Submitted:
14 July 2025
Posted:
15 July 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
2.1. Semantic Segmentation Methods for 3D Models
2.2. UAV Path Planning Methods for 3D Reconstruction
2.2.1. Model-Free Approaches
2.2.2. Model-Based Approaches
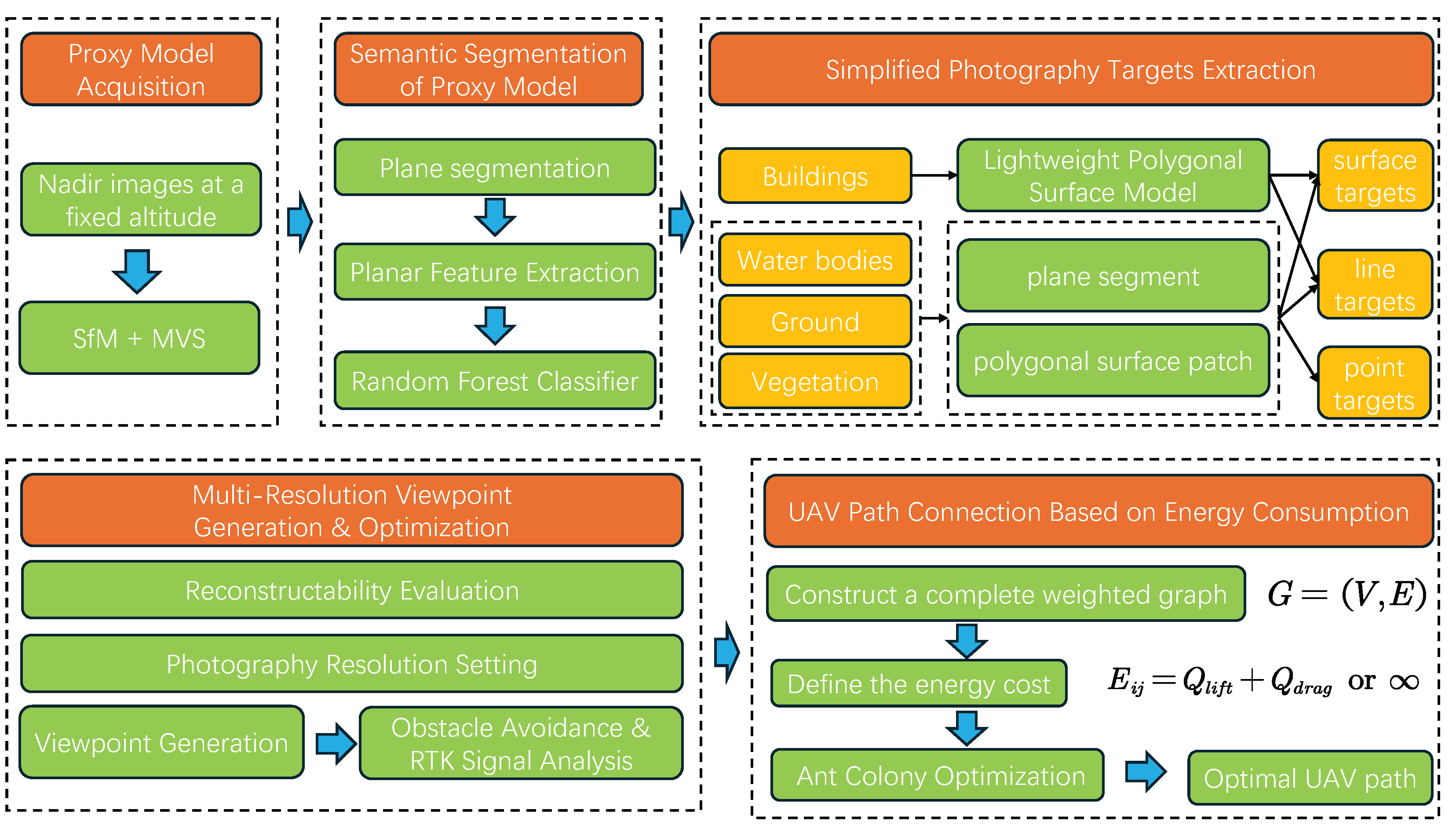
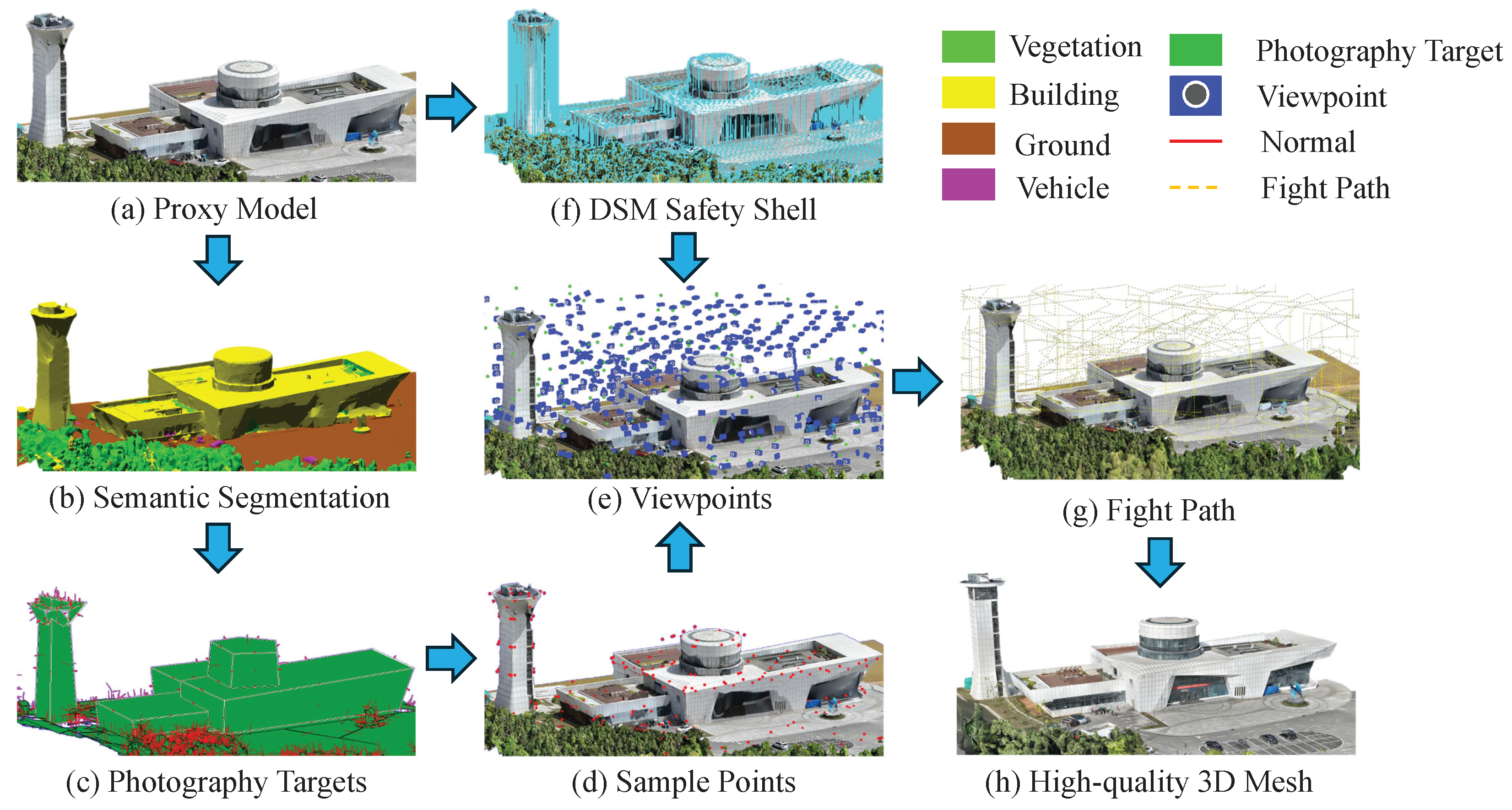
3. Proposed Method
3.1. Overview
3.2. Proxy Model Acquisition
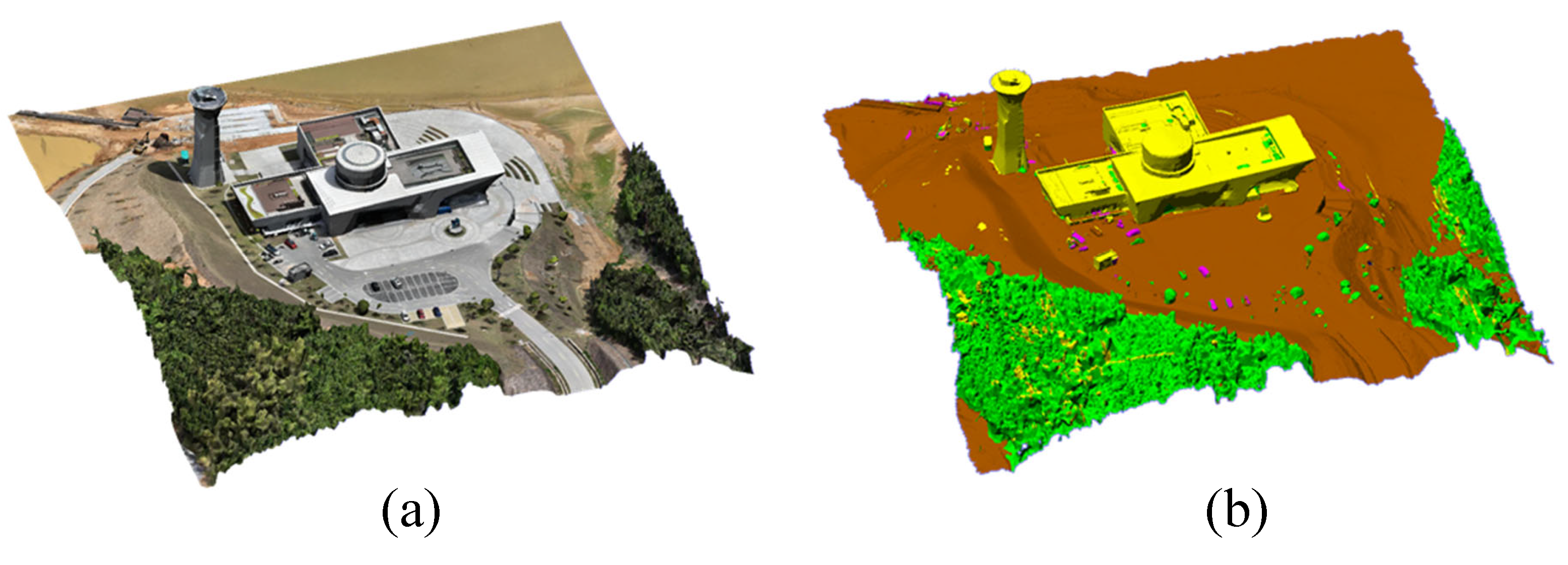
3.3. Semantic Segmentation of Proxy Model
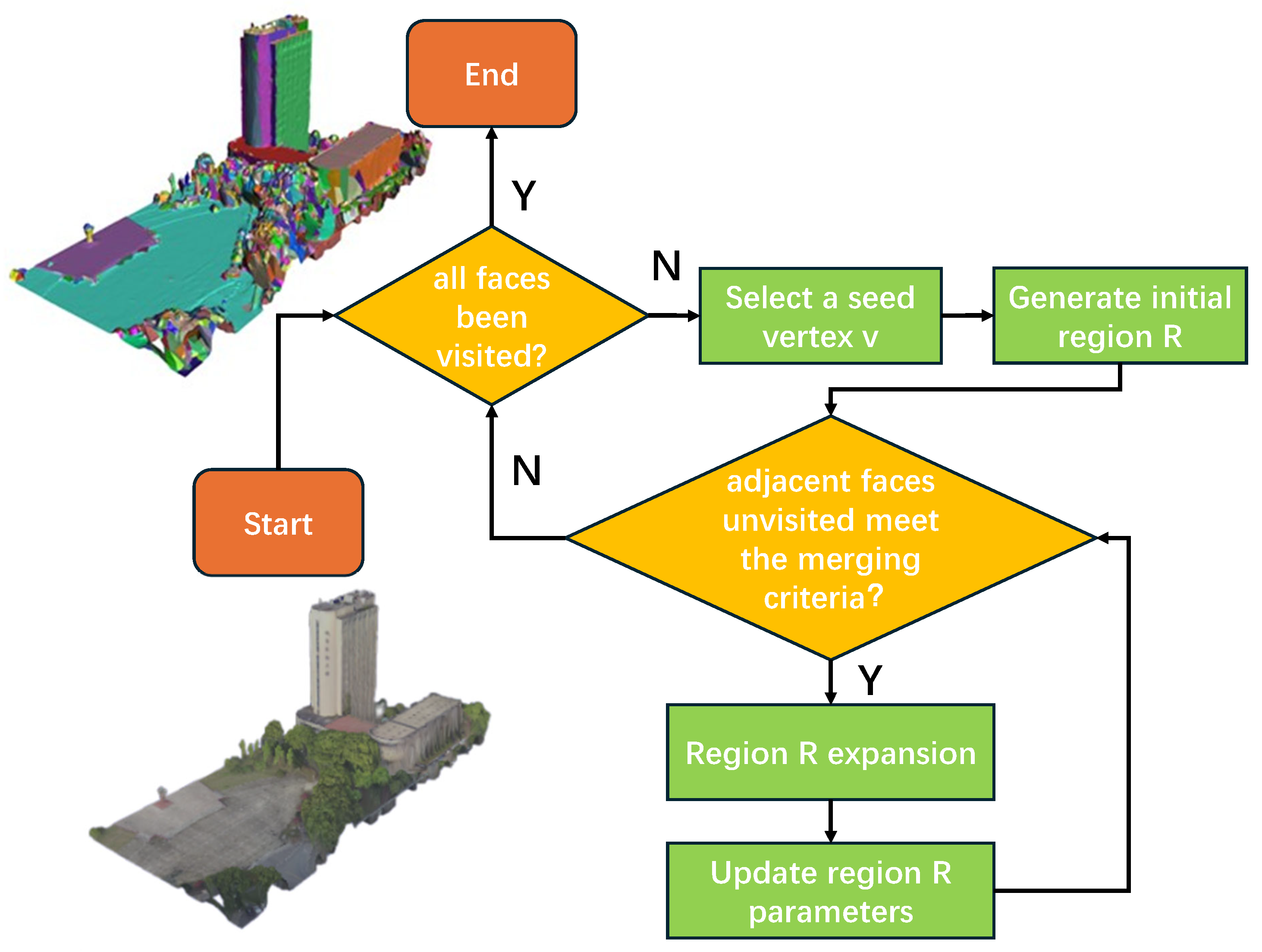
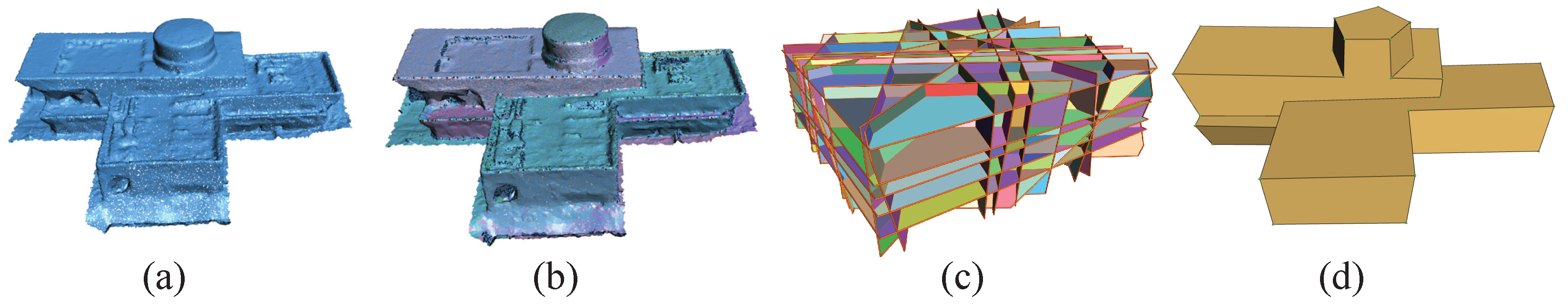
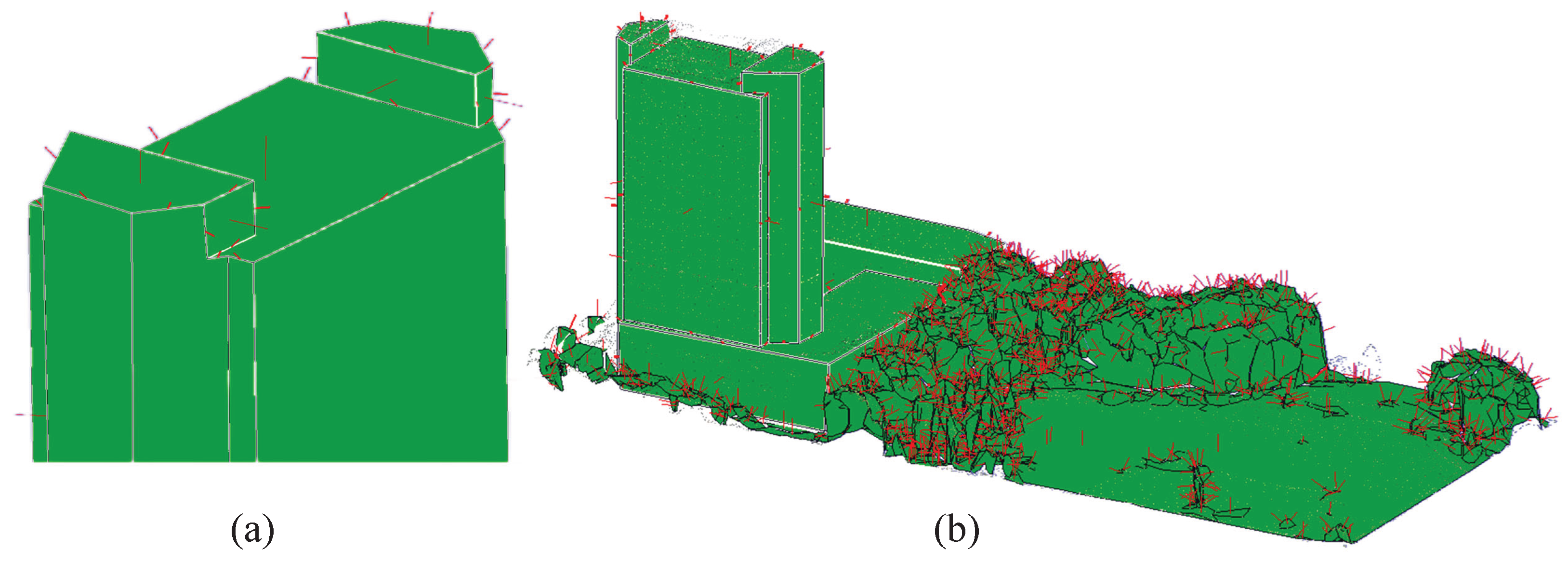
3.3.1. Plane Segmentation Based on Least Squares Plane Fitting
3.3.2. Planar Feature Extraction and Random Forest Classifier
3.4. Semantic Segmentation-Based Viewpoint Generation
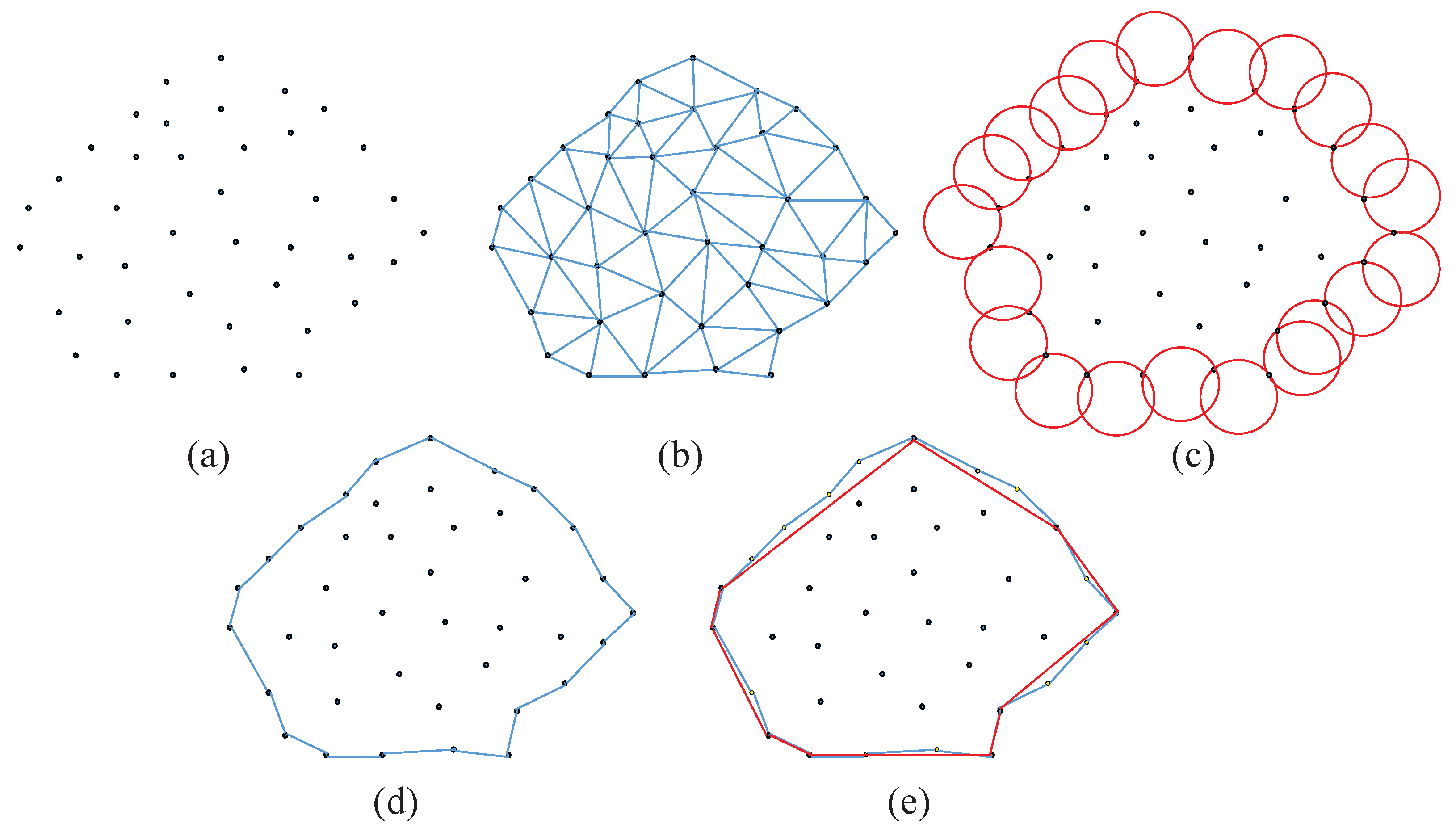
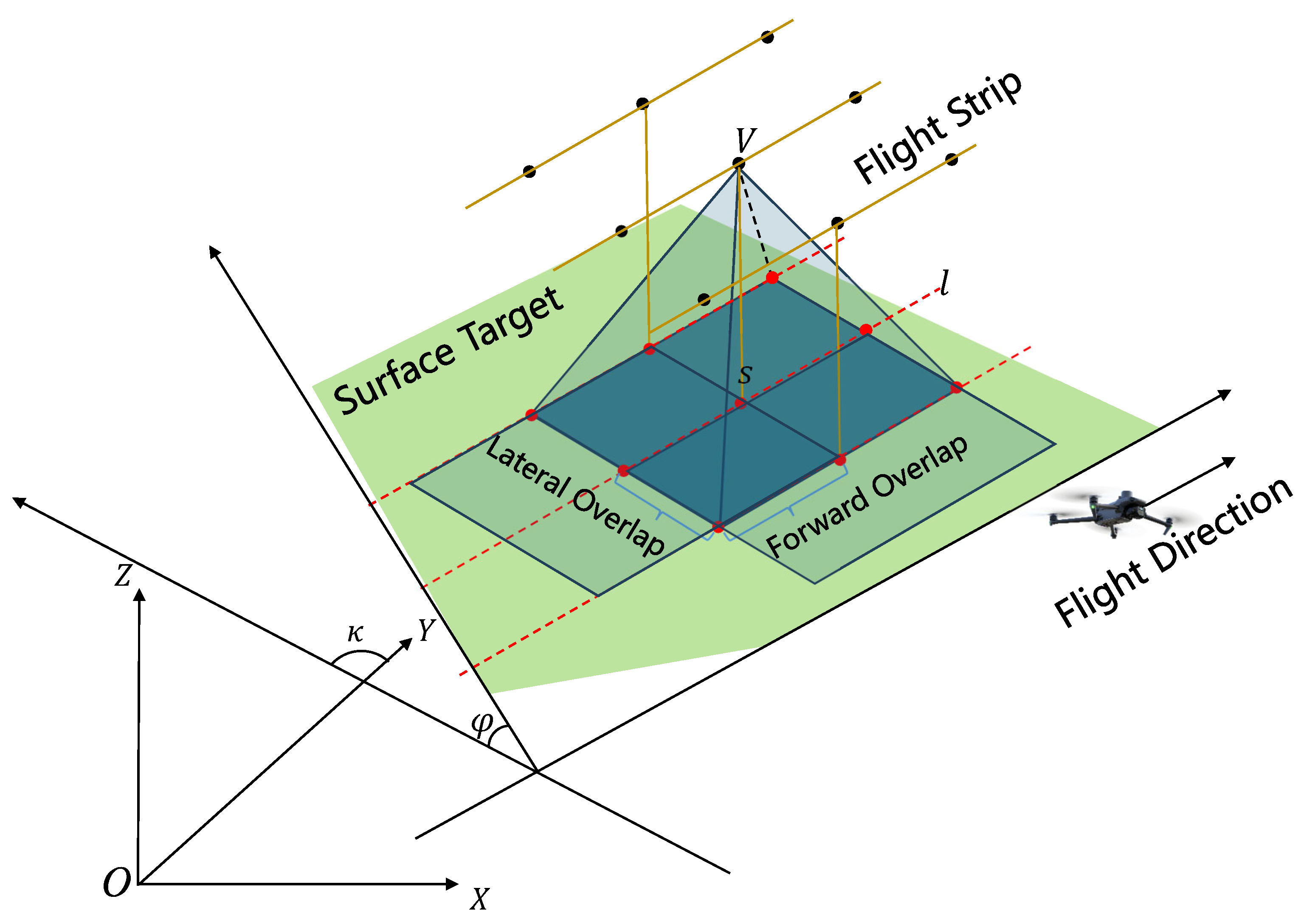
3.4.1. Simplified Photography Targets Extraction
3.4.2. Multi-Resolution Viewpoint Generation and Optimization
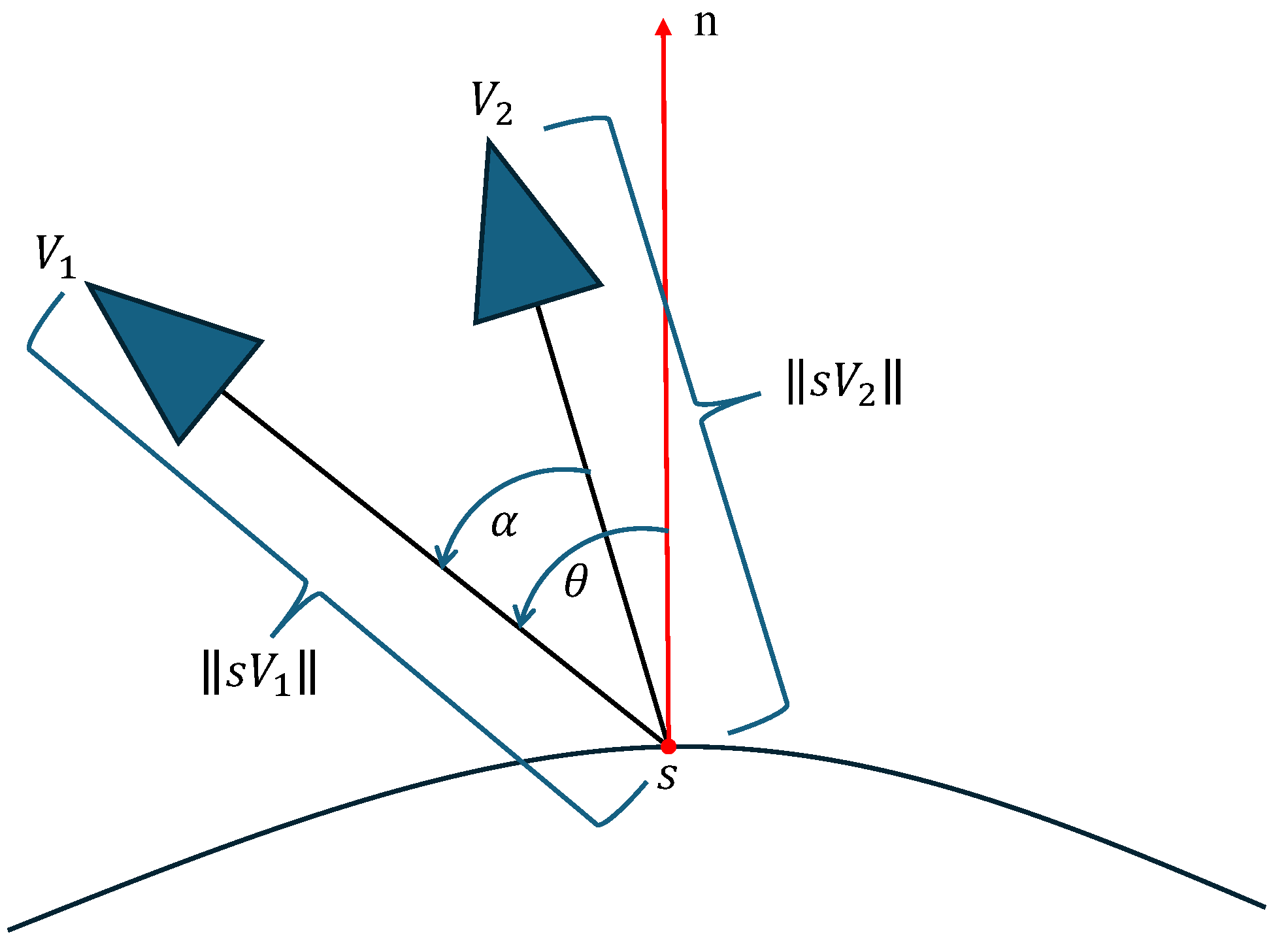
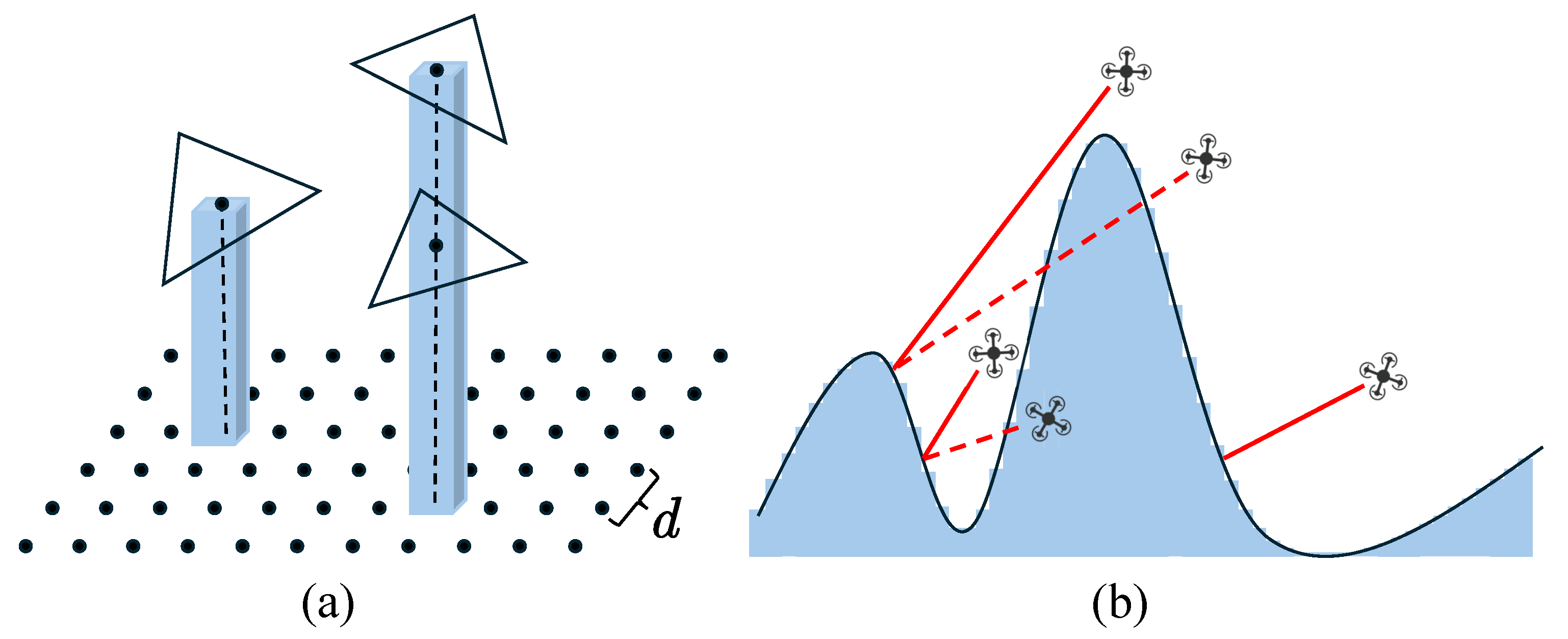
3.5. Obstacle-Aware and RTK Signal-Based Viewpoint Optimization
3.5.1. Obstacle Avoidance Analysis Based on DSM Safety Shell
3.5.2. RTK Signal Analysis and Optimization Based on Sky-View Maps
3.6. UAV Path Connection Based on Energy Consumption
4. Experimental Results
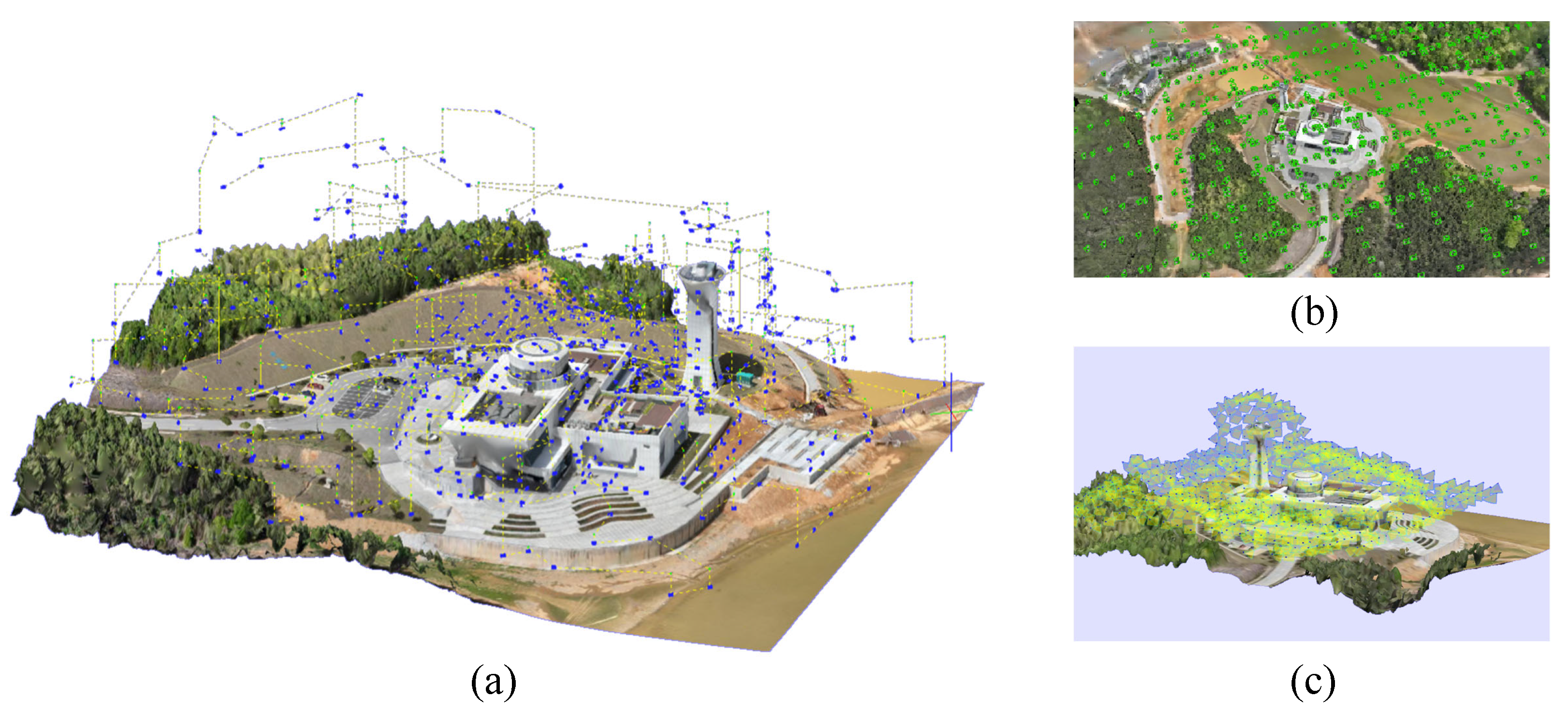
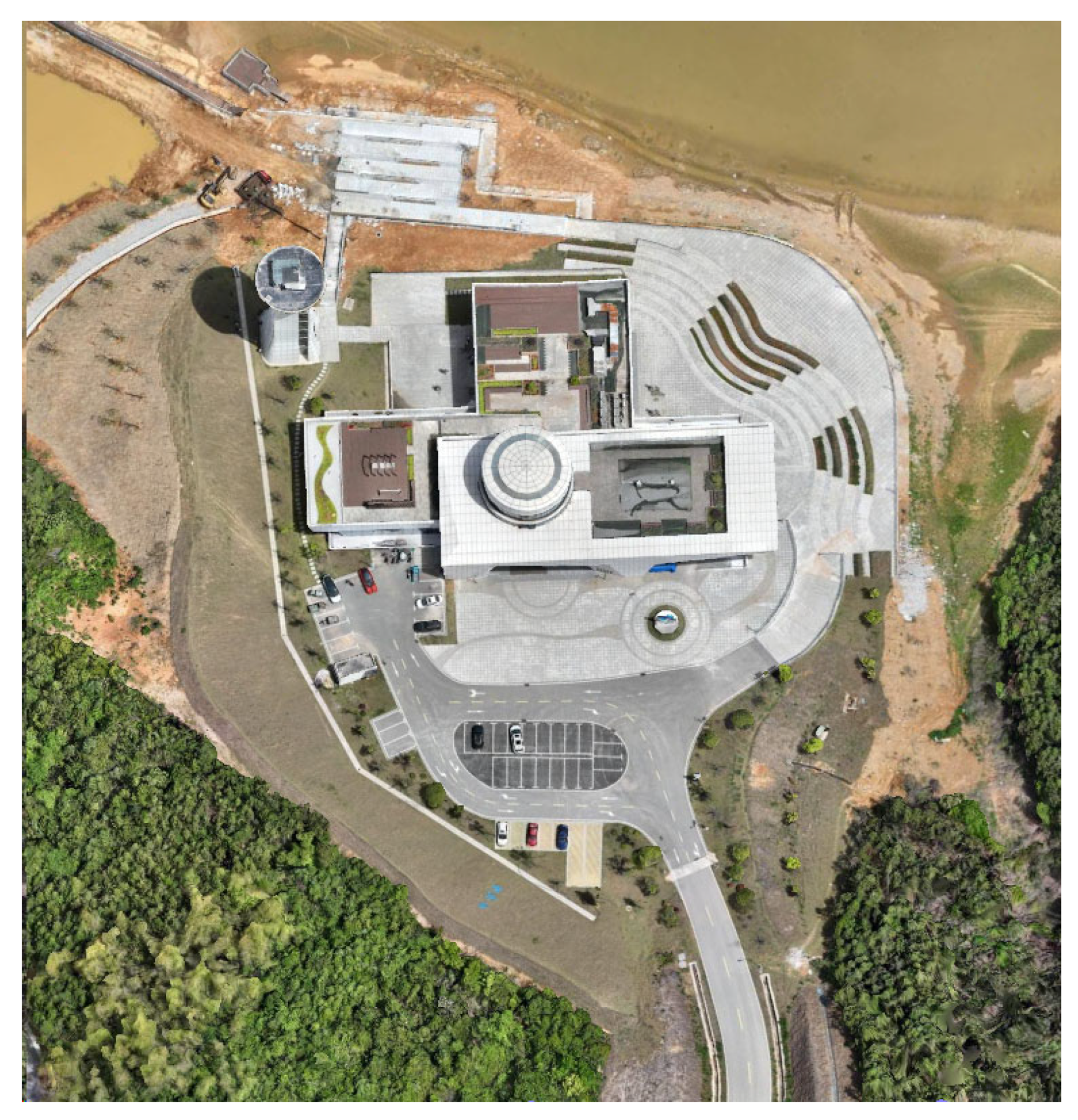
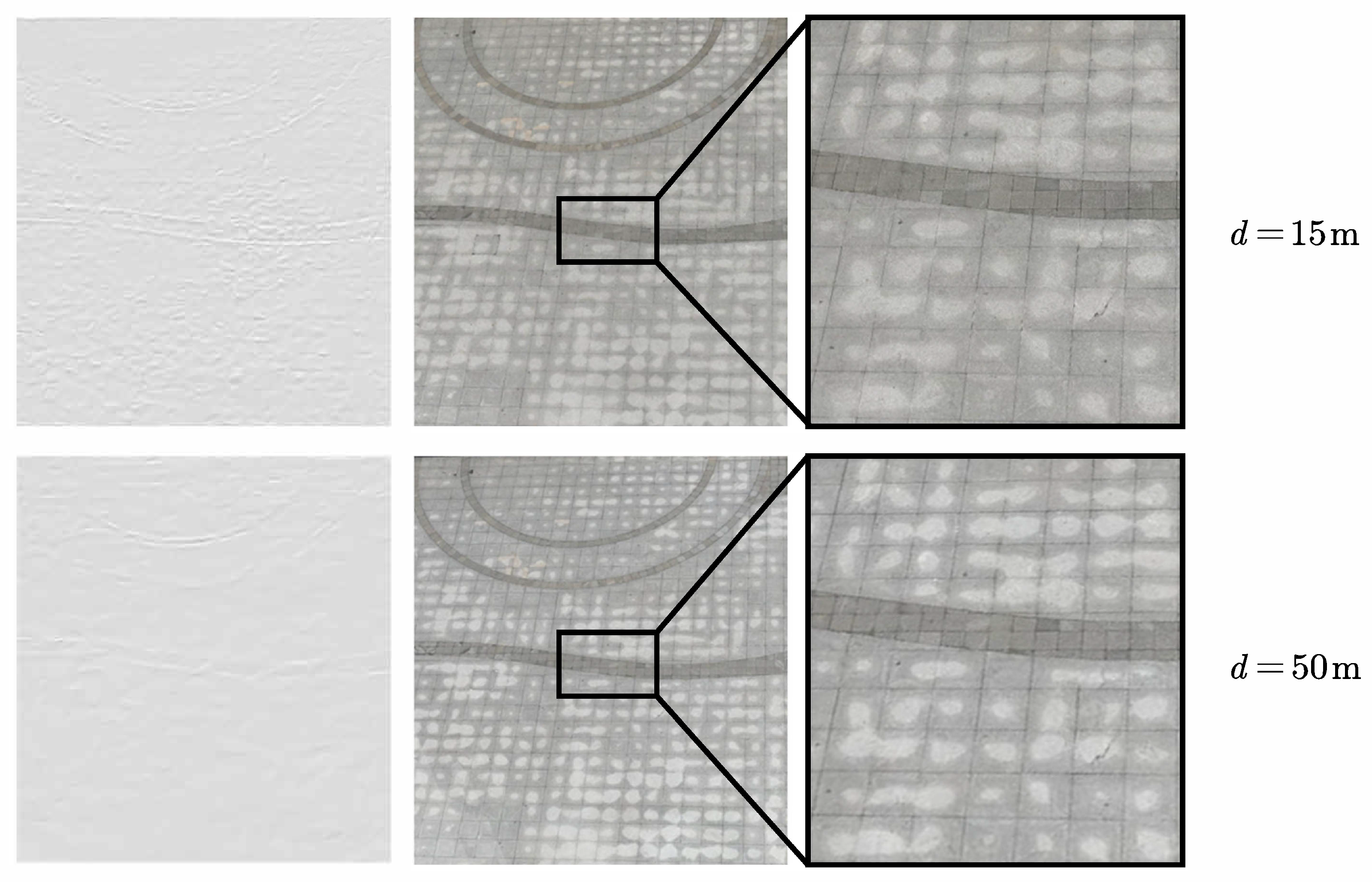
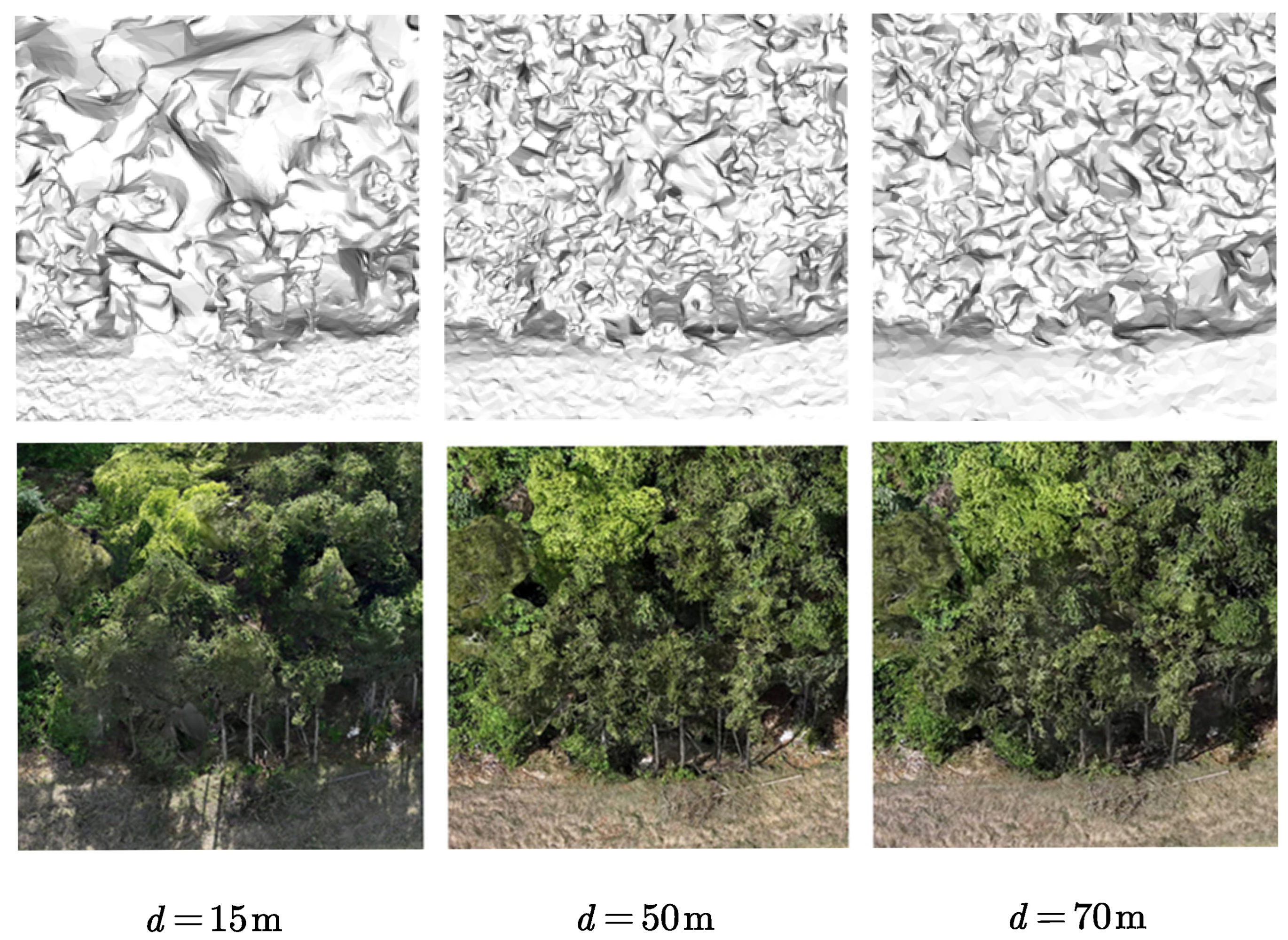
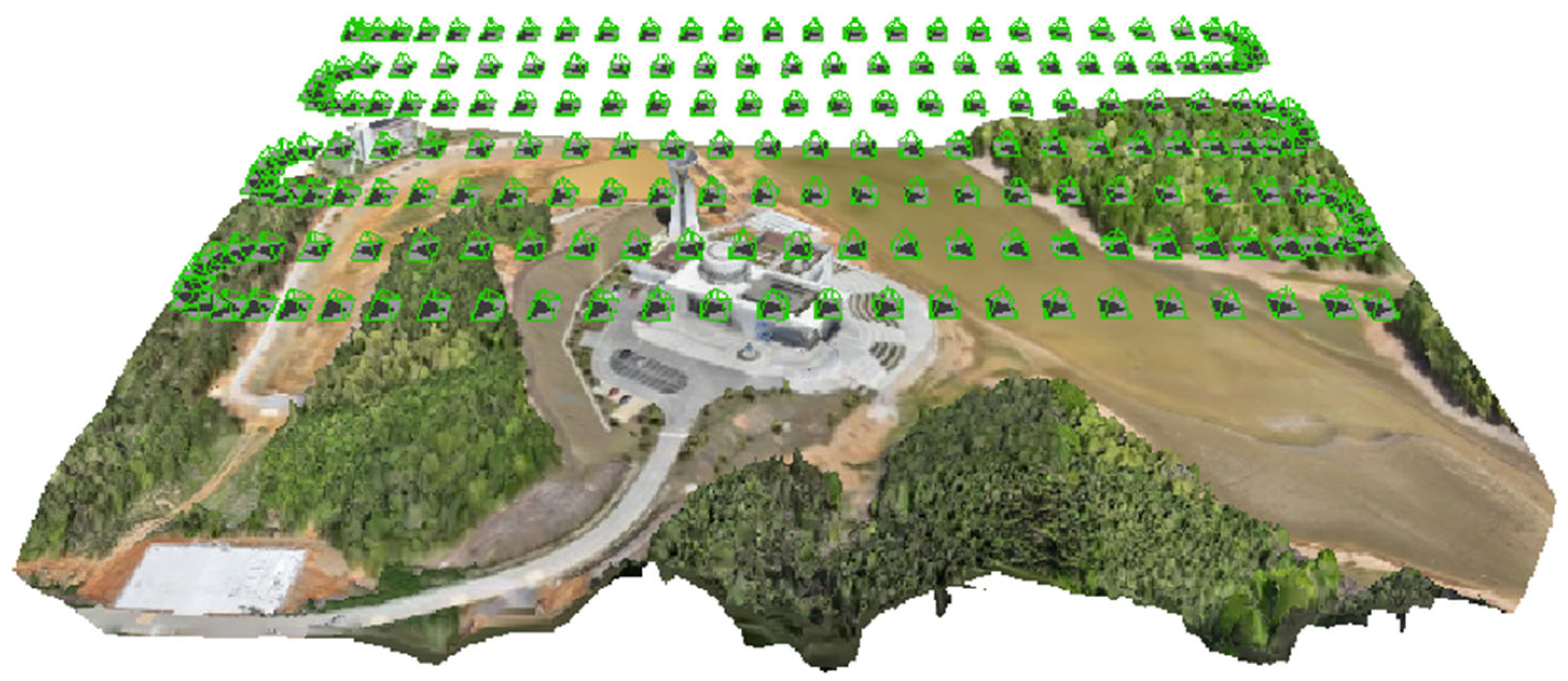
4.1. Experimental Setup
4.2. Experimental Procedure
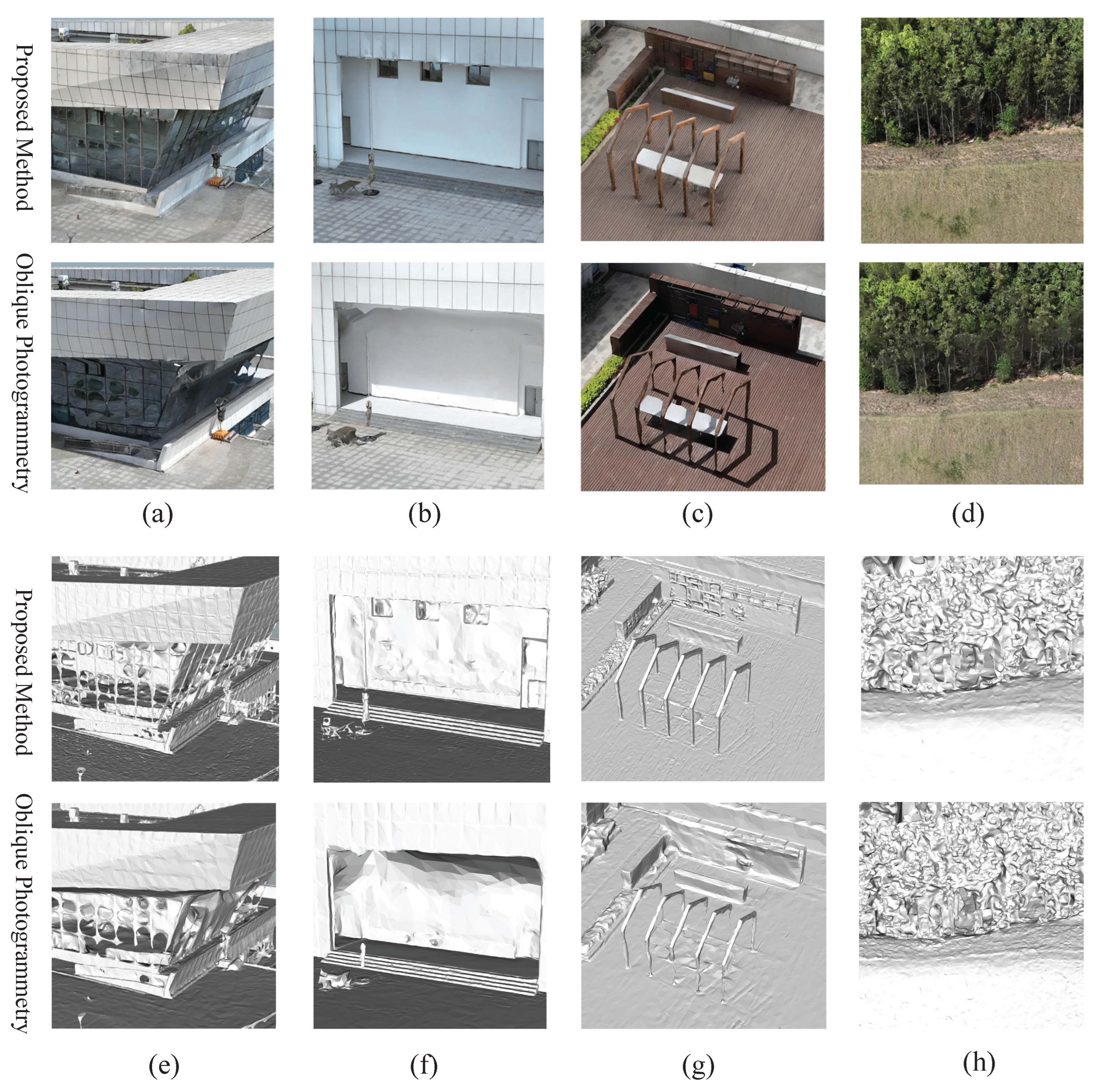
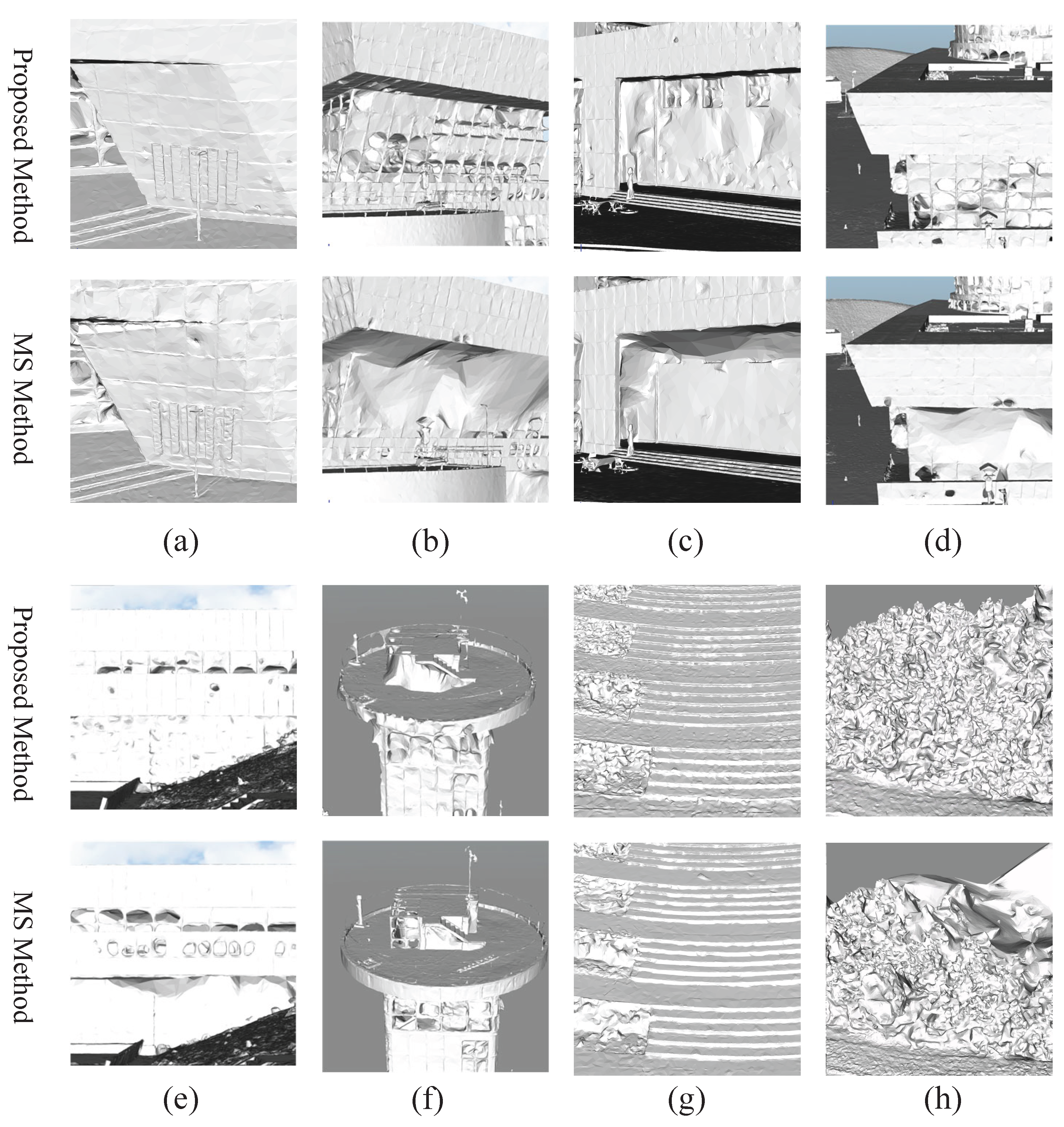
4.2.1. Proposed Method
4.2.2. Oblique Photogrammetry
4.2.3. Metashape (MS) Method
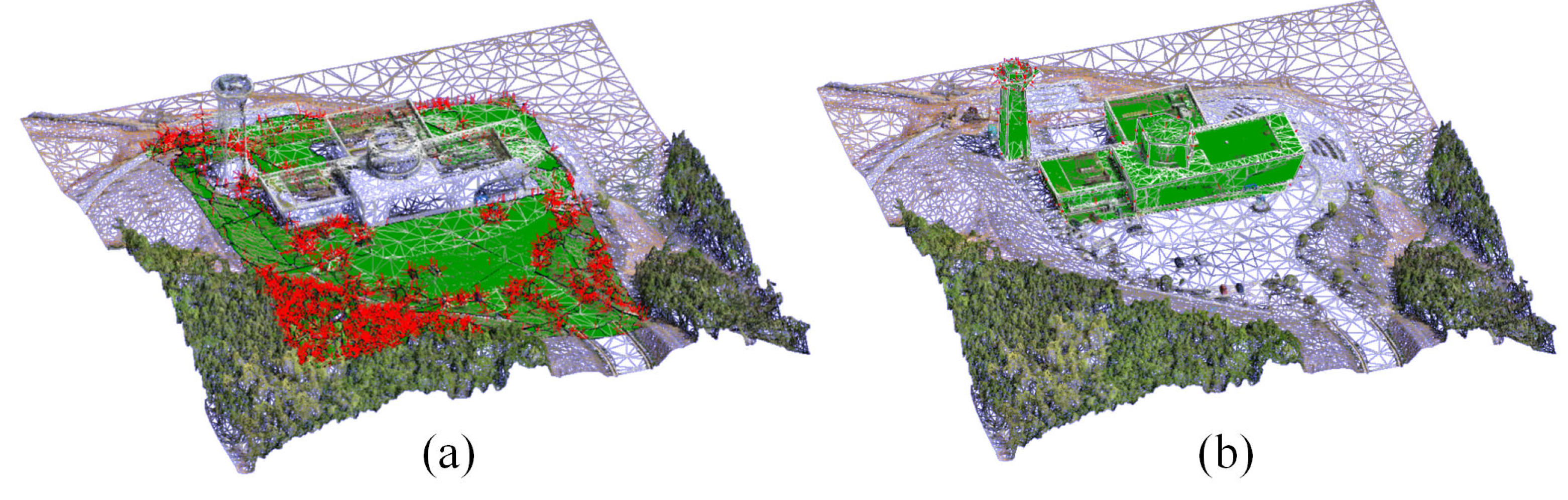
4.3. UAV Path Planning Methods Comparison
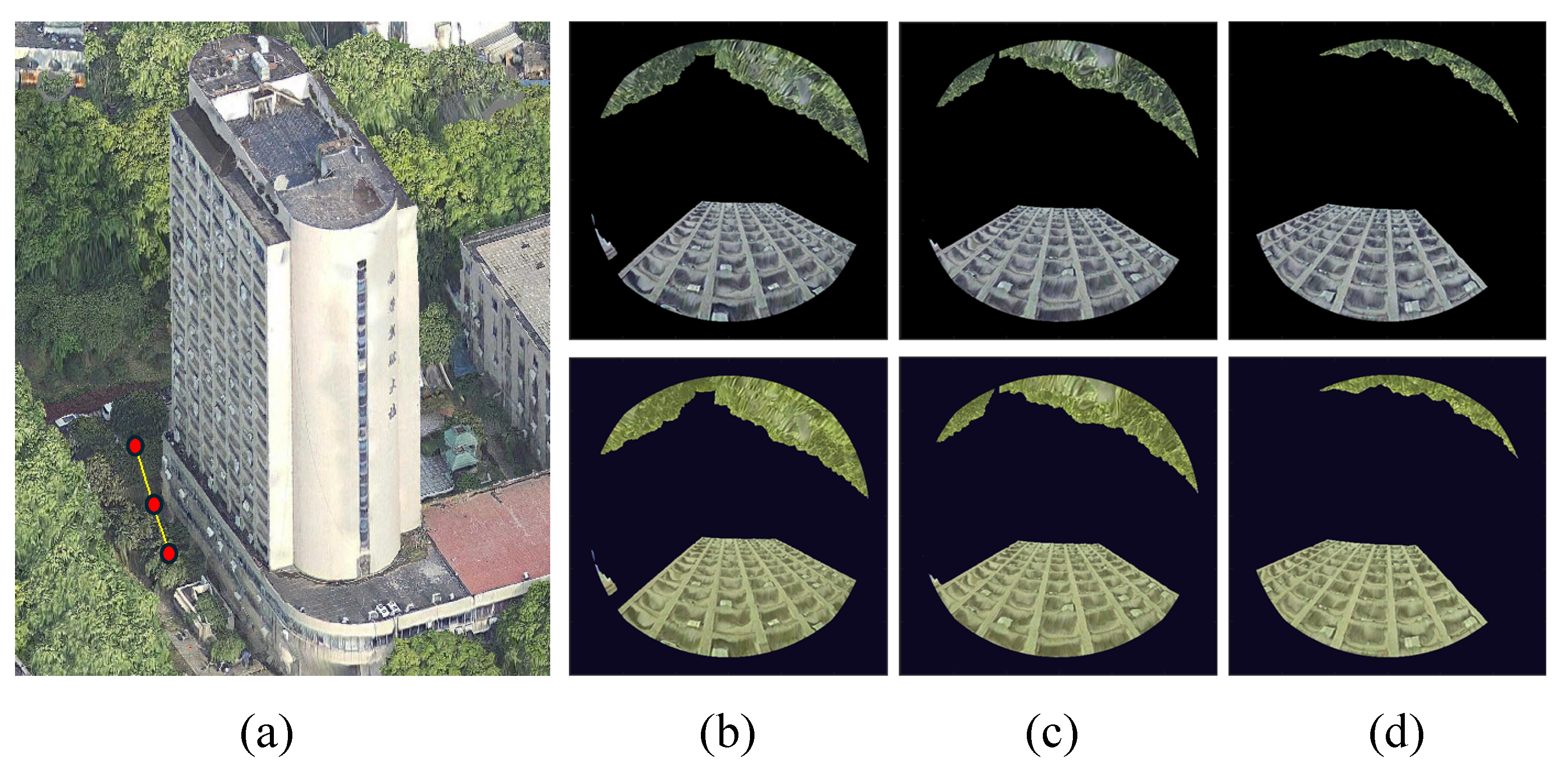
4.3.1. Quality Evaluation Metrics
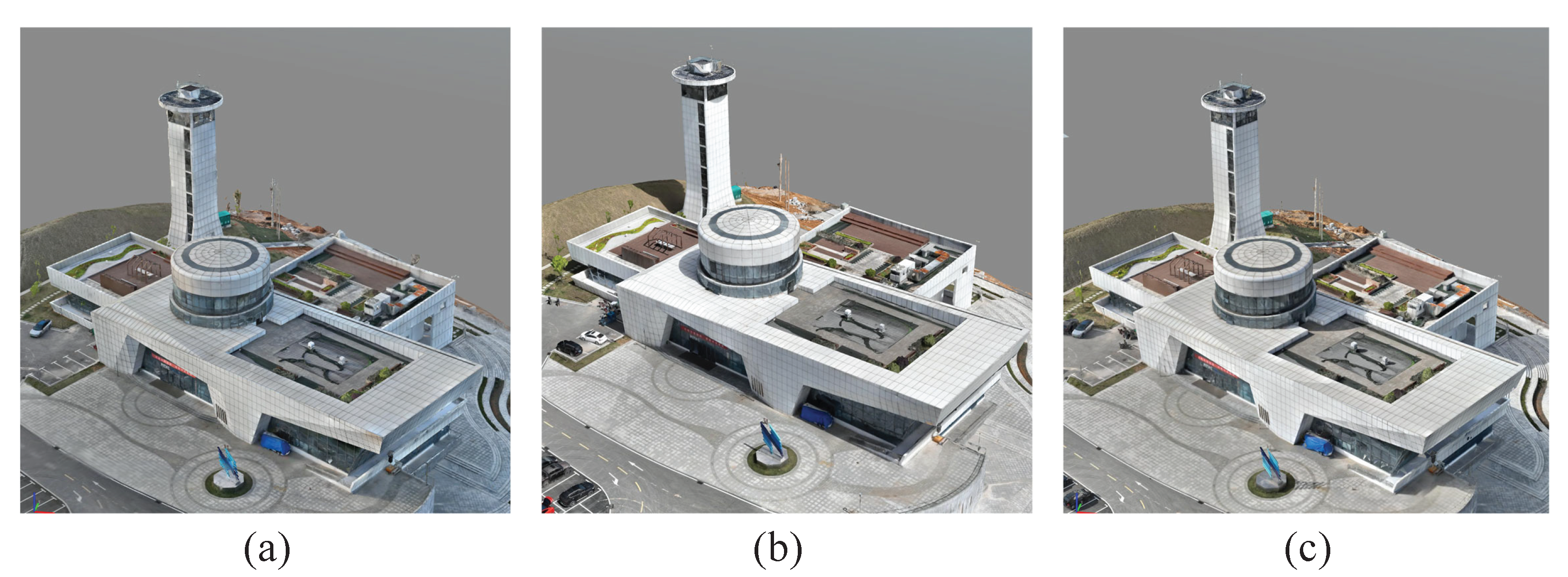
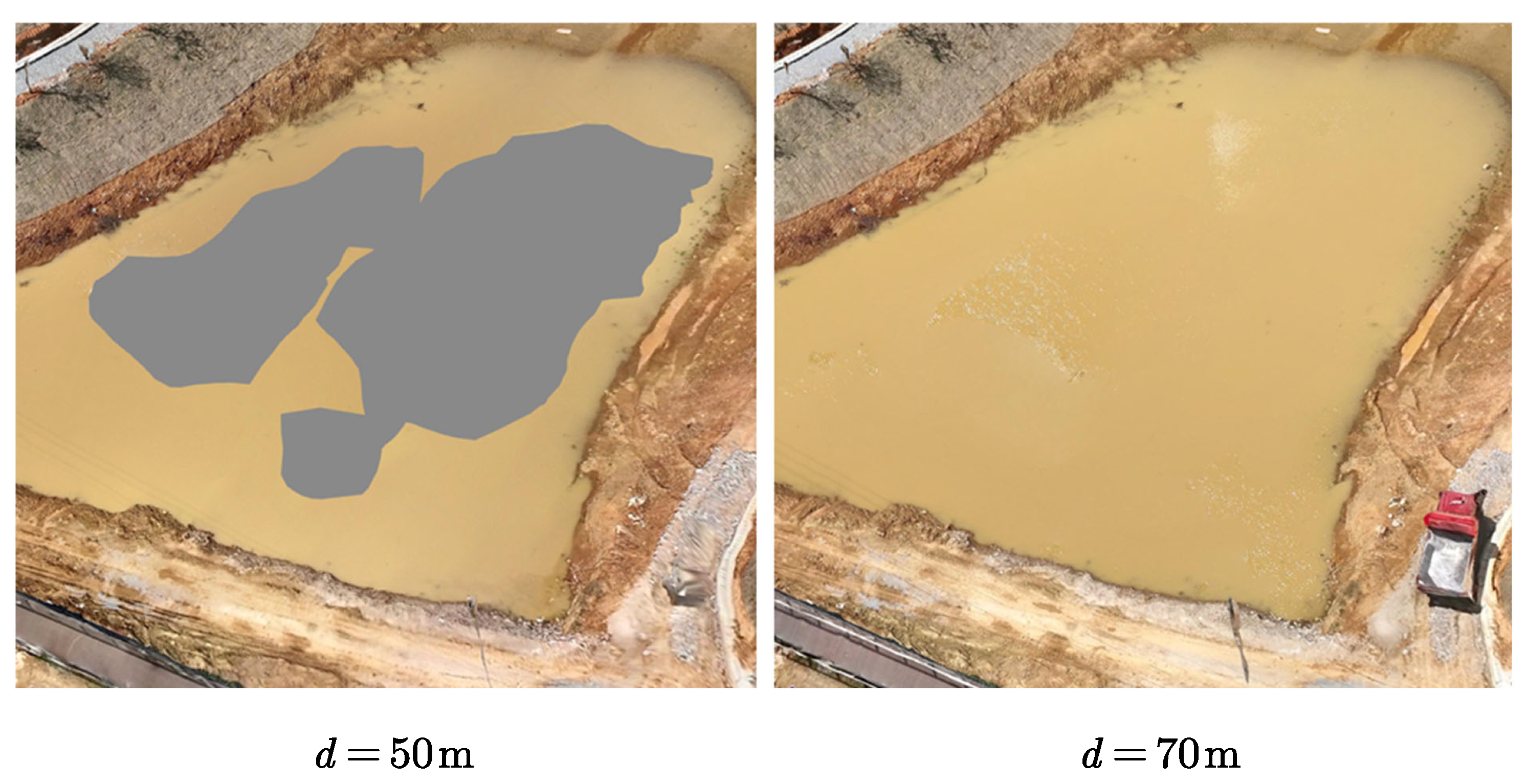
4.3.2. Comparison with Oblique Photogrammetry
4.3.3. Comparison with Metashape (MS) Method
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jovanović, D.; Milovanov, S.; Ruskovski, I.; Govedarica, M.; Sladić, D.; Radulović, A.; Pajić, V. Building virtual 3D city model for smart cities applications: A case study on campus area of the university of novi sad. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 2020, 9, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketzler, B.; Naserentin, V.; Latino, F.; Zangelidis, C.; Thuvander, L.; Logg, A. Digital twins for cities: A state of the art review. Built environment 2020, 46, 547–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remondino, F.; Rizzi, A. Reality-based 3D documentation of natural and cultural heritage sites—techniques, problems, and examples. Applied Geomatics 2010, 2, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, C.; Li, S.; Qiao, P. Emergency evacuation shelter management and online drill method driven by real scene 3D model. International journal of disaster risk reduction 2023, 97, 104057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amraoui, M.; Kellouch, S. Comparison assessment of digital 3d models obtained by drone-based lidar and drone imagery. The International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences 2021, 46, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westoby, M.J.; Brasington, J.; Glasser, N.F.; Hambrey, M.J.; Reynolds, J.M. ‘Structure-from-Motion’photogrammetry: A low-cost, effective tool for geoscience applications. Geomorphology 2012, 179, 300–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, Y.; Hernández, C.; et al. Multi-view stereo: A tutorial. Foundations and trends® in Computer Graphics and Vision 2015, 9, 1–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maboudi, M.; Homaei, M.; Song, S.; Malihi, S.; Saadatseresht, M.; Gerke, M. A review on viewpoints and path planning for UAV-based 3-D reconstruction. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing 2023, 16, 5026–5048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DJI. P4RTK System Specifications. https://www.dji.com/cn/support/product/phantom-4-rtk, 2019. Accessed: 2025-06-16.
- Zhang, S.; Liu, C.; Haala, N. Three-dimensional path planning of uavs imaging for complete photogrammetric reconstruction. ISPRS Annals of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences 2020, 1, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, W.; Polden, J.; Tao, P.Y.; Lin, W.; Shimada, K. View planning for 3D shape reconstruction of buildings with unmanned aerial vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2016 14th International Conference on Control, Automation, 2016, Robotics and Vision (ICARCV); pp. 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Xia, E.; Li, Z.; Zhou, Z. Sampling-based path planning for high-quality aerial 3D reconstruction of urban scenes. Remote Sensing 2021, 13, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Pei, H.; Wu, D.; Zeng, C.; Ai, X.; Duan, H. A Semantically Aware Multi-View 3D Reconstruction Method for Urban Applications. Applied Sciences 2024, 14, 2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, L.; Wonka, P. Polyfit: Polygonal surface reconstruction from point clouds. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, 2017, pp.
- Lee, M.J.L.; Lee, S.; Ng, H.F.; Hsu, L.T. Skymask matching aided positioning using sky-pointing fisheye camera and 3D City models in urban canyons. Sensors 2020, 20, 4728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, C.R.; Su, H.; Mo, K.; Guibas, L.J. Pointnet: Deep learning on point sets for 3d classification and segmentation. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2017, pp. [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.R.; Yi, L.; Su, H.; Guibas, L.J. PointNet++: Deep Hierarchical Feature Learning on Point Sets in a Metric Space. arXiv e-prints, 2017; arXiv:1706.02413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, N.; Belagiannis, V.; Dietmayer, K. Point Transformer. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 134826–134840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Chai, B.; Li, H.; Zheng, M.; Peng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Nie, X.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, X. Spiking Point Transformer for Point Cloud Classification. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence 2025, 39, 21563–21571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Feng, Y.; You, H.; Zhao, X.; Gao, Y. Meshnet: Mesh neural network for 3d shape representation. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, 2019, Vol. 33, pp. 8279–8286. [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.V.; Sheshappanavar, S.V.; Kambhamettu, C. Mesh Classification With Dilated Mesh Convolutions. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP); 2021; pp. 3138–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouhani, M.; Lafarge, F.; Alliez, P. Semantic segmentation of 3D textured meshes for urban scene analysis. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing 2017, 123, 124–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Nan, L.; Boom, B.; Ledoux, H. SUM: A benchmark dataset of semantic urban meshes. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing 2021, 179, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weixiao, G.; Nan, L.; Boom, B.; Ledoux, H. PSSNet: Planarity-sensible semantic segmentation of large-scale urban meshes. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing 2023, 196, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Tang, R.; Xia, M.; Zhang, C. A Texture Integrated Deep Neural Network for Semantic Segmentation of Urban Meshes. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing 2023, 16, 4670–4684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, G.; Yin, J.; Jia, X.; Mian, A. Mesh-Based DGCNN: Semantic Segmentation of Textured 3-D Urban Scenes. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 2023, 61, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, Q.; Wolpert, N.; Schömer, E. METNet: A mesh exploring approach for segmenting 3D textured urban scenes. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing 2024, 218, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maturana, D.; Scherer, S. VoxNet: A 3D Convolutional Neural Network for real-time object recognition. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS); 2015; pp. 922–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choy, C.; Gwak, J.; Savarese, S. 4D Spatio-Temporal ConvNets: Minkowski Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR); 2019; pp. 3070–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Maji, S.; Kalogerakis, E.; Learned-Miller, E. Multi-view Convolutional Neural Networks for 3D Shape Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV); 2015; pp. 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulch, A.; Guerry, J.; Le Saux, B.; Audebert, N. SnapNet: 3D point cloud semantic labeling with 2D deep segmentation networks. Computers & Graphics 2018, 71, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, L.; Guo, H.; Hu, X. Advances in UAV Path Planning: A Comprehensive Review of Methods, Challenges, and Future Directions. Drones 2025, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maboudi, M.; Homaei, M.; Song, S.; Malihi, S.; Saadatseresht, M.; Gerke, M. A Review on Viewpoints and Path Planning for UAV-Based 3-D Reconstruction. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing 2023, 16, 5026–5048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepp, B.; Dey, D.; Sinha, S.N.; Kapoor, A.; Joshi, N.; Hilliges, O. Learn-to-Score: Efficient 3D Scene Exploration by Predicting View Utility. arXiv e-prints, 2018; arXiv:1806.10354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Q.; Wu, J.; Pan, J.; Zhou, B. Real-Time UAV Path Planning for Autonomous Urban Scene Reconstruction. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA); 2020; pp. 1156–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Cui, R.; Xie, K.; Gong, M.; Huang, H. Aerial path planning for online real-time exploration and offline high-quality reconstruction of large-scale urban scenes. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 2021, 40, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzolo, E.; Stachniss, C. Effective Exploration for MAVs Based on the Expected Information Gain. Drones 2018, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Sun, W.; Long, P.; Huang, H.; Cohen-Or, D.; Gong, M.; Deussen, O.; Chen, B. Quality-driven Poisson-guided Autoscanning. ACM Transactions on Graphics 2014, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Shi, Y.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, J.; Liu, M.; Huang, H.; Su, H.; Cohen-Or, D.; Chen, B. 3D attention-driven depth acquisition for object identification. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 2016, 35, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almadhoun, R.; Abduldayem, A.; Taha, T.; Seneviratne, L.; Zweiri, Y. Guided next best view for 3D reconstruction of large complex structures. Remote Sensing 2019, 11, 2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Li, Y. Vision sensor planning for 3-D model acquisition. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B (Cybernetics) 2005, 35, 894–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.D.; Seo, J.H.; Kim, Y.M.; Choi, J.; Han, S.; Yoo, B. Automatic Pose Generation for Robotic 3-D Scanning of Mechanical Parts. IEEE Transactions on Robotics 2020, 36, 1219–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Jo, S. Surface-Based Exploration for Autonomous 3D Modeling. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA); 2018; pp. 4319–4326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, N.; Moehrle, N.; Goesele, M.; Heidrich, W. Aerial path planning for urban scene reconstruction: a continuous optimization method and benchmark. ACM Trans. Graph. 2018, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, T.; Körner, M.; Fraundorfer, F. Automatic and semantically-aware 3D UAV flight planning for image-based 3D reconstruction. Remote Sensing 2019, 11, 1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Xie, K.; Huang, K.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Gong, M.; Huang, H. Offsite aerial path planning for efficient urban scene reconstruction. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 2020, 39, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yao, Y.; Xie, K.; Fu, C.W.; Zhang, H.; Huang, H. Continuous aerial path planning for 3D urban scene reconstruction. ACM Trans. Graph. 2021, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Ji, Z.; You, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhao, K.; Lin, S.; Huang, X. Geometric primitive-guided UAV path planning for high-quality image-based reconstruction. Remote Sensing 2023, 15, 2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, M.; Shah, S.; Dey, D.; Truong, A.; Sinha, S.; Kapoor, A.; Hanrahan, P.; Joshi, N. Submodular Trajectory Optimization for Aerial 3D Scanning. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV); 2017; pp. 5334–5343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepp, B.; Nießner, M.; Hilliges, O. Plan3d: Viewpoint and trajectory optimization for aerial multi-view stereo reconstruction. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) 2018, 38, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Isler, V. Adaptive View Planning for Aerial 3D Reconstruction. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA); 2019; pp. 2981–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnabel, R.; Wahl, R.; Klein, R. Efficient RANSAC for point-cloud shape detection. In Proceedings of the Computer graphics forum, Vol. 26; 2007; pp. 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.T.; Schachter, B.J. Two algorithms for constructing a Delaunay triangulation. International Journal of Computer & Information Sciences 1980, 9, 219–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelsbrunner, H.; Kirkpatrick, D.; Seidel, R. On the shape of a set of points in the plane. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory 1983, 29, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, D.H.; Peucker, T.K. Algorithms for the reduction of the number of points required to represent a digitized line or its caricature. Cartographica: the international journal for geographic information and geovisualization 1973, 10, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorigo, M.; Gambardella, L.M. Ant colony system: a cooperative learning approach to the traveling salesman problem. IEEE Transactions on evolutionary computation 1997, 1, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Latif, E.I.A.; El-dosuky, M. Predicting power consumption of drones using explainable optimized mathematical and machine learning models. The Journal of Supercomputing 2025, 81, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




