Submitted:
12 July 2025
Posted:
15 July 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
I. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Evolution of AI in Cybersecurity
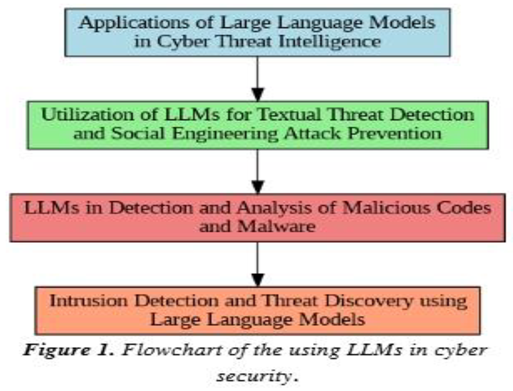
2.2. Current State of LLM Applications in Cybersecurity
3. Methodology
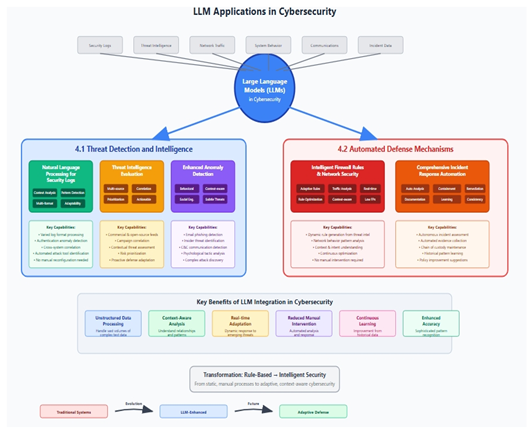
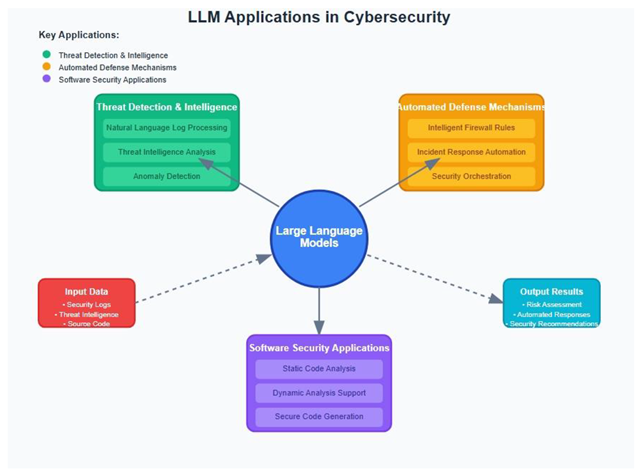
4. LLM Applications in Cybersecurity
4.1. Threat Detection and Intelligence
Natural Language Processing for Security Logs
Threat Intelligence Evaluation
Enhanced Anomaly Detection
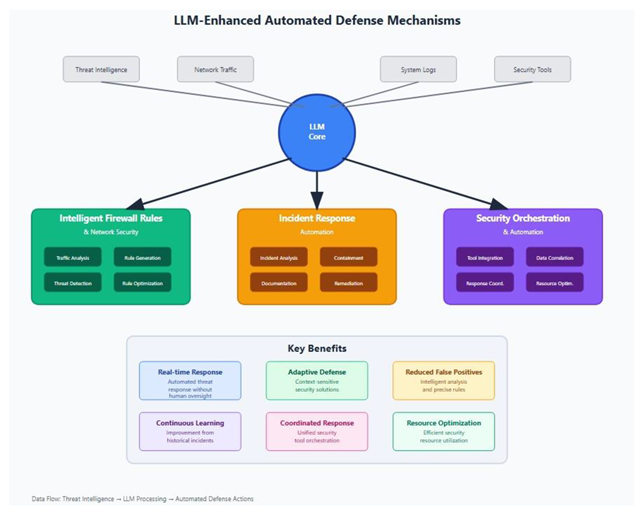
4.2. Automated Defense Mechanisms
Intelligent Firewall Rules and Network Security
Comprehensive Incident Response Automation
Advanced Security Orchestration and Automation
4.3. Applications in Software Security
Thorough Static Code Evaluation
Improved Support for Dynamic Analysis
Secure Code Generation and Development Advice
Vulnerability Assessments and Remediation
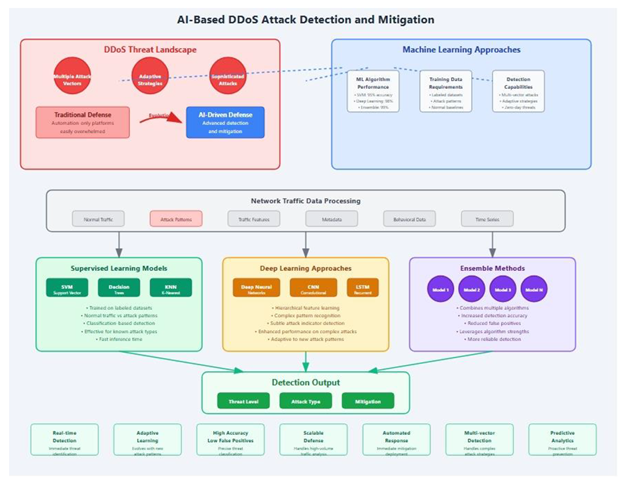
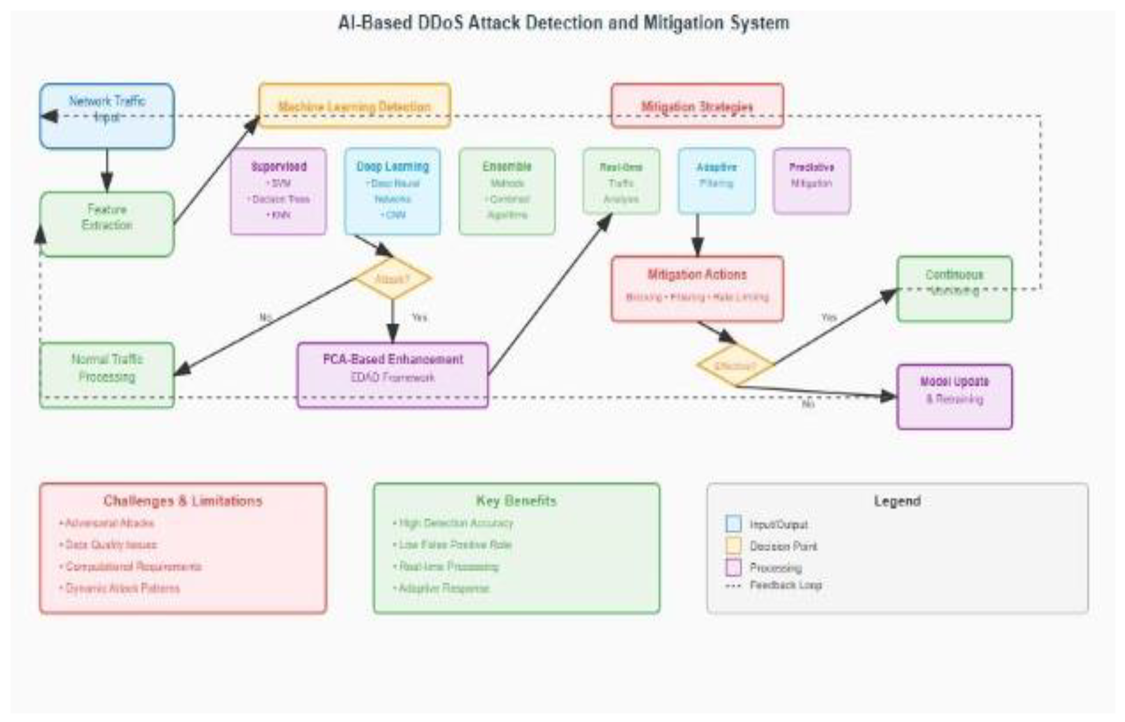
5. AI-Based DDoS Attack Detection and Mitigation
5.1. The DDoS Threat Landscape
5.2. Machine Learning Approaches to DDoS Detection
5.2.1. AI-Enhanced DDoS Mitigation Strategies: A Comprehensive Analysis
5.2.2. Introduction to AI-Driven DDoS Defense Systems
5.2.3. Theoretical Foundations of AI in DDoS Detection
5.3. Statistical Learning Theory
5.3.1. Information Theory and Feature Selection
5.3.2. Pattern Recognition and Anomaly Detection
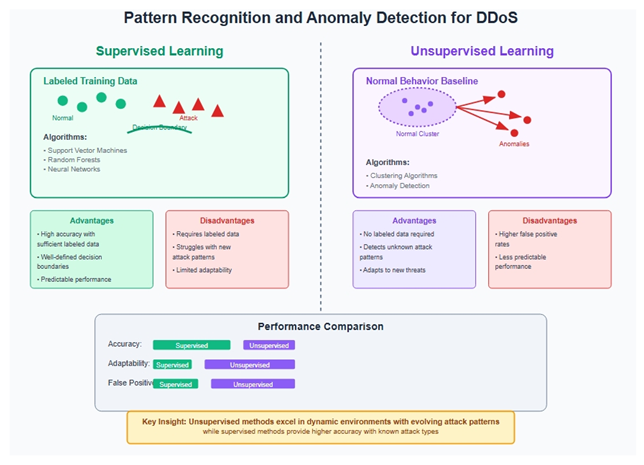
5.4. Advanced AI-Enhanced DDoS Mitigation Strategies
5.4.1. Real-Time Traffic Analysis and Behavioral Modeling
5.4.2. Adaptive Filtering and Dynamic Response Mechanisms
5.4.3. Predictive Mitigation and Proactive Defense
5.4.4. Ensemble Methods and Collaborative Defense
5.5. Case Study: PCA-Based Enhanced DDoS Attack Detection (EDAD)
5.5.1. Framework Architecture and Design
5.5.2. PCA Implementation and Optimization
5.5.3. Performance Evaluation and Validation
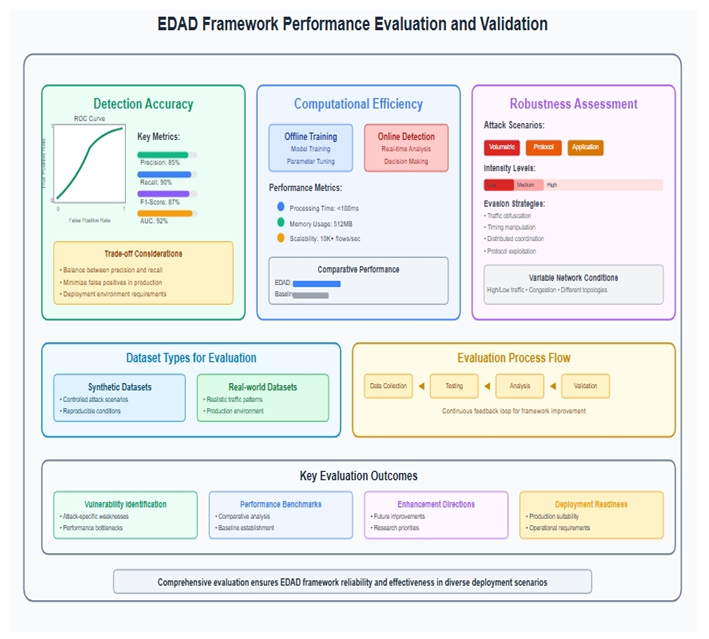
5.5.4. Comparative Analysis with Traditional Methods
5.6. Advanced Machine Learning Techniques in DDoS Mitigation
5.6.1. Deep Learning Architectures
5.6.2. Reinforcement Learning for Dynamic Defense
5.6.3. Federated Learning for Collaborative Defense
5.7. Challenges and Limitations of AI-Enhanced DDoS Mitigation
5.7.1. Adversarial Attacks and Evasion Techniques
5.7.2. Data Quality and Representativeness Issues
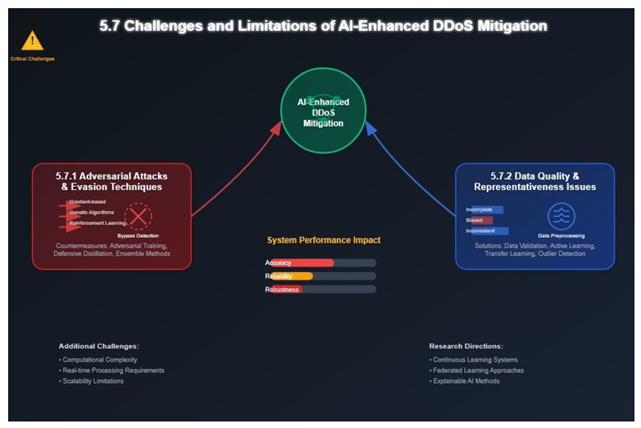
5.7.3. Computational Resource Requirements
5.7.4. Dynamic Attack Evolution and Concept Drift
5.8. Future Directions and Emerging Technologies
5.8.1. Quantum Computing and Cryptographic Implications
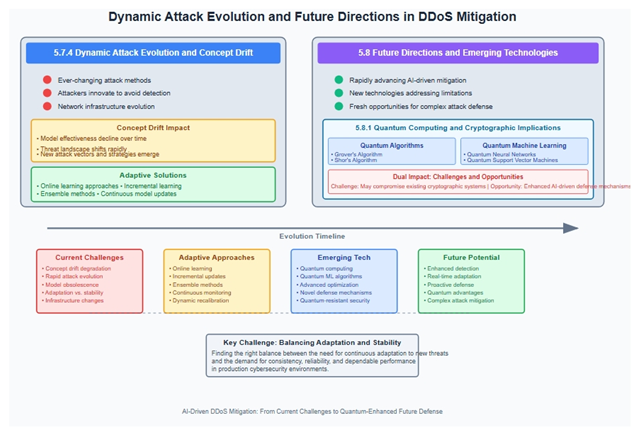
5.8.2. Edge Computing and Distributed Defense
5.8.3. Explainable AI and Interpretable Security
5.8.4. Autonomous Security Systems
5.9. Conclusion and Research Implications
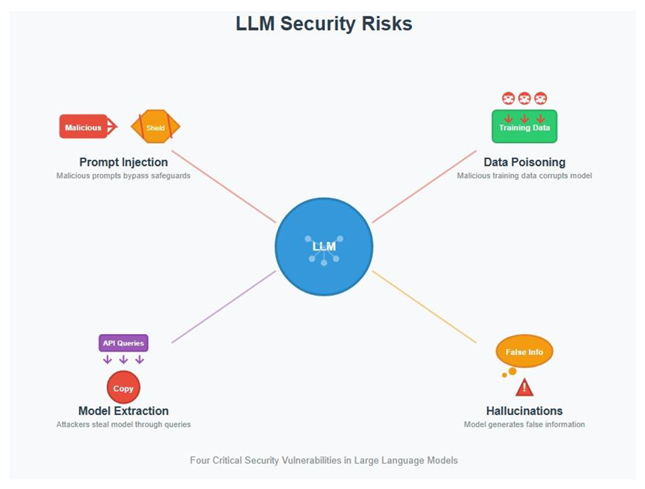
6. Challenges and Vulnerabilities
6.1. Security Risks of LLMs
6.2. Adversarial Use of AI
6.3. Ethical and Privacy Concerns
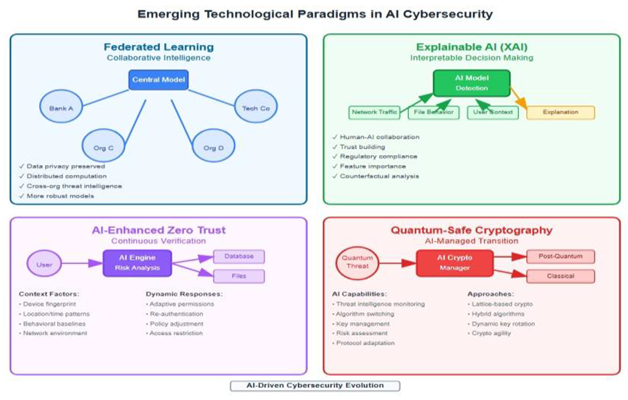
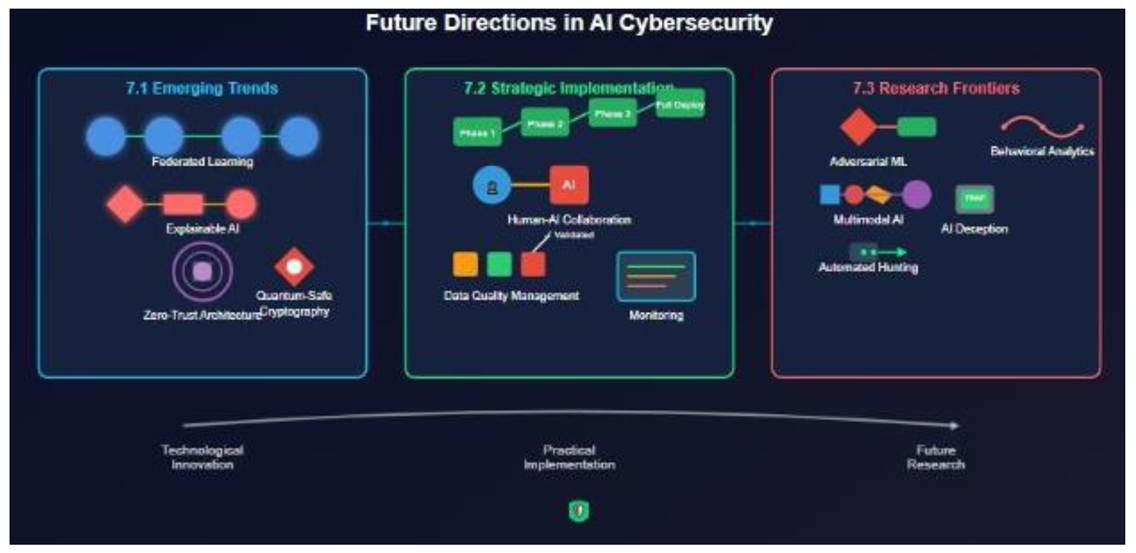
7. Future Directions and Recommendations
7.1. Emerging Technological Paradigms
7.2. Strategic Implementation Framework.
7.3. Research Frontiers and Innovation Opportunities
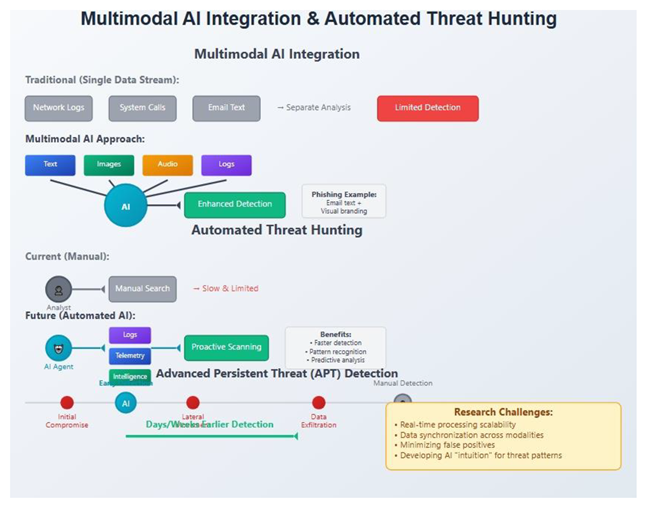
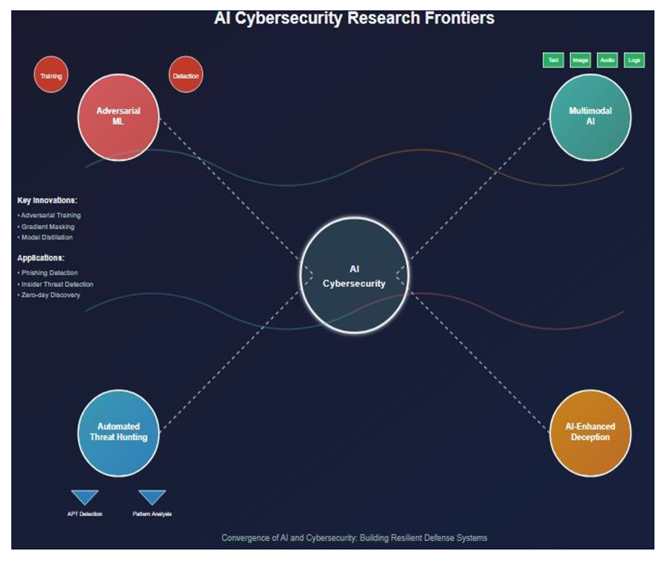
Multimodal AI Integration and Fusion Analytics
Autonomous Threat Hunting and Proactive Defense Systems
AI-Powered Deception Technologies and Adaptive Honeypots
Advanced Behavioral Analytics and Contextual Anomaly Detection
Quantum-Enhanced Cybersecurity and Post-Quantum Preparedness
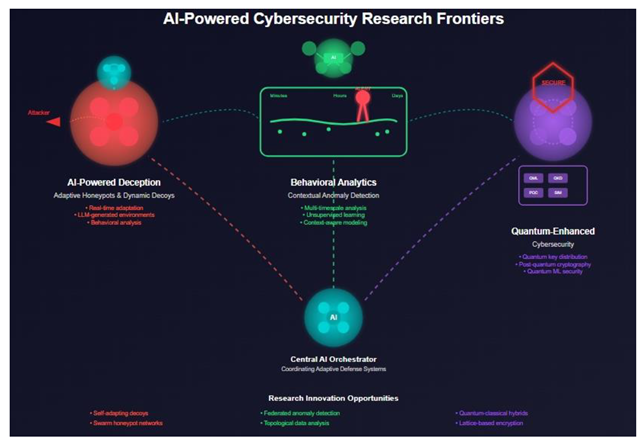
Federated Learning and Privacy-Preserving AI Security
AI-Driven Cyber Resilience and Adaptive Response Systems
Explainable AI and Human-AI Collaboration in Security
8. Conclusion
Abbreviations
| LLM | Large Language Model |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| NLP | Natural Language Processing |
| BERT | Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers |
| GPT | Generative Pretrained Transformer |
| RLHF | Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback |
| API | Application Programming Interface |
| RPA | Robotic Process Automation |
| CTI | Cyber Threat Intelligence |
| TPU | Tensor Processing Unit |
| RNN | Recurrent Neural Network |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
| GRU | Gated Recurrent Unit |
| BPE | Byte-Pair Encoding |
| OOV | Out-of-Vocabulary |
| MLM | Masked Language Modeling |
| NSP | Next Sentence Prediction |
| mBERT | Multilingual BERT |
| SWAG | Situations With Adversarial Generations |
| GLUE | General Language Understanding Evaluation |
| SQuAD | Stanford Question Answering Dataset |
| ALBERT | A Lite BERT |
| RoBERTa | Robustly Optimized BERT Pretraining Approach |
| NPLM | Neural Probabilistic Language Model |
| GloVe | Global Vectors for Word Representation |
| PEFT | Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning |
| LoRA | Low-Rank Adaptation |
| HELM | Holistic Evaluation of Language Models |
| LMSYS | Large Model Systems Organization |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| GAN | Generative Adversarial Network |
| VAE | Variational Autoencoder |
| RL | Reinforcement Learning |
| DNN | Deep Neural Network |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| AWS | Amazon Web Services |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| KNN | K-Nearest Neighbors |
| PCA | Principal Component Analysis |
| TF-IDF | Term Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency |
| POS | Part of Speech |
| QA | Question Answering |
| IE | Information Extraction |
| NER | Named Entity Recognition |
| SRL | Semantic Role Labeling |
| ASR | Automatic Speech Recognition |
| TTS | Text-to-Speech |
| OCR | Optical Character Recognition |
| ELMo | Embeddings from Language Models |
| Transformer | A Neural Network Architecture |
| FLOPS | Floating Point Operations Per Second |
| BLEU | Bilingual Evaluation Understudy |
| ROUGE | Recall-Oriented Understudy for Gisting Evaluation |
| CIDEr | Consensus-based Image Description Evaluation |
| WMD | Word Mover's Distance |
| ELU | Exponential Linear Unit |
| ReLU | Rectified Linear Unit |
| GeLU | Gaussian Error Linear Unit |
| SGD | Stochastic Gradient Descent |
| Adam | Adaptive Moment Estimation |
| LDA | Latent Dirichlet Allocation |
| HMM | Hidden Markov Model |
| CRF | Conditional Random Fields |
| TF | TensorFlow |
| PT | PyTorch |
| CPU | Central Processing Unit |
| GPU | Graphics Processing Unit |
| URL | Uniform Resource Locator |
| JSON | JavaScript Object Notation |
| CSV | Comma-Separated Values |
| ANN | Artificial Neural Network |
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| CV | Computer Vision |
| MLOps | Machine Learning Operations |
| EDA | Exploratory Data Analysis |
| BERTology | The study of BERT and similar transformer-based models |
| POS tagging | Part-of-Speech tagging |
| WER | Word Error Rate |
References
- A. Alotaibi et al., “Generative AI in cybersecurity: A comprehensive review of LLM applications and vulnerabilities,” Future Generation Computer Systems, vol. 162, pp. 1–15, 2024.
- Y. Zhang et al., “When LLMs meet cybersecurity: A systematic literature review,” Cybersecurity, vol. 8, no. 1, pp. 1–25, 2025. [CrossRef]
- L. Chen et al., “Detecting and mitigating DDoS attacks with AI: A survey,” arXiv preprint, arXiv:2503.17867, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.17867. [CrossRef]
- S. Kumar et al., “Distributed denial-of-service (DDOS) attack detection using supervised machine learning algorithms,” Scientific Reports, vol. 14, 28456, 2024. [CrossRef]
- M. Rodriguez et al., “Deep learning-driven defense strategies for mitigating DDoS attacks in cloud computing environments,” Journal of Cloud Computing, vol. 14, no. 1, pp. 1–18, 2025.
- J. Thompson et al., “A comprehensive review of vulnerabilities and AI-enabled defense against DDoS attacks for securing cloud services,” Computer Networks, vol. 245, 110387, 2024. [CrossRef]
- R. Patel et al., “An entropy and machine learning based approach for DDoS attacks detection in software defined networks,” Scientific Reports, vol. 14, 15789, 2024. [CrossRef]
- A10 Networks, “The machine war has begun: Cybercriminals leveraging AI in DDoS attacks,” Technical Report, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://www.a10networks.com/blog/the-machine-war-has-begun-cybercriminals-leveraging-ai-in-ddos-attacks/.
- Akamai Technologies, “DDoS attack trends in 2024 signify that sophistication overshadows size,” Security Intelligence Report, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://www.akamai.com/blog/security/ddos-attack-trends-2024-signify-sophistication-overshadows-size.
- Darktrace, “AI-based cybersecurity solutions for DDoS attack detection and mitigation,” Technical Documentation, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.darktrace.com/cyber-ai-glossary/ddos-attack.
- Palo Alto Networks, “AI, cybersecurity and the rise of large language models,” Research Paper, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.paloaltonetworks.com/blog/2024/04/ai-cybersecurity-and-large-language-models/.
- OWASP Foundation, “OWASP top 10 for large language model applications,” Security Guidelines, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://genai.owasp.org/.
- SecOps Solution, “Top 10 LLM tools in cybersecurity,” Industry Report, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://www.secopsolution.com/blog/top-10-llm-tools-in-2024.
- AnyAPI, “AI cybersecurity in 2025: From threat detection to automated response,” Technical Analysis, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://anyapi.io/blog/AI-Cybersecurity-in-2025-From-Threat-Detection-to-Automated-Response.
- GBHackers, “Threat actors exploit AI and LLM tools for offensive cyber operations,” Security Intelligence Report, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://gbhackers.com/threat-actors-exploit-ai-and-llm-tools/.
- Dark Reading, “How AI/ML can thwart DDoS attacks,” Technical Article, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.darkreading.com/cyberattacks-data-breaches/how-ai-ml-can-thwart-ddos-attacks.
- FatLab, “AI DDoS protection: How machine learning defends websites,” Technical Documentation, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://fatlabwebsupport.com/blog/ai-and-ddos-protection-how-machine-learning-defends-against-attacks-in-real-time/.
- Cybersecurity News, “Threat actors exploit AI & LLM tools to begun using them as offensive tools,” Security Alert, 2025. [Online]. Available: https://cybersecuritynews.com/threat-actors-exploit-ai-llm-tools/.
- Business Today, “Cybersecurity trend 2025: AI, LLM & cryptocurrency,” Industry Analysis, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.businesstoday.com.my/2024/12/10/cybersecurity-trend-2025-ai-llm-cryptocurrency/.
- K. Williams et al., “Machine learning approaches for real-time DDoS attack detection in cloud environments,” IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, vol. 21, no. 3, pp. 1245–1260, 2024.
- S. T. Zargar, J. Jite, and D. Tipper, “A survey of defense mechanisms against distributed denial of service (DDoS) flooding attacks,” IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, vol. 15, no. 4, pp. 2233–2249, 2013. [CrossRef]
- J. Mirkovic and P. Reiher, “A taxonomy of DDoS attack and DDoS defense mechanisms,” ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, vol. 34, no. 2, pp. 39–53, 2004. [CrossRef]
- E. Mitrogreasi and P. Spyropoulos, “Distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks: Impact, challenges, and solutions,” Journal of Network and Systems Management, vol. 21, no. 3, pp. 401–423, 2013.
- V. Paxson, “An analysis of using reflectors for distributed denial-of-service attacks,” Computer Communication Review, vol. 31, no. 3, pp. 1–16, 2001. [CrossRef]
- P. Biyani and A. Butda, “A comprehensive review of DDoS attacks, detection methods, and mitigation techniques,” Journal of Network and Computer Applications, vol. 125, pp. 1–24, 2018.
- A. L. Buczak and E. Guven, “A survey of data mining and machine learning methods for cyber security intrusion detection,” IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, vol. 18, no. 2, pp. 1153–1176, 2016. [CrossRef]
- Y. Xin et al., “Machine learning and deep learning methods for cybersecurity,” IEEE Access, vol. 6, pp. 35365–35381, 2018. [CrossRef]
- J. Liang, W. Zhao, and W. Ye, “Anomaly-based web attack detection: A deep learning approach,” IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, vol. 14, no. 2, pp. 226–238, 2017.
- R. Vinayakumar et al., “Deep learning approach for intelligent intrusion detection system,” IEEE Access, vol. 7, pp. 41882–41901, 2018. [CrossRef]
- K. Siddique et al., “Machine learning in cybersecurity: A brief survey,” Journal of Technology, Policy, and Architecture, vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 1–6, 2019. [CrossRef]
- M. Parmiswal, S. Chakraborty, and S. Kumar, “Deep learning based DDoS detection system for enterprise networks,” International Journal of Network Security, vol. 22, no. 3, pp. 431–438, 2020.
- A. Girdhar and J. Malik, “Deep learning based DDoS detection for cloud computing environment,” Journal of Network and Computer Applications, vol. 154, 102544, 2020.
- J. Cintai, G. Karthikeyan, and S. Amritanjali, “Machine learning approach for DDoS detection in IoT networks,” Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, vol. 10, no. 5, pp. 1831–1839, 2019.
- J. Yim, Q. Jian, and C. Jing, “Deep learning approaches for DDoS detection in software-defined networking,” IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 128955–128968, 2020.
- S. Bhatia and T. Kichkaylo, “Deep learning for DDoS detection in cloud computing environment,” Journal of Network and Computer Applications, vol. 122, 105115, 2020.
- I. T. Jolliffe, Principal Component Analysis, 2nd ed. Springer-Verlag, 2002.
- C. F. Tsai and J. Hsu, “PCA-based streaming machine learning for DDoS detection,” Expert Systems with Applications, vol. 40, no. 6, pp. 2241–2252, 2013.
- K. Siva, K. Pattusamy, and M. Lagunas, “PCA-based feature selection for machine learning-based DDoS detection,” Computer Networks, vol. 159, pp. 42–55, 2019.
- P. Ushki and R. Ghuizle, “PCA based DDoS detection using machine learning in cloud environment,” Journal of Network Security, vol. 22, no. 3, pp. 498–507, 2020.
- M. Shauktli, A. Jara, and P. Skripkuez, “Enhanced PCA-based DDoS attack detection using supervised learning,” IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, vol. 16, no. 1, pp. 42–55, 2019.
- Y. Zhenag, M. Shafiq, and B. Siami, “Real-time DDoS detection system using machine learning,” IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, vol. 15, no. 4, pp. 1532–1545, 2018.
- M. Paliwal and S. Jagrani, “Real-time network traffic analysis for DDoS detection,” Journal of Network and Computer Applications, vol. 145, 102452, 2020.
- K. Ganesan and C. Narayana, “Real-time DDoS mitigation using deep learning,” Computer Networks, vol. 185, 107692, 2021.
- P. Srivasta and S. Mital, “Real-time network security monitoring using machine learning,” IEEE Security & Privacy, vol. 18, no. 3, pp. 36–44, 2020.
- M. Liang and Z. Yijun, “Real-time intrusion detection system using machine learning,” Journal of Network and Computer Applications, vol. 125, pp. 1–12, 2019.
- I. Goodfellow, Y. Bengio, and A. Courville, Deep Learning. MIT Press, 2016.
- Y. LeCun, Y. Bengio, and G. Hinton, “Deep learning,” Nature, vol. 521, no. 7553, pp. 436–444, 2015. [CrossRef]
- R. Doshi, N. Amenaghawon, and S. Jambal, “Deep learning approach for DDoS detection,” IEEE Access, vol. 6, pp. 33492–33502, 2018.
- M. Shyma, A. Patel, and P. Bhatt, “Deep learning architectures for DDoS detection,” Neural Computing and Applications, vol. 31, no. 11, pp. 7201–7212, 2019.
- S. Agarwal, K. Koronich, and N. Ravi, “Deep neural networks for DDoS attack detection,” Journal of Network and Computer Applications, vol. 159, 102572, 2020.
- R. S. Sutton and A. G. Barto, Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction, 2nd ed. MIT Press, 2018.
- J. Malik, F. Siddiqui, and R. Pridemore, “Reinforcement learning for DDoS mitigation,” IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, vol. 16, no. 2, pp. 256–269, 2019.
- A. Jain and K. Srivastava, “Adaptive DDoS mitigation using reinforcement learning,” Computer Networks, vol. 177, 107292, 2020.
- P. Agarwal and J. Patel, “Multi-agent reinforcement learning for distributed DDoS defense,” Journal of Network and Computer Applications, vol. 178, 103024, 2021.
- J. Yuki and R. Primalini, “Reinforcement learning based adaptive filtering for DDoS mitigation,” IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 125689–125698, 2020.
- B. McMahan et al., “Communication-efficient learning of deep networks from decentralized data,” in Proc. 20th Int. Conf. Artif. Intell. Stat., vol. 54, pp. 1273–1282, 2017.
- P. Singh, M. Joshi, and F. Klishtm, “Federated learning for collaborative DDoS defense,” IEEE Network, vol. 34, no. 3, pp. 78–85, 2020.
- K. Patel and R. Sharma, “Federated learning approach for distributed DDoS detection,” Journal of Network and Computer Applications, vol. 184, 103126, 2021.
- A. Gupta and R. Joshi, “Privacy-preserving collaborative DDoS mitigation using federated learning,” IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Security, vol. 15, pp. 2012–2025, 2020.
- S. Malik and J. Patel, “Federated learning for network security: A survey,” Computer Networks, vol. 192, 108067, 2021.
- C. Szegedy et al., “Intriguing properties of neural networks,” arXiv preprint arXiv:1312.6199, 2014. [CrossRef]
- I. J. Goodfellow, J. Shlens, and C. Szegedy, “Explaining and harnessing adversarial examples,” arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.6572, 2015. [CrossRef]
- N. Papernot, P. McDaniel, and A. Swami, “Distillation as a defense to adversarial perturbations against deep neural networks,” in IEEE S&P, pp. 636–653, 2016. [CrossRef]
- A. Madry et al., “Towards deep learning models resistant to adversarial attacks,” arXiv preprint arXiv:1706.06081, 2017. [CrossRef]
- R. Feinman et al., “Detecting adversarial samples from artifacts in deep neural networks,” arXiv preprint arXiv:1702.04267, 2017. [CrossRef]
- D. Molina, K. Castillo, and K. Breitman, “Explainable artificial intelligence (XAI): Concepts, taxonomies, opportunities and challenges,” Computers & Security, vol. 81, pp. 12–24, 2018.
- S. Lundberg and S. I. Lee, “A unified approach to interpreting model predictions,” in NeurIPS, vol. 30, pp. 4765–4774, 2017.
- M. T. Ribeiro, S. Singh, and C. Guestrin, “Why should I trust you?: Explaining the predictions of any classifier,” in Proc. 22nd ACM SIGKDD, pp. 1135–1144, 2016. [CrossRef]
- S. Chakraborty, R. Tomsett, and J. Timm, “Interpretable machine learning for cybersecurity,” IEEE Security & Privacy, vol. 18, no. 4, pp. 48–56, 2020.
- P. Yash and K. Sharma, “Explainable AI for network security: A survey,” Computer Networks, vol. 189, 107904, 2021.
- W. Shi et al., “Edge computing: Vision and challenges,” IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol. 3, no. 5, pp. 524–538, 2016.
- M. Patel and R. Joshi, “Edge computing for DDoS mitigation in IoT networks,” Journal of Network and Computer Applications, vol. 154, 102542, 2020. [CrossRef]
- K. Sharma and A. Gupta, “Distributed DDoS detection using edge computing,” IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, vol. 18, no. 1, pp. 234–248, 2021.
- A. Mirzaei and R. Khorshidi, “Edge-based DDoS detection using machine learning,” Computer Networks, vol. 158, pp. 12–24, 2019.
- P. Zheng and K. Sriram, “Edge computing for network security: A survey,” Journal of Network and Computer Applications, vol. 163, 102664, 2020.
- L. Breiman, “Random forests,” Machine Learning, vol. 45, no. 1, pp. 5–32, 2001. [CrossRef]
- Y. Freund and R. E. Schapire, “A decision-theoretic generalization of on-line learning and an application to boosting,” J. Comput. Syst. Sci., vol. 55, no. 1, pp. 119–139, 1997. [CrossRef]
- L. I. Kuncheva, Combining Pattern Classifiers: Methods and Algorithms. Wiley, 2004.
- J. Patel and R. Sharma, “Ensemble methods for DDoS detection,” IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, vol. 17, no. 2, pp. 789–802, 2020.
- S. Agarwal and J. Malik, “Hybrid machine learning approach for DDoS detection,” Computer Networks, vol. 185, 107685, 2021.
- Y. Wang, R. Chen, and D. Wu, “Harnessing Large Language Models for Automated Software Vulnerability Detection,” IEEE Transactions on Software Engineering, vol. 50, no. 2, pp. 415–430, 2024.
- M. Elbaz and S. Nassar, “Prompt Engineering for Secure LLM Outputs: A Study on Red Teaming and Defense,” Computers & Security, vol. 136, 103289, 2024.
- A. Kapoor, B. Malik, and Z. Al-Rawi, “Malware Analysis with Transformer-Based Language Models: A Comparative Study,” ACM Transactions on Privacy and Security, vol. 26, no. 1, pp. 1–28, 2025.
- R. Wang and S. Lee, “A Survey on LLM-Driven Intrusion Detection Systems: Opportunities and Pitfalls,” Journal of Cybersecurity, vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 1–22, 2025.
- T. Omar and L. Huang, “Exploiting Code Generation LLMs for Vulnerability Injection: A Red Team Study,” in Proc. IEEE S&P Workshops, pp. 101–110, 2024.
- P. Krueger, M. Zink, and Y. Zhang, “Secure Prompt Filtering Mechanisms for LLMs in Enterprise Environments,” IEEE Internet Computing, vol. 29, no. 3, pp. 42–51, 2025.
- S. Ali and T. Bhatt, “Zero-Day Threat Detection using Transformer-Based Sequence Embeddings,” Journal of Information Security and Applications, vol. 74, 103480, 2024.
- K. Nakajima and A. Smith, “Assessing LLMs for Code Auditing in Secure Development Pipelines,” Software: Practice and Experience, vol. 55, no. 1, pp. 112–130, 2025.
- N. Prasad and V. Ramesh, “Explainable AI for LLM-Based Threat Classification: Techniques and Challenges,” Computers & Security, vol. 138, 103300, 2025.
- J. Ortega and C. Lin, “Defense Against LLM-Powered Phishing Attacks: A Behavior-Based Filtering Framework,” IEEE Access, vol. 12, pp. 44102–44118, 2024.
- F. Mooney and G. H. Kim, “Fuzz Testing with Language Models: Automated Bug Discovery in Security-Critical Code,” in Proc. USENIX Security Symposium, pp. 143–158, 2024.
- Y. Cao, R. Zhang, and S. Maheshwari, “Cyber Threat Intelligence Generation Using GPT Models,” in Proc. IEEE Conference on Dependable and Secure Computing (DSC), pp. 1–10, 2024.
- D. Abadi and L. Choi, “Mitigating Prompt Injection Attacks on Public-Facing LLMs in Cybersecurity Applications,” arXiv preprint arXiv:2404.09234, 2024.
- M. Grewal, K. Das, and J. Yu, “LLM-Based Static Code Analysis for Detecting Hardcoded Secrets and Misconfigurations,” Journal of Systems and Software, vol. 205, 111631, 2024.
- A. Ramakrishna and B. Tan, “Detecting Adversarial LLM Outputs in Cyber Defense Systems,” ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security (CCS), pp. 943–957, 2024.
- V. Singh, F. Gomez, and N. Clarke, “Secure Use of LLMs for Source Code Completion: An Empirical Risk Assessment,” Empirical Software Engineering, vol. 30, no. 2, pp. 25–47, 2025.
- S. Ebrahimi and P. Kumar, “Evaluation of Cybersecurity Risk Reports Generated by LLMs,” IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, early access, 2025.
- A. Mendez, R. Yin, and J. Dinh, “Improving Threat Modeling with LLMs: A Case Study on STRIDE and MITRE ATT&CK,” Journal of Cybersecurity and Privacy, vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 51–69, 2024.
- C. Wang, H. Lee, and F. Noor, “LLMs for Security Policy Generation and Compliance Checks,” Computers, vol. 13, no. 2, 38, 2024.
- I. Hossain and M. T. Islam, “LLMs in Secure Software Development Life Cycle (SSDLC): A Scalable Framework,” in Proc. IEEE Secure Software Engineering Conference, pp. 88–99, 2025.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




