Submitted:
02 July 2025
Posted:
03 July 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
- RQ1: What is the current state of research on Resilience-Based Maintenance in industrial and infrastructure systems?
- RQ2: Which Artificial Intelligence methods and tools are employed in RBM to support decision-making, adaptability, and learning?
- RQ3: How is RBM aligned with the pillars of Industry 5.0, particularly sustainability and human-centricity?
- RQ4: What are the key research challenges, gaps, and directions for future studies in this area?
2. Theoretical Background
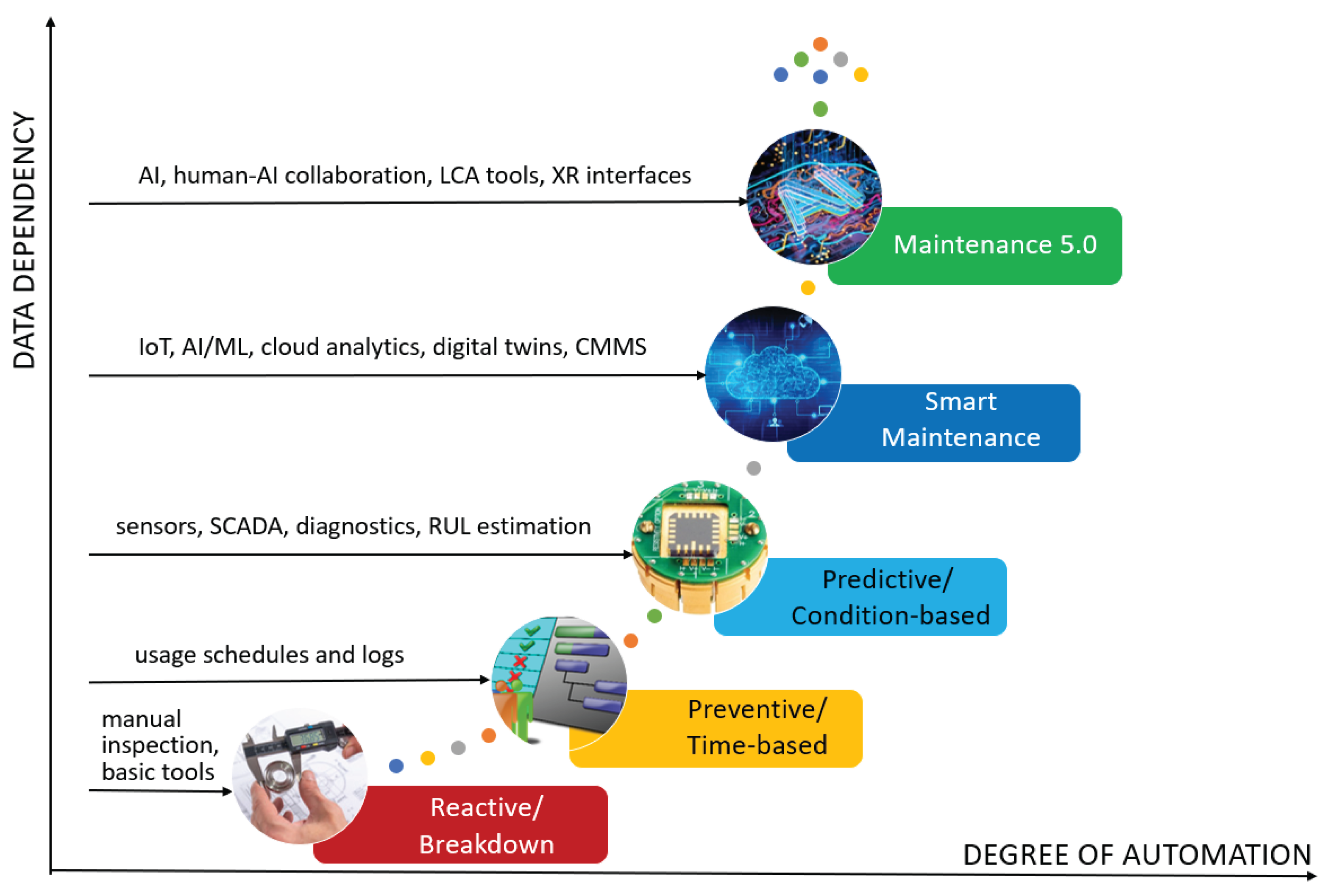
2.1. Evolution of Maintenance Concepts
| Generation | Main Paradigm | Objective | Key Technologies/ Tools | Data Dependency | Role of Human Operator | Integration Aspects |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st Gen | Reactive (Breakdown) | Restore function after failure | Manual inspection, basic tools | Very low | Manual diagnosis and repair | Isolated maintenance process |
| 2nd Gen | Preventive (Time-based) | Reduce unexpected failures | Maintenance schedules, usage logs | Low | Planner and executor | Linked to production planning |
| 3rd Gen | Predictive/ Condition-based | Predict failures before they occur | Sensors, SCADA, diagnostics, RUL estimation | Moderate to high | Data interpreter, condition assessor | Integrated with condition monitoring systems |
| 4th Gen | Smart Maintenance | Real-time, autonomous decision-making | IoT, AI/ML, edge/cloud analytics, digital twins, CMMS | High | Decision supervisor, system integrator | Embedded in cyber-physical production systems |
| 5th Gen | Maintenance 5.0 | Sustainable, resilient, human-centric | AI, knowledge graphs, human-AI collaboration, LCA tools, XR interfaces | Very high | Ethical co-designer, cognitive collaborator | Interdisciplinary and system-wide, resilience-focused |
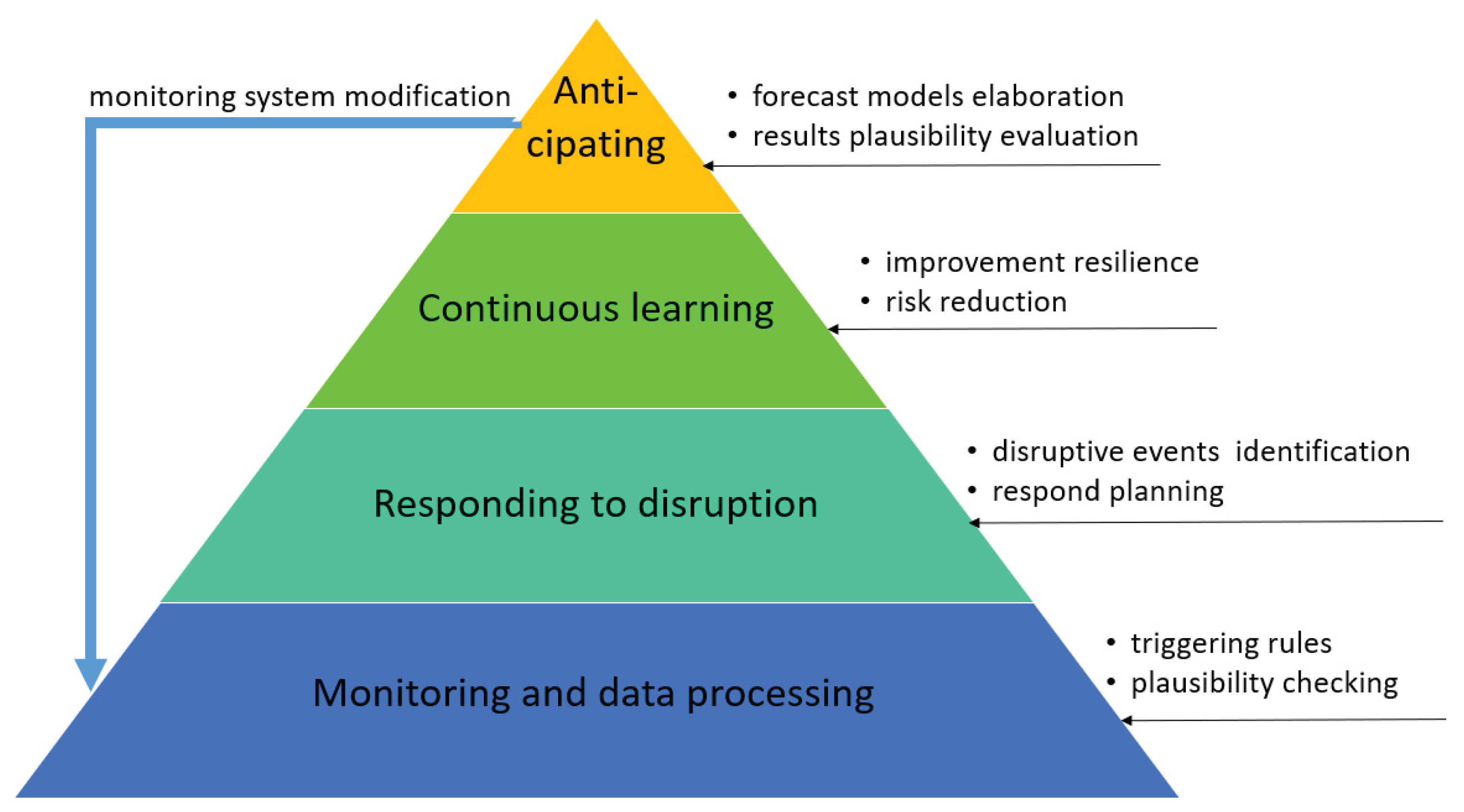
2.2. Resilience-Based Maintenance Approach
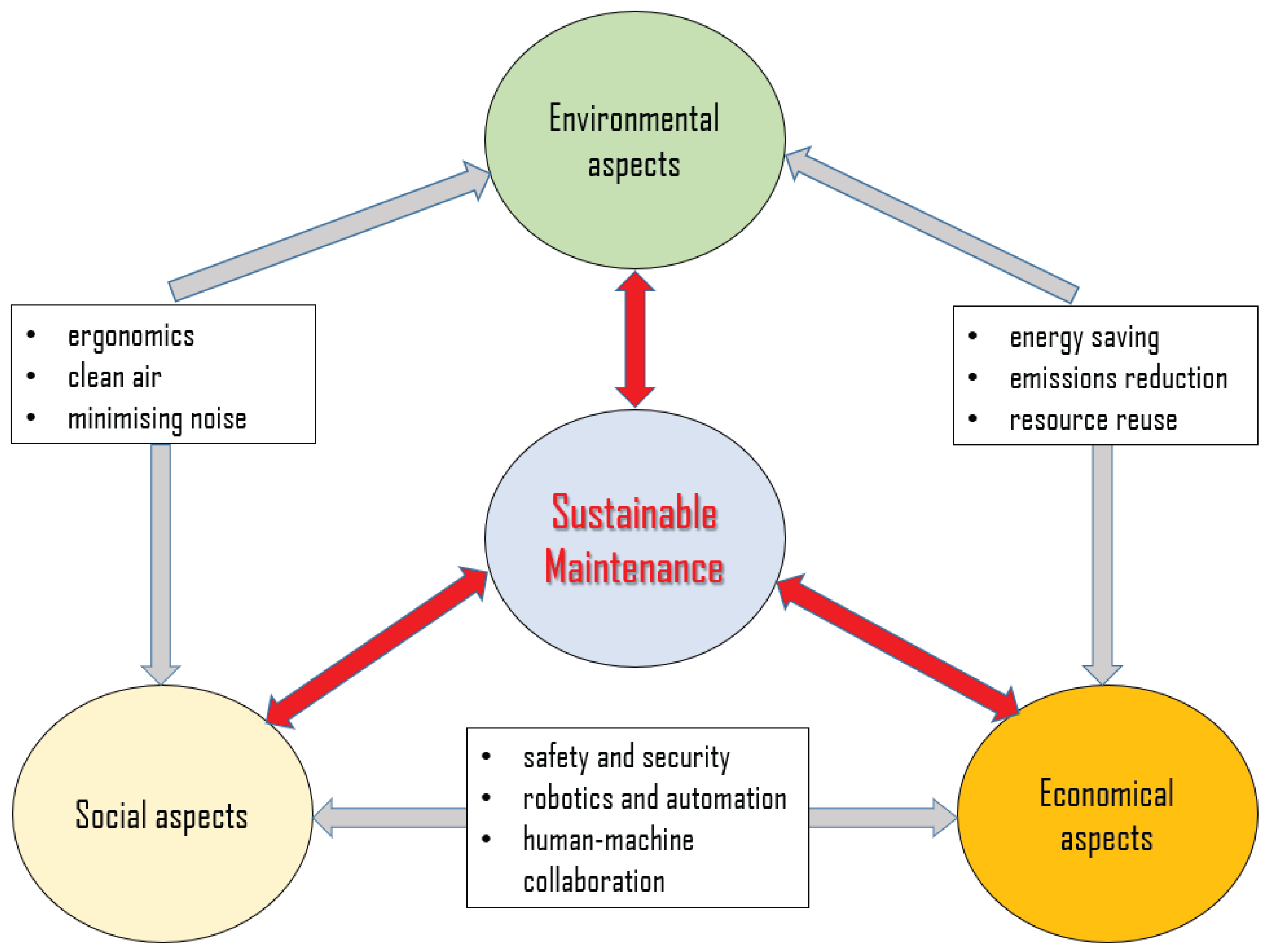
2.3. Sustainable Maintenance Approach
| Dimension | Category | Indicator | Unit/Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Environmental | Energy efficiency | Energy consumption per maintenance activity | kWh/task | Measures the energy used per maintenance intervention |
| Material sustainability | Percentage of recycled/reused parts | % | Share of reused or recycled components in total replaced items | |
| Environmental risk | Number of environmentally harmful incidents | count/year | Tracks incidents causing environmental harm (e.g., spills, emissions) | |
| Emissions reduction | The carbon footprint of maintenance operations | kg CO₂ eq./month | Estimates GHG emissions from maintenance-related activities | |
| Economic | Cost-effectiveness | Total cost of ownership (TCO) | currency/unit | A sum of acquisition, maintenance, and disposal costs over the asset lifecycle |
| Downtime minimization | Average unplanned downtime | hours/month | Measures operational losses due to unexpected maintenance needs | |
| Maintenance productivity | Mean time to repair (MTTR) | hours | Reflects the average time required to complete maintenance interventions | |
| Asset longevity | Asset life extension due to maintenance | % or years | Measures improvement in asset lifespan thanks to effective maintenance | |
| Social | Worker well-being | Number of safety incidents during maintenance | incidents/year | Tracks injuries or accidents during maintenance tasks |
| Ergonomics and workload | Physical/cognitive strain assessment (survey-based) | qualitative (Likert scale) | Subjective or assessed level of strain experienced by workers | |
| Competence development | Training hours per maintenance employee | hours/year | Measures annual training and upskilling efforts | |
| Human-machine collaboration | Adoption of ergonomic/assistive technologies (e.g., cobots, AR) | binary / % of tasks supported | Tracks implementation of human-assistive tech in daily maintenance operations |
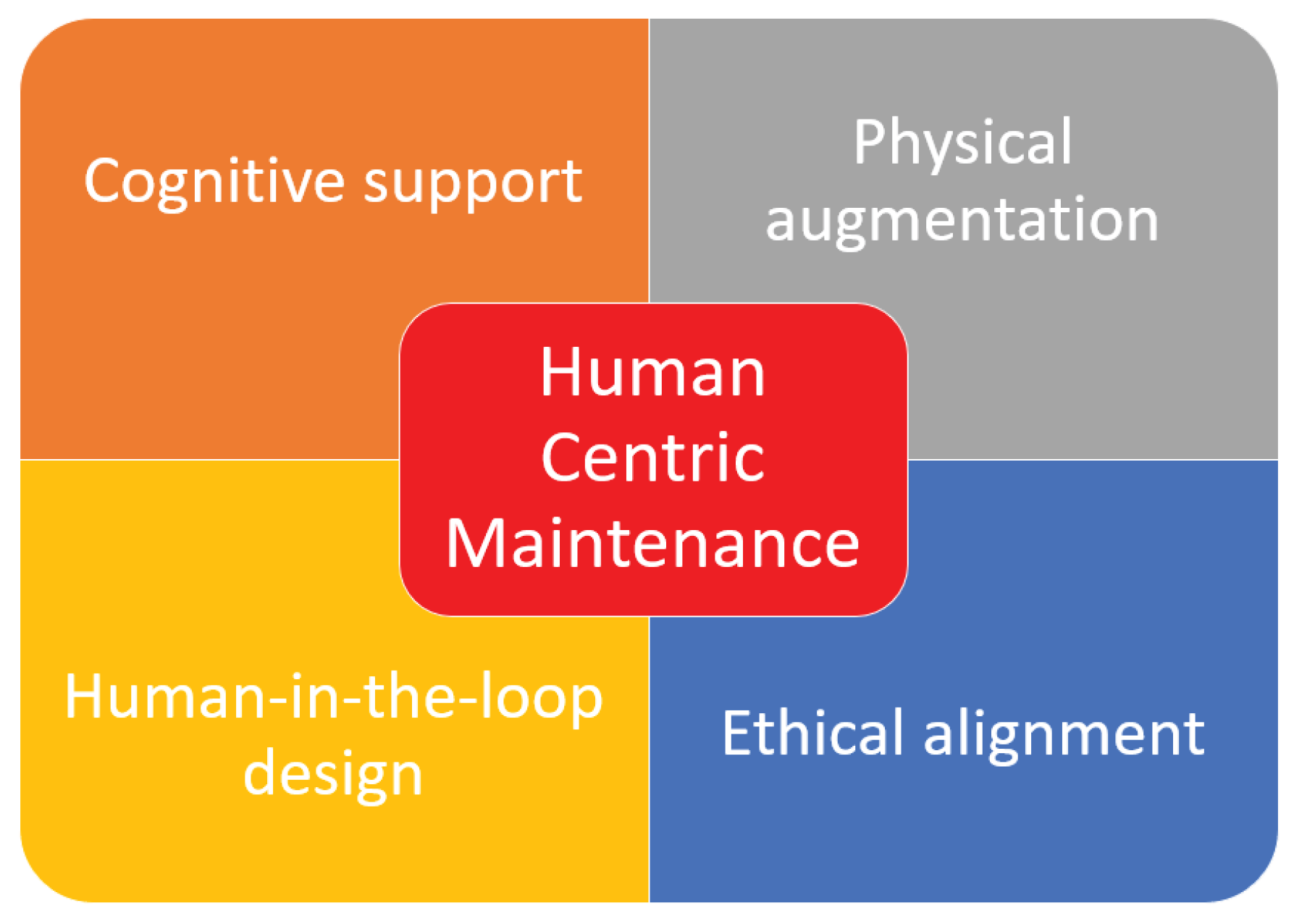
2.4. Human-Centric Maintenance
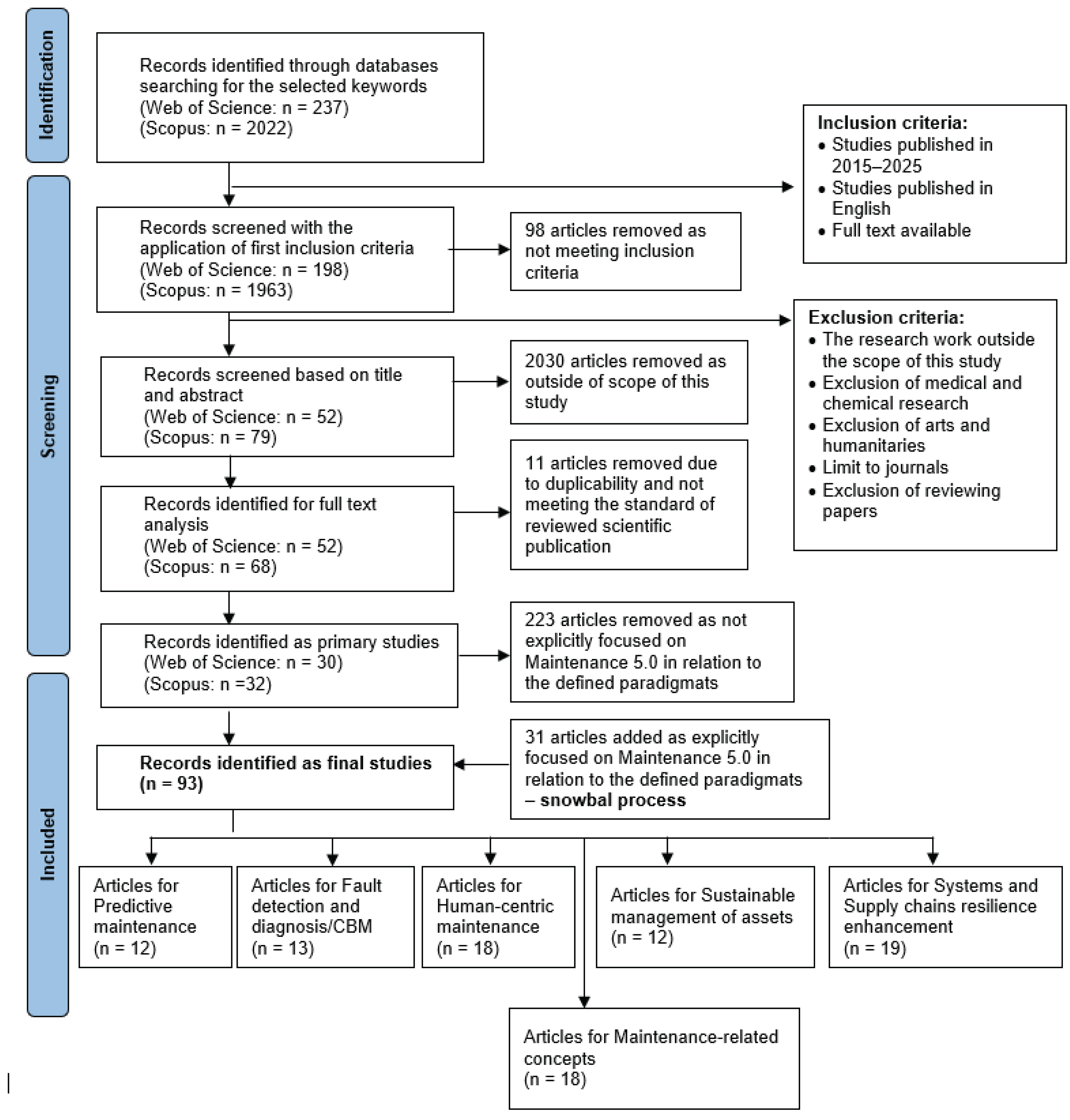
3. Review Methodology
3.1. Review Design and Protocol
- definition of research objectives and questions – establishing the scope of the evaluation, including the conceptual focus on RBM and its relation to other maintenance paradigms under Industry 5.0,
- search strategy development – formulating a comprehensive query string and selecting relevant databases (Scopus, Web of Science),
- screening and eligibility assessment – applying inclusion and exclusion criteria, removing duplicates, and performing title/abstract and full-text screenings,
- supplementary search – using snowballing techniques (both backward and forward citation tracking) to enhance literature coverage,
- data extraction, synthesis, and classification – analyzing and categorizing the final set of articles by themes, methods, application domains, and contributions.
3.2. Identification – Search Strategy
- Resilience engineering: resilience OR robustness OR adaptability OR recoverability,
- Maintenance domain: maintenance OR upkeep OR repair OR service OR fault OR failure OR diagnostics OR diagnosis OR prognosis OR inspection OR monitoring,
- Sustainability dimension: sustainable OR eco-friendly OR green OR environmental-friendly OR circular OR energy-efficient,
- Industrial context: industrial systems OR manufacturing OR production OR operations OR industrial processes,
- Industry 5.0 and human-centricity: Industry 5.0 OR human-centric OR human-centered OR user-centered OR people-oriented OR social OR human factor OR human-machine interaction OR human-in-the-loop OR anthropocentric OR ergonomics,
- Advanced intelligent technologies: Artificial Intelligence OR AI OR digital twin OR smart system OR intelligent system OR Machine Learning OR cyber-physical system OR IoT OR big data OR cloud computing OR edge computing OR augmented reality OR AR OR virtual reality OR VR OR blockchain.
3.3. Screening – Eligibility Criteria
- resilience, robustness, adaptability, or recovery in the context of industrial maintenance,
- integration of sustainable or circular principles into maintenance strategies,
- human-centric approaches (e.g., human-in-the-loop, Operator 4.0, ergonomics) in industrial systems,
- application of smart or intelligent technologies such as AI, digital twins, IoT, or cyber-physical systems in maintenance practices.
3.4. Inclusion – Full-Text Review and Selection
- relevance: articles had to present explicit models, frameworks, case studies, or methodologies related to RBM, predictive maintenance, or sustainability in industrial systems.,
- methodological soundness: publications were assessed for clarity of objectives, rigor in methodology, and robustness of results,
- contribution to knowledge: only articles that offered conceptual advances, empirical findings, or practical insights were included.
3.5. Snowball Process – Final Selection
3.6. Documenting the SLR Study
4. Systematic Literature Review Results
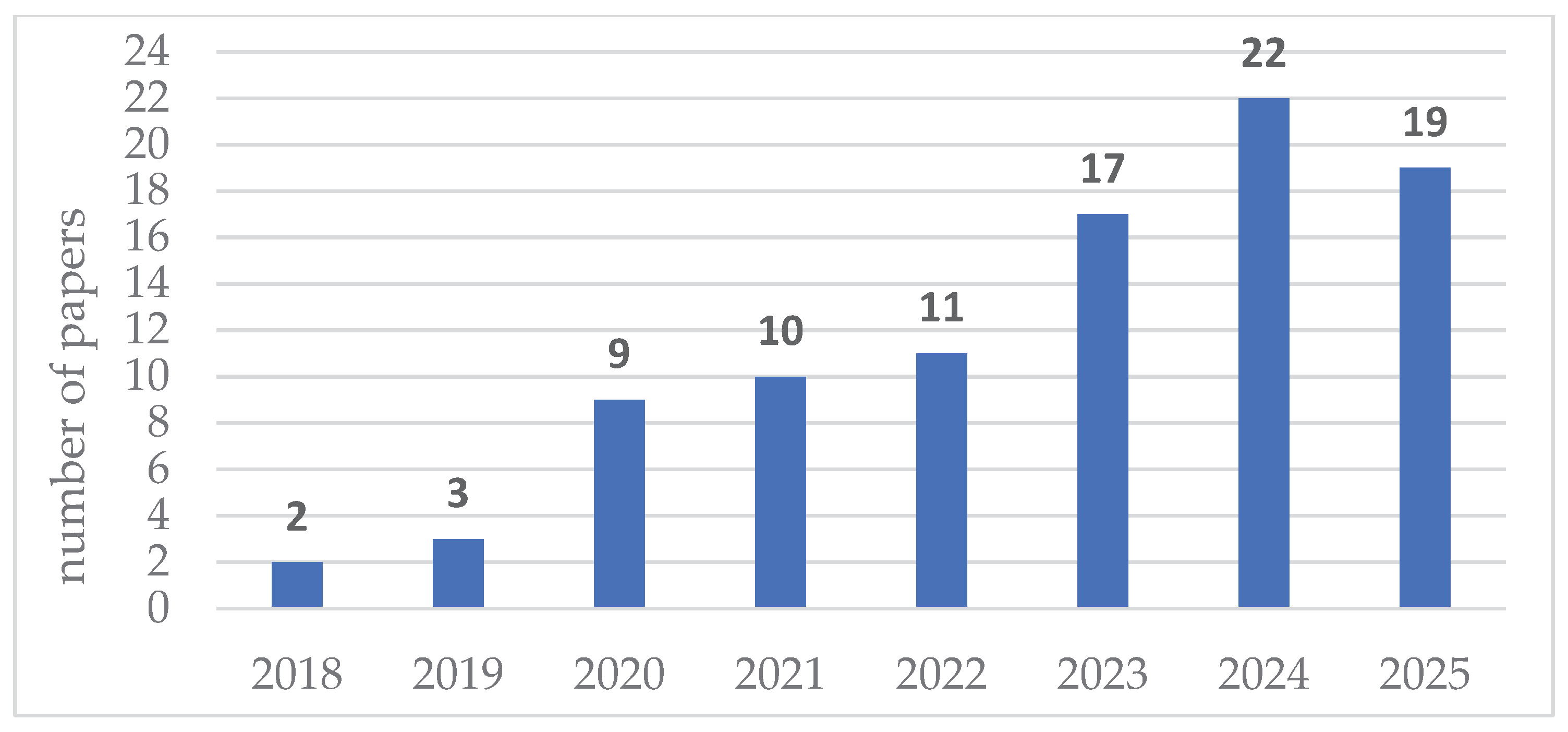
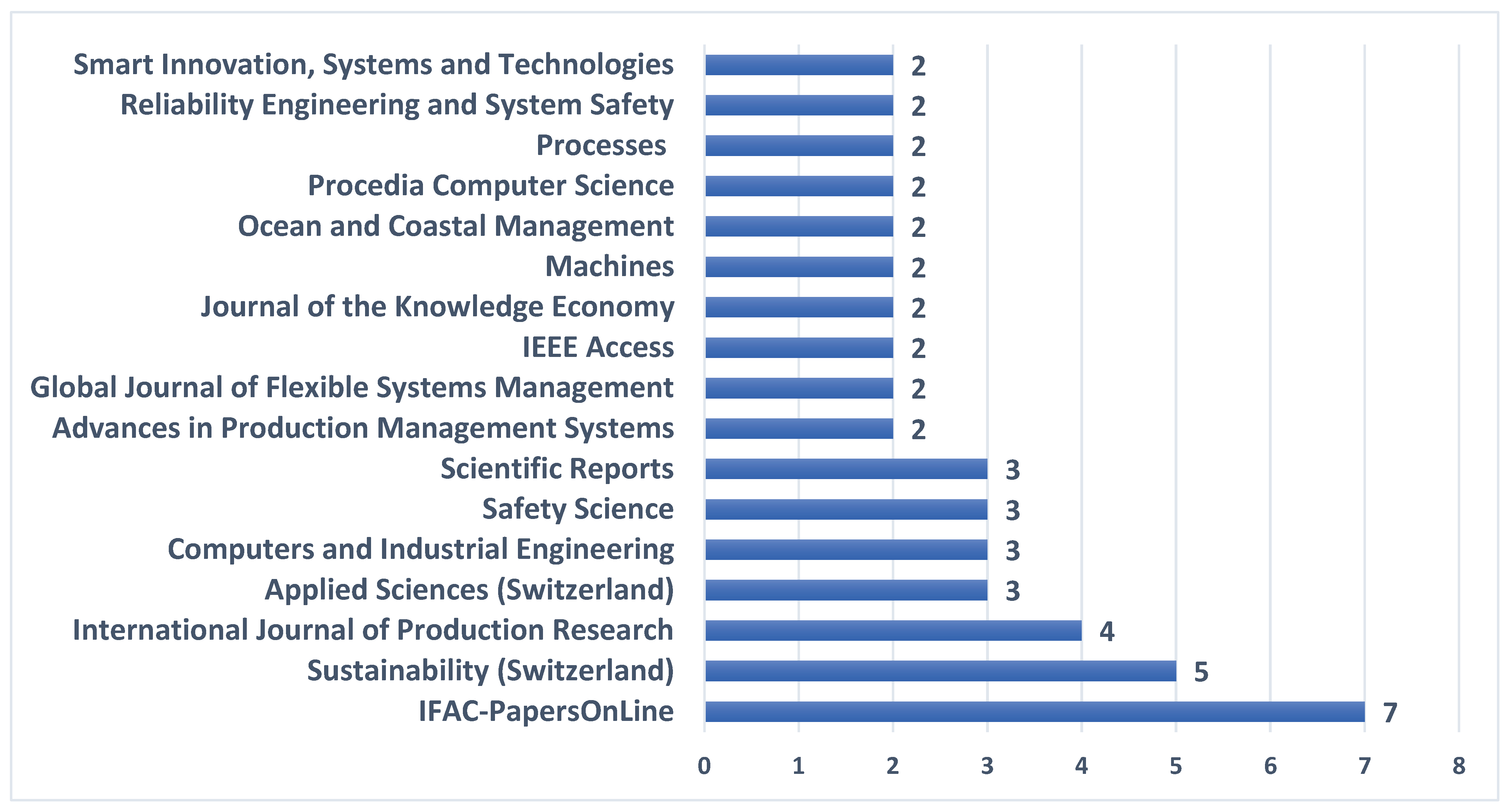
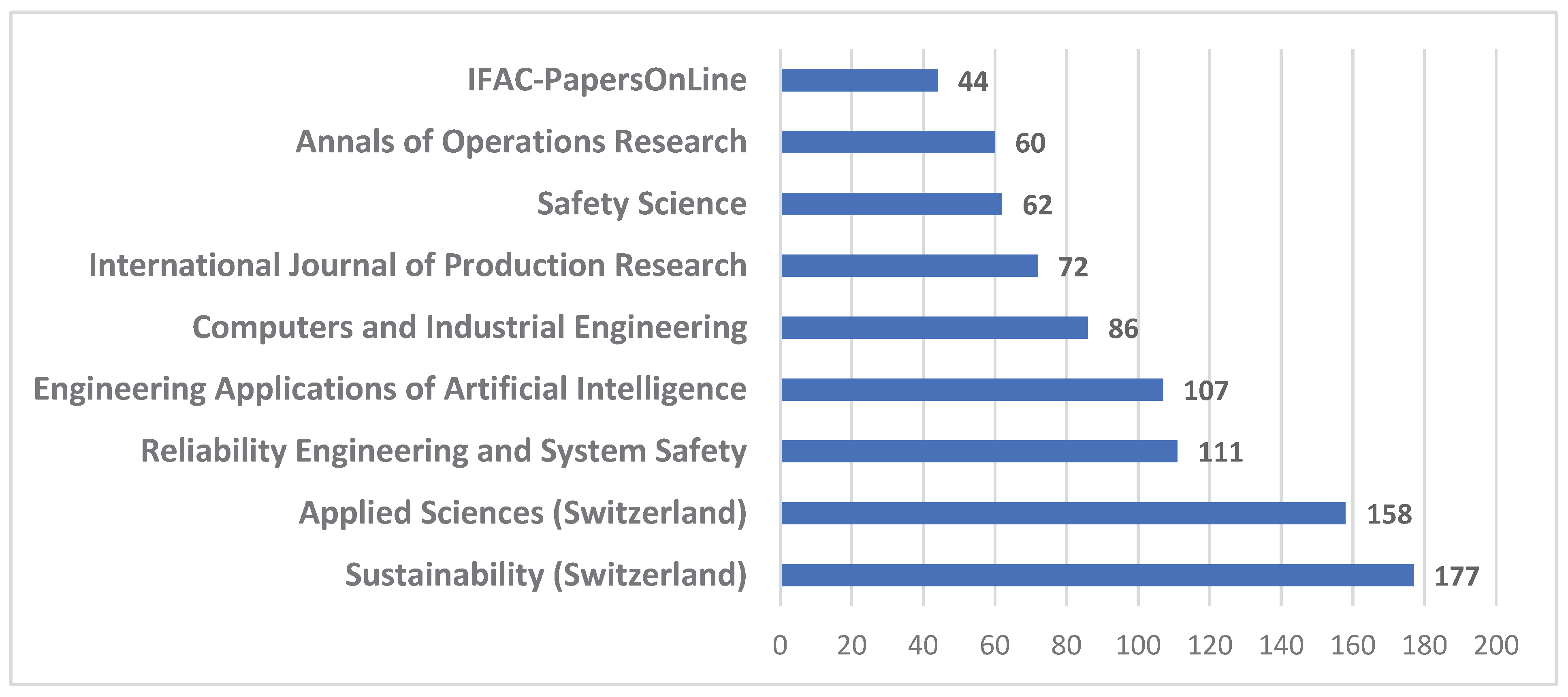
4.1. Bibliometric Analysis
- publication dynamics and source distribution – to identify temporal patterns and the increasing attention toward RBM-related topics, as well as to examine the scientific outlets (journals and conference proceedings) in which these studies are most frequently published, thereby revealing the disciplinary focus and visibility of the field,
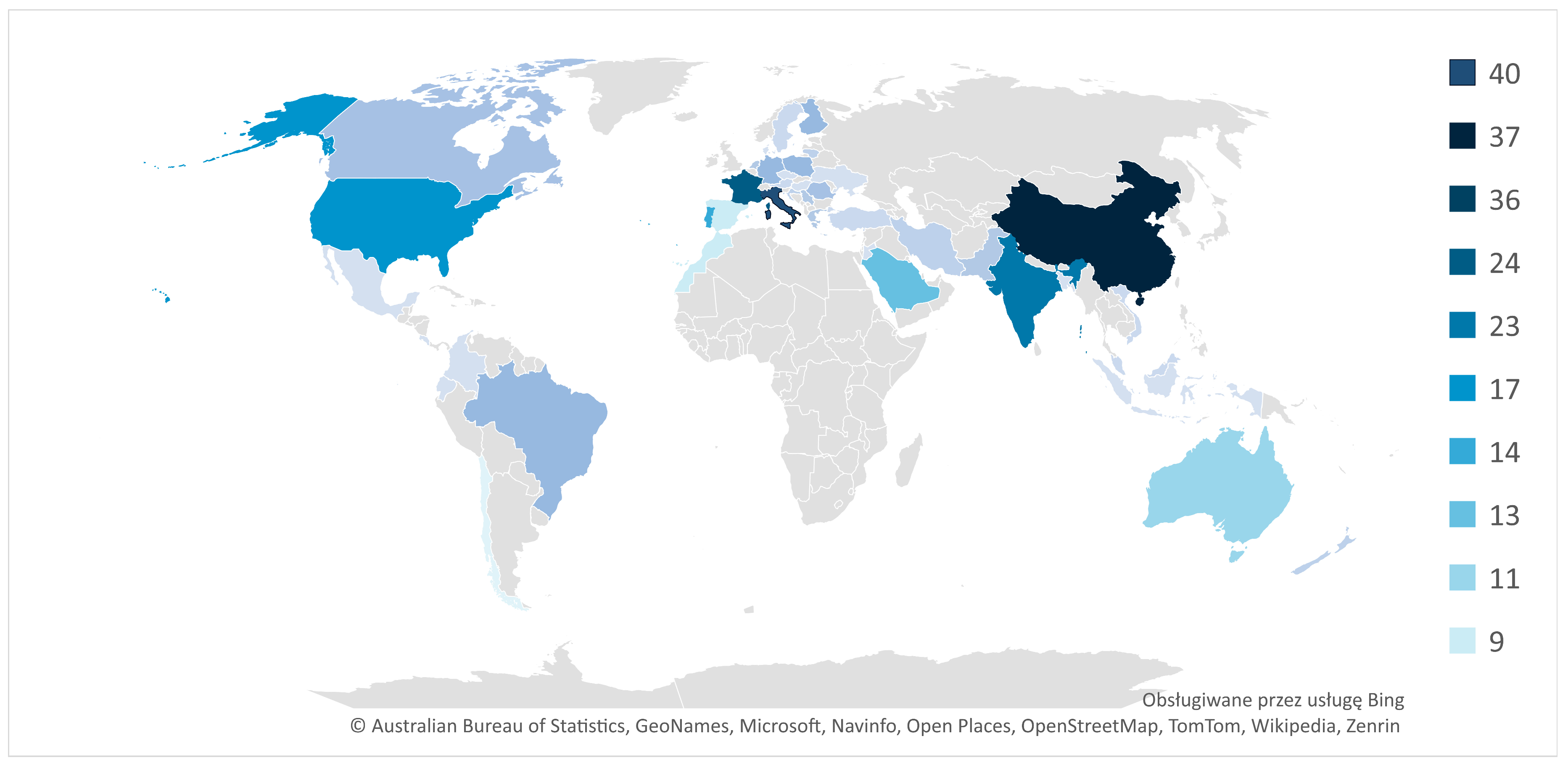
- country-level collaboration – to examine the geographic spread and international cooperation in RBM research,
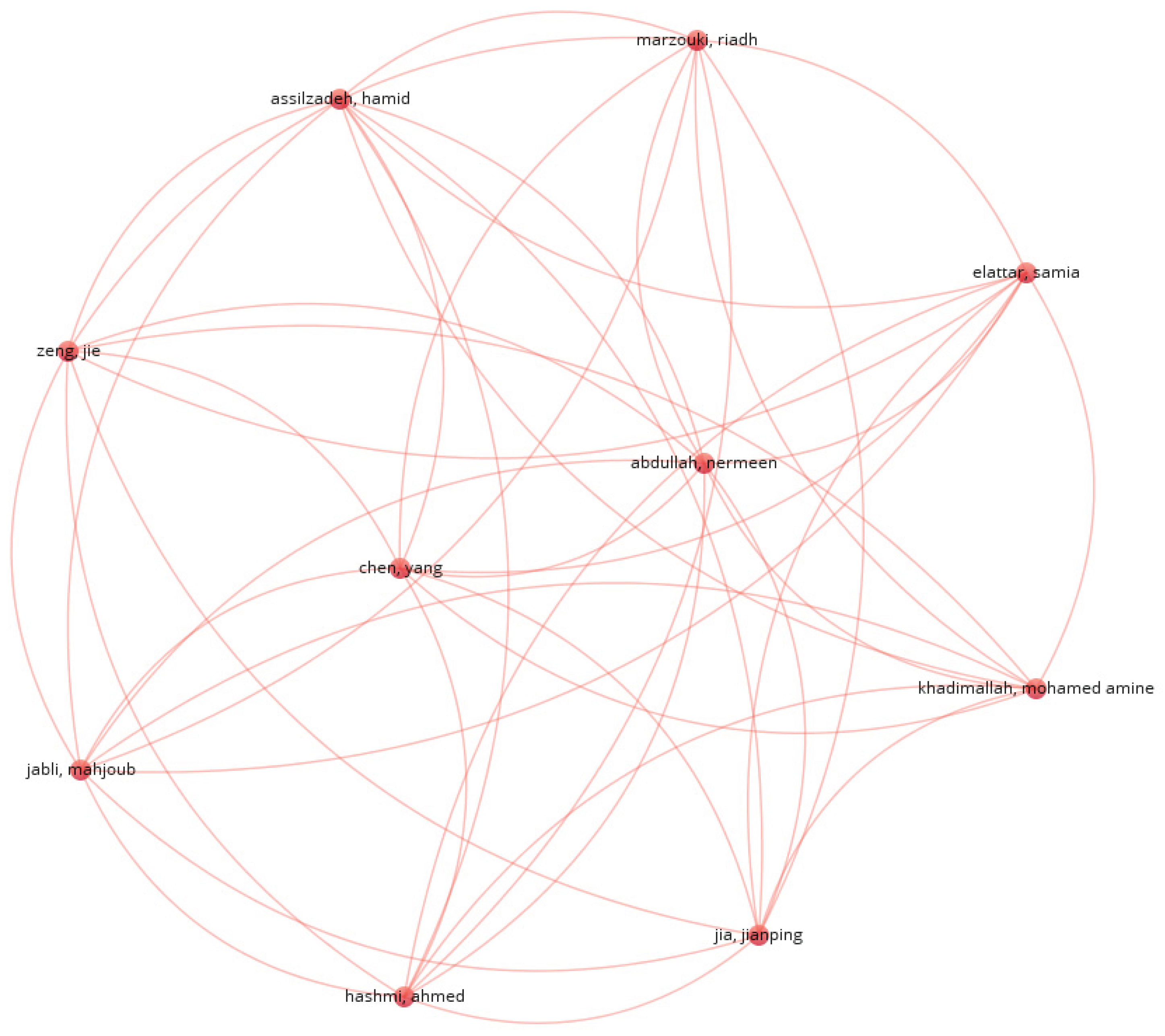
- co-authorship networks – to explore collaboration patterns among authors and institutions,
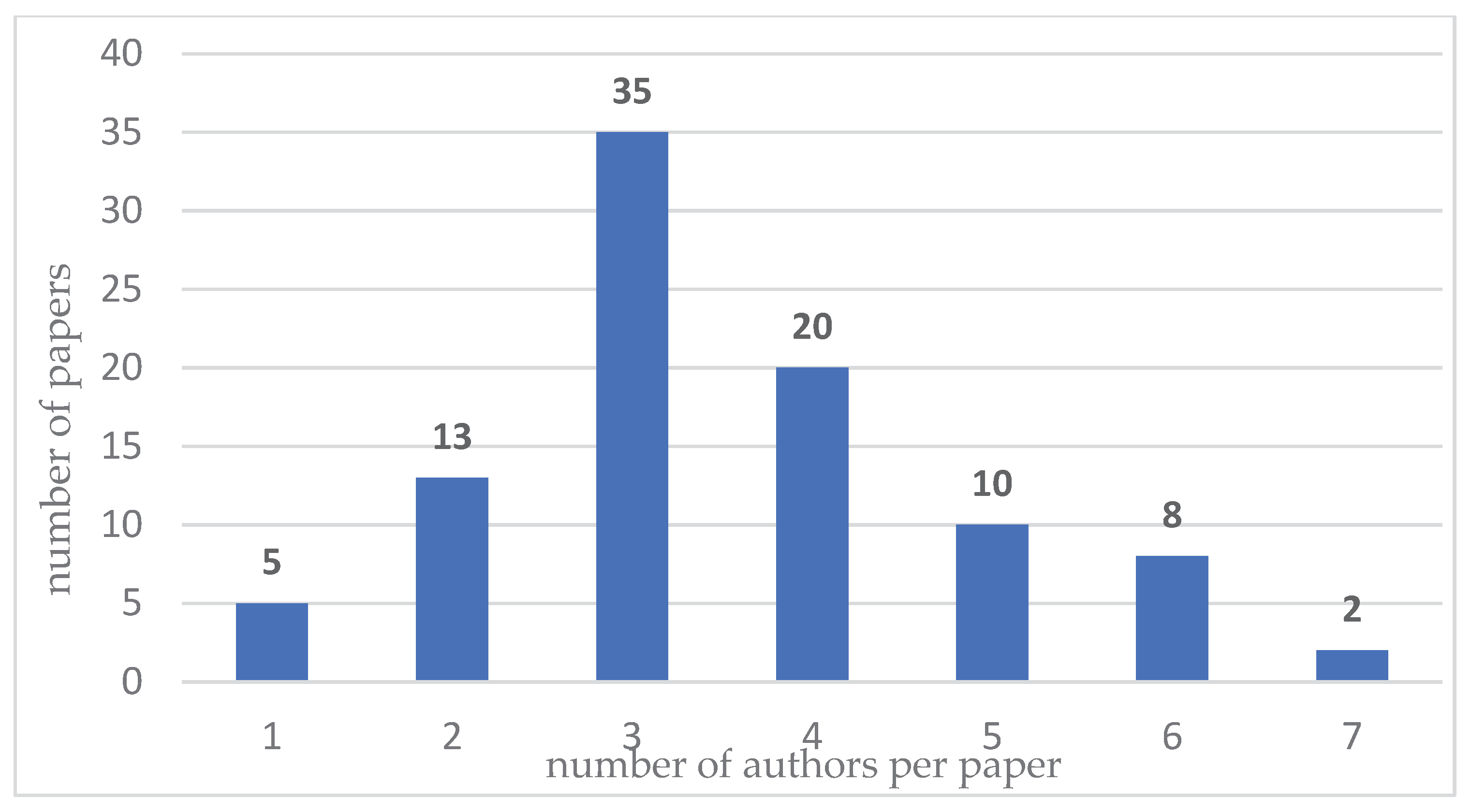
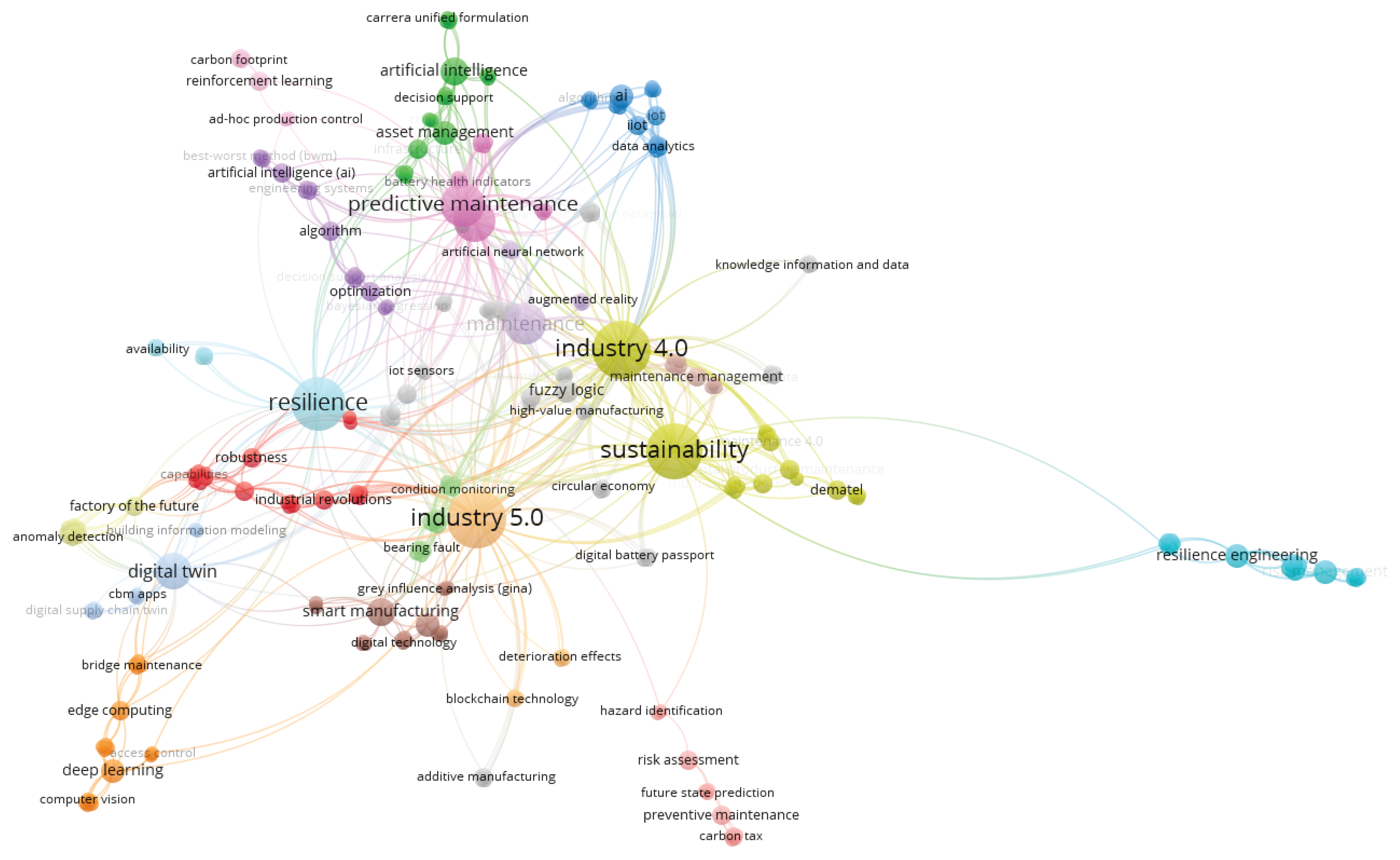
- co-occurrence of keywords – to identify thematic clusters, trends, and emerging research areas.
4.2. Content-Based Analysis
5. Discussion: Insights and Research Gaps
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Full Description |
| AHP AI AR CBM CM CMMS CNNs CPS CR DL DRL DT ERP GHG GINA HITL HMI HSM IoT ISM KPI LCA LCC MCDM MICMAC ML MTTR |
Analytical Hierarchy Process Artificial Intelligence Augmented Reality Condition-Based Maintenance Condition Monitoring Computerized Maintenance Management Systems Convolutional Neural Networks Cyber-physical System Corrective Maintenance Deep Learning Deep Reinforcement Learning Digital Twin Enterprise Resource Planning Greenhouse Gases Grey Influence Analysis Human-in-the-loop Human Machine Interface Health Status Monitoring Internet of Things Interpretive Structural Modeling Key Performance Indicator Life Cycle Assesment Life Cycle Costing Multi-criteria Decision-making Matrix of Cross-Impact Multiplications Applied to Classification Machine Learning Mean Time To Repair |
| O&M PdM PHM PM |
Operation and Maintenance Predictive Maintenance Prognostics and Health Management Preventive Maintenance |
| PRISMA RBM RCM RL RNNs RUL SCADA |
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyzes Resilience-based Maintenance Reliability Centered Maintenance Reinforcement Learning Recurrent Neural Networks Residual Lifetime Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition |
| SLR SMEs SVMs TBL TCO VR XR WoS |
Systematic Literature Review Small and Medium Enterprises Support Vector Machines Triple Bottom Line Total Cost of Ownership Virtual Reality Extended Reality Web of Science |
Appendix A
Appendix A.1
| No. | Ref. title | Source | Citation number according to Scopus database |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | A new concept of digital twin supporting optimization and resilience of factories of the future | Applied Sciences (Switzerland) | 140 |
| 2 | Artificial intelligence in prognostics and health management | Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence | 107 |
| 3 | Maintenance optimization in industry 4.0 | Reliability Engineering and System Safety | 107 |
| 4 | Predictive Maintenance Planning for Industry 4.0: Framework and Case Study | Sustainability (Switzerland) | 103 |
| 5 | Sustainable robust layout using Big Data approach | Journal of Cleaner Production | 98 |
| 6 | Artificial intelligence-based human-centric decision support framework under pandemic environments | Annals of Operations Research | 60 |
| 7 | Pattern recognition method of fault diagnostics for smart manufacturing | Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing | 53 |
| 8 | AIoT-informed digital twin communication for bridge maintenance | Automation in Construction | 51 |
| 9 | Predictive maintenance for industry 5.0: behavioural inquiries from a work system perspective | International Journal of Production Research | 49 |
| 10 | A new resilient risk management model for Offshore Wind Turbine maintenance | Safety Science | 42 |
| 11 | On sustainable predictive maintenance: Exploration of key barriers | Sustainable Production and Consumption | 37 |
| 12 | Process resilience analysis based data-driven maintenance optimization: cooling tower operations | Computers and Chemical Engineering | 35 |
| 13 | Resilience of process plant for safety and sustainability | Sustainability (Switzerland) | 35 |
| 14 | Human-oriented maintenance and disassembly in sustainable manufacturing | Computers and Industrial Engineering | 33 |
| 15 | Machine learning integrated design for resilient circular manufacturing systems | Computers and Industrial Engineering | 28 |
| 16 | Leveraging Blockchain for sustainability and supply chain resilience | Computers and Industrial Engineering | 25 |
| 17 | Digital twins for managing railway maintenance and resilience | Open Research Europe | 25 |
| 18 | Environmental issue in integrated production/remanufacturing systems | International Journal of Production Research | 22 |
| 19 | Condition-based monitoring as a robust strategy towards sustainable and resilient infrastructure | Sustainable and Resilient Infrastructure | 22 |
| 20 | Using fuzzy logic to support maintenance decisions according to resilience-based maintenance concept | Eksploatacja i Niezawodnosc | 21 |
| 21 | Contribution of Maintenance 4.0 in Sustainable Development with an Industrial Case Study | Sustainability (Switzerland) | 21 |
| 22 | Sustainability of maintenance management practices in hydropower plant | Materials Today: Proceedings | 20 |
| 23 | Developing resilience for safety management in building repair and maintenance | Safety Science | 20 |
| 24 | Integrating Industry 4.0 and Total Productive Maintenance for global sustainability | TQM Journal | 20 |
| 25 | Towards Human Digital Twins to enhance workers' safety and production system resilience | IFAC-PapersOnLine | 18 |
| 26 | A Human–Machine Interaction Mechanism: Additive Manufacturing for Industry 5.0 | Sustainability (Switzerland) | 18 |
| 27 | AI-Driven Supply Chain Transformation in Industry 5.0 | Journal of the Knowledge Economy | 16 |
| 28 | Machine Learning Aided Rail Corrugation Monitoring for Railway Track Maintenance | Structural Monitoring and Maintenance | 15 |
| 29 | Digital twins in condition-based maintenance apps: A case study for train axle bearings | Computers in Industry | 13 |
| 30 | Challenges of Human-Centered Manufacturing in Industry 5.0 | IFAC-PapersOnLine | 13 |
| 31 | XAI Sustainable Human in the Loop Maintenance | IFAC-PapersOnLine | 13 |
| 32 | Fast Augmented Reality Authoring for Maintenance Operations | IEEE Access | 12 |
| 33 | Simulation-Based Digital Twins Enabling Smart Services for Machine Operations | International Journal of Human-Computer Interaction | 12 |
| 34 | Fleet resilience: evaluating maintenance strategies in critical equipment | Applied Sciences (Switzerland) | 11 |
| 35 | Intelligent monitoring of multi-axis robots for online diagnostics | Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing | 11 |
| 36 | A Zero-Trust Network-Based Access Control Scheme for Industry 4.0 | IEEE Access | 10 |
| 37 | The Confluence of Digital Twin and Blockchain Technologies in Industry 5.0 | Journal of the Knowledge Economy | 10 |
| 38 | Proposal of Industry 5.0-Enabled Sustainability of Product–Service Systems | Processes | 10 |
| 39 | A fusion of neural, genetic and ensemble machine learning approaches for engineering predictive capabilities | Powder Technology | 9 |
| 40 | Synergies between Lean and Industry 4.0 for Enhanced Maintenance | Processes | 9 |
| 41 | Information technologies in complex socio-technical systems based on functional variability | Applied Sciences (Switzerland) | 7 |
| 42 | Toward sustainability and resilience with Industry 5.0 | Frontiers in Manufacturing Technology | 7 |
| 43 | Integration of MBSE into Mining Industry: Predictive Maintenance System | International Journal of Emerging Technology and Advanced Engineering | 6 |
| 44 | Deep learning based approaches for intelligent industrial machinery health management | Scientific Reports | 6 |
| 45 | A conceptual digital twin framework for supply chain recovery | Supply Chain Analytics | 6 |
| 46 | Human-in-the-loop control strategy for smart manufacturing using fuzzy control | Procedia Computer Science | 5 |
| 47 | Resilient manufacturing systems enabled by AI support to AR equipped operator | 2021 IEEE ICE/ITMC | 4 |
| 48 | Maintenance Strategies Definition Based on Systemic Resilience Assessment: A Fuzzy Approach | Mathematics | 4 |
| 49 | A human-centric approach to aid in assessing maintenance from the sustainable manufacturing perspective | Procedia Computer Science | 4 |
| 50 | A resilience-based maintenance optimisation framework using multiple criteria | Reliability Engineering and System Safety | 4 |
| 51 | Analyzing the role of digital twins in developing a resilient sustainable manufacturing supply chain | Technological Forecasting and Social Change | 4 |
| 52 | Integration of inspection and monitoring data for RL-enhanced life-cycle management | Structure and Infrastructure Engineering | 3 |
| 53 | Resilient Design of Product Service Systems with Automated Guided Vehicles | Vehicles | 3 |
| 54 | Fostering lithium-ion battery remanufacturing through Industry 5.0 | International Journal on Interactive Design and Manufacturing | 2 |
| 55 | A Framework for Integrating Vision Transformers with Digital Twins | Machines | 2 |
| 56 | Hybrid machine learning framework for predictive maintenance in lithium-ion batteries | Scientific Reports | 2 |
| 57 | How to Predict Disruptions in the Inbound Supply Chain | Advances in Transdisciplinary Engineering | 1 |
| 58 | A Decision Support Framework for Resilient and Sustainable Service Design | Global Journal of Flexible Systems Management | 1 |
| 59 | Architecture for Fault Detection in Sandwich Panel Production Using Visual Analytics | Hybrid Artificial Intelligent Systems | 1 |
| 60 | Embracing resilience in pharmaceutical manufacturing: “digital twins” | International Journal of Pharmaceutical and Healthcare Marketing | 1 |
| 61 | Distributed maintenance task scheduling for multiple technician teams | International Journal of Production Research | 1 |
| 62 | Guardians of Reliability, Robustness, and Resilience | Procedia Computer Science | 1 |
| 63 | Validation of computer vision-based ergonomic risk assessment in industrial settings | Scientific Reports | 1 |
| 64 | Proactive Maintenance Strategy Based on Resilience Empowerment for Complex Buildings | Smart Innovation, Systems and Technologies | 1 |
References
- Psarommatis, F.; May, G.; Azamfirei, V. Envisioning Maintenance 5.0: Insights from a Systematic Literature Review of Industry 4.0 and a Proposed Framework. J. Manuf. Syst. 2023, 68, 376–399. [CrossRef]
- Werbińska-Wojciechowska, S.; Winiarska, K. Maintenance Performance in the Age of Industry 4.0: A Bibliometric Performance Analysis and a Systematic Literature Review. Sensors 2023, 23, 1409. [CrossRef]
- Aktef, Z.; Cherrafi, A.; Elfezazi, S.; Skalli, D. Exploring the Transition from Maintenance 4.0 Towards Maintenance 5.0: A Systematic Literature Review BT - Industrial and Logistics Systems Design and Efficient Operation. In Industrial and Logistics Systems Design and Efficient Operation. SIL 2024. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 1332; Benmoussa, R., Benazzouz, T., Dahbi, S., Eds.; Springer Nature Switzerland: Cham, 2025; pp. 181–190 ISBN 978-3-031-87309-6.
- Bukowski, L.; Werbińska-Wojciechowska, S. Using Fuzzy Logic to Support Maintenance Decisions According to Resilience-Based Maintenance Concept. Eksploat. i Niezawodn. - Maint. Reliab. 2021, 23, 294–307. [CrossRef]
- Durán, O.; Vergara, B. Maintenance Strategies Definition Based on Systemic Resilience Assessment: A Fuzzy Approach. Mathematics 2022, 10. [CrossRef]
- Briatore, F.; Braggio, M. Resilience and Sustainability Plants Improvement through Maintenance 4.0: IoT, Digital Twin and CPS Framework and Implementation Roadmap. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2024, 58, 365–370. [CrossRef]
- Ahmed Murtaza, A.; Saher, A.; Hamza Zafar, M.; Kumayl Raza Moosavi, S.; Faisal Aftab, M.; Sanfilippo, F. Paradigm Shift for Predictive Maintenance and Condition Monitoring from Industry 4.0 to Industry 5.0: A Systematic Review, Challenges and Case Study. Results Eng. 2024, 24, 102935. [CrossRef]
- Farsi, M.; Mishra, R.K.; Erkoyuncu, J.A. Industry 5.0 for Sustainable Reliability Centered Maintenance. SSRN Electron. J. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Achouch, M.; Dimitrova, M.; Ziane, K.; Sattarpanah Karganroudi, S.; Dhouib, R.; Ibrahim, H.; Adda, M. On Predictive Maintenance in Industry 4.0: Overview, Models, and Challenges. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12. [CrossRef]
- Zonta, T.; da Costa, C.A.; da Rosa Righi, R.; de Lima, M.J.; da Trindade, E.S.; Li, G.P. Predictive Maintenance in the Industry 4.0: A Systematic Literature Review. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2020, 150, 106889. [CrossRef]
- Pech, M.; Vrchota, J.; Bednář, J. Predictive Maintenance and Intelligent Sensors in Smart Factory: Review. Sensors 2021, 21, 1–39. [CrossRef]
- Toumi, H.; Meddaoui, A.; Hain, M. The Influence of Predictive Maintenance in Industry 4.0: A Systematic Literature Review. In Proceedings of the 2022 2nd International Conference on Innovative Research in Applied Science, Engineering and Technology, IRASET 2022; IEEE, 2022; pp. 1–13.
- van Oudenhoven, B.; Van de Calseyde, P.; Basten, R.; Demerouti, E. Predictive Maintenance for Industry 5.0: Behavioural Inquiries from a Work System Perspective. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2023, 61, 7846–7865. [CrossRef]
- Devaraj Naik, B.; Soni, K. Research Review on Reliability Centred Maintenance. Int. J. Innov. Res. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2007, 5, 9605–9612.
- 15. Guide for Surveys Based on Machinery Reliability and Maintenance Techniques; 2016;
- Çinar, Z.M.; Nuhu, A.A.; Zeeshan, Q.; Korhan, O.; Asmael, M.; Safaei, B. Machine Learning in Predictive Maintenance towards Sustainable Smart Manufacturing in Industry 4.0. Sustain. 2020, 12. [CrossRef]
- Regona, M.; Yigitcanlar, T.; Hon, C.; Teo, M. Artificial Intelligence and Sustainable Development Goals: Systematic Literature Review of the Construction Industry. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 108, 105499. [CrossRef]
- Foresti, R.; Rossi, S.; Magnani, M.; Guarino Lo Bianco, C.; Delmonte, N. Smart Society and Artificial Intelligence: Big Data Scheduling and the Global Standard Method Applied to Smart Maintenance. Engineering 2020, 6, 835–846. [CrossRef]
- Ucar, A.; Karakose, M.; Kırımça, N. Artificial Intelligence for Predictive Maintenance Applications: Key Components, Trustworthiness, and Future Trends. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 898. [CrossRef]
- Di Nardo, M.; Donini, A.; Federico, V.; Gallab, M. Comparative Analysis Of Maintenance Practices In Industry 4.0 And Industry 5.0: Bridging Gaps. In Advances in Reliability, Safety and Security, ESREL 2024 Monograph Book Series; Polish Safety and Reliability Association, 2024; Vol. Part 6, pp. 37–46 ISBN 9788368136180.
- Kans, M.; Campos, J. Digital Capabilities Driving Industry 4.0 and 5.0 Transformation: Insights from an Interview Study in the Maintenance Domain. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2024, 10, 100384. [CrossRef]
- Aktef, Z.; Cherrafi, A.; Elfezazi, S. Analysis of Maintenance 5.0 Implementation Challenges: An Interpretive Structural Modeling (ISM) and Fuzzy MICMAC. In Intelligent and Fuzzy Systems. INFUS 2024. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol. 1089; Kahraman, C., Cevik Onar, S., Cebi, S., Oztaysi, B., Tolga, A.C., Ucal Sari, I., Eds.; Springer Nature Switzerland, 2024; pp. 649–657 ISBN 978-3-031-67195-1.
- Silvestri, L.; Forcina, A.; Introna, V.; Santolamazza, A.; Cesarotti, V. Maintenance Transformation through Industry 4.0 Technologies: A Systematic Literature Review. Comput. Ind. 2020, 123, 103335. [CrossRef]
- Jasiulewicz-Kaczmarek, M.; Voisin, A.; Franciosi, C.; Roda, I.; Bocewicz, G. Recent Advances in Smart and Sustainable Maintenance. In Proceedings of the 10th International Federation of Automatic Control (IFAC) Conference; 2021; p. 2021.
- Jasiulewicz-Kaczmarek, M.; Gola, A. Maintenance 4.0 Technologies for Sustainable Manufacturing - An Overview. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2019, 52, 91–96. [CrossRef]
- Saihi, A.; Ben-Daya, M.; As’ad, R.A. Maintenance and Sustainability: A Systematic Review of Modeling-Based Literature. J. Qual. Maint. Eng. 2023, 29, 155–187. [CrossRef]
- Bastas, A. Sustainable Manufacturing Technologies: A Systematic Review of Latest Trends and Themes. Sustain. 2021, 13. [CrossRef]
- Franciosi, C.; Iung, B.; Miranda, S.; Riemma, S. Maintenance for Sustainability in the Industry 4.0 Context: A Scoping Literature Review. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2018, 51, 903–908. [CrossRef]
- Franciosi, C.; Voisin, A.; Miranda, S.; Riemma, S.; Iung, B. Measuring Maintenance Impacts on Sustainability of Manufacturing Industries: From a Systematic Literature Review to a Framework Proposal. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 260, 121065. [CrossRef]
- Vrignat, P.; Kratz, F.; Avila, M. Sustainable Manufacturing, Maintenance Policies, Prognostics and Health Management: A Literature Review. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2022, 218. [CrossRef]
- Durán, O.; Aguilar, J.; Capaldo, A.; Arata, A. Fleet Resilience: Evaluating Maintenance Strategies in Critical Equipment. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1–17. [CrossRef]
- Ciccarelli, M.; Papetti, A.; Germani, M. Exploring How New Industrial Paradigms Affect the Workforce: A Literature Review of Operator 4.0. J. Manuf. Syst. 2023, 70, 464–483. [CrossRef]
- Madzik, P.; Falat, L.; Jum’a, L.; Vrábliková, M.; Zimon, D. Human-Centricity in Industry 5.0 – Revealing of Hidden Research Topics by Unsupervised Topic Modeling Using Latent Dirichlet Allocation. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2024, 28, 113–138. [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Cohen, V. Socio-Economic Dimensions and Human Centricity in Industry 5.0: A Study on Manufacturing Sectors in Central and Eastern European Economies. J. Econ. Stud. 2024. [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372. [CrossRef]
- Wohlin, C. Guidelines for Snowballing in Systematic Literature Studies and a Replication in Software Engineering. In Proceedings of the ACM International Conference Proceeding Series; 2014.
- Nowakowski, T.; Tubis, A.; Werbińska-Wojciechowska, S. Evolution of Technical Systems Maintenance Approaches – Review and a Case Study. In Intelligent Systems in Production Engineering and Maintenance. ISPEM 2018. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing; Burduk, A., Chlebus, E., Nowakowski, T., Tubis, A., Eds.; 2019; Vol. 835, pp. 161–174 ISBN 9783319974897.
- IEC 60300-3-14:2004 Dependability Management-Part 3-14: Application Guide-Maintenance and Maintenance Support; 2004;
- Giacotto, A.; Marques, H.C.; Martinetti, A. Prescriptive Maintenance: A Comprehensive Review of Current Research and Future Directions. J. Qual. Maint. Eng. 2025, 31, 129–173. [CrossRef]
- Sala, R.; Francalanza, E.; Arena, S. A Review on Three Decades of Manufacturing Maintenance Research: Past, Present and Future Directions. Prod. Manuf. Res. 2025, 13. [CrossRef]
- Werbińska-Wojciechowska, S. Technical System Maintenance. Delay-Time-Based Modelling; Springer Nature Switzerland, 2019; ISBN 978-3-030-10788-8.
- Deepak Prabhakar, P.; Jagathy Raj, V.P. CBM , TPM , RCM and A-RCM - A Qualitative Comparison of Maintenance Management Strategies. Int. J. Manag. Bus. Stud. 2014, 4, 49–56.
- Prajapati, A.; Bechtel, J.; Ganesan, S. Condition Based Maintenance: A Survey. J. Qual. Maint. Eng. 2012, 18, 384–400. [CrossRef]
- Nordal, H.; El-Thalji, I. Modeling a Predictive Maintenance Management Architecture to Meet Industry 4.0 Requirements: A Case Study. Syst. Eng. 2021, 24, 34–50. [CrossRef]
- Ravnå, R.; Schjolberg, P. Industry 4.0 and Maintenance; 2016;
- Al-Najjar, B.; Algabroun, H.; Jonsson, M. Maintenance 4.0 to Fulfill the Demands of Industry 4.0 and Factory of the Future. Basim Al-Najjar J. Eng. Res. Appl. 2018, 8, 20–31.
- Aktef, Z.; Cherrafi, A.; Elfezazi, S. Analysis of Maintenance 5.0 Implementation Challenges: An Interpretive Structural Modeling (ISM) and Fuzzy MICMAC BT - Intelligent and Fuzzy Systems.; Kahraman, C., Cevik Onar, S., Cebi, S., Oztaysi, B., Tolga, A.C., Ucal Sari, I., Eds.; Springer Nature Switzerland: Cham, 2024; pp. 649–657.
- Roda, I.; Macchi, M. Maintenance Concepts Evolution: A Comparative Review towards Advanced Maintenance Conceptualization. Comput. Ind. 2021, 133, 103531. [CrossRef]
- Hollnagel, E. From Safety-I to Safety-II : A Brief Introduction to Resilience Engineering. J. Oper. Res. Soc. Japan 2014, 59, 435–439.
- Bhamra, R.; Dani, S.; Burnard, K. Resilience: The Concept, a Literature Review and Future Directions. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2011, 49, 5375–5393. [CrossRef]
- Burnard, K.; Bhamra, R.; Tsinopoulos, C. Building Organizational Resilience: Four Configurations. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2018, 65, 351–362. [CrossRef]
- Fraccascia, L.; Giannoccaro, I.; Albino, V. Resilience of Complex Systems: State of the Art and Directions for Future Research. Complexity 2018, 2018, 1–44. [CrossRef]
- Sheffi, Y. The Resilient Enterprise: Overcoming Vulnerability for Competitive Advantage; the MIT Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts, London, England, 2007;
- Boudreau, J.F.; Abdul Nour, G.; Komljenovic, D. Risk-Informed Decision-Making in Asset Management as a Complex Adaptive System of Systems. Int. J. Strateg. Eng. Asset Manag. 2019, 3, 198. [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, N.M.; Silva, M.J.F.; Salvado, F.; Rodrigues, H.; Maletič, D. Risk-informed Performance-based Metrics for Evaluating the Structural Safety and Serviceability of Constructed Assets against Natural Disasters. Sustain. 2021, 13. [CrossRef]
- Hollnagel, E.; Woods, D.D.; Leveson, N. Resilience Engineering : Concepts and Precepts; CRC Press, 2006;
- Hollnagel, E. Resilience Engineering: A New Understanding of Safety. J. Ergon. Soc. Korea 2016, 35, 185–191. [CrossRef]
- Hollnagel, E. Resilience Engineering and the Built Environment. Build. Res. Inf. 2014, 42, 221–228. [CrossRef]
- Woods, D.D. Four Concepts for Resilience and the Implications for the Future of Resilience Engineering. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2015, 141, 5–9. [CrossRef]
- Leveson, N.; Dulac, N.; Zipkin, D.; Cutcher-Gershenfeld, J.; Carroll, J.; Barrett, B. Engineering Resilience into Safety-Critical Systems. In Resilience Engineering: Concepts and Precepts; Hollnagel, E., Woods, D.D., Leveson, N., Eds.; CRC PRess, 2012; pp. 95–124 ISBN 9780754681366.
- Hollnagel, E. Risk + Barriers = Safety? Saf. Sci. 2008, 46, 221–229. [CrossRef]
- Karar, A.N.; Labib, A.; Jones, D. A Resilience-Based Maintenance Optimisation Framework Using Multiple Criteria and Knapsack Methods. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2024, 241, 109674. [CrossRef]
- Leng, J.; Xie, J.; Li, R.; Zhou, X.; Gu, X.; Liu, Q.; Chen, X.; Zhang, W.; Kusiak, A. Resilient Manufacturing: A Review of Disruptions, Assessment, and Pathways. J. Manuf. Syst. 2025, 79, 563–583. [CrossRef]
- Pawar, B.; Park, S.; Hu, P.; Wang, Q. Applications of Resilience Engineering Principles in Different Fields with a Focus on Industrial Systems: A Literature Review. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2021, 69, 104366. [CrossRef]
- Wachter, C.; Beckschulte, S.; Hinrichs, M.P.; Sohnius, F.; Schmitt, R.H. Strategies for Resilient Manufacturing: A Systematic Literature Review of Failure Management in Production. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2024, 58, 1393–1402. [CrossRef]
- Terziyan, V.; Kaikova, O. Guardians of Reliability, Robustness, and Resilience: Adversarial Maintenance in the Era of Industry 4.0 and 5.0. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2025, 253, 13–24. [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Yang, M.; Wang, H. Resilience-Based Approach to Maintenance Asset and Operational Cost Planning. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 162, 987–997. [CrossRef]
- Selvik, J.T.; Aven, T. A Framework for Reliability and Risk Centered Maintenance. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2011, 96, 324–331. [CrossRef]
- Reliability-Centered Maintenance (RCM) Handbook; Direction of Commander,Naval Sea Systems Command, 2007; Vol. S9081-AB-G;
- Backlund, F. Reliability-Centred Maintenance. Identification of Management and Organisational Aspects of Importance When Introducing RCM, Lulea University of Technology, 1999.
- Rose, A. What Is Reliability Centered Maintenance ? A Brief History of RCM RCM in the Facility and Utility Arena. 2002.
- RCM Guide. Reliability-Centered Maintenance Guide for Facilities and Collateral Equipment; 2008;
- Kaewunruen, S.; Sresakoolchai, J.; Lin, Y. Digital Twins for Managing Railway Maintenance and Resilience. Open Res. Eur. 2021, 1, 91. [CrossRef]
- Ejjami, R.; Boussalham, K. Industry 5.0 in Manufacturing: Enhancing Resilience and Responsibility through AI-Driven Predictive Maintenance, Quality Control, and Supply Chain Optimization. Int. J. Multidiscip. Res. 2024, 6, 0–31. [CrossRef]
- Wiese, T.L. Predictive Maintenance Using Artificial Intelligence in Critical Infrastructure: A Decision-Making Framework. Int. J. Eng. Bus. Manag. 2024, 1–4. [CrossRef]
- Rane, N.L.; Choudhary, S.P.; Rane, J. Artificial Intelligence for Enhancing Resilience. J. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 5, 1–33. [CrossRef]
- Hami, N.; Shafie, S.M.; Omar, S.; Ibrahim, Y.M.; Abdulameer, S.S.; Muhamad, M.R. A Review of Sustainable Maintenance in the Manufacturing Companies. Int. J. Supply Chain Manag. 2020, 9, 935–944.
- Franciosi, C.; Roda, I.; Voisin, A.; Miranda, S.; Franciosi, C.; Roda, I.; Voisin, A.; Miranda, S.; Macchi, M. Sustainable Maintenance Performances and EN 15341:2019: An Integration Proposal. In Proceedings of the FIP International Conference on Advances in Production Management Systems, APMS 2021; 2021; pp. 401–409.
- Ahmad, S.; Wong, K.Y.; Rajoo, S. Sustainability Indicators for Manufacturing Sectors: A Literature Survey and Maturity Analysis from the Triple-Bottom Line Perspective. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2019, 30, 312–334. [CrossRef]
- Sandu, G.; Varganova, O.; Samii, B. Managing Physical Assets: A Systematic Review and a Sustainable Perspective. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2023, 61, 6652–6674. [CrossRef]
- Roda, I.; Garetti, M. The Link between Costs and Performances for Total Cost of Ownership Evaluation of Physical Asset: State of the Art Review. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Engineering, Technology and Innovation: Engineering Responsible Innovation in Products and Services, ICE 2014; IEEE, 2014; pp. 1–8.
- Ochella, S.; Shafiee, M.; Dinmohammadi, F. Artificial Intelligence in Prognostics and Health Management of Engineering Systems. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2022, 108, 104552. [CrossRef]
- Kunttu, S.; Reunanen, M.; Raukola, J.; Frankenhaeuser, K.; Frankenhaeuser, J. Engineering Asset Management - Systems, Professional Practices and Certification; 2014; Vol. 19; ISBN 978-3-319-09506-6.
- Arunraj, N.S.; Maiti, J. Risk-Based Maintenance-Techniques and Applications. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 142, 653–661. [CrossRef]
- Fitt, D. Adopting Risk-Based Maintenance: Enabled by SAP Asset Strategy and Performance Management 2019.
- Cortés-Leal, A.; Cárdenas, C.; Del-Valle-Soto, C. Maintenance 5.0: Towards a Worker-in-the-Loop Framework for Resilient Smart Manufacturing. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 11330. [CrossRef]
- Kayan, B.A.; Ashraf, N.N. Evaluating the Environmental Maintenance Impact (EMI): A Carbon Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) of the Singgora Roof Tiles Repair in Heritage Buildings. Int. J. Build. Pathol. Adapt. 2023, 41, 905–925. [CrossRef]
- Patalas-Maliszewska, J.; Łosyk, H. An Approach to Maintenance Sustainability Level Assessment Integrated with Industry 4.0 Technologies Using Fuzzy-TOPSIS: A Real Case Study. Adv. Prod. Eng. Manag. 2022, 17, 455–468. [CrossRef]
- Franciosi, C.; Roda, I.; Voisin, A.; Miranda, S.; Macchi, M.; Iung, B. Sustainable Maintenance Performances and EN 15341:2019: An Integration Proposal. In Advances in Production Management Systems. Artificial Intelligence for Sustainable and Resilient Production Systems. APMS 2021. IFIP Advances in Information and Communication Technology, vol 633; Dolgui, A., Bernard, A., Lemoine, D., von Cieminski, G., Romero, D., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2021; pp. 401–409 ISBN 978-3-030-85910-7.
- Jasiulewicz-Kaczmarek, M.; Żywica, P.; Gola, A. Fuzzy Set Theory Driven Maintenance Sustainability Performance Assessment Model: A Multiple Criteria Approach. J. Intell. Manuf. 2021, 32, 1497–1515. [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Nguyen, K.; Oh, I. Systematic Literature Review on Industry 5.0: Current Status and Future Research Directions with Insights for the Asia Pacific Countries. Asia Pacific Bus. Rev. 2025, 00, 1–28. [CrossRef]
- Tóth, A.; Nagy, L.; Kennedy, R.; Bohuš, B.; Abonyi, J.; Ruppert, T. The Human-Centric Industry 5.0 Collaboration Architecture. MethodsX 2023, 11. [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lim, C.P.; Tan, K.H.; Govindan, K.; Kumar, A. Artificial Intelligence-Based Human-Centric Decision Support Framework: An Application to Predictive Maintenance in Asset Management under Pandemic Environments. Ann. Oper. Res. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Verma, D. Industry 5.0: A Human-Centric and Sustainable Approach to Industrial Development. Int. J. Soc. Relev. Concern 2024, 12, 17–21. [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liu, Y.; Morgan, P.L. Human–Machine Interaction towards Industry 5.0: Human-Centric Smart Manufacturing. Digit. Eng. 2024, 2, 100013. [CrossRef]
- Romero, D.; Bernus, P.; Noran, O.; Stahre, J.; Fast-berglund, Å.; Romero, D.; Bernus, P.; Noran, O.; Stahre, J.; Operator, Å.F.T. The Operator 4.0: Human Cyber-Physical Systems Adaptive Automation Towards Human-Automation Symbiosis Work Systems. In Proceedings of the IFIP International Conference on Advances in Production Management Systems (APMS).; 2016; pp. 677–686.
- Bajestani, M.S.; Mahdi, M.M.; Mun, D. Human and Humanoid-in-the-Loop (HHitL) Ecosystem: An Industry 5.0 Perspective. Machines 2025, 13, 510. [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.C.; Chen, H.M.; Chen, H.K.; Li, C.L. Multi-Objective Optimization in Industry 5.0: Human-Centric AI Integration for Sustainable and Intelligent Manufacturing. Processes 2024, 12. [CrossRef]
- Wajid, U.; Nizamis, A.; Anaya, V. Towards Industry 5.0 – A Trustworthy AI Framework for Digital Manufacturing with Humans in Control. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the Workshop of I-ESA’22; CEUR Workshop Proceedings, 2022; Vol. 3214, pp. 0–5.
- Turner, C.; Okorie, O.; Oyekan, J. XAI Sustainable Human in the Loop Maintenance. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2022, 55, 67–72. [CrossRef]
- Fröhlich, P.; Mirnig, A.; Zafari, S.; Baldauf, M. The Human in the Loop in Automated Production Processes: Terminology, Aspects and Current Challenges in HCI Research. In Proceedings of the AutomationXP23: Intervening, Teaming, Delegating – Creating Engaging Automation Experiences; CEUR Workshop Proceedings, 2023; Vol. 3394, pp. 1–5.
- Passalacqua, M.; Pellerin, R.; Magnani, F.; Doyon-Poulin, P.; Del-Aguila, L.; Boasen, J.; Léger, P.M. Human-Centred AI in Industry 5.0: A Systematic Review; Taylor & Francis, 2024; Vol. 7543; ISBN 9783031217074.
- Fragiadakis, G.; Diou, C.; Kousiouris, G.; ... Evaluating Human-AI Collaboration: A Review and Methodological Framework. arXiv Prepr. 2024, arXiv:2407.19098. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, G.; Chang, F.; Ma, D.; Jing, Y.; Cheng, W.; Ding, K.; Zhao, D. Towards New-Generation Human-Centric Smart Manufacturing in Industry 5.0: A Systematic Review. Adv. Eng. Informatics 2023, 57, 102121. [CrossRef]
- Pizon, J.; Witczak, M.; Gola, A.; Swic, A. Challenges of Human-Centered Manufacturing in the Aspect of Industry 5.0 Assumptions. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2023, 56, 156–161. [CrossRef]
- Adel, A. Future of Industry 5.0 in Society: Human-Centric Solutions, Challenges and Prospective Research Areas. J. Cloud Comput. 2022, 11. [CrossRef]
- Valette, E.; Bril El-Haouzi, H.; Demesure, G. Industry 5.0 and Its Technologies: A Systematic Literature Review upon the Human Place into IoT- and CPS-Based Industrial Systems. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2023, 184, 109426. [CrossRef]
- Trstenjak, M.; Benešova, A.; Opetuk, T.; Cajner, H. Human Factors and Ergonomics in Industry 5.0—A Systematic Literature Review. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 1–53. [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, M.; Penica, M.; O’Connell, E.; Southern, M.; Hayes, M. Human-in-Loop: A Review of Smart Manufacturing Deployments. Systems 2023, 11, 1–25. [CrossRef]
- Dehbozorgi, M.H.; Postell, J.; Ward, D.; Leardi, C.; Sullivan, B.P.; Rossi, M. Human in the Loop: Revolutionizing Industry 5.0 with Design Thinking and Systems Thinking. In Proceedings of the International Design Conference - Design 2024, Proceedings of the Design Society; 2024; Vol. 4, pp. 245–254.
- Agrawal, S.; Oza, P.; Kakkar, R.; Tanwar, S.; Jetani, V.; Undhad, J.; Singh, A. Analysis and Recommendation System-Based on PRISMA Checklist to Write Systematic Review. Assess. Writ. 2024, 61, 100866. [CrossRef]
- Kitchenham, B. Procedures for Performing Systematic Reviews; 2004;
- Madhukar, P.; McCulloch, M.; Gorman, J.; Pai, N.P.; Enanoria, W.T.A.; Kennedy, G.E.; Tharyan, P.; Colford, J.M. Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: An Illustrated, Step-by-Step Guide. Natl. Med. J. India 2004, 17, 86–95.
- Lame, G. Systematic Literature Reviews: An Introduction. Proc. Int. Conf. Eng. Des. ICED 2019, 2019-Augus, 1633–1642. [CrossRef]
- Gray, A. Body as Voice: Restorative Dance/Movement Psychotherapy with Survivors of Relational Trauma. Routledge Int. Handb. Embodied Perspect. Psychother. Approaches from Danc. Mov. Body Psychother. 2019, 147–160. [CrossRef]
- VOSviewer, Https://Www.Vosviewer.Com/.
- van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Software Survey: VOSviewer, a Computer Program for Bibliometric Mapping. Scientometrics 2010, 84, 523–538. [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.A. da; Pedrosa, M.R. Using Reference Manager ( Mendeley ) in Systematic Reviews 2018.
- Kumar, R.S.; Singh, A.R.; Narayana, P.L.; Chandrika, V.S.; Bajaj, M.; Zaitsev, I. Hybrid Machine Learning Framework for Predictive Maintenance and Anomaly Detection in Lithium-Ion Batteries Using Enhanced Random Forest. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 1–20. [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Yang, L.; Alnowibet, K.A. Optimizing Structural Resilience of Composite Smart Structures Using Predictive Artificial Intelligence and Carrera Unified Formulation: A New Approach to Improve the Efficiency of Smart Building Construction. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 2025, 0, 1–20. [CrossRef]
- Guerroum, M.; Zegrari, M.; Amalik, H.; Elmahjoub, A.A. Integration of MBSE into Mining Industry: Predictive Maintenance System. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Adv. Eng. 2022, 12, 170–180. [CrossRef]
- Kovari, A. A Framework for Integrating Vision Transformers with Digital Twins in Industry 5.0 Context. Machines 2025, 13. [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Li, H.; Xiong, G.; Song, H. AIoT-Informed Digital Twin Communication for Bridge Maintenance. Autom. Constr. 2023, 150, 104835. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Paiva, A.R.; Gurciullo, C.S. Advancing from Predictive Maintenance to Intelligent Maintenance with AI and IIoT. In Proceedings of the Proc. of KDD’20, San Diego, Califorinia USA; 2020; pp. 1–6.
- Avinash, B.; Joseph, G. Embracing Resilience in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing: “Digital Twins” – Forging a Resilient Path in the VUCA Maze. Int. J. Pharm. Healthc. Mark. 2025. [CrossRef]
- Abidi, M.H.; Mohammed, M.K.; Alkhalefah, H. Predictive Maintenance Planning for Industry 4.0 Using Machine Learning for Sustainable Manufacturing. Sustain. 2022, 14. [CrossRef]
- Karuppiah, K.; Sankaranarayanan, B.; Ali, S.M. On Sustainable Predictive Maintenance: Exploration of Key Barriers Using an Integrated Approach. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 27, 1537–1553. [CrossRef]
- Rota, F.; Talamo, M.C.L.; Paganin, G. Proactive Maintenance Strategy Based on Resilience Empowerment for Complex Buildings; Springer International Publishing, 2020; Vol. 177 SIST; ISBN 9783030528683.
- Chen, Y.; Zeng, J.; Jia, J.; Jabli, M.; Abdullah, N.; Elattar, S.; Khadimallah, M.A.; Marzouki, R.; Hashmi, A.; Assilzadeh, H. A Fusion of Neural, Genetic and Ensemble Machine Learning Approaches for Enhancing the Engineering Predictive Capabilities of Lightweight Foamed Reinforced Concrete Beam. Powder Technol. 2024, 440, 119680. [CrossRef]
- Florez, S.L.; Silva, M.S.; González-Briones, A.; Chamoso, P. Architecture for Fault Detection in Sandwich Panel Production Using Visual Analytics. In Proceedings of the Hybrid Artificial Intelligent Systems: 17th International Conference, HAIS 2022, Salamanca, Spain, September 5–7, 2022, Proceedings; García Bringas, P., Pérez García, H., Martínez de Pisón, F.J., Villar Flecha, J.R., Troncoso Lora, A., de la Cal, E.A., Herrero, Á., Martínez Álvarez, F., Psaila, G., Quintián, H., Corchado, E., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2022; pp. 286–297.
- Kaewunruen, S.; Sresakoolchai, J.; Zhu, G. Machine Learning Aided Rail Corrugation Monitoring for Railway Track Maintenance. Struct. Monit. Maint. 2021, 8, 151–166. [CrossRef]
- Soualhi, M.; Nguyen, K.T.P.; Medjaher, K. Pattern Recognition Method of Fault Diagnostics Based on a New Health Indicator for Smart Manufacturing. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2020, 142, 106680. [CrossRef]
- CRESPO MARQUEZ, A.; MARCOS ALBERCA, J.A.; GUILLÉN LÓPEZ, A.J.; DE LA FUENTE CARMONA, A. Digital Twins in Condition-Based Maintenance Apps: A Case Study for Train Axle Bearings. Comput. Ind. 2023, 151. [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Dong, Y.; Frangopol, D.M. Integration of Inspection and Monitoring Data for RL-Enhanced Sustainable Life-Cycle Management of Infrastructure Networks. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2025, 0, 1–15. [CrossRef]
- Soualhi, M.; Nguyen, K.T.P.; Medjaher, K.; Lebel, D.; Cazaban, D. Intelligent Monitoring of Multi-Axis Robots for Online Diagnostics of Unknown Arm Deviations. J. Intell. Manuf. 2023, 34, 1743–1759. [CrossRef]
- Urrea, C.; Sari, P. Symmetry-Driven Fault-Tolerant Synchronization in Multi-Robot Systems: Comparative Simulation of Adaptive Neural and Classical Controllers. Symmetry (Basel). 2025, 17. [CrossRef]
- Saeed, A.; A. Khan, M.; Akram, U.; J. Obidallah, W.; Jawed, S.; Ahmad, A. Deep Learning Based Approaches for Intelligent Industrial Machinery Health Management and Fault Diagnosis in Resource-Constrained Environments. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 1–30. [CrossRef]
- Mislav, S.; Mirko, T.; Leo, M. Using CNNs for Photovoltaic Panel Defect Detection via Infrared Thermography to Support Industry 4.0. Bus. Syst. Res. 2024, 15, 45–66. [CrossRef]
- Yodo, N.; Afrin, T.; Yadav, O.P.; Wu, D.; Huang, Y. Condition-Based Monitoring as a Robust Strategy towards Sustainable and Resilient Multi-Energy Infrastructure Systems. Sustain. Resilient Infrastruct. 2023, 8, 170–189. [CrossRef]
- Almeida, J.C.; Ribeiro, B.; Cardoso, A. A Human-Centric Approach to Aid in Assessing Maintenance from the Sustainable Manufacturing Perspective. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2023, 220, 600–607. [CrossRef]
- Rani, S.; Jining, D.; Shoukat, K.; Shoukat, M.U.; Nawaz, S.A. A Human–Machine Interaction Mechanism: Additive Manufacturing for Industry 5.0—Design and Management. Sustain. 2024, 16. [CrossRef]
- Fatehi Karjou, P.; Stupperich, F.; Stoffel, P.; Müller, D. Human-in-the-Loop Control Strategy for IoT-Based Smart Thermostats with Deep Reinforcement Learning. Energy AI 2025, 20, 100490. [CrossRef]
- Sesana, M.; Tavola, G. Resilient Manufacturing Systems Enabled by AI Support to AR Equipped Operator. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Engineering, Technology and Innovation, ICE/ITMC 2021 - Proceedings; IEEE, 2021; pp. 1–5.
- Berti, N.; Finco, S.; Guidolin, M.; Battini, D. Towards Human Digital Twins to Enhance Workers’ Safety and Production System Resilience. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2023, 56, 11062–11067. [CrossRef]
- Verdugo-Cedeño, M.; Jaiswal, S.; Ojanen, V.; Hannola, L.; Mikkola, A. Simulation-Based Digital Twins Enabling Smart Services for Machine Operations: An Industry 5.0 Approach. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Interact. 2023, 40, 6327–6343. [CrossRef]
- Denu, M.; David, P.; Mangione, F.; Landry, A. Towards Human-Centric Digital Simulation: Guidelines to Simulate Operators Skills Acquisition and Health in Circular Manufacturing Systems. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2024, 58, 445–450. [CrossRef]
- Agostinelli, T.; Generosi, A.; Ceccacci, S.; Mengoni, M. Validation of Computer Vision-Based Ergonomic Risk Assessment Tools for Real Manufacturing Environments. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1–19. [CrossRef]
- Sbaragli, A.; Tomelleri, F.; Picariello, F.; Picariello, E.; Pilati, F. Safe Operator 5.0 Digital Architecture: Towards Resilient Human-Centric Manufacturing Systems. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2024, 58, 265–270. [CrossRef]
- de Souza, I.T.; Rosa, A.C.; Vidal, M.C.R.; Najjar, M.K.; Hammad, A.W.A.; Haddad, A.N. Information Technologies in Complex Socio-Technical Systems Based on Functional Variability: A Case Study on Hvac Maintenance Work Orders. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1–20. [CrossRef]
- Siew, C.Y.; Chang, M.M.L.; Ong, S.K.; Nee, A.Y.C. Human-Oriented Maintenance and Disassembly in Sustainable Manufacturing. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2020, 150, 106903. [CrossRef]
- Slavic, D.; Romero, D.; Pezzotta, G.; Marjanovic, U.; Savkovic, B.; Popan, I.A.; Rakic, S. Towards Human-Centric Digital Services: A Development Framework. In Proceedings of the Advances in Production Management Systems. Production Management Systems for Volatile, Uncertain, Complex, and Ambiguous Environments. APMS 2024. IFIP Advances in Information and Communication Technology, vol 732; Thürer, M., Riedel, R., von Cieminski, G., Romero, D., Eds.; Springer Nature Switzerland: Cham, 2024; pp. 184–197.
- Azevedo, A.; Couto, P.; Silva, J.; Salvado, F.; Lima, R. Maintenance and Asset Management Improvement Based on Resilience and Sustainability Classification Systems. OMAINTEC J. 2023, 4, 93–103. [CrossRef]
- Paraschos, P.D.; Xanthopoulos, A.S.; Koulinas, G.K.; Koulouriotis, D.E. Machine Learning Integrated Design and Operation Management for Resilient Circular Manufacturing Systems. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2022, 167, 107971. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Singh, S.P.; Lamba, K. Sustainable Robust Layout Using Big Data Approach: A Key towards Industry 4.0. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 204, 643–659. [CrossRef]
- Ndhaief, N.; Nidhal, R.; Hajji, A.; Bistorin, O. Environmental Issue in an Integrated Production and Maintenance Control of Unreliable Manufacturing/Remanufacturing Systems. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2020, 58, 4182–4200. [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Singh, S.; Vardhan, S.; Patnaik, A. Sustainability of Maintenance Management Practices in Hydropower Plant: A Conceptual Framework. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 28, 1569–1574. [CrossRef]
- Abuhasel, K.A. A Zero-Trust Network-Based Access Control Scheme for Sustainable and Resilient Industry 5.0. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 116398–116409. [CrossRef]
- Bamdad, S. Leveraging Machine Learning and Decision Analytics for Sustainable and Resilient Environmental Monitoring in Metal Processing Industries: A Step towards Industry 5.0. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2025, 7543. [CrossRef]
- El kihel, Y.; El kihel, A.; Bouyahrouzi, E.M. Contribution of Maintenance 4.0 in Sustainable Development with an Industrial Case Study. Sustain. 2022, 14. [CrossRef]
- Caillaud, E.; Goepp, V.; Berrah, L. Towards “Transformative” Resilience for the Sustainability of Industry 4.0. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2024, 58, 391–396. [CrossRef]
- Fallahiarezoudar, E.; Ahmadipourroudposht, M.; Bagherian Rafi, M.H.; Ngadiman, N.H.A. A Systematic Approach of Maintenance 4.0 Towards a Sustainable Manufacturing Policy: A Case Study on an Automobile Company. Process Integr. Optim. Sustain. 2025. [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Chen, H.; Hu, F. Proposal of Industry 5.0-Enabled Sustainability of Product–Service Systems and Its Quantitative Multi-Criteria Decision-Making Method. Processes 2024, 12. [CrossRef]
- Ogunsoto, O.V.; Olivares-Aguila, J.; ElMaraghy, W. A Conceptual Digital Twin Framework for Supply Chain Recovery and Resilience. Supply Chain Anal. 2025, 9, 100091. [CrossRef]
- Bécue, A.; Maia, E.; Feeken, L.; Borchers, P.; Praça, I. A New Concept of Digital Twin Supporting Optimization and Resilience of Factories of the Future. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10. [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.M.H.; Aliahmadi, S.Z.; Quaddus, M.A.; Ansaripoor, A.H.; Mirjalili, S. A Decision Support Framework for Resilient and Sustainable Service Design. Glob. J. Flex. Syst. Manag. 2024, 26, 25–55. [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Liu, J.; Liang, B. AI-Driven Supply Chain Transformation in Industry 5.0: Enhancing Resilience and Sustainability; Springer US, 2024; Vol. 0; ISBN 1313202401.
- Malmstedt, A.; Bäckstrand, J. How to Predict Disruptions in the Inbound Supply Chain in a Volatile Environment. Adv. Transdiscipl. Eng. 2022, 21, 638–649. [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Rajesh, R.; Misra, S.C.; Singh, S. Analyzing the Role of Digital Twins in Developing a Resilient Sustainable Manufacturing Supply Chain: A Grey Influence Analysis (GINA) Approach. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2024, 209, 123763. [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.; KC, S. Leveraging Blockchain for Sustainability and Supply Chain Resilience in E-Commerce Channels for Additive Manufacturing: A Cognitive Analytics Management Framework-Based Assessment. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2023, 176, 108995. [CrossRef]
- Zhen, Z.; Yao, Y. The Confluence of Digital Twin and Blockchan Technologies in Industry 5.0: Transforming Supply Chain Management for Innovation and Sustainability. J. Knowl. Econ. 2024, 5295–5321. [CrossRef]
- Mentes, A.; Turan, O. A New Resilient Risk Management Model for Offshore Wind Turbine Maintenance. Saf. Sci. 2019, 119, 360–374. [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Bai, D.; Han, G.; Feng, R.; Hao, J.; Yao, B. Resilience Maintenance Strategy for Mixed Vehicle Traffic on Port Expressway Based on Lane Management. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2025, 265, 107645. [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.; Pistikopoulos, E.N.; Mannan, M.S. Process Resilience Analysis Based Data-Driven Maintenance Optimization: Application to Cooling Tower Operations. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2019, 121, 27–45. [CrossRef]
- Maurer, F.; Schumacher, J. Organizational Robustness and Resilience as Calatyst to Boost Innovation in Smart Service Factories of the Future. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Engineering, Technology and Innovation (ICE/ITMC), Stuttgart, Germany; 2018; pp. 1–9.
- Stetter, R. Resilient Design of Product Service Systems with Automated Guided Vehicles. Vehicles 2023, 5, 780–801. [CrossRef]
- Arias-Vargas, M.; Sanchis, R.; Poler, R. Capitalising Artificial Intelligence Capabilities to Foster Disruptive Events Anticipation and Proactive Resilience. In Proceedings of the Decision Sciences. DSA ISC 2024. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14778; Juan, A.A., Faulin, J., Lopez-Lopez, D., Eds.; Springer Nature Switzerland: Cham, 2025; pp. 306–319.
- Štreimikienė, D.; Bathaei, A.; Streimikis, J. Enhancing Sustainable Global Supply Chain Performance: A Multi-Criteria Decision-Making-Based Approach to Industry 4.0 and AI Integration. Sustain. 2025, 17. [CrossRef]
- Palmarini, R.; Del Amo, I.F.; Ariansyah, D.; Khan, S.; Erkoyuncu, J.A.; Roy, R. Fast Augmented Reality Authoring: Fast Creation of AR Step-by-Step Procedures for Maintenance Operations. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 8407–8421. [CrossRef]
- Minea, M.; Minea, V.; Semenescu, A. Smart Preventive Maintenance of Hybrid Networks and IoT Systems Using Software Sensing and Future State Prediction. Sensors 2023, 23, 1–9.
- Pinciroli, L.; Baraldi, P.; Zio, E. Maintenance Optimization in Industry 4.0. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2023, 234, 109204. [CrossRef]
- Mendes, D.; Gaspar, P.D.; Charrua-Santos, F.; Navas, H. Synergies between Lean and Industry 4.0 for Enhanced Maintenance Management in Sustainable Operations: A Model Proposal. Processes 2023, 11, 2691. [CrossRef]
- Pilanawithana, N.M.; Feng, Y.; London, K.; Zhang, P. Developing Resilience for Safety Management Systems in Building Repair and Maintenance: A Conceptual Model. Saf. Sci. 2022, 152, 105768. [CrossRef]
- Pasman, H.; Kottawar, K.; Jain, P. Resilience of Process Plant: What, Why, and How Resilience Can Improve Safety and Sustainability. Sustain. 2020, 12, 1–21. [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, R.; Yan, B.; Liu, X. Distributed Maintenance Task Scheduling for Multiple Technician Teams Considering Uncertain Durations and Deterioration Effects towards Industry 5.0. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2025, 7543. [CrossRef]
- He, J.J.; Wu, J.; Siau, K.L. Task Scheduling Strategy for 3DPCP Considering Multidynamic Information Perturbation in Green Scene. J. Glob. Inf. Manag. 2024, 32, 1–23. [CrossRef]
- Samadhiya, A.; Agrawal, R.; Garza-Reyes, J.A. Integrating Industry 4.0 and Total Productive Maintenance for Global Sustainability. TQM J. 2024, 36, 24–50. [CrossRef]
- Neri, A.; Butturi, M.A.; Tomasin da Silva, L.; Lolli, F.; Gamberini, R.; Sellitto, M.A. Fostering Lithium-Ion Battery Remanufacturing through Industry 5.0. Int. J. Interact. Des. Manuf. 2025. [CrossRef]
- Aheleroff, S.; Huang, H.; Xu, X.; Zhong, R.Y. Toward Sustainability and Resilience with Industry 4.0 and Industry 5.0. Front. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 2, 1–20. [CrossRef]

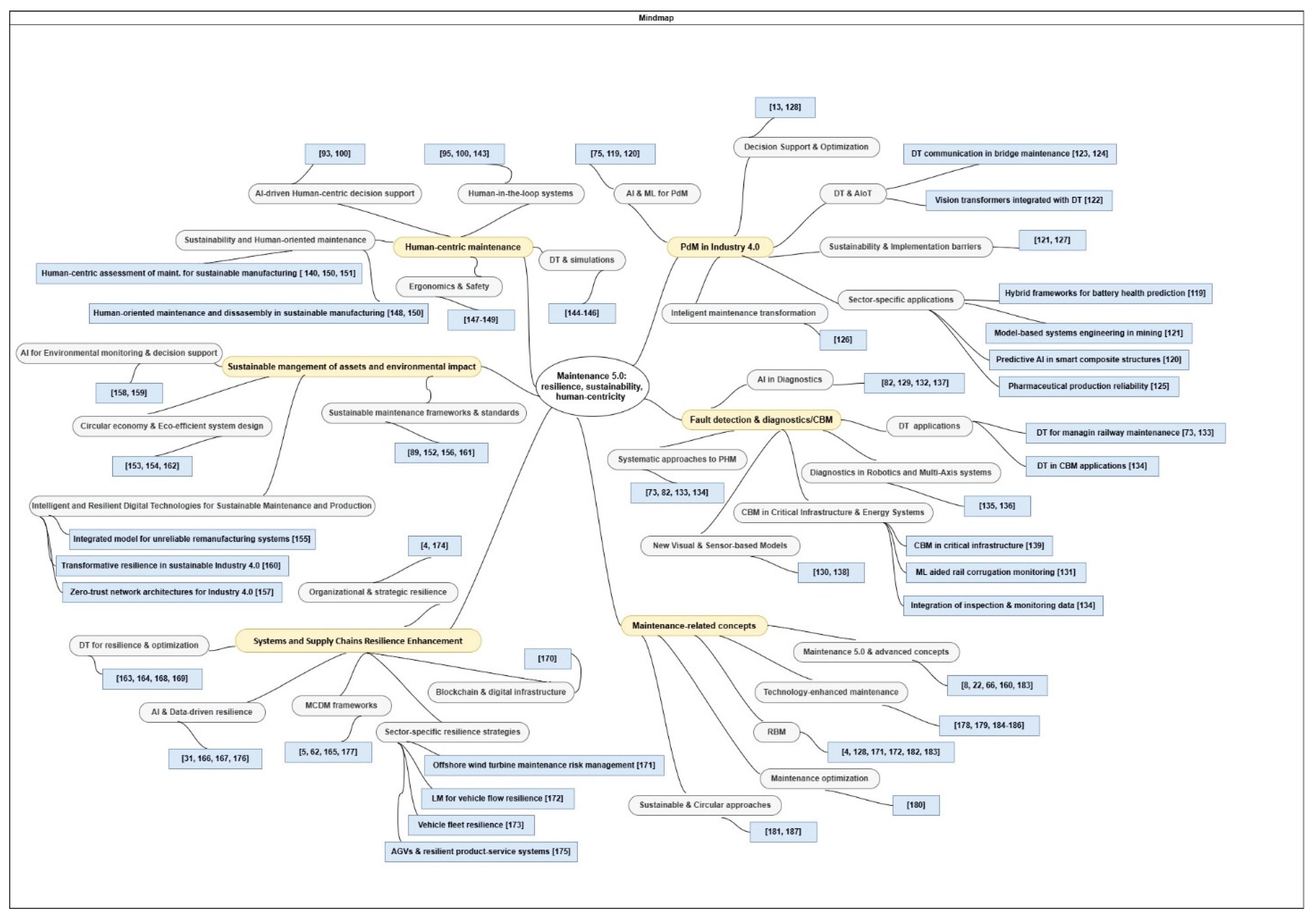
| Ref. | Publ. Year | Research Objectives | Maintenance focus | Scope/ Industry context | Review type | Identified Gaps |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [25] | 2019 | To explore how Maintenance 4.0 technologies support sustainable manufacturing by enhancing equipment longevity, reducing downtime, and addressing economic, environmental, and social dimensions of value creation. | Maintenance 4.0 & Sustainability | Sustainable manufacturing | Overview review | Lack of practical tools and digital maturity models |
| [10] | 2020 | To systematically review and classify predictive maintenance initiatives in Industry 4.0, highlighting methods, standards, and challenges while proposing a novel taxonomy to guide multidisciplinary research. | Predictive maintenance methods and tools | Industry 4.0 | Systematic Literature Review | Does not address future shift toward Industry 5.0; lacks coverage of human and cyber dimensions |
| [27] | 2021 | To identify trends in sustainable manufacturing technologies through a systematic literature review and develop a conceptual research framework. | Sustainable Manufacturing | Production, eco-innovation | Systematic Review | Lack of integration of human-centric approach and workers’ experience |
| [9] | 2022 | To review and categorize intelligent predictive maintenance models and workflows in Industry 4.0 and propose a decision-support platform to enhance smart maintenance practices. | Predictive maintenance – models and technical challenges | Industry 4.0 | Systematic Literature Review | Little focus on human and sustainability dimensions; lacks Industry 5.0 alignment |
| [12] | 2022 | To conduct a systematic review of predictive maintenance challenges and propose a new classification framework, emphasizing its ongoing relevance in Industry 4.0 environments. | Predictive Maintenance | Industry 4.0, smart factories | Systematic Literature Review | Focused only on predictive maintenance in I4.0 environments |
| [1] | 2023 | To develop an integrated Maintenance 5.0 framework that bridges traditional and advanced maintenance strategies by addressing sustainability, human-centricity, and the adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies, especially in SMEs. | Transition from Maintenance 4.0 to 5.0 (human-centric, AI-driven, sustainable) | Global manufacturing, focus on SMEs and Zero-Defect Manufacturing | Systematic Literature Review | Lack of sustainability/environmental KPIs, limited integration of human factors, and missing transition paths for SMEs |
| [2] | 2023 | To systematically review and categorize key technological domains of Maintenance 4.0 - AR/VR, system architecture, data-driven decisions, Operator 4.0, and cybersecurity - to identify research trends and gaps guiding future studies. | Maintenance performance indicators in Industry 4.0 context | Broad industrial context | Bibliometric + Systematic Review | Weak mapping of human-centric aspects |
| [13] | 2023 | To investigate human, task, and organizational factors affecting Predictive Maintenancesystems’ acceptance and identify key enablers for successful PdM adoption through literature synthesis and expert interviews. | Predictive Maintenance with a human-centric approach | Human-machine collaboration in Industry 5.0 | Conceptual review with empirical elements | Need for human-behaviour integration in maintenance planning and execution |
| [26] | 2023 | To review and analyze sustainable maintenance decision-making models, focusing on integrating economic, environmental, and social dimensions, and to identify research trends, gaps, and opportunities for developing implementable, data-driven solutions. | Sustainability in Maintenance | Modeling-based academic research | Systematic Literature Review | Limited integration of sustainability indicators into maintenance decision models |
| [7] | 2024 | To develop a multi-layered framework integrating Industry 5.0 principles with predictive maintenance and condition monitoring to enhance sustainability, resilience, and human-centricity. | Predictive maintenance and condition monitoring evolution | Industry-wide + case study | Systematic Review + Case Study | Weak attention to cybersecurity |
| [20] | 2024 | To compare maintenance strategies in Industry 4.0 and Industry 5.0, evaluate their technological, procedural, and human-centric shifts, and guide industrial stakeholders in adapting maintenance approaches for enhanced resilience and competitiveness. | Comparative: I4.0 vs I5.0 Maintenance | Industrial evolution toward human-centric and sustainable systems | Comparative Review | Lack of clear transition models, human-role redefinition, and socio-technical frameworks |
| [3] | 2025 | To review the evolution from Maintenance 4.0 to 5.0 by analyzing sustainability integration and human-centric challenges in the transition framework. | Shift toward Maintenance 5.0, human and sustainability dimensions | Cross-industry, Industry 5.0 | Systematic Literature Review | Lack of integration of social and human dimensions; limited guidance for technological-human convergence |
| Feature / Strategy | Reliability-Centered Maintenance (RCM) | Predictive Maintenance (PdM) | Resilience-Based Maintenance (RBM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Objective | Failure prevention | Failure prediction | System adaptability and recovery |
| Analytical Focus | Failure modes and criticality | Degradation patterns, sensor data | System behavior under uncertainty |
| Risk Consideration | Known risks | Partially known (data-driven) risks | Known + unknown risks |
| Data Usage | Historical data, expert judgment | Real-time condition monitoring | Multi-source data, simulation, feedback |
| Role of AI | Limited (e.g., FMEA support) | Prognostics, ML-based diagnostics | RL, Digital Twins, Knowledge Graphs |
| Human-Centric Integration | Minimal | Limited | Strong (decision support, cognitive AI) |
| Reaction to Unexpected Events | Low | Moderate | High (adaptive, learning-based) |
| Maintenance Action Type | Prescriptive | Predictive | Adaptive and Resilient |
| Aspect | Traditional Maintenance | Smart Maintenance (4.0) | Sustainable Maintenance (5.0) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Paradigm | Reactive/Preventive | Predictive/Prescriptive | Human-centric, sustainable, and resilient |
| Primary Goal | Restore function | Optimize asset performance | Balance performance with sustainability and social impact |
| Decision-making | Human-driven, rule-based | Data-driven, algorithm-based | Context-aware, value-based, collaborative |
| Technology Enablers | Basic sensors, manual tools | IoT, AI, Digital Twins, AR | Integrated CPS, green analytics, worker-assistive tech |
| Data Usage | Limited or non-existent | Extensive, real-time | Real-time + LCA metrics, social impact data |
| Environmental Focus | Minimal | Efficiency-oriented | Lifecycle optimization, emission minimization |
| Economic Perspective | Short-term cost reduction | Asset efficiency, reduced downtime | Lifecycle cost optimization and circular economy |
| Social Considerations | Low (focus on output) | Medium (operator efficiency) | High (safety, training, inclusion, job satisfaction) |
| Resilience Integration | Absent | Indirect (redundancy, alerts) | Direct (resilience engineering, adaptability, human-in-the-loop) |
| Role of Human | Executor | Supervisor/Monitor | Partner/Collaborator in hybrid systems |
| Technology | Human-Centric Element | Example Application |
|---|---|---|
| AR-based Diagnostics | Reduced cognitive load | Step-by-step AR-guided pump inspection |
| AI Decision Support | Explainability, confidence rating | Predictive maintenance with user validation |
| Digital Twin | Visual feedback, intuitive interaction | Operator-controlled system simulations |
| Exoskeletons/Cobots | Physical support and safety | Assisting in heavy part replacement tasks |
| VR-based Training | Skill development and scenario rehearsal | Emergency repair simulations for new workers |
| Aspect | Maintenance 1.0 | Maintenance 2.0 | Maintenance 3.0 | Maintenance 4.0 | Maintenance 5.0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Operator Role | Manual execution of repairs | Schedule-based execution, low autonomy | Increasing involvement in diagnostics, still reactive | Role shifts toward data interpretation and system oversight | Active co-decision-maker; empowered, context-aware, and ergonomically supported |
| Decision-Making Model | Fully manual decisions post-failure | Based on rules and fixed intervals | Data-informed decisions with human supervision | AI-supported decisions with limited human feedback | Human-in-the-loop and human-on-the-loop frameworks fully integrated |
| Human-Technology Interaction | Tools only, no digital interface | Paper-based logs, basic CMMS | Use of sensors and dashboards | IoT interfaces, AR/VR systems, mobile apps | Seamless and personalized interfaces (wearables, XR, cognitive support) |
| Safety and Ergonomics | Minimal, reactive | Basic compliance-based ergonomics | Condition monitoring supports safety | Real-time alerts, digital twins for safe task execution | Proactive ergonomics, well-being analytics, worker co-designed systems |
| Learning and Skills Development | Learning through experience, manuals | Structured training programs | Training in digital tools, early simulations | Digital learning platforms, AR-based instruction | Continuous, AI-driven upskilling; personalized and inclusive learning pathways |
| Ethics and Inclusion | Not considered | Rarely addressed | Initial considerations in system design | Inclusion as a feature in HMI design | Core principle: equity, transparency, inclusion, and ethics embedded from design to operation |
| AI Technique | Application in RBM | Benefits in RBM | Example Studies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Machine Learning (ML) | Predictive modeling of failures; estimation of Remaining Useful Life (RUL) | Improves failure anticipation; supports dynamic maintenance planning | [119,153,158,180] |
| Deep Learning (DL) | Fault detection in complex systems; diagnostics based on image/signal data | High accuracy in anomaly detection; effective in unstructured data environments | [137,138,142] |
| Reinforcement Learning (RL) | Adaptive maintenance scheduling; autonomous decision-making in uncertain conditions | Enables learning-based optimization; adapts to changing operational contexts | [134,142,179] |
| Fuzzy Logic | Modeling expert knowledge; decision-making under uncertainty | Captures imprecise criteria; facilitates resilience modeling with linguistic variables | [4,5,66] |
| Hybrid Models (e.g., ML + Fuzzy + RL) | Robust diagnostics; multi-objective maintenance optimization | Combines interpretability and adaptability; enhances model performance in uncertain settings | [66,129,134,180] |
| Explainable AI (XAI) | Transparent support for maintenance decisions; human-centric diagnostics | Enhances trust; enables operator involvement; supports regulatory requirements | [93,100] |
| Genetic Algorithms/ Evolutionary Methods | Optimization of maintenance scheduling and resource allocation | Efficient in complex search spaces; supports multi-criteria resilience planning | [62,129] |
| Computer Vision/ CNNs | Visual inspection of assets; ergonomic and defect detection | Enables non-invasive diagnostics; enhances safety and reliability assessment | [130,138,147,148] |
| Digital Twins (DTs) + AI | Predictive simulation; dynamic decision-making and system modeling | Supports resilience scenarios; integrates real-time data for continuous system awareness | [122,123,125,144,164,168] |
| AIoT (AI + Internet of Things) | Autonomous diagnostics; condition monitoring in cyber-physical systems | Real-time data-driven insights; improves responsiveness and situational awareness | [124,158,176] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).