Submitted:
08 August 2025
Posted:
12 August 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
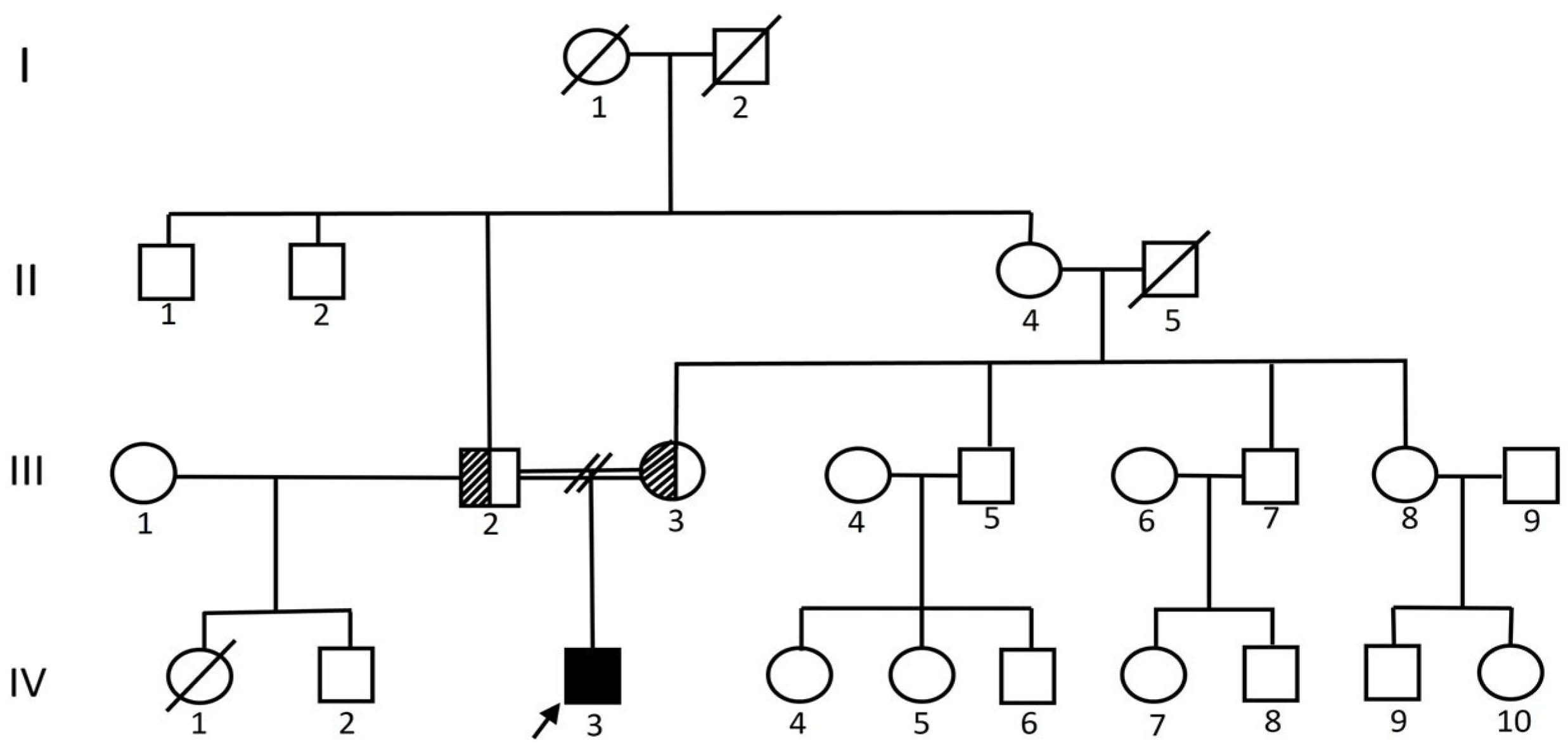
2.1. Clinical Evaluation
2.2. Whole-Exome and Whole Genome Sequencing
2.3. Long-Read Whole-Genome Sequencing
2.4. Variant Calling and Interpretation
2.5. RNA Sequencing
2.6. Detection of Splicing Aberration
2.7. Western Blot
2.8. Fibroblast Culture and Confocal Immunofluorescence Imaging
3. Results
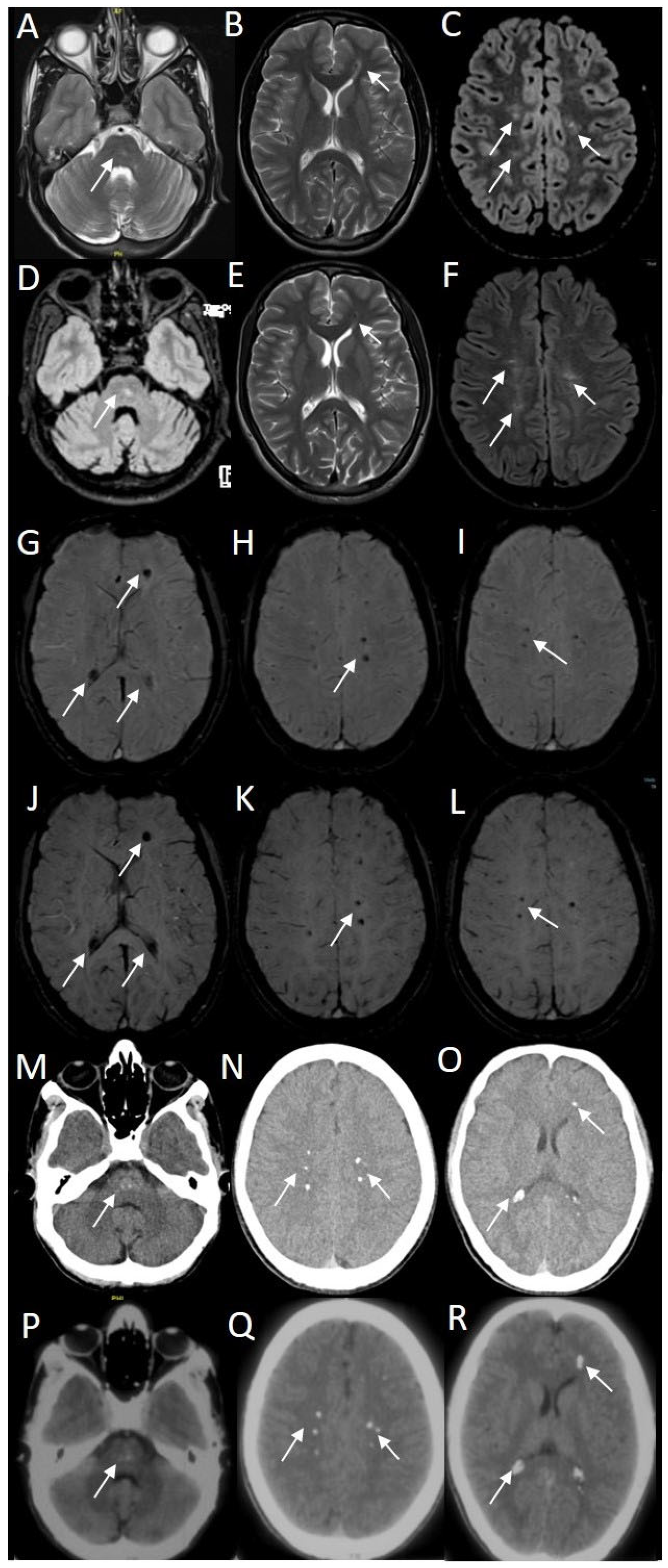
3.1. Clinical Outcome at Follow-Up
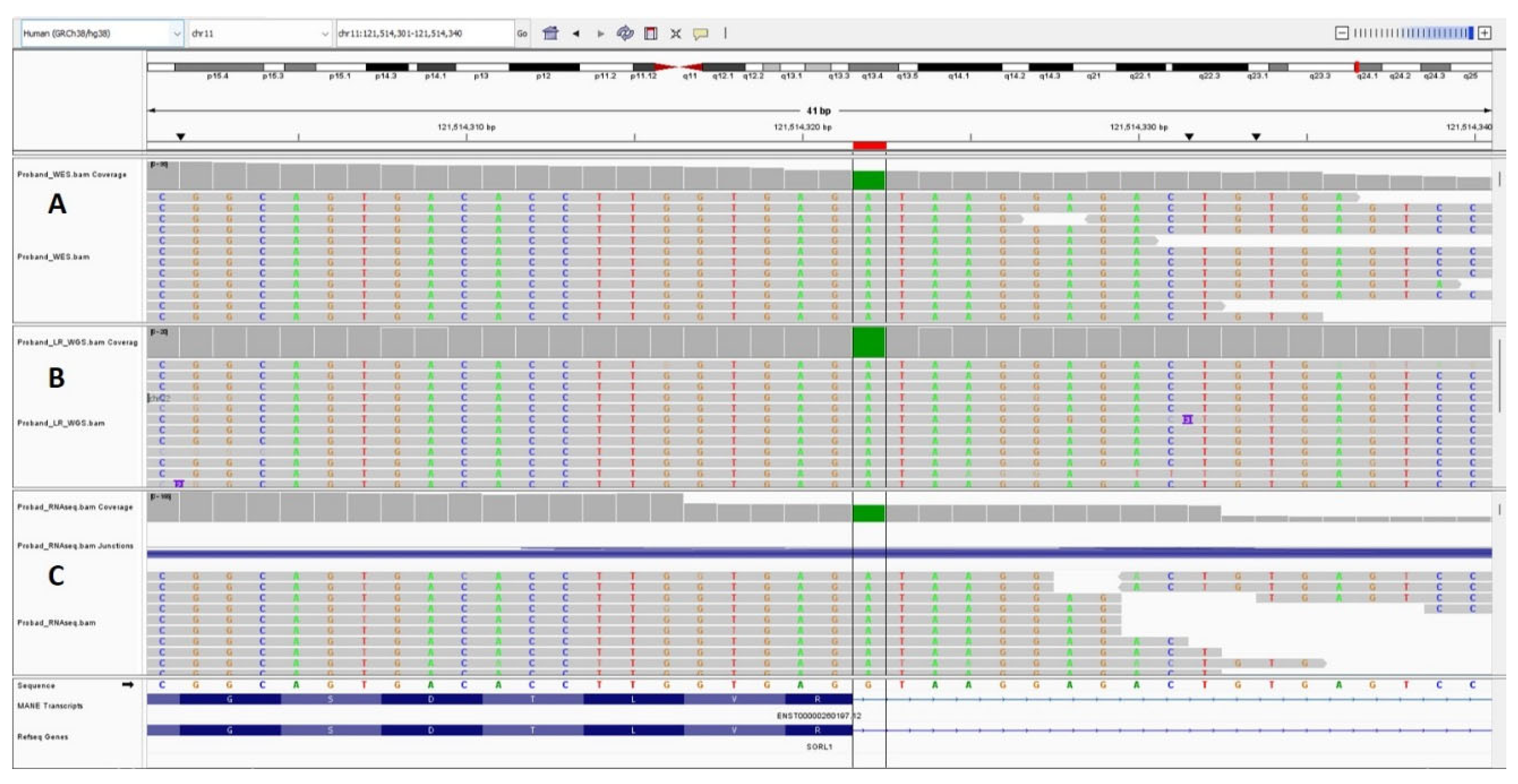
3.2. Results of WES and WGS
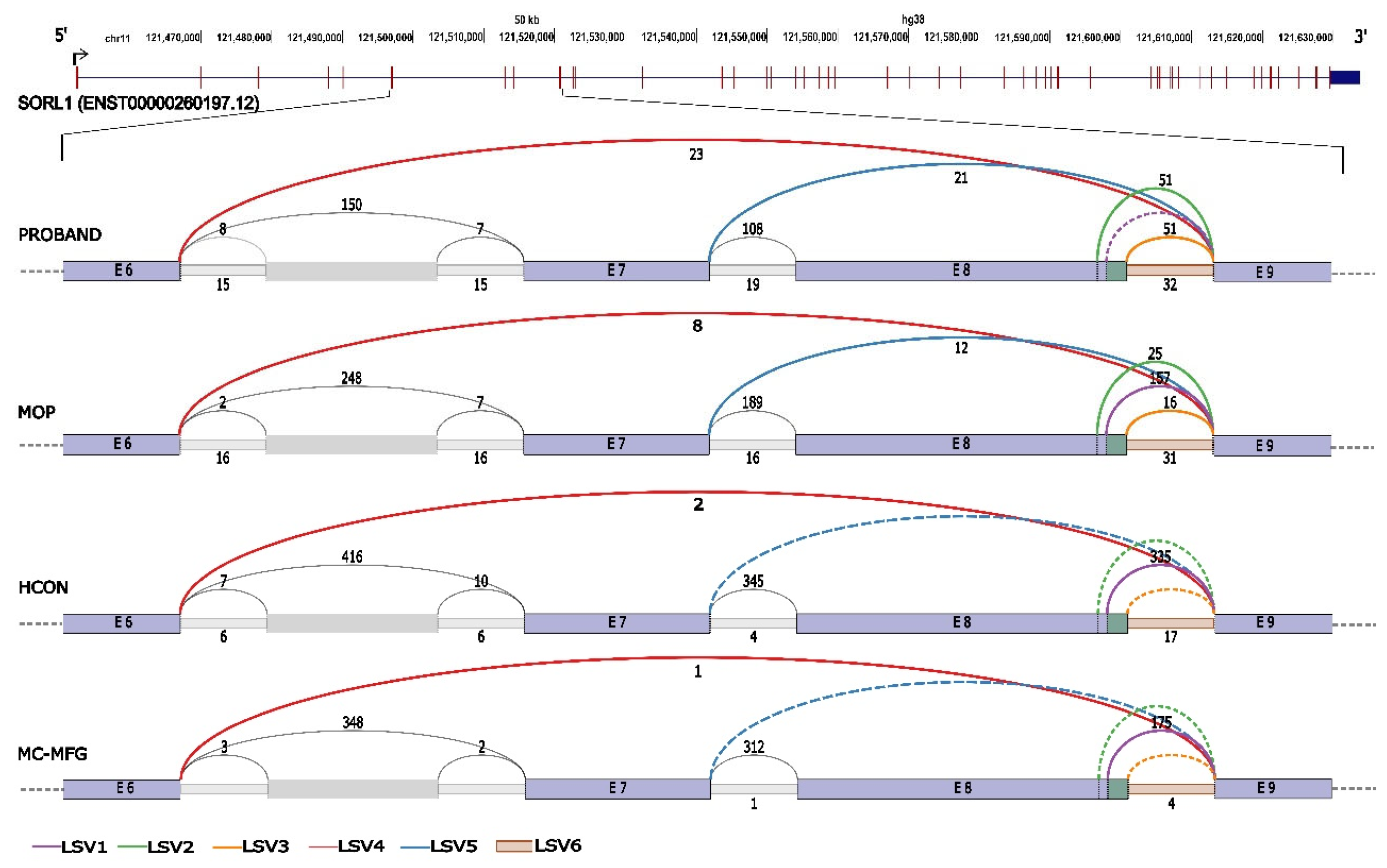
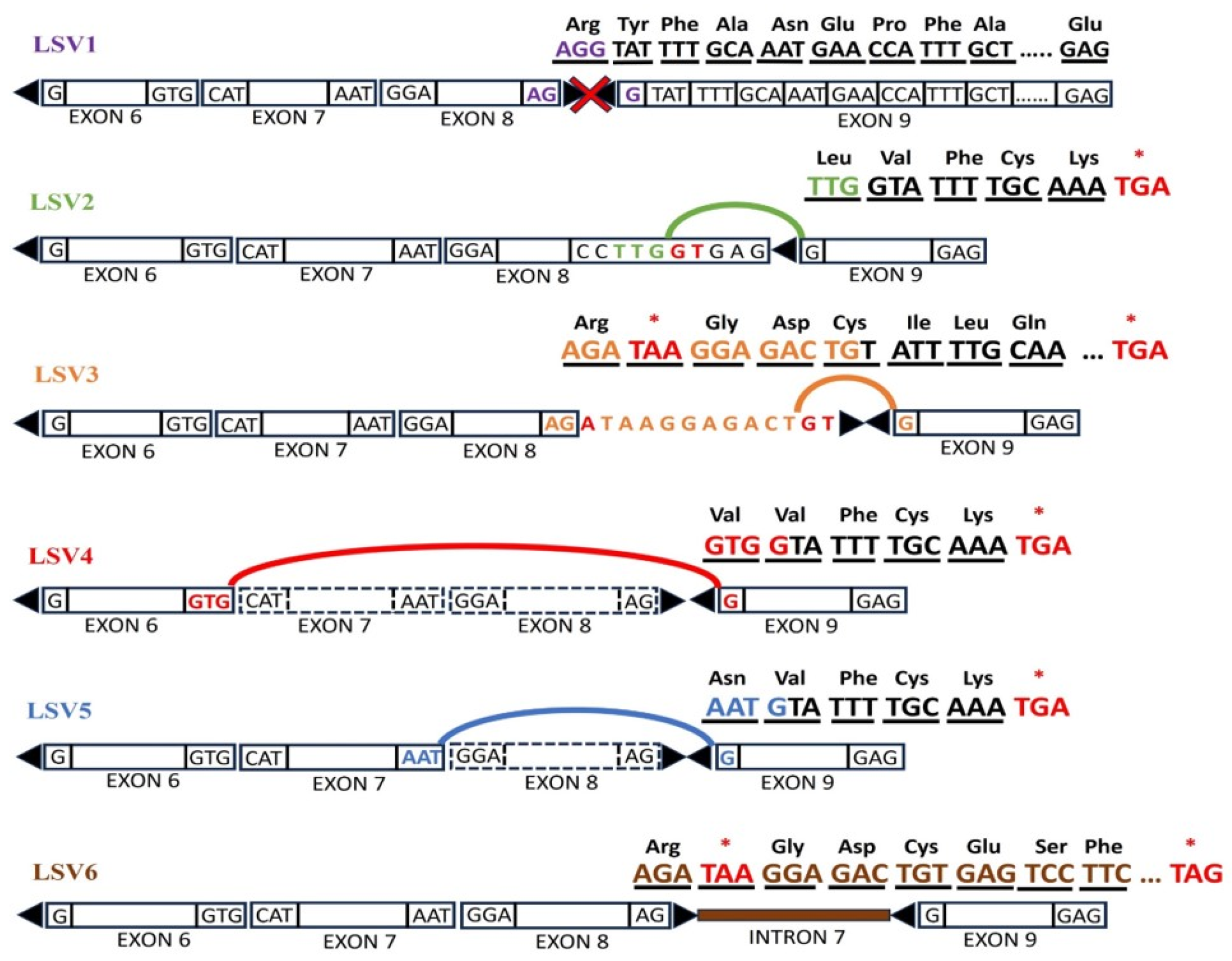
3.3. Aberrant RNA Phenotype
3.4. In Silico Functional Analysis of DEGs
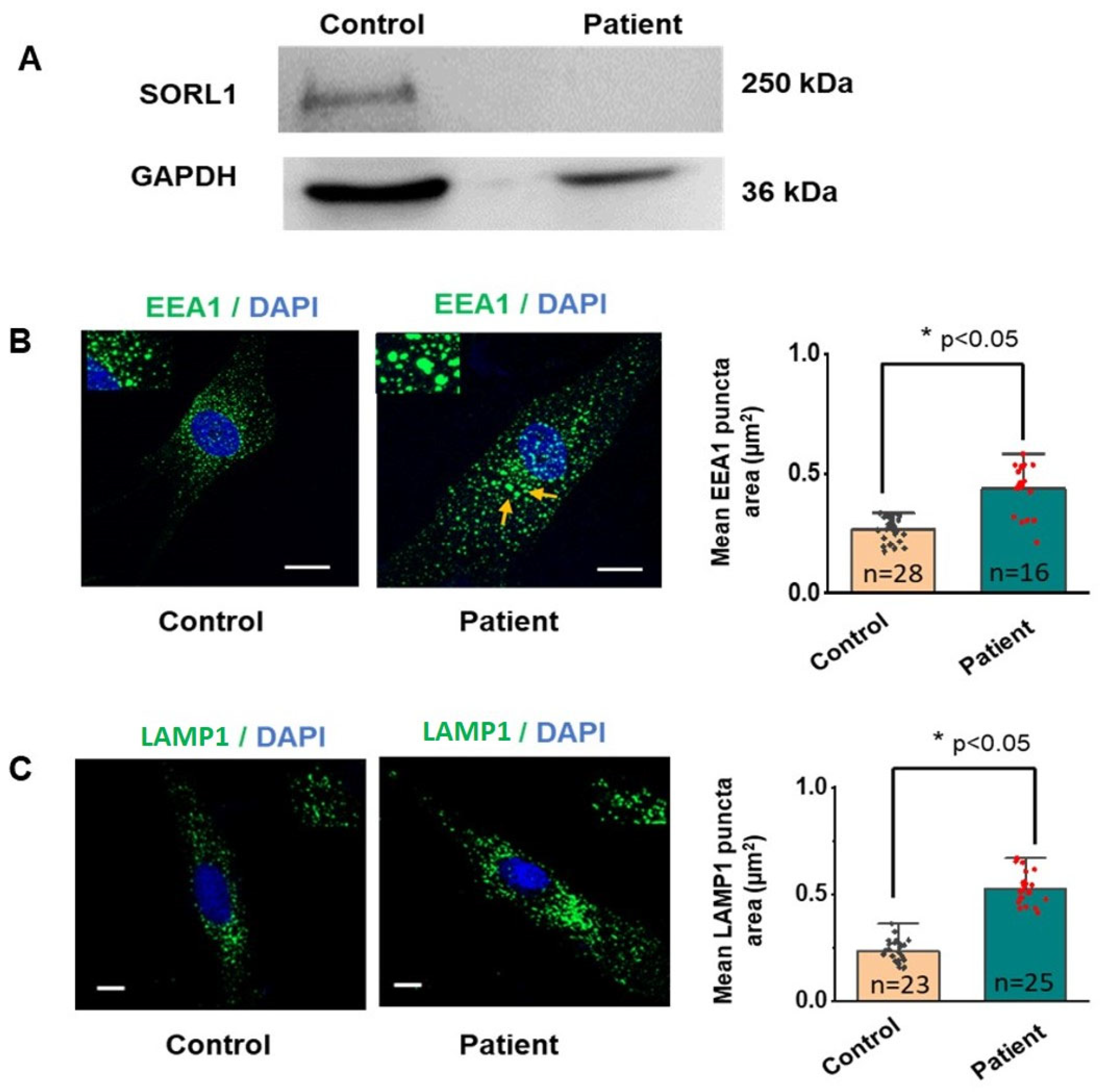
3.5. Western Blot and Immunofluorescence Analysis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shribman, S.; Reid, E.; Crosby, A.H.; Houlden, H.; Warner, T.T. Hereditary spastic paraplegia: from diagnosis to emerging therapeutic approaches. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 1136–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, J.K. Hereditary spastic paraplegia: clinico-pathologic features and emerging molecular mechanisms. Acta Neuropathol. 2013, 126, 307–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toupenet Marchesi, L.; Leblanc, M.; Stevanin, G. Current Knowledge of Endolysosomal and Autophagy Defects in Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia. Cells. 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Huang, T.; Hong, Y.; Yang, W.; Zhang, X.; Luo, H.; et al. The Retromer Complex and Sorting Nexins in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verheijen, J.; Van den Bossche, T.; van der Zee, J.; Engelborghs, S.; Sanchez-Valle, R.; Llado, A.; et al. A comprehensive study of the genetic impact of rare variants in SORL1 in European early-onset Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 132, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogaeva, E.; Meng, Y.; Lee, J.H.; Gu, Y.; Kawarai, T.; Zou, F.; et al. The neuronal sortilin-related receptor SORL1 is genetically associated with Alzheimer disease. Nat Genet. 2007, 39, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Liu, C.; Ma, C.; Xu, X.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, H.; et al. Cerebral amyloid angiopathy-related inflammation: a case report presenting with a rare variant in SORL1 gene. BMC Neurol. 2019, 19, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, C.; Tuck, E.; Stubbs, V.; van der Lee, S.J.; Aalfs, C.; van Spaendonk, R.; et al. SORL1 deficiency in human excitatory neurons causes APP-dependent defects in the endolysosome-autophagy network. Cell Rep. 2021, 35, 109259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, O.M.; Bogh, N.; Landau, A.M.; Ploen, G.G.; Jensen, A.M.G.; Monti, G.; Sorensen, C.B. A genetically modified minipig model for Alzheimer's disease with SORL1 haploinsufficiency. Cell Rep Med 2022, 3, 100740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelban, V.; Breza, M.; Szaruga, M.; Vandrovcova, J.; Murphy, D.; Lee, C.J.; et al. Spastic paraplegia preceding PSEN1-related familial Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement (Amst). 2021, 13, e12186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinodoz, M.; Peter, V.G.; Bedoni, N.; Royer Bertrand, B.; Cisarova, K.; Salmaninejad, A.; et al. AutoMap is a high performance homozygosity mapping tool using next-generation sequencing data. Nat Commun. 2021, 12, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; et al. STAR: ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics. 2013, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anders, S.; Pyl, P.T.; Huber, W. HTSeq--a Python framework to work with high-throughput sequencing data. Bioinformatics. 2015, 31, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patro, R.; Duggal, G.; Love, M.I.; Irizarry, R.A.; Kingsford, C. Salmon provides fast and bias-aware quantification of transcript expression. Nat Methods. 2017, 14, 417–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Wang, J.; Jaehnig, E.J.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, B. WebGestalt 2019: gene set analysis toolkit with revamped UIs and APIs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W199–W205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaquero-Garcia, J.; Aicher, J.K.; Jewell, S.; Gazzara, M.R.; Radens, C.M.; Jha, A.; et al. RNA splicing analysis using heterogeneous and large RNA-seq datasets. Nat Commun. 2023, 14, 1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knupp, A.; Mishra, S.; Martinez, R.; Braggin, J.E.; Szabo, M.; Kinoshita, C.; et al. Depletion of the AD Risk Gene SORL1 Selectively Impairs Neuronal Endosomal Traffic Independent of Amyloidogenic APP Processing. Cell Rep. 2020, 31, 107719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannello, G.; Patel, A.; Sirabella, D.; Diaz, A.G.; Hoover, B.N.; Sarmah, H.; et al. Simple, Fast, and Efficient Method for Derivation of Dermal Fibroblasts From Skin Biopsies. Curr Protoc. 2023, 3, e714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.R.; Williams, E.; Foulger, R.E.; Leigh, S.; Daugherty, L.C.; Niblock, O.; et al. PanelApp crowdsources expert knowledge to establish consensus diagnostic gene panels. Nat Genet. 2019, 51, 1560–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danecek, P.; Bonfield, J.K.; Liddle, J.; Marshall, J.; Ohan, V.; Pollard, M.O.; et al. Twelve years of SAMtools and BCFtools. Gigascience. 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redaelli, V.; Ricci, M.; Del Sole, A.; Piccione, M.; Prioni, S.; Rossi, G. A novel SORL1 mutation in a pedigree affected by early-onset Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis Rep. 2025, 9, 25424823241296017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Francioli, L.C.; Goodrich, J.K.; Collins, R.L.; Kanai, M.; Wang, Q.; et al. A genomic mutational constraint map using variation in 76,156 human genomes. Nature. 2024, 625, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, J.A.; Baldarelli, R.; Kadin, J.A.; Richardson, J.E.; Smith, C.L.; Bult, C.J.; et al. Mouse Genome Database (MGD): Knowledgebase for mouse-human comparative biology. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D981–D87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Mora, M.I.; Blanco-Palmero, V.A.; Quesada-Espinosa, J.F.; Arteche-Lopez, A.R.; Llamas-Velasco, S.; Palma Milla, C.; et al. Heterozygous and Homozygous Variants in SORL1 Gene in Alzheimer's Disease Patients: Clinical, Neuroimaging and Neuropathological Findings. Int J Mol Sci. 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Guennec, K.; Tubeuf, H.; Hannequin, D.; Wallon, D.; Quenez, O.; Rousseau, S.; et al. Biallelic Loss of Function of SORL1 in an Early Onset Alzheimer's Disease Patient. J Alzheimers Dis. 2018, 62, 821–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyle, M.C.; Kolakada, D.; Cortazar, M.A.; Jagannathan, S. How to get away with nonsense: Mechanisms and consequences of escape from nonsense-mediated RNA decay. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2020, 11, e1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schad, E.; Kalmar, L.; Tompa, P. Exon-phase symmetry and intrinsic structural disorder promote modular evolution in the human genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 4409–4422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamyshev, A.L.; Karamysheva, Z.N. Lost in Translation: Ribosome-Associated mRNA and Protein Quality Controls. Front Genet. 2018, 9, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capsoni, S.; Carlo, A.S.; Vignone, D.; Amato, G.; Criscuolo, C.; Willnow, T.E.; et al. SorLA deficiency dissects amyloid pathology from tau and cholinergic neurodegeneration in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 2013, 33, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, J.M.; Lathuiliere, A.; Su, E.J.; Song, Y.; Torrente, D.; Jo, Y.; et al. SORL1 is a receptor for tau that promotes tau seeding. J Biol Chem. 2024, 300, 107313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazeli, E.; Child, D.D.; Bucks, S.A.; Stovarsky, M.; Edwards, G.; Rose, S.E.; et al. A familial missense variant in the Alzheimer's disease gene SORL1 impairs its maturation and endosomal sorting. Acta Neuropathol. 2024, 147, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringman, J.M.; Dorrani, N.; Fernandez, S.G.; Signer, R.; Martinez-Agosto, J.; Lee, H.; et al. Characterization of spastic paraplegia in a family with a novel PSEN1 mutation. Brain Commun. 2023, 5, fcad030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karczewski, K.J.; Francioli, L.C.; Tiao, G.; Cummings, B.B.; Alfoldi, J.; Wang, Q.; et al. The mutational constraint spectrum quantified from variation in 141,456 humans. Nature. 2020, 581, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodson, S.E.; Andersen, O.M.; Karmali, V.; Fritz, J.J.; Cheng, D.; Peng, J.; et al. Loss of LR11/SORLA enhances early pathology in a mouse model of amyloidosis: evidence for a proximal role in Alzheimer's disease. J Neurosci. 2008, 28, 12877–12886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, A.; Thorleifsson, G.; Gudbjartsson, D.F.; Masson, G.; Sigurdsson, A.; Jonasdottir, A.; et al. Fine-scale recombination rate differences between sexes, populations and individuals. Nature. 2010, 467, 1099–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pemberton, T.J.; Absher, D.; Feldman, M.W.; Myers, R.M.; Rosenberg, N.A.; Li, J.Z. Genomic patterns of homozygosity in worldwide human populations. Am J Hum Genet. 2012, 91, 275–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felsky, D.; Szeszko, P.; Yu, L.; Honer, W.G.; De Jager, P.L.; Schneider, J.A.; et al. The SORL1 gene and convergent neural risk for Alzheimer's disease across the human lifespan. Mol Psychiatry. 2014, 19, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummings, B.B.; Karczewski, K.J.; Kosmicki, J.A.; Seaby, E.G.; Watts, N.A.; Singer-Berk, M.; et al. Transcript expression-aware annotation improves rare variant interpretation. Nature. 2020, 581, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolkman, J.A.; Stemmer, W.P. Directed evolution of proteins by exon shuffling. Nat Biotechnol. 2001, 19, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, E.H.; Overly, C.C.; Jones, A.R. The Allen Human Brain Atlas: comprehensive gene expression mapping of the human brain. Trends Neurosci. 2012, 35, 711–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ament, S.A.; Adkins, R.S.; Carter, R.; Chrysostomou, E.; Colantuoni, C.; Crabtree, J.; et al. The Neuroscience Multi-Omic Archive: a BRAIN Initiative resource for single-cell transcriptomic and epigenomic data from the mammalian brain. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D1075–D85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Small, S.A.; Simoes-Spassov, S.; Mayeux, R.; Petsko, G.A. Endosomal Traffic Jams Represent a Pathogenic Hub and Therapeutic Target in Alzheimer's Disease. Trends Neurosci. 2017, 40, 592–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cataldo, A.M.; Mathews, P.M.; Boiteau, A.B.; Hassinger, L.C.; Peterhoff, C.M.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Down syndrome fibroblast model of Alzheimer-related endosome pathology: accelerated endocytosis promotes late endocytic defects. Am J Pathol. 2008, 173, 370–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulk, M.; Moursel, L.G.; van der Graaf, L.M.; van Veluw, S.J.; Greenberg, S.M.; van Duinen, S.G.; et al. Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy With Vascular Iron Accumulation and Calcification. Stroke. 2018, 49, 2081–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| LSV ID | LSV description |
Junction coordinates (GRCh38) |
Median Ψ Values | |||
| Proband | MOP | HCON | MC-MFG | |||
| LSV1 | Canonical 5' splice junction (exon 8) | chr11:121514321-121520657 | 0 | 0.6249 | 0.9083 | 0.9565 |
| LSV2 | Alternative 5' splice junction – single target LSV (exon 8) | chr11:121514316-121520657 | 0.2908 | 0.1006 | 0 | 0 |
| LSV3 | Alternative 5' splice junction – single target LSV (exon 8) | chr11:121514332-121520657 | 0.2829 | 0.0652 | 0 | 0 |
| LSV4 | Exon skipping – single source LSV (exon 6 to exon 9) |
chr11:121497049-121520657 | 0.1236 | 0.0295 | 0.006 | 0.0012 |
| LSV5 | Exon skipping – single source LSV (exon 7 to exon 9) |
chr11:121513104-121520657 | 0.1184 | 0.0469 | 0 | 0 |
| LSV6 | Intron retention (intron 8) |
chr11:121514322-121520656 | 0.1868 | 0.1245 | 0.084 | 0.0388 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





