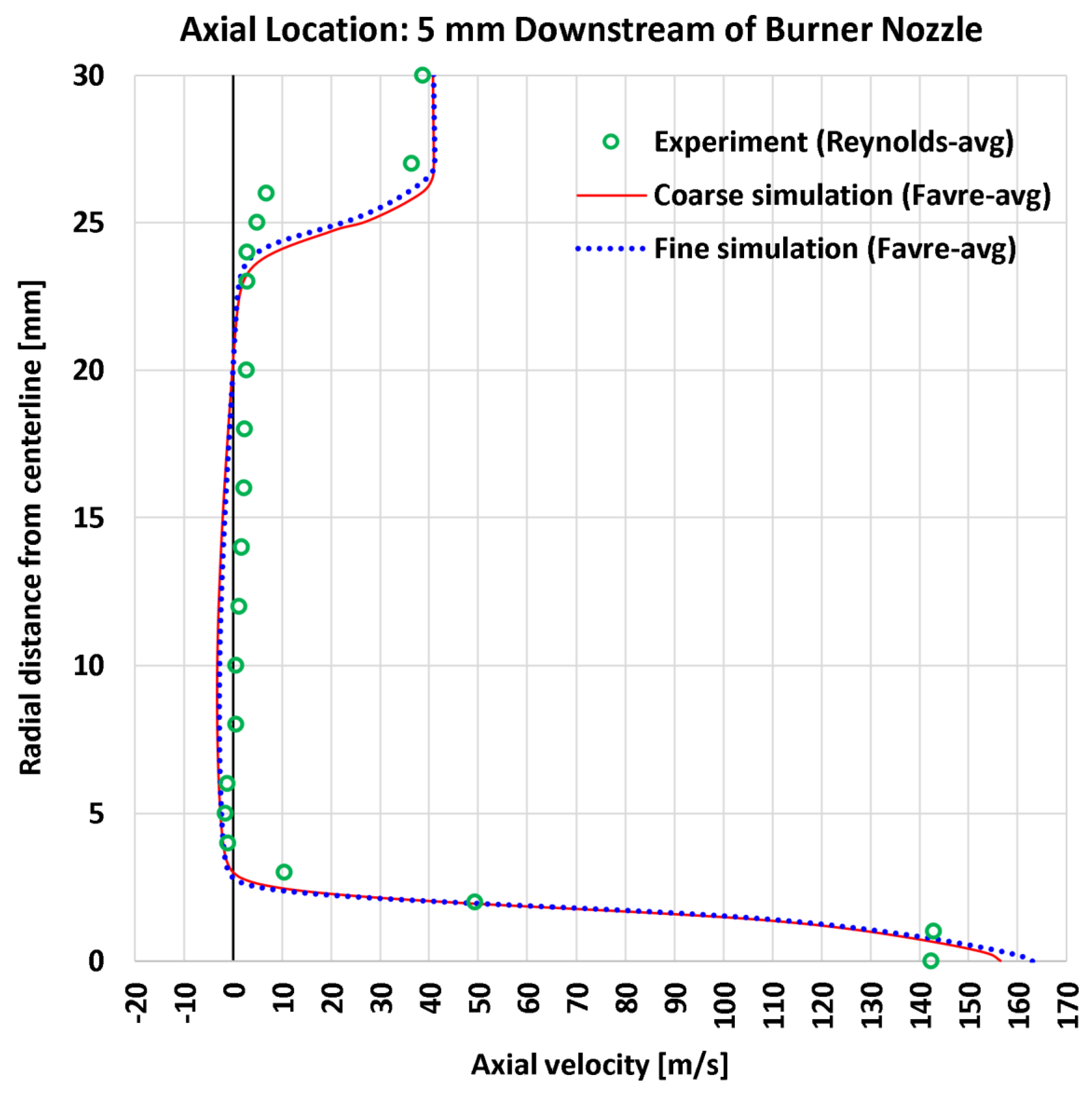
| 1 | Radial | Axial velocity at 5 mm | 20 | m/s | 7.06 | 6.54 | 10.41 | 9.80 |
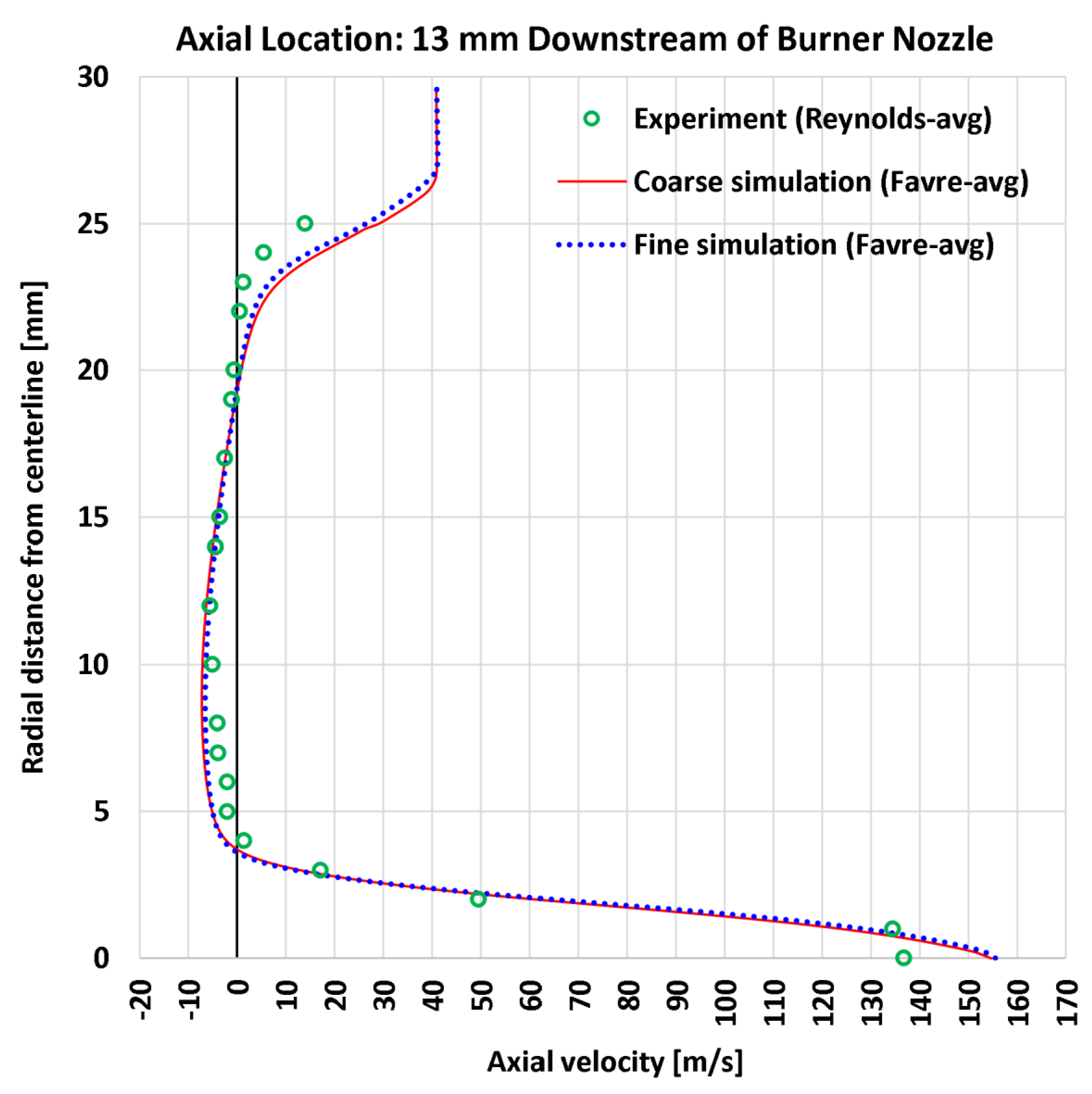
| 2 | Radial | Axial velocity at 13 mm | 22 | m/s | 5.11 | 4.66 | 7.11 | 6.79 |
| 3 | Radial | Axial velocity at 30 mm | 21 | m/s | 6.16 | 5.99 | 8.31 | 7.91 |
| 4 | Radial | Axial velocity at 45 mm | 22 | m/s | 6.88 | 6.48 | 9.94 | 9.60 |
| 5 | Radial | Axial velocity at 65 mm | 24 | m/s | 6.16 | 5.57 | 7.56 | 6.90 |
| 6 | Radial | Radial velocity at 5 mm | 20 | m/s | 0.77 | 0.78 | 0.91 | 0.87 |
| 7 | Radial | Radial velocity at 13 mm | 22 | m/s | 0.53 | 0.54 | 0.63 | 0.65 |
| 8 | Radial | Radial velocity at 30 mm | 21 | m/s | 1.23 | 1.24 | 1.68 | 1.70 |
| 9 | Radial | Radial velocity at 45 mm | 22 | m/s | 0.94 | 0.94 | 1.39 | 1.37 |
| 10 | Radial | Radial velocity at 65 mm | 24 | m/s | 1.58 | 1.58 | 2.22 | 2.21 |
| 11 | Radial | CH4 mass fraction at 13 mm | 9 | - | 0.04850 | 0.04985 | 0.06283 | 0.06255 |
| 12 | Radial | CH4 mass fraction at 30 mm | 13 | - | 0.05462 | 0.05199 | 0.07626 | 0.07223 |
| 13 | Radial | H2O mass fraction at 13 mm | 9 | - | 0.01759 | 0.01668 | 0.02342 | 0.02206 |
| 14 | Radial | H2O mass fraction at 30 mm | 13 | - | 0.01895 | 0.01896 | 0.02065 | 0.02104 |
| 15 | Axial | CH4 mass fraction at 1.1 mm | 6 | - | 0.04359 | 0.05175 | 0.05079 | 0.05941 |
| 16 | Axial | H2O mass fraction at 1.1 mm | 6 | - | 0.00792 | 0.00937 | 0.00934 | 0.01088 |
| 17 | Axial | Temperature at 1.1 mm | 6 | °C | 123 | 127 | 133 | 136 |
| Index | Profile Type | HM1 Variable | Maximum (Experimental) | Unit | %MAD | %RMS | ||
| Coarse | Fine | Coarse | Fine | |||||
| 1 | Radial | Axial velocity at 5 mm | 142.95 | m/s | 4.939% | 4.575% | 7.282% | 6.857% |
| 2 | Radial | Axial velocity at 13 mm | 136.84 | m/s | 3.731% | 3.404% | 5.198% | 4.960% |
| 3 | Radial | Axial velocity at 30 mm | 113.51 | m/s | 5.426% | 5.275% | 7.320% | 6.969% |
| 4 | Radial | Axial velocity at 45 mm | 63.54 | m/s | 10.821% | 10.203% | 15.637% | 15.111% |
| 5 | Radial | Axial velocity at 65 mm | 58.90 | m/s | 10.456% | 9.462% | 12.832% | 11.723% |
| 6 | Radial | Radial velocity at 5 mm | 3.82 | m/s | 20.19% | 23.73% | 20.37% | 22.69% |
| 7 | Radial | Radial velocity at 13 mm | 1.41 | m/s | 37.93% | 38.39% | 44.70% | 45.89% |
| 8 | Radial | Radial velocity at 30 mm | 2.72 | m/s | 45.15% | 45.58% | 61.93% | 62.36% |
| 9 | Radial | Radial velocity at 45 mm | 4.70 | m/s | 20.07% | 20.07% | 29.53% | 29.21% |
| 10 | Radial | Radial velocity at 65 mm | 3.48 | m/s | 45.44% | 45.33% | 63.66% | 63.47% |
| 11 | Radial | CH4 mass fraction at 13 mm | 0.86616 | - | 5.600% | 5.756% | 7.254% | 7.222% |
| 12 | Radial | CH4 mass fraction at 30 mm | 0.71701 | - | 7.618% | 7.251% | 10.636% | 10.073% |
| 13 | Radial | H2O mass fraction at 13 mm | 0.15302 | - | 11.497% | 10.900% | 15.307% | 14.418% |
| 14 | Radial | H2O mass fraction at 30 mm | 0.14422 | - | 13.138% | 13.149% | 14.321% | 14.592% |
| 15 | Axial | CH4 mass fraction at 1.1 mm | 0.81633 | - | 5.339% | 6.339% | 6.221% | 7.278% |
| 16 | Axial | H2O mass fraction at 1.1 mm | 0.11439 | - | 6.925% | 8.188% | 8.165% | 9.514% |
| 17 | Axial | Temperature at 1.1 mm | 1,224 | °C | 10.051% | 10.413% | 10.828% | 11.088% |
| Average for 12 profiles (excluding the five radial velocity profiles ) | 7.962% | 7.910% | 10.083% | 9.984% | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





