Submitted:
01 July 2025
Posted:
03 July 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
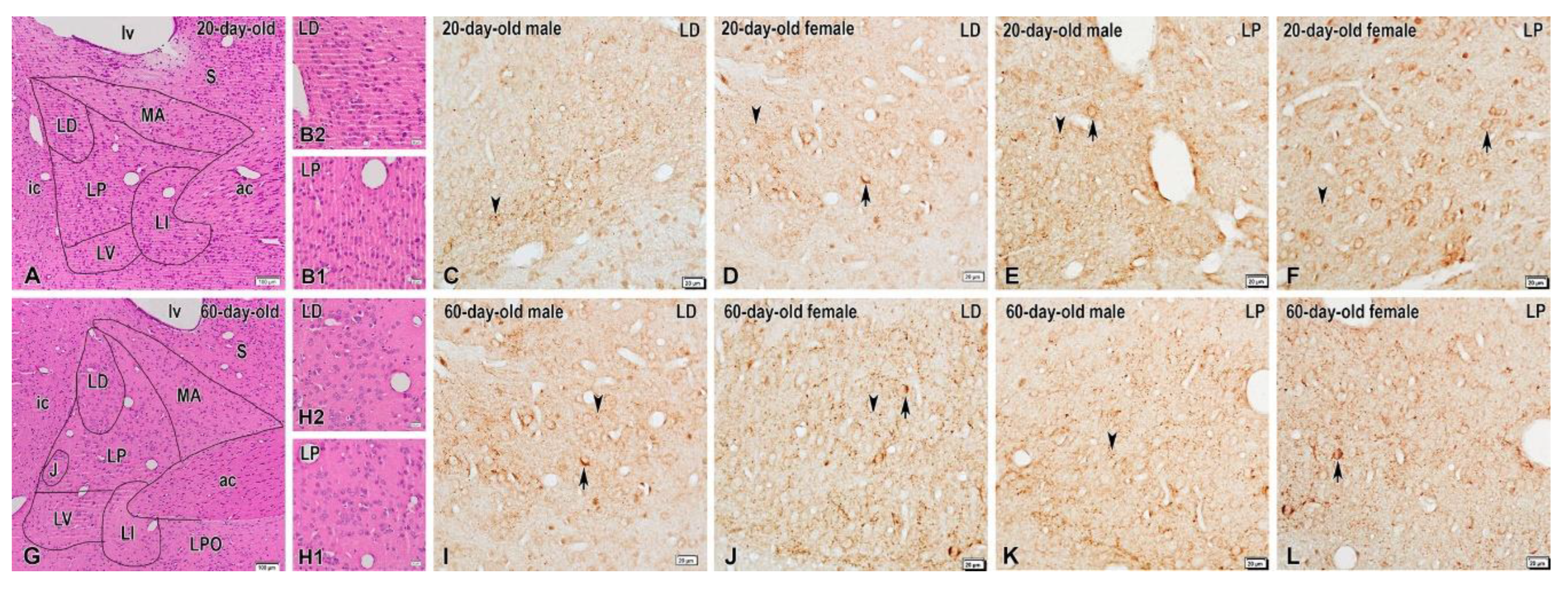
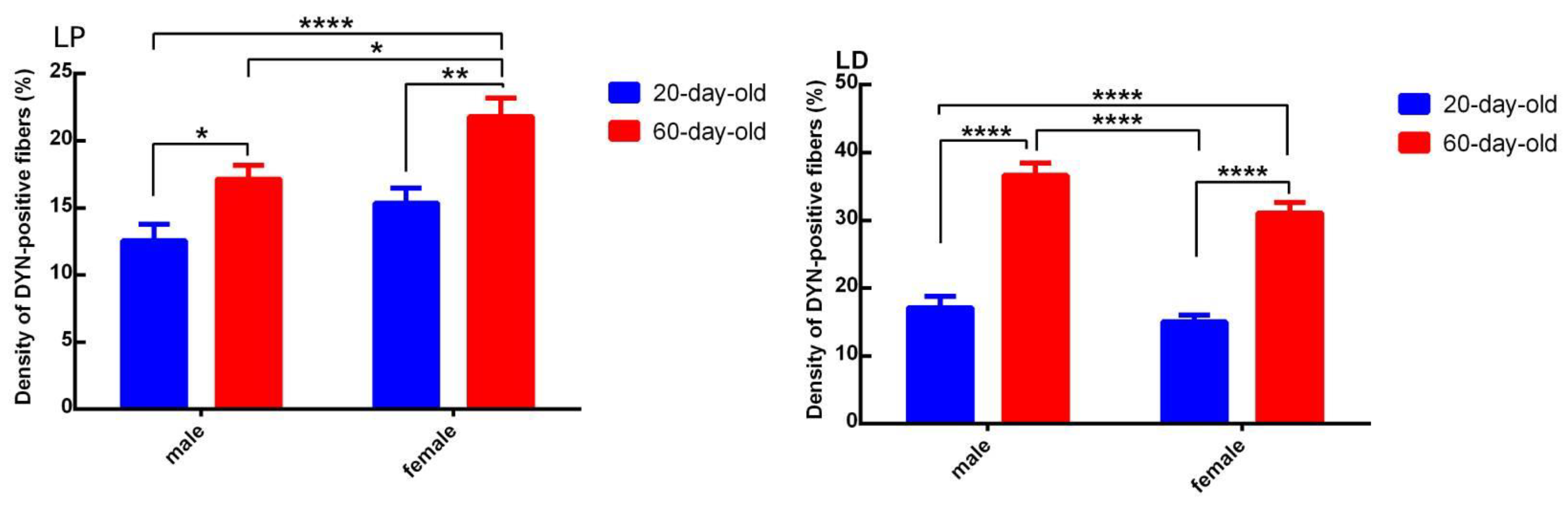
2.1. Dynorphin
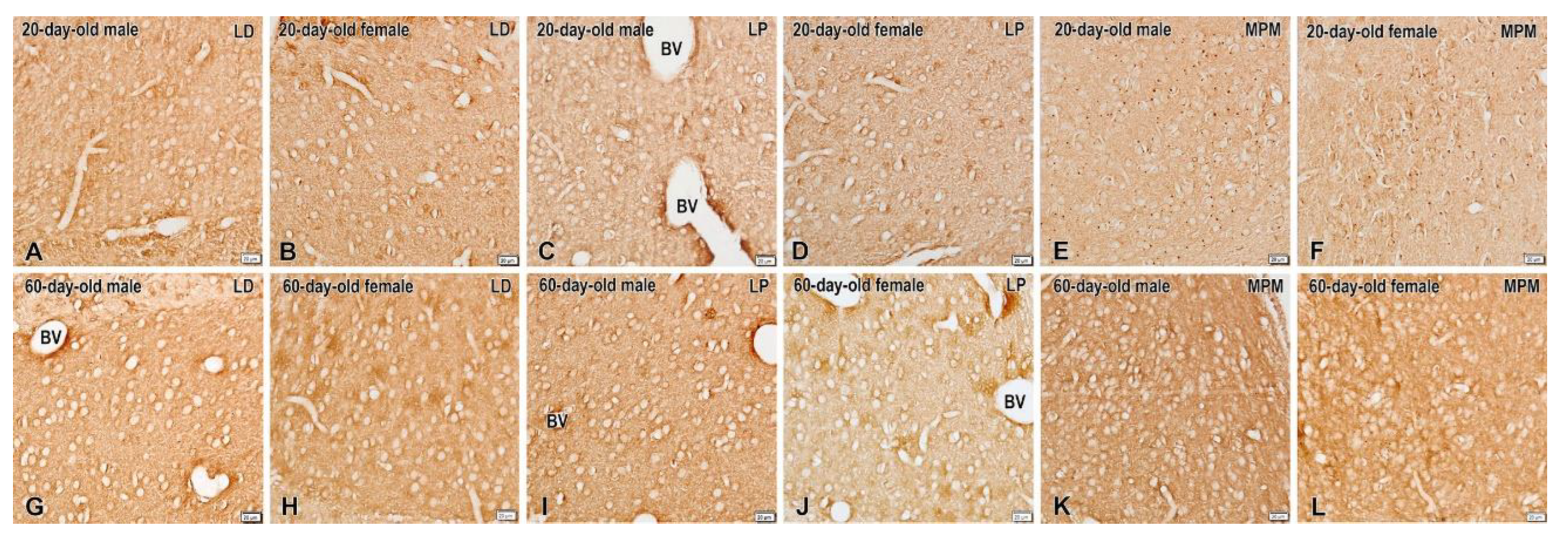
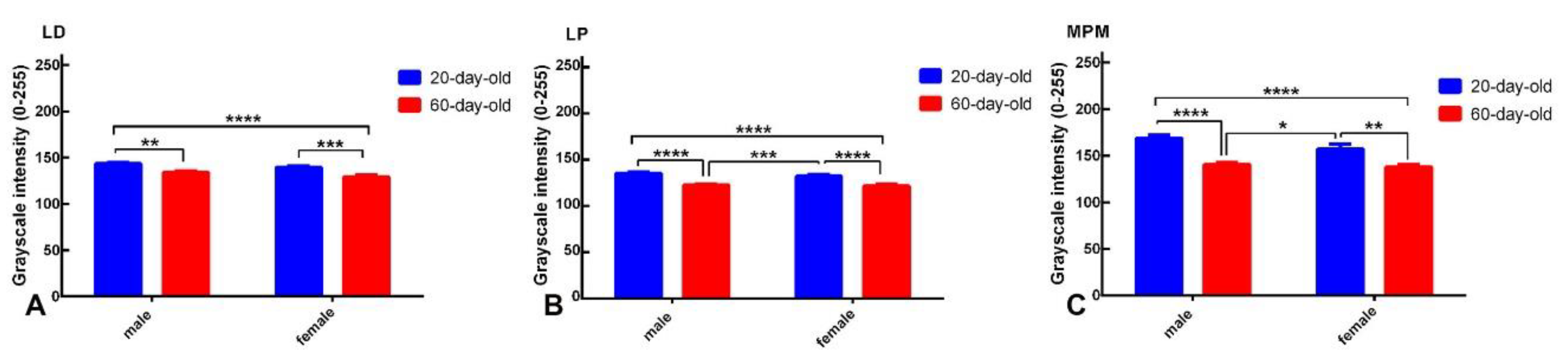
2.1. Kappa-Opioid Receptors
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Animals
4.2. Tissue Preparation
4.3. Immunohistochemical Procedure
4.4. Antisera Specificity Tests
4.1. Image Analysis and Statistics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Becker, J.; Chartoff, E. Sex differences in neural mechanisms mediating reward and addiction. Neuropsychopharmacology 2019, 44, 166–183. [CrossRef]
- De Olmos, J.S.; Beltramino, C.A.; Alheid, G. Amygdala and extended amygdala of the rat: a cytoarchitectonical, fibroarchitectonical, and chemoarchitectonical survey. In The Rat Nervous System, 3rd ed.; Paxinos, G.; Ed.; Elsevier Academic Press: Amsterdam, 2004, pp 509-605, . [CrossRef]
- Swanson L.W. Brain maps 4.0-Structure of the rat brain: An open access atlas with global nervous system nomenclature ontology and flatmaps. J. Comp. Neurol. 2018, 526, 935–943. [CrossRef]
- Lebow, M.A.; Chen, A. Overshadowed by the amygdala: the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis emerges as key to psychiatric disorders. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 450–463. [CrossRef]
- van de Poll, Y.; Cras, Y.; Ellender, T.J. The neurophysiological basis of stress and anxiety - comparing neuronal diversity in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BNST) across species. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1225758. [CrossRef]
- Stefanova, N.; Bozhilova-Pastirova, A.; Ovtscharoff, W. Distribution of GABA-immunoreactive nerve cells in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis in male and female rats. Eur. J. Histochem. 1997, 41, 23–28. PMID: 9174842.
- Nguyen, A.Q.; Dela Cruz, J.A.; Sun, Y.; Holmes, T.C.; Xu, X. Genetic cell targeting uncovers specific neuronal types and distinct subregions in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis. J. Comp. Neurol. 2016, 524, 2379–2399. [CrossRef]
- Welch, J.D.; Kozareva, V.; Ferreira, A.; Vanderburg, C.; Martin, C.; Macosko, E.Z. Single-cell multi-omic integration compares and contrasts features of brain cell identity. Cell 2019, 177, 1873–1887.e17. [CrossRef]
- Beyeler, A.; Dabrowska, J. Neuronal diversity of the amygdala and the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis. Handb. Behav. Neurosci. 2020, 26, 63–100. [CrossRef]
- Hammack, S.E.; Braas, K.M.; May, V. Chemoarchitecture of the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis: Neurophenotypic diversity and function. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2021, 179, 385–402. [CrossRef]
- Chavkin, C.; James, I.F.; Goldstein, A. Dynorphin is a specific endogenous ligand of the kappa opioid receptor. Science 1982, 215, 413–415. [CrossRef]
- Mansour, A.; Fox, C.A.; Burke, S.; Akil, H.; Watson, S.J. Immunohistochemical localization of the cloned mu opioid receptor in the rat CNS. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 1995, 8, 283–305. [CrossRef]
- Cahill, C.; Tejeda, H.A.; Spetea, M.; Chen, C.; Liu-Chen, L.Y. Fundamentals of the dynorphins/kappa opioid receptor system: from distribution to signaling and function. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2022, 271, 3–21. [CrossRef]
- Poulin, J.F.; Arbour, D.; Laforest, S.; Drolet, G. Neuroanatomical characterization of endogenous opioids in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 33, 1356–1365. [CrossRef]
- Mansour, A.; Fox, C.A.; Burke, S.; Meng, F.; Thompson, R.C.; Akil, H.; Watson, S.J. Mu, delta, and kappa opioid receptor mRNA expression in the rat CNS: an in situ hybridization study. J. Comp. Neurol. 1994, 350, 412–438. [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Pleil, K.E.; Stamatakis, A.M.; Busan, S.; Vong, L.; Lowell, B.B.; Stuber, G.D.; Kash, T.L Presynaptic inhibition of gamma-aminobutyric acid release in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis by kappa opioid receptor signaling. Biol. Psych. 2012, 71, 725–732. [CrossRef]
- Crowley, N.A.; Bloodgood, D.W.; Hardaway, J.A.; Kendra, A.M.; McCall, J.G.; Al-Hasani, R.; McCall, N.M.; Yu, W.; Schools, Z.L.; Krashes, M.J.; Lowell, B.B.; Whistler, J.L.; Bruchas, M.R.; Kash, T.L. Dynorphin controls the gain of an amygdalar anxiety circuit. Cell Rep. 2016, 14, 2774–2783. [CrossRef]
- Rose, J.H.; Karkhanis, A.N.; Chen, R.; Gioia, D.; Lopez, M.F.; Becker, H.C.; McCool, B.A.; Jones, S.R. Supersensitive kappa opioid receptors promotes ethanol withdrawal-related behaviors and reduce dopamine signaling in the nucleus accumbens. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016, 19, pyv127. [CrossRef]
- Limoges, A.; Yarur, H.E.; Tejeda, H.A. Dynorphin/kappa opioid receptor system regulation on amygdaloid circuitry: Implications for neuropsychiatric disorders. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 963691. [CrossRef]
- Estave, P.M., Spodnick, M.B.; Karkhanis, A.N. KOR control over addiction processing: an exploration of the mesolimbic dopamine pathway. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2022, 271, 351–377. [CrossRef]
- Bruchas, M.R.; Land, B.B.; Chavkin, C. The dynorphin/kappa opioid system as a modulator of stress-induced and pro-addictive behaviors. Brain Res. 2010, 1314, 44–55. [CrossRef]
- Darcq, E.; Kieffer, B.L. Opioid receptors: drivers to addiction? Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2018, 19, 499–514. [CrossRef]
- Centanni, S.W., Morris, B.D.; Luchsinger, J.R.; Bedse, G.; Fetterly, T.L.; Patel, S.; Winder, D.G. Endocannabinoid control of the insular-bed nucleus of the stria terminalis circuit regulates negative affective behavior associated with alcohol abstinence. Neuropsychopharmacology 2019, 44, 526–537. [CrossRef]
- Flook, E.A.; Feola, B.; Benningfield, M.M.; Silveri, M.M.; Winder, D.G. Blackford, J.U. Alterations in BNST intrinsic functional connectivity in early abstinence from alcohol use disorder. Alcohol Alcohol. 2023, 58, 298–307. [CrossRef]
- Gray, K.M.; Squeglia, L.M. Research Review: What have we learned about adolescent substance use? J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2018, 59, 618–627. [CrossRef]
- Holland-Hall, C.; Burstein, G. Adolescent physical and social development. In Nelson’s Textbook of Pediatrics, 20th ed.; Kliegman, R.M.; Stanton, B.F.; St. Geme, III J.W.; Schor, N.F.; Behrman, R.E., Eds.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, USA, 2016, pp 926–931.
- Schulz, K.M.; Molenda-Figureueira, H.A., Sisk, C.L. Back to the future: The organizational-activational hypothesis adapted to puberty and adolescence. Horm. Behav. 2009, 55, 597–604. [CrossRef]
- Normandeau, C.P.; Torruella Suárez, M.L.; Sarret, P.; McElligott, Z.A.; Dumont, E.C. Neurotensin and dynorphin Bi-Directionally modulate CeA inhibition of oval BNST neurons in male mice. Neuropharmacology 2018, 143, 113–121. [CrossRef]
- Marchant, N.J.; Densmore, V.S.; Osborne, P.B. Coexpression of prodynorphin and corticotrophin-releasing hormone in the rat central amygdala: Evidence of two distinct endogenous opioid systems in the lateral division. J. Comp. Neurol. 2007, 504, 702–715. [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.W.; Petrovich, G.D.; Swanson, L.W. Topography of projections from amygdala to bed nuclei of the stria terminalis. Brain Res. Rev. 2001, 38, 192–246. [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.W.; Swanson, L.W. Organization of axonal projections from the anterolateral area of the bed nuclei of the stria terminalis. J. Comp. Neurol. 2004, 468, 277–298. [CrossRef]
- Bloodgood, D.W.; Hardaway, J.A.; Stanhope, C.M.; Pati, D.; Pina, M.M.; Neira, S.; Desai, S.; Boyt, K.M.; Palmiter, R.D.; Kash, T.L. Kappa opioid receptor and dynorphin signaling in the central amygdala regulates alcohol intake. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 2187–2199. [CrossRef]
- Kissler, J.L.; Sirohi, S.; Reis, D.J.; Jansen, H.T.; Quock, R.M.; Smith, D.G.; Walker, B.M. The one-two punch of alcoholism: role of central amygdala dynorphins/kappa-opioid receptors. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 75, 774–782. [CrossRef]
- Haun, H.L.; Lebonville, C.L.; Solomon, M.G.; Griffin, W.C.; Lopez, M.F.; Becker, H.C. Dynorphin/kappa opioid receptor activity within the extended amygdala contributes to stress-enhanced alcohol drinking in mice. Biol. Psychiatry 2022, 91, 1019–1028. [CrossRef]
- Avery, S.N.; Clauss, J.A.; Blackford, J.U. The human BNST: functional role in anxiety and addiction. Neuropsychopharmacology 2016, 41, 126–141. [CrossRef]
- Patton, G.C.; McMorris, B.J.; Toumbourou, J.W.; Hemphill, S.A.; Donath, S.; Catalano, R.F. Puberty and the onset of substance use and abuse. Pediatrics 2004, 114, e300-6. doi.org10.1542/peds.2003-0626-F.
- Jordan, C.J.; Andersen, S.L. Sensitive periods of substance abuse: Early risk for the transition to dependence. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 2017, 25, 29–44. [CrossRef]
- Pirino, B.E.; Kelley, A.M.; Karkhanis, A.N.; Barson, J.R. A critical review of effects on ethanol intake of the dynorphin/kappa opioid receptor system in the extended amygdala: From inhibition to stimulation. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. (Hoboken) 2023, 47, 1027–1038. [CrossRef]
- Haun, H.L.; Griffin, W.C.; Lopez, M.F.; Becker, H.C. Kappa opioid receptors in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis regulate binge-like alcohol consumption in male and female mice. Neuropharmacology 2020, 167, 107984. [CrossRef]
- Erikson, C.M.; Wei, G.; Walker, B.M. Maladaptive behavioral regulation in alcohol dependence: Role of kappa-opioid receptors in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis. Neuropharmacology 2018, 140, 162–173. [CrossRef]
- Browne, C.A.; Wulf, H.; Lucki, I. Kappa opioid receptors in the pathology and treatment of major depressive disorder. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2022, 271, 493–524. [CrossRef]
- Chu, P.; Murray, S.; Lissin, D.; von Zastrow, M. Delta and kappa opioid receptors are differentially regulated by dynamin-dependent endocytosis when activated by the same alkaloid agonist. J Biol Chem. 1997, 272(43), 27124-27130. [CrossRef]
- Jordan, B.A.; Cvejic, S.; Devi, L.A. Kappa opioid receptor endocytosis by dynorphin peptides. DNA Cell Biol. 2000, 19(1), 19-27. [CrossRef]
- Stefanova, N.; Ovtscharoff, W. Sexual dimorphism of the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis and the amygdala. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2000, 158:III-X, 1–78. [CrossRef]
- Rasakham, K.; Liu-Chen, L.Y. Sex differences in kappa opioid pharmacology. Life Sci. 2011, 88, 2–16. [CrossRef]
- Russell, S.E.; Rachlin, A.B.; Smith, K.L.; Muschamp, J.; Berry, L.; Zhao, Z.; Chartoff, E.H. Sex differences in sensitivity to the depressive-like effects of the kappa opioid receptor agonist U-50488 in rats. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 76, 213–222. [CrossRef]
- Chartoff, E.H.; Mavrikaki, M. Sex differences in kappa opioid receptor function and their potential impact on addiction. Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 466. [CrossRef]
- Spodnick, M.B.; Amirault, R.T.; Towner, T.T.; Varlinskaya, E.I.; Spear, L.P., Karkhanis, A.N. Adolescent intermittent ethanol exposure effects on kappa opioid receptor mediated dopamine transmission: sex and age of exposure matter. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 472. [CrossRef]
- Varlinskaya, E.I.; Spear, L.P.; Diaz, M.R. Stress alters social behavior and sensitivity to pharmacological activation of kappa opioid receptors in an age-specific manner in Sprague Dawley rats. Neurobiol. Stress 2018, 9, 124–132. [CrossRef]
- Peltier, M.R.; Verplaetse, T.L.; Mineur, Y.S.; Petrakis, I.L.; Cosgrove, K.P.; Picciotto, M.R.; McKee, S.A. Sex differences in stress-related alcohol use. Neurobiol. Stress 2019, 10, 100149. [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, M.M.; Arnold, A.P. Reframing sexual differentiation of the brain. Nat. Neurosci. 2011, 14, 677–683. [CrossRef]
- Reardon, L.E.; Leen-Feldner, E.W.; Hayward, C. (2009). A critical review of the empirical literature on the relation between anxiety and puberty. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2009, 29, 1–23. [CrossRef]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 6th ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, USA, 2007.
- Bota, M.; Swanson, L.W. Collating and curating neuroanatomical nomenclatures: principles and use of the Brain Architecture Knowledge Management System (BAMS). Front. Neuroinform. 2010, 4, 1–16. doi.org10.3389/fninf.2010.00003.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




