Submitted:
28 July 2025
Posted:
29 July 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Toxic Leadership and the Toxic Leader
1.2. Nursing Staff Retention
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Aim of the Study
2.2. Design
2.3. Identifying Relevant Studies
| Term | Boolean Operator | Term | Boolean Operator | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toxic1 Leadership | AND | Healthcare Organizations | ||
| Toxic Leadership | AND | Nursing Staff | ||
| Toxic Leadership | AND | Healthcare Organizations | AND | Nursing Staff |
| Toxic Leadership | OR | Nursing Staff | AND | Healthcare Organizations |
| Healthcare Organizations | OR | Nursing Staff | AND | Toxic Leadership |
2.4. Study Selection
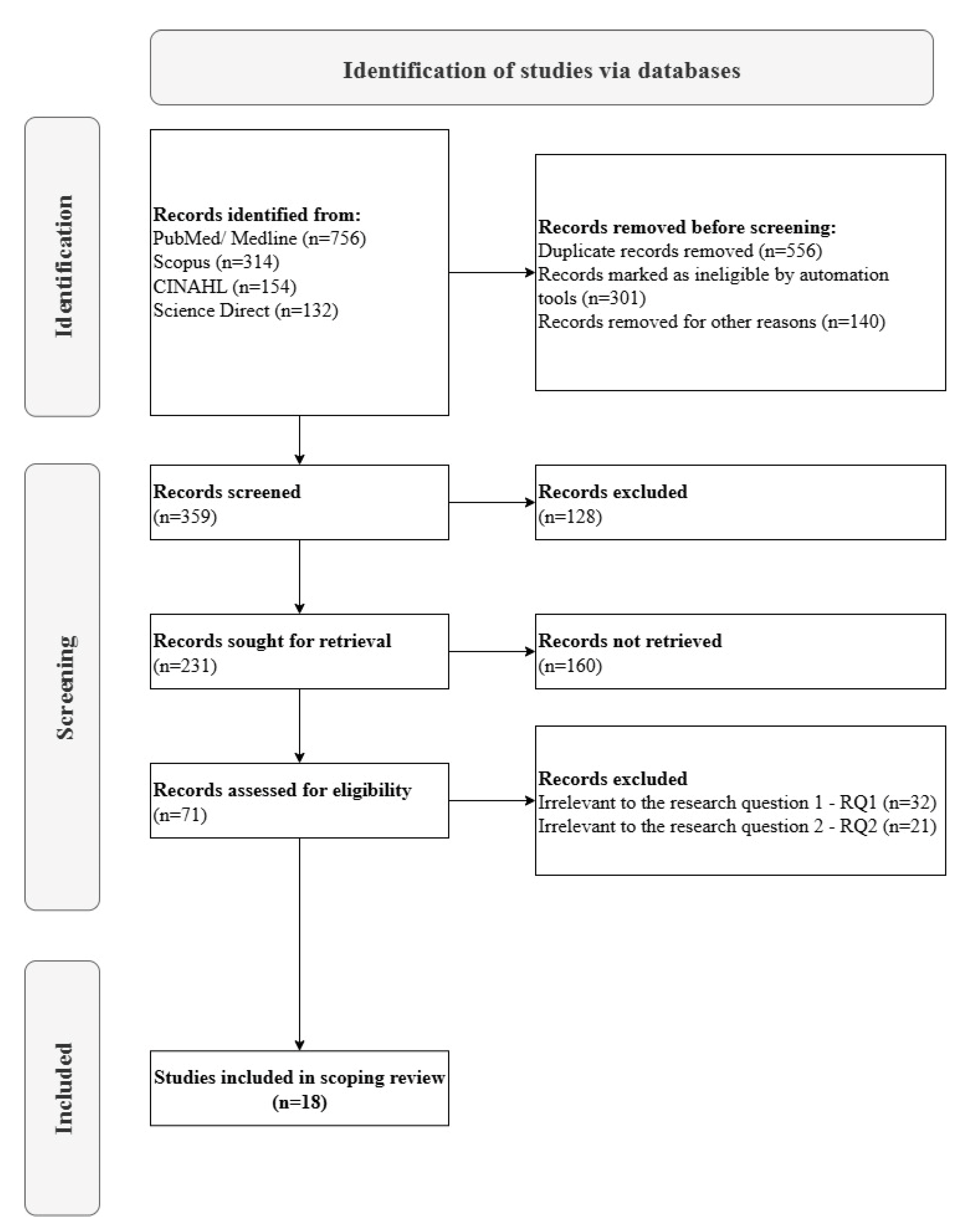
2.5. Charting the Data
2.6. Data Analysis
2.7. Consultation
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Included Studies
| Characteristics | Studies n (%) |
|---|---|
| Area of Studies | |
| Europe | 2 (11.1) |
| Asia | 8 (44.4) |
| USA | 1 (5.6) |
| Africa | 7 (38.9) |
| Year of publication | |
| 2019 | 3 (16.7) |
| 2020 | 2 (11.1) |
| 2021 | 2 (11.1) |
| 2022 | 5 (27.8) |
| 2023 | 3 (16.7) |
| 2024 | 2 (11.1) |
| 2025 | 1 (5.6) |
| Type of studies | |
| quantitative study | 10 (55.6) |
| qualitative study | 2 (11.1) |
| mixed methods | 6 (33.3) |
| Categorization of studies | |
| key dimensions shaping perceptions of toxic leadership | 5 (27.8) |
| impact of toxic leadership on nursing staff retention | 13 (72.2) |
3.2. Perceptions of Toxic Leadership Key Dimensions
3.3. Toxic Leadership and Its Impact on Staff Retention
4. Discussion
5. Limitations and Strengths
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| A/A | Author(s), Year | Country | Aim | Data Sample | Study Design | Data Collection Method | Data Analysis Method | Finding(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Labrague et al., 2020 [1] |
Philippines | This study examined the influence of toxic and transformational leadership practices on nurses' job satisfaction, psychological distress, absenteeism, and intent to leave the organization or the nursing profession. | 770 | Cross-sectional study | Toxic Leadership Behaviors of Nurse Managers Scale, Global Transformational Leadership , Job Satisfaction Index , Perceived Stress Scale, Two single-item measures developed by O'Driscoll and Beehr, Absenteeism was assessed using a researcher-designed single item question |
SPSS | Toxic leadership increased distress and absenteeism; transformational leadership improved job satisfaction. |
| 2. | Hossny et al., 2023 [2] | Egypt | This study was designed to assess nurses’ perception of the effects of organizational climate and toxic leadership behaviors on their intention to stay and the differences in these domains between the two hospitals studied |
250 | descriptive comparative study |
the organizational climate questionnaire (42 items categorized into nine domains), the toxic leadership scale (30 items categorized into five domains), and the Chinese version of the intent-to-stay scale. |
IBM SPSS Statistics Version 22.0, Microsoft Excel, GraphPad Prism 5 |
Positive organizational climate and supportive systems increased nurses' intention to stay. |
| 3. | Ofei, 2022 [3] | Ghana | This study aimed at assessing the nature and effect of toxic leadership of nurse managers on the perceived job satisfaction and productivity of the nursing workforce. | 943 | Cross-sectional descriptive study | Toxic Leadership Behaviors of Nurse Managers’ Scale, Perceived Productivity Questionnaire, and the Minnesota Satisfaction Questionnaire (MSQ-short version) |
SPSS software version 26 | Toxic leadership reduced nurses' job satisfaction and productivity. |
| 4. | Ramdan and Eid., 2020 [4] | Egypt | This study envisioned to compare toxic leadership among intensive care nursing staff at Tanta University Hospital and El Menshawy hospital and assess its relation to their conflict management style used and organizational commitment at the two hospitals. | 544 | Descriptive, comparative, cross-sectional study | Toxic Leadership Assessment Scale , Conflict Management Styles, Assessment Scale, Organizational Commitment Assessment Scale |
IBM SPSS software package version 20.0. |
Toxic leadership reduced organizational commitment and influenced conflict management styles. |
| 5. | Xueqin Guo et al., 2022 [5] | China | The aim of this study is to explore the perceptions of Chinese registered nurses on toxic leadership behaviors of nurse managers and to determine its type, cause and response measures | 12 | Phenomenological qualitative study | semi-structured in-depth interviews | Colaizzi seven-step analysis method | Nurses working with a transformational leader report higher job contentment and lower intent to leave the nursing profession. Nurses who work for a manager with toxic leadership behaviors demonstrated lower job contentment, higher stress levels, frequent absenteeism and higher intent to leave the nursing profession. |
| 6. | Siyal et al., 2021 [6] | China | The aim of this study is to develop and empirically test a mediation model to examine the indirect impact of abusive supervision on employee performance. |
430 | Empirical, experimental study | The 10-item scale version of the 15-item scale developed by Tepper, 4-item scale validated by Amabile et al., general satisfaction 5-item measure by Hackman and Oldham , the 4-item scale to measure employee performance developed by Liden et al. |
Model development and empirical testing | Abusive supervision reduced employee performance. |
| 7. | Durrah et al., 2024 [7] |
France | The current study aims to examine how toxic management styles can lead to both psychological and physical withdrawal of employees in the healthcare sector | 413 | Quantitative study | Self-developed questionnaire | SmartPLS 3.3.9 |
Toxic leadership increased both psychological and physical withdrawal behaviors |
| 8. | Trepanier et al., 2019 [8] | Canada | The aim of this paper is to investigate the psychological and motivational processes involved in the relationship between two forms of destructive leadership (tyrannical and laissez-faire) and employee health (burnout, affective commitment and job performance) | 399 | Cross-sectional study | The Destructive Leadership Scale, The French version of the Psychological Need Thwarting Scale, The Multidimensional Work Motivation Scale, The Maslach Burnout Inventory General Survey, The occupational commitment questionnaire A self-reported scale consisting of 4 items adapted from the in-role performance subscale of the organizational citizenship behavior scale |
Structural equation modeling analysis. | Tyrannical leadership frustrates autonomy, competence, and relatedness, leading to burnout and lower performance. |
| 9. | Erschens et al., 2022 [9] |
Germany | The aim of this study is to investigate the association of general well-being and different leadership styles among employees in a German tertiary hospital. | 1137 | Cross-sectional study | Module A and D of the standardized Questionnaire on Integrative Leadership, the five-item World Health Organization wellbeing index |
IBM SPSS version 25 |
Transformational and transactional leadership styles are associated with higher well-being scores among hospital employees, while laissez-faire and destructive leadership styles are associated with lower scores across all professional groups. |
| 10. | Low et al., 2019 [10] | Malaysia | The aims of this research are to address the two fundamental research questions: 1) What are the antecedents that lead to counterproductive work behavior (CWB) of nurses in public hospitals? 2) How effective are the moderating roles of power distance orientation (a cultural factor) and locus of control (an individual factor) in impacting CWB? |
337 | Quantitative study | Tepper’s (2000) 15-item abusive supervision Measure, Colquitt’s (2001) 20-item scale 24-item measure adapted from Mitchell and Ambrose (2007) and Bennett and Robinson , six-item scale developed by Dorfman and Howell (1988) and Farh, Hackett and Liang (2007), 16-item Work Locus of Control Scale |
structural equation modeling |
Abusive supervision leads to counterproductive work behavior in nurses |
| 11. | Shipl et al., 2022 [11] | Egypt | This study aimed to investigate the relationship between toxic leadership and nurse followership effectiveness | 343 | Cross-sectional study | The Toxic Leadership Scale and the Followership Styles Questionnaire |
IBM SPSS, version 25 |
Toxic leadership negatively correlated with nurse followership effectiveness |
| 12. | Berma et al., 2021[12] | Egypt | This study aimed to investigate the relationship between workplace toxicity, organizational silence and thriving among nurses. | 235 | descriptive correlational research | Toxic Workplace Environment Questionnaire, Organizational Silence Scale, Thriving at Work Scale |
SPSS version 22.0 |
Workplace toxicity leads to increased organizational silence, reducing thriving among nurses and potentially leading to staff resignation |
| 13. | Bakkal et al., 2019 [13] | Turkey | The aim of this study is to investigate the effects of the toxic leadership of healthcare employees on the turnover intention and the mediating effects of job satisfaction |
658 | cross-sectional descriptive study |
The Toxic Leadership Scale, the Minnesota Job Satisfaction Questionnaire, a turnover intention scale (Rosin & Korabik, 1995 |
Confirmatory Factor Analysis, Structural Equation Model SPSS 24.0 and AMOS 24.0 |
Toxic leadership negatively impacts job satisfaction, which in turn increases turnover intention among healthcare personnel |
| 14. | Budak & Erdal, 2022 [14] | Turkey | The aim of this study is to investigate the mediating effect of burnout syndrome on toxic leadership and job satisfaction |
412 | cross-sectional study | Toxic Leadership Scale, Burnout Scale, Job Satisfaction Scale |
Structural Model Analysis |
Toxic leadership negatively affects job satisfaction and increases burnout syndrome |
| 15. | Mrayyan, 2025 [15] |
Jordan | The aim of this research is to investigate nursing leaders' toxic leadership, nurses' workplace satisfaction, job engagement, and turnover intention in Jordan and whether toxic leadership and sample characteristics predict nurses' work- place satisfaction, job engagement, and turnover intention. |
384 |
cross-sectional study | Toxic Leadership Scale, Nursing Workplace Satisfaction Scale, Job Engagement Scale, Turnover Intention Scale |
Online survey, SPSS program version 25 |
Toxic leadership results in low job satisfaction, stress and emotional exhaustion, and, in turn, decreased quality of nursing care |
| 16. | Labrague, 2024 [16] | Philippines | The aim of this study is to examine the mediating effects of work-family conflict on the relationship between toxic leadership behaviors of nurse managers and psychological distress and work satisfaction among emergency nurses. |
283 | cross-sectional study | Toxic Leadership Behaviors of Nurse Managers Scale, Work-Family Conflict Scale, Job Stress Scale and the Job Satisfaction Index |
Mediation analyses were conducted using the PROCESS Macro with Model 4. |
Toxic leadership reduced work satisfaction and increased psychological distress |
| 17. | Farghaly Abdelaliem & Abou Zeid, 2023 [17] | Egypt | The aim of this study is to assess toxic leadership and organizational performance among nurses of a University Hospital, and explore the mediating effect of nurses ‘silence |
750 |
cross-sectional study |
The toxic leadership scale, the organizational performance questionnaire |
structured equation modeling |
Toxic leadership had a significant negative relationship with organizational performance and the nurses’ silence |
| 18. | Ofei et al., 2023 [18] | Ghana |
The aim of this study is to investigate the mediating role of job satisfaction on toxic leadership and turnover intentions of nurses |
943 |
cross-sectional study |
The Turnover Intention, Minnesota Satisfaction Scale and the Toxic Leadership Behaviors of Nurse Managers’ Scale |
SPSS software version 26, descriptive and differential statistics |
Job satisfaction acts as a mediating factor for toxic leadership behaviour and nurses’ turnover intentions |
References
- Benmira, S.; Agboola, M. Evolution of leadership theory. BMJ Leader 2021, 5, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajoria, P.; Sharma, A.; Sharma, M.; Sumaiya, B. Leadership Style and Organisational Success. World Journal of English Language 2022, 12, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydogdu, A.L.F. Exploring Different Aspects of Nursing Leadership: An Integrative Review of Qualitative Studies. Modern Care Journal 2023, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scully, N.J. Leadership in nursing: The importance of recognising inherent values and attributes to secure a positive future for the profession. Collegian 2015, 22, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ćeranić, J.; Peličić, D.; Saveljić, M. Building leadership in nursing practice. Sanamed 2024, 19, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashlan, M.A.; et al. Nursing Leadership and Its Impact on Healthcare Quality: A Systematic Review. Journal of Ecohumanism 2024, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazer, C.; Sullivan, D. The nuts & bolts of being a nursing leader. Part 1: Leadership in nursing series. Teaching and Learning in Nursing 2025, 20, 46–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Naemi, I.A. Nursing Leadership Role in Healthcare Transformation – A Critical Overview. Saudi Journal of Nursing and Health Care 2023, 6, 310–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rezende, H. How relational leadership can enhance nurses’ well-being and productivity. Nursing Standard 2024, 39, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atalla, A.D.G.; Mostafa, W.H. Relationship between Toxic Leadership and Work Outcomes: A Cross-sectional Study. Egyptian Journal of Health Care 2023, 14, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labrague, L.J. Influence of nurse managers’ toxic leadership behaviours on nurse-reported adverse events and quality of care. J Nurs Manag 2021, 29, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsadaan, N.; Alqahtani, M. Toxic Leadership in Emergency Nurses: Assessing Abusive Supervision and Its Team-Level Impacts on Conflict Management and Organizational Commitment. J Nurs Manag 2024, 2024, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labrague, L.J. Toxic leadership and its relationship with outcomes on the nursing workforce and patient safety: a systematic review. Leadership in Health Services 2024, 37, 192–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.A.; Hanges, P.J. Title of Document: DEVELOPMENT AND VALIDATION OF THE TOXIC LEADERSHIP SCALE.
- Bas, B. Toxic Leadership in Education. International Journal of Educational Administration, Management, and Leadership, pp. 97–104, Nov. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Smith, N.; Fredricks-Lowman, I. Conflict in the workplace: a 10-year review of toxic leadership in higher education. International Journal of Leadership in Education 2020, 23, 538–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paltu, A.; Brouwers, M. Toxic leadership: Effects on job satisfaction, commitment, turnover intention and organisational culture within the South African manufacturing industry. SA Journal of Human Resource Management 2020, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, K.L. Leader toxicity: An empirical investigation of toxic behavior and rhetoric. Leadership 2010, 6, 373–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milosevic, I.; Maric, S.; Lončar, D. Defeating the Toxic Boss: The Nature of Toxic Leadership and the Role of Followers. J Leadersh Organ Stud 2020, 27, 117–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satiani, B.; Satiani, A. Recognizing and Managing a Toxic Leader: A Case Study. Physician Leadersh J 2022, 9, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbogast, G.; Jadav, A. Investigating business toxic leadership. Journal of Management and Engineering Integration 2024, 17, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, H.; Iqbal, J. What Happens When a Leader is Toxic? A Qualitative Investigation. Bulletin of Business and Economics (BBE) 2024, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Chawla, S. Toxic Leadership in Workplaces: Insights from Bibliometric, Thematic Analysis, and TCM Framework. International Journal of Organizational Leadership 2024, 13, 179–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodin, H.J. The nursing shortage in the United States of America: an integrative review of the literature. J Adv Nurs 2003, 43, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, A.; Duff, J.; Munday, J. Perioperative Nursing Shortages: An Integrative Review of Their Impact, Causal Factors, and Mitigation Strategies. J Nurs Manag 2024, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, M. Time to solve persistent, pernicious and widespread nursing workforce shortages. Int Nurs Rev 2023, 70, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Wyk, S.N.; Naicker, V. A review of the effect of nurse shortages on existing nurse workforces in South Africa and Ukraine. Technology audit and production reserves 2023, 4, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmon, M.; et al. How is ‘shortage’ defined? Exploring Nursing Workforce Data across Canada 2015-2022: An Ecological Study. Int J Popul Data Sci 2024, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaboyan, Y.S.; Pivkina, A.I. Nursing staff as a provider of safe and high-quality medical care. Public Health 2022, 2, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; et al. The effect of nurse staffing on patient-safety outcomes: A cross-sectional survey. J Nurs Manag 2020, 28, 1758–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, P.; et al. Nurse staffing and patient outcomes: Strengths and limitations of the evidence to inform policy and practice. A review and discussion paper based on evidence reviewed for the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence Safe Staffing guideline development. Int J Nurs Stud 2016, 63, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Ora, C.; Saville, C.; Rubbo, B.; Turner, L.Y.; Jones, J.; Griffiths, P. Nurse staffing levels and patient outcomes: a systematic review of longitudinal studies. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Needleman, J.; Liu, J.; Shang, J.; Larson, E.L.; Stone, P.W. Association of registered nurse and nursing support staffing with inpatient hospital mortality. BMJ Qual Saf 2020, 29, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assaye, A.M.; Wiechula, R.; Schultz, T.J.; Feo, R. Impact of nurse staffing on patient and nurse workforce outcomes in acute care settings in low- and middle-income countries: a systematic review. JBI Evid Synth 2021, 19, 751–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, J.E.; Murrells, T.; Rafferty, A.M.; Morrow, E.; Griffiths, P. ‘Care left undone’ during nursing shifts: associations with workload and perceived quality of care. BMJ Qual Saf 2014, 23, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, P.; et al. The association between nurse staffing and omissions in nursing care: A systematic review. J Adv Nurs 2018, 74, 1474–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.; Lee, J.; You, S.J.; Song, K.J.; Hong, K.J. Nurse staffing, nurses prioritization, missed care, quality of nursing care, and nurse outcomes. Int J Nurs Pract, 2020, 26. [CrossRef]
- Ramsey, Z.; Palter, J.; Hardwick, J.; Moskoff, J.; Christian, E.; Bailitz, J. Decreased Nursing Staffing Adversely Affects Emergency Department Throughput Metrics. Western Journal of Emergency Medicine 2018, 19, 496–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marufu, T.C.; Collins, A.; Vargas, L.; Gillespie, L.; Almghairbi, D. Factors influencing retention among hospital nurses: systematic review. British Journal of Nursing 2021, 30, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leveck, M.L.; Jones, C.B. The nursing practice environment, staff retention, and quality of care. Res Nurs Health 1996, 19, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mara, S.O. 121 The factors influencing nursing staff retention in the ICU setting: a scoping review. Ann Work Expo Health 2024, 68 Suppl. 1, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conroy, N.; Patton, D.; Moore, Z.; O’Connor, T.; Nugent, L.; Derwin, R. The Relationship between Transformational Leadership and Staff Nurse Retention in Hospital Settings: A Systematic Review. J Nurs Manag 2023, 2023, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marufu, T.C.; Collins, A.; Vargas, L.; Gillespie, L.; Almghairbi, D. Factors influencing retention among hospital nurses: systematic review. British Journal of Nursing 2021, 30, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamanga, E.; Dyson, J.; Loke, J.; McKeown, E. Factors influencing the recruitment and retention of registered nurses in adult community nursing services: an integrative literature review. Prim Health Care Res Dev 2020, 21, e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arksey, H.; O’Malley, L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. Int J Soc Res Methodol 2005, 8, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricco, A.C.; et al. PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and Explanation. Ann Intern Med 2018, 169, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; et al. Chinese nurses’ perceptions on toxic leadership behaviours of nurse managers: A qualitative study. J Nurs Manag 2022, 30, 3256–3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durrah, O.; Alkhalaf, T.; Sharbatji, O. Toxic leadership as a predictor of physical and psychological withdrawal behaviours in the healthcare sector. J Soc Psychol 2024, 164, 1159–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BAKKAL, E.; SERENER, B.; MYRVANG, N.A. oxic Leadership and Turnover Intention: Mediating Role of Job Satisfaction. Revista de Cercetare si Interventie Sociala 2019, 66, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofei, A.M.A.; Poku, C.A.; Paarima, Y.; Barnes, T.; Kwashie, A.A. Toxic leadership behaviour of nurse managers and turnover intentions: the mediating role of job satisfaction. BMC Nurs 2023, 22, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossny, E.K.; et al. Influence of nurses’ perception of organizational climate and toxic leadership behaviors on intent to stay: A descriptive comparative study. Int J Nurs Stud Adv 2023, 5, 100147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labrague, L.J.; Nwafor, C.E.; Tsaras, K. Influence of toxic and transformational leadership practices on nurses’ job satisfaction, job stress, absenteeism and turnover intention: A cross-sectional study. J Nurs Manag 2020, 28, 1104–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofei, A.M.A.; Paarima, Y.; Barnes, T.; Poku, C.A. Toxic leadership behaviour of nurse managers on perceived job satisfaction and productivity of nursing workforce in sub-Saharan Ghana: A multi-centre cross-sectional study. J Nurs Manag 2022, 30, 2733–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramdan, A.H.A.; Eid, W.M. Toxic Leadership: Conflict Management Style and Organizational Commitment among Intensive Care Nursing Staff. Evidence-Based Nursing Research 2020, 2, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siyal, S.; Saeed, M.; Pahi, M.H.; Solangi, R.; Xin, C. They can’t treat you well under abusive supervision: Investigating the impact of job satisfaction and extrinsic motivation on healthcare employees. Rationality and Society 2021, 33, 401–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trépanier, S.-G.; Boudrias, V.; Peterson, C. Linking destructive forms of leadership to employee health. Leadership & Organization Development Journal 2019, 40, 803–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erschens, R.; et al. The association of perceived leadership style and subjective well-being of employees in a tertiary hospital in Germany. PLoS One 2022, 17, e0278597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, Y.M.; Sambasivan, M.; Ho, J.A. Impact of abusive supervision on counterproductive work behaviors of nurses. Asia Pacific Journal of Human Resources 2021, 59, 250–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Fatah Shipl, A.M.A.; Nabawy, Z.M.; Al anwer Ashour, H.M. The relationship between toxic leadership and nurses’ followership effectiveness. Central European Journal of Nursing and Midwifery 2022, 13, 730–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berma, A.; Mohamed, H.; Nosier, H. Organizational Silence as a Mediator Factor between Workplace Toxicity and Thriving among Nurses. Assiut Scientific Nursing Journal 2021, 9, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budak, O.; Erdal, N. The Mediating Role of Burnout Syndrome in Toxic Leadership and Job Satisfaction in Organizations. Southeast European Journal of Economics and Business 2022, 17, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrayyan, M.T. Effects of Nursing Leaders’ Toxic Leadership on Nurses’ Workplace Satisfaction, Job Engagement, and Turnover Intention: An Online Cross-Sectional Study. J Adv Nurs, Mar. [CrossRef]
- Labrague, L.J. Linking Toxic Leadership With Work Satisfaction and Psychological Distress in Emergency Nurses: The Mediating Role of Work-Family Conflict. J Emerg Nurs 2024, 50, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelaliem, S.M.F.; Zeid, M.A.G.A. The relationship between toxic leadership and organizational performance: the mediating effect of nurses’ silence. BMC Nurs 2023, 22, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukacik, E.-R.; Bourdage, J.S. Exploring the Influence of Abusive and Ethical Leadership on Supervisor and Coworker-Targeted Impression Management. J Bus Psychol 2019, 34, 771–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.; Nambudiri, R.; Selvaraj, P.; Sadh, A. A temporal study on subordinate’s response to destructive leadership: voice withdrawal as a conflict coping mechanism. International Journal of Conflict Management 2021, 32, 886–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhu, J. Destructive Leadership, Employees’ Voice, and Organization. 2016, pp. 205–221. [CrossRef]
- Joseph, S.; Shetty, N. An empirical study on the impact of employee voice and silence on destructive leadership and organizational culture. Asian Journal of Business Ethics 2022, 11, 85–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazmi, S.A.; USMANI, S.; Raza, S. Effect of Despotic Leadership on the Employee Work Withdrawal Behavior and Acquiescent Silence. Reviews of Management Sciences 2022, 4, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaubroeck, J.M.; Shen, Y.; Chong, S. A dual-stage moderated mediation model linking authoritarian leadership to follower outcomes. . Journal of Applied Psychology 2017, 102, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Huang, X.; Sun, J.; Zheng, Y.; Graham, L.; Jiang, J. The virtue of a controlling leadership style: Authoritarian leadership, work stressors, and leader power distance orientation. Asia Pacific Journal of Management 2024, 41, 507–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousa, W.; EldinFekry, N.; Elewa, A. Relationship between nurse manager leadership style and staff nurses’ work engagement. Egyptian Nursing Journal 2019, 16, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, R.; Glazer, S.; Leiva, D. Leaders Condition the Work Experience: A Test of a Job Resources-Demands Model Invariance in Two Countries. J Nurs Manag 2023, 2023, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asiri, A.M.; Mahran, S.M.; Elseesy, N.A. A study of staff nurses’ perceptions of nursing leadership styles and work engagement levels in Saudi general hospitals. International Journal of ADVANCED AND APPLIED SCIENCES 2023, 10, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pishgooie, A.H.; Atashzadeh-Shoorideh, F.; Falcó-Pegueroles, A.; Lotfi, Z. Correlation between nursing managers’ leadership styles and nurses’ job stress and anticipated turnover. J Nurs Manag 2019, 27, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Specchia, M.L.; et al. Leadership Styles and Nurses’ Job Satisfaction. Results of a Systematic Review. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2021, 18, 1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellali, T.; et al. Assessing the Effect of Transactional Leadership and Empowerment on Nursing Staff’s Satisfaction: A Cross-Sectional Study. Florence Nightingale J Nurs 2024, 32, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suliman, M.; Almansi, S.; Mrayyan, M.; ALBashtawy, M.; Aljezawi, M. Effect of nurse managers’ leadership styles on predicted nurse turnover. Jul. 14, 2020, RCN Publishing Company Ltd. [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Gu, D.; Liang, C.; Zhao, S.; Ma, Y. How transformational leadership and clan culture influence nursing staff’s willingness to stay. J Nurs Manag 2020, 28, 1515–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gashaye, M.; Tilahun, D.; Belay, A.; Bereka, B. Perceived Utilization of Leadership Styles Among Nurses. Risk Manag Healthc Policy 2023, 16, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malak, H.M.; Lorman, W.; Rundio, A.; Simion, D.; Simion, M.G. Predominantly practiced leadership styles of Chief Nursing Officers in healthcare organizations. J Interprof Educ Pract 2022, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsadaan, N.; Alqahtani, M. Toxic Leadership in Emergency Nurses: Assessing Abusive Supervision and Its Team-Level Impacts on Conflict Management and Organizational Commitment. J Nurs Manag 2024, 2024, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahgob, G.A.-N.H.; Adam, S.M.A.; El-sayed, S.M. Staff Nurses ’Perception Regarding Toxic Leadership Behavior of Head Nurses and it’s Relation to their Work Engagement. Egyptian Journal of Health Care 2024, 15, 511–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palvimo, T.; Vauhkonen, A.; Hult, M. The Associations among Destructive Leadership, Job Demands and Resources, and Burnout among Nurses: A Cross-Sectional Survey Study. J Nurs Manag 2023, 2023, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, A.; Palma-Moreira, A. Toxic Leadership and Turnover Intentions: The Role of Burnout Syndrome. Adm Sci 2024, 14, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solehudin, S.; Syabanasyah, I. Impact of toxic leadership on nurses’ motivation, job satisfaction, productivity, and turnover intentions. Journal of Health Science and Medical Therapy 2024, 2, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaghini, F.; Fiorini, J.; Piredda, M.; Fida, R.; Sili, A. The relationship between nurse managers’ leadership style and patients’ perception of the quality of the care provided by nurses: Cross sectional survey. Int J Nurs Stud 2020, 101, 103446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.A.O.; Zhang, J.; Fouad, A.S.; Mousa, K.; Nour, H.M. The Dark Side of Leadership: How Toxic Leadership Fuels Counterproductive Work Behaviors Through Organizational Cynicism and Injustice. Sustainability 2024, 17, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapalme, M.; Guerrero, S. How do I stand compared to agency workers? Justice perceptions and employees’ counterproductive work behaviours. J Nurs Manag 2019, 27, 1471–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- KAYANI, M.B.; ALASAN, I.I. Impact of Toxic Leadership on Counterproductive Work Behavior with the Mediating role of Psychological Contract Breach and Moderating role of Proactive Personality. Studies of Applied Economics 2021, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| 1 | The primary search term 'toxic leadership' was systematically expanded to include conceptually related terms such as 'abusive leadership,' 'destructive leadership,' and 'oppressive leadership' to ensure comprehensive coverage of the literature. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





