Submitted:
29 August 2025
Posted:
01 September 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
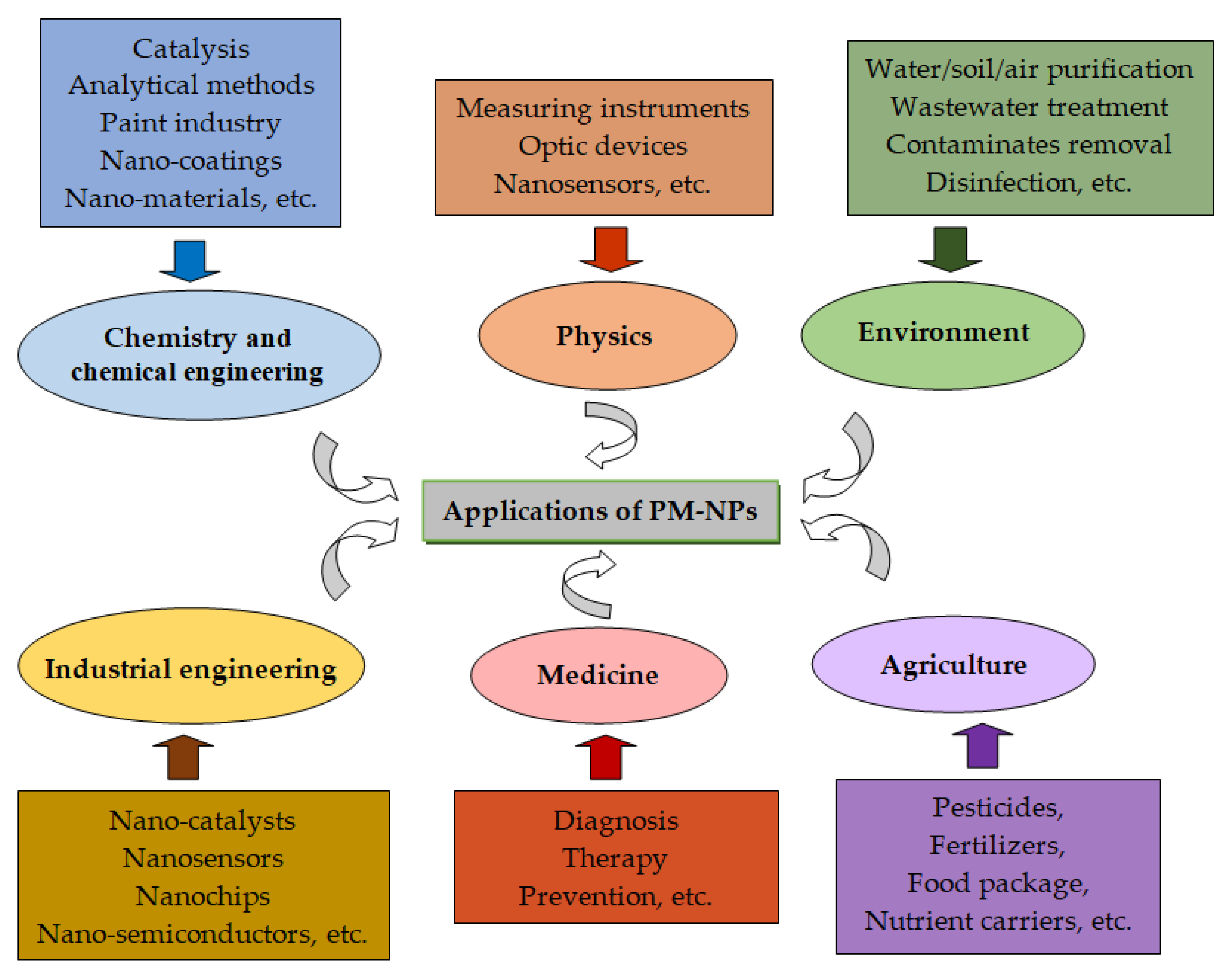
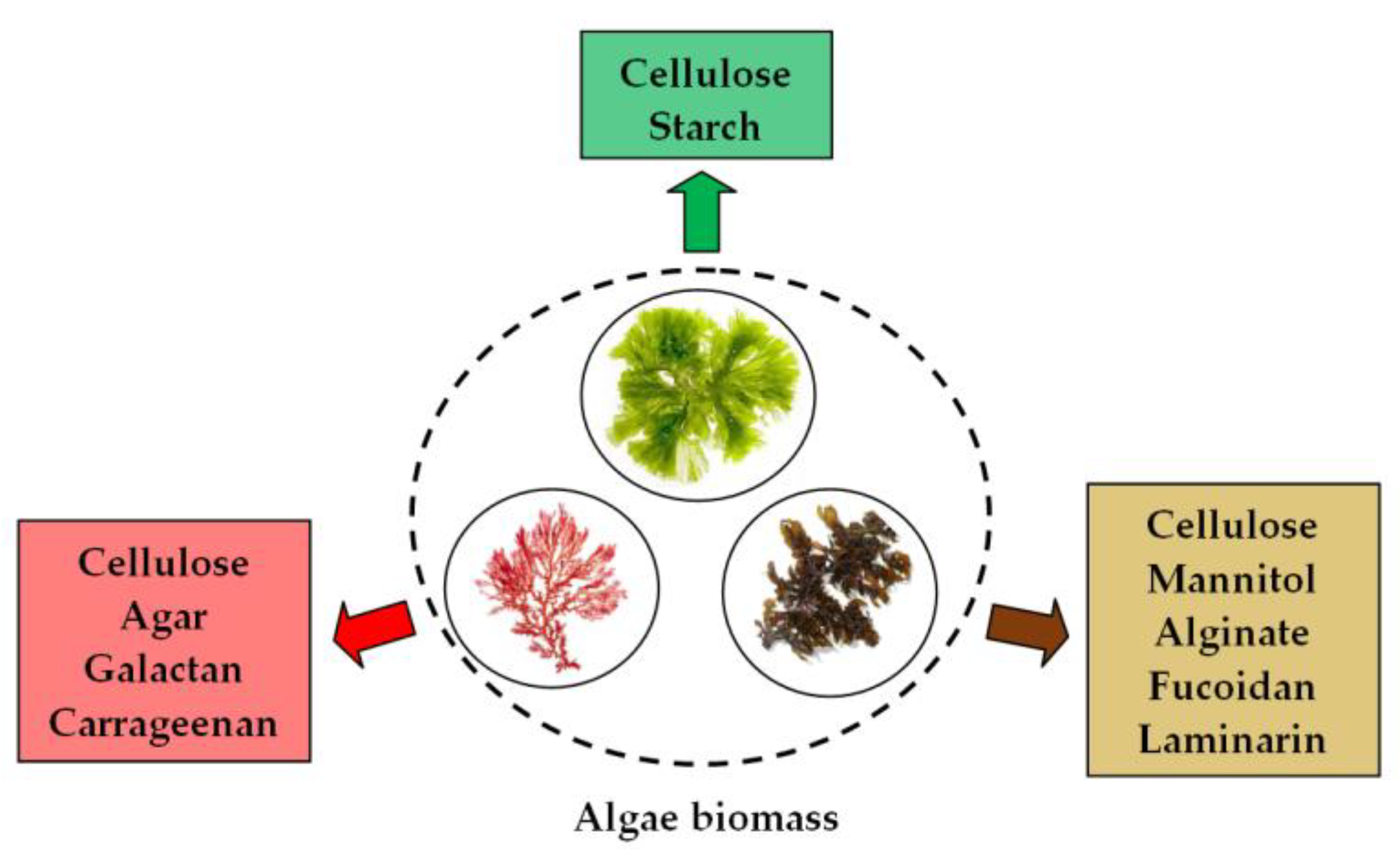
2. Precious Metal Nanoparticles: Characteristics and Applications
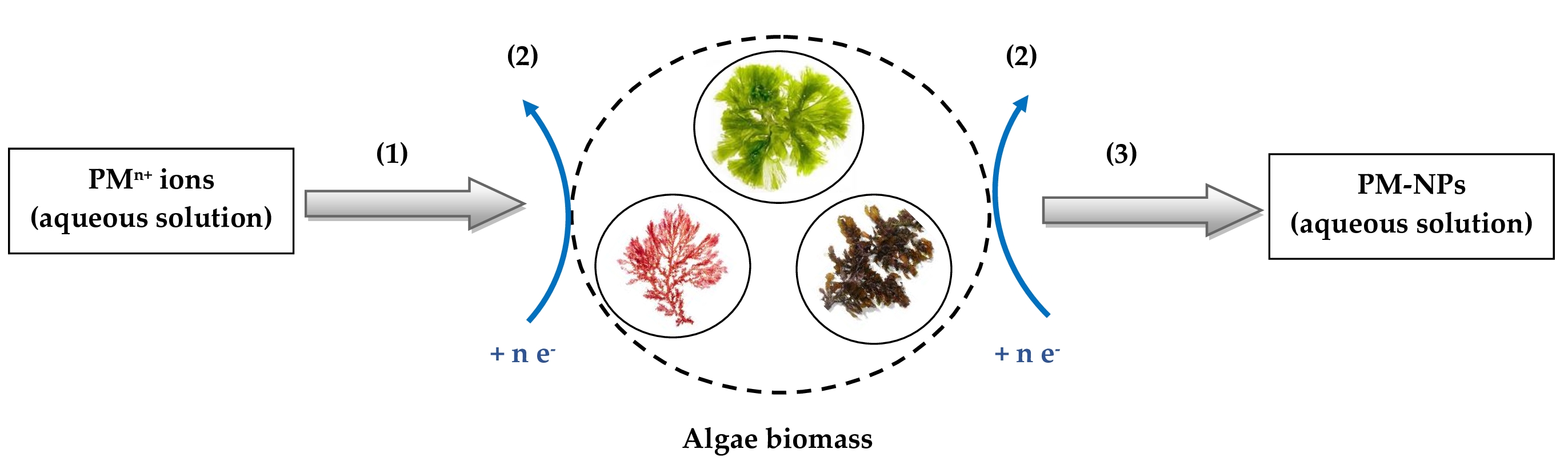
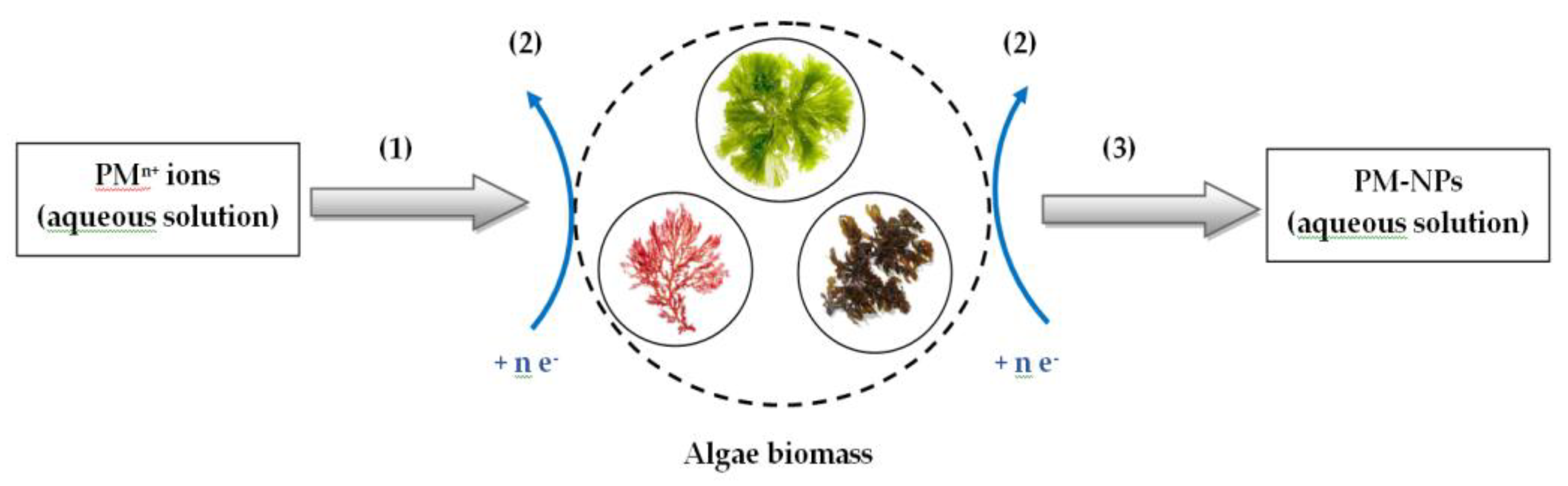
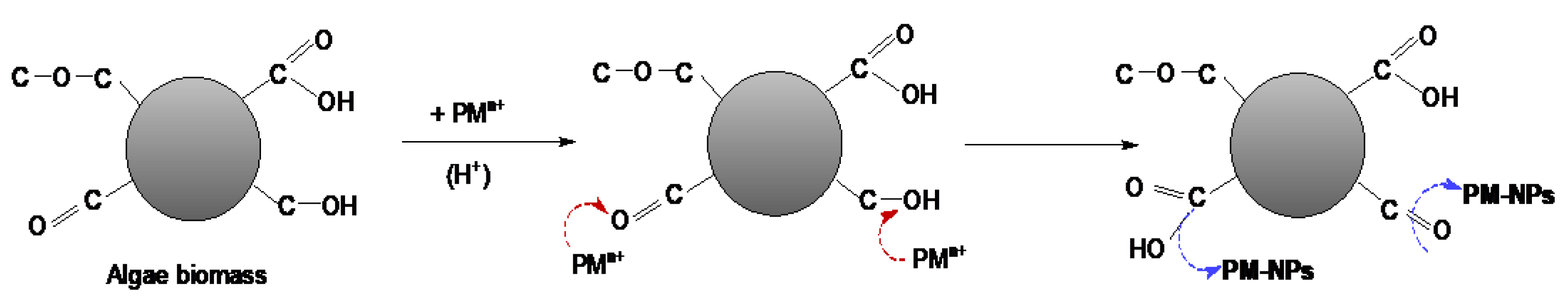
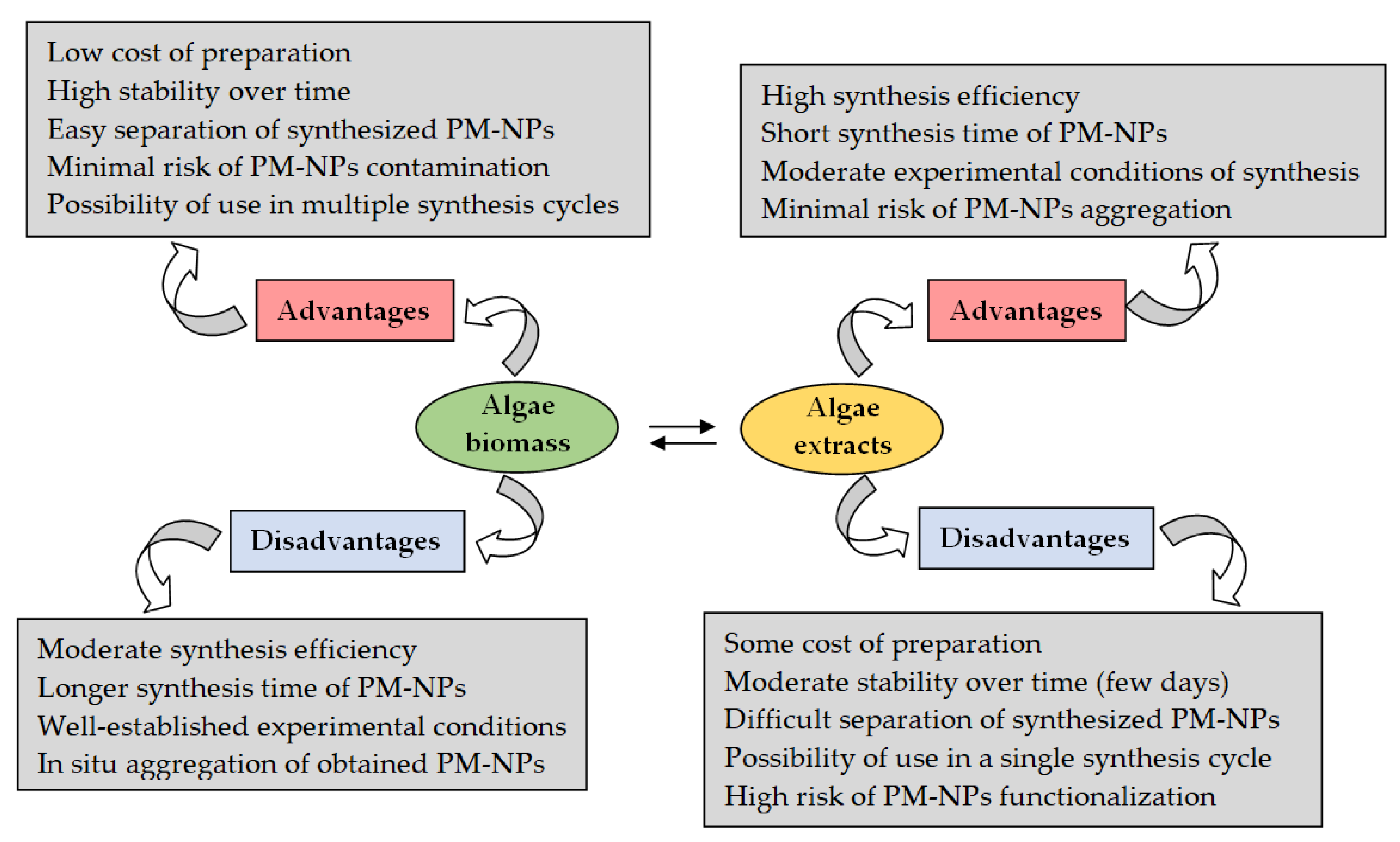
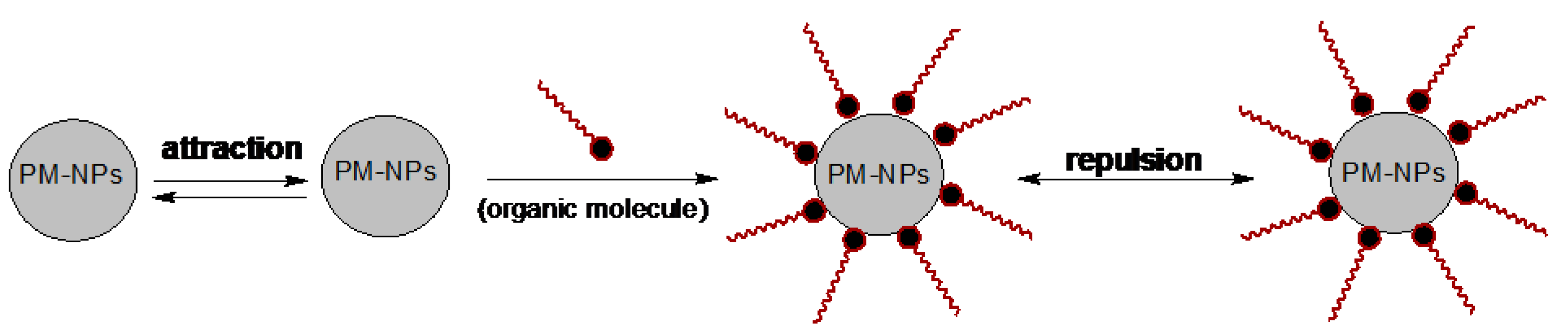
3. Synthesis Mechanism of PM-NPs Using Algae Biomass
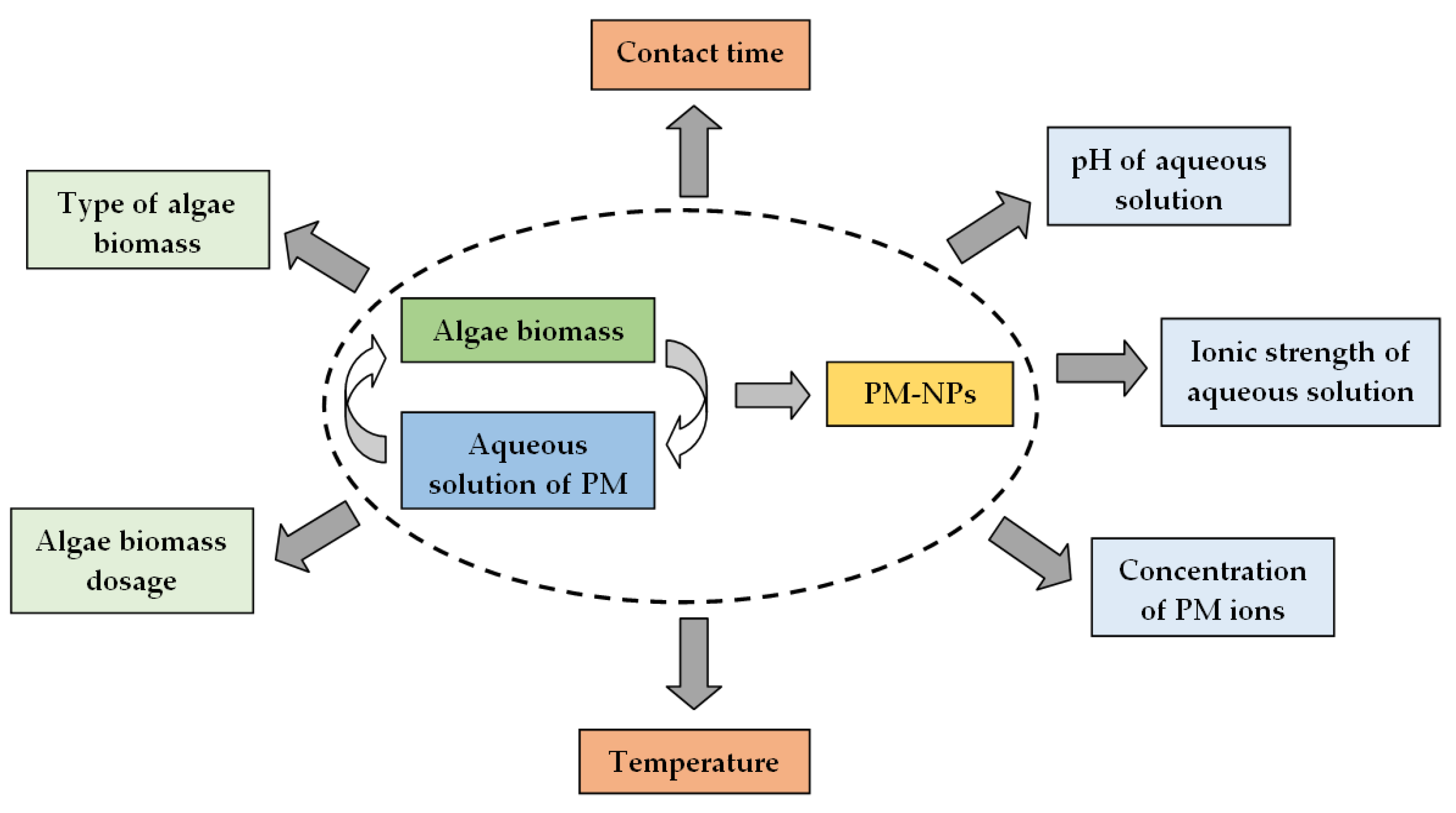
4. Experimental Factors Influencing the Synthesis of PM-NPs
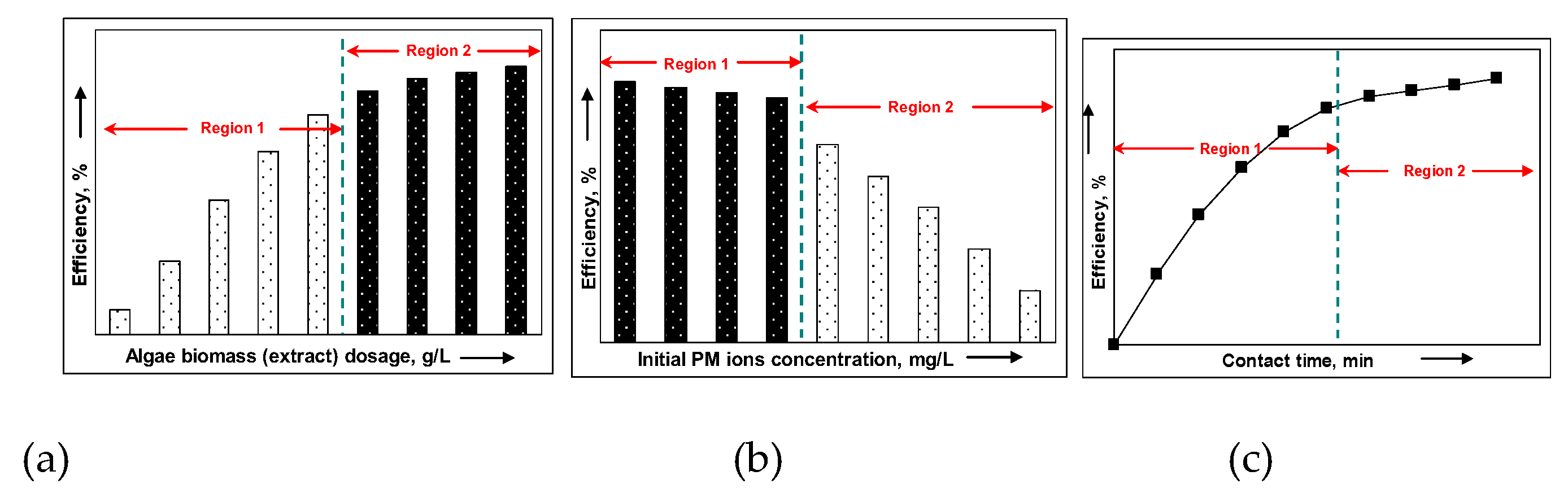
4.2. Algae Biomass (Extract) Dosage
4.3. Concentration of PM Ions in Aqueous Solution
4.4. Contact Time
4.5. Temperature
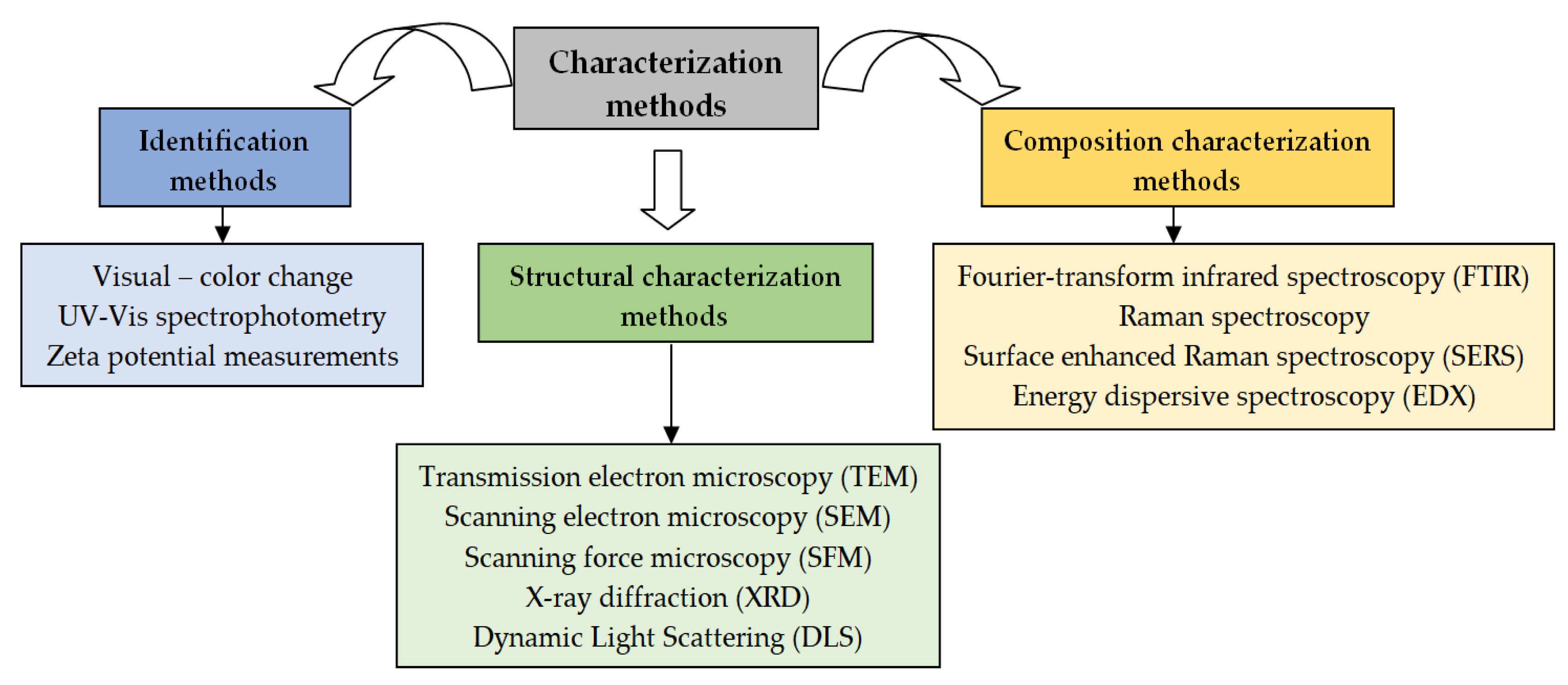
5. Characterization Methods of PM-NPs
5.1. Identification Methods
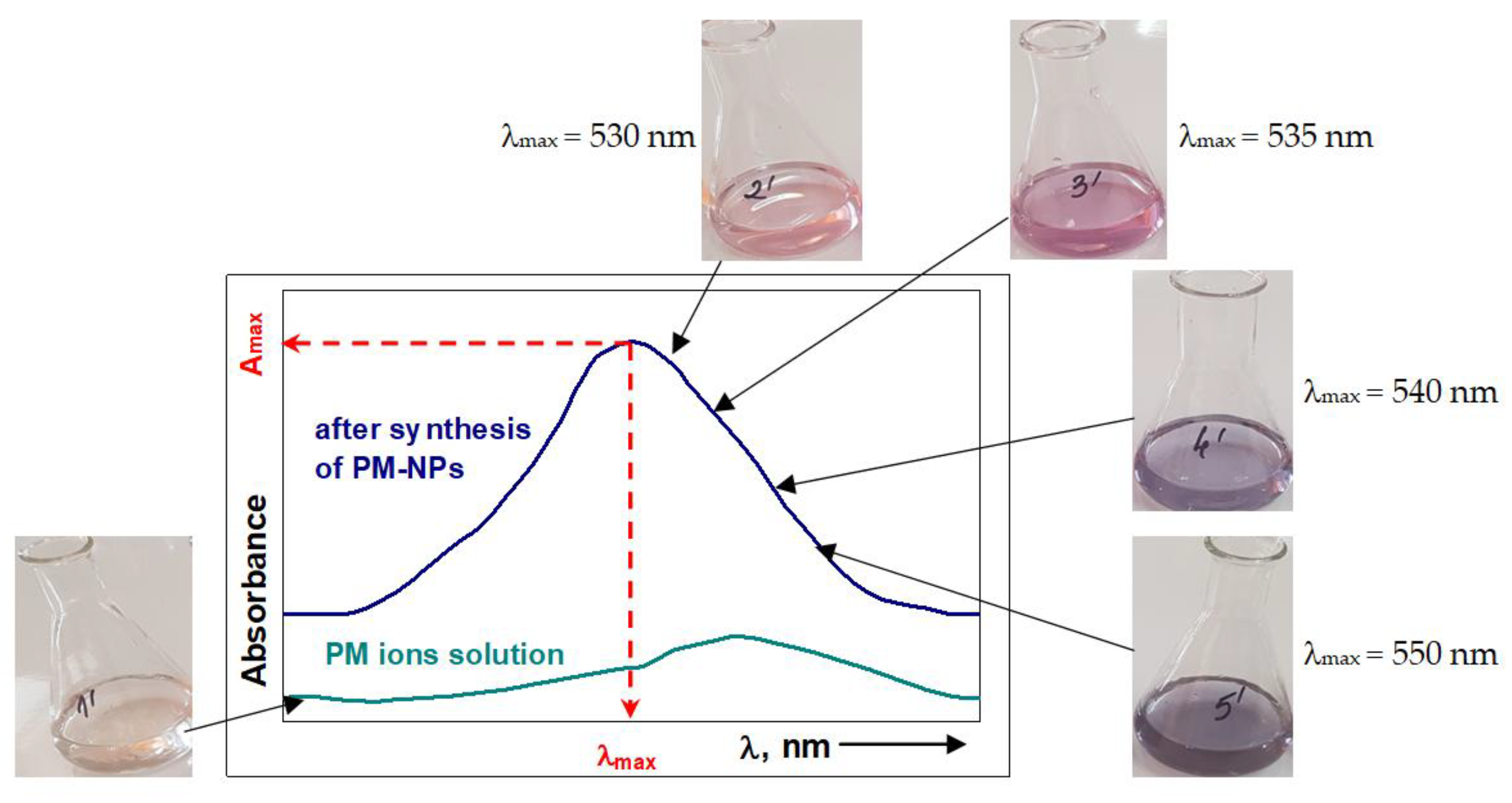
5.1.1. Visual – Color Change
5.1.2. UV-Vis Spectrophotometry
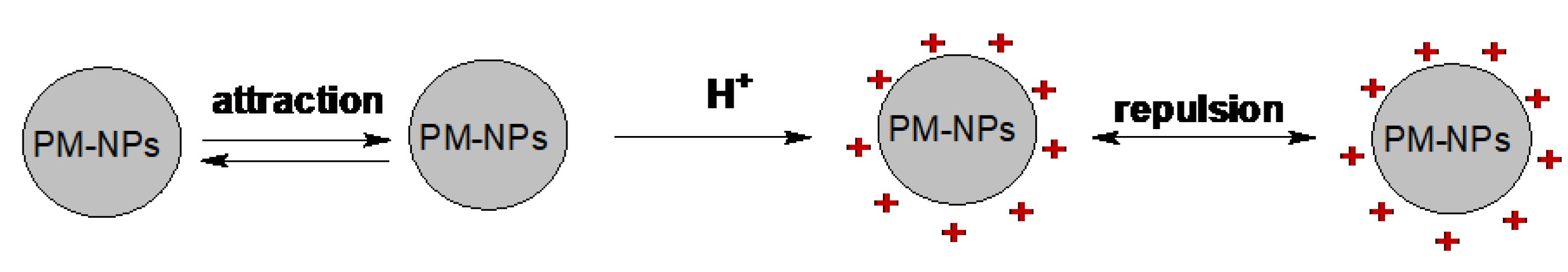
5.1.3. Zeta Potential Measurements
5.2. Structural Characterization Methods
5.2.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
5.2.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
5.2.3. Scanning Force Microscopy (SFM)
5.2.4. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
5.2.4. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
5.3. Composition Characterization Methods
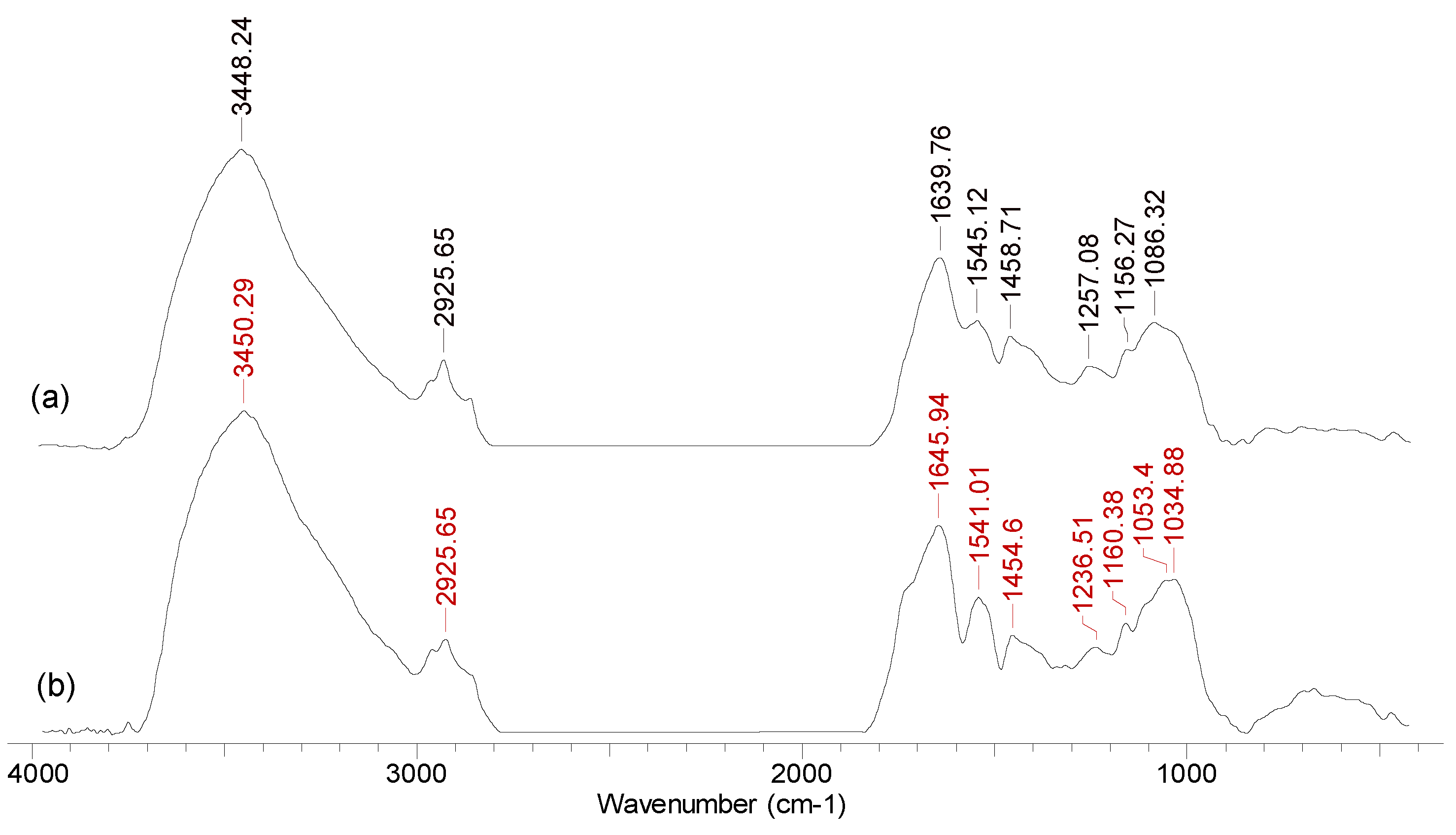
5.3.1. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
5.3.2. Raman Spectroscopy and Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy (SERS)
5.3.3. Energy Dispersive X-Ray Spectroscopy (EDX)
6. Challenges and Future Research
7. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramaraj, N.; Thiripuranathar, G.; Ekanayake, S.; Attanayake, K.; Marapana, U. Phyco-synthesized inorganic nanoparticles and their biomedical applications. RSC Sustainability 2025, 3, 2567–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, J.; Gomaa, A.M.A.; Singh, G.P.; Assiri, M.A.; Bauddh, K. Phytoremediation of metal nanoparticles from the contaminated water bodies: A review. Egypt. J. Chem. 2024, 67, 31–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.K.; Yang, T.; Chen, M.L.; Wang, J.H. Recent Advances in Nanomaterials for Analysis of Trace Heavy Metals. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2021, 51, 353–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, N.; Choudhary, M.; Singhal, G.; Bhagyawant, S.S. SEM studies of saponin silver nanoparticles isolated from leaves of Chenopodium album L. for in vitro anti-acne activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. India Sect. B Biol. Sci. 2020, 90, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terra, A.L.M.; Kosinski, R.D.C.; Moreira, J.B.; Costa, J.A.V.; Morais, M.G.D. Microalgae biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles for application in the control of agricultural pathogens. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 2019, 54, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, J.M.; Ravindran, R.; Narayanan, M.; Samuel, S.M.; Pugazhendhi, A.; Kumar, G. Microalgae: a prospective low cost green alternative for nanoparticle synthesis. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2021, 20, 100–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borah, D.; Das, N.; Das, N.; Bhattacharjee, A.; Sarmah, P.; Ghosh, K.; Chandel, M.; Rout, J.; Pandey, P.; Ghosh, N.N.; Bhattacharjee, C.R. Alga-mediated facile green synthesis of silver nanoparticles: photophysical, catalytic and antibacterial activity. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2020, 34, e5597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Dutta, T.; Kim, K.H.; Rawat, M.; Samddar, P.; Kumar, P. „Green”synthesis of metals and their oxide nanoparticles: applications for environmental remediation. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, R.; Narasimhalu, P.; Joseph, A.I.J.; Pugazhendhi, A. Synthesis of silver nanoparticle from X-ray film and its application in production of biofuel from jatropha oil. Int. J. Energy Res. 2021, 45, 17378–17388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Chen, J.P. A comprehensive review on biosorption of heavy metals by algal biomass: materials, performances, chemistry, and modeling simulation tools. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 160, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, A.; Sarkar, D.; Sasmal, S. A Review of Green Synthesis of Metal Nanoparticles Using Algae. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 693899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Raouf, N.; Al-Enazi, N.M.; Ibraheem, I. B. Green biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles using Galaxaura elongata and characterization of their antibacterial activity. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S3029–S3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lespes, G.; Faucher, S.; Slaveykova, V.I. Natural nanoparticles, anthropogenic nanoparticles, where is the frontier? Front. Environ. Sci. 2020, 8, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponnuchamy, K.; Jacob, J.A. Metal nanoparticles from marine seaweeds - A review. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2016, 5, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Pandit, C.; Gacem, A.; Alqahtani, M.S.; Bilal, M.; Islam, S.; Hossain, J.; Jameel, M. Biologically Derived Gold Nanoparticles and Their Applications. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2022, 8184217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pareek, V.; Bhargava, A.; Gupta, R.; Jain, N.; Panwar, J. Synthesis and Applications of Noble Metal Nanoparticles: A Review. Adv. Sci. Eng. Med. 2017, 9, 527–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibullah, G.; Viktorova, J.; Ruml, T. Current Strategies for Noble Metal Nanoparticle Synthesis. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachem, K.; Ansari, M.J.; Saleh, R.O.; Kzar, H.H.; Al-Gazally, M.E.; Altimari, U.S.; Hussein, S.A.; Mohammed, H.T.; Hammid, A.T.; Kianfar, E. Methods of Chemical Synthesis in the Synthesis of Nanomaterial and Nanoparticles by the Chemical Deposition Method: A Review. BioNanoScience 2022, 12, 1032–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, A.; Komal, P.; Gautam, P.; Sharma, A.; Kumar, N.; Jung, J.P. Recent Trends in Noble Metal Nanoparticles for Colorimetric Chemical Sensing and Micro-Electronic Packaging Applications. Metals 2021, 11, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Hua, Y.; Zhang, X.; Di, L. Rapid Synthesis of Noble Metal Colloids by Plasma–Liquid Interactions. Materials 2024, 17, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Yoo, T.Y.; Bootharaju, M.S.; Kim, J.H.; Chung, D.Y.; Hyeon, T. Noble Metal-Based Multimetallic Nanoparticles for Electrocatalytic Applications. Adv. Sci. 2021, 9, 2104054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, P.F.M.; Torresi, R.M.; Emmerling, F.; Camargo, P.H.C. Challenges and opportunities in the bottom-up mechanochemical synthesis of noble metal nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 16114–16141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjelajac, A.; Phillipe, A.-M.; Guillot, J.; Fleming, Y.; Chemin, J.-B.; Choquet, P.; Bulou, S. Gold nanoparticles synthesis and immobilization by atmospheric pressure DBD plasma torch method. Nanoscale Adv. 2023, 5, 2573–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badoni, A.; Prakash, J. Noble metal nanoparticles and graphene oxide based hybrid nanostructures for antibacterial applications: Recent advances, synergistic antibacterial activities, and mechanistic approaches. Micro Nano Eng. 2024, 22, 100239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrulolum, H.; Nooraei, S.; Javanshir, N.; Tarrahimofrad, H.; Mirbagheri, V.S.; Easton, A.J.; Ahmadian, G. Green synthesis of metal nanoparticles using microorganisms and their application in the agrifood sector. J Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadoun, S.; Chauhan, N.P.S.; Zarrintaj, P.; Barani, M.; Varma, R.S.; Chinnam, S.; Rahdar, A. Synthesis of nanoparticles using microorganisms and their applications: a review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 3153–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamida, R.S.; Ali, M.A.; Alkhateeb, M.A.; Alfassam, H.E.; Momenah, M.A.; Bin-Meferij, M.M. Algal-Derived Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using the Unicellular ulvophyte sp. MBIC10591: Optimisation, Characterisation, and Biological Activities. Molecules 2023, 28, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, R.; Nawaz, K.; Khan, A.K.; Hano, C.; Abbasi, B.H.; Anjum, S. AnOverview of the Algae-Mediated Biosynthesis of Nanoparticles and Their Biomedical Applications. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadoun, S.; Arif, R.; Jangid, N.K.; Meena, R.K. Green synthesis of nanoparticles using plant extracts: A review. Env. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 355–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hano, C.; Abbasi, B.H. Plant-Based Green Synthesis of Nanoparticles: Production, Characterization and Applications. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sahlany, S.T.G.; Niamah, A.K.; Verma, D.K.; Prabhakar, P.; Patel, A.R.; Thakur, M.; Singh, S. Applications of Green Synthesis of Nanoparticles Using Microorganisms in Food and Dairy Products: Review. Processes 2025, 13, 1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, N.K.; Choudhury, R.; Gogoi, B.; Chang, C.M.; Pandey, R.P. Microbial Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles and their Application. Curr. Drug Targets 2022, 23, 752–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.T.; Chen, Y.; Fei, Y.F.; Loo, S.L.; Chen, G.; Hu, M.; Song, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J. An overview of nanomaterial-based novel disinfection technologies for harmful microorganisms: Mechanism, synthesis, devices and application. Sci. Total.Environ. 2022, 837, 155720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamal, G.; Singh, M.; Pardha-Saradhi, P.; Rao, K.S. Roots of Pennisetum sp.possess the competence to generate nanoparticles of noble metals. Indian J. Biochem. Biophys. 2022, 59, 461–467. [Google Scholar]
- Mickymaray, S. One-step Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Saudi Arabian Desert Seasonal Plant Sisymbrium irio and Antibacterial Activity Against Multidrug-Resistant Bacterial Strains. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, S.K.; Jha, A. Plant Extract Mediated Synthesis of Metal Nanoparticles, their Characterization and Applications: A Green Approach. Curr. Green Chem. 2021, 8, 185–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhani, G.B.B.; Di Filippo, L.D.; de Paula, G.A.; Mantovanelli, V.R.; da Fonseca, P.P.; Tashiro, F.M.; Monteiro, D.C.; Fonseca-Santos, B.; Duarte, J.L.; Chorilli, M. High-Tech Sustainable Beauty: Exploring Nanotechnology for the Development of Cosmetics Using Plant and Animal By-Products. Cosmetics 2024, 11, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, M.; Santos, D.; Soares, B.B.; Farias De Sousa, L.; Alves, E.C. Cleaner Production Alternatives for a Cosmetics Industry in Southern Bahia. Indep. J. Manag. Prod. 2021, 12, 1068–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ealayawi, Z.A.; Al-Dulaimy, A.F.Z. Marine Algae and Applications to Plant Nutrition: A review. IOP Conf. Series: Earth Environ. Sci. 2023, 1158, 042004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, N.; Lo, E.; Legall, N.; Philippidis, G.P. A Critical Review of Growth Media Recycling to Enhance the Economics and Sustainability of Algae Cultivation. Energies 2023, 16, 5378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loke Show, P. Global market and economic analysis of microalgae technology: Status and perspectives. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 357, 127329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.N.; Wang, R.; Ho, S.H. Algae-mediated biosystems for metallic nanoparticle production: From synthetic mechanisms to aquatic environmental applications. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 420, 126625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampath, S.; Madhavan, Y.; Muralidharan, M.; Sunderam, V.; Lawrance, A.V.; Muthupandian, S. A review on algal mediated synthesis of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles and their emerging biomedical potential. J. Biotechnol. 2022, 360, 92–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojha, S.; Khan, A.; Sahoo, C.R.; Mohapatra, R.K.; Tripathi, D.K.; Mukherjee, M.; Guldhe, A.; Nayak, M. A Review on Biosynthesis of Nanoparticles via Microalgal Technology and Their Biomedical Applications. BioNanoSci. 2025, 15, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, L.C.; Figueiredo, R.C.; Ribeiro-Andrade, R.; Pontes-Silva, A.V.; Arantes, M.L.; Giani, A.; Figueredo, C.C. High diversity of microalgae as a tool for the synthesis of different silver nanoparticles: A species-specific green synthesis. Coll. Interf. Sci. Comm. 2021, 42, 100420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruzik, L. Microalgae with active biological metal-nanoparticles as a novel food. Biosynthesis, characterization and bioavailability investigation – Review. Trend Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 139, 104127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Sharma, S.; Sharma, K.; Chetri, S.P.; Vashishtha, A.; Singh, P.; Kumar, R.; Rathi, B.; Agrawal, V. Algae as crucial organisms in advancing nanotechnology: A systematic review. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 1759–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincy, W.; Mahathalana, T.J.; Sukumaran, S.; Jeeva, S. Algae as a source for synthesis of nanoparticles-a review. Int. J. Latest Trends Eng. Technol. 2017, 5–9. [Google Scholar]
- Uzair, B.; Liaqat, A.; Iqbal, H.; Menaa, B.; Razzaq, A.; Thiripuranathar, G.; Rana, N.F.; Menaa, F. Green and Cost-Effective Synthesis of Metallic Nanoparticles by Algae: Safe Methods for Translational Medicine. Bioengineering 2020, 7, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slepicka, P.; Slepicková Kasálková, N.; Siegel, J.; Kolská, Z.; Švorcík, V. Methods of Gold and Silver Nanoparticles Preparation. Materials 2020, 13, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chugh, D.; Viswamalya, V.S.; Das, B. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles with algae and the importance of capping agents in the process. J. Genetic Eng. Biotechnol. 2021, 19, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, J.A. Handbook of Analytical Chemistry, Mc-Grow Hill Inc., New York, USA, 1995.
- Jin, R. The impacts of nanotechnology on catalysis by precious metal nanoparticles. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2012, 1, 31–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; Wang, Z.; Ming, N. Shape-Selective Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles with Controlled Sizes, Shapes, and Plasmon Resonances. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2007, 17, 3295–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lou, Z.; Li, B. Nanostructured materials with localized surface plasmon resonance for photocatalysis. Chinese Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 1154–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Kafshgari, M.H.; Meunier, M. Optical Properties and Applications of Plasmonic-Metal Nanoparticles. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2005400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Yu, G.; Zhang, Z.; Han, Y.; Guan, G.; Yang, W.; Han, M.Y. Intrinsic Optical Properties and Emerging Applications of Gold Nanostructures. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2206700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Zhu, Y.K.; Feng, J.; Ge, Z.H. Precious metal nanoparticles dispersing toward highly enhanced mechanical and thermoelectric properties of copper sulfides. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 892, 162035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kus-Liskiewicz, M.; Fickers, P.; Tahar, I.B. Biocompatibility and Cytotoxicity of Gold Nanoparticles: Recent Advances in Methodologies and Regulations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorovskikh, S.I.; Vikulova, E.S.; Sergeevichev, D.S.; Guselnikova, T.Y.; Korolkov, I.V.; Fedorenko, A.D.; Nasimov, D.A.; Vasilieva, M.B.; Chepeleva, E.V.; Zherikova, K.V.; Basova, T.V.; Morozova, N.B. Heterostructures Based on Noble Metal Films with Ag and Au Nanoparticles: Fabrication, Study of In Vivo Biocompatibility and Antibacterial Activity. Coatings 2023, 13, 1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pechyen, C.; Ponsanti, K.; Tangnorawich, B.; Ngernyuang, N. Waste fruit peel e Mediated green synthesis of biocompatible gold nanoparticles. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 14, 2982–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talarska, P.; Boruczkowski, M.; Zurawski, J. Current Knowledge of Silver and Gold Nanoparticles in Laboratory Research – Application, Toxicity, Cellular Uptake. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behzad, F.; Naghib, S.M.; Kouhbanani, M.A.J.; Tabatabaei, S.N.; Zare, Y.; Rhee, K.Y. An overview of the plant-mediated green synthesis of noble metal nanoparticles for antibacterial applications. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 94, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mammari, N.; Lamouroux, E.; Boudier, A.; Duval, R.E. Current Knowledge on the Oxidative-Stress-Mediated Antimicrobial Properties of Metal-Based Nanoparticles. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Doyle-Davis, K.; Li, R.; Wang, Z.; Sun, X. Advanced Support Materials and Interactions for Atomically Dispersed Noble-Metal Catalysts: From Support Effects to Design Strategies. Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 12, 2102556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDarby, S.P.; Wang, C.J.; King, M.E.; Personick, M.L. An Integrated Electrochemistry Approach to the Design and Synthesis of Polyhedral Noble Metal Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 21322–21335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritea, L.; Banica, F.; Costea, T.O.; Moldovan, L.; Dobjanschi, L.; Muresan, M.; Cavalu, S. Metal Nanoparticles and Carbon-Based Nanomaterials for Improved Performances of Electrochemical (Bio)Sensors with Biomedical Applications. Materials 2021, 14, 6319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldosari, F.M.M. Characterization of Labeled Gold Nanoparticles for Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering. Molecules 2022, 27, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Qiao, Q.; Cao, J.; Li, H.; Bian, Z. Precious metal recovery. Joule 2021, 5, 3097–3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadaf, S.J.; Jadhav, N.R.; Naikwadi, H.S.; Savekar, P.L.; Sapkal, I.D.; Kambli, M.M.; Desai, I.A. Green synthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles: Updates on research, patents, and future prospects. OpenNano 2022, 8, 100076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, N.S.; Alsubhi, N.S.; Felimban, A.I. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using medicinal plants: characterization and application. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2022, 15, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, A.I.; Zhang, Y.; Farghali, M.; Rashwan, A.K.; Eltaweil, A.E.; Abd El-Monaem, E.M.; Mohamed, I.M.A.; Badr, M.M.; Ihara, I.; Rooney, D.W.; Yap, P.S. Synthesis of green nanoparticles for energy, biomedical, environmental, agricultural, and food applications: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2024, 22, 841–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premarathna, K.S.D.; Lau, S.Y.; Chiong, T.; Show, P.L.; Vithanage, M.; lm, M.K. Greening up the fight against emerging contaminants: algae-based nanoparticles for water remediation. Clean Techn. Environ. Policy 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreira, A.R.F.; Veloso, T.; Macario, I.P.E.; Pereira, J.L.; Ventura, S.P.M.; Passos, H.; Coutinho, J.A.P. The role of biomass elemental composition and ion-exchange in metal sorption by algae. Chemosphere 2023, 314, 137675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Znad, H.; Awual, R.; Martini, S. The Utilization of Algae and Seaweed Biomass for Bioremediation of Heavy Metal-Contaminated Wastewater. Molecules 2022, 27, 1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonelli, F.M.P.; Silva, C.S.; Delgado, V.M.S.; Tonelli, F.C.P. Algae-based green AgNPs, AuNPs, and FeNPs as potential nanoremediators. Green Proc. Synthesis 2023, 12, 20230008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, P.; Kaur, A.; Goyal, D. Algae-based metallic nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization and applications. J. Microbiol. Meth. 2019, 163, 105656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santhosh, P.B.; Genova, J.; Chamati, H. Green Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles: An Eco-Friendly Approach. Chemistry 2022, 4, 345–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Ballesteros, N.; Prado-López, S.; Rodríguez-González, J.B.; Lastra, M.; Rodríguez-Argüelles, M.C. Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using brown algae Cystoseira baccata: Its activity in colon cancer cells. Colloids Surf. B. Biointerfaces 2017, 153, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mata, Y.; Torres, E.; Blazquez, M.; Ballester, A.; González, F.; Munoz, J. Gold (III) biosorption and bioreduction with the brown alga Fucus vesiculosus. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 166, 612–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeshkumar, S.; Kannan, C.; Annadurai, G. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using marine brown algae Turbinaria conoides and its antibacterial activity. Int. J. Pharma. Bio Sci. 2012, 3, 502–510. [Google Scholar]
- Pugazhendhi, A.; Prabakar, D.; Jacob, J.M.; Karuppusamy, I.; Saratale, R.G. Synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using Gelidium amansii and its antimicrobial property against various pathogenic bacteria. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 114, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naveena, B.E.; Prakash, S. Biological synthesis of gold nanoparticles using marine algae Gracilaria corticata and its application as a potent antimicrobial and antioxidant agent. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2013, 6, 179–182. [Google Scholar]
- Bhimba, B.; Kumari, P. Phytosynthesis of silver nanoparticles from the extracts of seaweed Ulva lactuca and its antimicrobial activity. Int. J. Pharm. BioSci. 2014, 5, 666–677. [Google Scholar]
- Manikandakrishnan, M.; Palanisamy, S.; Vinosha, M.; Kalanjiaraja, B.; Mohandoss, S.; Manikandan, R.; Tabarsa, M.; You, S.G.; Prabhu, N.M. Facile green route synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Caulerpa racemosa for biomedical applications. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 101345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostică, A.G.; Bulgariu, L. Utilization of Marine Algae Biomass for Eco friendly Obtaining of Gold Nanoparticles. Proceeding of The 11th IEEE International Conference on E-Health and Bioengineering - EHB 2023, IEEE-979-8-3503-2887-5/23.
- Rajasulochana, P.; Dhamotharan, R.; Murugakoothan, P.; Murugesan, S.; Krishnamoorthy, P. Biosynthesis and characterization of gold nanoparticles using the alga Kappaphycus alvarezii. Int. J. Nanosci. 2010, 9, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, V.; Aruna Devi, J.; Astalakshmi, A.; Nima, P.; Thangaraja, A. Eco-friendly synthesis of silver nanoparticles using a seaweed, Kappaphycus alvarezii (Doty) Doty ex PC Silva. Int. J. Eng. Adv. Technol. 2013, 2, 559–563. [Google Scholar]
- Chellapandian, C.; Ramkumar, B.; Puja, P.; Shanmuganathan, R.; Pugazhendhi, A.; Kumar, P. Gold nanoparticles using red seaweed Gracilaria verrucosa: Green synthesis, characterization and biocompatibility studies. Proc. Biochem. 2019, 80, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, R.; Priya, M.; Indurthi, L.; Radhakrishnan, V.; Sudhakaran, R. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using red algae Portieria hornemannii and its antibacterial activity against fish pathogens. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 138, 103780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathiyaraj, G.; Manikandakrishnan, M.V.M.; Sangeetha, D.; Sonaimuthu, S.P.M.; Manikandan, R.; You, S.G.; Prabhu, N.M. Bio-directed synthesis of Pt-nanoparticles from aqueous extract of red algae Halymenia dilatata and their biomedical applications. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 618, 126434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeshkumar, S.; Sherif, M.H.; Malarkodi, C.; Ponnanikajamideen, M.; Arasu, M.V.; Al-Dhabi, N.A.; Roopan, S.M. Cytotoxicity behaviour of response surface model optimized gold nanoparticles by utilizing fucoidan extracted from padina tetrastromatica. J. Molec. Struc. 2021, 1228, 129440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramkumar, V.S.; Pugazhendhi, A.; Prakash, S.; Ahila, N.K.; Vinoj, G.; Selvam, S.; Kumar, G.; Kannapiran, E.; Rajendran, R.B. Synthesis of platinum nanoparticles using seaweed Padina gymnospora and their catalytic activity as PVP/PtNPs nanocomposite towards biological applications. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 92, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Ballesteros, N.; Diego-González, L.; Lastra-Valdor, M.; Cavazza, A.; Bigi, F.; Rodríguez-Argüelles, M.C.; Grimaldi, M.; Simón-Vázquez, R. Immunomodulatory and Antitumoral Activity of Gold Nanoparticles Synthesized by Red Algae Aqueous Extracts. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madani, M.; Hosny, S.; Alshangiti, D.M.; Nady, N.; Alkhursani, S.A.; Alkhaldi, H.; Al-Gahtany, S.A.; Ghobashy, M.M.; Gaber, G.A. Green Synthesis of Nanoparticles for Varied Applications: Green Renewable Resources and Energy-Efficient Synthetic Routes. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2022, 11, 731–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montasser, M.S.; Younes, A.M.; Hegazi, M.M.; Dashti, N.H.; El-Sharkawey, A.E.; Beall, G.W. A Novel Eco-friendly Method of Using Red Algae (Laurencia papillosa) to Synthesize Gold Nanoprisms. J. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Koçer, A.T.; Özçimen, D. Eco-friendly synthesis of silver nanoparticles from macroalgae: optimization, characterization and antimicrobial activity. Biomass Conv.Bioref. 2025, 15, 1995–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algotiml, R.; Gab-Alla, A.; Seoudi, R.; Abulreesh, H.H.; El-Readi, M.Z.; Elbanna, K. Anticancer and antimicrobial activity of biosynthesized Red Sea marine algal silver nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.H.; Yuan, Z.Q.; Li, G.K. Preparation of phytosterols and phytol from edible marine algae by microwave-assisted extraction and high-speed counter-current chromatography. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 104, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Ballesteros, N.; Fernandes, M.; Machado, R.; Gomes, A.C.; Cavazza, A.; Sampaio, P.; Bigi, F.; Rodríguez-Argüelles, M.C. Valorisation of the Invasive Macroalgae Undaria pinnatifida (Harvey) Suringar for the Green Synthesis of Gold and Silver Nanoparticles with Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Potential. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aboeita, N.M.; Fahmy, S.A.; El-Sayed, M.M.H.; El-Said Azzazy, H.M.; Shoeib, T. Enhanced Anticancer Activity of Nedaplatin Loaded onto Copper Nanoparticles Synthesized Using Red Algae. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, S.; Palaniyandi, T.; Shanmugam, R.; Karunakaran, S.; Pandi, M.; Wahab, M.R.A.; Baskar, G.; Rajendran, B.K.; Sivaji, A.; Moovendhan, M. Synthesis, characterization, cytotoxicity, and antimicrobial studies of green synthesized silver nanoparticles using red seaweed Champia parvula. Biomass Convers. Bioref. 2024, 14, 7387–7400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarif, W.M.; Shaban, Y.A.; Orif, M.I.; Ghandourah, M.A.; Alorfi, H.S.; Tadros, H.R.Z. Green Synthesis of TiO2 Nanoparticles Using Natural Marine Extracts for Antifouling Activity. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi Tarighat, M.; Ghorghosheh, F.H.; Abdi, G. Fe3O4@SiO2-Ag nanocomposite colorimetric sensor for determination of arginine and ascorbic acid based on synthesized small size AgNPs by cystoseria algae extract. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2022, B283, 115855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, D.; Patel, B.; Yadav, V.K.; Sudhakar, M.P.; Alharbi, S.A.; Salmen, S.H.; Patel, I.; Choudhary, N.; Patel, A. Silver nanoparticles synthesized from marine algae Spatoglossum asperum: Antioxidant properties and seed germination enhancement. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2024, 16, 100478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, S.J.; Ul Haq Bhat, I.; Yusoff, H.M.; Razali, M.H.; Kadir, M.A.; Ern, L.K. Brown algae-based preparation, characterization and application of Pd nanocatalyst for enhanced reductive azo dye degradation. Cleaner Eng. Technol. 2021, 4, 100172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, C.J.; Sau, T.K.; Gole, A.M.; Orendorff, C.J.; Gao, J.; Gou, L.; Hunyadi, S.E.; Li, T. Anisotropic metal nanoparticles: Synthesis, assembly, and optical applications. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 13857–13870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, K.J.M.; Biswal, S.L.; Bharti, B. Active Colloids as Models, Materials, and Machines. Ann. Rev. Chem. Biomolec. Eng. 2023, 14, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, D.W.; Phiri, M.M.; Jordaan, A.; Vorster, B.C. Modified HEPES one-pot synthetic strategy for gold nanostars. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2019, 6, 190160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millstone, J.E.; Hurst, S.J.; Métraux, G.S.; Cutler, J.I.; Mirkin, C.A. Colloidal Gold and Silver Triangular Nanoprisms. Small 2009, 5, 646–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastús, N.G.; Merkoçi, F.; Piella, J.; Puntes, V. Synthesis of Highly Monodisperse Citrate-Stabilized Silver Nanoparticles of up to 200 nm: Kinetic Control and Catalytic Properties. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 2836–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Leis, A.; Garcia-Ramos, J.V.; Sanchez-Cortes, S. Silver Nanostars with High SERS Performance. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 7791–7795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, C.Z.; Xia, Y. Synthesis of Ag Nanocubes 18–32 nm in Edge Length: The Effects of Polyol on Reduction Kinetics, Size Control, and Reproducibility. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 1941–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagao, H.; Ichiji, M.; Hirasawa, I. Synthesis of Platinum Nanoparticles by Reductive Crystallization Using Polyethyleneimine. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2017, 40, 1242–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herricks, T.; Chen, J.; Xia, Y. Polyol Synthesis of Platinum Nanoparticles: Control of Morphology with Sodium Nitrate. Nano Letters 2004, 4, 2367–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walbrück, K.; Kuellmer, F.; Witzleben, S.; Guenther, K. Synthesis and Characterization of PVP-Stabilized Palladium Nanoparticles by XRD, SAXS, SP-ICP-MS, and SEM. J. Nanomater. 2019, 2019, 4758108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iben Ayad, A.; Belda Marín, C.; Colaco, E.; Lefevre, C.; Méthivier, C.; Ould Driss, A.; Landoulsi, J.; Guénin, E. “Water soluble” palladium nanoparticle engineering for C–C coupling, reduction and cyclization catalysis. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 6646–6657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, E.G.A.; Tofanello, A.; Brito, A.M.M.; Lopes, D.M.; Albuquerque, L.J.C.; de Castro, C.E.; Costa, F.N.; Giacomelli, F.C.; Ferreira, F.F.; Araújo-Chaves, J.C.; Nantes, I.L. Effects of Gold Salt Speciation and Structure of Human and Bovine Serum Albumins on the Synthesis and Stability of Gold Nanostructures. Frontiers Chem. 2016, 4, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pargar, F.; Koleva, D. Polarization Behaviour of Silver in Model Solutions. Int. J. Struct. Civ. Eng. Res. 2017, 6, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, Y.; Hiraiwa, K.; Sasaki, Y.; Fujiwara, I.; Tagashira, S. Surfactant Gel Adsorption of Platinum(II), (IV) and Palladium(II) as Chloro complexes and Kinetic Separation of Palladium from Platinum Using EDTA. Anal. Sci. 2007, 23, 1147–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucaci, A.R; Bulgariu, D.; Bulgariu, L. Green Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles Using Marine Red Algae Biomass. The 9th IEEE International Conference on E-Health and Bioengineering - EHB 2021, IEEE 978-1-6654-4000-4/21.
- Palaniyandi, T.; Viswanathan, S.; Prabhakaran, P.; Baskar, G.; Wahab, M.R.A.; Sivaji, A.; Ravi, M.; Rajendran, B.K.; Moovendhan, M.; Surendran, H.; Kumarasamy, S. Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using Halymenia pseudofloresii extracts and their antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anti-cancer activities. Biomass Convers. Bioref. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, J.; Manivasagan, P.; Kim, S.K.; Kirthi, A.V.; Marimuthu, S.; Rahuman, A.A. Marine algae-mediated synthesis of gold nanoparticles using a novel Ecklonia cava. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2014, 37, 1591–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singaravelu, G.; Arockiamary, J.S.; Kumar, V.G.; Govindaraju, K. Anovel extracellular synthesis of monodisperse gold nanoparticles using marine alga, Sargassum wightii Greville. Coll. Surf. B Biointerf. 2007, 57, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhas, T.S.; Kumar, V.G.; Abraham, L.S.; Karthick, V.; Govindaraju, K. Sargassum myriocystum mediated biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles. Spectrochim. Acta A Molec. Biomolec. Spectr. 2012, 99, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayaraghavan, K.; Mahadevan, A.; Sathishkumar, M.; Pavagadhi, S.; Balasubramanian, R. Biosynthesis of Au(0) from Au(III) via biosorption and bioreduction using brown marine alga Turbinaria conoides. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 167, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodeiro, P.; Sillanpää, M. Gold recovery from artificial seawater using synthetic materials and seaweed biomass to induce gold nanoparticles formation in batch and column experiments. Marine Chem. 2013, 152, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogmaz, S.; Cavas, L. Biohydrogen production via green silver nanoparticles synthesized through biomass of Ulva lactuca bloom. Biores. Technol. 2023, 379, 129028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboelfetoh, E.F.; El-Shenody, R.A.; Ghobara, M.M. Eco-friendly synthesis of silver nanoparticles using green algae (Caulerpa serrulata): reaction optimization, catalytic and antibacterial activities. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massironi, A.; Morelli, A.; Grassi, L.; Puppi, D.; Braccini, S.; Maisetta, G.; Esin, S.; Batoni, G.; Pina, C.D.; Chiellini, F. Ulvan as novel reducing and stabilizing agent from renewable algal biomass: Application to green synthesis of silver nanoparticles. Carbohydrate Polym. 2019, 203, 310–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azizi, S.; Namvar, F.; Mahdavi, M.; Ahmad, M.B.; Mohamad, R. Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Brown Marine Macroalga, Sargassum Muticum Aqueous Extract. Materials 2013, 6, 5942–5950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivagnanam, S.P.; Getachew, A.T.; Choi, J.H.; Park, Y.B.; Woo, H.C.; Chun, B.S. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from deoiled brown algal extract via Box-Behnken based design and their antimicrobial and sensing properties. Green Process. Synth. 2017, 6, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinayagam, R.; Nagendran, V.; Goveas, L.C.; Narasimhan, M.K.; Varadavenkatesan, T.; Chandrasekar, N.; Selvaraj, R. Structural characterization of marine macroalgae derived silver nanoparticles and their colorimetric sensing of hydrogen peroxide. Mater. Chem. Physic. 2024, 313, 128787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindaraju, K.; Kiruthiga, V.; Kumar, V.G.; Singaravelu, G. Extracellular Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles by a Marine Alga, Sargassum Wightii Grevilli and Their Antibacterial Effects. J. Nanoscie. Nanotechnol. 2009, 9, 5497–5501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şahin, M.; Arslan, Y.; Tomul, F.; Akgül, F.; Akgül, R. Green synthesis of metal nanoparticles from Codium macroalgae for wastewater pollutants removal by adsorption. Clean- Soil, Air, Water. 2024, 52, 2300187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, T.; Henriques, B.; Ferreira, N.; Pinto, R.J.B.; Monteiro, F.L.S.; Pereira, E. Insight into the mechanisms involved in the removal of toxic, rare earth, and platinum elements from complex mixtures by Ulva sp. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 453, 139630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shargh, A.Y.; Sayadi, M.H.; Heidari, A. Green Biosynthesis of Palladium Oxide Nanoparticles Using Dictyota indica Seaweed and its application for adsorption. J. Water Environ. Nanotechnol., 2018, 3, 337–347. [Google Scholar]
- Sonbol, H.; Ameen, F.; Al Yahya, S.; Almansob, A.; Alwakee, S. Padina boryana mediated green synthesis of crystalline palladium nanoparticles as potential nanodrug against multidrug resistant bacteria and cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edo, G.I.; Mafe, A.N.; Ali, A.B.M.; Akpoghelie, P.O.; Yousif, E.; Isoje, E.F.; Igbuku, U.A.; Ismael, S.A.; Essaghah, A.E.A.; Ahmed, D.S.; Ozsahin, D.U.; Umar, H.; Alamiery, A.A. Green Biosynthesis of Nanoparticles Using Plant Extracts: Mechanisms, Advances, Challenges, and Applications. BioNanoSci. 2025, 15, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Desimone, M.F.; Pandya, S.; Jasani, S.; George, N.; Adnan, M.; Aldarhami, A.; Bazaid, A.S.; Alderhami, S.A. Revisiting the green syn thesis of nanoparticles: Uncovering influences of plant extracts as reducing agents for enhanced synthesis efficiency and its bio medical applications. Int. J. Nanomedic. 2023, 18, 4727–4750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, R.H.; Shanab, S.M.; Shalaby, E.A. Algal biomass nanoparticles: chemical characteristics, biological actions, and applications. Biomass Conv.Bioref. 2023, 13, 11441–11455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyaraj, M.; Gurunathan, S.; Qasim, M.; Kang, M.H.; Kim, J.H. AComprehensive Review on the Synthesis, Characterization, and Biomedical Application of Platinum Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doak, J.; Gupta, R.K.; Manivannan, K.; Ghosh, K.; Kahol, P.K. Effect of particle size distributions on absorbance spectra of gold nanoparticles. Physica E 2010, 42, 1605–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, M.J.; Mehdi, M.S. Study of morphology and zeta potential analyzer for the silver nanoparticles. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2014, 5, 381–385. [Google Scholar]
- Tantra, R.; Schulze, P.; Quincey, P. Effect of nanoparticle concentration on zeta-potential measurement results and reproducibility. Particuology 2010, 8, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre, F.M.A.; Bazán-Díaz, L.; Mendoza-Cruz, R.; Gómez-Rodríguez, A.; Zorrilla-Cangas, C.; Herrera-Becerra, R. Nano Phase Characterization by Transmission Electron Microscopy: Experimental and Simulation. Mater. Sci. Appl. 2015, 6, 935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I. , Saeed, K., Khan, I., Nanoparticles: properties, applications and toxicities. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 908–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santosh Kumar, S.R.; Bongale, M.M.; Sachidanandam, M.; Maurya, G.; Yuvraj, M.; Sarwade, P.P. A Review on Green Synthesized Metal Nanoparticles Applications. J. Res. Appl. Sci. Biotechol. 2024, 3, 80–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingham, B. , X-ray scattering characterisation of nanoparticles. Crystallogr. Rev. 2015, 21, 229–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, T.; Hegmann, T. Determining the composition of gold nanoparticles: a compilation of shapes, sizes, and calculations using geometric considerations. J. Nanopart. Res. 2016, 18, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomaszewska, E.; Soliwoda, K.; Kadziola, K.; Celichowski, G.; Cichomski, M.; Szmaja, W.; Grobelny, J. Detection limits of DLS and UV-Vis spectroscopy in characterization of polydisperse nanoparticles colloids. J. Nanomater. 2013, 2013, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brar, S.K.; Verma, M. Measurement of nanoparticle by light scattering techniques. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2011, 30, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.C.; Lin, S.; Wang, P.C.; Sridhar, R. Techniques for physicochemical characterization of nanomaterials. Biotechnol. Adv. 2014, 32, 711–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, B.; Cher, M.T.; Jeng, C.K. FTIR spectroscopy as a tool for nano-material characterization. Inf. Biophys. Technol. 2010, 53, 434–438. [Google Scholar]
- Menon, S.; Rajeshkumar, S.; Kumar, V. A review on biogenic synthesis of gold nanoparticles, characterization, and its applications. Resource-Efficient Technol. 2017, 3, 516–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayan, S.R.; Santhiyagu, P.; Singamuthu, M.; Kumari Ahila, N.; Jayaraman, R.; Ethiraj, K. Synthesis and characterization of silver and gold nanoparticles using aqu eous extract of seaweed, Turbinaria conoides, and their antimicrofouling activity. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 938272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghodake, G.; Lee, D.S. Biological synthesis of gold nanoparticles using the aqueous extract of the brown algae Laminaria japonica. J. Nanoelectron. Optoelectron. 2011, 6, 268–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Kalaivani, R.; Manikandan, S.; Sangeetha, N.; Kumaraguru, A.K. Facile green synthesis of variable metallic gold nanoparticle using Padina gymnospora, a brown marine macroalga. Appl. Nanosci. 2013, 3, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varun, S.; Sudha, S.; Kumar, P.S. Biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles from aqueous extract of Dictyota Bartayresiana and their antifungal activity. Indian J. Adv. Chem. Sci. 2014, 2, 190–193. [Google Scholar]
- Ramakrishna, M.; Babu, D.R.; Gengan, R.M.; Chandra, S.; Rao, G.N. Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using marine algae and evaluation of their catalytic activity. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 2016, 6, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, L.; Blázquez, M.L.; Muñoz, J.A.; González, F.; Ballester, A. Biological synthesis of metallic nanoparticles using algae. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2013, 7, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanalakshmi, P.K.; Azeez, R.; Rekha, R.; Poonkodi, S.; Nallamuthu, T. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using green and brown seaweeds. Phykos 2012, 42, 39–45. [Google Scholar]
- Rahimi, Z.; Yousefzadi, M.; Noori, A. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Ulva flexousa from the Persian Gulf, Iran. J. Persian Gulf. 2014, 5, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Sinha, S.N.; Paul, D.; Halder, N.; Sengupta, D.; Patra, S.K. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using fresh water green alga Pithophora oedogonia (Mont.) Wittrock and evaluation of their antibacterial activity. Appl. Nanosci. 2015, 5, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinjarkar, H.; Gaikwad, S.; Ingle, A.P.; Gade, A.; Rai, M. Phycofabrication of silver nanoparticles and their antibacterial activity against human pathogens. Adv. Mater. Lett. 2016, 7, 1010–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathiraven, T.; Sundaramanickam, A.; Shanmugam, N.; Balasubramanian, T. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using marine algae Caulerpa racemosa and their antibacterial activity against some human pathogens. Appl. Nanosci. 2015, 5, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Aragao, A.P.; de Oliveira, T.M.; Quelemes, P.V.; Perfeito, M.L.G.; Araujo, M.C.; Santiago, J.D.A.S.; Cardoso, V.S.; Quaresma, P.; de Almeida, J.R.D.S.; da Silva, D.A. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using the seaweed Gracilaria birdiae and their antibacterial activity. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 4182–4188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindaraju, K.; Krishnamoorthy, K.; Alsagaby, S.A.; Singaravelu, G.; Premanathan, M. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles for selective toxicity towards cancer cells. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2015, 9, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanisamy, S.; Anjali, R.; Jeneeta, S.; Mohandoss, S.; Keerthana, D.; Shin, I.S.; You, S.G.; Prabhu, N.M. An effective bio-inspired synthesis of platinum nanoparticles using Caulerpa sertularioides and investigating their antibacterial and antioxidant activities. Bioproc. Biosys. Eng. 2023, 46, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, B.; Padmesh, T. Seaweed (Sargassum ilicifolium) assisted green synthesis of palladium nanoparticles. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2014, 5, 229–231. [Google Scholar]
- Momeni, S.; Nabipour, I. A simple green synthesis of palladium nanoparticles with Sargassum alga and their electrocatalytic activities towards hydrogen peroxide. App. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 176, 1937–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Precious metal | Au | Ag | Pt | Pd |
| Atomic number (Z) Atomic weight (A) Oxidation state Electronegativity (Pauling scale) Standard redox potential, V Density (at 20 °C), g/cm3 Meting point, °C Atomic radius, pm |
79 196.97 +3, +1 2.54 +1.5000 19.283 1064.18 144.0 |
47 107.87 +1 1.93 +0.7994 10.503 961.78 144.0 |
78 195.08 +2, +4 2.28 +1.2000 21.452 1768.3 139.0 |
46 106.42 +2, +4 2.20 +0.9200 12.007 1554.9 137.0 |
| Ionic radius, pm | 85.0 | 126.0 | 62.5 | 64.0 |
| Precious metal | Chemical reaction | logβ |
| Au | Au3+ (H+) + 4 Cl- → AuCl4- | 24.49 |
| Ag | Ag+ (H+) + Cl-→ AgCl↓ | 1.1 10−10* |
| Pt | Pt2+ (H+) + 4 Cl- → PtCl42- | 13.99 |
| Pd | Pd2+ (H+) + 4 Cl- → PdCl42- | 27.20 |
| Marine algae | Type of algae | PM-NPs | Notable features | Reference |
| Ulva lactuca | Green algae | Au, Ag | Successfully used in eco-friendly synthesis | [84] |
| Caulerpa racemose | Green algae | Ag | Spherical and triangle stable nanoparticles | [85] |
| Cladophora vagabunda | Green Algae | Au | High efficiency, long stable nanoparticles | [86] |
| Kappaphycus alvarezii | Red algae | Au, Ag | Stable and monodisperse nanoparticles | [87,88] |
| Gracilaria edulis | Red algae | Au | Produces uniform and stable nanoparticles | [89] |
| Galaxaura elongata | Red algae | Au | High efficiency, stable and spherical nanoparticles | [12] |
| Portieria hornemannii | Red algae | Ag | Stable and monodisperse nanoparticles | [90] |
| Halymenia dilatata | Red algae | Pt | Stable and monodisperse nanoparticles | [91] |
| Fucus vesiculosus | Brown algae | Au | Active functional groups (carboxyl, phenol); increased efficiency | [80] |
| Padina pavonica | Brown algae | Au | Efficient and rapid synthesis | [92] |
| Padina gymnospora | Brown algae | Pt | Efficient and rapid synthesis | [93] |
| Algae | g, biomass | Solvent | T,°C | t, min | Reference |
| Laurencia papillosa | 5.0 | distilled water | 70-80 | 5 | [96] |
| Ulva lactuca | 1.0 | distilled water | 70-80 | 45 | [97] |
| Halopteris scoparia | |||||
| Ulva rigida | 10 | distilled water | 70 | 15 | [98] |
| Gracilaria foliifera | |||||
| Cystoseira myrica | |||||
| Undaria pinnatifida | 15.0 | 1.5 mol/L ethanol | microwave | 200 | [99] |
| Sargassum fusiform | |||||
| Undaria pinnatifida | distilled water | 100 | 15 | [100] | |
| Pterocladia capillacea | 5.0 | distilled water | ultrasonication | 240 | [101] |
| Champia parvula | 1.0 | distilled water | 60 | 20 | [102] |
| Bostrychia tenella | 100 | methanol | Room temperature | - | [103] |
| Laurencia obtusa | |||||
| Cystoseria sp. | 2.0 | distilled water | 60 | 20 | [104] |
| Spatoglossum asperum | 5.0 | distilled water | 60 | 20 | [105] |
| Saragassum cervicorne | 5.0 | distilled water | 85-90 | 60 | [106] |
| PM-NPs | Stabilizing agent | Size, nm | Shape | Reference |
| Au | Sodium citrate | 3.5 – 4.0 | Spherical | [107] |
| Poly-vinyl-pyrrolidone | 37.0 ± 2.0 | Nano-stars | [109] | |
| Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide | 144.0 ± 25.0 | Nano-prisms | [110] | |
| Ag | Sodium citrate | 10.0 – 200.0 | Spherical | [111] |
| Citric acid | cca. 300 | Nano-stars | [112] | |
| Poly-vinyl-pyrrolidone | 15.0 – 35.0 | Cubic | [113] | |
| Pt | Poly-ethylen-imine | 4.9 | Spherical | [114] |
| 5.2 | Cubic | |||
| Poly-vinyl-pyrrolidone | 3.0 – 30.0 | Octahedral | [115] | |
| Pd | Poly-vinyl-pyrrolidone | 5.0 – 15.0 | Spherical | [116] |
| Phosphonic acids | 50.0 | Nanodendrites | [117] |
| PM-NPs | Algae biomass | pH | Biomass dose | PM ions concentration, mg/L | Contact time, min | Temperature,°C | Reference |
| Au | Ulva lactuca | 2.0 | 4.0 g/L | 40.0 | 1440 | 22 | [86] |
| Cladophora vagabunda | 2.0 | 4.0 g/L | 40.0 | 1440 | 22 | ||
| Callithamnion corymbosum | 4.0 | 4.0 g/L | 240.0 | 60 | 21 | [121] | |
| Halymenia pseudoforesii | - | 1.0 g/L | 150.0 | 20 | 60 | [122] | |
| Fucus vesiculosus | 7.0 | 1.0 g/L | 100.0 | 480 | 23 | [80] | |
| Ecklonia cava (extract) | - | 1.0 g/mL | 50.0 | 10 | 80 | [123] | |
| Sargassum wightii | - | 1.0 g/L | 200.0 | 720 | 25 | [124] | |
| Sargassum muticum | - | 1.0 g/L | 200.0 | 15 | 76 | [125] | |
| Undaria pinnatifida (extract) | - | 1.0 g/mL | 50.0 | 1440 | 100 | [94] | |
| Turbinaria conoides | 2.0 | 2.0 g/L | 100.0 | 60 | - | [126] | |
| Sargassum muticum | 2.6-3.2 | 4.0 g/L | 50.0 | 75 | - | [127] | |
| Ag | Ulva lactuca (extract) | 11.0 | 10 mg/mL | 150.0 | 60 | 25 | [128] |
| Ulva lactuca | 3.0 | - | 50-100 | 60 | 25 | [97] | |
| Caulerpa serrulata | 4.1 | 1.0 g/L | 150.0 | 1440 | 27 | [129] | |
| Ulva armoricana | 3.0 | 0.5 g/L | 100.0 | 360 | 20 | [130] | |
| Portieria hornemannii (extract) | - | 5.0 mL | 150.0 | 1440 | 25 | [90] | |
| Sargassum muticum (extract) | 5.6 | 1.0 g/mL | 55.0 | 30 | 35 | [131] | |
| Undaria pinnatifida (extract) | - | 0.5 g/mL | 25.0 | 1440 | 100 | [94] | |
| Saccharina japonica (extract) | - | 50.0 mL | 150-170 | 45 | 40 | [132] | |
| Sargassum spp. (extract) | - | 25.0 mL | 25.0 | 60 | 80 | [133] | |
| Sargassum wightti | - | 1.0 g/L | 150.0 | 1440 | 25 | [134] | |
| Pt | Padina gymnospora (extract) | - | 10.0 mL | 100.0 | 1440 | 100 | [93] |
| Codium sp. (extract) | - | 10.0 mL | 200.0 | 120 | 45 | [135] | |
| Ulva sp. | 7.8-8.0 | 3.0 g/L | 0.1 | 720 | 20 | [136] | |
| Pd | Codium sp. (extract) | - | 10.0 mL | 100.0 | 120 | 45 | [135] |
| Dictyota indica (extract) | 8.0 | 20.0 mL | 120.0 | 120 | 60 | [137] | |
| Padina boryana (extract) | - | 5.0 mL | 120.0 | 120 | 60 | [138] |
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages | Reference |
| SEM | - evaluation of morphology, surface distribution - fast analysis - 3D images of the surface |
- moderate resolution - required conductive coating |
[146] |
| TEM | - evaluation of size, shape, and internal structure - very high resolution - detailed images |
- high cost - complex sample preparation |
[147] |
| SFM | - nanoscale topography - does not require vacuum - can analyze sample in liquid media |
- longer analysis time - small scan area |
[142] |
| XRD | - identification of structure and degree of crystallinity | - does not detect amorphous PM-NPs - requires sufficient amount of sample |
[148] |
| DLS | - evaluation of the average size and the size distribution - short working time, simplicity - non-invasive method -allows direct analysis of suspensions |
- high sensitivity to impurities - difficulties in analyzing polydisperse samples - does not provide morphological details |
[149] |
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages | Reference |
| FTIR | - rapid and easy to use method - identification of functional groups - identifies surface modifications |
- limited sensitivity for small PM-NPs |
[153] |
| Raman | - reduced cost and complexity in sample preparation - non-destructive method, complementary to FTIR |
- moderate sensitivity - possible interferences |
[155] |
| SERS | - very high sensitivity - reduced interferences - destructive method |
- high cost and complexity in sample preparation |
[154] |
| EDX | - allows the determination of elemental composition - short working time - non-destructive method -integrable with SEM/TEM |
- high sensitivity to impurities - low sensitivity to light elements |
[156] |
| PM | Algae biomass | Characterization method | Size, nm | Morphology | Reference |
| Au | Sargassum sp. | UV-Vis, AFM, TEM, XRD, FTIR | 300 – 400 | hexagonal, truncated triangular |
[125] |
| Laminaria japonica | UV-Vis, TEM, XRD, FTIR | 15 – 20 | spherical | [157] | |
| Fucus vesiculosus | XRD, SEM, EDS, TEM, FTIR | 20 – 50 | spherical | [80] | |
| Padina gymnospora | UV-Vis, XRD, AFM, TEM, FTIR | 8 – 21 | spherical | [158] | |
| Dictyota bartayresiana | UV-Vis, FTIR, SEM | poly-size | spherical | [159] | |
| Sargassum tenerrimum | UV-Vis, Zeta potential, TEM, FTIR, DLS | 5 – 45 | polymorphic | [160] | |
| Chondrus crispus | UV-Vis, TEM, SEM, EDX, FTIR | 30 – 50 | spherical, polyhedral | [161] | |
| Galaxaura elongata | Zeta potential, TEM, FTIR | 3.85 – 77.13 | triangular, hexagonal | [12] | |
| Ecklonia cava | UV-Vis, XRD, SEM, TEM, FTIR, EDX | 20 – 50 | spherical, triangular | [123] | |
| Ag | Ulva reticulata | UV-Vis, FTIR, SEM, XRD | 40 – 50 | spherical | [162] |
| Ulva lactuca | UV-Vis, Zeta potential, FTIR, SEM, XRD | 48.9 | spherical | [84] | |
| Ulva flexousa | UV-Vis, XRD, FTIR, TEM | 2 – 32 | spherical | [163] | |
| Pithophora oedogonia | UV-Vis, EDX, SEM, DLS, FTIR | 25 – 44 | cubical, hexagonal | [164] | |
| Spirogyra sp. | UV-Vis, FTIR, TEM | 40 – 80 | spherical | [165] | |
| Caulerpa serrulata | UV-Vis, FTIR, XRD, TEM | 10 ± 2 | spherical | [129] | |
| Caulerpa racemosa | UV-Vis, XRD, TEM, FTIR | 5 – 25 | face centered cubic | [166] | |
| Gracilaria birdiae | UV-Vis, Zeta potential, TEM, FTIR, DLS | 20.30 | spherical | [167] | |
| Sargassum vulgare | TEM, XRD, TEM, FTIR, EDX | 10.00 | spherical | [168] | |
| Pt | Padina gymnospora | UV-Vis, XRD, SEM, TEM, EDX | 5 - 50 | octahedral | [93] |
| Caulerpa sertularioide | UV-Vis, XRD, SEM, TEM, DLS, FTIR, EDX | 6 – 22 | spherical | [169] | |
| Codium sp. | UV-Vis, SEM, TEM, FTIR, EDX | 15.97 | cubic | [135] | |
| Pd | Sargassum ilicifolium | UV-Vis, SEM | 60 – 80 | spherical | [170] |
| Sargassum bovinum | UV–Vis, TEM, XRD, EDX, FTIR | 5 – 10 | octahedral | [171] | |
| Codium sp. | UV-Vis, SEM, TEM, FTIR, EDX | 11.38 | hexagonal | [135] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





