Submitted:
29 August 2025
Posted:
02 September 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General Experimental Paradigm: Probabilistic Reversal Learning
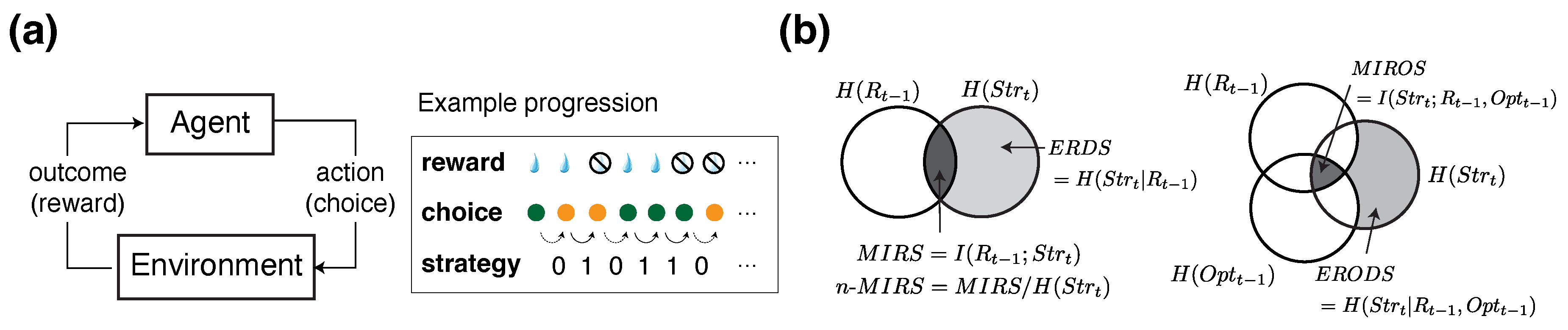
2.2. Information-Theoretic Metrics
2.2.1. Decomposition of Information-Theoretic Metrics
2.2.2. Normalization of Mutual Information Metrics
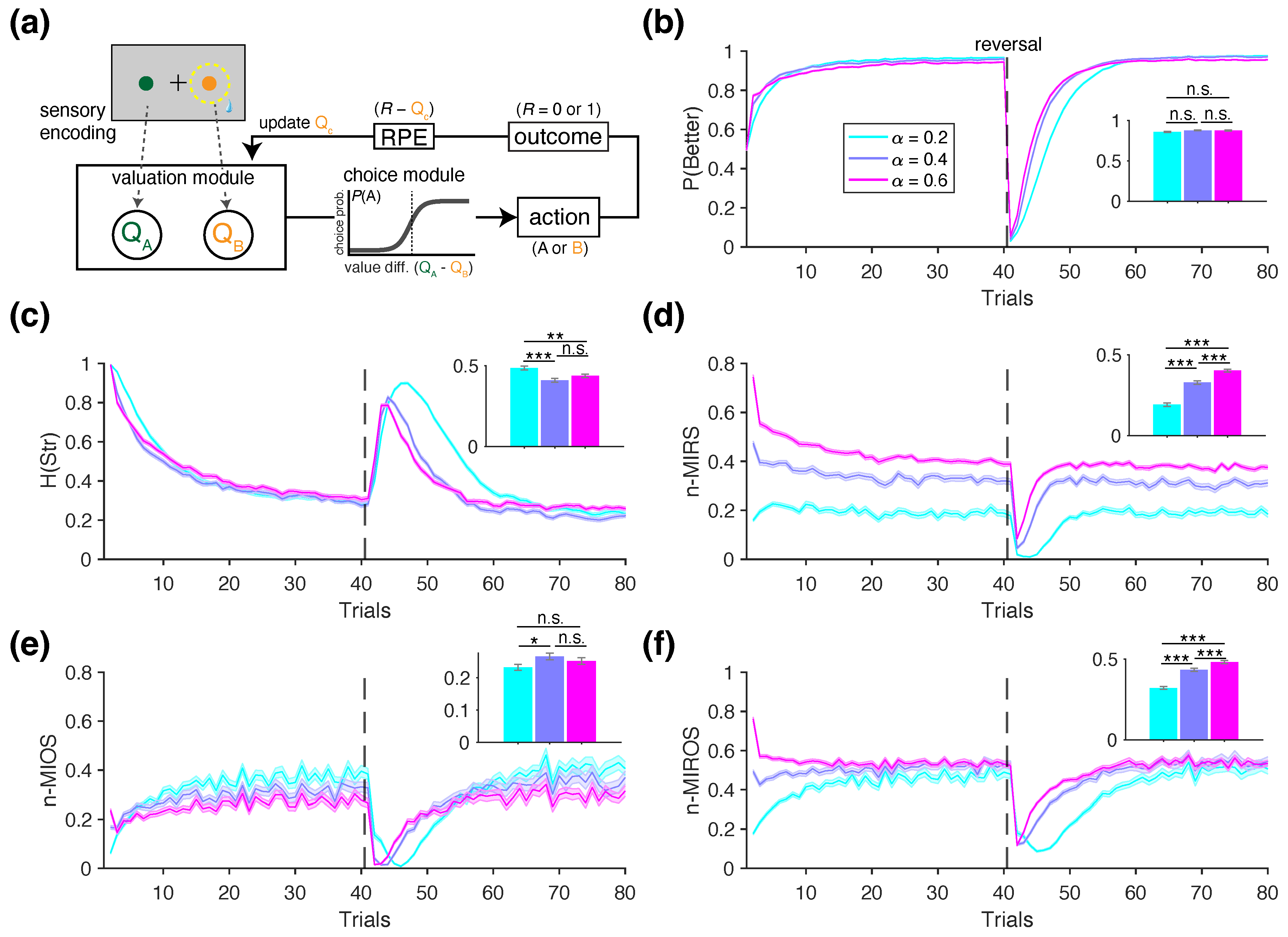
2.3. Reinforcement Learning Models and Simulations
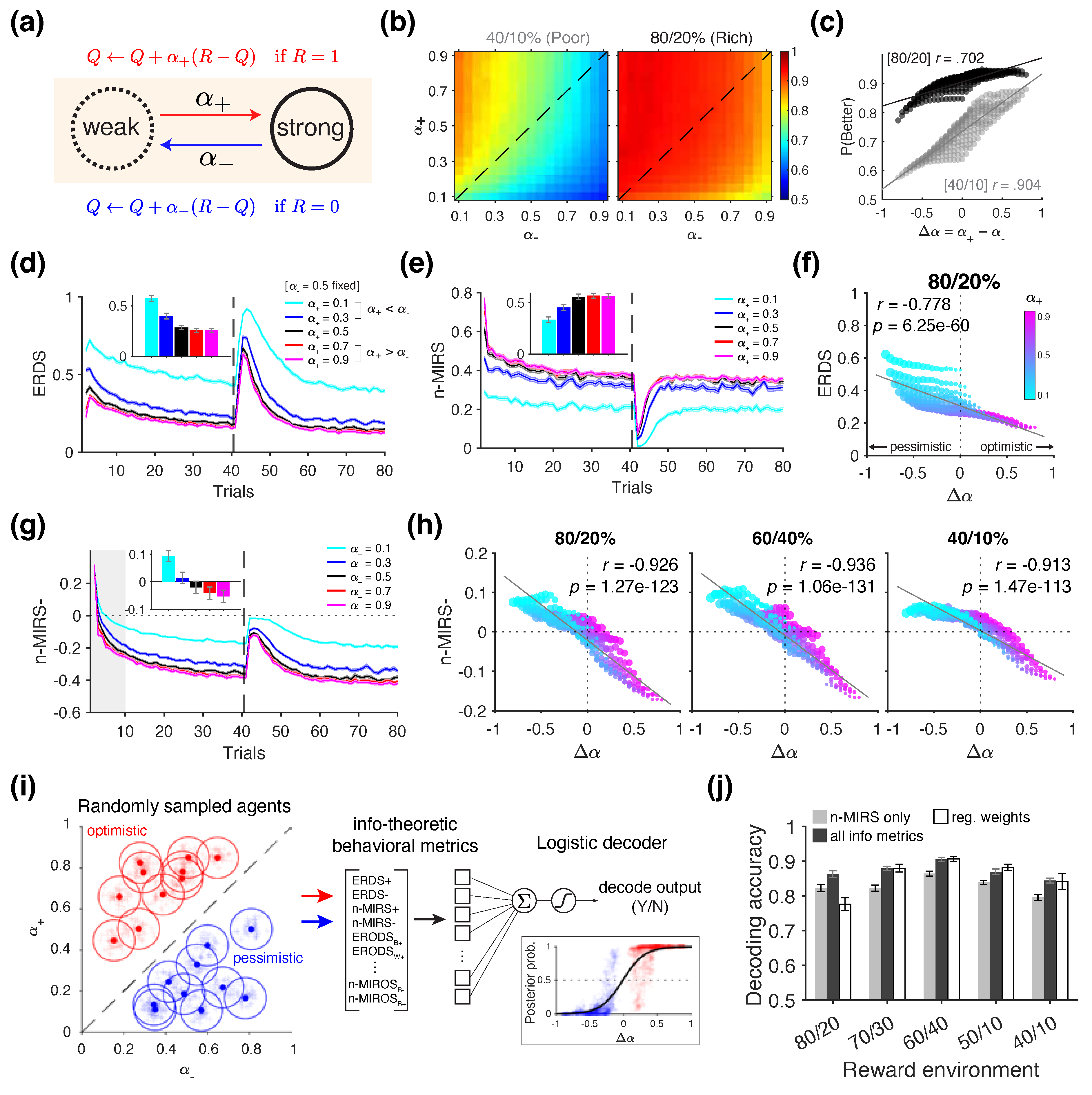
2.3.1. Simulations of Positivity Bias
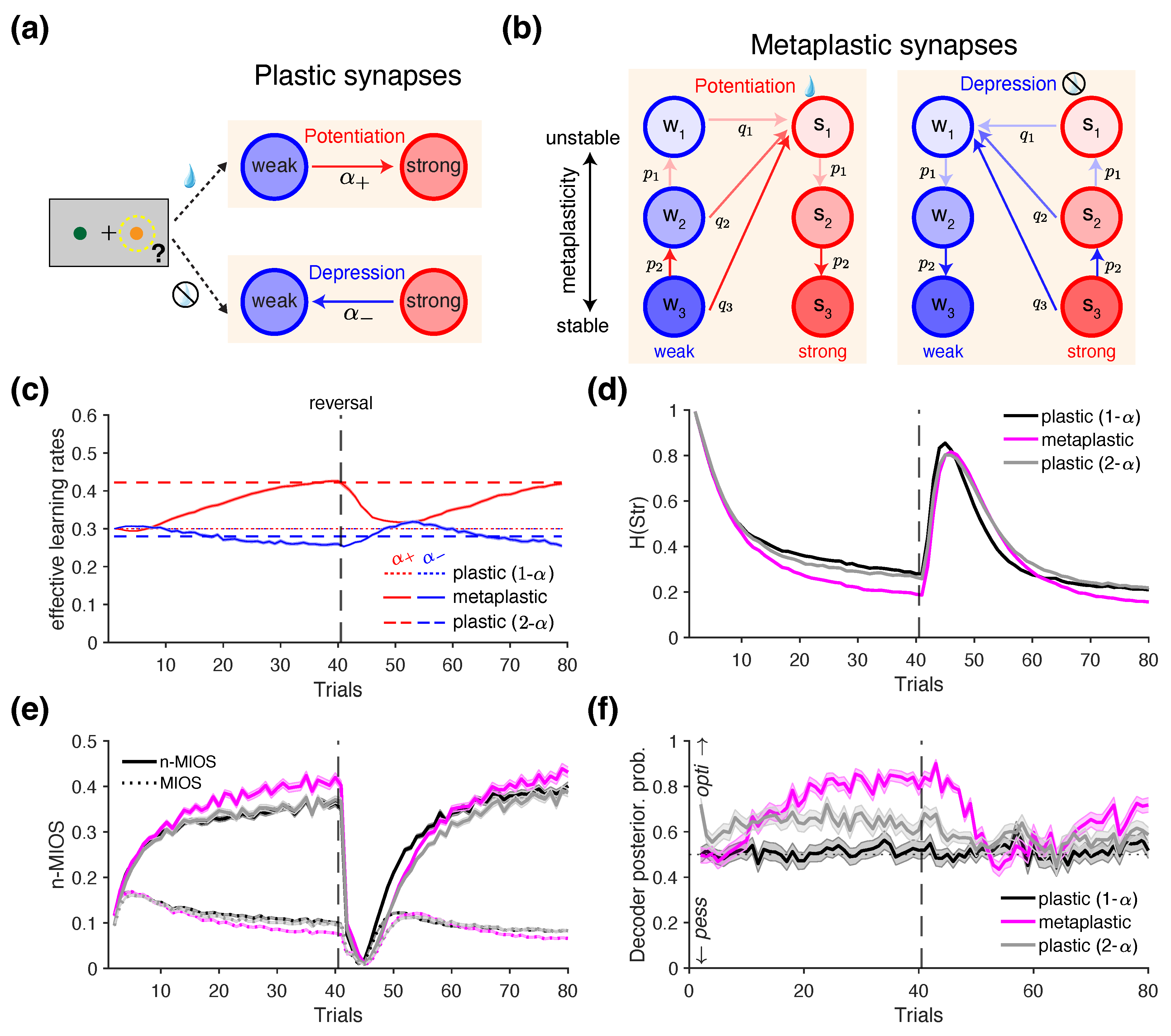
2.3.2. Simulations of Reward-Dependent Metaplasticity
2.3.3. Simulations of Reward Harvest Rate Effects on Behavior
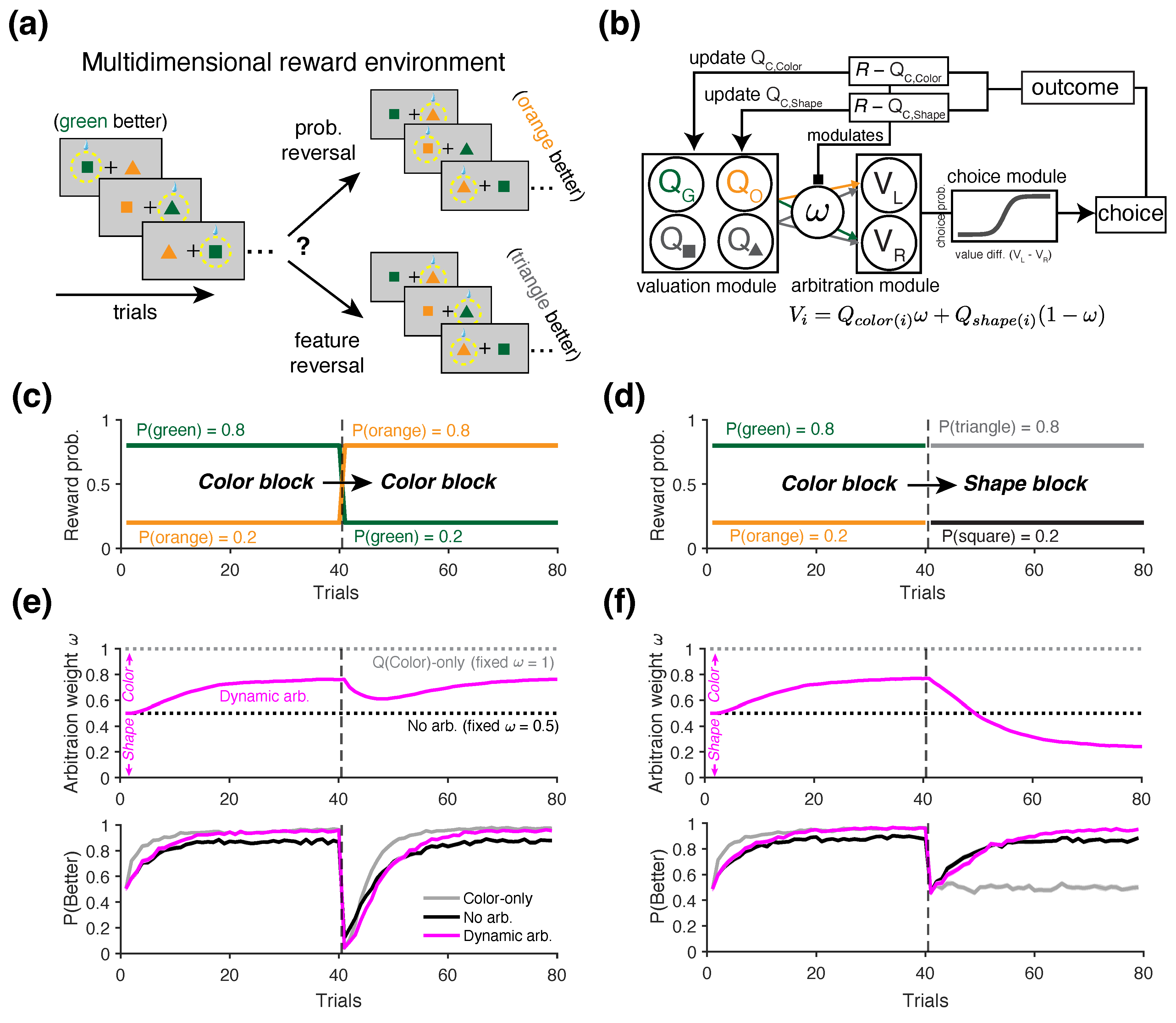
2.3.4. Simulations of Learning in Multidimensional Reward Environments
3. Results
3.1. Revealing Positivity Bias
3.2. Revealing Reward-Dependent Metaplasticity
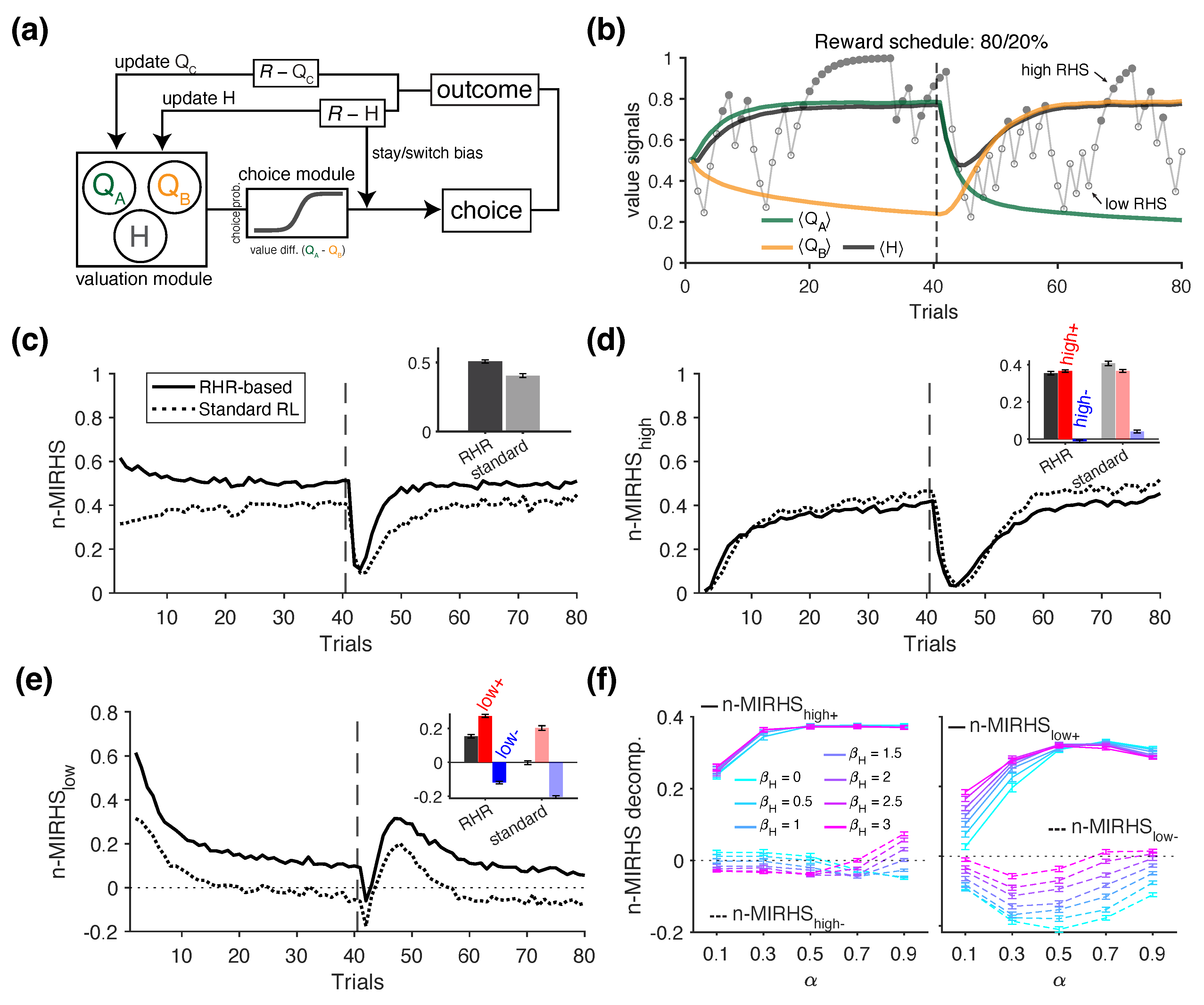
3.3. Revealing Behavioral Adjustments due to Reward Harvest Rate
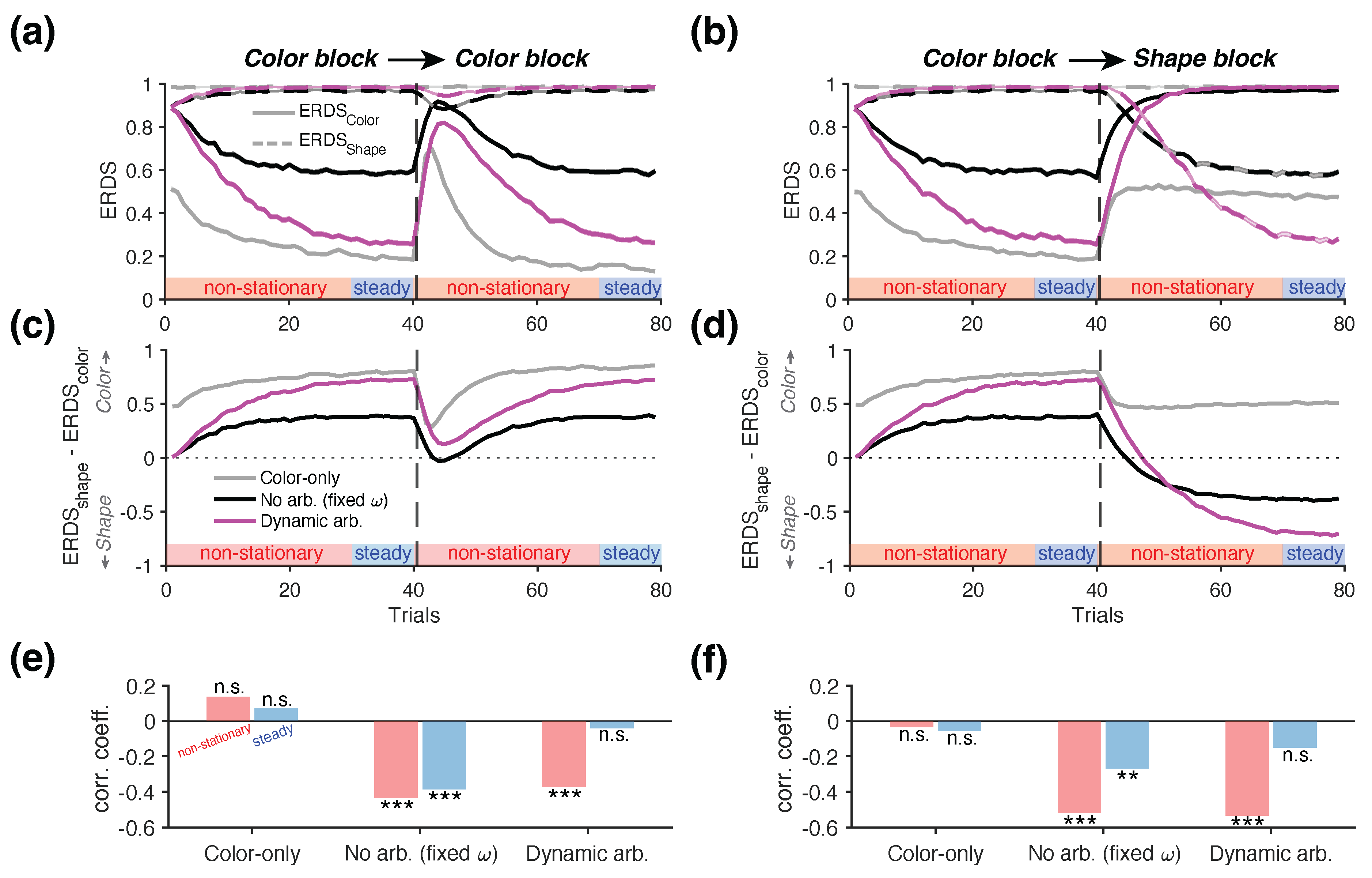
3.4. Revealing the Presence of Alternative Learning Strategies in Multidimensional Reward Environments
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lungarella, M.; Sporns, O. Mapping information flow in sensorimotor networks. PLoS computational biology 2006, 2, e144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmigiano, A.; Geisel, T.; Wolf, F.; Battaglia, D. Flexible information routing by transient synchrony. Nature Neuroscience 2017, 20, 1014–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honey, C.J.; Kötter, R.; Breakspear, M.; Sporns, O. Network structure of cerebral cortex shapes functional connectivity on multiple time scales. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2007, 104, 10240–10245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stramaglia, S.; Wu, G.R.; Pellicoro, M.; Marinazzo, D. Expanding the transfer entropy to identify information circuits in complex systems. Phys. Rev. E 2012, 86, 066211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novelli, L.; Wollstadt, P.; Mediano, P.; Wibral, M.; Lizier, J.T. Large-scale directed network inference with multivariate transfer entropy and hierarchical statistical testing. Network Neuroscience 2019, 3, 827–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, R.; Wibral, M.; Lindner, M.; Pipa, G. Transfer entropy—a model-free measure of effective connectivity for the neurosciences. Journal of computational neuroscience 2011, 30, 45–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursino, M.; Ricci, G.; Magosso, E. Transfer Entropy as a Measure of Brain Connectivity: A Critical Analysis With the Help of Neural Mass Models. Front Comput Neurosci 2020, 14, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strong, S.P.; Koberle, R.; De Ruyter Van Steveninck, R.R.; Bialek, W. Entropy and Information in Neural Spike Trains. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 80, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourévitch, B.; Eggermont, J.J. Evaluating Information Transfer Between Auditory Cortical Neurons. Journal of Neurophysiology 2007, 97, 2533–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cofré, R.; Maldonado, C. Information Entropy Production of Maximum Entropy Markov Chains from Spike Trains. Entropy (Basel) 2018, 20, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shorten, D.P.; Spinney, R.E.; Lizier, J.T. Estimating Transfer Entropy in Continuous Time Between Neural Spike Trains or Other Event-Based Data. PLOS Computational Biology 2021, 17, e1008054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strange, B.A.; Duggins, A.; Penny, W.; Dolan, R.J.; Friston, K.J. Information theory, novelty and hippocampal responses: unpredicted or unpredictable? Neural Networks 2005, 18, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bach, D.R.; Dolan, R.J. Knowing how much you don’t know: a neural organization of uncertainty estimates. Nat Rev Neurosci 2012, 13, 572–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayood, K. Information Theory and Cognition: A Review. Entropy (Basel) 2018, 20, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiler, J.P.H.; Dan, O.; Tüscher, O.; Loewenstein, Y.; Rumpel, S. Experienced entropy drives choice behavior in a boring decision-making task. Sci Rep 2022, 12, 3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jepma, M.; Nieuwenhuis, S. Pupil diameter predicts changes in the exploration-exploitation trade-off: evidence for the adaptive gain theory. J Cogn Neurosci 2011, 23, 1587–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.Z.; Hayden, B.Y. Monkeys are curious about counterfactual outcomes. Cognition 2019, 189, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, J.H.; Azab, H.; Jahn, A.; Hayden, B.; Brown, J.W. The PRO model accounts for the anterior cingulate cortex role in risky decision-making and monitoring. Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience 2022, 22, 952–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Conroy, M.L.; McGreevy, B.P.; Barraclough, D.J. Reinforcement learning and decision making in monkeys during a competitive game. Cognitive Brain Research 2004, 22, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; McGreevy, B.P.; Barraclough, D.J. Learning and decision making in monkeys during a rock–paper–scissors game. Cognitive Brain Research 2005, 25, 416–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H.; Izuma, K.; Matsumoto, M.; Matsumoto, K.; Omori, T. The Anterior Insula Tracks Behavioral Entropy during an Interpersonal Competitive Game. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0123329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutton, R.S.; Barto, A.G. Reinforcement Learning, second edition: An Introduction; MIT Press, 2018. Google-Books-ID: uWV0DwAAQBAJ.
- Dayan, P.; Daw, N.D. Decision theory, reinforcement learning, and the brain. Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience 2008, 8, 429–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niv, Y. Reinforcement learning in the brain. Journal of Mathematical Psychology 2009, 53, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, K.T. An introduction to reinforcement learning for neuroscience. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2311.07315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckstein, M.K.; Wilbrecht, L.; Collins, A.G. What do reinforcement learning models measure? Interpreting model parameters in cognition and neuroscience. Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences 2021, 41, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nussenbaum, K.; Hartley, C.A. Reinforcement learning across development: What insights can we draw from a decade of research? Dev Cogn Neurosci 2019, 40, 100733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolo, R.; Averbeck, B.B. Prefrontal cortex predicts state switches during reversal learning. Neuron 2020, 106, 1044–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trepka, E.; Spitmaan, M.; Bari, B.A.; Costa, V.D.; Cohen, J.Y.; Soltani, A. Entropy-based metrics for predicting choice behavior based on local response to reward. Nat Commun 2021, 12, 6567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, C.D.; Bari, B.A.; Cohen, J.Y. Serotonin neurons modulate learning rate through uncertainty. Curr Biol 2022, 32, 586–599.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.A.; Jung, M.W.; Lee, S.W. Striatal arbitration between choice strategies guides few-shot adaptation. Nature Communications 2025, 16, 1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, M.R.; Wilson, R.C.; Heasly, B.; Gold, J.I. An Approximately Bayesian Delta-Rule Model Explains the Dynamics of Belief Updating in a Changing Environment. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 12366–12378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farashahi, S.; Xu, J.; Wu, S.W.; Soltani, A. Learning arbitrary stimulus-reward associations for naturalistic stimuli involves transition from learning about features to learning about objects. Cognition 2020, 205, 104425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cinotti, F.; Coutureau, E.; Khamassi, M.; Marchand, A.R.; Girard, B. Regulation of reinforcement learning parameters captures long-term changes in rat behaviour. European Journal of Neuroscience 2024, 60, 4469–4490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittmann, M.K.; Fouragnan, E.; Folloni, D.; Klein-Flügge, M.C.; Chau, B.K.; Khamassi, M.; Rushworth, M.F. Global reward state affects learning and activity in raphe nucleus and anterior insula in monkeys. Nature communications 2020, 11, 3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W.; Shimojo, S.; O’doherty, J.P. Neural computations underlying arbitration between model-based and model-free learning. Neuron 2014, 81, 687–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charpentier, C.J.; Iigaya, K.; O’Doherty, J.P. A neuro-computational account of arbitration between choice imitation and goal emulation during human observational learning. Neuron 2020, 106, 687–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, J.H.; Costa, V.D.; Taswell, C.A.; Rothenhoefer, K.M.; Averbeck, B.B.; Soltani, A. Contribution of amygdala to dynamic model arbitration under uncertainty. bioRxiv 2024, 2024.09.13.612869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippe, R.; Janet, R.; Khalvati, K.; Rao, R.P.; Lee, D.; Dreher, J.C. Neurocomputational mechanisms involved in adaptation to fluctuating intentions of others. Nature communications 2024, 15, 3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, A.G.E.; Shenhav, A. Advances in modeling learning and decision-making in neuroscience. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2022, 47, 104–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, J.H.; Aguirre, C.G.; Bari, B.A.; Tsutsui, K.I.; Grabenhorst, F.; Cohen, J.Y.; Schultz, W.; Izquierdo, A.; Soltani, A. Mechanisms of adjustments to different types of uncertainty in the reward environment across mice and monkeys. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci 2023, 23, 600–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, G.; Lebreton, M.; Meyniel, F.; Bourgeois-Gironde, S.; Palminteri, S. Behavioural and neural characterization of optimistic reinforcement learning. Nat Hum Behav 2017, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palminteri, S.; Lefebvre, G.; Kilford, E.J.; Blakemore, S.J. Confirmation bias in human reinforcement learning: Evidence from counterfactual feedback processing. PLoS computational biology 2017, 13, e1005684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefebvre, G.; Summerfield, C.; Bogacz, R. A normative account of confirmation bias during reinforcement learning. Neural Comput 2022, 34, 307–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palminteri, S.; Lebreton, M. The computational roots of positivity and confirmation biases in reinforcement learning. Trends in Cognitive Sciences 2022, 26, 607–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farashahi, S.; Donahue, C.H.; Khorsand, P.; Seo, H.; Lee, D.; Soltani, A. Metaplasticity as a Neural Substrate for Adaptive Learning and Choice under Uncertainty. Neuron 2017, 94, 401–414.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorsand, P.; Soltani, A. Optimal structure of metaplasticity for adaptive learning. PLoS Comput Biol 2017, 13, e1005630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niv, Y.; Daw, N.D.; Joel, D.; Dayan, P. Tonic dopamine: opportunity costs and the control of response vigor. Psychopharmacology 2007, 191, 507–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukumar, S.; Shadmehr, R.; Ahmed, A.A. Effects of reward and effort history on decision making and movement vigor during foraging. Journal of neurophysiology 2024, 131, 638–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, A.; Koechlin, E. Computational models of adaptive behavior and prefrontal cortex. Neuropsychopharmacology 2022, 47, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Doherty, J.P.; Lee, S.W.; Tadayonnejad, R.; Cockburn, J.; Iigaya, K.; Charpentier, C.J. Why and how the brain weights contributions from a mixture of experts. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews 2021, 123, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, Y.C.; Radulescu, A.; Daniel, R.; DeWoskin, V.; Niv, Y. Dynamic interaction between reinforcement learning and attention in multidimensional environments. Neuron 2017, 93, 451–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farashahi, S.; Rowe, K.; Aslami, Z.; Lee, D.; Soltani, A. Feature-based learning improves adaptability without compromising precision. Nature Communications 2017, 8, 1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radulescu, A.; Niv, Y.; Ballard, I. Holistic reinforcement learning: the role of structure and attention. Trends in cognitive sciences 2019, 23, 278–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farashahi, S.; Soltani, A. Computational mechanisms of distributed value representations and mixed learning strategies. Nature Communications 2021, 12, 7191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.C.; Soltani, A. Contributions of Attention to Learning in Multidimensional Reward Environments 2025. Publisher: Society for Neuroscience Section: Research Articles. [CrossRef]
- Wise, T.; Emery, K.; Radulescu, A. Naturalistic reinforcement learning. Trends in Cognitive Sciences 2024, 28, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdanpanah, A.; Wang, M.C.; Trepka, E.; Benz, M.; Soltani, A. Contributions of statistical learning to learning from reward feedback. bioRxiv 2024. Publisher: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory _eprint: https://www.biorxiv.org/content/early/2024/07/26/2024.04.27.591445.full.pdf. [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo, A.; Brigman, J.L.; Radke, A.K.; Rudebeck, P.H.; Holmes, A. The neural basis of reversal learning: An updated perspective. Neuroscience 2017, 345, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, V.D.; Dal Monte, O.; Lucas, D.R.; Murray, E.A.; Averbeck, B.B. Amygdala and ventral striatum make distinct contributions to reinforcement learning. Neuron 2016, 92, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bari, B.A.; Grossman, C.D.; Lubin, E.E.; Rajagopalan, A.E.; Cressy, J.I.; Cohen, J.Y. Stable representations of decision variables for flexible behavior. Neuron 2019, 103, 922–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, A.A.; Pettibone, J.R.; Mabrouk, O.S.; Hetrick, V.L.; Schmidt, R.; Vander Weele, C.M.; Kennedy, R.T.; Aragona, B.J.; Berke, J.D. Mesolimbic dopamine signals the value of work. Nature Neuroscience 2016, 19, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre, C.G.; Woo, J.H.; Romero-Sosa, J.L.; Rivera, Z.M.; Tejada, A.N.; Munier, J.J.; Perez, J.; Goldfarb, M.; Das, K.; Gomez, M.; et al. Dissociable Contributions of Basolateral Amygdala and Ventrolateral Orbitofrontal Cortex to Flexible Learning Under Uncertainty 2024. Publisher: Society for Neuroscience Section: Research Articles. [CrossRef]
- Rutledge, R.B.; Lazzaro, S.C.; Lau, B.; Myers, C.E.; Gluck, M.A.; Glimcher, P.W. Dopaminergic Drugs Modulate Learning Rates and Perseveration in Parkinson’s Patients in a Dynamic Foraging Task. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 15104–15114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunwald, P.; Vitanyi, P. Shannon Information and Kolmogorov Complexity. 2004, arXiv:cs/0410002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizier, J.T. Measuring the Dynamics of Information Processing on a Local Scale in Time and Space. In Directed Information Measures in Neuroscience; Wibral, M., Vicente, R., Lizier, J.T., Eds.; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2014; pp. 161–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y. Information-theoretic measures for knowledge discovery and data mining. Entropy measures, maximum entropy principle and emerging applications 2003, pp. 115–136.
- Kvålseth, T.O. On normalized mutual information: measure derivations and properties. Entropy 2017, 19, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amelio, A.; Pizzuti, C. Correction for Closeness: Adjusting Normalized Mutual Information Measure for Clustering Comparison. Computational Intelligence 2017, 33, 579–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorov, E. Efficient computation of optimal actions. Proceedings of the national academy of sciences 2009, 106, 11478–11483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Ruiz, J.; Grytskyy, D.; Mastrogiuseppe, C.; Habib, Y.; Moreno-Bote, R. Complex behavior from intrinsic motivation to occupy future action-state path space. Nature Communications 2024, 15, 6368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donahue, C.H.; Lee, D. Dynamic routing of task-relevant signals for decision making in dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. Nature neuroscience 2015, 18, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, A.; Wang, X.J. A biophysically based neural model of matching law behavior: melioration by stochastic synapses. Journal of Neuroscience 2006, 26, 3731–3744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, A.; Wang, X.J. Synaptic Computation Underlying Probabilistic Inference. Nat Neurosci 2010, 13, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farashahi, S.; Donahue, C.H.; Hayden, B.Y.; Lee, D.; Soltani, A. Flexible combination of reward information across primates. Nature human behaviour 2019, 3, 1215–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazé, R.D.; van der Meer, M.A. Adaptive properties of differential learning rates for positive and negative outcomes. Biological cybernetics 2013, 107, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iigaya, K. Adaptive learning and decision-making under uncertainty by metaplastic synapses guided by a surprise detection system. eLife 2016, 5, e18073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassar, M.R.; Frank, M.J. Taming the beast: extracting generalizable knowledge from computational models of cognition. Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences 2016, 11, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palminteri, S.; Wyart, V.; Koechlin, E. The importance of falsification in computational cognitive modeling. Trends in cognitive sciences 2017, 21, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sifar, A.; Srivastava, N. Over-precise Predictions Cannot Identify Good Choice Models. Computational Brain & Behavior 2022, 5, 378–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.C.; Collins, A.G. Ten simple rules for the computational modeling of behavioral data. Elife 2019, 8, e49547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyniel, F.; Dehaene, S. Brain networks for confidence weighting and hierarchical inference during probabilistic learning. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2017, 114, E3859–E3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, T. Measuring Information Transfer. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 85, 461–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossomaier, T.; Barnett, L.; Harré, M.; Lizier, J.T. Transfer Entropy. In An Introduction to Transfer Entropy. In An Introduction to Transfer Entropy: Information Flow in Complex Systems; Bossomaier, T., Barnett, L., Harré, M., Lizier, J.T., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2016; pp. 65–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraskov, A.; Stögbauer, H.; Grassberger, P. Estimating mutual information. Phys. Rev. E 2004, 69, 066138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Kannan, S.; Oh, S.; Viswanath, P. Estimating Mutual Information for Discrete-Continuous Mixtures. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Curran Associates, Inc., 2017, Vol. 30.
- Ross, B.C. Mutual Information between Discrete and Continuous Data Sets. PLOS ONE 2014, 9, e87357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, P.L.; Beer, R.D. Nonnegative Decomposition of Multivariate Information. 2010, arXiv:1004.2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luppi, A.I.; Rosas, F.E.; Mediano, P.A.M.; Menon, D.K.; Stamatakis, E.A. Information decomposition and the informational architecture of the brain. Trends in Cognitive Sciences 2024, 28, 352–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




