Submitted:
04 August 2025
Posted:
05 August 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Eukaryotic Transcription and Its Regulation
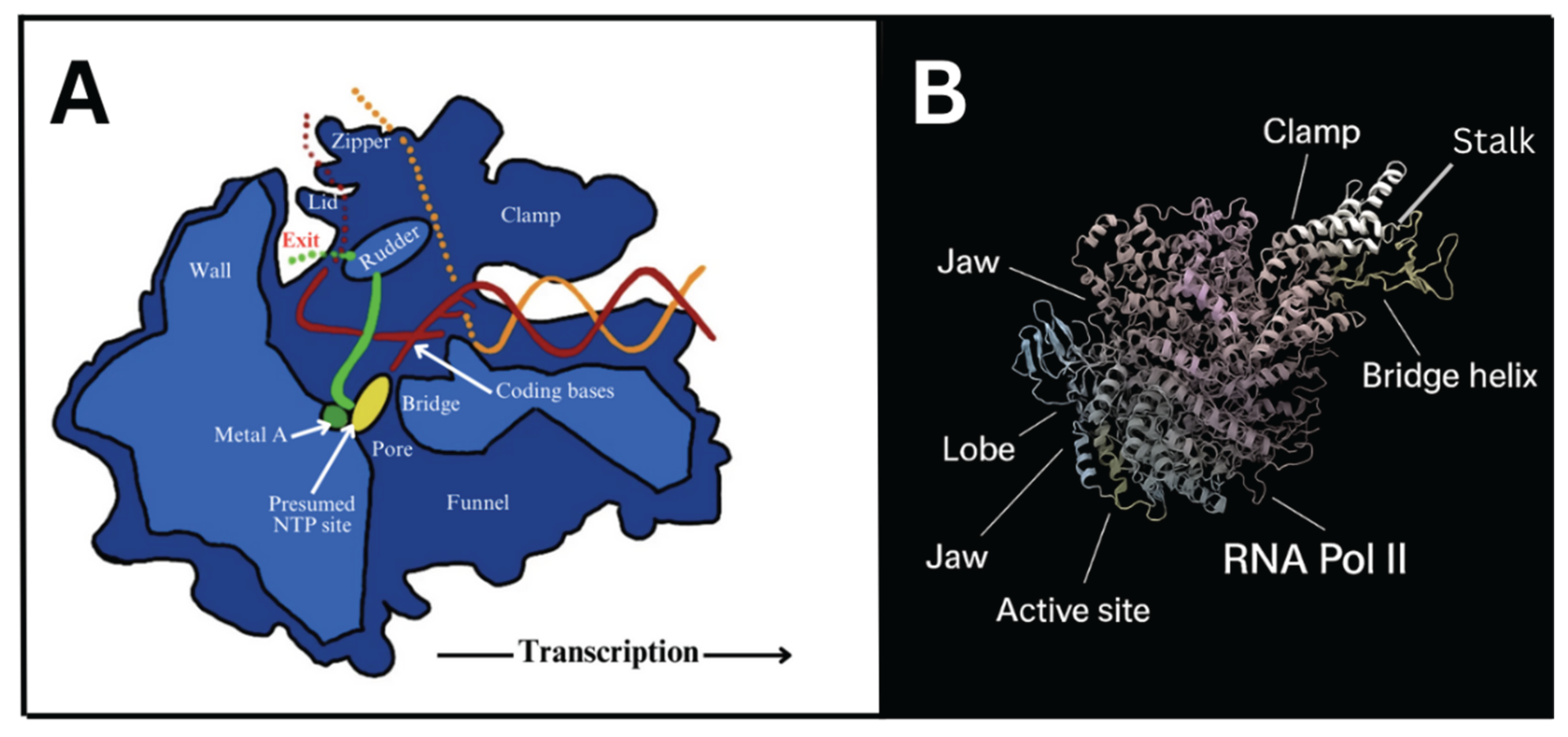
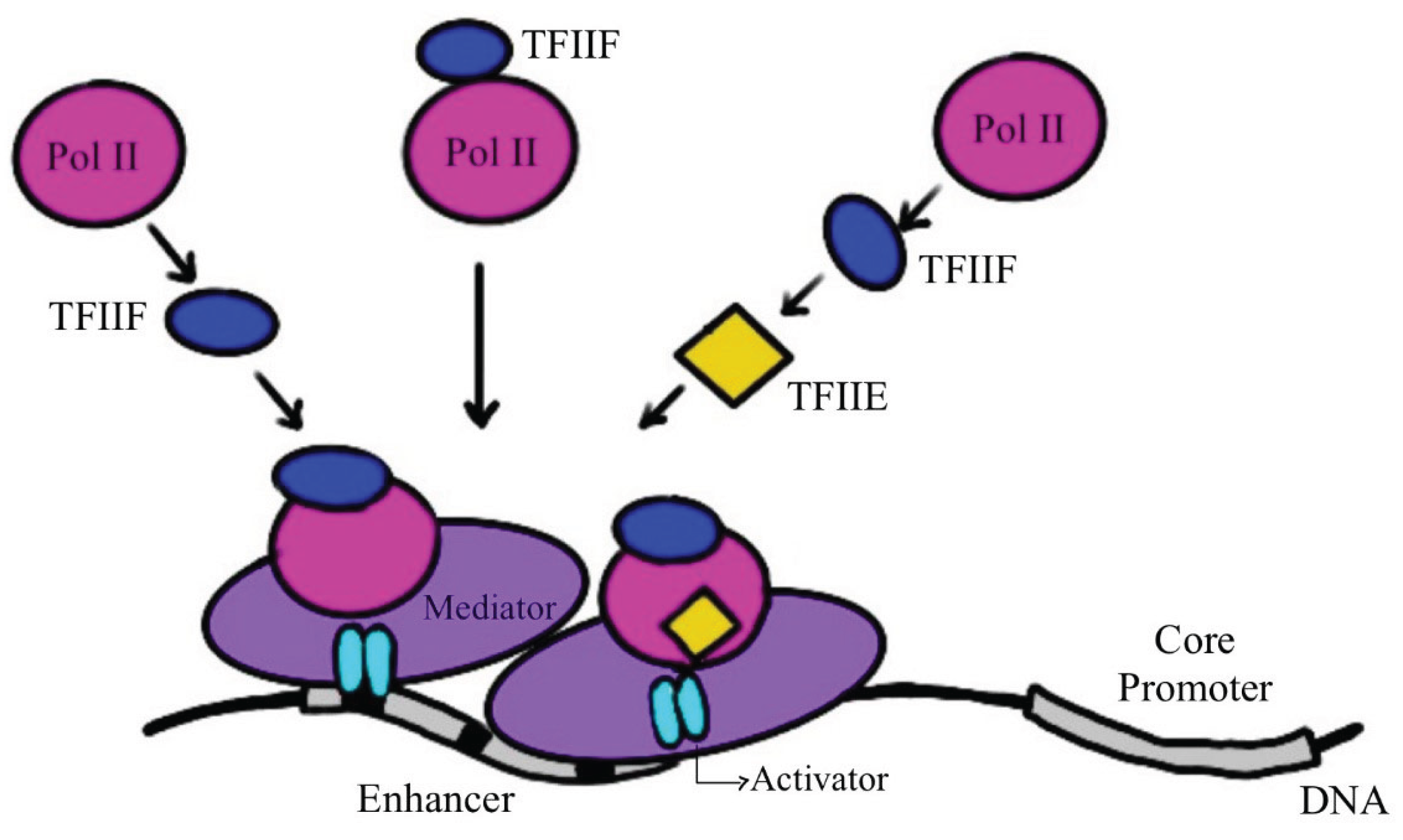
2. RNA Polymerase, the Molecular Machine Responsible for Transcription
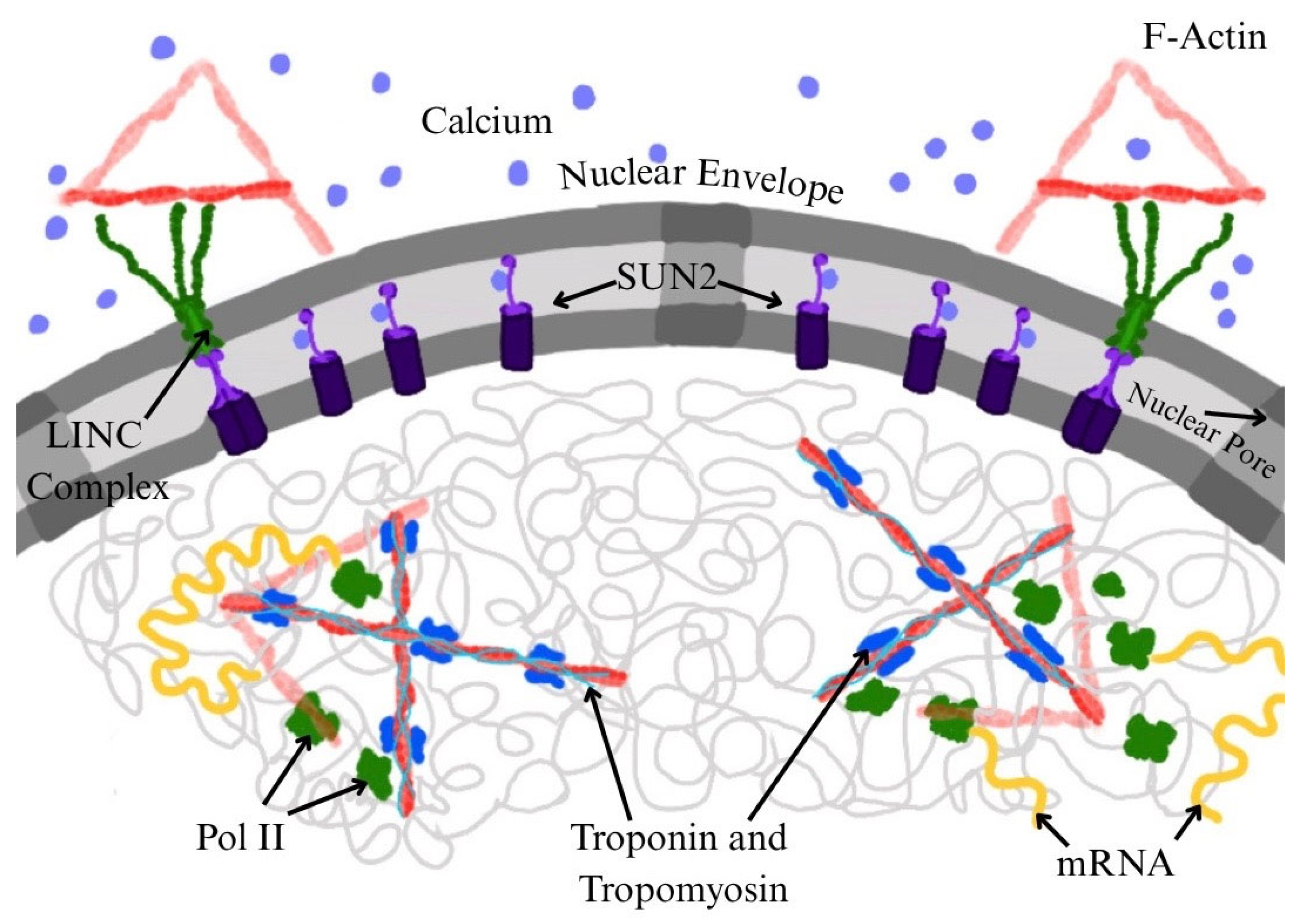
3. Requirement of Nuclear Actin for RNA Pol II Function
4. Troponin and Tropomyosin as Potential Modulators of Nuclear Actin and Transcription
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Arp2/3 | Actin-related proteins 2/3 |
| ARP4 | Actin-related protein 4 |
| BAF complex | BRG/BRM-associated factor complex |
| CaMKII | Ca2+-calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II |
| CaN | Calcineurin |
| ChromExM | Chromatin expansion microscopy |
| CREB | Cyclic-AMP response element-binding |
| CTD | Disordered carboxy-terminal domain of RNA Pol II |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic acid |
| ERK1/2 | Extracellular signal-related kinases 1 and 2 |
| F-actin | Filamentous (polymerized) actin |
| G-actin | Globular (monomeric) actin |
| GTP | Guanosine triphosphate |
| HDAC | Histone deacetylase |
| INM | Inner nuclear membrane |
| IP3 | Inositol trisphosphate |
| LINC | Linker of nucleoskeleton and cytoskeleton |
| MAL | Megakaryocytic acute leukemia protein |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| miRNAs | microRNAs |
| MRFs | Myogenic regulatory factors |
| mRNA | Messenger ribonucleic acid |
| MyoD | Myoblast determination protein |
| NFAT | Nuclear factor of activated T-cells |
| NM1 | Nuclear myosin 1 |
| NMVI | Nuclear myosin VI |
| PIC | Pre-initiation complex for transcription |
| Pol I | RNA polymerase I |
| Pol II | RNA polymerase II |
| Pol III | RNA polymerase III |
| Pol IV | RNA polymerase IV |
| Pol V | RNA polymerase V |
| pre-mRNA | Pre-messenger RNA |
| P-TEFb | Positive transcription elongation factor b |
| rDNA | Gene for a ribosomal RNA |
| RNA | Ribonucleic acid |
| rRNA | Ribosomal ribonucleic acid |
| snRNAs | small nuclear RNAs |
| SRF | Serum response factor |
| SUMO | Small ubiquitin-like modifier protein |
| SWI/SNF | switch/sucrose non-fermentable chromatin-remodeling complex |
| TBP | TATA-binding protein |
| TFs | Transcription factors |
| Tn | Troponin |
| TnC | Troponin C subunit of troponin |
| TnI | Troponin I subunit of troponin |
| TnT | Troponin T subunit of troponin |
| Tm | Tropomysin |
| tRNA | Transfer ribonucleic acid |
| Ubc9 | ubiquitin conjugating enzyme Ubc9 (E2I) |
| YAP | Yes-associated protein |
References
- Piccolino, M., Biological machines: from mills to molecules. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2000, 1, (2), 149-53. [CrossRef]
- van den Heuvel, M. G. L.; Dekker, C., Motor proteins at work for nanotechnology. Science 2007, 317, (5836), 333-6. [CrossRef]
- Cramer, P., A Tale of Chromatin and Transcription in 100 Structures. Cell 2014, 159, (5), 985-994. [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, D. V.; Nag, S.; Spudich, A.; Ruppel, K. M.; Spudich, J. A., The Myosin Family of Mechanoenzymes: From Mechanisms to Therapeutic Approaches. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Roeder, R. G., 50+ years of eukaryotic transcription: an expanding universe of factors and mechanisms. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2019, 26, (9), 783-791. [CrossRef]
- Pownall, M. E.; Miao, L.; Vejnar, C. E.; M'Saad, O.; Sherrard, A.; Frederick, M. A.; Benitez, M. D. J.; Boswell, C. W.; Zaret, K. S.; Bewersdorf, J.; Giraldez, A. J., Chromatin expansion microscopy reveals nanoscale organization of transcription and chromatin. Science 2023, 381, (6653), 92-100. [CrossRef]
- Stasevich, T. J.; Kimura, H., An expanded view of transcription. Science 2023, 381, (6653), 26-27. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V. Q.; Ranjan, A.; Liu, S.; Tang, X.; Ling, Y. H.; Wisniewski, J.; Mizuguchi, G.; Li, K. Y.; Jou, V.; Zheng, Q.; Lavis, L. D.; Lionnet, T.; Wu, C., Spatiotemporal coordination of transcription preinitiation complex assembly in live cells. Mol. Cell 2021, 81, (17), 3560-3575 e6. [CrossRef]
- Baek, I.; Friedman, L. J.; Gelles, J.; Buratowski, S., Single-molecule studies reveal branched pathways for activator-dependent assembly of RNA polymerase II pre-initiation complexes. Mol. Cell 2021, 81, (17), 3576-3588 e6. [CrossRef]
- Ling, Y. H.; Ye, Z.; Liang, C.; Yu, C.; Park, G.; Corden, J. L.; Wu, C., Disordered C-terminal domain drives spatiotemporal confinement of RNAPII to enhance search for chromatin targets. Nat. Cell. Biol. 2024, 26, (4), 581-592. [CrossRef]
- Casamassimi, A.; Ciccodicola, A., Transcriptional Regulation: Molecules, Involved Mechanisms, and Misregulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, (6). [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.; Song, C.; Tang, H., Transcriptional regulation in cardiovascular diseases. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2024, 11, 1360765. [CrossRef]
- Fuda, N. J.; Ardehali, M. B.; Lis, J. T., Defining mechanisms that regulate RNA polymerase II transcription in vivo. Nature 2009, 461, (7261), 186-92. [CrossRef]
- Filipovski, M.; Soffers, J. H. M.; Vos, S. M.; Farnung, L., Structural basis of nucleosome retention during transcription elongation. Science 2022, 376, (6599), 1313-1316. [CrossRef]
- Olson, E. N., Regulation of muscle transcription by the MyoD family. The heart of the matter. Circ. Res. 1993, 72, (1), 1-6. [CrossRef]
- Olson, E. N., Signal transduction pathways that regulate skeletal muscle gene expression. Mol. Endocrinol. 1993, 7, (11), 1369-78. [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Olson, E. N., Regulation of muscle cell growth and differentiation by the MyoD family of helix-loop-helix proteins. Adv. Cancer Res. 1992, 58, 95-119. [CrossRef]
- Braun, T.; Gautel, M., Transcriptional mechanisms regulating skeletal muscle differentiation, growth and homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 12, (6), 349-61. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, D.-Z.; Hockemeyer, D.; McAnally, J.; Nordheim, A.; Olson, E. N., Myocardin and ternary complex factors compete for SRF to control smooth muscle gene expression. Nature 2004, 428, (6979), 185-9. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, D. Z.; Pipes, G. C.; Olson, E. N., Myocardin is a master regulator of smooth muscle gene expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, (12), 7129-34. [CrossRef]
- Estrella, N. L.; Naya, F. J., Transcriptional networks regulating the costamere, sarcomere, and other cytoskeletal structures in striated muscle. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2014, 71, (9), 1641-56. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Han, M.; Bernier, M.; Wen, J.-k., Nuclear actin and actin-binding proteins in the regulation of transcription and gene expression. FEBS J. 2009, 276, (10), 2669-85. [CrossRef]
- Roeder, R. G.; Rutter, W. J., Multiple forms of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase in eukaryotic organisms. Nature 1969, 224, (5216), 234-7. [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Wu, X.-X.; Fang, C.-L.; Xu, Z.-G.; Zhang, H.-W.; Gao, J.; Zhou, C.-M.; You, L.-L.; Gu, Z.-X.; Mu, W.-H.; Feng, Y.; Wang, J.-W.; Zhang, Y., Pol IV and RDR2: A two-RNA-polymerase machine that produces double-stranded RNA. Science 2021, 374, (6575), 1579-1586. [CrossRef]
- Engel, C.; Sainsbury, S.; Cheung, A. C.; Kostrewa, D.; Cramer, P., RNA polymerase I structure and transcription regulation. Nature 2013, 502, (7473), 650-5. [CrossRef]
- Obrdlik, A.; Louvet, E.; Kukalev, A.; Naschekin, D.; Kiseleva, E.; Fahrenkrog, B.; Percipalle, P., Nuclear myosin 1 is in complex with mature rRNA transcripts and associates with the nuclear pore basket. FASEB J. 2010, 24, (1), 146-57. [CrossRef]
- Turowski, T. W.; Tollervey, D., Transcription by RNA polymerase III: insights into mechanism and regulation. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2016, 44, (5), 1367-1375. [CrossRef]
- Cech, T. R.; Steitz, J. A., The noncoding RNA revolution-trashing old rules to forge new ones. Cell 2014, 157, (1), 77-94. [CrossRef]
- Rinn, J.; Guttman, M., RNA Function. RNA and dynamic nuclear organization. Science 2014, 345, (6202), 1240-1. [CrossRef]
- Kopp, F.; Mendell, J. T., Functional Classification and Experimental Dissection of Long Noncoding RNAs. Cell 2018, 172, (3), 393-407. [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Kim, M.; Han, J.; Yeom, K.-H.; Lee, S.; Baek, S. H.; Kim, V. N., MicroRNA genes are transcribed by RNA polymerase II. EMBO J. 2004, 23, (20), 4051-60. [CrossRef]
- Rissland, O. S.; Norbury, C. J., The Cid1 poly(U) polymerase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1779, (4), 286-94. [CrossRef]
- Schier, A. C.; Taatjes, D. J., Structure and mechanism of the RNA polymerase II transcription machinery. Genes Dev. 2020, 34, (7-8), 465-488. [CrossRef]
- Khatter, H.; Vorländer, M. K.; Müller, C. W., RNA polymerase I and III: similar yet unique. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2017, 47, 88-94. [CrossRef]
- Kostrewa, D.; Zeller, M. E.; Armache, K.-J.; Seizl, M.; Leike, K.; Thomm, M.; Cramer, P., RNA polymerase II-TFIIB structure and mechanism of transcription initiation. Nature 2009, 462, (7271), 323-30. [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Yan, C.; Fang, J.; Inouye, C.; Tjian, R.; Ivanov, I.; Nogales, E., Near-atomic resolution visualization of human transcription promoter opening. Nature 2016, 533, (7603), 359-65. [CrossRef]
- Vos, S. M.; Farnung, L.; Urlaub, H.; Cramer, P., Structure of paused transcription complex Pol II-DSIF-NELF. Nature 2018, 560, (7720), 601-606. [CrossRef]
- Vos, S. M.; Farnung, L.; Boehning, M.; Wigge, C.; Linden, A.; Urlaub, H.; Cramer, P., Structure of activated transcription complex Pol II-DSIF-PAF-SPT6. Nature 2018, 560, (7720), 607-612. [CrossRef]
- Vos, S. M.; Farnung, L.; Linden, A.; Urlaub, H.; Cramer, P., Structure of complete Pol II-DSIF-PAF-SPT6 transcription complex reveals RTF1 allosteric activation. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2020, 27, (7), 668-677. [CrossRef]
- Kettenberger, H.; Armache, K.-J.; Cramer, P., Complete RNA polymerase II elongation complex structure and its interactions with NTP and TFIIS. Mol. Cell 2004, 16, (6), 955-65. [CrossRef]
- Aibara, S.; Schilbach, S.; Cramer, P., Structures of mammalian RNA polymerase II pre-initiation complexes. Nature 2021, 594, (7861), 124-128. [CrossRef]
- Schier, A. C.; Taatjes, D. J., Everything at once: cryo-EM yields remarkable insights into human RNA polymerase II transcription. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2021, 28, (7), 540-543. [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, W.; Ren, Y.; Qu, X.; Li, J.; Yin, X.; Xu, Y., Structures of +1 nucleosome-bound PIC-Mediator complex. Science 2022, 378, (6615), 62-68. [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yin, X.; Li, J.; Wu, Z.; Qi, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, W.; Xu, Y., Structures of the human Mediator and Mediator-bound preinitiation complex. Science 2021, 372, (6546). [CrossRef]
- Hou, T. Y.; Kraus, W. L., Come one, come all? Re-evaluating RNA polymerase II pre-initiation complex assembly using single-molecule microscopy. Mol. Cell 2021, 81, (17), 3443-3445. [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Qi, Y.; Wu, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Zhao, D.; Hou, H.; Li, Y.; Yu, Z.; Liu, W.; Wang, M.; Ren, Y.; Li, Z.; Yang, H.; Xu, Y., Structural insights into preinitiation complex assembly on core promoters. Science 2021, 372, (6541). [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Bushnell, D. A.; Kornberg, R. D., RNA polymerase II transcription: structure and mechanism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1829, (1), 2-8. [CrossRef]
- Donczew, R.; Hahn, S., Mechanistic Differences in Transcription Initiation at TATA-Less and TATA-Containing Promoters. Mol Cell Biol 2018, 38, (1). [CrossRef]
- Yella, V. R.; Bansal, M., DNA structural features of eukaryotic TATA-containing and TATA-less promoters. FEBS Open Bio 2017, 7, (3), 324-334. [CrossRef]
- Pugh, B. F.; Tjian, R., Transcription from a TATA-less promoter requires a multisubunit TFIID complex. Genes Dev. 1991, 5, (11), 1935-45. [CrossRef]
- Harlen, K. M.; Churchman, L. S., The code and beyond: transcription regulation by the RNA polymerase II carboxy-terminal domain. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, (4), 263-273. [CrossRef]
- Barbosa-Morais, N. L.; Irimia, M.; Pan, Q.; Xiong, H. Y.; Gueroussov, S.; Lee, L. J.; Slobodeniuc, V.; Kutter, C.; Watt, S.; Çolak, R.; Kim, T.; Misquitta-Ali, C. M.; Wilson, M. D.; Kim, P. M.; Odom, D. T.; Frey, B. J.; Blencowe, B. J., The evolutionary landscape of alternative splicing in vertebrate species. Science 2012, 338, (6114), 1587-93. [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Opazo, N.; Nadal-Ginard, B., α-tropomyosin gene organization: alternative splicing of duplicated isotype-specific exons accounts for the production of smooth and striated muscle isoforms. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, (10), 4755-65. [CrossRef]
- Schiaffino, S.; Reggiani, C., Molecular diversity of myofibrillar proteins: gene regulation and functional significance. Physiol. Rev. 1996, 76, (2), 371-423. [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, S. I.; Milligan, R. A., Fine tuning a molecular motor: the location of alternative domains in the Drosophila myosin head. J. Mol. Biol. 1997, 271, (1), 1-6. [CrossRef]
- Perry, S. V., Troponin T: genetics, properties and function. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 1998, 19, (6), 575-602. [CrossRef]
- Perry, S. V., Vertebrate tropomyosin: distribution, properties and function. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 2001, 22, (1), 5-49. [CrossRef]
- Swank, D. M.; Kronert, W. A.; Bernstein, S. I.; Maughan, D. W., Alternative N-terminal regions of Drosophila myosin heavy chain tune muscle kinetics for optimal power output. Biophys. J. 2004, 87, (3), 1805-14. [CrossRef]
- Labeit, S.; Lahmers, S.; Burkart, C.; Fong, C.; McNabb, M.; Witt, S.; Witt, C.; Labeit, D.; Granzier, H., Expression of distinct classes of titin isoforms in striated and smooth muscles by alternative splicing, and their conserved interaction with filamins. J. Mol. Biol. 2006, 362, (4), 664-81. [CrossRef]
- Sheng, J. J.; Jin, J.-P., Gene regulation, alternative splicing, and posttranslational modification of troponin subunits in cardiac development and adaptation: a focused review. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 165. [CrossRef]
- Viita, T.; Kyheröinen, S.; Prajapati, B.; Virtanen, J.; Frilander, M. J.; Varjosalo, M.; Vartiainen, M. K., Nuclear actin interactome analysis links actin to KAT14 histone acetyl transferase and mRNA splicing. J. Cell. Sci. 2019, 132, (8). [CrossRef]
- Huxley, H. E., The mechanism of muscular contraction. Science 1969, 164, (3886), 1356-1366. [CrossRef]
- Cooke, R., The mechanism of muscle contraction. CRC Crit. Rev. Biochem. 1986, 21, (1), 53-118. [CrossRef]
- Holmes, K. C.; Kabsch, W., Muscle proteins: actin. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 1991, 1, (2), 270-280. [CrossRef]
- Pollard, T. D.; Cooper, J. A., Actin, a central player in cell shape and movement. Science 2009, 326, (5957), 1208-12. [CrossRef]
- Risi, C. M.; Pepper, I.; Belknap, B.; Landim-Vieira, M.; White, H. D.; Dryden, K.; Pinto, J. R.; Chase, P. B.; Galkin, V. E., The Structure of the Native Cardiac Thin Filament at Systolic Ca2+ Levels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, (13), e2024288118. [CrossRef]
- Risi, C. M.; Belknap, B.; Atherton, J.; Coscarella, I. L.; White, H. D.; Chase, P. B.; Pinto, J. R.; Galkin, V. E., Troponin structural dynamics in the native cardiac thin filament revealed by cryo electron microscopy. J. Mol. Biol. 2024, 436, (6), 168498. [CrossRef]
- Ohnishi, T.; Kawamura, H.; Tanaka, Y., [Actin and Myosin-Like Proteins in the Calf Thymus Cell Nucleus]. J. Biochem. 1964, 56, 6-15. [CrossRef]
- Ohnishi, T.; Kawamura, H.; Yamamoto, T., [Extraction of a Protein Resembling Actin from the Cell Nucleus of the Calf Thymus]. J. Biochem. 1963, 54, 298-300. [CrossRef]
- Jockusch, B. M.; Schoenenberger, C.-A.; Stetefeld, J.; Aebi, U., Tracking down the different forms of nuclear actin. Trends Cell. Biol. 2006, 16, (8), 391-6. [CrossRef]
- Pederson, T., As functional nuclear actin comes into view, is it globular, filamentous, or both? J. Cell. Biol. 2008, 180, (6), 1061-4. [CrossRef]
- Baarlink, C.; Wang, H.; Grosse, R., Nuclear actin network assembly by formins regulates the SRF coactivator MAL. Science 2013, 340, (6134), 864-7. [CrossRef]
- Feric, M.; Brangwynne, C. P., A nuclear F-actin scaffold stabilizes ribonucleoprotein droplets against gravity in large cells. Nat. Cell. Biol. 2013, 15, (10), 1253-9. [CrossRef]
- Kelpsch, D. J.; Tootle, T. L., Nuclear Actin: From Discovery to Function. Anat. Rec. 2018, 301, (12), 1999-2013. [CrossRef]
- Ulferts, S.; Lopes, M.; Miyamoto, K.; Grosse, R., Nuclear actin dynamics and functions at a glance. J. Cell. Sci. 2024, 137, (6). [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, W. A.; de Lanerolle, P., Nuclear actin: to polymerize or not to polymerize. J. Cell. Biol. 2006, 172, (4), 495-6. [CrossRef]
- Kloc, M.; Chanana, P.; Vaughn, N.; Uosef, A.; Kubiak, J. Z.; Ghobrial, R. M., New Insights into Cellular Functions of Nuclear Actin. Biology 2021, 10, (4). [CrossRef]
- Serebryannyy, L. A.; Parilla, M.; Annibale, P.; Cruz, C. M.; Laster, K.; Gratton, E.; Kudryashov, D.; Kosak, S. T.; Gottardi, C. J.; de Lanerolle, P., Persistent nuclear actin filaments inhibit transcription by RNA polymerase II. J. Cell. Sci. 2016, 129, (18), 3412-25. [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, W. A.; Arduini, A.; Nicol, S. M.; Camacho, C. J.; Lessard, J. L.; Fuller-Pace, F. V.; de Lanerolle, P., SUMOylation of nuclear actin. J. Cell. Biol. 2009, 186, (2), 193-200. [CrossRef]
- Pollard, T. D., Actin and Actin-Binding Proteins. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2016, 8, (8). [CrossRef]
- Falahzadeh, K.; Banaei-Esfahani, A.; Shahhoseini, M., The potential roles of actin in the nucleus. Cell J. 2015, 17, (1), 7-14. [CrossRef]
- Vartiainen, M. K.; Guettler, S.; Larijani, B.; Treisman, R., Nuclear actin regulates dynamic subcellular localization and activity of the SRF cofactor MAL. Science 2007, 316, (5832), 1749-52. [CrossRef]
- Sen, B.; Xie, Z.; Thomas, M. D.; Pattenden, S. G.; Howard, S.; McGrath, C.; Styner, M.; Uzer, G.; Furey, T. S.; Rubin, J., Nuclear actin structure regulates chromatin accessibility. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, (1), 4095. [CrossRef]
- Vandekerckhove, J.; Weber, K., At least six different actins are expressed in a higher mammal: an analysis based on the amino acid sequence of the amino-terminal tryptic peptide. J. Mol. Biol. 1978, 126, (4), 783-802. [CrossRef]
- Rajakylä, E. K.; Vartiainen, M. K., Rho, nuclear actin, and actin-binding proteins in the regulation of transcription and gene expression. Small GTPases 2014, 5, e27539. [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Shuai, K., Regulation of the sumoylation system in gene expression. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2008, 20, (3), 288-93. [CrossRef]
- Baek, S. H., A novel link between SUMO modification and cancer metastasis. Cell Cycle 2006, 5, (14), 1492-5. [CrossRef]
- Batut, P. J.; Bing, X. Y.; Sisco, Z.; Raimundo, J.; Levo, M.; Levine, M. S., Genome organization controls transcriptional dynamics during development. Science 2022, 375, (6580), 566-570. [CrossRef]
- Miralles, F.; Posern, G.; Zaromytidou, A.-I.; Treisman, R., Actin dynamics control SRF activity by regulation of its coactivator MAL. Cell 2003, 113, (3), 329-42. [CrossRef]
- Arsenian, S.; Weinhold, B.; Oelgeschläger, M.; Rüther, U.; Nordheim, A., Serum response factor is essential for mesoderm formation during mouse embryogenesis. EMBO J. 1998, 17, (21), 6289-99. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, M.; Fang, H.; El-Mounayri, O.; Rodenberg, J. M.; Imbalzano, A. N.; Herring, B. P., The SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex regulates myocardin-induced smooth muscle-specific gene expression. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2009, 29, (6), 921-8. [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, K.; Gurdon, J. B., Transcriptional regulation and nuclear reprogramming: roles of nuclear actin and actin-binding proteins. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, (18), 3289-302. [CrossRef]
- Alfert, A.; Moreno, N.; Kerl, K., The BAF complex in development and disease. Epigenetics Chromatin 2019, 12, (1), 19. [CrossRef]
- Petrusová, J.; Manning, J.; Filipp, D., Envisioning a role for nuclear actin in prophase I spermatocytes. Front Cell Dev Biol 2023, 11, 1295452. [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Fan, X.; Ding, M.; Li, R.; Shao, S.; Hou, Y.; Meng, S.; Tang, F.; Li, C.; Sun, Y., Nuclear actin regulates inducible transcription by enhancing RNA polymerase II clustering. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, (16), eaay6515. [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, K.; Gurdon, J. B., Nuclear actin and transcriptional activation. Commun. Integr. Biol. 2011, 4, (5), 582-3. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22046469.
- Core, L.; Adelman, K., Promoter-proximal pausing of RNA polymerase II: a nexus of gene regulation. Genes Dev. 2019, 33, (15-16), 960-982. [CrossRef]
- Kyheröinen, S.; Prajapati, B.; Sokolova, M.; Schmitz, M.; Viita, T.; Geyer, M.; Vartiainen, M. K., Actin associates with actively elongating genes and binds directly to the Cdk9 subunit of P-TEFb. J. Biol. Chem. 2024, 300, (3), 105698. [CrossRef]
- Belin, B. J.; Cimini, B. A.; Blackburn, E. H.; Mullins, R. D., Visualization of actin filaments and monomers in somatic cell nuclei. Mol. Biol. Cell 2013, 24, (7), 982-94. [CrossRef]
- Wineland, D. M.; Kelpsch, D. J.; Tootle, T. L., Multiple Pools of Nuclear Actin. Anat. Rec. 2018, 301, (12), 2014-2036. [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, P.; Shen, X., Mechanisms of nuclear actin in chromatin-remodeling complexes. Trends Cell. Biol. 2014, 24, (4), 238-46. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Park, J.-I., Nuclear Actin Dynamics in Gene Expression, DNA Repair, and Cancer. Results Probl Cell Differ 2022, 70, 625-663. [CrossRef]
- Saidova, A. A.; Vorobjev, I. A., What Actin and Myosin Do in the Nucleus: New Functions of the Well-Known Proteins. Mol Biol (Mosk) 2024, 58, (3), 349-362. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/39707848.
- de Lanerolle, P.; Serebryannyy, L., Nuclear actin and myosins: life without filaments. Nat. Cell. Biol. 2011, 13, (11), 1282-8. [CrossRef]
- de Lanerolle, P., Nuclear actin and myosins at a glance. J. Cell. Sci. 2012, 125, (Pt 21), 4945-9. [CrossRef]
- Philimonenko, V. V.; Zhao, J.; Iben, S.; Dingova, H.; Kysela, K.; Kahle, M.; Zentgraf, H.; Hofmann, W. A.; de Lanerolle, P.; Hozak, P.; Grummt, I., Nuclear actin and myosin I are required for RNA polymerase I transcription. Nat. Cell. Biol. 2004, 6, (12), 1165-72. [CrossRef]
- Khanna, N.; Hu, Y.; Belmont, A. S., HSP70 transgene directed motion to nuclear speckles facilitates heat shock activation. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, (10), 1138-44. [CrossRef]
- van Steensel, B.; Belmont, A. S., Lamina-Associated Domains: Links with Chromosome Architecture, Heterochromatin, and Gene Repression. Cell 2017, 169, (5), 780-791. [CrossRef]
- Pestic-Dragovich, L.; Stojiljkovic, L.; Philimonenko, A. A.; Nowak, G.; Ke, Y.; Settlage, R. E.; Shabanowitz, J.; Hunt, D. F.; Hozak, P.; de Lanerolle, P., A myosin I isoform in the nucleus. Science 2000, 290, (5490), 337-41. [CrossRef]
- Vreugde, S.; Ferrai, C.; Miluzio, A.; Hauben, E.; Marchisio, P. C.; Crippa, M. P.; Bussi, M.; Biffo, S., Nuclear myosin VI enhances RNA polymerase II-dependent transcription. Mol. Cell 2006, 23, (5), 749-55. [CrossRef]
- Hari-Gupta, Y.; Fili, N.; Dos Santos, Á.; Cook, A. W.; Gough, R. E.; Reed, H. C. W.; Wang, L.; Aaron, J.; Venit, T.; Wait, E.; Grosse-Berkenbusch, A.; Gebhardt, J. C. M.; Percipalle, P.; Chew, T.-L.; Martin-Fernandez, M.; Toseland, C. P., Myosin VI regulates the spatial organisation of mammalian transcription initiation. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, (1), 1346. [CrossRef]
- Asumda, F. Z.; Chase, P. B., Nuclear cardiac troponin and tropomyosin are expressed early in cardiac differentiation of rat mesenchymal stem cells. Differentiation 2012, 83, (3), 106-115. [CrossRef]
- Chase, P. B.; Szczypinski, M. P.; Soto, E. P., Nuclear tropomyosin and troponin in striated muscle: new roles in a new locale? J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 2013, 34, (3-4), 275-284. [CrossRef]
- Arifulin, E. A.; Sheval, E. V., Non-Canonical Localization of Cardiac Troponins: Expanding Functions or Causing Pathologies? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, (6). [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Birbrair, A.; Wang, Z. M.; Taylor, J.; Messi, M. L.; Delbono, O., Troponin T nuclear localization and its role in aging skeletal muscle. Age 2013, 35, (2), 353-370. [CrossRef]
- Johnston, J. R.; Chase, P. B.; Pinto, J. R., Troponin through the looking-glass: emerging roles beyond regulation of striated muscle contraction. Oncotarget 2018, 9, (1), 1461-1482. [CrossRef]
- Gordon, A. M.; Homsher, E.; Regnier, M., Regulation of contraction in striated muscle. Physiol. Rev. 2000, 80, (2), 853-924. [CrossRef]
- Risi, C. M.; Belknap, B.; White, H. D.; Dryden, K.; Pinto, J. R.; Chase, P. B.; Galkin, V. E., High-resolution cryo-EM structure of the junction region of the native cardiac thin filament in relaxed state. PNAS Nexus 2023, 2, (1), pgac298. [CrossRef]
- Risi, C. M.; Landim-Vieira, M.; Belknap, B.; Chase, P. B.; Pinto, J. R.; Galkin, V. E., The role of the troponin T interactions with actin in regulation of cardiac thin filament revealed by the troponin T pathogenic variant Ile79Asn. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2025, 204, 55-67. [CrossRef]
- Yamada, Y.; Namba, K.; Fujii, T., Cardiac muscle thin filament structures reveal calcium regulatory mechanism. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, (1), 153. [CrossRef]
- Oda, T.; Yanagisawa, H.; Wakabayashi, T., Cryo-EM structures of cardiac thin filaments reveal the 3D architecture of troponin. J. Struct. Biol. 2020, 209, (3), 107450. [CrossRef]
- Ebashi, S.; Kodama, A., Interaction of troponin with F-actin in the presence of tropomyosin. J. Biochem. 1966, 59, (4), 425-6. [CrossRef]
- Potter, J. D., The content of troponin, tropomyosin, actin, and myosin in rabbit skeletal muscle myofibrils. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1974, 162, (2), 436-441. [CrossRef]
- Potter, J. D.; Gergely, J., The calcium and magnesium binding sites on troponin and their role in the regulation of myofibrillar adenosine triphosphatase. J. Biol. Chem. 1975, 250, (12), 4628-4633. [CrossRef]
- Isambert, H.; Venier, P.; Maggs, A. C.; Fattoum, A.; Kassab, R.; Pantaloni, D.; Carlier, M.-F., Flexibility of actin filaments derived from thermal fluctuations. Effect of bound nucleotide, phalloidin, and muscle regulatory proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, (19), 11437-44. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7744781.
- Loong, C. K. P.; Zhou, H.-X.; Chase, P. B., Persistence length of human cardiac α-tropomyosin measured by single molecule direct probe microscopy. PLoS One 2012, 7, (6), e39676. [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, O.; Bhardwaj, R. D.; Bernard, S.; Zdunek, S.; Barnabé-Heider, F.; Walsh, S.; Zupicich, J.; Alkass, K.; Buchholz, B. A.; Druid, H.; Jovinge, S.; Frisén, J., Evidence for cardiomyocyte renewal in humans. Science 2009, 324, (5923), 98-102. [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, O.; Zdunek, S.; Alkass, K.; Druid, H.; Bernard, S.; Frisén, J., Identification of cardiomyocyte nuclei and assessment of ploidy for the analysis of cell turnover. Exp. Cell. Res. 2011, 317, (2), 188-94. [CrossRef]
- Franklin, S.; Zhang, M. J.; Chen, H.; Paulsson, A. K.; Mitchell-Jordan, S. A.; Li, Y.; Ping, P.; Vondriska, T. M., Specialized compartments of cardiac nuclei exhibit distinct proteomic anatomy. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2011, 10, (1), M110 000703. [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Zhao, J.; Hoffmann-Rohrer, U.; Grummt, I., Nuclear myosin I acts in concert with polymeric actin to drive RNA polymerase I transcription. Genes Dev. 2008, 22, (3), 322-30. [CrossRef]
- Sahota, V. K.; Grau, B. F.; Mansilla, A.; Ferrús, A., Troponin I and Tropomyosin regulate chromosomal stability and cell polarity. J. Cell. Sci. 2009, 122, (Pt 15), 2623-31. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Birbrair, A.; Delbono, O., Nonmyofilament-associated troponin T3 nuclear and nucleolar localization sequence and leucine zipper domain mediate muscle cell apoptosis. Cytoskeleton 2013, 70, (3), 134-47. [CrossRef]
- Nunez Lopez, Y. O.; Messi, M. L.; Pratley, R. E.; Zhang, T.; Delbono, O., Troponin T3 associates with DNA consensus sequence that overlaps with p53 binding motifs. Exp. Gerontol. 2018, 108, 35-40. [CrossRef]
- Ljubojevic, S.; Bers, D. M., Nuclear calcium in cardiac myocytes. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2015, 65, (3), 211-7. [CrossRef]
- Berridge, M. J.; Bootman, M. D.; Roderick, H. L., Calcium signalling: dynamics, homeostasis and remodelling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003, 4, (7), 517-29. [CrossRef]
- Ljubojevic, S.; Radulovic, S.; Leitinger, G.; Sedej, S.; Sacherer, M.; Holzer, M.; Winkler, C.; Pritz, E.; Mittler, T.; Schmidt, A.; Sereinigg, M.; Wakula, P.; Zissimopoulos, S.; Bisping, E.; Post, H.; Marsche, G.; Bossuyt, J.; Bers, D. M.; Kockskämper, J.; Pieske, B., Early remodeling of perinuclear Ca2+ stores and nucleoplasmic Ca2+ signaling during the development of hypertrophy and heart failure. Circulation 2014, 130, (3), 244-55. [CrossRef]
- Powell, J. A.; Carrasco, M. A.; Adams, D. S.; Drouet, B.; Rios, J.; Müller, M.; Estrada, M.; Jaimovich, E., IP3 receptor function and localization in myotubes: an unexplored Ca2+ signaling pathway in skeletal muscle. J. Cell. Sci. 2001, 114, (Pt 20), 3673-83. [CrossRef]
- Powell, J. A.; Molgó, J.; Adams, D. S.; Colasante, C.; Williams, A.; Bohlen, M.; Jaimovich, E., IP3 receptors and associated Ca2+ signals localize to satellite cells and to components of the neuromuscular junction in skeletal muscle. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, (23), 8185-92. [CrossRef]
- Ulferts, S.; Grosse, R., SUN2 mediates calcium-triggered nuclear actin polymerization to cluster active RNA polymerase II. EMBO Rep. 2024, 25, (11), 4728-4748. [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, I.; McCollum, D., Control of cellular responses to mechanical cues through YAP/TAZ regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, (46), 17693-17706. [CrossRef]
- Fischer, M.; Rikeit, P.; Knaus, P.; Coirault, C., YAP-Mediated Mechanotransduction in Skeletal Muscle. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 41. [CrossRef]
- Dupont, S.; Morsut, L.; Aragona, M.; Enzo, E.; Giulitti, S.; Cordenonsi, M.; Zanconato, F.; Le Digabel, J.; Forcato, M.; Bicciato, S.; Elvassore, N.; Piccolo, S., Role of YAP/TAZ in mechanotransduction. Nature 2011, 474, (7350), 179-83. [CrossRef]
- Kobirumaki-Shimozawa, F.; Inoue, T.; Shintani, S. A.; Oyama, K.; Terui, T.; Minamisawa, S.; Ishiwata, S.; Fukuda, N., Cardiac thin filament regulation and the Frank-Starling mechanism. J. Physiol. Sci. 2014, 64, (4), 221-32. [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.; Tainter, C.; Regnier, M.; Martyn, D. A., Cooperative cross-bridge activation of thin filaments contributes to the Frank-Starling mechanism in cardiac muscle. Biophys. J. 2009, 96, (9), 3692-702. [CrossRef]
- Bensley, J. G.; De Matteo, R.; Harding, R.; Black, M. J., Three-dimensional direct measurement of cardiomyocyte volume, nuclearity, and ploidy in thick histological sections. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23756. [CrossRef]
- Landim-Vieira, M.; Schipper, J. M.; Pinto, J. R.; Chase, P. B., Cardiomyocyte nuclearity and ploidy: when is double trouble? J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 2020, 41, 329-340. [CrossRef]
- Laflamme, M. A.; Murry, C. E., Heart regeneration. Nature 2011, 473, (7347), 326-35. [CrossRef]
- Jungbluth, H.; Gautel, M., Pathogenic mechanisms in centronuclear myopathies. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2014, 6, 339. [CrossRef]
- Mazzotti, A. L.; Coletti, D., The Need for a Consensus on the Locution "Central Nuclei" in Striated Muscle Myopathies. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 577. [CrossRef]
- Ross, J. A.; Stroud, M. J., THE NUCLEUS: Mechanosensing in cardiac disease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell. Biol. 2021, 137, 106035. [CrossRef]
- Coscarella, I. L.; Landim-Vieira, M.; Rastegarpouyani, H.; Chase, P. B.; Irianto, J.; Pinto, J. R., Nucleus mechanosensing in cardiomyocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, (17), 13341. [CrossRef]
- Landim-Vieira, M.; Nieto Morales, P. F.; ElSafty, S.; Kahmini, A. R.; Ranek, M. J.; Solís, C., The role of mechanosignaling in the control of myocardial mass. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2025, 328, (3), H622-H638. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Pereyra, A. S.; Wang, Z.-M.; Birbrair, A.; Reisz, J. A.; Files, D. C.; Purcell, L.; Feng, X.; Messi, M. L.; Feng, H.; Chalovich, J.; Jin, J.-P.; Furdui, C.; Delbono, O., Calpain inhibition rescues troponin T3 fragmentation, increases Cav1.1, and enhances skeletal muscle force in aging sedentary mice. Aging Cell 2016, 15, (3), 488-98. [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Huang, K.; Shi, M.; Huo, Y.; Han, L.; Liu, B.; Li, Y., Research Advances in the Role of the Tropomyosin Family in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, (17). [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




