Submitted:
25 August 2025
Posted:
25 August 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
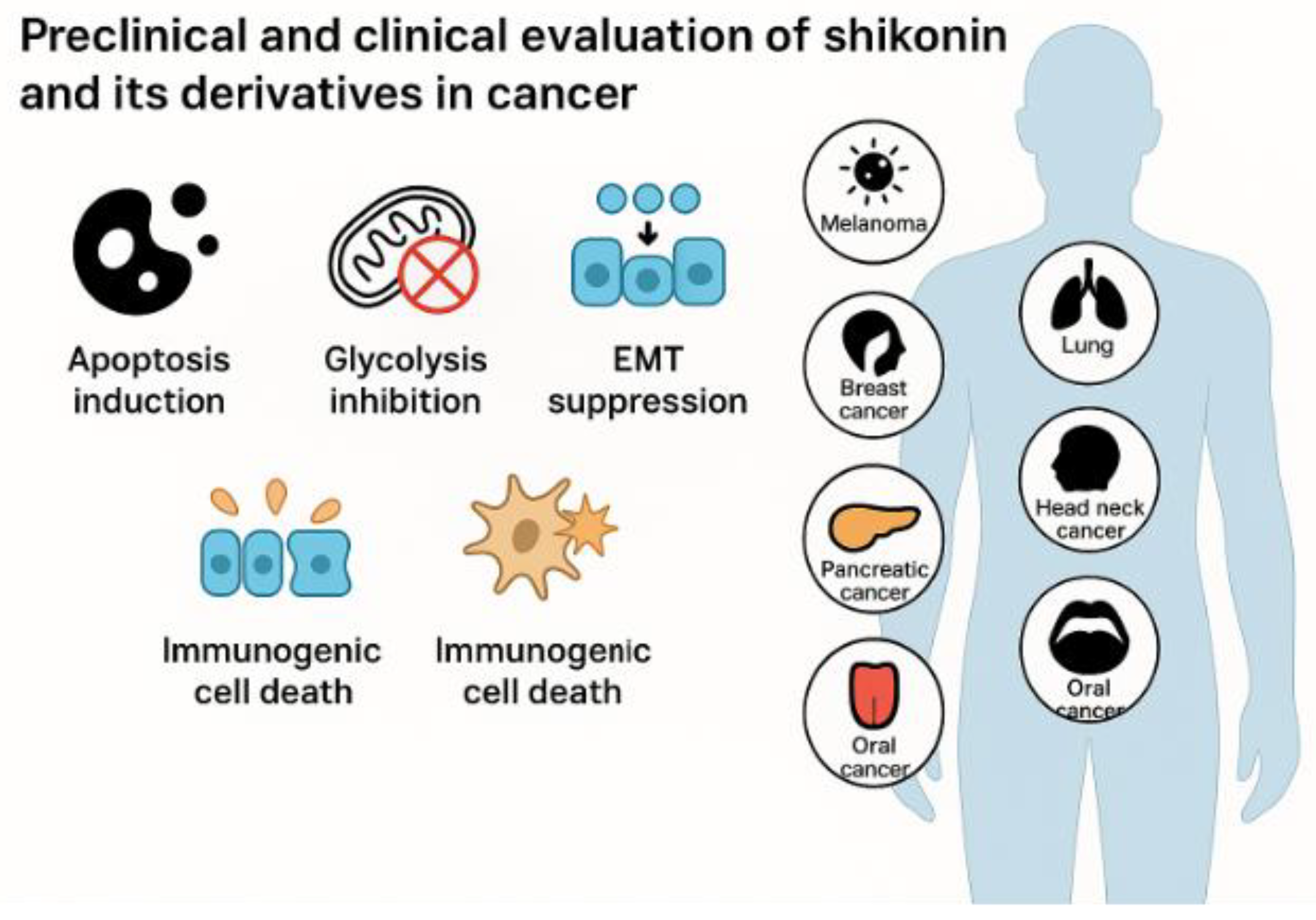
Shikonin, a naphthoquinone from Lithospermum erythrorhizon, exhibits broad anticancer potential through multiple regulated cell death pathways. It induces apoptosis via mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signalling, reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation, endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, and p53 activation, and also triggers necroptosis through receptor-interacting protein kinase 1 (RIPK1), receptor-interacting protein kinase 3 (RIPK3), and mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein (MLKL), as well as ferroptosis and pyroptosis. Beyond cytotoxicity, shikonin suppresses metastasis by blocking epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) and downregulating matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) and matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9). It further disrupts tumour metabolism by targeting pyruvate kinase isoform M2 (PKM2) and modulating the Warburg effect. In combination, shikonin enhances the efficacy of chemotherapy (cisplatin, paclitaxel), targeted therapy (tamoxifen), and immunotherapy (anti-programmed cell death protein 1 [anti-PD-1]), thereby overcoming resistance. To address poor bioavailability, nanoparticles, liposomes, and derivatives such as β, β-dimethylacrylshikonin have been developed to improve potency and reduce toxicity. Preclinical studies show strong tumour regression in melanoma, breast, and ovarian cancer models. Although clinical validation remains limited, shikonin’s multifaceted actions, favourable safety, and therapeutic synergy highlight the need for rigorous clinical trials to define its oncological value.
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Chemistry and Pharmacokinetics
3. Mechanisms of Anticancer Action
3.1. Induction of Apoptosis by Shikonin
3.1.1. Shikonin-Induced Intrinsic Apoptosis via MAPK Signalling and ROS-Mediated ER Stress
3.1.2. Extrinsic Apoptotic Pathways Triggered by Shikonin: Death Receptor and Caspase-8 Activation
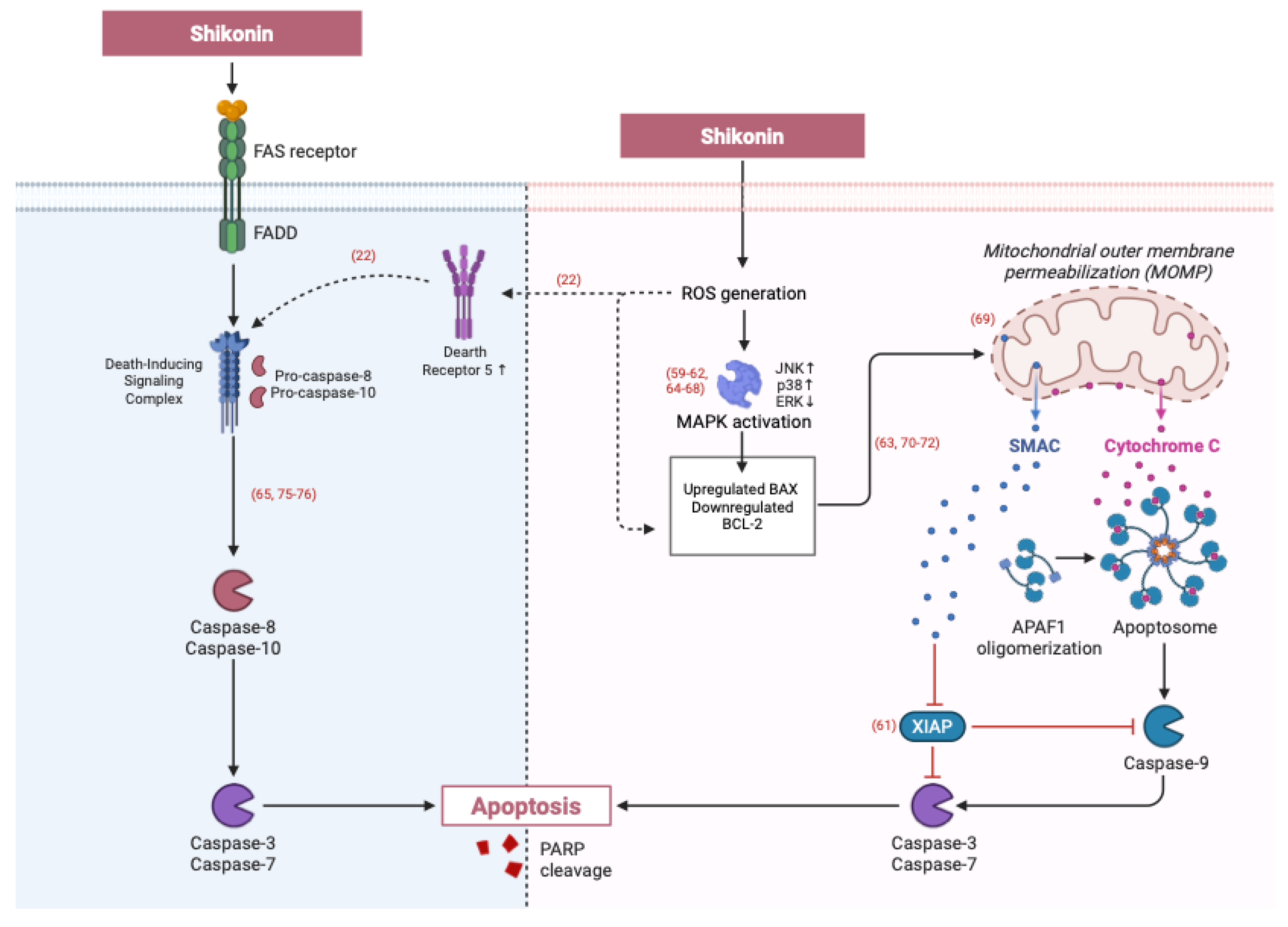
3.1.3. Induction of Apoptosis Through Unique Signalling Pathways
3.1.4. Shikonin and Its Derivatives Induces Apoptosis in drug-Resistant Cancer Cells
3.1.5. Apoptosis Effects of Shikonin Derivatives
| Shikonin Derivatives | Target Cancer Types | Pathways | Results | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acetylshikonin | Leukaemia K562 | Intrinsic | Increase levels of cleaved caspase 3, cleaved PARP, and caspase 9 |
[94] |
| β-hydroxyisovaleryl-shikonin |
Ovarian cancer HeLa cells | PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling | PI3K, AKT, mTOR and P70S6K mRNA expression levels decreased | [48] |
| Shikonin M12 | Colorectal cancer | Intrinsic | ROS generation, downregulated the mitochondrial membrane potential |
[93] |
| β, β-Dimethylacrylshikonin | HCT-116 cells | Intrinsic | Downregulate Bcl-2, upregulate Bax | [41] |
| BRAF and NRAS-mutated skin cancer cells |
Intrinsic | NOXA-mediated, caspase 3 activation |
[95] | |
| Chordoma MUG-Chor1 and U-CH2 cell lines |
Intrinsic | Upregulate NOXA and PUMA genes | [96] | |
| Cyclopropyl-acetylshikonin | Skin cancer WM9 and WM164 cells | Intrinsic | Activation of caspase 3/7 cascade- 3 | [91] |
| Acetylshikonin and cyclopropylshikonin | Chondrosarcoma Cal 78 and SW-1353 cell | Intrinsic | Upregulation caspase -7 and -9, pro-apoptotic NOXA genes, and γH2AX DNA damage marker |
[61] |
| E2 | Human triple-negative breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cell line | Glucose metabolism regulator PDK1 and PDHC/PDK axis | Accumulate ROS, upregulate Bax and Fas protein | [92] |
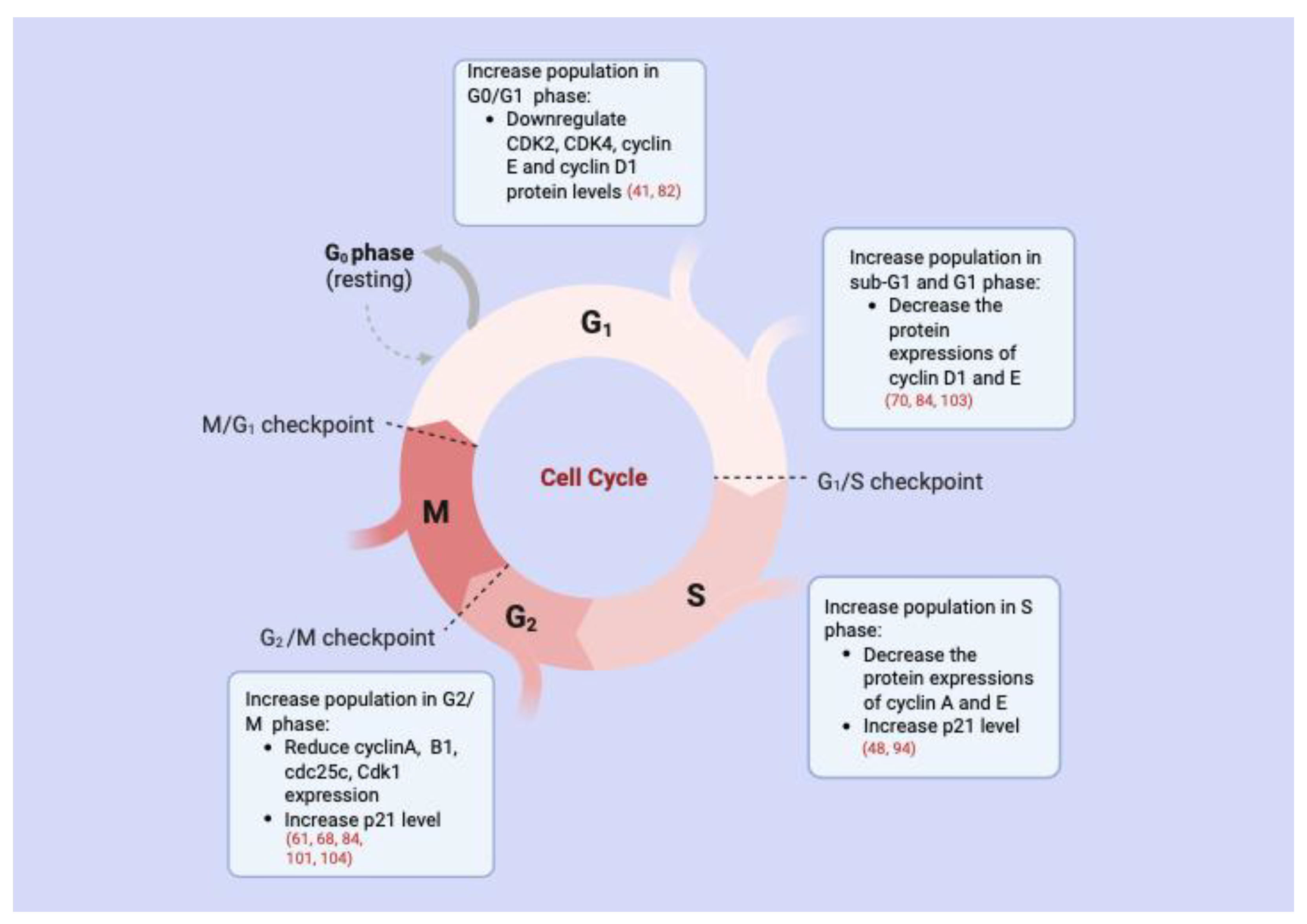
3.2. Cell Cycle Arrest
3.3. Suppression of Metastasis and Invasion
3.4. Induction of Necroptosis

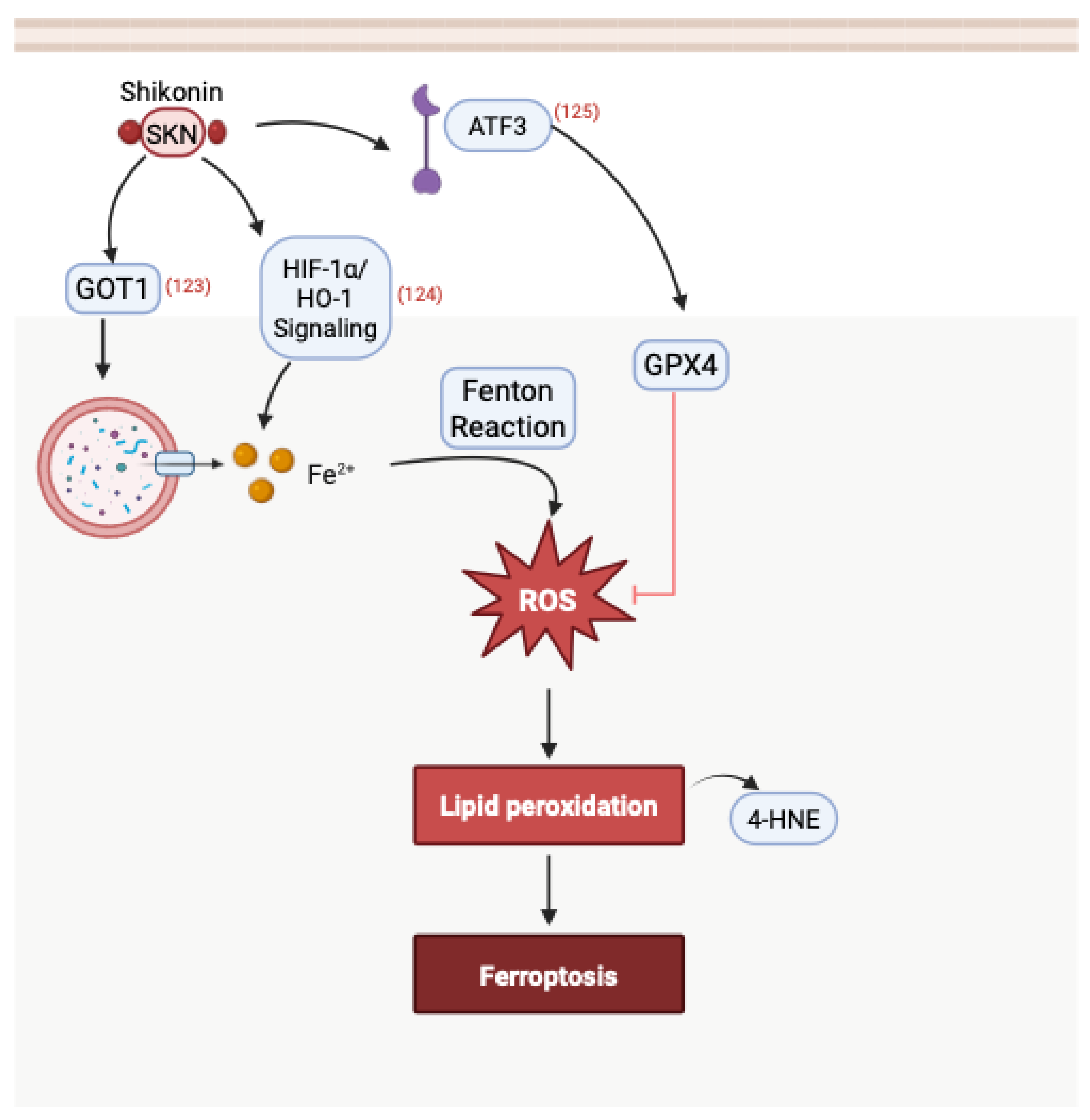
3.5. Induction of Ferroptosis
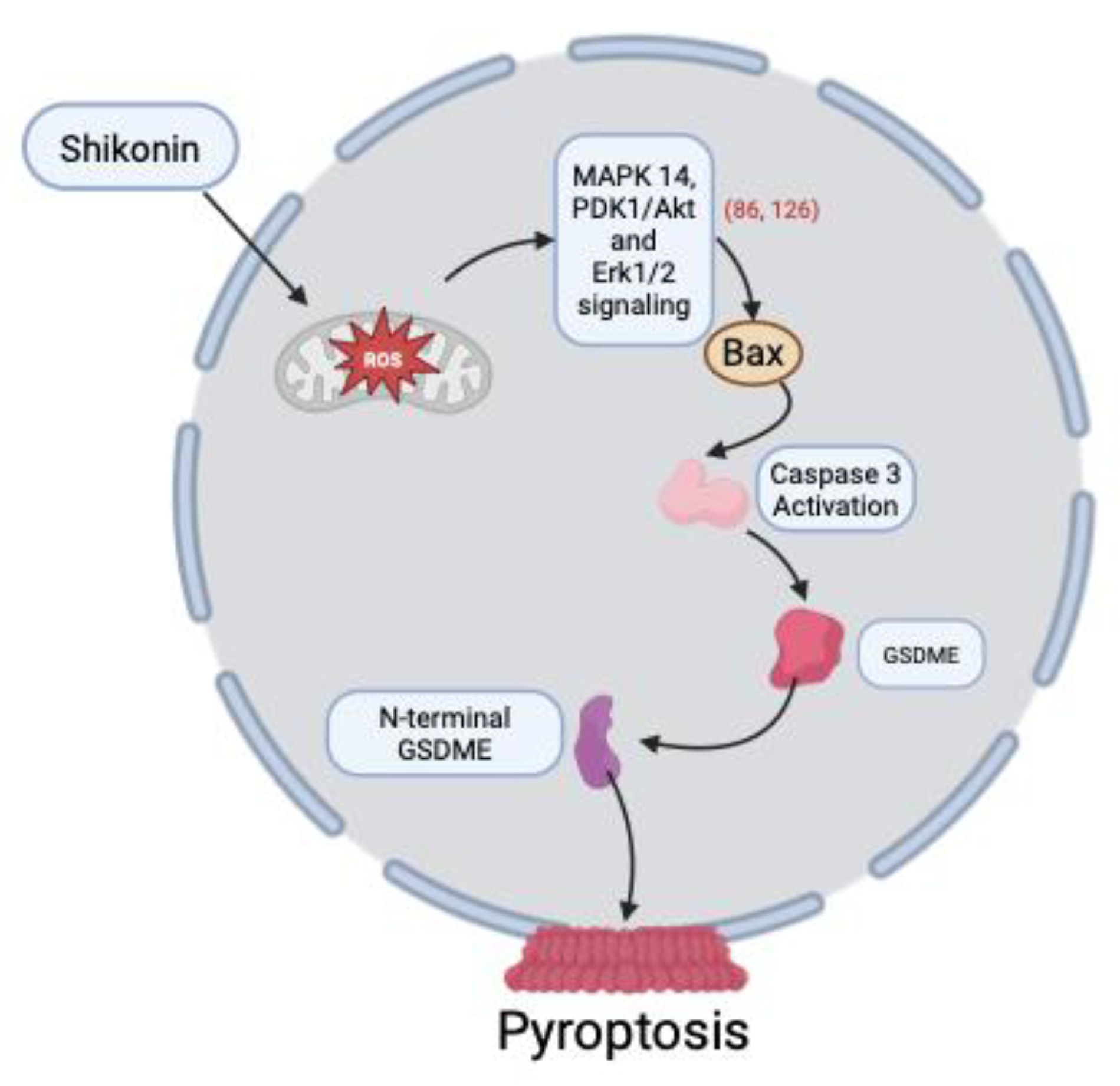
3.6. Induction of Pyroptosis
3.7. Inhibition of Tumour Metabolism
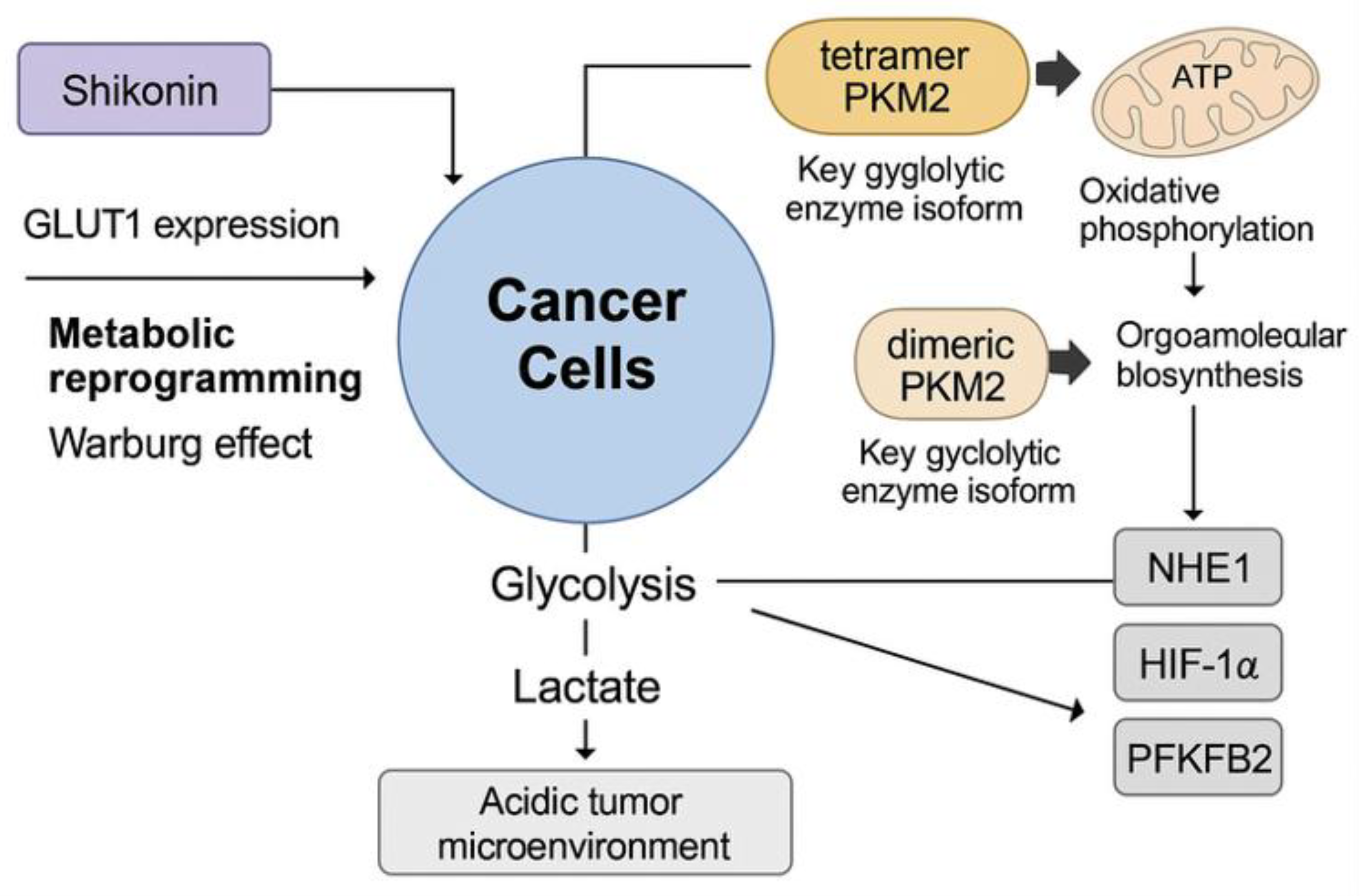
4. Combination Therapy
4.1. Shikonin as a Chemosensitizer: Enhancing Chemotherapy and Overcoming Resistance
4.2. Endocrine-Targeted Therapy and Resistance Modulation by Shikonin
4.3. Shikonin Enhances Immunotherapy via Immunogenic Cell Death
4.4. Shikonin Derivative β, β-Dimethylacrylshikonin Enhances Radiotherapy
| Cancer Type | Combination | IC₅₀ (μM) Reduction | Apoptosis (% Annexin V+) | Key Molecular Changes | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lung A549, PC9 |
Shikonin + Cisplatin |
A549: 5.74 µM PC9: 6.30 µM |
A549: + 650% PC9: + 525% |
↓ PKM2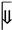 ↓ Glycolysis 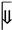 ↓ Exosome |
[134] |
| Ovary A2780/DDP, SKOV3/DDP, OVCAR4/DDP |
Shikonin + Cisplatin |
A2780/DDP: 23.46 µM SKOV3/DDP: 50.06 µM OVCAR4/DDP: 18.06 µM |
Not reported |
↑ HMOX1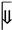 ↑ heme breakdown 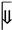 ↑ Fe²⁺ 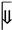 ↑ ROS 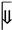 ↑ Lipid peroxidation 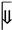 ↑ Ferroptosis |
[140,142] |
| Esophagus KYSE-150, KYSE-270 |
Shikonin + Paclitaxel |
Not reported |
KYSE270: + ~367% |
↑ p53 activation ↓ Bcl-2 expression |
[147] |
| Pancreas PANC-1, BxPC-3 |
Shikonin + Gemcitabine |
PANC-1: 1.800 μM BxPC-3: 3.18 μM |
PANC-1: 14.66% (3 μM) 83.35% (5 μM) 90.50% (10 μM) BxPC-3: ~7% (3 μM) ~14% (5 μM) ~17% (10 μM) |
↓ PAK1 ↓ Downstream signalling  ↑ Apoptosis |
[154] |
| Breast MDA-MB-435, MCF-7 |
Shikonin + 4-hydroxytamoxifen |
Not reported |
MDA-MB-435S: 26.3% MCF-7: 22.9% |
↑ ROS ↓ MMP  ↑ Apoptosis |
[159] |
| Breast MCF-7R |
Shikonin + Tamoxifen |
Not reported | Not reported | ↑ lncRNA uc.57; ↓ BCL11A; ↓PI3K/AKT & MAPK pathways | [163] |
| Breast MDA-MB-468 |
Shikonin + anti-PD-1 |
3.59 μM | ~2% (Z-VAD-FMK) ~39% (Nec-1) |
↑ RIP1K & RIP3K; ↑ ROS; ↓ mitochondrial membrane potential; necroptosis | [170] |
| Colon CT26 |
Shikonin + anti-PD-1 |
Not reported | 12.47% (5 μM) 20.17% (10 μM) |
↑ calreticulin exposure; ↑ Hsp70; antigen-presenting cell activation | [174] |
| Colon HCT116 LN428 H460 A549 |
β, β-Dimethylacrylshikonin + IR |
Not reported | ~200% | ↑ ROS ↑ DNA damage  ↑ Apoptosis |
[143] |
| Kidney SKRC-17 RCC-53 |
Shikonin + Ipilimumab |
1.32 μM | ~344% | ↓ FoxP3⁺ Tregs; ↑ activation of CD8⁺ and CD4⁺ effector T cells | [178] |
5. Preclinical and Clinical Studies
| Cancer Type/ Model | Agent | Mechanism of action | Main Outcomes | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Melanoma (A375 xenograft, mice) | Shikonin (5.0 mg/kg) | ↑ Apoptotic proteins | Greater tumour suppression vs dacarbazine | [104] |
| Melanoma (B16F10 lung metastasis, mice) | Shikonin + Quercetin | PKM2 inhibition, ↓ platelet–tumour interaction, ↓ glycolysis |
Fewer metastatic nodules; no adverse effects | [179] |
| Breast cancer (Orthotopic; TNBC, MCF-7) | Shikonin | PDK1 inhibition, EMT suppression | ↓ Tumour invasion & growth; TNBC sensitivity | [17,180] |
| Breast cancer (MCF-7 xenograft, mice) | Shikonin + siRNA/TGF-β nanoparticle | ICD induction (calreticulin exposure), improved biodistribution | 21.8% ICD; tumour-specific targeting | [181] |
| HNSCC (xenograft, mice) | Shikonin | Suppression of FAM83A/PKM2 axis | ↓ PKM2 expression; ↓ tumour progression | [182] |
| Cervical & ovarian cancer (xenograft) | Shikonin | Apoptosis, anti-metastatic activity | ↓ Tumour growth; ↑ cisplatin sensitivity | [17,140] |
| Oral cancer (mouse model) | Shikonin | Apoptosis induction | Tumour growth inhibition | [183] |
| Pancreatic cancer (cell models) | β-hydroxyisovaleryl-shikonin | ↑ ROS, apoptosis | Enhanced cytotoxicity | [147] |
| Clinical trial (lung cancer, 1991) | Shikonin (dose unclear) | Not reported | >25% tumour reduction; mean survival ~10 months | [184] |
6. Challenges and Future Perspectives
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 1-κB⍺ | I kappaB alpha |
| 4-OHT | 4-hydroxytamoxifen |
| 5-FU | 5-fluorouracil |
| AMPK | AMP-activated protein kinase |
| ATF4 | Activating transcription factor 4 |
| β-carotene | Beta-carotene |
| Bax | Bcl-2-associated X protein |
| Bcl | B-cell lymphoma |
| Bid | BH3-interacting domain death agonist |
| Ca²⁺ | Calcium |
| ccRCC | Clear cell renal cell carcinoma |
| CDK | Cyclin-dependent kinase |
| CHOP | C/EBP homologous protein |
| CML | Chronic myeloid leukaemia |
| CRC | Colorectal cancer |
| CRT | Calreticulin |
| CSCs | Cancer stem cells |
| CTL | Cytotoxic T lymphocytes |
| DAMPs | Damage-associated molecular patterns |
| DC | Dendritic cells |
| DISC | Death-inducing signalling complex |
| DNases | Deoxyribonucleases |
| DR | Death receptor |
| DX | Doxorubicin |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor |
| EMT | Epithelial-mesenchymal transition |
| ER | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| ER⁺ | Oestrogen receptor–positive |
| ER⁻ | Oestrogen receptor–negative |
| ERK | Extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| ESCC | Oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma |
| ESM1 | Endothelial cell specific molecule 1 |
| FADD | Fas-associated death domain |
| FASL | Fas ligand |
| Fe²⁺ | Ferrous iron |
| FPE | First-pass effect |
| GC | Gastric cancer |
| GOT-1 | Glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase 1 |
| GPER | G protein-coupled oestrogen receptor |
| GRP78 | Glucose-regulated protein 78 |
| GSDME | Gasdermin E |
| GTPBP4 | Guanosine triphosphate binding protein 4 |
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| HDAC | Histone deacetylase |
| HIF-1α | Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha |
| HMOX1 | Heme oxygenase 1 |
| HNSCC | Head and neck squamous cell carcinomas |
| HPLC | High-performance liquid chromatography |
| HSCCC | High-speed counter-current chromatography |
| ICD | Immunogenic cell death |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
| IR | Ionising radiation |
| IV | Intravenous |
| JNK | c-Jun N-terminal kinase |
| KM | Kunming |
| KRAS | Kirsten rat sarcoma virus |
| lncRNAs | Long non-coding RNAs |
| MAE | Microwave-assisted extraction |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| MitoROS | Mitochondrial ROS |
| MLKL | Mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein |
| MM | Multiple myeloma |
| MMP | Mitochondrial membrane potential |
| MMP-2 | Matrix metalloproteinase-2 |
| MMP-9 | Matrix metalloproteinase-9 |
| MS | Murashige and Skoog |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor kappa B |
| NHE1 | Sodium–hydrogen exchanger 1 |
| NSCLC | Non-small cell lung cancer |
| OSCC | Oral squamous cell carcinoma |
| OXA | Oxaliplatin |
| PAK1 | p21-activated kinase 1 |
| PAMPs | Pathogen-associated molecular patterns |
| PARP | Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase |
| PBMC | Patient peripheral blood mononuclear cell |
| PCD | Programmed cell death |
| PDK1 | Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1 |
| PFKFB2 | 6-phosphofruto-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-biphosphate |
| PHD3 | Prolyl hydroxylase 3 |
| PKM2 | Pyruvate kinase isoform M2 |
| PTEN | Phosphatase and tensin homologue |
| PUMA | p53 upregulated modulator of apoptosis |
| PYCR1 | Pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase 1 |
| rhApo2L/TRAIL | Apo2 ligand/ tumour necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand |
| RIPK1 | Receptor-interacting protein kinase1 |
| RIPK3 | Receptor-interacting protein kinase3 |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| RT-PCR | Real-time polymerase chain reaction |
| SC-CO₂ | Supercritical carbon dioxide |
| SCLC | Small cell lung cancer |
| SD | Sprague-Dawley |
| TAM | Tamoxifen |
| TCM | Traditional Chinese Medicine |
| TGF-β | Transforming growth factor β |
| TIME | Tumour immune microenvironment |
| TLRs | Toll-like receptors |
| TME | Tumour microenvironment |
| TNBC | Triple negative breast cancer |
| TNFα | Tumour necrosis factor-α |
| TRAP1 | Tumour necrosis factor receptor-associated protein 1 |
| TrxR1 | Thioredoxin reductase 1 |
| UAE | Ultrasonic-assisted extraction |
| XBP-1 | X-box binding protein 1 |
References
- Siegel RL, Kratzer TB, Giaquinto AN, Sung H, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2025. CA. 2025;75(1):10–45. [CrossRef]
- Debela DT, Muzazu SG, Heraro KD, Ndalama MT, Mesele BW, Haile DC, Kitui SK, Manyazewal T. New approaches and procedures for cancer treatment: Current perspectives. SAGE Open Med. 2021;9:20503121211034366. [CrossRef]
- Khan SU, Fatima K, Aisha S, Malik F. Unveiling the mechanisms and challenges of cancer drug resistance. Cell Commun Signal. 2024;22(1):109. [CrossRef]
- Katta B, Vijayakumar C, Dutta S, Dubashi B, Nelamangala Ramakrishnaiah VP. The incidence and severity of patient-reported side effects of chemotherapy in routine clinical care: A prospective observational study. Cureus. 2023;15(4):e38301. [CrossRef]
- Kennedy LB, Salama AKS. A review of cancer immunotherapy toxicity. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70(2):86–104. [CrossRef]
- Rathee S, Patil UK, Jain SK. Exploring the Potential of Dietary Phytochemicals in Cancer Prevention: A Comprehensive Review. J Explor Res Pharmacol. 2024;9(1):34–47. [CrossRef]
- Kumar A, P N, Kumar M, Jose A, Tomer V, Oz E, Proestos C, Zeng M, Elobeid T, K S, Oz F. Major Phytochemicals: Recent Advances in Health Benefits and Extraction Method. Molecules. 2023;28(2):887. [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal Y, Liang Z, Zhao Z. Botanical drugs in Ayurveda and Traditional Chinese Medicine. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016;194:245–59. [CrossRef]
- Gupta J, Sharma B, Sorout R, Singh RG, Ittishree, Sharma MC. Ginger (Zingiber officinale) in traditional Chinese medicine: A comprehensive review of its anti-inflammatory properties and clinical applications. Pharmacol Res Mod Chin Med. 2025;14:100561. [CrossRef]
- Hossain MS, Wazed MA, Asha S, Amin MR, Shimul IM. Dietary phytochemicals in health and disease: Mechanisms, clinical evidence, and applications: A comprehensive review. Food Sci Nutr. 2025;13(3):e70101. [CrossRef]
- Gezer A, Üstündağ H, Özkaraca M, Sari EK, Gür C. Therapeutic effects of resveratrol and β-carotene on L-arginine-induced acute pancreatitis through oxidative stress and inflammatory pathways in rats. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):32068. [CrossRef]
- Song Y, Ding Q, Hao Y, Cui B, Ding C, Gao F. Pharmacological effects of shikonin and its potential in skin repair: A review. Molecules. 2023;28(24):7950. [CrossRef]
- Malik S, Brudzyńska P, Khan MR, Sytar O, Makhzoum A, Sionkowska A. Natural plant-derived compounds in food and cosmetics: A paradigm of shikonin and its derivatives. Materials. 2023;16(12):4377. [CrossRef]
- Andújar I, Ríos JL, Giner RM, Recio MC. Pharmacological properties of shikonin: A review of literature since 2002. Planta Med. 2013;79:1685–97. [CrossRef]
- Barkizatova G, Turgumbayeva A, Zhakipbekov K, Bekesheva K, Arystanov Z, Arystanova T, Kayupova F, Zhumalina K, Toxanbayeva Z, Ibragimova A, Blinova O, Utegenova G, Iztileu N, Shynykul Z. Exploring the pharmacological potential of Lithospermum officinale L.: A review of phytochemicals and ethnomedicinal uses. Molecules. 2024;29(8):1856. [CrossRef]
- Gautam S, Lapčík L, Lapčíková B. Pharmacological significance of Boraginaceae with special insights into shikonin and its potential in the food industry. Foods. 2024;13(9):1350. [CrossRef]
- Pandey P, Lakhanpal S, Jamuna KV, Singh A, Abohassan M, Park MN, Shin SW, Kang HN, Zahera M, Saeed M, Khan F, Kim B. Review projecting shikonin as a therapeutic candidate in female carcinomas: A preclinical perspective. Front Pharmacol. 2025;16:1627124. [CrossRef]
- Yan C, Li Q, Sun Q, Yang L, Liu X, Zhao Y, Shi M, Li X, Luo K. Promising nanomedicines of shikonin for cancer therapy. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023;18:1195–218. [CrossRef]
- Yazaki, K. Lithospermum erythrorhizon cell cultures: Present and future aspects. Plant Biotechnol. 2017;34(3):131–42. [CrossRef]
- Huang XY, Fu HL, Tang HQ, Yin ZQ, Zhang W, Shu G, Yin LZ, Zhao L, Yan XR, Lin JC. Optimization extraction of shikonin using ultrasound-assisted response surface methodology and antibacterial studies. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020;2020:1208617. [CrossRef]
- Leote RJB, Sanz CG, Diculescu VC. Electrochemical characterization of shikonin and in-situ evaluation of interaction with DNA. J Electroanal Chem. 2022;921:116663. [CrossRef]
- Qi K, Li J, Hu Y, Qiao Y, Mu Y. Research progress in mechanism of anticancer action of shikonin targeting reactive oxygen species. Front Pharmacol. 2024;15:1416781. [CrossRef]
- Sagratini G, Cristalli G, Giardinà D, Gioventù G, Maggi F, Ricciutelli M, Vittori S. Alkannin/shikonin mixture from roots of Onosma echioides (L.) L.: Extraction method study and quantification. J Sep Sci. 2008;31(6–7):945–52. [CrossRef]
- Azuma H, Li J, Youda R, Suzuki T, Miyamoto K, Taniguchi T, Nagasaki T. Improved isolation procedure for shikonin from the root of the Chinese medicinal plant Lithospermum erythrorhizon and its solubilization with cyclodextrins. J Appl Res Med Aromat Plants. 2016;3(2):58–63. [CrossRef]
- Gheisary B, Fattahi M, Alipour H. Enhancing extraction of shikonin and phenolic antioxidants from Echium italicum L. using ultrasound and response surface methodology: optimizing temperature, time, and liquid–solid ratio. Biomass Convers Biorefinery. 2025;15(10):15619–30. [CrossRef]
- Shen L, Pang S, Zhong M, Sun Y, Qayum A, Liu Y, Rashid A, Xu B, Liang Q, Ma H, Ren X. A comprehensive review of ultrasonic assisted extraction (UAE) for bioactive components: Principles, advantages, equipment, and combined technologies. Ultrason Sonochem. 2023;101:106646. [CrossRef]
- MS U, Ferdosh S, Haque Akanda MdJ, Ghafoor K, A.H. R, Ali MdE, Kamaruzzaman B.Y., M.B. F, S. H, Shaarani S, Islam Sarker MdZ. Techniques for the extraction of phytosterols and their benefits in human health: a review. Sep Sci Technol. 2018;53(14):2206–23. [CrossRef]
- Uwineza PA, Waśkiewicz A. Recent advances in supercritical fluid extraction of natural bioactive compounds from natural plant materials. Molecules. 2020;25(17):3847. [CrossRef]
- Liu T, Ma C, Yang L, Wang W, Sui X, Zhao C, Zu Y. Optimization of shikonin homogenate extraction from Arnebia euchroma using response surface methodology. Molecules. 2013;18(1):466–81. [CrossRef]
- Akgun IH, Erkucuk A, Pilavtepe M, Yesil-Celiktas O. Optimization of total alkannin yields of Alkanna tinctoria by using sub- and supercritical carbon dioxide extraction. J Supercrit Fluids. 2011;57(1):31–7. [CrossRef]
- Assimopoulou AN, Sturm S, Stuppner H, Papageorgiou VP. Preparative isolation and purification of alkannin/shikonin derivatives from natural products by high-speed counter-current chromatography. Biomed Chromatogr BMC. 2009;23(2):182–98. [CrossRef]
- Bagheri F, Tahvilian R, Karimi N, Chalabi M, Azami M. Shikonin production by callus culture of Onosma bulbotrichom as active pharmaceutical ingredient. Iran J Pharm Res. 2018;17(2):495–504.
- Yazaki K, Tanaka S, Matsuoka H, Sato F. Stable transformation of Lithospermum erythrorhizon by Agrobacterium rhizogenes and shikonin production of the transformants. Plant Cell Rep. 1998;18(3–4):214–9. [CrossRef]
- Yadav S, Sharma A, Nayik GA, Cooper R, Bhardwaj G, Sohal HS, Mutreja V, Kaur R, Areche FO, AlOudat M, Shaikh AM, Kovács B, Mohamed Ahmed AE. Review of Shikonin and Derivatives: Isolation, Chemistry, Biosynthesis, Pharmacology and Toxicology. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:905755. [CrossRef]
- Wang F, Yao X, Zhang Y, Tang J. Synthesis, biological function and evaluation of Shikonin in cancer therapy. Fitoterapia. 2019;134:329–39. [CrossRef]
- Wang R, Guo H, Cui J, Li S. A novel and efficient total synthesis of shikonin. Tetrahedron Lett. 2012;53(31):3977–80. [CrossRef]
- Zhou W, Peng Y, Li SS. Semi-synthesis and anti-tumor activity of 5,8-O-dimethyl acylshikonin derivatives. Eur J Med Chem. 2010;45(12):6005–11. [CrossRef]
- Huang G, Zhao HR, Meng QQ, Zhang QJ, Dong JY, Zhu BQ, Li SS. Synthesis and biological evaluation of sulfur-containing shikonin oxime derivatives as potential antineoplastic agents. Eur J Med Chem. 2018;143:166–81. [CrossRef]
- Bhat AM, Bhat IA, Abdullah ST. Melanogenesis inhibition by (2-methylbutyryl) shikonin, a naturally occurring naphthoquinone, potentiates dacarbazine anti-melanoma efficacy via ROS-mediated apoptotic pathway. Pharmacol Res Mod Chin Med. 2025;16:100651. [CrossRef]
- Todorovic Z, Milovanovic J, Arsenijevic D, Vukovic N, Vukic M, Arsenijevic A, Djurdjevic P, Milovanovic M, Arsenijevic N. Shikonin Derivatives from Onsoma visianii Decrease Expression of Phosphorylated STAT3 in Leukemia Cells and Exert Antitumor Activity. Nutrients. 2021;13(4):1147. [CrossRef]
- Fan Y, Jin S, He J, Shao Z, Yan J, Feng T, Li H. Effect of β,β-Dimethylacrylshikonin on Inhibition of Human Colorectal Cancer Cell Growth in Vitro and in Vivo. Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13(7):9184–98. [CrossRef]
- Shen ZJ, Zhang YY, Feng YY, Ji SJ, Yu J, Zhou XW, Chen J, Xu Y, Zhang LM. β,β-Dimethylacrylshikonin exerts antitumor activity via Notch-1 signaling pathway in vitro and in vivo. Biochem Pharmacol. 2012;84(4):507–12. [CrossRef]
- Hasenoehrl C, Schwach G, Ghaffari-Tabrizi-Wizsy N, Fuchs R, Kretschmer N, Bauer R, Pfragner R. Anti-tumor effects of shikonin derivatives on human medullary thyroid carcinoma cells. Endocr Connect. 2017;6(2):53–62. [CrossRef]
- Shao KY, Luo SD, Huang EY, Chang TM, Botcha L, Sehar M, Liu JF, Chuang PK. Acetylshikonin induces cell necroptosis via mediating mitochondrial function and oxidative stress-regulated signaling in human Oral Cancer cells. Bioorganic Chem. 2025;159:108396. [CrossRef]
- Tang Y, Wang Y, Wang X, Zhao Z, Cai H, Xie M, Jiang X, Zhang L, Cheng J, Yang L, Wang L, Zhao C, Huang X. Acetylshikonin exerts anti-tumor effects on non-small cell lung cancer through dual inhibition of STAT3 and EGFR. Phytomedicine. 2022;101:154109. [CrossRef]
- Lin H, Ma X, Yang X, Chen Q, Wen Z, Yang M, Fu J, Yin T, Lu G, Qi J, Han H, Yang Y. Natural shikonin and acetyl-shikonin improve intestinal microbial and protein composition to alleviate colitis-associated colorectal cancer. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022;111:109097. [CrossRef]
- Zeng Y, Zhang H, Zhu M, Pu Q, Li J, Hu X. β-Hydroxyisovaleryl-Shikonin Exerts an Antitumor Effect on Pancreatic Cancer Through the PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway. Front Oncol. 2022;12:904258. [CrossRef]
- Lu D, Qian J, Li W, Feng Q, Pan S, Zhang S. β-hydroxyisovaleryl-shikonin induces human cervical cancer cell apoptosis via PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling. Oncol Lett. 2015;10(6):3434–42. [CrossRef]
- Lee CY, Chen PN, Kao SH, Wu HH, Hsiao YH, Huang TY, Wang PH, Yang SF. Deoxyshikonin triggers apoptosis in cervical cancer cells through p38 MAPK-mediated caspase activation. Environ Toxicol. 2024;39(9):4308–17. [CrossRef]
- Park DG, Kim DJ, Woo BH, Kim HJ, Choi YW, Park HR. Isobutyrylshikonin has a potentially stronger cytotoxic effect in oral cancer cells than its analogue shikonin in vitro. Arch Oral Biol. 2020;116:104774. [CrossRef]
- Li M, Chen X, Hu S, Wang R, Peng X, Bai X. Determination of blood concentrations of main active compounds in Zi-Cao-Cheng-Qi decoction and their total plasma protein binding rates based on hollow fiber liquid phase microextraction coupled with high performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr B. 2018;1072:355–61. [CrossRef]
- Shao YY, Yin Y, Lian BP, Leng JF, Xia YZ, Kong LY. Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel shikonin-benzo[b]furan derivatives as tubulin polymerization inhibitors targeting the colchicine binding site. Eur J Med Chem. 2020;190:112105. [CrossRef]
- Iranzadeh S, Dalil D, Kohansal S, Isakhani M. Shikonin in breast cancer treatment: a comprehensive review of molecular pathways and innovative strategies. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2024;76(8):967–82. [CrossRef]
- Huang CS, Chen HW, Lin TY, Lin AH, Lii CK. Shikonin upregulates the expression of drug-metabolizing enzymes and drug transporters in primary rat hepatocytes. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018;216:18–25. [CrossRef]
- Li H, Luo S, Zhou T. Studies on in vitro metabolism of shikonin. Phytotherapy Research. 1999;13(3):236–8. [CrossRef]
- Los M, Mozoluk M, Ferrari D, Stepczynska A, Stroh C, Renz A, Herceg Z, Wang ZQ, Schulze-Osthoff K. Activation and caspase-mediated inhibition of PARP: a molecular switch between fibroblast necrosis and apoptosis in death receptor signaling. Mol Biol Cell. 2002;13(3):978–88. [CrossRef]
- Kim JW, Kim K, Kang K, Joe CO. Inhibition of homodimerization of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase by its C-terminal cleavage products produced during apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 2000 Mar 17;275(11):8121–5. [CrossRef]
- Chaitanya GV, Alexander JS, Babu PP. PARP-1 cleavage fragments: signatures of cell-death proteases in neurodegeneration. Cell Commun Signal. 2010;8:31. [CrossRef]
- Alam MM, Kariya R, Boonnate P, Kawaguchi A, Okada S. Induction of apoptosis by shikonin through ROS-mediated intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic pathways in primary effusion lymphoma. Transl Oncol. 2021;14(3):101006. [CrossRef]
- Shilnikova K, Piao MJ, Kang KA, Fernando PDSM, Herath HMUL, Cho SJ, Hyun JW. Natural compound shikonin induces apoptosis and attenuates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in radiation-resistant human colon cancer cells. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2022;30(2):137–44. [CrossRef]
- Lohberger B, Glänzer D, Kaltenegger H, Eck N, Leithner A, Bauer R, Kreutz D. Shikonin derivatives cause apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in human chondrosarcoma cells via death receptors and MAPK regulation. BMC Cancer. 2022;22:758. [CrossRef]
- Tsai MF, Chen SM, Ong AZ, Chung YH, Chen PN, Hsieh YH, Hsieh YS. Shikonin induced programmed cell death through generation of reactive oxygen species in renal cancer cells. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021;10(11):1831. [CrossRef]
- Boonnate P, Kariya R, Okada S. Shikonin induces ROS-dependent apoptosis via mitochondria depolarization and ER stress in adult T cell leukemia/lymphoma. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023;12(4):864. [CrossRef]
- Lee JH, Han SH, Kim YM, Kim SH, Yoo ES, Woo JS, Kim HJ, Baek NI, Lee SH, Lee CW, Kim KH. Shikonin inhibits proliferation of melanoma cells by MAPK pathway-mediated induction of apoptosis. Biosci Rep. 2021;41(1):BSR20203834. [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, P. ROS mediated apoptotic pathways in primary effusion lymphoma: Comment on induction of apoptosis by shikonin through ROS-mediated intrinsic and extrinsic pathways in primary effusion lymphoma. Transl Oncol. 2021;14(7):101061. [CrossRef]
- Zhang N, Peng F, Wang Y, Yang L, Wu F, Wang X, Ye C, Han B, He G. Shikonin induces colorectal carcinoma cell apoptosis and autophagy by targeting galectin-1/JNK signaling axis. Int J Biol Sci. 2020;16(1):147–61. [CrossRef]
- Király J, Szabó E, Fodor P, Fejes Z, Nagy B, Juhász É, Földesi I, Gubán B, Jóna Á, Póka R, Kiss I. Shikonin causes an apoptotic effect on human kidney cancer cells through Ras/MAPK and PI3K/AKT pathways. Molecules. 2023;28(18):6725. [CrossRef]
- Wang F, Mayca Pozo F, Tian D, Geng X, Yao X, Zhang Y, Guo M. Shikonin inhibits cancer through p21 upregulation and apoptosis induction. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:861. [CrossRef]
- Qi H, Zhang X, Liu H, Han M, Tang X, Qu S, Li S, Li J, Song G, Li B. Shikonin induced apoptosis mediated by endoplasmic reticulum stress in colorectal cancer cells. J Cancer. 2022;13(1):243–52. [CrossRef]
- Shan ZL, Zhong L, Xiao CL, Gan LG, Xu T, Song H, Zhou J, Chen J, Liu B, Xu J. Shikonin suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis in human leukemia NB4 cells through modulation of MAPKs and c-Myc. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16(3):3055–60. [CrossRef]
- Ma X, Yu M, Hao C, Yang W. Shikonin induces tumor apoptosis in glioma cells via endoplasmic reticulum stress, and Bax/Bak mediated mitochondrial outer membrane permeability. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020;263:113059. [CrossRef]
- Zhang J, Guo J, Gu B, Wang F, Li Y, Shang L, Sun S, Zhao Y, Zhao Z. Shikonin induces autophagy and apoptosis in esophageal cancer EC9706 cells by regulating the AMPK/mTOR/ULK axis. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2024;2024:7752299. [CrossRef]
- Ashkenazi, A. Targeting the extrinsic apoptotic pathway in cancer: lessons learned and future directions. J Clin Invest. 2015 Feb 2;125(2):487–9. [CrossRef]
- Ashkenazi, A. Targeting the extrinsic apoptosis pathway in cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2008;19(3–4):325–31. [CrossRef]
- Liu C, Xuan LQ, Li K, Feng Z, Lv C, Li XJ, Zhang J, Zhao Z, Wu Q. Shikonin inhibits cholangiocarcinoma cell line QBC939 by regulating apoptosis, proliferation, and invasion. Cell Transplant. 2021;30:0963689720979162. [CrossRef]
- Chang YH, Lin YJ, Huang CY, Harnod T, Ding DC. Shikonin impedes type 2 ovarian cancer progression via FasL/caspase-8 and miR-874-3p/XIAP axis and prohibits the properties of stemness. Am J Cancer Res. 2022;12(10):4584–601. PMID:36381841.
- Zhang J, Shang L, Jiang W, Wu W. Shikonin induces apoptosis and autophagy via downregulation of pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase 1 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Bioengineered. 2022;13(3):7904–18. [CrossRef]
- Wang H, Liu Z, Li X, Zhao R, Pu Y, Wu H, Liu J, Wang F. Shikonin causes apoptosis by disrupting intracellular calcium homeostasis and mitochondrial function in human hepatoma cells. Exp Ther Med. 2018;15(2):1484–92. [CrossRef]
- Zhang H, Chen Z, Zhao X, Huo Q, Cheng X. Shikonin induces hepatocellular carcinoma cell apoptosis by suppressing PKM2/PHD3/HIF-1α signaling pathway. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2023;43(1):92–8. [CrossRef]
- Huang J, Zhao L, Gong C, Wang Y, Qu Y, Ji C, Zhang H, Wang J. Shikonin promotes apoptosis and attenuates migration and invasion of human esophageal cancer cells by inhibiting tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated protein 1 expression and AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021;2021:5386050. [CrossRef]
- Pan J, Li M, Yu F, Zhu F, Wang L, Ning D, Liu Y, Dong X, Zhang Y, Guo J. Up-regulation of p53/miR-628-3p pathway, a novel mechanism of shikonin on inhibiting proliferation and inducing apoptosis of A549 and PC-9 non–small cell lung cancer cell lines. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:766165. [CrossRef]
- Wang H, Zuo J. Shikonin inhibits non-small-cell lung cancer H1299 cell growth through survivin signaling pathway. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2021;2021:6435393. [CrossRef]
- Liu X, Yang Y, Tang X, Guo L, Tang X, Zhu T, Zhao L, Liu H. Shikonin mediates apoptosis through G protein-coupled estrogen receptor of ovarian cancer cells. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022;2022:6517732. [CrossRef]
- Cao HH, Liu DY, Lai YC, Chen YY, Yu LZ, Shao M, Lin ZX. Inhibition of the STAT3 signaling pathway contributes to the anti-melanoma activities of shikonin. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:748. [CrossRef]
- Shi W, Men L, Pi X, Jiang T, Peng D, Huo S, Huang Y, Zhang Y, Zhang H, Zhang L, Sun M, Tang Y, Zhao C. Shikonin suppresses colon cancer cell growth and exerts synergistic effects by regulating ADAM17 and the IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathway. Int J Oncol. 2021;59(6):99. [CrossRef]
- Cao S, Li H, Ye X, Xing X, Xie Y, Zeng X, Zhou L, Wang J, Xu Y, Hu H, Wu B, Yu Y. Shikonin induces the apoptosis and pyroptosis of EGFR-T790M-mutant drug-resistant non-small cell lung cancer cells via the degradation of cyclooxygenase-2. Eur J Med Res. 2024;29:611. [CrossRef]
- Lin H, Han H, Yang M, Wen Z, Chen Q, Ma Y, Li Y, Liu J, Sun X, Wang L, Xu Z. PKM2/PDK1 dual-targeted shikonin derivatives restore the sensitivity of EGFR-mutated NSCLC cells to gefitinib by remodeling glucose metabolism. Eur J Med Chem. 2023;249:115166. [CrossRef]
- Zhang Z, Shen C, Zhou F, Zhang Y. Shikonin potentiates therapeutic efficacy of oxaliplatin through reactive oxygen species-mediated intrinsic apoptosis and endoplasmic reticulum stress in oxaliplatin-resistant colorectal cancer cells. Drug Dev Res. 2023;84(3):542–55. [CrossRef]
- Piao MJ, Han X, Kang KA, Fernando PDSM, Herath HMUL, Hyun JW. The endoplasmic reticulum stress response mediates shikonin-induced apoptosis of 5-fluorouracil–resistant colorectal cancer cells. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2022;30(3):265–72. [CrossRef]
- Ma Y, Sun Y, Tu Q, Lin F, Mei F, Chen Q, Li X, Zhou Y, Zhao H. Novel phenoxyacetic acid (4-aminophenoacetic acid) shikonin ester kills KRAS mutant colon cancer cells via targeting the Akt allosteric site. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2025;105(5):70125. [CrossRef]
- Stallinger A, Kretschmer N, Kleinegger F, Brvar L, Liegl-Atzwanger B, Prokesch A, Rinner B, Kiesslich T, Heffeter P, Berger W, Lackner A, Dolznig H, Hohenegger M, Knausz H, Raml R, Ghaffari-Tabrizi-Wizsy N, Mühleisen A, Jakab M, Schicho R, Hufner A. β,β-Dimethylacrylshikonin induces apoptosis in melanoma cell lines by NOXA upregulation. J Nat Prod. 2020;83(2):305-315. [CrossRef]
- Chen Q, Han H, Lin F, Yang L, Feng L, Lai X, Xu L, Wang C, Ma Y, Sun Y, Zhang Y, Wen Z, Han S, Li P. Novel shikonin derivatives suppress cell proliferation, migration and induce apoptosis in human triple-negative breast cancer cells via regulating PDK1/PDHC axis. Life Sci. 2022;310:121077. [CrossRef]
- Han H, Wen Z, Yang M, Wang C, Ma Y, Chen Q, Xu L, Li P, Zhang Y, Sun Y, Feng L. Shikonin derivative suppresses colorectal cancer cell growth via reactive oxygen species-mediated mitochondrial apoptosis and PI3K/AKT pathway. Chem Biodivers. 2025;22(4):e202403291. [CrossRef]
- Hao G, Zhai J, Jiang H, Zhang Y, Wu M, Qiu Y, Zhu X, Zhao J, Xu W. Acetylshikonin induces apoptosis of human leukemia cell line K562 by inducing S phase cell cycle arrest, modulating ROS accumulation, depleting Bcr-Abl and blocking NF-κB signaling. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;122:109677. [CrossRef]
- Durchschein C, Hufner A, Rinner B, Stallinger A, Deutsch A, Lohberger B, Kretschmer N. Synthesis of novel shikonin derivatives and pharmacological effects of cyclopropylacetylshikonin on melanoma cells. Molecules. 2018;23(11):2820. [CrossRef]
- Jahanafrooz Z, Stallinger A, Anders I, Kleinegger F, Lohberger B, Durchschein C, Kretschmer N. Influence of silibinin and β,β-dimethylacrylshikonin on chordoma cells. Phytomedicine. 2018;49:32-40. [CrossRef]
- Otto T, Sicinski P. Cell cycle proteins as promising targets in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2017;17(2):93-115. [CrossRef]
- Malumbres M, Barbacid M. Cell cycle, CDKs and cancer: a changing paradigm. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9(3):153-166. [CrossRef]
- Massagué, J. G1 cell-cycle control and cancer. Nature. 2004;432(7015):298-306. [CrossRef]
- Vermeulen K, Van Bockstaele DR, Berneman ZN. The cell cycle: a review of regulation, deregulation and therapeutic targets in cancer. Cell Prolif. 2003;36(3):131-149. [CrossRef]
- Markowitsch SD, Juetter KM, Schupp P, Hauschulte K, Vakhrusheva O, Slade KS, Thomas A, Kitanovic J, Sommer AK, Eckstein N, Gandesiri M, Bernhart SH, Kalbacher H, Wehland M, Grimm D, Efferth T, Barreto G. Shikonin reduces growth of docetaxel-resistant prostate cancer cells mainly through necroptosis. Cancers (Basel). 2021;13(4):882. [CrossRef]
- Markowitsch SD, Vakhrusheva O, Schupp P, Akele Y, Kitanovic J, Slade KS, Thomas A, Juetter KM, Efferth T, Barreto G. Shikonin inhibits cell growth of sunitinib-resistant renal cell carcinoma by activating the necrosome complex and inhibiting the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Cancers (Basel). 2022;14(5):1114. [CrossRef]
- Cha HS, Lee HK, Park SH, Nam MJ. Acetylshikonin induces apoptosis of human osteosarcoma U2OS cells by triggering ROS-dependent multiple signal pathways. Toxicology in Vitro. 2023;86:105521. [CrossRef]
- Bhat AM, Bhat IA, Malik MA, Kaiser P, Ramajayan P, Rayees SR, Rather RA, Hamid A, Sharma PR, Ahmad SM, Rather MA. Inhibition of IKK complex by (2-methylbutyryl) shikonin, a naturally occurring naphthoquinone, abrogates melanoma growth and progression via modulation of the IKK/NF-κB/EMT signaling axis. International Immunopharmacology. 2025;148:114026. [CrossRef]
- Huang Y, Hong W, Wei X. The molecular mechanisms and therapeutic strategies of EMT in tumor progression and metastasis. Journal of Hematology & Oncology. 2022;15:129. [CrossRef]
- Bao C, Liu T, Qian L, Xiao C, Zhou X, Ai H, Wang Y, Wu B, Shi S, Wang T. Shikonin inhibits migration and invasion of triple-negative breast cancer cells by suppressing epithelial–mesenchymal transition via miR-17-5p/PTEN/Akt pathway. Journal of Cancer. 2021;12(1):76–88. [CrossRef]
- Mustafa S, Koran S, AlOmair L. Insights into the role of matrix metalloproteinases in cancer and its various therapeutic aspects: a review. Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences. 2022;9:896099. [CrossRef]
- Chen Y, Zheng L, Liu J, Zhou Z, Cao X, Lv X, Chen F. Shikonin inhibits prostate cancer cells metastasis by reducing matrix metalloproteinase-2/-9 expression via AKT/mTOR and ROS/ERK1/2 pathways. International Immunopharmacology. 2014;21(2):447–455. [CrossRef]
- Zhang J, Zhou J, Xiao S. Shikonin inhibits growth, invasion and glycolysis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells through inactivating the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT signal pathway. Anticancer Drugs. 2020;31(9):932–941. [CrossRef]
- Mo L, Xu L, Jia M, Su B, Hu Y, Hu Z, Hu S, Zhao H, Lin J, Wu X, Ma Y. Shikonin suppresses the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by downregulating NHE1 in bladder cancer cells. Journal of Cancer. 2021;12(22):6814–6824. [CrossRef]
- Tabari AR, Gavidel P, Sabouni F, Gardaneh M. Synergy between sublethal doses of shikonin and metformin fully inhibits breast cancer cell migration and reverses epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Mol Biol Rep. 2022;49(6):4307–4319. [CrossRef]
- Zhang F, Liu Z, Wang Y, Zuo L, Xu S, Liu Y, Chen J, Zhou J, Wang Y. Shikonin inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition in glioblastoma cells by upregulating p53 and promoting miR-361-5p level to suppress ZEB1 expression. BMC Neurosci. 2025;26:37. [CrossRef]
- Lu J, Fei F, Wu C, Mei J, Xu J, Lu P. ZEB1: Catalyst of immune escape during tumor metastasis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;153:113490. [CrossRef]
- Tong X, Tang R, Xiao M, Xu J, Wang W, Zhang B, Li L, Liu J, Liu Q, Guo J, Zhang Y, Chen Y, Sun Y, Gao Y, Liu Z. Targeting cell death pathways for cancer therapy: recent developments in necroptosis, pyroptosis, ferroptosis, and cuproptosis research. J Hematol Oncol. 2022;15:174. [CrossRef]
- Guo Z, Liu Y, Chen D, Sun Y, Li D, Meng Y, Zhang H, Xie J. Targeting regulated cell death: Apoptosis, necroptosis, pyroptosis, ferroptosis, and cuproptosis in anticancer immunity. J Transl Int Med. 2025;13(1):10–32. [CrossRef]
- Ai Y, Meng Y, Yan B, Zhou Q, Wang X. The biochemical pathways of apoptotic, necroptotic, pyroptotic, and ferroptotic cell death. Mol Cell. 2024;84(1):170–179. [CrossRef]
- Huang X, Chen Z, Ni F, Ye X, Qian W. Shikonin overcomes drug resistance and induces necroptosis by regulating the miR-92a-1-5p/MLKL axis in chronic myeloid leukemia. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(17):17662–17680. [CrossRef]
- Lu B, Gong X, Wang ZQ, Ding Y, Wang C, Luo TF, Li C, Liu J. Shikonin induces glioma cell necroptosis in vitro by ROS overproduction and promoting RIP1/RIP3 necrosome formation. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2017;38(11):1543–1553. [CrossRef]
- Qin X, Zhang L, Liu J, Lu Y, Zhou F, Jin F. Shikonin induces glioma necroptosis, stemness decline, and impedes (immuno)proteasome activity. Stem Cells Int. 2024;2024:1348269. [CrossRef]
- Warnes, G. Flow cytometric detection of hyper-polarized mitochondria in regulated and accidental cell death processes. Apoptosis. 2020;25(7):548–557. [CrossRef]
- Chen C, Xiao W, Huang L, Yu G, Ni J, Yang L, Li X, Xu H, Zou C, Liu Y. Shikonin induces apoptosis and necroptosis in pancreatic cancer via regulating the expression of RIP1/RIP3 and synergizes the activity of gemcitabine. Am J Transl Res. 2017;9(12):5507–5517. [PubMed]
- Zhang Y, Sun S, Xu W, Yang R, Yang Y, Guo J, Dong Z, Zhou F, Zhang X, Wang H. Thioredoxin reductase 1 inhibitor shikonin promotes cell necroptosis via SecTRAPs generation and oxygen-coupled redox cycling. Free Radic Biol Med. 2022;180:52–62. [CrossRef]
- Li W, Fu H, Fang L, Chai H, Gao T, Chen Z, Wu J, Liu J, Zhou Y. Shikonin induces ferroptosis in multiple myeloma via GOT1-mediated ferritinophagy. Front Oncol. 2022;12:1025067. [CrossRef]
- Qian X, Zhu L, Xu M, Liu H, Yu X, Shao Q, Song H, Wang X, Chen Y. Shikonin suppresses small cell lung cancer growth via inducing ATF3-mediated ferroptosis to promote ROS accumulation. Chem Biol Interact. 2023;382:110588. [CrossRef]
- Lu C, Zhang Z, Fan Y, Wang X, Qian J, Bian Z. Shikonin induces ferroptosis in osteosarcomas through the mitochondrial ROS-regulated HIF-1α/HO-1 axis. Phytomedicine. 2024;135:156139. [CrossRef]
- Ju X, Zhang H, Wang J, Sun Z, Guo L, Wang Q. Shikonin triggers GSDME-mediated pyroptosis in tumours by regulating autophagy via the ROS-MAPK14/p38α axis. Phytomedicine. 2023;109:154596. [CrossRef]
- Finley LWS. What is cancer metabolism? Cell. 2023;186(8):1670–1688. [CrossRef]
- DeBerardinis RJ, Chandel NS. We need to talk about the Warburg effect. Nat Metab. 2020;2(2):127–129. [CrossRef]
- Long L, Xiong W, Lin F, Hou J, Chen G, Peng T, Li Q, Zhao Y, Zhang Y. Regulating lactate-related immunometabolism and EMT reversal for colorectal cancer liver metastases using shikonin targeted delivery. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023;42:117. [CrossRef]
- Zhang Z, Deng X, Liu Y, Liu Y, Sun L, Chen F. PKM2, function and expression and regulation. Cell Biosci. 2019;9:52. [CrossRef]
- Huang B, Wang Q, Jiang L, Lu S, Li C, Xu C, Zhang T, Liu Z. Shikonin ameliorated mice colitis by inhibiting dimerization and tetramerization of PKM2 in macrophages. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:926945. [CrossRef]
- Zahra K, Dey T, Ashish A, Mishra SP, Pandey U. Pyruvate kinase M2 and cancer: the role of PKM2 in promoting tumorigenesis. Front Oncol. 2020;10:159. [CrossRef]
- Zhou Q, Yin Y, Yu M, Gao D, Sun J, Yang Z, Han X, Chen H, Li W, Xu F, Pan Y. GTPBP4 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression and metastasis via the PKM2 dependent glucose metabolism. Redox Biol. 2022;56:102458. [CrossRef]
- Dai Y, Liu Y, Li J, Jin M, Yang H, Huang G. Shikonin inhibited glycolysis and sensitized cisplatin treatment in non-small cell lung cancer cells via the exosomal pyruvate kinase M2 pathway. Bioengineered. 2022;13(5):13906–13918. [CrossRef]
- Zhang J, Ouyang F, Gao A, Zeng T, Li M, Li H, Xie L, Wang Y, Zhou X. ESM1 enhances fatty acid synthesis and vascular mimicry in ovarian cancer by utilizing the PKM2-dependent Warburg effect within the hypoxic tumor microenvironment. Mol Cancer. 2024;23:94. [CrossRef]
- Sha L, Lv Z, Liu Y, Zhang Y, Sui X, Wang T, Wang G, Sun H. Shikonin inhibits the Warburg effect, cell proliferation, invasion and migration by downregulating PFKFB2 expression in lung cancer. Mol Med Rep. 2021;24(2):560. [CrossRef]
- Sun Y, Liu Y, Ma X, Hu H. The Influence of Cell Cycle Regulation on Chemotherapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(13):6923. [CrossRef]
- Rihan M, Sharma SS. Inhibition of Pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2) by shikonin attenuates isoproterenol-induced acute myocardial infarction via reduction in inflammation, hypoxia, apoptosis, and fibrosis. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024;397(1):145–159. [CrossRef]
- Chen X, Chen S, Yu D. Protein kinase function of pyruvate kinase M2 and cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2020;20(1):523. [CrossRef]
- Ni M, Zhou J, Zhu Z, Xu Q, Yin Z, Wang Y, Liu X, Zhang H. Shikonin and cisplatin synergistically overcome cisplatin resistance of ovarian cancer by inducing ferroptosis via upregulation of HMOX1 to promote Fe²⁺ accumulation. Phytomedicine. 2023;112:154701. [CrossRef]
- Chen X, Kang R, Kroemer G, Tang D. A narrative review of mechanisms of ferroptosis in cancer: new challenges and opportunities. Front Oncol. 2021;11:743940. [CrossRef]
- Yeudall S, Upchurch CM, Leitinger N. The clinical relevance of heme detoxification by the macrophage heme oxygenase system. Front Immunol. 2024;15:1379967. [CrossRef]
- Kwak SY, Jeong YK, Kim BY, Lee JY, Ahn HJ, Jeong JH, Kim HR, Kim IK. β,β-Dimethylacrylshikonin sensitizes human colon cancer cells to ionizing radiation through the upregulation of reactive oxygen species. Oncol Lett. 2014;7(6):1812–1818. [CrossRef]
- Liu Z, Pan S, Xu F, Wang Z, Zhao C, Xu X, Li J, Chen L, Wang H, Zhang L. Revealing the fundamental role of MoO₂ in promoting efficient and stable activation of persulfate by iron–carbon based catalysts: efficient Fe²⁺/Fe³⁺ cycling to generate reactive species. Water Res. 2022;225:119142. [CrossRef]
- Endale HT, Tesfaye W, Mengstie TA. ROS induced lipid peroxidation and their role in ferroptosis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023;11:1226044. [CrossRef]
- Zheng Y, Sun J, Luo Z, Li Y, Huang Y. Emerging mechanisms of lipid peroxidation in regulated cell death and its physiological implications. Cell Death Dis. 2024;15(11):859. [CrossRef]
- Du W, Hao X, Yuan Z, Wang Y, Zhang X, Liu J. Shikonin potentiates paclitaxel antitumor efficacy in esophageal cancer cells via the apoptotic pathway. Oncol Lett. 2019;18(3):3195–3201. [CrossRef]
- Wang H, Guo M, Wei H, Chen Y. Targeting p53 pathways: mechanisms, structures and advances in therapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023;8:92. [CrossRef]
- Ma J, Zhao J, Zhang C, Tan J, Cheng A, Niu Z, Wu H, Li F, Zhou Q, Han J. Cleavage of CAD by caspase-3 determines the cancer cell fate during chemotherapy. Nat Commun. 2025;16:5006. [CrossRef]
- Boudreau MW, Peh J, Hergenrother PJ. Procaspase-3 overexpression in cancer: a paradoxical observation with therapeutic potential. ACS Chem Biol. 2019;14(11):2335–2348. [CrossRef]
- Jiang M, Qi L, Li L, Li Y. The caspase-3/GSDME signal pathway as a switch between apoptosis and pyroptosis in cancer. Cell Death Discov. 2020;6:112. [CrossRef]
- Maji S, Panda S, Samal SK, Shriwas O, Rath R, Pellecchia M, Emdad L, Das SK, Fisher PB, Dash R. Bcl-2 antiapoptotic family proteins and chemoresistance in cancer. Adv Cancer Res. 2018;137:37–75. [CrossRef]
- Yuan B, Hao J, Zhang Q, Wang Y, Zhu Y. Role of Bcl-2 on drug resistance in breast cancer polyploidy-induced spindle poisons. Oncol Lett. 2020;19(3):1701–1710. [CrossRef]
- Ji W, Sun X, Gao Y, Lu M, Zhu L, Wang D, Xiang D, Zhang G, Wang H, Shao J. Natural compound shikonin is a novel PAK1 inhibitor and enhances efficacy of chemotherapy against pancreatic cancer cells. Molecules. 2022;27(9):2747. [CrossRef]
- Wang J, Zhu Y, Chen J, Yang Y, Zhu L, Zhao J, Xu N, Huang M, Qian J, Zhang S. Identification of a novel PAK1 inhibitor to treat pancreatic cancer. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2020;10(4):603–614. [CrossRef]
- Grebeňová D, Holoubek A, Röselová P, Obr A, Brodská B, Kuželová K. PAK1, PAK1Δ15, and PAK2: similarities, differences and mutual interactions. Sci Rep. 2019;9:17171. [CrossRef]
- Xiang Y, Liu X, Wang Y, Zheng D, Meng Q, Jiang L, Wu S, Yu H, Li Z. Mechanisms of resistance to targeted therapy and immunotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer: promising strategies to overcoming challenges. Front Immunol. 2024;15:1366260. [CrossRef]
- Sun R, Hou Z, Zhang Y, Jiang B. Drug resistance mechanisms and progress in the treatment of EGFR-mutated lung adenocarcinoma. Oncol Lett. 2022;24(5):408. [CrossRef]
- Lin HY, Han HW, Wang YS, He DL, Sun WX, Feng L, Yang ZX, Li ZX, Xu WH, Xu XX, Cui RJ. Shikonin and 4-hydroxytamoxifen synergistically inhibit the proliferation of breast cancer cells through activating apoptosis signaling pathway in vitro and in vivo. Chin Med. 2020;15:23. [CrossRef]
- Yang JT, Li ZL, Wu JY, Lu FJ, Chen CH. An oxidative stress mechanism of shikonin in human glioma cells. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(4):e94180. [CrossRef]
- Zhao RZ, Jiang S, Zhang L, Yu ZB. Mitochondrial electron transport chain, ROS generation and uncoupling (Review). Int J Mol Med. 2019;44(1):3–15. [CrossRef]
- Reis Y, Bernardo-Faura M, Richter D, Wolf T, Brors B, Hamacher-Brady A, Brady NR. Multi-parametric analysis and modeling of relationships between mitochondrial morphology and apoptosis. PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e28694. [CrossRef]
- Zhang CH, Wang J, Zhang LX, Lu YH, Ji TH, Xu L, Wang W, Zhang Y. Shikonin reduces tamoxifen resistance through long non-coding RNA uc.57. Oncotarget. 2017;8(51):88658–69. [CrossRef]
- Xue X, Yang YA, Zhang A, Fong K, Kim J, Song B, Li S, Zhao JC, Yu J. LncRNA HOTAIR enhances ER signaling and confers tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. Oncogene. 2016;35(21):2746–55. [CrossRef]
- Loureiro G, Bahia DM, Lee MLM, de Souza MP, Kimura EYS, Rezende DC, Araujo GHR, Gonçalves AC, Faria FC, Borges KS, Lucena-Araujo AR, de Castro FA, Schamber-Reis BL. MAPK/ERK and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways are activated in adolescent and adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2023;6(12):e1912. [CrossRef]
- Rascio F, Spadaccino F, Rocchetti MT, Castellano G, Stallone G, Netti GS, Ranieri E, Gesualdo L, Castellano G. The pathogenic role of PI3K/AKT pathway in cancer onset and drug resistance: an updated review. Cancers (Basel). 2021;13(16):3949. [CrossRef]
- He Y, Sun MM, Zhang GG, Yang J, Chen KS, Xu WW, Li B. Targeting PI3K/Akt signal transduction for cancer therapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021;6:425. [CrossRef]
- Chen Y, Wang Z, Zhang C, Su Y, Zhou T, Hu K. Revealing the mechanism of natural product-induced immunogenic cell death: opening a new chapter in tumor immunotherapy. Front Immunol. 2024;15:1470071. [CrossRef]
- Arimoto K, Miyauchi S, Liu M, Zhang DE. Emerging role of immunogenic cell death in cancer immunotherapy. Front Immunol. 2024;15:1390263. [CrossRef]
- Shahsavari Z, Karami-Tehrani F, Salami S, Ghasemzadeh M. RIP1K and RIP3K provoked by shikonin induce cell cycle arrest in the triple negative breast cancer cell line, MDA-MB-468: necroptosis as a desperate programmed suicide pathway. Tumour Biol. 2016;37(4):4479–91. [CrossRef]
- Grootjans S, Vanden Berghe T, Vandenabeele P. Initiation and execution mechanisms of necroptosis: an overview. Cell Death Differ. 2017;24(7):1184–95. [CrossRef]
- Yao K, Shi Z, Zhao F, Tan C, Zhang Y, Fan H, Li Z, Wang J. RIPK1 in necroptosis and recent progress in related pharmaceutics. Front Immunol. 2025;16:1480027. [CrossRef]
- Galluzzi L, Kepp O, Chan FKM, Kroemer G. Necroptosis: mechanisms and relevance to disease. Annu Rev Pathol. 2017;12:103–30. [CrossRef]
- Chen J, Liu J, Liu X, Wang J, Wang X, Ye X, Zhang Y, Li W. Shikonin improves the effectiveness of PD-1 blockade in colorectal cancer by enhancing immunogenicity via Hsp70 upregulation. Mol Biol Rep. 2024;51(1):86. [CrossRef]
- Zhang B, Qi R. The dual function of HSP70 in immune response and tumor immunity: from molecular regulation to therapeutic innovations. Front Immunol. 2025;16:1587414. [CrossRef]
- Albakova Z, Armeev GA, Kanevskiy LM, Kovalenko EI, Sapozhnikov AM. HSP70 multi-functionality in cancer. Cells. 2020;9(3):587. [CrossRef]
- Shevtsov M, Multhoff G. Heat shock protein–peptide and HSP-based immunotherapies for the treatment of cancer. Front Immunol. 2016;7:171. [CrossRef]
- Lyu C, Stadlbauer B, Wang L, Buchner A, Pohla H. Identification of a novel combination treatment strategy in clear cell renal cell carcinoma stem cells with shikonin and ipilimumab. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1186388. [CrossRef]
- Zhu J, Wang R, Yang C, Shao X, Zhang Y, Hou J, Liu H, Li X. Blocking tumor–platelet crosstalk to prevent tumor metastasis via reprogramming glycolysis using biomimetic membrane-hybridized liposomes. J Control Release. 2024;366:328–41. [CrossRef]
- Zhong W, Shen Z, Wang M, Wang H, Sun Y, Tao X, Xu J, Li Q. Tumor microenvironment-responsive nanomicelle with folic acid modification co-delivery of doxorubicin/shikonin for triple-negative breast cancer treatment. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023;16(3):374. [CrossRef]
- Li J, Zhao M, Liang W, Wu S, Wang Z, Wang D. Codelivery of Shikonin and siTGF-β for enhanced triple negative breast cancer chemo-immunotherapy. J Control Release. 2022;342:308–320. [CrossRef]
- Zhang Y, Ji H, Liu X, Guo R, Zhao Z, Wang J, Song L, Wei Q, Zhou Q, Zhou X. FAM83A promotes the progression and metastasis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma via PKM2-mediated aerobic glycolysis. FASEB J. 2025;39(14):e70796. [CrossRef]
- Wu MH, Chen CM, Chou PY, Wang CC, Tang YJ. Shikonin inhibits oral cancer progression through suppression of metastasis and angiogenesis and induction of autophagy and apoptosis. J Jundishapur Nat Pharm Prod. 2024;19:e151564. [CrossRef]
- Guo XP, Zhang XY, Zhang SD. Clinical trial on the effects of shikonin mixture on later stage lung cancer. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 1991;11(10):598–599, 580. PMID:1831527.
- Zhu H, Jia Z, Li YR, Danelisen I. Molecular mechanisms of action of metformin: latest advances and therapeutic implications. Clin Exp Med. 2023;23(7):2941–2951. [CrossRef]
- Xu XY, Kalambhe DR, Yu Y, Yu LX, Gu ZW, Jin XY, Liu GY, Yang B, Ren YP, Wu Y, Yang L. Co-delivery of shikonin and JQ1 inhibits triple-negative breast tumor progression and lung metastasis through inhibition of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and vasculogenic mimicry. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025. [CrossRef]
- Chen L, Zhao D, Ren X, Ren J, Meng X, Fu C, Zhang J, Wang J, Lu S. Shikonin-loaded hollow Fe-MOF nanoparticles for enhanced microwave thermal therapy. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2023;9(9):5405–5417. [CrossRef]
- Liang J, Tian X, Zhou M, Yan F, Fan J, Qin Y, Yu Z, Zhang J, Zhang Q. Shikonin and chitosan-silver nanoparticles synergize against triple-negative breast cancer through RIPK3-triggered necroptotic immunogenic cell death. Biomaterials. 2024;309:122608. [CrossRef]
| Shikonin derivatives | Chemical Structure | Cancer Types | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5, 8-O-dimethyl acylshikonin | 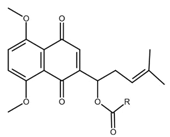 |
Colon cancer Leukaemia Breast cancer |
[37] |
| Shikonin oxime derivative | 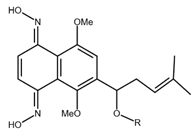 |
Breast cancer Leukaemia Prostate cancer |
[38] |
| α-methylbutyrylshikonin | 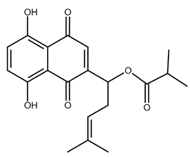 |
Melanoma Leukaemia |
[39,40] |
| β-β-dimethylacrylshikonin | 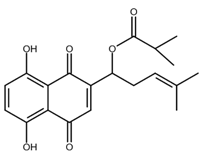 |
Colorectal cancer Gastric cancer Medullary thyroid cancer |
[41,42,43] |
| Acetylshikonin | 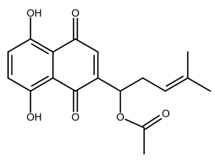 |
Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) Colorectal cancer |
[44,45,46,47] |
| β-hydroxyisovalerylshikonin | 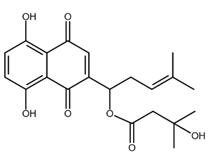 |
Pancreatic cancer Cervical cancer |
[47,48] |
| Deoxyshikonin | 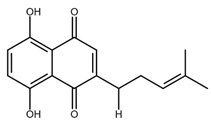 |
Cervical cancer | [49] |
| Isobutyrylshikonin | 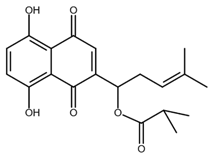 |
Oral cancer | [50] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





