Submitted:
28 August 2025
Posted:
30 August 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
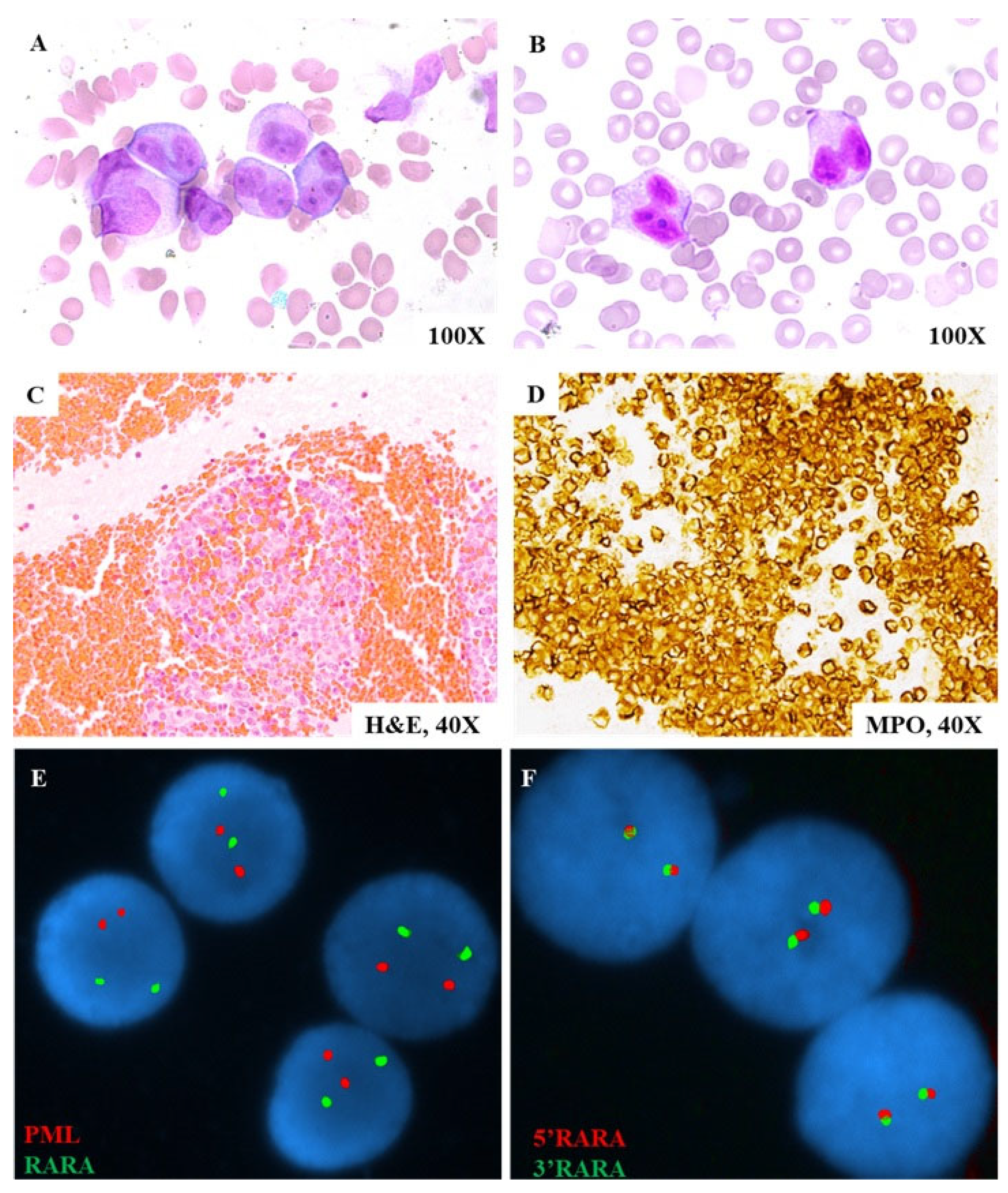
2.1. Clinical and Pathological Examination
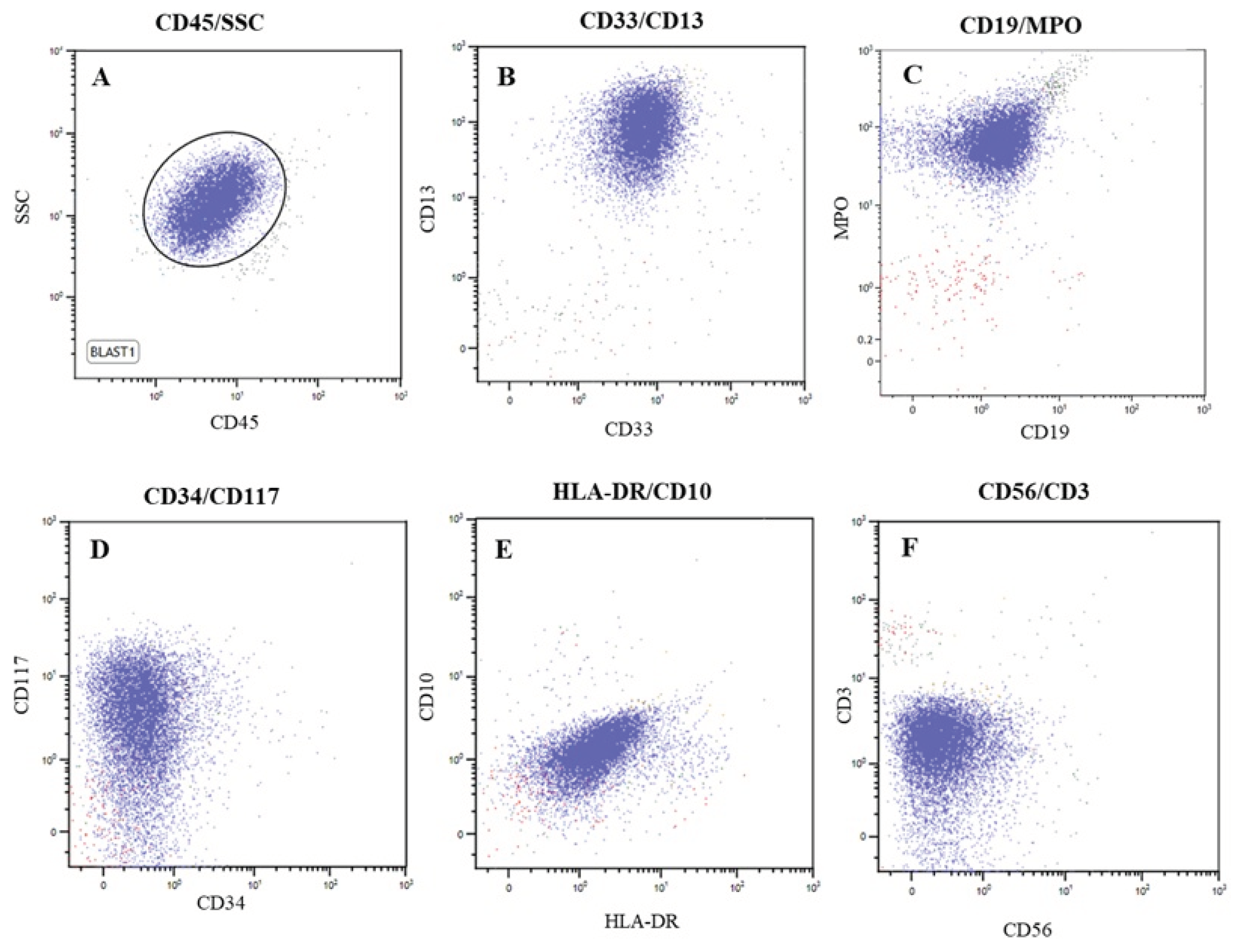
2.2. Flow Cytometry
2.3. Conventional Cytogenetic and Interphase Fluorescence in Situ Hybridization (FISH) Studies
2.4. Literature Review
3. Results
3.1. Case Study
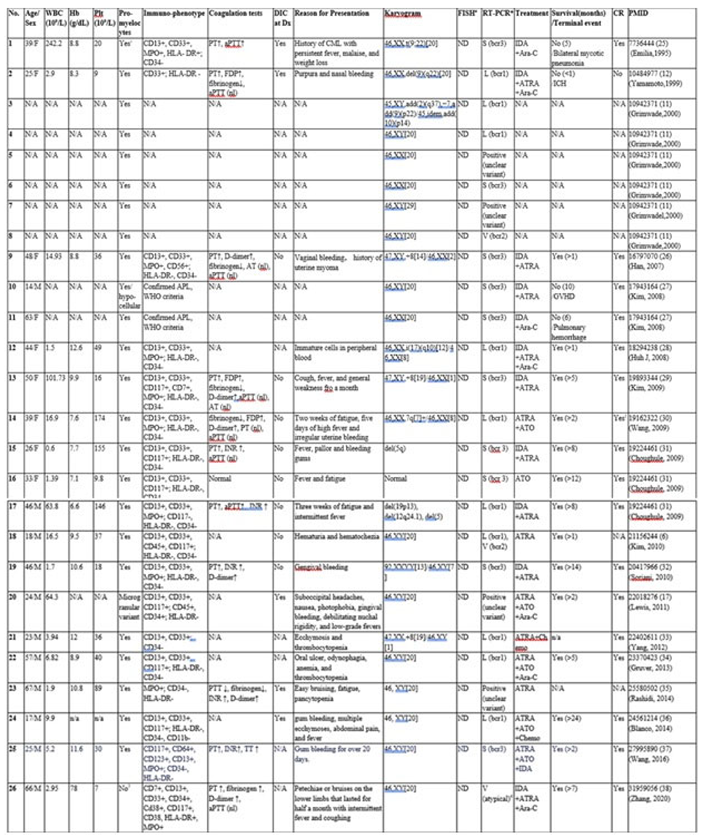
3.2. Literature Review
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mai B, Liang C, Nguyen A, Wahed A, Chen L. Cryptic Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia (APL) Presenting as Seizures in an Adolescent. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2020;50(2):270-3.
- Li G, Wu J, Li R, Pan Y, Ma W, Xu J, et al. Improvement of Early Death in Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia: A Population-Based Analysis. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2023;23(2):e78-e84. [CrossRef]
- Zhang X, Sun J, Yu W, Jin J. Current views on the genetic landscape and management of variant acute promyelocytic leukemia. Biomark Res. 2021;9(1):33. [CrossRef]
- Guarnera L, Ottone T, Fabiani E, Divona M, Savi A, Travaglini S, et al. Atypical Rearrangements in APL-Like Acute Myeloid Leukemias: Molecular Characterization and Prognosis. Front Oncol. 2022;12:871590. [CrossRef]
- Gagnon MF, Berg HE, Meyer RG, Sukov WR, Van Dyke DL, Jenkins RB, et al. Typical, atypical and cryptic t(15;17)(q24;q21) (PML::RARA) observed in acute promyelocytic leukemia: A retrospective review of 831 patients with concurrent chromosome and PML::RARA dual-color dual-fusion FISH studies. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2022;61(10):629-34. [CrossRef]
- Kim MJ, Cho SY, Kim MH, Lee JJ, Kang SY, Cho EH, et al. FISH-negative cryptic PML-RARA rearrangement detected by long-distance polymerase chain reaction and sequencing analyses: a case study and review of the literature. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2010;203(2):278-83. [CrossRef]
- Rashidi A, Fisher SI. FISH-negative, cytogenetically cryptic acute promyelocytic leukemia. Blood Cancer J. 2015;5(6):e320. [CrossRef]
- Campbell LJ, Oei P, Brookwell R, Shortt J, Eaddy N, Ng A, et al. FISH detection of PML-RARA fusion in ins(15;17) acute promyelocytic leukaemia depends on probe size. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:164501. [CrossRef]
- George GV, Elsadawi M, Evans AG, Ali S, Zhang B, Iqbal MA. Utilization of RT-PCR and Optical Genome Mapping in Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia with Cryptic PML::RARA Rearrangement: A Case Discussion and Systemic Literature Review. Genes (Basel). 2024;16(1). [CrossRef]
- Goldschmidt N, Yehuda-Gafni O, Abeliovich D, Slyusarevsky E, Rund D. Interstitial insertion of RARalpha gene into PML gene in a patient with acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) lacking the classic t(15;17). Hematology. 2010;15(5):332-7.
- Grimwade D, Biondi A, Mozziconacci MJ, Hagemeijer A, Berger R, Neat M, et al. Characterization of acute promyelocytic leukemia cases lacking the classic t(15; 17): results of the European Working Party. Groupe Francais de Cytogenetique Hematologique, Groupe de Francais d'Hematologie Cellulaire, UK Cancer Cytogenetics Group and BIOMED 1 European Community-Concerted Action "Molecular Cytogenetic Diagnosis in Haematological Malignancies". Blood. 2000; 96(4):1297‐308. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K, Hamaguchi H, Kobayashi M, Tsurukubo Y, Nagata K. Terminal deletion of the long arm of chromosome 9 in acute promyelocytic leukemia with a cryptic PML/RAR alpha rearrangement. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1999;113(2):120-5. [CrossRef]
- Carvalho CM, Lupski JR. Mechanisms underlying structural variant formation in genomic disorders. Nat Rev Genet. 2016;17(4):224-38. [CrossRef]
- Weckselblatt B, Rudd MK. Human Structural Variation: Mechanisms of Chromosome Rearrangements. Trends Genet. 2015;31(10):587-99. [CrossRef]
- Brockman SR, Paternoster SF, Ketterling RP, Dewald GW. New highly sensitive fluorescence in situ hybridization method to detect PML/RARA fusion in acute promyelocytic leukemia. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2003;145(2):144-51.
- Avgerinou G, Katsibardi K, Filippidou M, Tzanoudaki M, Papadhimitriou SI, Kattamis A. Cytogenetically cryptic and fish negative PML/RARA rearrangement in acute promyelocytic leukemia detected by RT-PCR. Leuk Lymphoma. 2020;61(14):3526-8. [CrossRef]
- Lewis C, Patel V, Abhyankar S, Zhang D, Ketterling RP, McClure RF, et al. Microgranular variant of acute promyelocytic leukemia with normal conventional cytogenetics, negative PML/RARA FISH and positive PML/RARA transcripts by RT-PCR. Cancer Genet. 2011;204(9):522-3. [CrossRef]
- Bennour A, Tabka I, Youssef YB, Zaier M, Hizem S, Khelif A, et al. A PML/RARA chimeric gene on chromosome 12 in a patient with acute promyelocytic leukemia (M4) associated with a new variant translocation: t(12;15;17)(q24;q24;q11). Med Oncol. 2013;30(1):409. [CrossRef]
- Welch JS, Westervelt P, Ding L, Larson DE, Klco JM, Kulkarni S, et al. Use of whole-genome sequencing to diagnose a cryptic fusion oncogene. JAMA. 2011;305(15):1577-84.
- Karlin K, Bryke C, Dias A, Michaels P. Cytogenetically cryptic PML::RARA fusion in acute promyelocytic leukemia: Testing strategies in the modern era. Leuk Res Rep. 2022;17:100320. [CrossRef]
- Weckselblatt B, Hermetz KE, Rudd MK. Unbalanced translocations arise from diverse mutational mechanisms including chromothripsis. Genome Res. 2015;25(7):937-47. [CrossRef]
- Liquori A, Ibanez M, Sargas C, Sanz MA, Barragan E, Cervera J. Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia: A Constellation of Molecular Events around a Single PML-RARA Fusion Gene. Cancers (Basel). 2020;12(3).
- Fasan A, Haferlach C, Perglerova K, Kern W, Haferlach T. Molecular landscape of acute promyelocytic leukemia at diagnosis and relapse. Haematologica. 2017;102(6):e222-e4. [CrossRef]
- Iaccarino L, Ottone T, Alfonso V, Cicconi L, Divona M, Lavorgna S, et al. Mutational landscape of patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia at diagnosis and relapse. Am J Hematol. 2019;94(10):1091-7. [CrossRef]
- Emilia G, Marasca R, Longo G, Ferrari MG, Notohamiprodjo M, Temperani P, et al. Detection of PML-RAR alpha fusion transcript in Ph positive leukemia with acute promyelocytic phenotype lacking the t(15;17) cytogenetic abnormality. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1995;80(2):95-9. [CrossRef]
- Han JY, Kim KE, Kim KH, Park JI, Kim JS. Identification of PML-RARA rearrangement by RT-PCR and sequencing in an acute promyelocytic leukemia without t(15;17) on G-banding and FISH. Leuk Res. 2007;31(2):239-43. [CrossRef]
- Kim M, Lim J, Kim Y, Han K, Lee DH, Chung NG, et al. The genetic characterization of acute promyelocytic leukemia with cryptic t(15;17) including a new recurrent additional cytogenetic abnormality i(17)(q10). Leukemia. 2008;22(4):881-3. [CrossRef]
- Huh J, Moon H, Chi H, Chung W. Acute promyelocytic leukemia with i(17)(q10) on G-banding and PML/RARA rearrangement by RT-PCR without evidence of PML/RARA rearrangement on FISH. Int J Lab Hematol. 2009;31(3):372-4.
- Kim KE, Woo KS, Kim SH, Han JY. [Detection of PML/RARA rearrangement by reverse transcriptase-PCR and sequencing in a case of microgranular acute promyelocytic leukemia lacking t(15;17) on karyotype and FISH]. Korean J Lab Med. 2009;29(5):379-83. [CrossRef]
- Wang Y, Fang M, Jing Y, Li J, Jiang F, Wang Y. Derivative (7)t(7;8): The sole karyotype abnormality in acute promyelocytic leukemia with PML/RARA rearrangement identified by RT-PCR and sequence analysis. Leuk Res. 2009;33(7):e55-8. [CrossRef]
- Choughule A, Polampalli S, Amre P, Shinde S, Banavali S, Prabhash K, et al. Identification of PML/RARalpha fusion gene transcripts that showed no t(15;17) with conventional karyotyping and fluorescent in situ hybridization. Genet Mol Res. 2009;8(1):1-7. [CrossRef]
- Soriani S, Cesana C, Farioli R, Scarpati B, Mancini V, Nosari A. PML/RAR-alpha fusion transcript and polyploidy in acute promyelocytic leukemia without t(15;17). Leuk Res. 2010;34(9):e261-3. [CrossRef]
- Yang JJ, Park TS, Kim MJ, Cho EH, Oh SH, Jeon BR, et al. Acute promyelocytic leukemia with trisomy 8 showing normal PML-RARA FISH signal patterns: diagnostic application of long-distance polymerase chain reaction in molecularly discrepant leukemia cases. Ann Hematol. 2012;91(10):1645-8. [CrossRef]
- Gruver AM, Rogers HJ, Cook JR, Ballif BC, Schultz RA, Batanian JR, et al. Modified array-based comparative genomic hybridization detects cryptic and variant PML-RARA rearrangements in acute promyelocytic leukemia lacking classic translocations. Diagn Mol Pathol. 2013;22(1):10-21.
- Rashidi A, Fisher SI. FISH: negative. Morphology: positive. Blood. 2014;124(23):3501. [CrossRef]
- Blanco EM, Curry CV, Lu XY, Sarabia SF, Redell MS, Lopez-Terrada DH, et al. Cytogenetically cryptic and FISH-negative PML/RARA rearrangement in acute promyelocytic leukemia detected only by PCR: an exceedingly rare phenomenon. Cancer Genet. 2014;207(1-2):48-9. [CrossRef]
- Wang YF, Liu J, Dong F, Tian L, Wang J, Xi LY, et al. [The study of one case of APL with rare cryptic PML-RARalpha fusion gene and the literatures review]. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2016;37(11):1001-2.
- Zhang Z, Xu Y, Jiang M, Kong F, Chen Z, Liu S, et al. Identification of a new cryptic PML-RARalpha fusion gene without t(15;17) and biallelic CEBPA mutation in a case of acute promyelocytic leukemia: a case detected only by RT-PCR but not cytogenetics and FISH. Cancer Biol Ther. 2020;21(4):309-14. [CrossRef]
- Schultz MJ, Blackburn PR, Cogbill CH, Pitel BA, Smadbeck JB, Johnson SH, et al. Characterization of a cryptic PML-RARA fusion by mate-pair sequencing in a case of acute promyelocytic leukemia with a normal karyotype and negative RARA FISH studies. Leuk Lymphoma. 2020;61(4):975-8. [CrossRef]
- Arumugam JR, Karthik Bommannan BK, Kalaiyarasi JP, Sundersingh S. Cytogenetics and FISH negative cryptic acute promyelocytic leukemia with CD56 expression. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2021;64(2):406-9.
- Mohebnasab M, Li P, Hong B, Dunlap J, Traer E, Fan G, et al. Cytogenetically Cryptic Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia: A Diagnostic Challenge. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(17). [CrossRef]
 |
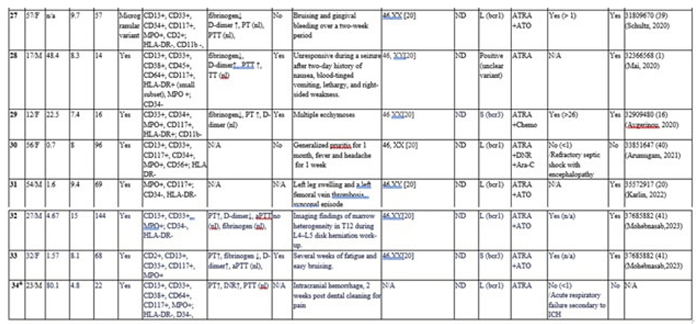 |
| Abbreviations: Dx: diagnosis; CR: complete remission; nl: normal; ND: not detected; N/A: not available; ATRA: all-trans retinoic acid; ATO: arsenic trioxide; IDA: Idarubicin; Ara-C: Cytarabine; AT: antithrombin; PT: prothrombin time; aPTT: activated partial thromboplastin time; PTT: partial thromboplastin time; FDP: fibrin degradation products; INR: international normalized ratio; GVHD: graft-versus-host disease; ICH: Intracranial hemorrhage. 1 Mixture of classic hypergranular promyelocytes with an unusually high proportion of microgranular promyelocytes. 2 Hematologic complete remission without molecular remission. 3 Bone marrow cells displayed irregular nuclear shapes and misty nucleoli, weakly positive for POX cytochemical staining, consistent with AML- FAB M5. 4 Novel cryptic atypical V (bcr2) transcript. ¥ Two cases with normal karyograms and negative FISH results in the initial study [9,10] were excluded, as abnormal FISH findings were identified retrospectively. # Includes testing with dual-color, dual-fusion PML/RARA translocation probe set and/or break-apart RARA probe. * Includes RT-PCR, qRT-PCR, and multiplex nested RT-PCR, with or without subsequent cDNA sequencing. & The current case. |
| Method | Application | Abnormalities detected | APL yield | STAT TAT | Causes of error | Availability | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Karyotyping | Standard of care | t(15;17) and all other chromosomal alterations | >96% | 2 days | Poor metaphase quality, culture failure, submicroscopic cryptic translocations | Widely available | Low |
| FISH -PML/RARA DCDF | Standard of care; Diagnostic confirmation | Typical and atypical PML::RARA fusion | ~98% | 3 hours | Hybridization failure, signal overlap, small insertions leading to absent or weak signals | Widely available | Low -Moderate |
| FISH -RARA BAP | Standard of care; Diagnostic confirmation | RARA rearrangements (PML and non-PML partners) | ~100% | 3 hours | Hybridization failure, signal overlap, small insertions leading to absent or weak signals | Widely available | Low -Moderate |
| RT-PCR | Diagnostic confirmation | PML::RARA transcript isoforms | >95% | 4 hours | Sample contamination, primer errors due to novel breakpoints | Widely available | Low -Moderate |
| qRT-PCR | MRD monitoring | PML::RARA transcript isoforms | >95% | 4 hours | Sample contamination, primer errors due to novel breakpoints | Widely available | Low -Moderate |
| RT-PCR +cDNA sequencing | Diagnostic confirmation | PML::RARA transcript isoforms, fusion breakpoints | >95% | 2 days | Sequencing errors, mis-priming, low-quality RNA | Moderate | Moderate |
| tCGH/cCGH/Mpseq | Advanced genomic assessment for rare cases (at low resolution) | PML::RARA transcript isoforms; additional non-diagnostic genomic aberrations | Unknown, very limited studies to date | 3 days | Undetectable balanced rearrangements and unmapped sequences, oversight of low-level mosaicism, inaccurate CNV calls | Limited | Moderate |
| OGM | Advanced genomic assessment for rare cases (at medium resolution) | PML::RARA and non-PML::RARA transcript isoforms; fusion breakpoints; additional non-diagnostic genomic aberrations | Unknown, requires further validation for standard APL diagnostics | 3~5 days | Poor recovery of HMW DNA, complex rearrangement miscalls, undetectable polyploidy, unresolved centromeric/p-arm rearrangements, missed low-level mosaicism | Limited | Moderate-high |
| WGS/WES | Advanced genomic assessment for rare cases (at high resolution) | PML::RARA and non-PML::RARA transcript isoforms; fusion breakpoints; additional non-diagnoatic genomic aberrations | Unknown, primarily used in research or complex cases rather than routine APL diagnosis | 3~5 days | Sequencing artifacts, bioinformatics miscalls, over-sight of low-level mosaicism, variant validation challenges, interpretation challenges, conditional detection of structural rearrangements | Limited | High |
| Tier | Methods | Clinical Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| First line | FISH (DCDF and BAP), Karypotying, RT-PCR |
High-yield, fast, easily accessible |
| Advanced | OGM, CMA, targeted sequencing, long read sequencing |
Complex cases |
| High-resolution/ research-oriented |
WGS/WES, other omics | High-complexity cases, with inconclusive results |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




