Submitted:
27 August 2025
Posted:
28 August 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Corpora and Socio-Demographic Data
2.2. Kolmogorov Complexity as a Measure of Language Complexity
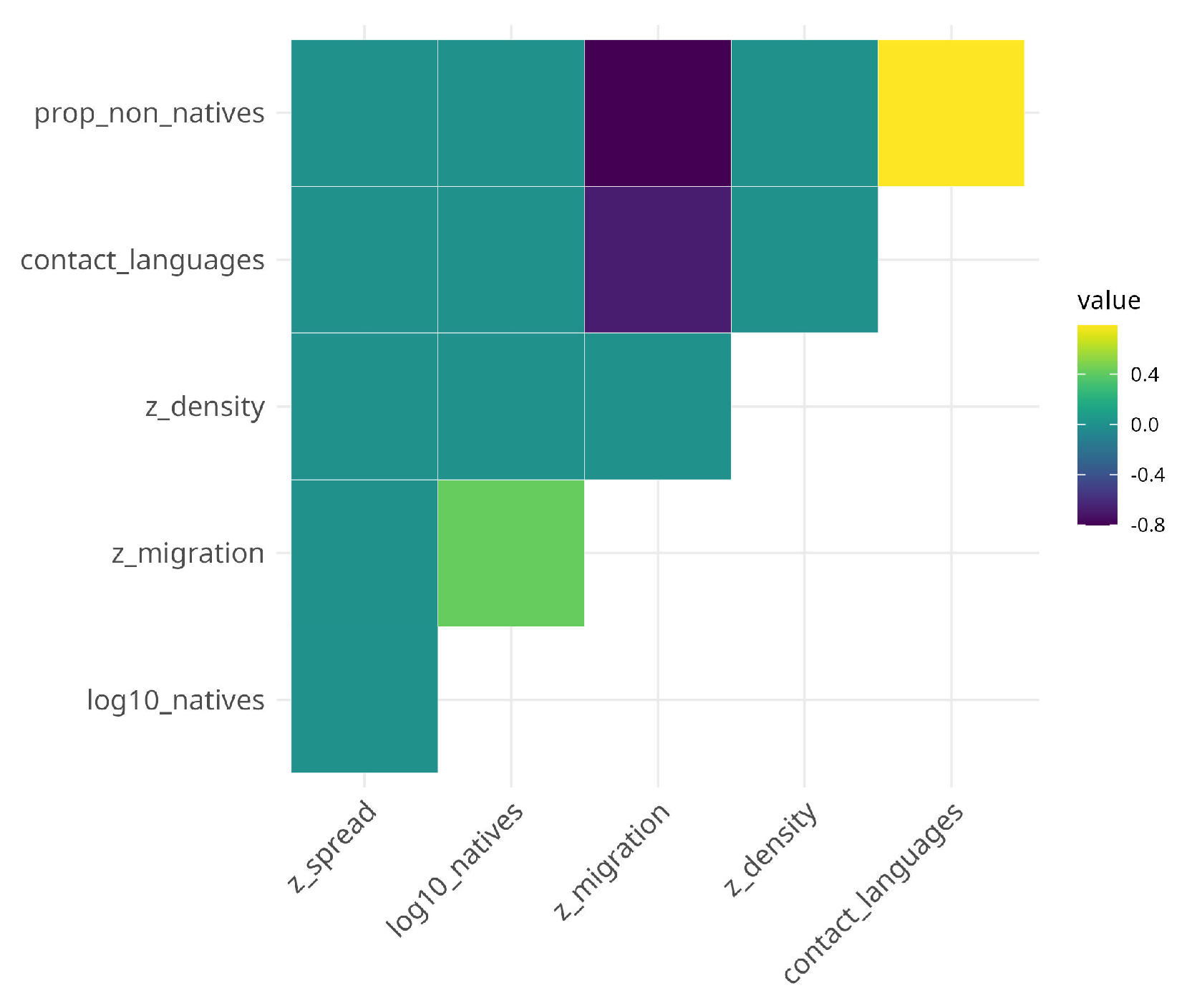
2.3. Statistical Methods
3. Results
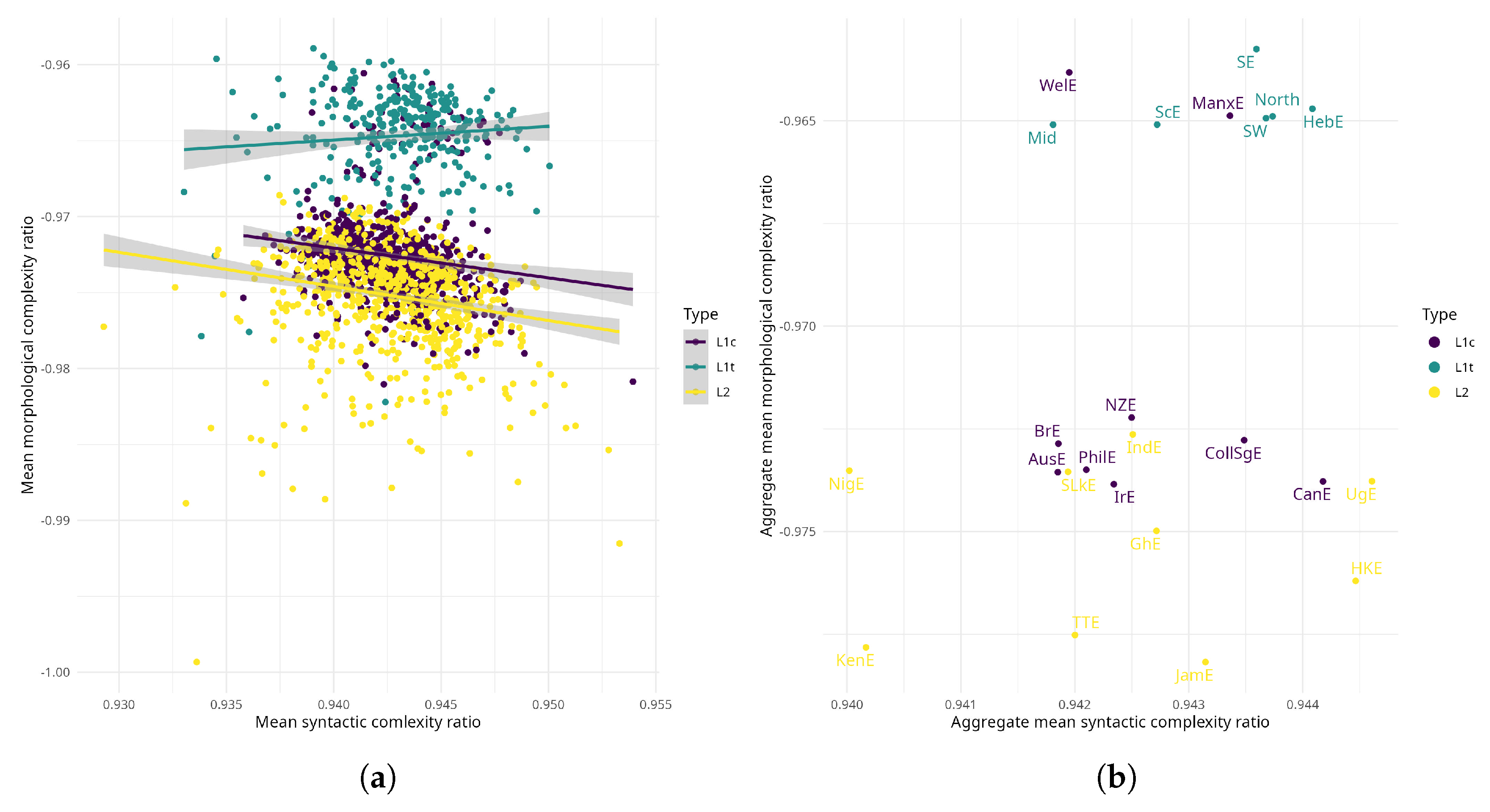
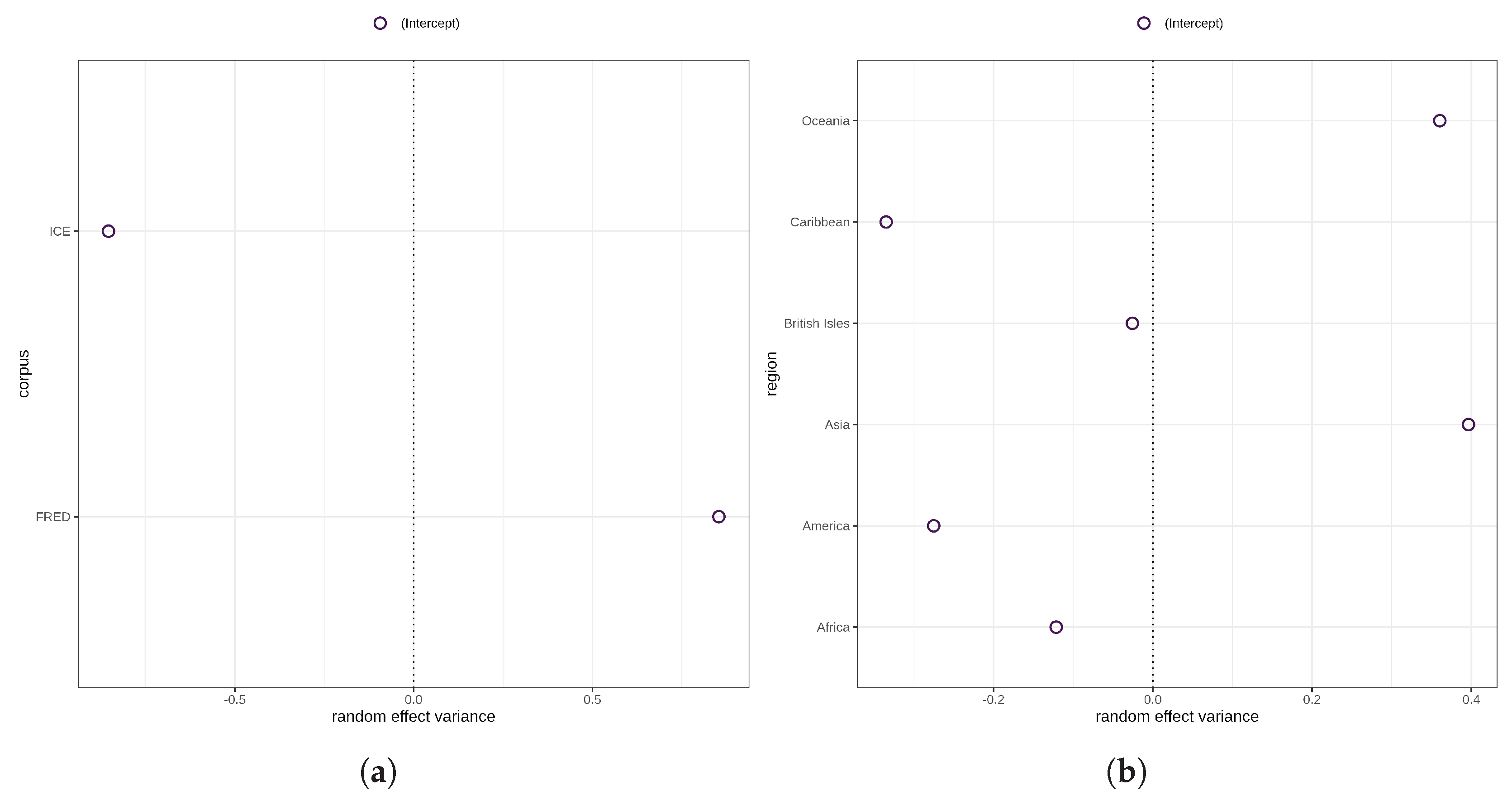
3.1. Kolmogorov-Based Complexity of English Varieties
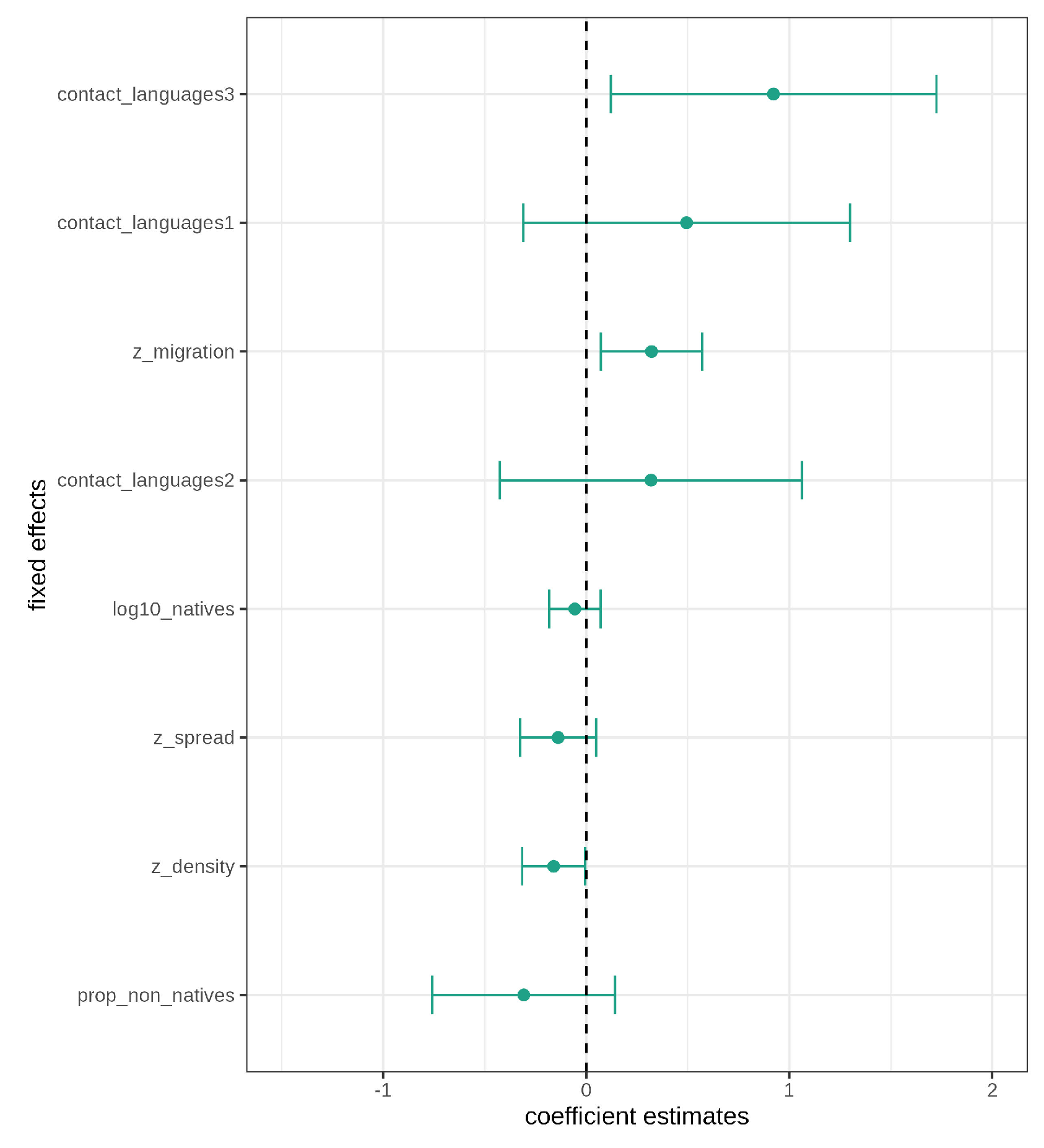
3.2. Kolmogorov-Based Complexity and Socio-Demographic Triggers
4. Discussion
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations of English Varieties
| Variety | Abbreviation |
| Australian English | AusE |
| British English | BrE |
| Canadian English | CanE |
| Colloquial American English | CollAmE |
| Colloquial Singapore English | CollSgE |
| English dialects in the Midlands | Mid |
| English dialects in the North of England | North |
| English dialects in the Southeast of England | SE |
| English dialects in the Southwest of England | SW |
| Ghanaian English | GhE |
| Hebridean English | HebE |
| Indian English | IndE |
| Irish English | IrE |
| Jamaican English | JamE |
| Kenyan English | KenE |
| Manx English | ManxE |
| New Zealand English | NZE |
| Nigerian English | NigE |
| Philippine English | PhilE |
| Scottish English | ScE |
| Sri Lankan English | SLkE |
| Trinidadian English | TTE |
| Ugandan English | UgE |
| Welsh English | WelW |
References
- Mufwene, S.; Coupé, C.; Pellegrino, F. Complexity in language: Developmental and evolutionary perspectives; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge & New York, 2017.
- Baerman, M.; Brown, D.; Corbett, G.G., Eds. Understanding and measuring morphological complexity; Oxford University Press: New York, 2015.
- Kortmann, B.; Szmrecsanyi, B., Eds. Linguistic complexity: Second Language Acquisition, Indigenization, Contact; Lingua & Litterae, Walter de Gruyter: Berlin, 2012.
- McWhorter, J. The world’s simplest grammars are creole grammars. Linguistic Typology 2001, 6, 125–166.
- Miestamo, M. Grammatical complexity in a cross-linguistic perspective. In Language Complexity: Typology, Contact, Change; Miestamo, M.; Sinnemäki, K.; Karlsson, F., Eds.; John Benjamins: Amsterdam/Philadelphia, 2008; pp. 23–41.
- Ehret, K.; Berdicevskis, A.; Bentz, C.; Blumenthal-Dramé, A. Measuring language complexity: challenges and opportunities. Linguistics Vanguard 2023, 9, 1–8. Publisher: De Gruyter Mouton, . [CrossRef]
- Ehret, K.; Blumenthal-Dramé, A.; Bentz, C.; Berdicevskis, A. Meaning and measures: interpreting and evaluating complexity metrics. Frontiers in Communication 2021, 6, 640510. Publisher: Frontiers, . [CrossRef]
- Berdicevskis, A.; Çöltekin, c.; Ehret, K.; von Prince, K.; Ross, D.; Thompson, B.; Yan, C.; Demberg, V.; Lupyan, G.; Rama, T.; et al. Using Universal Dependencies in cross-linguistic complexity research. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the Second Workshop on Universal Dependencies (UDW 2018), 2018.
- Ehret, K. An information-theoretic view on language complexity and register variation: Compressing naturalistic corpus data. Corpus Linguistics and Linguistic Theory 2021, 17, 383–410. Publisher: De Gruyter Mouton. [CrossRef]
- Audring, J. Calibrating complexity: How complex is a gender system? Language Sciences 2017, 60, 53–68. [CrossRef]
- Koplenig, A. Language structure is influenced by the number of speakers but seemingly not by the proportion of non-native speakers. Royal Society Open Science 2019, 6, 181274. [CrossRef]
- Sinnemäki, K.; Di Garbo, F. Language Structures May Adapt to the Sociolinguistic Environment, but It Matters What and How You Count: A Typological Study of Verbal and Nominal Complexity. Frontiers in Psychology 2018, 9, 1141. [CrossRef]
- Bentz, C.; Winter, B. Languages with More Second Language Learners Tend to Lose Nominal Case. Language Dynamics and Change 2013, 3, 1–27. [CrossRef]
- Lupyan, G.; Dale, R. Language Structure Is Partly Determined by Social Structure. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, 1–10. [CrossRef]
- Trudgill, P. Sociolinguistic typology: Social determinants of linguistic complexity; Oxford University Press: Oxford; New York, 2011.
- Wray, A.; Grace, G.W. The consequences of talking to strangers: Evolutionary corollaries of socio-cultural influences on linguistic form. Lingua 2007, 117, 543–578. Publisher: Elsevier. [CrossRef]
- Kauhanen, H.; Walkden, G.; Einhaus, S. Language structure is influenced by the proportion of non-native speakers: A reply to Koplenig (2019). Journal of Language Evolution 2023, pp. 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Koplenig, A. Still No Evidence for an Effect of the Proportion of Non-Native Speakers on Natural Language Complexity. Entropy 2024, 26, 993. [CrossRef]
- Shcherbakova, O.; Michaelis, S.M.; Haynie, H.J.; Passmore, S.; Gast, V.; Gray, R.D.; Greenhill, S.J.; Blasi, D.E.; Skirgård, H. Societies of strangers do not speak less complex languages. Science Advances 2023, 9, eadf7704. [CrossRef]
- Ehret, K.; Szmrecsanyi, B. An information-theoretic approach to assess linguistic complexity. In Complexity, Isolation, and Variation; Baechler, R.; Seiler, G., Eds.; Walter de Gruyter: Berlin/Boston, 2016; pp. 71–94.
- Szmrecsanyi, B. Typological parameters of intralingual variability: Grammatical analyticity versus syntheticity in varieties of English. Language Variation and Change 2009, 21, 319–353. [CrossRef]
- Szmrecsanyi, B.; Kortmann, B. Between simplification and complexification: Non-standard varieties of English around the world. In Language complexity as an evolving variable; Sampson, G.; Gil, D.; Trudgill, P., Eds.; Oxford University Press, 2009; pp. 64–79.
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria, 2025.
- Du Bois, J.W.; Chafe, W.L.; Meyer, C.; Thompson, S.A.; Martey, N. Santa barbara corpus of spoken american english. CD-ROM. Philadelphia: Linguistic Data Consortium 2000, 2005.
- Kortmann, B.; Lunkenheimer, K.; Ehret, K., Eds. The Electronic World Atlas of Varieties of English; 2020.
- Comrie, B. Linguistic typology. Annual Review of Anthropology 1988, 17, 145–159. [CrossRef]
- Ehret, K., Ed. Morphosyntactic-Variation-in-Englishes/DOVE: DOVE v1.0 (v1.0); Zenodo, 2025.
- Cheng, L.S.P.; Burgess, D.; Vernooij, N.; Solís-Barroso, C.; McDermott, A.; Namboodiripad, S. The Problematic Concept of Native Speaker in Psycholinguistics: Replacing Vague and Harmful Terminology With Inclusive and Accurate Measures. Frontiers in Psychology 2021, 12, 715843. [CrossRef]
- Ehret, K. How to obtain speaker numbers for English varieties around the world: Theoretical concepts, challenges and estimations. English World-Wide accepted.
- Berdicevskis, A.; Semenuks, A. Different trajectories of morphological overspecification and irregularity under imperfect language learning. In Proceedings of the The Complexities of Morphology; Arkadiev, P.; Gardani, F., Eds. Oxford University Press, 2020, pp. 283–305.
- Bentz, C.; Berdicevskis, A. Learning pressures reduce morphological complexity: Linking corpus, computational and experimental evidence. In Proceedings of the COLING 2016, 2016, pp. 222–232.
- Atkinson, M.; Smith, K.; Kirby, S. Adult Learning and Language Simplification. Cognitive Science 2018, pp. 1–37. _eprint: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/cogs.12686, . [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Gil, D.; Gaponov, S.; Reifegerste, J.; Yuditha, T.; Tatarinova, T.; Progovac, L.; Benítez-Burraco, A. Linguistic correlates of societal variation: A quantitative analysis. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0300838. [CrossRef]
- Thomason, S.G.; Kaufman, T. Language Contact, Creolization, and Genetic Linguistics; University of California Press: Berkeley, 1991.
- Lunkenheimer, K. Typological profile: L2 varieties. The Mouton World Atlas of Variation in English. Berlin: Mouton de Gruyter 2012, pp. 844–873.
- Kortmann, B.; Wolk, C. Morphosyntactic variation in the anglophone world: A global perspective. The Mouton world atlas of variation in English 2012, pp. 906–936.
- Szmrecsanyi, B. Typological profile: L1 varieties. The Mouton world atlas of variation in English 2012, pp. 826–843.
- Kolmogorov, A.N. Three Approaches to the Quantitative Definition of Information. Problemy Peredachi Informatsii 1965, 1, 3–11. [CrossRef]
- Kolmogorov, A. On Tables of Random Numbers. Sankhya 1963, 25, 369–375. [CrossRef]
- Juola, P. Measuring linguistic complexity: The morphological tier. Journal of Quantitative Linguistics 1998, 5, 206–213. [CrossRef]
- Juola, P. Assessing linguistic complexity. In Language Complexity: Typology, Contact, Change; Miestamo, M.; Sinnemäki, K.; Karlsson, F., Eds.; John Benjamins: Amsterdam & Philadelphia, 2008; pp. 89–107.
- Ehret, K.; Szmrecsanyi, B. An information-theoretic approach to assess linguistic complexity. In Complexity, Isolation, and Variation; Baechler, R.; Seiler, G., Eds.; Walter de Gruyter: Berlin, 2016; pp. 71–94.
- Ehret, K. An information-theoretic view on language complexity and register variation: Compressing naturalistic corpus data. Corpus Linguistics and Linguistic Theory 2021, 17, 383–410. [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Vitányi, P.M.B. An introduction to Kolmogorov complexity and its applications; Springer-Verlag: New York, 1997.
- Li, M.; Chen, X.; Li, X.; Ma, B.; Vitányi, P.M.B. The similarity metric. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory 2004, 50, 3250–3264. [CrossRef]
- Ehret, K. An information-theoretic approach to language complexity: Variation in naturalistic corpora. PhD thesis, University of Freiburg, Freiburg, Germany, 2017.
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using lme4. Journal of Statistical Software 2015, 67, 1–48. [CrossRef]
- Barr, D.J.; Levy, R.; Scheepers, C.; Tily, H.J. Random effects structure for confirmatory hypothesis testing: Keep it maximal. Journal of memory and language 2013, 68, 255–278. [CrossRef]
- Kortmann, B.; Szmrecsanyi, B. World Englishes between simplification and complexification. In World Englishes - Problems, Properties and Prospects: selected papers from the 13th IAWE conference; Siebers, L.; Hoffmann, T., Eds.; John Benjamins: Amsterdam, 2009; pp. 265–285.
- Greenbaum, S. Standard English and the international corpus of English. World Englishes 1990, 9, 79–83. [CrossRef]
- Guzmán Naranjo, M.; Becker, L. Statistical bias control in typology. Linguistic Typology 2022, 26, 605–670. [CrossRef]
- Sinnemäki, K. Complexity in core argument marking and population size. In Language Complexity as an Evolving Variable; Sampson, G.; Gil, D.; Trudgill, P., Eds.; Oxford University Press, 2009; pp. 126–140.
- Bentz, C.; Verkerk, A.; Kiela, D.; Hill, F.; Buttery, P. Adaptive Communication: Languages with More Non-Native Speakers Tend to Have Fewer Word Forms. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128254. [CrossRef]
- Koplenig, A.; Wolfer, S. Languages with more speakers tend to be harder to (machine-) learn. Scientific Reports 2023, 13, 18521.
- Roberts, S.G. Robust, causal, and incremental approaches to investigating linguistic adaptation. Frontiers in psychology 2018, 9, 166. [CrossRef]
- Cameron, D. The commodification of language: English as a global commodity. In The Oxford Handbook of the History of English; Nevalainen, T.; Traugott Closs, E., Eds.; Oxford University Press: New York, 2012; pp. 352–362.
- Tupas, R. Unequal Englishes as a sociolinguistics of globalization. Journal of English Studies and Comparative Literature 2019, 18, 1–17.
- Nichols, J. Linguistic complexity: a comprehensive definition and survey. In Language Complexity as an Evolving Variable; Sampson, G.; Gil, D.; Trudgill, P., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, 2009; pp. 64–79.
| 1 | |
| 2 | Subsequent inspection of boxplots revealed that the entire SBCSAE is an outlier. Thus, the corpus was excluded from further analyses. |
| 3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



