Submitted:
06 September 2025
Posted:
08 September 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Global Context: Challenges Linked to Wastewater Pollution
1.2. Limitations of Conventional Wastewater Treatment Technologies
1.3. The Role of Coagulants in Wastewater Treatment Chains
1.4. Objective of the Review
- Identify recent progress in the development of multifunctional, hybrid, or composite coagulants capable of broadening the range of pollutants removed while minimizing environmental impact—such as magnetic or bio-functional coagulants ;
- Assess emerging technological potentials, including assisted electrocoagulation, high-turbulence processes optimized through Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD), and real-time adaptive dosing systems;
- Highlight sustainability criteria, including treatment efficiency, reduced coagulant toxicity, ease of sludge valorization, and compatibility with biological or membrane processes.
- Explore the integration of intelligent systems, notably coupling coagulation with automated technologies, IoT-enabled monitoring, and artificial intelligence to dynamically adjust treatment parameters according to load variability;
- Compare findings from applied studies on representative effluents—such as textile, agro-industrial, and petrochemical wastewater—to provide a rigorous synthesis of the optimal conditions for next-generation coagulation–flocculation technologies ;
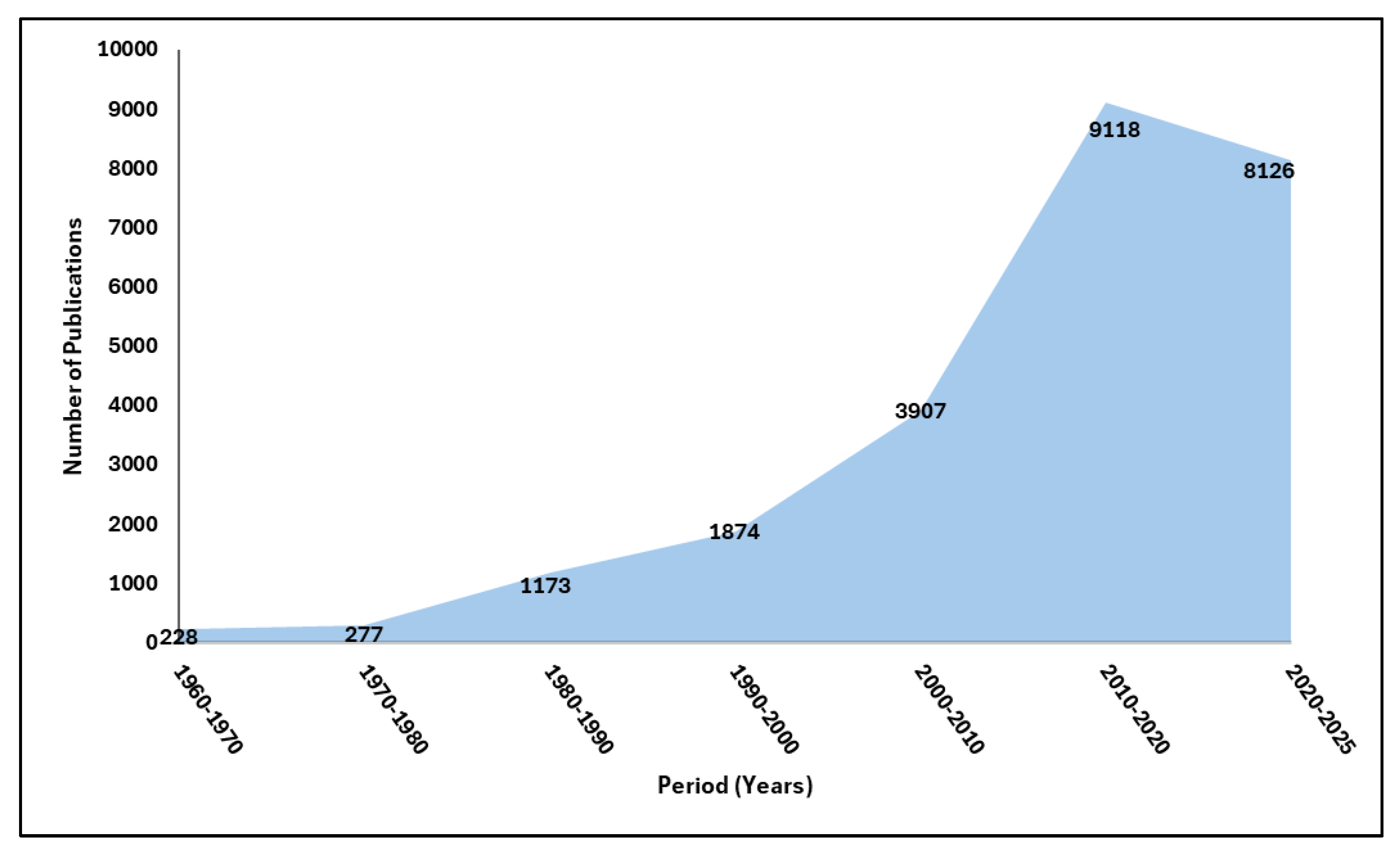
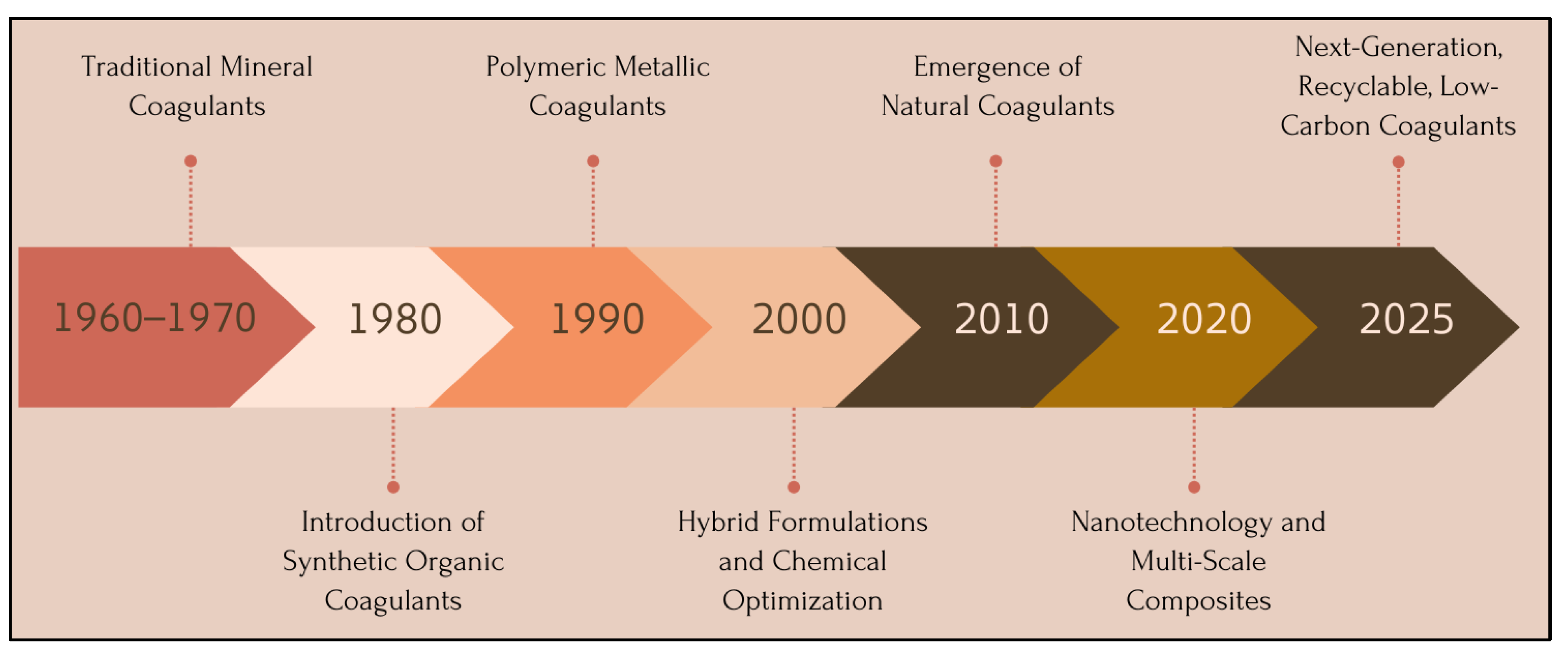
2. Evolution of Coagulant Technologies for Wastewater Treatment
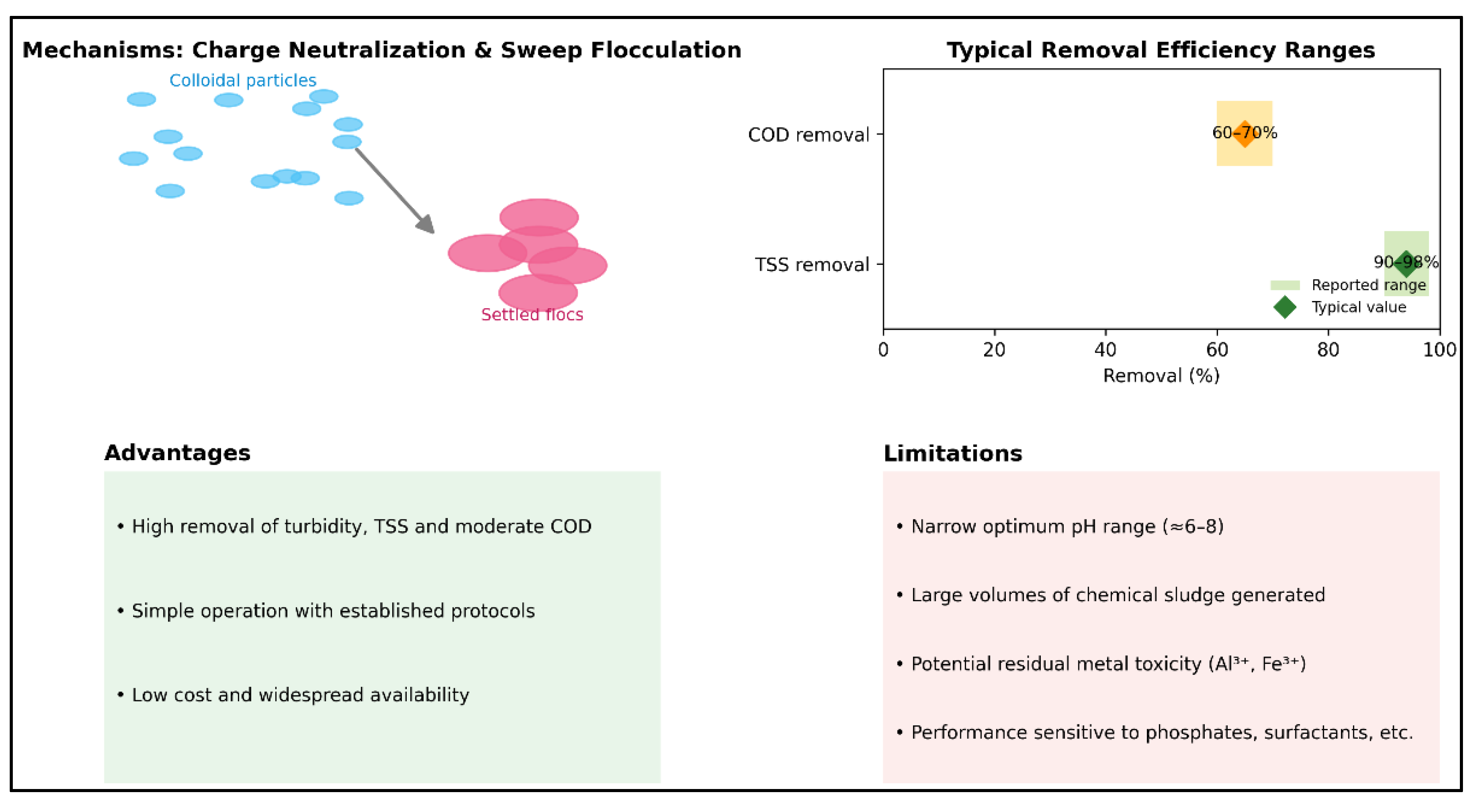
2.1. Traditional Mineral Coagulants (Before the 1960s)
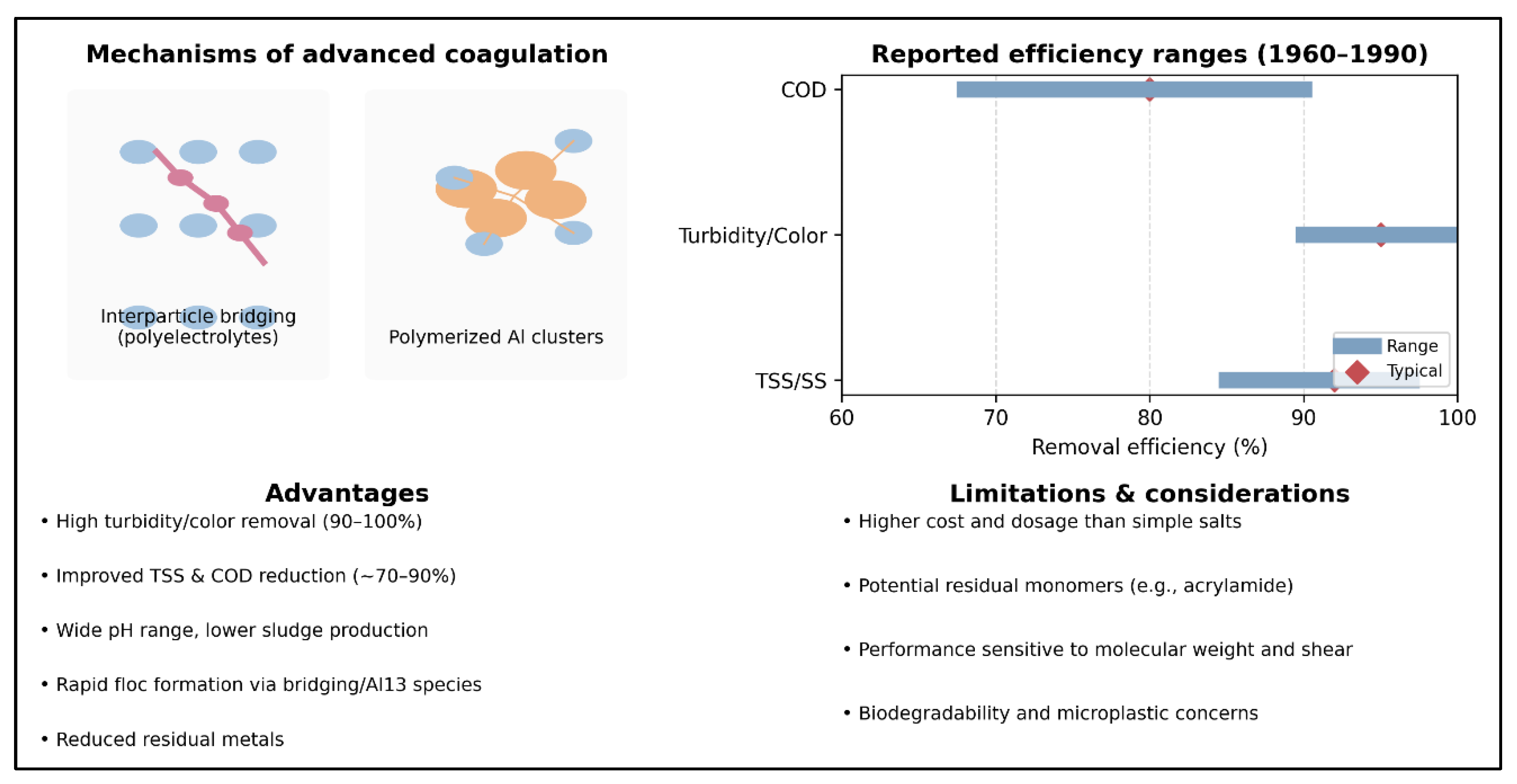
2.2. Emergence of Synthetic Organic Coagulants and Improved Mineral Formulations (1960–1990)
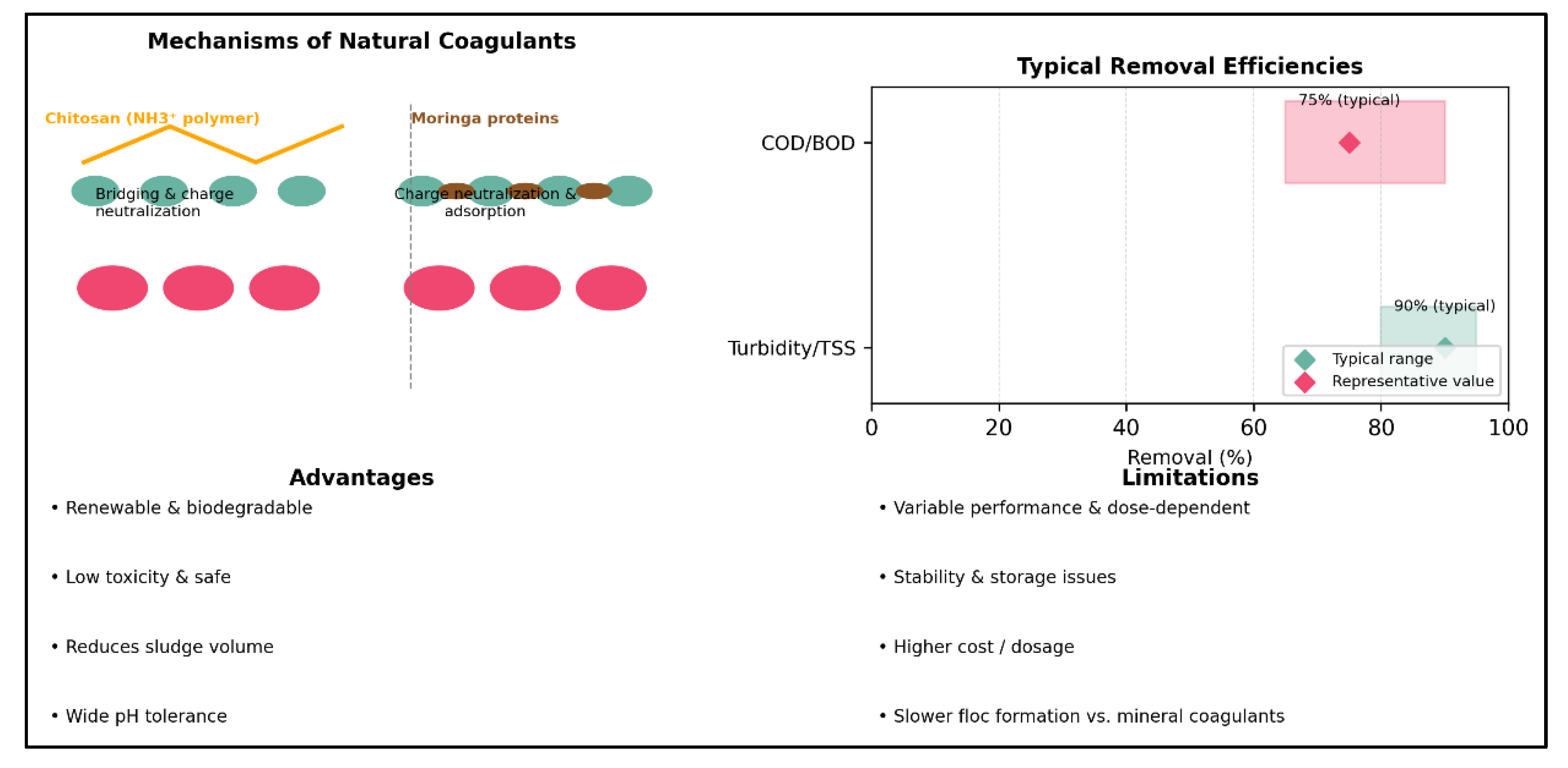
2.3. Revival of Natural and Bio-Based Coagulants (1990–2010)
2.4. Recent Innovative and Hybrid Technologies (2010–2025)
3. Coagulation/Flocculation Mechanisms and Performance Criteria
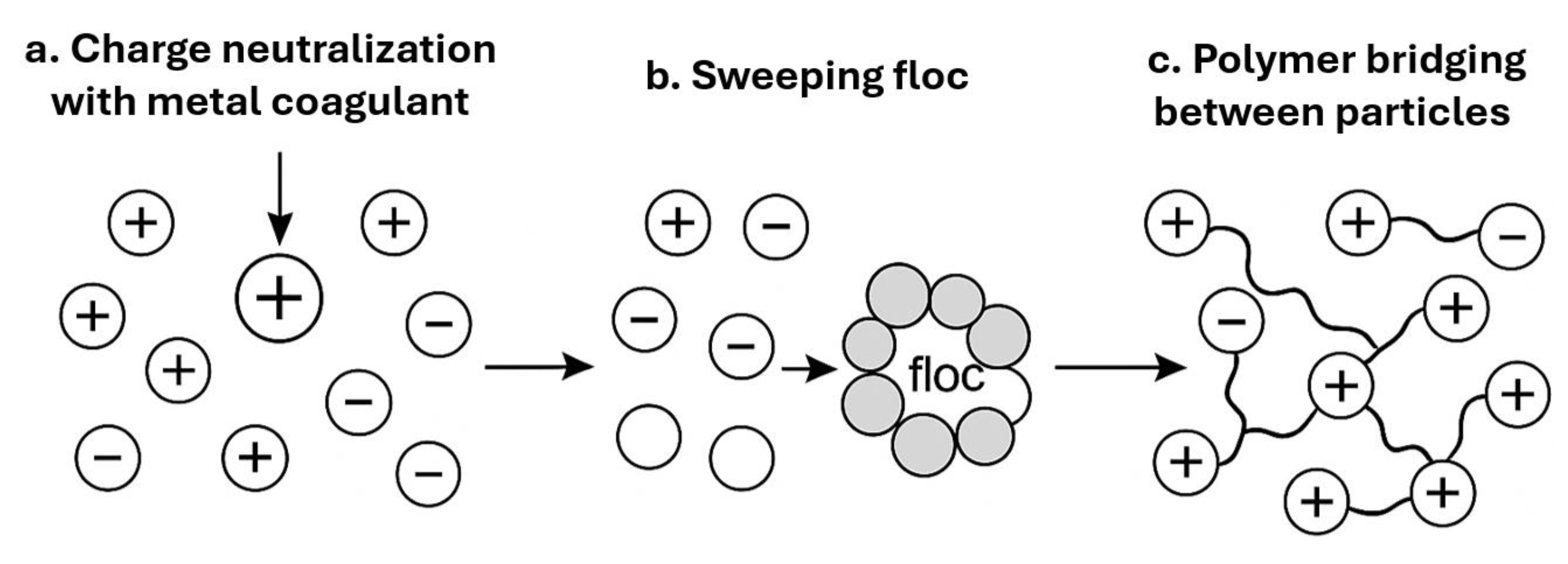
3.1. Fundamentals of Coagulation/Flocculation Mechanisms
3.2. Comparative Performance of Different Categories of Coagulants
3.3. Criteria for Selecting a Coagulant (Efficiency, Cost, Sustainability, Toxicity, etc.)
4. Scientific Gaps, Technological Limits and Current Challenges
4.1. Scientific Gaps in the Understanding of Coagulation/Flocculation Mechanisms
- Advanced molecular characterization of natural and hybrid coagulants;
- Multi-scale analysis of floc structures using microscopy, spectroscopy, and modeling;
- Development of robust kinetic models, experimentally validated across different effluent types;
- Integration of experiments, online sensing, and simulation to enable real-time process optimization.
4.2. Technological Limitations and Application Constraints
4.3. Current Challenges and Open Questions
5. Recommendations and Future Perspectives
5.1. Immediate and Practical Recommendations
5.1.1. Research Directions
- Development of Innovative Coagulants
- Integration into industrial treatment trains
5.2. Long-Term Perspectives
5.2.1. Toward Intelligent Coagulation
5.2.2. Disruptive Innovation: Electrocoagulation and Biocoagulation
5.2.3. Toward a Circular Economy of Coagulants
5.2.4. Interdisciplinary Approach and Multi-Stakeholder Partnerships
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abu Bakar, A. F., & Halim, A. A. (2013). Treatment of automotive wastewater by coagulation-flocculation using poly-aluminum chloride (PAC), ferric chloride (FeCl3) and aluminum sulfate (alum). AIP Conference Proceedings, 1571, 524–529. [CrossRef]
- Abujazar, M. S. S., Karaağaç, S. U., Abu Amr, S. S., Alazaiza, M. Y. D., & Bashir, M. J. (2022a). Recent advancement in the application of hybrid coagulants in coagulation-flocculation of wastewater: A review. In Journal of Cleaner Production (Vol. 345). Elsevier Ltd. [CrossRef]
- Abujazar, M. S. S., Karaağaç, S. U., Abu Amr, S. S., Alazaiza, M. Y. D., & Bashir, M. J. (2022b). Recent advancement in the application of hybrid coagulants in coagulation-flocculation of wastewater: A review. Journal of Cleaner Production, 345. [CrossRef]
- Adeleke, V. T., Madlala, N. E., Adeniyi, A. A., & Lokhat, D. (2022). Molecular Interactions Associated with Coagulation of Organic Pollutants by 2S Albumin of Plant Proteins: A Computational Approach. Molecules, 27(5). [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H. M., El-Khateeb, M. A., Mohamed, N. Y., Sobhy, N. A., & Fawzy, M. E. (2024). Evaluation of different natural waste materials as bio-coagulants for domestic wastewater treatment. Desalination and Water Treatment, 317. [CrossRef]
- Al-Jadabi, N., Laaouan, M., El Hajjaji, S., Mabrouki, J., Benbouzid, M., & Dhiba, D. (2023). The Dual Performance of Moringa Oleifera Seeds as Eco-Friendly Natural Coagulant and as an Antimicrobial for Wastewater Treatment: A Review. In Sustainability (Switzerland) (Vol. 15, Issue 5). MDPI. [CrossRef]
- Alekseev, E., & Shambina, S. (2021). Coagulation of waste water from the point of view of physic-chemical interactions. E3S Web of Conferences, 263, 04011. [CrossRef]
- Alibeigi-Beni, S., Habibi Zare, M., Pourafshari Chenar, M., Sadeghi, M., & Shirazian, S. (2021). Design and optimization of a hybrid process based on hollow-fiber membrane/coagulation for wastewater treatment. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(7), 8235–8245. [CrossRef]
- Amin, N. K., Abdelwahab, O., El-Ashtoukhy, E. S. Z., & Abdel-Aziz, M. H. (2025). Comparative analysis of new natural coagulant extracts for turbidity removal in water systems. Water Science and Technology : A Journal of the International Association on Water Pollution Research, 91(7), 797–810. [CrossRef]
- Amoohadi, V., Pasalari, H., Esrafili, A., Gholami, M., & Farzadkia, M. (2023). A comparative study on polyaluminum chloride (PACl) and Moringa oleifera (MO) chemically enhanced primary treatment (CEPT) in enhanced biogas production: anaerobic digestion performance and the Gompertz model. RSC Advances, 13(25), 17121–17129. [CrossRef]
- Amuda, O. S., & Alade, A. (2006). Coagulation/flocculation process in the treatment of abattoir wastewater. Desalination, 196(1–3), 22–31. [CrossRef]
- Aragaw, T. A., & Bogale, F. M. (2023a). Role of coagulation/flocculation as a pretreatment option to reduce colloidal/bio-colloidal fouling in tertiary filtration of textile wastewater: A review and future outlooks. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 11, 1142227. [CrossRef]
- Aragaw, T. A., & Bogale, F. M. (2023b). Role of coagulation/flocculation as a pretreatment option to reduce colloidal/bio-colloidal fouling in tertiary filtration of textile wastewater: A review and future outlooks. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 11. [CrossRef]
- Asadollahfardi, G., Zangooei, H., Motamedi, V., & Davoodi, M. (2018). Selection of coagulant using jar test and analytic hierarchy process: A case study of Mazandaran textile wastewater. Advances in Environmental Research, 7(1), 1–11.
- Badawi, A. K., Salama, R. S., & Mostafa, M. M. M. (2023a). Natural-based coagulants/flocculants as sustainable market-valued products for industrial wastewater treatment: a review of recent developments. In RSC Advances (Vol. 13, Issue 28, pp. 19335–19355). Royal Society of Chemistry. [CrossRef]
- Badawi, A. K., Salama, R. S., & Mostafa, M. M. M. (2023b). Natural-based coagulants/flocculants as sustainable market-valued products for industrial wastewater treatment: a review of recent developments. RSC Advances, 13(28), 19335. [CrossRef]
- Badawi, A. K., Salama, R. S., & Mostafa, M. M. M. (2023c). Natural-based coagulants/flocculants as sustainable market-valued products for industrial wastewater treatment: a review of recent developments. In RSC Advances (Vol. 13, Issue 28, pp. 19335–19355). Royal Society of Chemistry. [CrossRef]
- Badawi, A. K., Salama, R. S., & Mostafa, M. M. M. (2023d). Natural-based coagulants/flocculants as sustainable market-valued products for industrial wastewater treatment: a review of recent developments. In RSC Advances (Vol. 13, Issue 28, pp. 19335–19355). Royal Society of Chemistry. [CrossRef]
- Badawi, A. K., & Zaher, K. (2021). Hybrid treatment system for real textile wastewater remediation based on coagulation/flocculation, adsorption and filtration processes: Performance and economic evaluation. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 40. [CrossRef]
- Bahrodin, M. B., Zaidi, N. S., Hussein, N., Sillanpää, M., Prasetyo, D. D., & Syafiuddin, A. (2021a). Recent Advances on Coagulation-Based Treatment of Wastewater: Transition from Chemical to Natural Coagulant. Current Pollution Reports, 7(3), 379–391. [CrossRef]
- Bahrodin, M. B., Zaidi, N. S., Hussein, N., Sillanpää, M., Prasetyo, D. D., & Syafiuddin, A. (2021b). Recent Advances on Coagulation-Based Treatment of Wastewater: Transition from Chemical to Natural Coagulant. Current Pollution Reports, 7(3), 379–391. [CrossRef]
- Bhagawan, D., Chandan, V., Srilatha, K., Shankaraiah, G., Rani, M. Y., & Himabindu, V. (2018). Industrial wastewater treatment using electrochemical process. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 191(1). [CrossRef]
- Bhamidipati, S. H., Vadlamudi, D. P., & Moka, S. (2021a). Polymers as Coagulants for Wastewater Treatment. Advanced Materials and Technologies for Wastewater Treatment, 85–114. [CrossRef]
- Bhamidipati, S. H., Vadlamudi, D. P., & Moka, S. (2021b). Polymers as Coagulants for Wastewater Treatment. In Advanced Materials and Technologies for Wastewater Treatment (pp. 85–114). CRC Press. [CrossRef]
- Cainglet, A., Tesfamariam, A., & Heiderscheidt, E. (2020). Organic polyelectrolytes as the sole precipitation agent in municipal wastewater treatment. Journal of Environmental Management, 271. [CrossRef]
- Chen, H., Li, C., Zhang, Y., Fang, W., Zou, L., & Chi, R. (2025). Investigation of Solution Microstructure in Ferric Sulfate Coagulation-Assisted Precipitation of Fluoride Ions. Molecules, 30(6), 1362. [CrossRef]
- Chen, J., Lin, J., Li, W., Wang, Y., & Huang, H. (2024). Coagulative removal of polyethylene microplastics using polyaluminum chloride in conjunction with laminarin. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 212, 230–239. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y., Nan, J., Guo, M., Zhang, Y., Wang, J., Wang, Q., & Fang, R. (2025). Novel cationic and amphoteric starch-modified coagulants for efficient treatment of relatively high turbidity and large organic matter source waters: Performance, predictive modeling and mechanism analysis. Separation and Purification Technology, 359. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z., Lai, J., Kang, Y., Wei, Y., Xu, X., & Wang, S. (2025). A Tough and Sustainable Bioinspired Low-Carbon Building Material Reinforced by Glass Fibers. Small, 21(18). [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, A. K., Kumar, S., & Sharma, C. (2015). Removal of chloro-organics and color from pulp and paper mill wastewater by polyaluminium chloride as coagulant. Desalination and Water Treatment, 53(3), 697–708. [CrossRef]
- Coello-Cabezas, J., Verdezoto Carvajal, M., Mejía Cabezas, N., Sánchez-Moreno, H., Basantes Basantes, E., Estrella Semblantes, M., Gavilanez Alvarez, I., & Ormaza Hugo, R. (2024). Organic coagulant combined with magnetite nanoparticles for the treatment of mercury-contaminated waters. Case Studies in Chemical and Environmental Engineering, 9. [CrossRef]
- Dandesa, B., Akuma, D. A., & Alemayehu, E. (2023). Water purification improvement using moringa oleifera seed extract pastes for coagulation follow scoria filtration. Heliyon, 9(7), e17420. [CrossRef]
- Dao, M. T., Nguyen, V. C. N., Tran, T. N., Nguyen, X. Du, Vo, D. T., Nguyen, V. K., & Hoang, L. T. T. T. (2021). Pilot-Scale Study of Real Domestic Textile Wastewater Treatment Using Cassia fistula Seed-Derived Coagulant. Journal of Chemistry, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Das, O., Restás, Á., Shanmugam, V., Sas, G., Försth, M., Xu, Q., Jiang, L., Hedenqvist, M. S., & Ramakrishna, S. (2021). Demystifying Low-Carbon Materials. Materials Circular Economy, 3(1), 1–11. [CrossRef]
- Dash, S., Raj, A., & Vara, S. (2024a). Experimental screening and selection criteria of natural coagulants towards wastewater treatment. Journal of Applied and Natural Science, 16(3), 1096–1105. [CrossRef]
- Dash, S., Raj, A., & Vara, S. (2024b). Experimental screening and selection criteria of natural coagulants towards wastewater treatment. Journal of Applied and Natural Science, 16(3), 1096–1105. [CrossRef]
- Dawood, A. T., Abdul-Bary, H. I., Alazzawi, K. S. A., Salman, I. H., & A., K. (2024). Removal of Colloidal Suspension through Coagulation – Flocculation Process In Water Purification – A Review. Journal of Biotechnology Research Center, 18(2), 38–64. [CrossRef]
- De Gisi, S., & Notarnicola, M. (2017). Industrial Wastewater Treatment. In Encyclopedia of Sustainable Technologies (pp. 23–42). Elsevier. [CrossRef]
- de Sousa Silva, R., Rengel, H. D., Voigt, F. D., Machado, R. A. F., de Fátima Peralta Muniz Moreira, R., & Marangoni, C. (2023). Treatment of real textile wastewater by coagulation/flocculation integrated with direct contact membrane distillation. Separation Science and Technology (Philadelphia), 58(13), 2394–2410. [CrossRef]
- Demissie, E., Baylie, H., Tesfa, G., & Asefa, E. (2019). Comparison on The Effectiveness of Hydrated Aluminum Sulfate and Ferric Chloride as A Coagulant in Brewery Wastewater Treatment. The Case of Walia Brewery, Heineken Ethiopia. Global Scientific Journals, 7(5), 325–336.
- Dhrubo, A. A. K., Jannat, M., & Hossain, M. S. (2023). Enhancing the performance of coagulants for wastewater treatment by varying and optimizing the experimental parameters. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 55, 104144. [CrossRef]
- Diver, D., Nhapi, I., & Ruziwa, W. R. (2023). The potential and constraints of replacing conventional chemical coagulants with natural plant extracts in water and wastewater treatment. In Environmental Advances (Vol. 13). Elsevier Ltd. [CrossRef]
- Drechsel, P., Qadir, M., & Galibourg, D. (2022). The WHO Guidelines for Safe Wastewater Use in Agriculture: A Review of Implementation Challenges and Possible Solutions in the Global South. Water, 14(6). [CrossRef]
- Duan, J., & Gregory, J. (2003). Coagulation by hydrolysing metal salts. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 100(SUPPL.), 475–502. [CrossRef]
- Dwarakanath, B., Kalpana Devi, P., Ranjith Kumar, A., Metwally, A. S. M., Ashraf, G. A., & Thamineni, B. L. (2023). Smart IoT-based water treatment with a Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) system process. Water Reuse, 13(3), 411–431. [CrossRef]
- El Foulani, A. A., Ounas, O., Tahiri, M., & Chafi, M. (2023). A Comparative Study of the Performance of Polyaluminum Chloride-Sodium Alginate and Polyaluminum Chloride-Chitosan Composite Coagulants in Dam Water Treatment. Journal of Polymers and the Environment, 31(11), 4909–4918. [CrossRef]
- El Ouadrhiri, F., Althomali, R. H., Adachi, A., Abdu Musad Saleh, E., Husain, K., Lhassani, A., Hassan, I., Mostafa Moharam, M., Kassem, A. F., Chaouch, M., Ali Oturan, M., & Lahkimi, A. (2023). Nitrogen and phosphorus co-doped carbocatalyst for efficient organic pollutant removal through persulfate-based advanced oxidation processes. Journal of Saudi Chemical Society, 27(3), 101648. [CrossRef]
- El Ouadrhiri, F., Elyemni, M., Lahkimi, A., Lhassani, A., Chaouch, M., & Taleb, M. (2021). Mesoporous carbon from optimized date stone hydrochar by catalytic hydrothermal carbonization using response surface methodology: application to dyes adsorption. International Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2021(1), 5555406.
- Ersoy, B., Tosun, I., Günay, A., & Dikmen, S. (2009). Turbidity Removal from Wastewaters of Natural Stone Processing by Coagulation/Flocculation Methods. Clean-Soil Air Water, 37(3), 225–232. [CrossRef]
- Facchino, M., Pietrelli, L., Menegoni, P., Capocelli, M., Limiti, E., Trombetta, M., Basoli, F., & De Falco, M. (2025). Greener Microplastics Removal: Progressive Replacement of Iron-Based Coagulants with Sodium Alginate and Chitosan to Enhance Sustainability. ChemPlusChem, 90(5). [CrossRef]
- Fang, X., Zhai, Z., Zang, J., & Zhu, Y. (2022). An Intelligent Dosing Algorithm Model for Wastewater Treatment Plant. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2224(1). [CrossRef]
- Gao, B. Y., Chu, Y. B., Yue, Q. Y., Wang, B. J., & Wang, S. G. (2005). Characterization and coagulation of a polyaluminum chloride (PAC) coagulant with high Al13 content. Journal of Environmental Management, 76(2), 143–147. [CrossRef]
- Gao, B. Y., Hahn, H. H., & Hoffmann, E. (2002). Evaluation of aluminum-silicate polymer composite as a coagulant for water treatment. Water Research, 36(14), 3573–3581. [CrossRef]
- Gao, B. Y., Yue, Q. Y., Wang, B. J., & Chu, Y. B. (2003). Poly-aluminum-silicate-chloride (PASiC)—a new type of composite inorganic polymer coagulant. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 229(1–3), 121–127. [CrossRef]
- Garomsa, F. S., Berhanu, Y. M., Desta, W. M., & Bidira, F. (2024). Indigenous bio-coagulant assisted electrocoagulation process for the removal of contaminants from brewery wastewater: Performance evaluation and response surface methodology optimization. Heliyon, 10(22). [CrossRef]
- Ghernaout, D., & Ghernaout, B. (2012). Sweep flocculation as a second form of charge neutralisation—a review. Desalination and Water Treatment, 44(1–3), 15–28. [CrossRef]
- Gotlib, I. Y., Korchak, P. A., Safonova, E. A., Volkova, A. V., & Victorov, A. I. (2025). Poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride) in water and aqueous salt solution: Explicit solvent molecular dynamics and experiment. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 422, 126946. [CrossRef]
- Haddaji, C., Khattabi Rifi, S., Digua, K., Madinzi, A., Chatoui, M., Driouich, A., Ettaloui, Z., Agustiono Kurniawan, T., Anouzla, A., & Souabi, S. (2024). Optimization of the coagulation-flocculation process using response surface methodology for wastewater pretreatment generated by vegetable oil refineries: A path towards environmental sustainability. Environmental Nanotechnology, Monitoring & Management, 22. [CrossRef]
- Hamidi, A. A., Alias, S., Assari, F., & Adlan, M. N. (2007). The use of alum, ferric chloride and ferrous sulphate as coagulants in removing suspended solids, colour and COD from semi-aerobic landfill leachate at controlled pH. Waste Management and Research, 25(6), 556–565. [CrossRef]
- Hosomi, M. (2016). New challenges on wastewater treatment. Clean Technologies and Environmental Policy, 18(3), 627–628. [CrossRef]
- Hubert, M., Meyn, T., Hansen, M. C., Hale, S. E., & Arp, H. P. H. (2024). Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substance (PFAS) removal from soil washing water by coagulation and flocculation. Water Research, 249. [CrossRef]
- Iman, L., Afshin, E., & Mehdi, H. (2014). Comparison study of turbidity removal using synthetized poly-aluminum chloride-sulfate and poly-aluminum chloride in aqueous solutions. International Journal of Environmental Health Engineering, 3(3). [CrossRef]
- Issahaku, I., Tetteh, I. K., & Tetteh, A. Y. (2023). Chitosan and chitosan derivatives: Recent advancements in production and applications in environmental remediation. In Environmental Advances (Vol. 11, p. 100351). Elsevier. [CrossRef]
- Jagaba, A., Abubakar, S., Lawal, I., Latiff, A., & Umaru, I. (2018). Wastewater Treatment Using Alum, the Combinations of Alum-Ferric Chloride, Alum-Chitosan, Alum-Zeolite and Alum- Moringa Oleifera as Adsorbent and Coagulant. International Journal of Engineering, 2(3), 67. [CrossRef]
- Javan, K., Altaee, A., BaniHashemi, S., Darestani, M., Zhou, J., & Pignatta, G. (2024). A review of interconnected challenges in the water–energy–food nexus: Urban pollution perspective towards sustainable development. In Science of the Total Environment (Vol. 912, p. 169319). Elsevier. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J. Q. (2015). The role of coagulation in water treatment. Current Opinion in Chemical Engineering, 8, 36–44. [CrossRef]
- Jianlong, W., Hanchang, S., & Yi, Q. (2000). Wastewater treatment in a hybrid biological reactor (HBR): Effect of organic loading rates. Process Biochemistry, 36(4), 297–303. [CrossRef]
- Jin, X., Liu, Y., Wang, Y., Zhang, S., Zhang, W., Jin, P., Xu, L., Shi, X., Wang, X. C., & Lv, S. (2020). Towards a comparison between the hybrid ozonation-coagulation (HOC) process using Al- and Fe-based coagulants: Performance and mechanism. Chemosphere, 253. [CrossRef]
- Jo, S., Kadam, R., Jang, H., Seo, D., & Park, J. (2024). Recent Advances in Wastewater Electrocoagulation Technologies: Beyond Chemical Coagulation. In Energies (Vol. 17, Issue 23). Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute (MDPI). [CrossRef]
- Juliana, J., Jesintha, K. L., Mariaamalraj, S., Padmanaban, V. C., Neelakandan, A. R., & Rajanikant, G. K. (2021). Biopolymers as a Sustainable Approach for Wastewater Treatment. Sustainable Technologies for Water and Wastewater Treatment, 259–274. [CrossRef]
- Karnena, M. K., & Saritha, V. (2020a). Natural Coagulants for the Treatment of Water and Wastewater: A Futuristic Option for Sustainable Water Clarification. Recent Innovations in Chemical Engineering (Formerly Recent Patents on Chemical Engineering), 14(2), 120–147. [CrossRef]
- Karnena, M. K., & Saritha, V. (2020b). Natural Coagulants for the Treatment of Water and Wastewater: A Futuristic Option for Sustainable Water Clarification. Rice, 13(2), 120–147. [CrossRef]
- Karyab, H., Ghasemi, M., Ghotbinia, F., & Nazeri, N. (2023). Efficiency of chitosan nanoparticle with polyaluminum chloride in dye removal from aqueous solutions: Optimization through response surface methodology (RSM) and central composite design (CCD). International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 249. [CrossRef]
- Kato, S., & Kansha, Y. (2024). Comprehensive review of industrial wastewater treatment techniques. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2024 31:39, 31(39), 51064–51097. [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, S. (1991). Integrated design of water treatment facilities. Choice Reviews Online, 29(04), 29-2124-29–2124. [CrossRef]
- Keawchouy, S., Na-Phatthalung, W., Keaonaborn, D., Jaichuedee, J., Musikavong, C., & Sinyoung, S. (2022). Enhanced coagulation process for removing dissolved organic matter, microplastics, and silver nanoparticles. Journal of Environmental Science and Health - Part A Toxic/Hazardous Substances and Environmental Engineering, 57(13–14), 1084–1098. [CrossRef]
- Ketheesan, B., & Stuckey, D. C. (2015). Effects of hydraulic/organic shock/transient loads in anaerobic wastewater treatment: A review. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 45(24), 2693–2727. [CrossRef]
- Khalidi-Idrissi, A., Hartal, O., Madinzi, A., El-Abbadi, K., & Souabi, S. (2025). Natural flotation and coagulation–flocculation: a dual approach to refinery wastewater treatment. Euro-Mediterranean Journal for Environmental Integration, 10(3), 1425–1443. [CrossRef]
- Khan, M., Ashraf, S., Alhuzaymi, T. M., Ghani, L., & Um, W. (2024). Low level radioactive waste treatment by coagulation flocculation technique: a review. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 333(12), 6079–6091. [CrossRef]
- Khan, M. T., Ahmad, M., Hossain, M. F., Nawab, A., Ahmad, I., Ahmad, K., & Panyametheekul, S. (2023). Microplastic removal by coagulation: a review of optimizing the reaction conditions and mechanisms. In Water Emerging Contaminants and Nanoplastics (Vol. 2, Issue 4, p. N/A-N/A). OAE Publishing Inc. [CrossRef]
- Khan, N. A., Ahmed, S., Vambol, S., Vambol, V., & Farooqi, I. H. (2019). Field hospital wastewater treatment scenario. Ecological Questions, 30(3), 57–69. [CrossRef]
- Koul, B., Bhat, N., Abubakar, M., Mishra, M., Arukha, A. P., & Yadav, D. (2022). Application of Natural Coagulants in Water Treatment: A Sustainable Alternative to Chemicals. Water 2022, Vol. 14, Page 3751, 14(22), 3751. [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, S. jayant. (2017). Coagulation for Wastewater Treatment : A Review on Investigations and Studies. International Journal of Scientific Research in Science and Technology, 3(2), 501–505. [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, S. B., Abdullah, S. R. S., Imron, M. F., Said, N. S. M., Ismail, N. ‘Izzati, Hasan, H. A., Othman, A. R., & Purwanti, I. F. (2020). Challenges and Opportunities of Biocoagulant/Bioflocculant Application for Drinking Water and Wastewater Treatment and Its Potential for Sludge Recovery. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2020, Vol. 17, Page 9312, 17(24), 9312. [CrossRef]
- Kweinor Tetteh, E., & Rathilal, S. (2020a). Application of Organic Coagulants in Water and Wastewater Treatment. In Organic Polymers. IntechOpen. [CrossRef]
- Kweinor Tetteh, E., & Rathilal, S. (2020b). Application of Organic Coagulants in Water and Wastewater Treatment. Organic Polymers. [CrossRef]
- Lan, S. H., Wang, C. L., Sun, J. H., & Zhang, H. (2014). Study on treatment of dyeing wastewater by Fe0-H2O2 system. Advanced Materials Research, 1048, 507–510. [CrossRef]
- Lau, S. Y., Tien, P. T. K., Choy, S. Y., Jeevanandam, J., Show, P. L., Lam, M. K., Tan, Y. H., & Lim, S. (2024). Unleashing the power of plant-based modified starch as a game-changing natural coagulant. In Process Biochemistry (Vol. 147, pp. 213–227). Elsevier Ltd. [CrossRef]
- Lee, K. E., Hanafiah, M. M., Halim, A. A., & Mahmud, M. H. (2015). Primary Treatment of Dye Wastewater Using Aloe Vera-aided Aluminium and Magnesium Hybrid Coagulants. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 30, 56–61. [CrossRef]
- Lema, M. W. (2025). Wastewater crisis in East African cities: challenges and emerging opportunities. Discover Environment, 3(1), 1–19. [CrossRef]
- LEON ZERPA, F., CHIRINZA, N. P., MUGUIRRIMA, P. V., MENDIETA PINO, C. A., & RAMOS MARTIN, A. (2025). MORINGA OLEIFERA SEED EXTRACT AS A COAGULANT IN THE TREATMENT OF DRINKING WATER. DYNA, 100(1), 5–5. [CrossRef]
- Levakov, I., Maor, I., Barak, C., Kirshenbaum, Y., & Rytwo, G. (2023). Colorimetric Quantification for Residual Poly-DADMAC in Water Treatment. Water (Switzerland), 15(19), 3352. [CrossRef]
- Liao, L., & Zhang, P. (2018). Preparation and Characterization of Polyaluminum Titanium Silicate and its Performance in the Treatment of Low-Turbidity Water. Processes 2018, Vol. 6, Page 125, 6(8), 125. [CrossRef]
- Liu, W., & Ratnaweera, H. (2017). Feed-forward-based software sensor for outlet turbidity of coagulation process considering plug flow condition. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 14(8), 1689–1696. [CrossRef]
- López-Maldonado, E. A., Oropeza-Guzmán, M. T., & Ochoa-Terán, A. (2014). Improving the efficiency of a coagulation-flocculation wastewater treatment of the semiconductor industry through zeta potential measurements. Journal of Chemistry, 2014. [CrossRef]
- Lucas, M. S., Teixeira, A. R., Jorge, N., & Peres, J. A. (2025a). Industrial Wastewater Treatment by Coagulation–Flocculation and Advanced Oxidation Processes: A Review. Water 2025, Vol. 17, Page 1934, 17(13), 1934. [CrossRef]
- Lucas, M. S., Teixeira, A. R., Jorge, N., & Peres, J. A. (2025b). Industrial Wastewater Treatment by Coagulation–Flocculation and Advanced Oxidation Processes: A Review. Water 2025, Vol. 17, Page 1934, 17(13), 1934. [CrossRef]
- Lucas, M. S., Teixeira, A. R., Jorge, N., & Peres, J. A. (2025c). Industrial Wastewater Treatment by Coagulation–Flocculation and Advanced Oxidation Processes: A Review. In Water (Switzerland) (Vol. 17, Issue 13, p. 1934). Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute. [CrossRef]
- Luo, F., Wu, Z., Wang, M., Shu, X., Shu, X., Jia, P., & Li, Q. (2020). High-Performance Flocculants for Purification: Solving the Problem of Waste Incineration Bottom Ash and Unpurified Water. ACS Omega, 5(22), 13259–13267. [CrossRef]
- Ma, S., Fu, M., Li, F., Wu, N., Yang, J., Jia, H., Wang, B., & Cheng, R. (2011). Preparation of a New Inorganic-Organic Composite Dual-Coagulant and Application of Oily Wastewater Treatment. Advanced Materials Research, 233–235, 523–527. [CrossRef]
- Macieja, S., Środa, B., Zielińska, B., Roy, S., Bartkowiak, A., & Łopusiewicz, Ł. (2022). Bioactive Carboxymethyl Cellulose (CMC)-Based Films Modified with Melanin and Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs)—The Effect of the Degree of CMC Substitution on the In Situ Synthesis of AgNPs and Films’ Functional Properties. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(24), 15560. [CrossRef]
- Mailler, R., Mèche, P., Sauvignet, P., Azimi, S., & Rocher, V. (2021). Normalization of wastewater coagulation-flocculation trials and implications in terms of variability in treatment performance and comparison of commercial coagulants. Environmental Technology, 42(25), 4015–4026. [CrossRef]
- Maknakorn, W., Jutaporn, P., & Khongnakorn, W. (2019). Coagulation and adsorption as pretreatments of thin-film composite-forward osmosis (TFC-FO) for ink printing wastewater treatment. Water Science and Technology : A Journal of the International Association on Water Pollution Research, 79 5(5), 877–887. [CrossRef]
- Malkoske, T. A., Bérubé, P. R., & Andrews, R. C. (2020). Coagulation/flocculation prior to low pressure membranes in drinking water treatment: A review. In Environmental Science: Water Research and Technology (Vol. 6, Issue 11, pp. 2993–3023). Royal Society of Chemistry. [CrossRef]
- Manamperuma, L., Wei, L., & Ratnaweera, H. (2017). Multi-parameter based coagulant dosing control. Water Science and Technology, 75(9), 2157–2162. [CrossRef]
- Manohara, H. M., Nayak, S. S., Franklin, G., Nataraj, S. K., & Mondal, D. (2021). Progress in marine derived renewable functional materials and biochar for sustainable water purification. Green Chemistry, 23(21), 8305–8331. [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y., Zhao, Y., & Cotterill, S. (2023). Examining Current and Future Applications of Electrocoagulation in Wastewater Treatment. Water 2023, Vol. 15, Page 1455, 15(8), 1455. [CrossRef]
- Marques, D. G., de Melo Franco Domingos, J., Nolasco, M. A., & Campos, V. (2025). Textile effluent treatment using coagulation-flocculation and a hydrodynamic cavitation reactor associated with ozonation. Chemical Engineering Science, 304. [CrossRef]
- Matesun, J., Petrik, L., Musvoto, E., Ayinde, W., & Ikumi, D. (2024a). Limitations of wastewater treatment plants in removing trace anthropogenic biomarkers and future directions: A review. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 281. [CrossRef]
- Matesun, J., Petrik, L., Musvoto, E., Ayinde, W., & Ikumi, D. (2024b). Limitations of wastewater treatment plants in removing trace anthropogenic biomarkers and future directions: A review. In Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety (Vol. 281). Academic Press. [CrossRef]
- Mian, M. M., & Liu, G. (2019). Sewage sludge-derived TiO2/Fe/Fe3C-biochar composite as an efficient heterogeneous catalyst for degradation of methylene blue. Chemosphere, 215, 101–114. [CrossRef]
- Miranda, R., Latour, I., & Blanco, A. (2020a). Understanding the Efficiency of Aluminum Coagulants Used in Dissolved Air Flotation (DAF). Frontiers in Chemistry, 8, 27. [CrossRef]
- Miranda, R., Latour, I., & Blanco, A. (2020b). Understanding the Efficiency of Aluminum Coagulants Used in Dissolved Air Flotation (DAF). Frontiers in Chemistry, 8, 27. [CrossRef]
- Mishra, B., Kallem, P., Yadavalli, R., Mandal, S. K., Reddy, C. N., Sumithra, B., Lakshmayya, N. S. V., & Bana, F. (2025). Industrial wastewater treatment using extracellular polymer substances/bioflocculants: a review. Applied Water Science 2025 15:3, 15(3), 1–20. [CrossRef]
- Mohamed Noor, M. H., & Ngadi, N. (2024a). Ecotoxicological risk assessment on coagulation-flocculation in water/wastewater treatment: a systematic review. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 31(40), 52631–52657. [CrossRef]
- Mohamed Noor, M. H., & Ngadi, N. (2024b). Ecotoxicological risk assessment on coagulation-flocculation in water/wastewater treatment: a systematic review. In Environmental Science and Pollution Research (Vol. 31, Issue 40, pp. 52631–52657). Springer. [CrossRef]
- Mora-León, A. G., Castro-Jiménez, C. C., Saldarriaga-Molina, J. C., García A, E. F., & Correa-Ochoa, M. A. (2022). Aluminium recovered coagulant from water treatment sludge as an alternative for improving the primary treatment of domestic wastewater. Journal of Cleaner Production, 346. [CrossRef]
- Narges, S., Ghorban, A., Hassan, K., & Mohammad, K. (2021). Prediction of the optimal dosage of coagulants in water treatment plants through developing models based on artificial neural network fuzzy inference system (ANFIS). Journal of Environmental Health Science and Engineering, 19(2), 1543–1553. [CrossRef]
- Nasir, M., Javaid, F., Masood, M. T., Arshad, M., Yasir, M., Sedlarik, V., Qadir, M. A., Qiblawey, H., Zhang, W., Deen, K. M., Asselin, E., & Ahmad, N. M. (2024). Regenerable chitosan-embedded magnetic iron oxide beads for nitrate removal from industrial wastewater. Environmental Science: Advances, 3(4), 572–584. [CrossRef]
- Oshogwue Etafo, N., Daniel, ·, Adekanmi, G., Olaolu, ·, Awobifa, S., Refugio, J., Torres, P., Luis, ·, Ibarra Herrera, A., Oluwaseyi, ·, & Awobifa, A. (2025). Clean and green: the multifaceted solution of the electrocoagulation technology in emerging contaminants in wastewater. Discover Civil Engineering 2025 2:1, 2(1), 1–48. [CrossRef]
- Otálora, M. C., Wilches-Torres, A., Lara, C. R., Díaz-Gómez, J., Gómez Castaño, J. A., & Cifuentes, G. R. (2023). Assessment of Prickly Pear Fruit Peel Mucilage in Form of Gel as a Green Coagulant for the Tertiary Treatment of Domestic Wastewater. Gels, 9(9), 723. [CrossRef]
- Owodunni, A. A., Ismail, S., Kurniawan, S. B., Ahmad, A., Imron, M. F., & Abdullah, S. R. S. (2023). A review on revolutionary technique for phosphate removal in wastewater using green coagulant. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 52. [CrossRef]
- Ozgur, C., Gurhan, A. B., & Bekaroglu, S. S. K. (2025a). A Multicriteria Decision-Making Model for the Selection of Conventional/Hybrid Coagulants in Water Treatment. Integrated Environmental Assessment and Management, 21(3), 614–627. [CrossRef]
- Ozgur, C., Gurhan, A. B., & Bekaroglu, S. S. K. (2025b). A multicriteria decision-making model for the selection of conventional/hybrid coagulants in water treatment. Integrated Environmental Assessment and Management, 21(3), 614–627. [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, H. G. J., Elguera, N. Y., Ancco, M., Castro, A. E. L. F., Meza, M. E. B., & Almeida, V. C. (2023). Combined coagulation-electrocoagulation process using biocoagulant from the Opuntia ficus-indica for treatment of cheese whey wastewater. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 195(4). [CrossRef]
- Padilla-Rivera, A., Morgan-Sagastume, J. M., & Güereca-Hernández, L. P. (2019). Sustainability Assessment of Wastewater Systems: An Environmental and Economic Approach. Journal of Environmental Protection, 10(02), 241–259. [CrossRef]
- Pariente, M. I., Segura, Y., Molina, R., & Martínez, F. (2019). Wastewater treatment as a process and a resource. Wastewater Treatment Residues as Resources for Biorefinery Products and Biofuels, 19–45. [CrossRef]
- Parween, M., & Ramanathan, A. (2018). Wastewater Management to Environmental Materials Management. Handbook of Environmental Materials Management, 1–24. [CrossRef]
- Patil, B., Patil, S., & Ravande, K. (2025). Use of electrocoagulation for treatment of wastewater. Materials Research Proceedings, 48, 764–773. [CrossRef]
- Pawak, V. S., Loganathan, V. A., & Sabapathy, M. (2023). Efficient removal of nanoplastics from synthetic wastewater using electrocoagulation. http://arxiv.org/abs/2302.08451.
- Prasetyo, S., Santos, C. A., Sugih, A. K., & Kristianto, H. (2025). Utilization of chitosan as a natural coagulant for polyethylene microplastic removal. Sustainable Chemistry for the Environment, 9, 100225. [CrossRef]
- Precious Sibiya, N., Rathilal, S., & Kweinor Tetteh, E. (2021). Coagulation Treatment of Wastewater: Kinetics and Natural Coagulant Evaluation. Molecules, 26(3). [CrossRef]
- Qian, S. (n.d.). Study on Treatment of Simulated Wastewater by Composite Aluminum-zinc-iron(PAZF) Coagulant. Liaoning Chemical Industry. Retrieved August 12, 2025.
- Raja, A. G., Selva Arasu, K. A., & Rajaram, R. (2022). Synthesis, Characterization and Application of Chitosan-TPP-ZnO Nanocomposite for Efficient Treatment of Effluent Containing Sulphur Dye. Materials Today: Proceedings, 68, 483–490. [CrossRef]
- Ramlee, A. A., Som, A. M., Puasa, S. W., & Hamid, H. A. A. (2023). Coagulation–flocculation mechanism and characterisation of Hylocereus undatus foliage as a natural coagulant in industrial wastewater treatment. Chemical Papers, 77(10), 6083–6093. [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y., Liu, S., Tan, Y., Liu, Y., Yuan, T., Shen, Z., & Cheng, Z. (2022). Application of QSAR for investigation on coagulation mechanisms of textile wastewater. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 244. [CrossRef]
- Righetto, I., Al-Juboori, R. A., Kaljunen, J. U., & Mikola, A. (2021a). Wastewater treatment with starch-based coagulants for nutrient recovery purposes: Testing on lab and pilot scales. Journal of Environmental Management, 284. [CrossRef]
- Righetto, I., Al-Juboori, R. A., Kaljunen, J. U., & Mikola, A. (2021b). Wastewater treatment with starch-based coagulants for nutrient recovery purposes: Testing on lab and pilot scales. Journal of Environmental Management, 284. [CrossRef]
- Ruprecht, J. E., Birrer, S. C., Dafforn, K. A., Mitrovic, S. M., Crane, S. L., Johnston, E. L., Wemheuer, F., Navarro, A., Harrison, A. J., Turner, I. L., & Glamore, W. C. (2021). Wastewater effluents cause microbial community shifts and change trophic status. Water Research, 200. [CrossRef]
- Sabahaudin, M. F. H., Kadir, A. A., Detho, A., Hassan, M. I. H., Hashar, N. N. H., & Hissham, N. F. N. (2025). Utilization of Sludge from Water Treatment Plant as Fired Clay Brick. Archives of Metallurgy and Materials, 70(1), 253–258. [CrossRef]
- Sakthivel, E., & Manoj Suburam, R. (2022). Performance evaluation of composite coagulant in treating textile wastewater. Materials Today: Proceedings, 62, 1708–1711. [CrossRef]
- Saladino, G. M., Hamawandi, B., Vogt, C., Rajarao, G. K., & Toprak, M. S. (2020). Click chemical assembly and validation of bio-functionalized superparamagnetic hybrid microspheres. Applied Nanoscience (Switzerland), 10(6), 1861–1869. [CrossRef]
- Sarp Akarsu, M., & Tokgöz Güneş, S. (2024). The Role of PHREEQC Model and Sensor Analysis in Chemical Coagulation Processes Supported by Online Sensors. Journal of Anatolian Environmental and Animal Sciences, 9(1), 45–52. [CrossRef]
- Shadan, B., Jafari, A., & Gharibshahi, R. (2024). Enhanced drilling waste-water treatment through magnetic nano-composite coagulant application: A central composite design study. Heliyon, 10(24), e40450. [CrossRef]
- Shamshad, J., & Ur Rehman, R. (2025). Innovative approaches to sustainable wastewater treatment: a comprehensive exploration of conventional and emerging technologies. Environmental Science: Advances, 4(2), 189–222. [CrossRef]
- Singh, S., Sivaram, N., Nath, B., Khan, N. A., Singh, J., & Ramamurthy, P. C. (2024). Metal organic frameworks for wastewater treatment, renewable energy and circular economy contributions. Npj Clean Water 2024 7:1, 7(1), 1–22. [CrossRef]
- Solmaz, A., Bölükbaşi, Ö. S., & Sari, Z. A. (2024). Green industry work: production of FeCl3 from iron and steel industry waste (mill scale) and its use in wastewater treatment. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 31(13), 19795–19814. [CrossRef]
- Sun, C., Qiu, J., Zhang, Z., Marhaba, T. F., & Zhang, Y. (2016a). Coagulation behavior and floc characteristics of a novel composite poly-ferric aluminum chloride-polydimethyl diallylammonium chloride coagulant with different OH/(Fe3+ + Al3+) molar ratios. Water Science and Technology : A Journal of the International Association on Water Pollution Research, 74 7(7), 1636–1643. [CrossRef]
- Sun, C., Qiu, J., Zhang, Z., Marhaba, T. F., & Zhang, Y. (2016b). Coagulation behavior and floc characteristics of a novel composite poly-ferric aluminum chloride-polydimethyl diallylammonium chloride coagulant with different OH/(Fe3+ + Al3+) molar ratios. Water Science and Technology, 74(7), 1636–1643. [CrossRef]
- Tahraoui, H., Toumi, S., Boudoukhani, M., Touzout, N., Sid, A. N. E. H., Amrane, A., Belhadj, A. E., Hadjadj, M., Laichi, Y., Aboumustapha, M., Kebir, M., Bouguettoucha, A., Chebli, D., Assadi, A. A., & Zhang, J. (2024a). Evaluating the Effectiveness of Coagulation–Flocculation Treatment Using Aluminum Sulfate on a Polluted Surface Water Source: A Year-Long Study. Water (Switzerland), 16(3), 400. [CrossRef]
- Tahraoui, H., Toumi, S., Boudoukhani, M., Touzout, N., Sid, A. N. E. H., Amrane, A., Belhadj, A. E., Hadjadj, M., Laichi, Y., Aboumustapha, M., Kebir, M., Bouguettoucha, A., Chebli, D., Assadi, A. A., & Zhang, J. (2024b). Evaluating the Effectiveness of Coagulation–Flocculation Treatment Using Aluminum Sulfate on a Polluted Surface Water Source: A Year-Long Study. Water (Switzerland), 16(3), 400. [CrossRef]
- Tarigan, M., Raji, S., Al-Fatesh, H., Czermak, P., & Ebrahimi, M. (2025). The Occurrence of Micropollutants in the Aquatic Environment and Technologies for Their Removal. Processes 2025, Vol. 13, Page 843, 13(3), 843. [CrossRef]
- Teh, C. Y., Budiman, P. M., Shak, K. P. Y., & Wu, T. Y. (2016). Recent Advancement of Coagulation-Flocculation and Its Application in Wastewater Treatment. In Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research (Vol. 55, Issue 16, pp. 4363–4389). American Chemical Society. [CrossRef]
- Tolkou, A. K. ; K. ;, Tsoutsa, E. K., Tolkou, A. K., Kyzas, G. Z., & Katsoyiannis, I. A. (2024). New Trends in Composite Coagulants for Water and Wastewater Treatment. Macromol 2024, Vol. 4, Pages 509-532, 4(3), 509–532. [CrossRef]
- Tolkou, A. K., & Zouboulis, A. I. (2020). Application of Composite Pre-Polymerized Coagulants for the Treatment of High-Strength Industrial Wastewaters. Water, 12(5). [CrossRef]
- Tong, C. Y., Che Yusuf, F. H. B., & Derek, C. J. C. (2022). Optimization of Moringa oleifera seed extract and chitosan as natural coagulant in treatment of fish farm wastewater. Desalination and Water Treatment, 256, 99–113. [CrossRef]
- Tsoutsa, E. K., Tolkou, A. K., Kyzas, G. Z., & Katsoyiannis, I. A. (2024). New Trends in Composite Coagulants for Water and Wastewater Treatment. Macromol, 4(3), 509–532. [CrossRef]
- Turna, T., & Yıldız, Y. (2024). Treatment of Vegetable Oil Industry Wastewaters with Coagulation-flocculation Methods. DÜMF Mühendislik Dergisi. [CrossRef]
- Turunen, J., Karppinen, A., & Ihme, R. (2019a). Effectiveness of biopolymer coagulants in agricultural wastewater treatment at two contrasting levels of pollution. SN Applied Sciences, 1(3). [CrossRef]
- Turunen, J., Karppinen, A., & Ihme, R. (2019b). Effectiveness of biopolymer coagulants in agricultural wastewater treatment at two contrasting levels of pollution. SN Applied Sciences, 1(3). [CrossRef]
- Tzfati, E., Sein, M., Rubinov, A., Raveh, A., & Bick, A. (2011). Pretreatment of wastewater: Optimal coagulant selection using Partial Order Scaling Analysis (POSA). Journal of Hazardous Materials, 190(1–3), 51–59. [CrossRef]
- Tzoupanos, N. D., & Zouboulis, a I. (2008). Coagulation-Flocculation Processes in Water / Wastewater Treatment : the Application of New Generation of Chemical Reagents. 6th IASME/WSEAS International Conference on HEAT TRANSFER, THERMAL ENGINEERING and ENVIRONMENT, 309–317.
- Usman, I. M. T., Ho, Y. C., Lam, M. K., Show, P. L., & Sujarwo, W. (2023). Continuous-Flow Grafting of LENFLOCTM Coagulant for Water Treatment toward Circular Economy. Water 2023, Vol. 15, Page 2484, 15(13), 2484. [CrossRef]
- Vadasarukkai, Y. S., & Gagnon, G. A. (2017). Influence of the Mixing Energy Consumption Affecting Coagulation and Floc Aggregation. Environmental Science & Technology, 51 6(6), 3480–3489. [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Velez, C. D., Sánchez Ortiz, I. A., & Masumoto, T. (2025). Recovery of coagulants via acid treatment in potabilization sludges and their reuse in raw and urban wastewaters. Water Science and Technology, 91(9), 1010–1021. [CrossRef]
- Vigneshwaran, S., Karthikeyan, P., Sirajudheen, P., & Meenakshi, S. (2020). Optimization of sustainable chitosan/Moringa. oleifera as coagulant aid for the treatment of synthetic turbid water – A systemic study. Environmental Chemistry and Ecotoxicology, 2, 132–140. [CrossRef]
- Vijayakumar, V., & Khastgir, D. (2018). Hybrid composite membranes of chitosan/sulfonated polyaniline/silica as polymer electrolyte membrane for fuel cells. Carbohydrate Polymers, 179, 152–163. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J., Yue, W., Wang, Z., Bai, Y., & Song, J. (2023). Removal effect of trihalomethanes (THMs) and halogenated acetic acids (HAAs) precursors in reclaimed water by polyaluminum chloride (PACl) coagulation. Water Science and Technology, 87(3), 672–684. [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z., Long, W., Li, S., Zhao, Y., Yu, S., & Zhou, F. (2024). Preparation of Cationic Polyacrylamide Suspension and Its Application in Oilfield Wastewater Treatment. Polymers, 16(1), 151. [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J., Ma, R., Tian, Y., Yang, L., He, Y., Qian, J., Wu, W., Gao, Y., Luo, J., Xu, D., & Shen, J. (2024). Improvement of Coagulation and Membrane Filtration Performance in Hybrid Coagulation-UF-RO System for Chemical Mechanical Polishing Wastewater Treatment: Effect of Coagulants. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 235(8). [CrossRef]
- Xu, X., Chen, Z., Wan, X., Wang, Z., Zhang, Y., Meng, J., Jiang, L., & Wang, S. (2023). Colonial sandcastle-inspired low-carbon building materials. Matter, 6(11), 3864–3876. [CrossRef]
- Yang, P., Zhang, X., Qu, C., & Zhang, R. (2024). Efficient treatment of polyacrylamide wastewater by cascade heterogeneous Fenton and magnetic flocculation process. Geoenergy Science and Engineering, 242, 213287. [CrossRef]
- Yeoh, J. X., Siti Nurul, S. N. A., Syukri, F., Koyama, M., & Nourouzi Mobarekeh, M. (2022). Comparison between Conventional Treatment Processes and Advanced Oxidation Processes in Treating Slaughterhouse Wastewater: A Review. Water 2022, Vol. 14, Page 3778, 14(22), 3778. [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M., Bustamante, H., Mahmoudi, N., & Gradzielski, M. (2024). Colloidal Chemistry in Water Treatment: The Effect of Ca2+ on the Interaction between Humic Acid and Poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride) (PDADMAC). Langmuir, 40(8), 4108–4121. [CrossRef]
- Zaharia, C., Musteret, C. P., & Afrasinei, M. A. (2024). The Use of Coagulation–Flocculation for Industrial Colored Wastewater Treatment—(I) The Application of Hybrid Materials. Applied Sciences, 14(5). [CrossRef]
- Zaki, N., Charki, A., Hadoudi, N., Fraiha, O., El Ouarghi, H., Salhi, A., Amhamdi, H., & Ahari, M. (2024). Coagulation-flocculation parameters for simultaneous removal of nitrates, nitrites, phosphates, and ammonium from wastewater: A mini review. E3S Web of Conferences, 527. [CrossRef]
- Zaki, N., Hadoudi, N., Charki, A., Bensitel, N., Ouarghi, H. El, Amhamdi, H., & Ahari, M. (2023). Advancements in the chemical treatment of potable water and industrial wastewater using the coagulation–flocculation process. In Separation Science and Technology (Philadelphia) (Vol. 58, Issues 15–16, pp. 2619–2630). Taylor and Francis Ltd. [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H., Sun, X., Zhang, J., & Li, D. (2025). Enhanced ballasted magnetic coagulation process based on one-step pyrolysis synthesis of sludge-derived AC@MNPs for advanced purification of secondary effluent from wastewater treatment plants: Specific removal of low molecular weight organic matter. Separation and Purification Technology, 359. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C., Chen, X., Chen, M., Ding, N., & Liu, H. (2023). Response Surface Optimization on Ferrate-Assisted Coagulation Pretreatment of SDBS-Containing Strengthened Organic Wastewater. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(6), 5008. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H., Lin, H., Li, Q., Cheng, C., Shen, H., Zhang, Z., Zhang, Z., & Wang, H. (2021). Removal of refractory organics in wastewater by coagulation/flocculation with green chlorine-free coagulants. Science of the Total Environment, 787. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y., Diehl, A., Lewandowski, A., Gopalakrishnan, K., & Baker, T. (2020). Removal efficiency of micro- and nanoplastics (180 nm–125 μm) during drinking water treatment. Science of the Total Environment, 720. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L., Zhou, H., & Yang, X. (2019). Preparation and performance of a novel starch-based inorganic/organic composite coagulant for textile wastewater treatment. Separation and Purification Technology, 210, 93–99. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G., & Chen, J. (2021). Developing Magnetic Material for Remediation of Aquatic Nitrogen Pollution in Water Facilities. Journal of Metallic Material Research, 4(2), 22–25. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z., & Xu, Z. (2020). The rational design of biomass-derived carbon materials towards next-generation energy storage: A review. In Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews (Vol. 134). Elsevier Ltd. [CrossRef]
- Zouboulis, A. I., Sarasidis, V., & Moussas, P. A. (2010). Removal of Copper From Synthetic Wastewaters by the Hybrid Coagulation–Microfiltration Process. Separation Science and Technology, 45(11), 1658–1666. [CrossRef]
| Category | Typical efficacy† | Usual dose (mg L⁻¹) | Optimum pH | ndicative cos (€/kg) | Advantages | Disadvantages | Typical applications | Key references |
| Minerals (alun, PAC, FeCl₃/Fe₂(SO₄)₃) | Turbidity > 90 %, MES > 85 %, DCO 20-60 %, heavy metals 40-80 % | 10-60 (Al₂(SO₄)₃) / 15-25 (PAC) / 20-60 (Fe³⁺) | 5,5-7,5 (Al, PAC) ; 4-6 (Fe³⁺) | 0,1-0,4 | • Low cost - Availability - Fast kinetics | • Abundant sludge - Sensitive to pH and alkalinity | Urban processing, metallurgy, textiles | (H. Chen et al., 2025; Dhrubo et al., 2023; Iman et al., 2014; Narges et al., 2021; Tahraoui et al., 2024a) |
| Synthetic polymers (PAM, polyDADMAC, polyamines) | Turbidity > 95 %, MES > 90 %, DCO 30-70 %, good performance on colorants | 0,2-10 | 4-9 (large) | 2-3 | Very low dosage - Wide pH range - Dense flocs | High price - Organic residual potential - Sensitivity to shear | Refineries, paper and cardboard, activated sludge | (J. Chen et al., 2024; Gotlib et al., 2025; Levakov et al., 2023; Yang et al., 2024; Yuan et al., 2024) |
| Natural (chitosan, Moringa, mucilage, lignin) | Turbidity 70-95 %, MES 60-90 %, metals 40-70 % | 10-300 (variable depending on biomass) | 5-8 (chitosan ≤ 7) | 1-2 (seeds) à > 50 (chitosan) | Biodegradable - Low toxicity - Renewable source | • Batch variability - Limited storage - Extra cost (chitosan) | Decentralized processes, agro-industries, micropollutants |
(Amin et al., 2025; Dandesa et al., 2023; Koul et al., 2022; Otálora et al., 2023; Prasetyo et al., 2025) |
| Advanced hybrids (chitosan-Fe₃O₄, MOF, PAC-AC, GO-nano-Fe) | Turbidity > 95 %, MES > 90 %, DCO 40-80 %, metals > 90 % | 5-30 | 6-8 (souvent) | > 5 | Multifunctional (adsorption + coag.) - Magnetic separation - Low sludge | Synthesis cost - Large-scale validation missing | Complex industrial discharges, drilling water, reuse. | (Nasir et al., 2024; Shadan et al., 2024, 2024; Singh et al., 2024; A. K. ; K. ; Tolkou et al., 2024) |
| Scientific Gaps (missing knowledge) | Technological Limitations (of the current process) | Current Challenges (improvement directions) |
| Incomplete understanding of microscopic mechanisms of coagulation–flocculation (precise roles of active chemical species, interfacial interactions) | Partial effectiveness on certain pollutants: conventional coagulants poorly remove dissolved organic matter and micropollutants (pharmaceuticals, microplastics, etc.) | Combining coagulation–flocculation with other processes to treat refractory pollutants (coupling with advanced oxidation, membranes, etc.) |
| Limited predictive modeling – dependence on empirical jar tests for optimal dosage due to lack of robust mathematical models capturing the process complexity | Generation of large volumes of chemical sludge, concentrating pollutants instead of destroying them, causing treatment/disposal issues | Sludge valorization within a circular economy (reuse as fertilizer if non-toxic, recovery of metals, etc.) |
| Lack of standardization in experimental protocols (pH, mixing speed, contact time), making comparison across studies difficult | Dependence on strict conditions: requires optimal pH and precise doses (otherwise efficiency drops), secondary impacts (pH shifts, added salts in treated water) | Development of alternative “green” coagulants (biopolymers, plant extracts, magnetic nanomaterials) that are efficient and stable to reduce reliance on metal salts |
| Poorly studied multi-contaminant interactions: how the simultaneous presence of diverse pollutants in industrial effluents influences floc formation and removal efficiency | Reduced effectiveness on highly loaded or recalcitrant effluents: coagulation–flocculation alone cannot handle wastewater with low biodegradability or high toxicity | Adaptation to variable effluents: designing flexible systems (sensors, real-time control, AI) capable of adjusting dosing in response to fluctuations in industrial wastewater quality |
| Unclear mechanisms of natural/bio-based coagulants: difficulty identifying the dominant active principle and predicting large-scale performance | Risks associated with chemical coagulants: residual metals (Al, Fe) in treated water may pose health risks (e.g., aluminum neurotoxicity) and ecological issues (increased salinity) | Compliance with stricter regulations: meeting new discharge standards (heavy metals, CMR, etc.) and integrating tertiary treatments (activated carbon, ozonation, membranes) |
| Insufficient pilot/full-scale data: most studies are lab-scale; more real-world evidence is needed to validate long-term performance and reliability | High reagent consumption and costs: heavy use of alum, ferric chloride, and polymers with significant economic and carbon footprint (production, transport) | Economic and environmental optimization: lifecycle assessment and cost–benefit analysis to minimize reagents, energy use, and global environmental impact |
| Strategic axes | Short-term recommendations | Medium/long-term perspectives |
| Mechanistic understanding | – Molecular studies of coagulant–pollutant interactions (simulation, spectroscopies) to identify active sites.– Standardized protocols (zeta potential, DoE) to optimize doses.– Introduce co-adsorption to model multi-mechanism effects. | – Online sensors + AI models to track floc formation in real time (texture, predicted turbidity) and refine kinetics.– Hybrid AI + mechanistic models (e.g., PHREEQC) to forecast coagulation chemistry versus conditions. |
| Innovative coagulants | – Chemical modification of biopolymers (modified chitosan, tannins) to improve stability/reactivity.– Organo-mineral hybrids (e.g., chitosan–silica) combining adsorption & flocculation.– Embed nanoparticles (magnetic, etc.) to add functionalities (magnetic recovery). | – Smart, stimuli-responsive coagulants adapting to pH, T, magnetic field (in development).– Targeted nanosystems to selectively coagulate specific micropollutants. |
| Process integration | – Coagulation + membranes (UF/NF) to reduce fouling and improve water quality.– Coagulation + AOP (Fenton, ozone) for refractory pollutants.– Technical guides: optimal combined conditions, automation, monitoring KPIs. | – Modular integrated trains where coagulation is co-optimized with biological/membrane/AOP steps in an intelligent plant (“Coagulation 4.0”).– AI-based, whole-train optimization (predict membrane fouling, adjust coagulant dose, etc.). |
| Intelligent control | – Deploy multi-parameter sensors (turbidity, TOC, UV254) on raw water to quickly adjust dosing; pilot experiences.– Advanced control (e.g., MPC) using real-time signals to minimize effluent variability. | – Predictive, adaptive dosing via AI: ~30% coagulant savings observed at full scale.– IoT/Cloud platforms integrating sensor data and decision models into plant SCADA.– Soft sensors delivering instant estimates (e.g., effluent turbidity) to boost control responsiveness. |
| Disruptive alternatives | – Electrocoagulation (EC) pilots assessing feasibility across effluents.– Trials of biocoagulants (plant extracts, algal/microbial polymers) as partial substitutes for metal salts. | – Hybrid EC + biocoagulant systems: near-total removals for organics in case studies (≥99% COD/turbidity for brewery wastewater), with lower sludge and chemical footprint.– Energy-optimized EC (renewables, durable electrodes) for sustainable industrial rollout.– Microbial/enzymatic biocoagulation targeting specific pollutants (microplastics, PFAS). |
| Circular economy | – Valorize local wastes as coagulants: chitosan from crustacean shells; fly ash/biochars as coagulant–adsorbents.– Pilot reuse of coagulation sludges: characterize potential as soil amendment or construction material. | – Local closed loops: coagulant from local by-products, used in treatment, sludges recycled into bricks/cement or agriculture—zero-waste loops.– Recover critical metals (Al, Fe, rare earths) from sludges via hydrometallurgy for reuse (incl. re-manufacturing coagulants). |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





