Submitted:
30 June 2025
Posted:
01 July 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
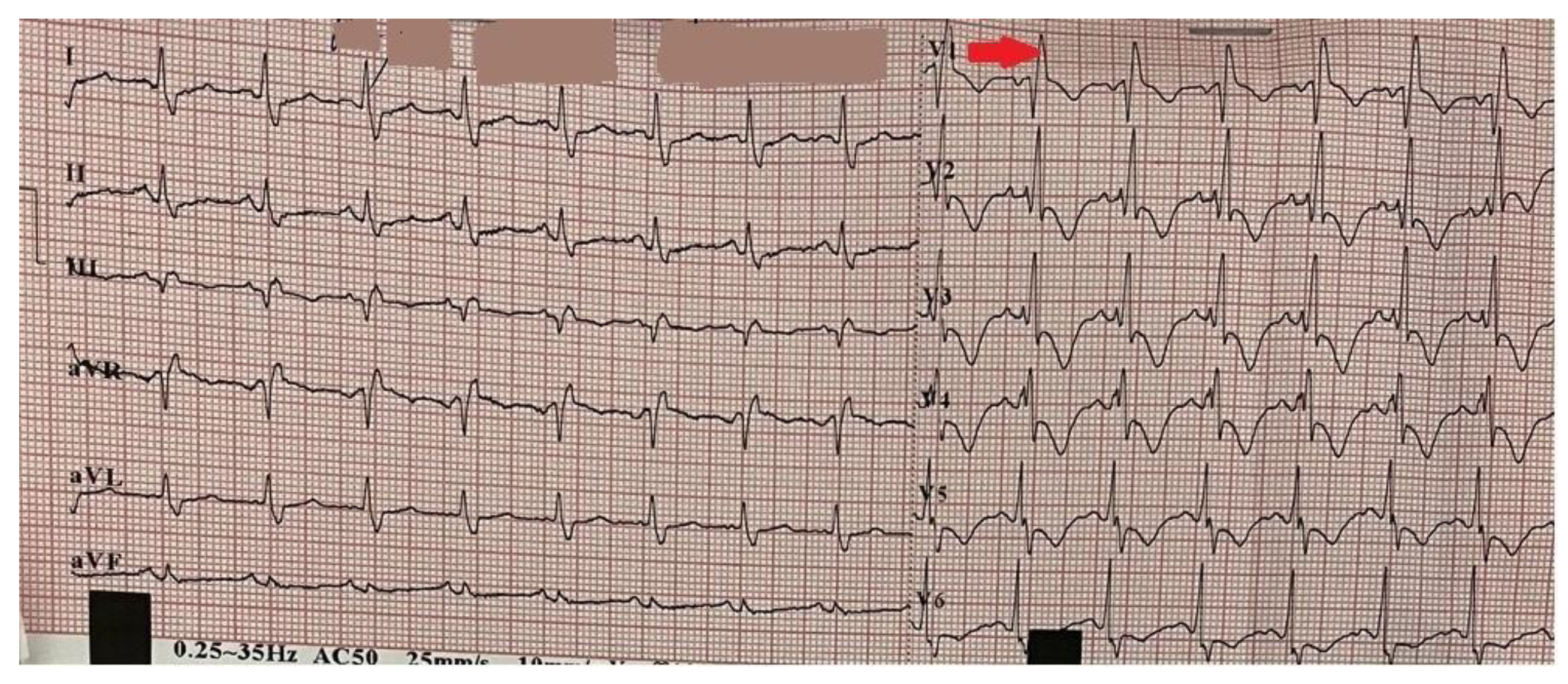
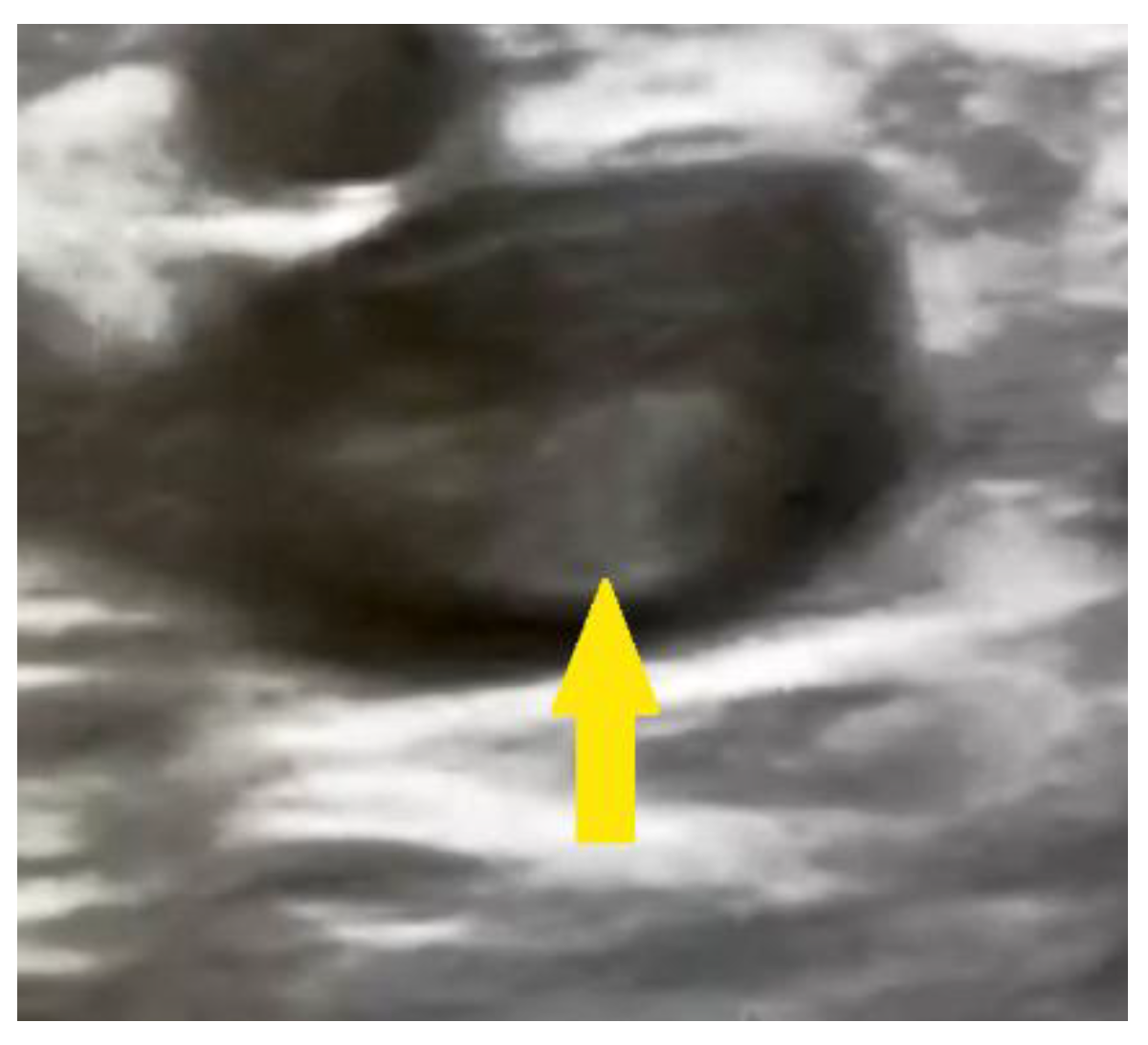
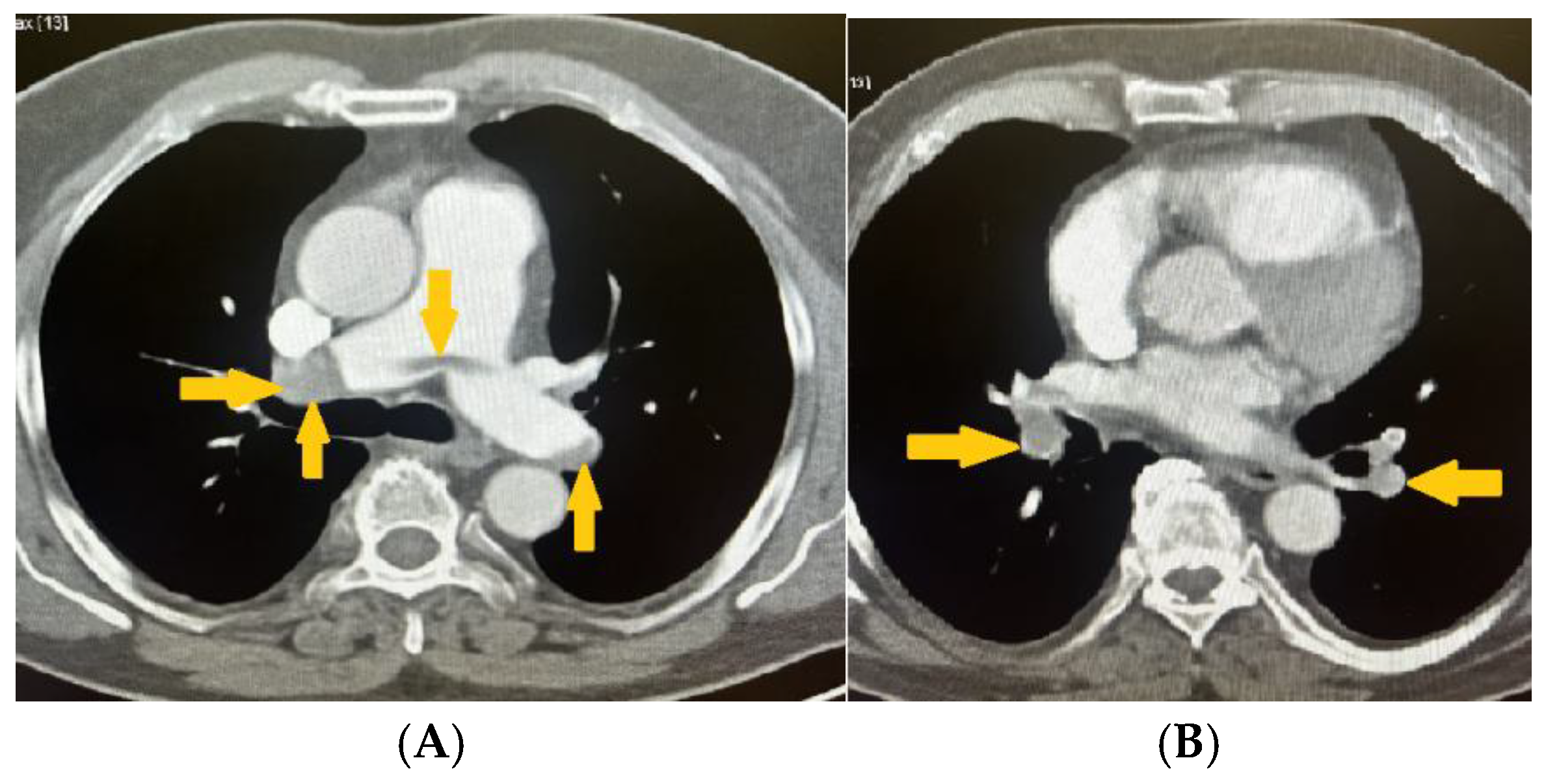
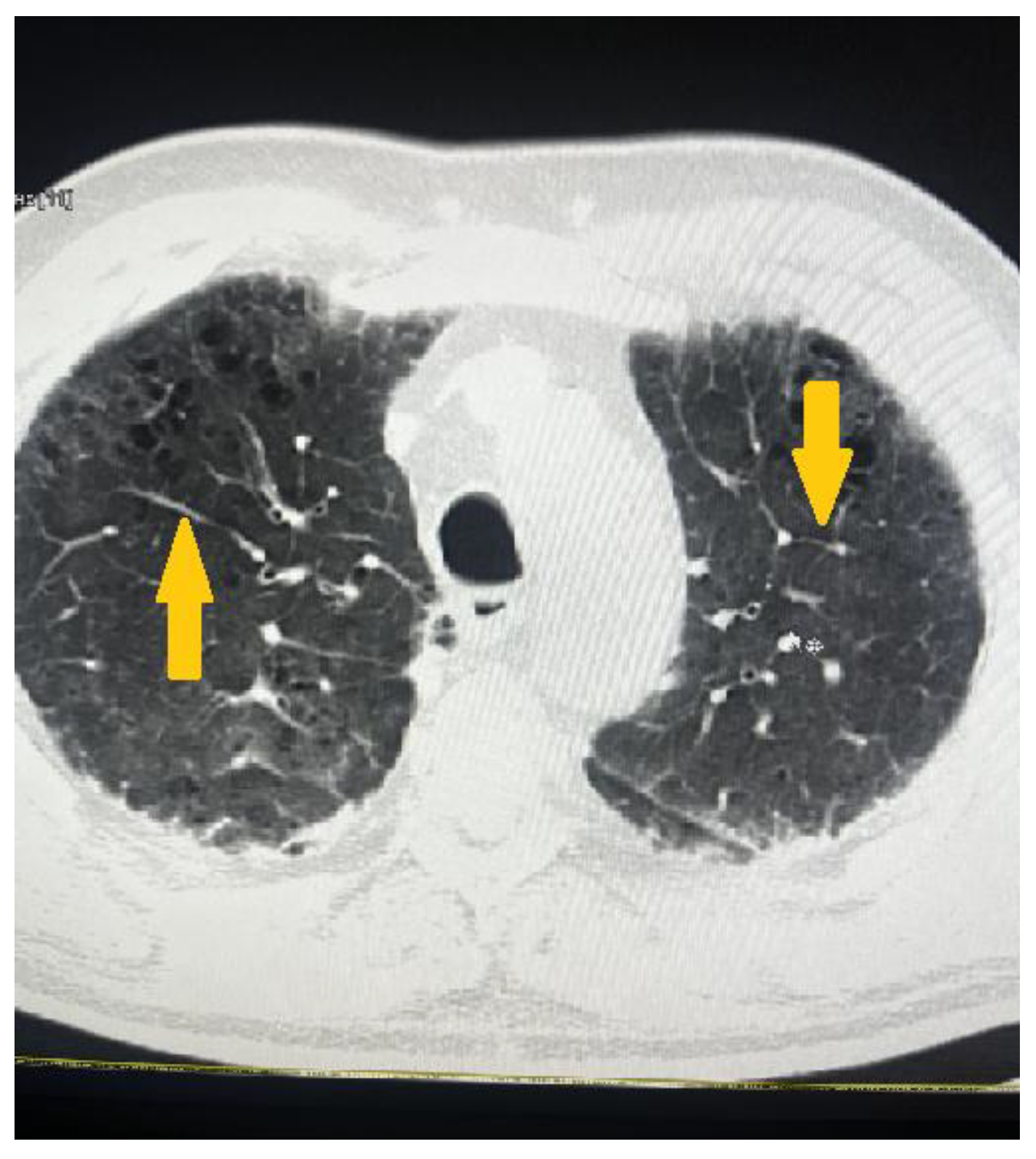
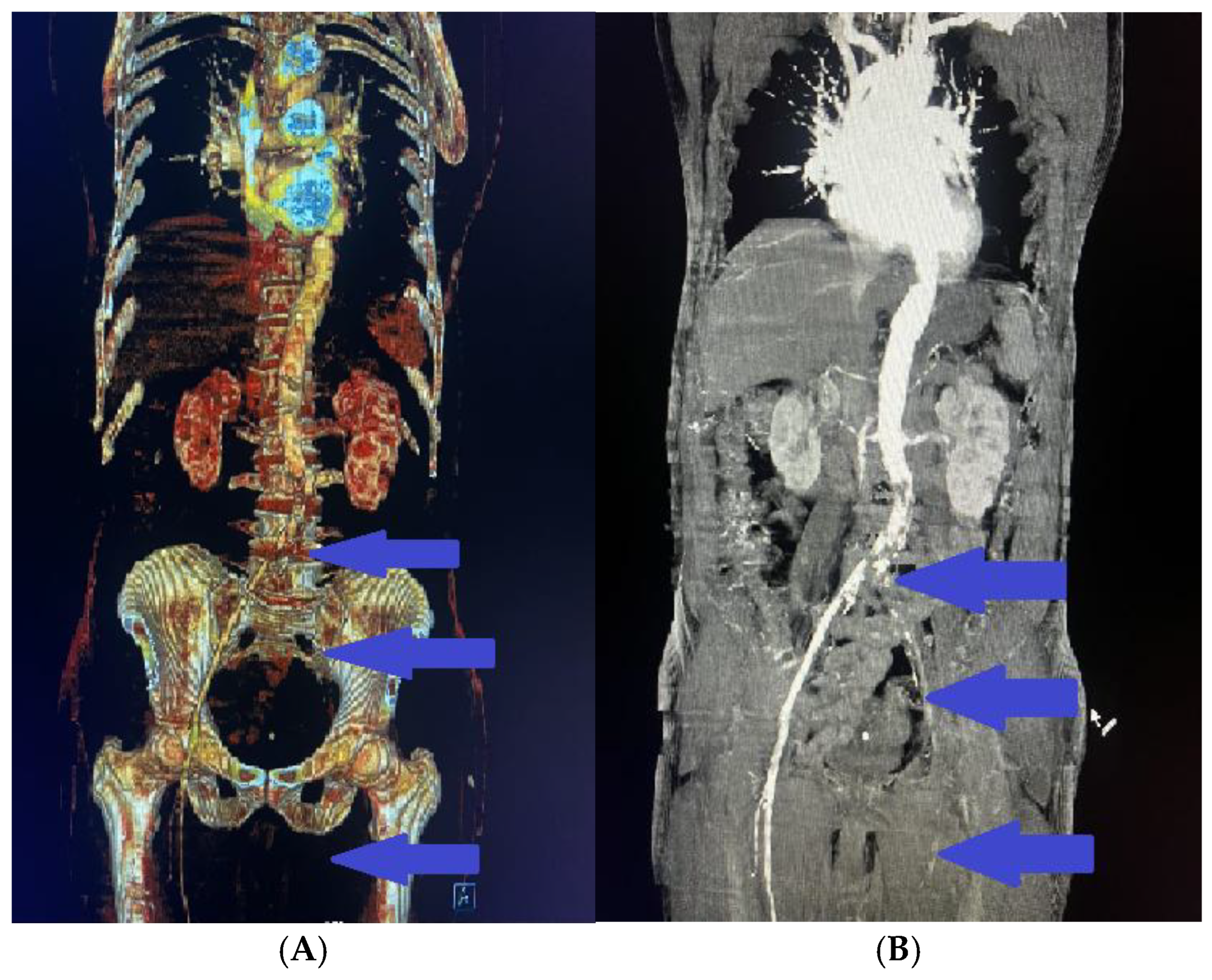
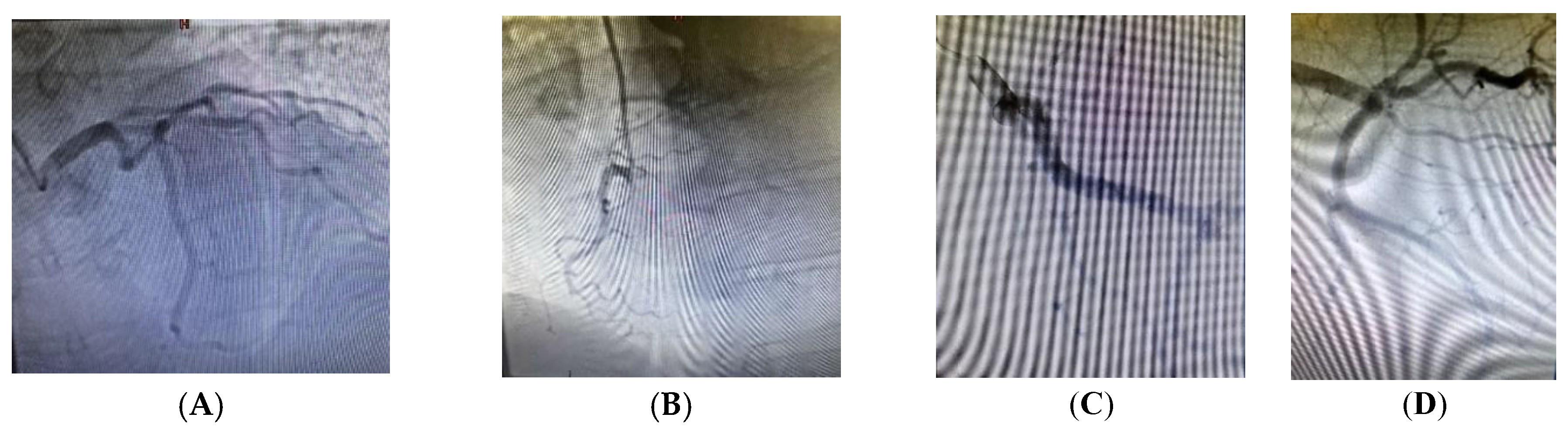
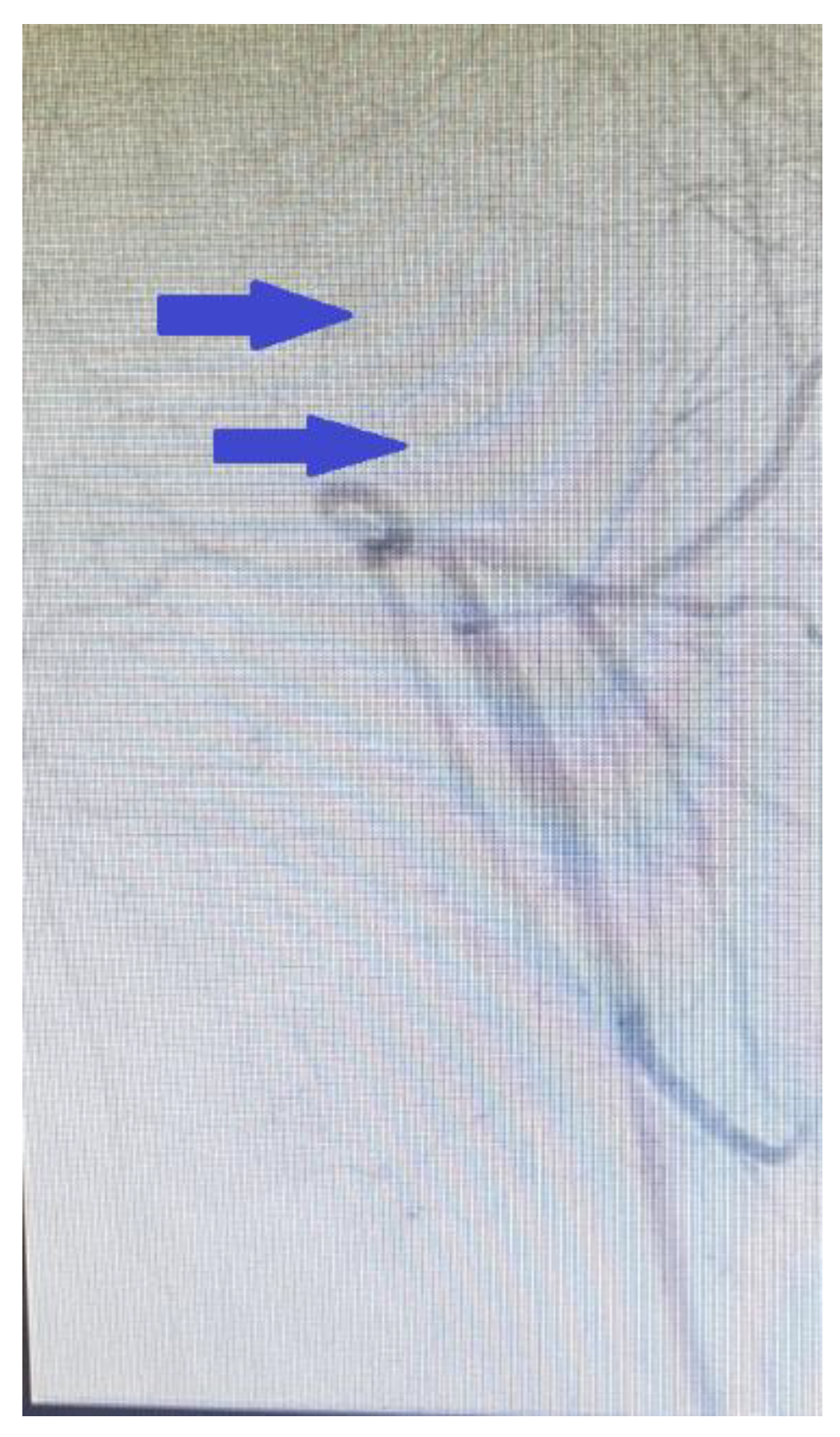
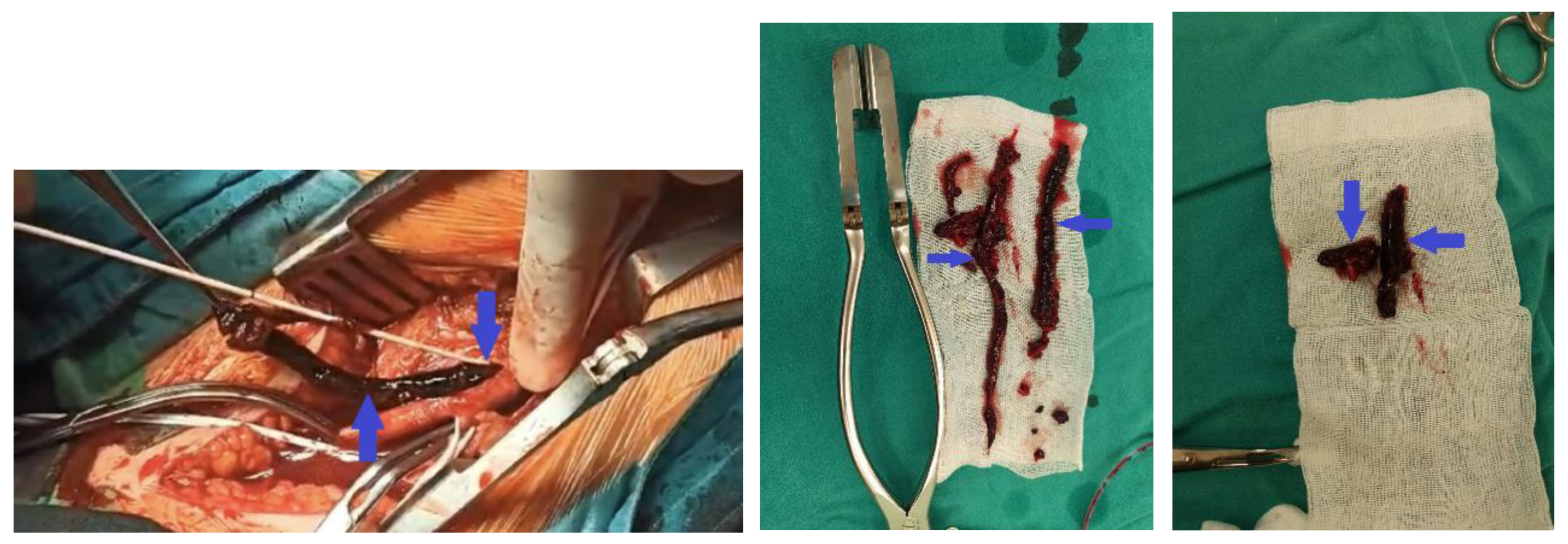
2. Clinical Case Presentation
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PE | pulmonary embolism |
| DVT | deep vein thrombosis |
| DOACs | direct oral anticoagulants |
| VTE | venous thromboembolism |
| FVL | Factor V Leiden |
| MTHFR | methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase |
| PAI-1 | plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 |
| I/D | insertion/deletion |
| ACE | angiotensin-converting enzyme |
| ECG | electrocardiogram |
| CT | computed tomography |
| aPTT | activated partial thromboplastin time |
| HIT | heparin-induced thrombocytopenia |
| TEA | thromboendarterectomy |
| tPA | tissue plasminogen activator |
| F | factor |
| APS | antiphospholipid syndrome |
| aPL | antiphospholipid antibody |
| LAC | lupus anticoagulant |
| aCL | anticardiolipin antibodies |
| anti-β2GPI | anti-β2 glycoprotein I antibodies |
| ACR | American College of Rheumatology |
| EULAR | European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology |
| APC | activated protein C |
| uPA | urokinase plasminogen activator |
| 4G/5G | guanosine polymorphism |
| C | cytosine |
| T | thymine |
| NO | nitric oxide |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| VCAM-1 | vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 |
| NF-κB | Nuclear Factor- kappaB |
| mRNA | messenger ribonucleic acid |
References
- Park, B.J.; Johnston-Cox, H. Simultaneous arterial and venous thromboembolism. Circ. 2023, 81, 3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benmalek, R.; Mechal, H.; Zahidi, H.; Mounaouir, K.; Arous, S.; Benouna, M.E.G.; Drighil, A.; Habbal, R. Combined venous and arterial thrombosis revealing underlying myeloproliferative disorder in a young patient: a case report. J. Med Case Rep. 2021, 15, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munaim, J.R.; Thwe, E.E.; Ibrahim, S.; Easley, L.; Loli, A. Simultaneous arterial and venous system thrombus in patient with suspected malignancy. Circ. 2024, 83, 4168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmon, C.T. Basic mechanisms and pathogenesis of venous thrombosis. Blood Rev. 2009, 23, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libby, P.; Ridker, P.M.; Hansson, G.K. Progress and challenges in translating the biology of atherosclerosis. Nature 2011, 473, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segal, J.B.; Brotman, D.J.; Necochea, A.J.; Emadi, A.; Samal, L.; Wilson, L.M.; Crim, M.T.; Bass, E.B. Predictive Value of Factor V Leiden and Prothrombin G20210A in Adults With Venous Thromboembolism and in Family Members of Those With a Mutation: A Systematic Review. JAMA 2009, 301, 2472–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lijfering, W.M.; Middeldorp, S.; Veeger, N.J.; Hamulyák, K.; Prins, M.H.; BülLer, H.R.; van der Meer, J. Risk of Recurrent Venous Thrombosis in Homozygous Carriers and Double Heterozygous Carriers of Factor V Leiden and Prothrombin G20210A. Circulation 2010, 121, 1706–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segal, J.B.; Brotman, D.J.; Necochea, A.J.; Emadi, A.; Samal, L.; Wilson, L.M.; Crim, M.T.; Bass, E.B. Predictive Value of Factor V Leiden and Prothrombin G20210A in Adults With Venous Thromboembolism and in Family Members of Those With a Mutation: A Systematic Review. JAMA 2009, 301, 2472–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartori, M.T.; Danesin, C.; Saggiorato, G.; Tormene, D.; Simioni, P.; Spiezia, L.; Patrassi, G.M.; Girolami, A. The PAI-I gene 4G/5G Polymorphism and Deep Vein Thrombosis in Patients with Inherited Thrombophilia. Clin. Appl. Thromb. 2003, 9, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien-An Hsieh, Yu-Lin Ko,Yu-Lin Ko, et al. Angiotensin-I Converting Enzyme Gene Polymorphisms and the Risk of Venous Thromboembolism in an Ethnically Chinese Population Living in Taiwan. Acta Cardiologica Sinica, 2011, 27(4).
- Makris, T.K.; Stavroulakis, G.A.; Dafni, U.G.; Gialeraki, A.E.; Krespi, P.G.; Hatzizacharias, A.N.; Tsoukala, C.G.; Vythoulkas, J.S.; Kyriakidis, M.K. ACE/DD genotype is associated with hemostasis balance disturbances reflecting hypercoagulability and endothelial dysfunction in patients with untreated hypertension. Am. Hear. J. 2000, 140, 760–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambien F, Poirier O, Lecerf L, et al. Deletion polymorphism in the gene for angiotensin-converting enzyme is a potent risk factor for myocardial infarction. Nature, 1992 Oct 15;359(6396):641-4. [CrossRef]
- Konstantinides, S.V.; Meyer, G.; Becattini, C.; Bueno, H.; Geersing, G.J.; Harjola, V.-P.; Huisman, M.V.; Humbert, M.; Jennings, C.S.; Jiménez, D.; et al. 2019 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism developed in collaboration with the European Respiratory Society (ERS). Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 543–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, G.; Vicaut, E.; Danays, T.; Agnelli, G.; Becattini, C.; Beyer-Westendorf, J.; Bluhmki, E.; Bouvaist, H.; Brenner, B.; Couturaud, F.; et al. Fibrinolysis for Patients with Intermediate-Risk Pulmonary Embolism. New Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 1402–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, R. Pentoxifylline -- a biomedical profile. . 1979, 10, 307–29. [Google Scholar]
- Saraste, A.; Knuuti, J. ESC 2019 guidelines for the diagnosis and management of chronic coronary syndromes: Recommendations for cardiovascular imaging. Herz 2020, 45, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerhard-Herman, M.D.; Gornik, H.L.; Barrett, C.; Barshes, N.R.; Corriere, M.A.; Drachman, D.E.; Fleisher, L.A.; Flowkes, F.G.R.; Hamburg, N.M.; Kinlay, S.; et al. 2016 AHA/ACC Guideline on the Management of Patients With Lower Extremity Peripheral Artery Disease: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2017, 135, e726–e779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creager, M.A.; Hamburg, N.M.; Calligaro, K.D.; Casanegra, A.I.; Freeman, R.; Gordon, P.A.; Gornik, H.L.; Kim, E.S.; Leeper, N.J.; Merli, G.J.; et al. 2021 ACC/AHA/SVM/ACP Advanced Training Statement on Vascular Medicine (Revision of the 2004 ACC/ACP/SCAI/SVMB/SVS Clinical Competence Statement on Vascular Medicine and Catheter-Based Peripheral Vascular Interventions). Circ. 2020, 77, 998–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsico, F.; Ruggiero, D.; Parente, A.; Pirozzi, E.; Musella, F.; Iudice, F.L.; Savarese, G.; Losco, T.; Giugliano, G.; Rengo, G.; et al. Prevalence and severity of asymptomatic coronary and carotid artery disease in patients with lower limbs arterial disease. Atherosclerosis 2013, 228, 386–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hokusai-VTE Investigators. Edoxaban versus Warfarin for the Treatment of Symptomatic Venous Thromboembolism. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 1406–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, H.; Yagi, S.; Torii, Y.; Amano, R.; Oomichi, Y.; Sangawa, T.; Fukuda, D.; Kadota, M.; Ise, T.; Ueno, R.; et al. Edoxaban improves acute venous thromboembolism while preserving protein C and protein S levels. J. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallelli, G.; Di Mizio, G.; Palleria, C.; Siniscalchi, A.; Rubino, P.; Muraca, L.; Cione, E.; Salerno, M.; De Sarro, G.; Gallelli, L. Data Recorded in Real Life Support the Safety of Nattokinase in Patients with Vascular Diseases. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, R.; Ielapi, N.; Bitonti, A.; Candido, S.; Fregola, S.; Gallo, A.; Loria, A.; Muraca, L.; Raimondo, L.; Velcean, L.; et al. Efficacy of a Low-Dose Diosmin Therapy on Improving Symptoms and Quality of Life in Patients with Chronic Venous Disease: Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2021, 13, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyakis, S.; Lockshin, M.D.; Atsumi, T.; Branch, D.W.; Brey, R.L.; Cervera, R.; Derksen, R.H.W.M.; De Groot, P.G.; Koike, T.; Meroni, P.L.; et al. International consensus statement on an update of the classification criteria for definite antiphospholipid syndrome (APS). J. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 4, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbhaiya, M.; Zuily, S.; Naden, R.; Hendry, A.; Manneville, F.; Amigo, M.-C.; Amoura, Z.; Andrade, D.; Andreoli, L.; Artim-Esen, B.; et al. 2023 ACR/EULAR antiphospholipid syndrome classification criteria. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2023, 82, 1258–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, C.; Linnemann, B. Laboratory Diagnostics in Thrombophilia. Hamostaseologie 2019, 39, 049–061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arachchillage, D.J.; Mackillop, L.; Chandratheva, A.; Motawani, J.; MacCallum, P.; Laffan, M. Thrombophilia testing: A British Society for Haematology guideline. Br. J. Haematol. 2022, 198, 443–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.S.W.; Hii, I.; Rahman, A.; Johnson, T.; Kanakakis, J.; Akhtar, M.M.; A Patel, P. Simultaneous multiple organ emboli in a patient with solid organ malignancy: a case report. Eur. Hear. J. - Case Rep. 2019, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimon, S.; Roman, S. Case report of simultaneous phlegmasia cerulea dolens and acute limb ischemia. Int. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2024, 125, 110596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kun, J.; Hunter, J. Massive arterial and venous thrombosis from smouldering multiple myeloma: further evidence for monoclonal gammopathy of thrombotic significance. BMJ Case Rep. 2024, 17, e260061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiew, Y.R.; Kong, Y. Encephalopathy as the Only Manifestation in Simultaneous Arterial Infarct and Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis in Recent COVID-19 Infection. Am. J. Case Rep. 2022, 24, e938571–1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, D.A.; Grant, P.J. Role of hemostatic gene polymorphisms in venous and arterial thrombotic disease. Blood 2000, 95, 1517–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzimiri, N.; Meyer, B. World distribution of factor V Leiden. Lancet 1996, 347, 481–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorelli E, Kaufman RJ, Dahlbäck B. Cleavage of factor V at Arg 506 by activated protein C and the expression of anticoagulant activity of factor V. Blood. 1999 Apr 15;93(8):2552-8.
- Manten, B.; Westendorp, R.G.J.; Koster, T.; Reitsma, P.H.; Rosendaal, F.R. Risk Factor Profiles in Patients with Different Clinical Manifestations of Venous Thromboembolism: A Focus on the Factor V Leiden Mutation. Thromb. Haemost. 1996, 76, 510–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandegar, M.H.; Saidi, B.; Roshanali, F. Extensive arterial thrombosis in a patient with factor V Leiden mutation. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2010, 11, 127–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metsvaht, T.; Hermlin, T.; Kern, H.; Kahre, T.; Starkopf, J. Aortic Arch Thrombosis in a Neonate With Heterozygous Carrier Status of Factor V Leiden Mutation. Congenit. Hear. Dis. 2006, 1, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, N.; Brown, J.; Edmondson, R.; Tillyer, M. LESSON OF THE MONTH – Catastrophic Arterial Thromboembolism Associated with Factor V Leiden. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2000, 19, 551–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, B.R.; Christ, G.; Gruber, F.; Grubic, N.; Hufnagl, P.; Krebs, M.; Mihaly, J.; Prager, G.W. Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1: physiological and pathophysiological roles. News Physiol. Sci. 2002, 17, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baglin, T. Inherited and Acquired Risk Factors for Venous Thromboembolism. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 33, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Jin, Y.; Li, X.; Peng, X.; Peng, N.; Song, J.; Xu, M. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) 4G/5G promoter polymorphisms and risk of venous thromboembolism – a meta-analysis and systematic review. Vasa 2020, 49, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Chen, N.; Shu, C.; Guo, . ; He, Y.; Zhou, Y. Association between the plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 4G/5G polymorphism and risk of venous thromboembolism: A meta-analysis. Thromb. Res. 2014, 134, 1241–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiklund, P.-G.; Nilsson, L.; Ardnor, S.N.; Eriksson, P.; Johansson, L.; Stegmayr, B.; Hamsten, A.; Holmberg, D.; Asplund, K.; C, L.; et al. Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 4G/5G Polymorphism and Risk of Stroke: Replicated Findings in Two Nested Case–Control Studies Based on Independent Cohorts. Stroke 2005, 36, 1661–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margaglione, M.; Cappucci, G.; Colaizzo, D.; Giuliani, N.; Vecchione, G.; Grandone, E.; Pennelli, O.; Di Minno, G. The PAI-1 Gene Locus 4G/5G Polymorphism Is Associated With a Family History of Coronary Artery Disease. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1998, 18, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frosst, P.; Blom, H.J.; Milos, R.; Goyette, P.; Sheppard, C.A.; Matthews, R.G.; Boers, G.J.H.; den Heijer, M.; Kluijtmans, L.A.J.; van den Heuve, L.P.; et al. A candidate genetic risk factor for vascular disease: a common mutation in methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase. Nat. Genet. 1995, 10, 111–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblatt, D.S. Inherited Disorders of Folate and Cobalamin. In: Graham, I., Refsum, H., Rosenberg, I.H., Ueland, P.M., Shuman, J.M. (eds) Homocysteine Metabolism: From Basic Science to Clinical Medicine. Developments in Cardiovascular Medicine, vol 196, 1997. Springer, Boston, MA. [CrossRef]
- Castro, R.; Rivera, I.; Ravasco, P.; Jakobs, C.; Blom, H.; Camilo, M.; de Almeida, I. 5,10-Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase 677C→T and 1298A→C mutations are genetic determinants of elevated homocysteine. Qjm: Int. J. Med. 2003, 96, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Harker, L.; Harlan, J.M.; Ross, R. Effect of sulfinpyrazone on homocysteine-induced endothelial injury and arteriosclerosis in baboons. Circ. Res. 1983, 53, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Harker, L.; Ross, R.; Slichter, S.J.; Scott, C.R. Homocystine-induced arteriosclerosis. The role of endothelial cell injury and platelet response in its genesis. J. Clin. Investig. 1976, 58, 731–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthias, D.; Becker, C.-H.; Riezler, R.; Kindling, P. Homocysteine induced arteriosclerosis-like alterations of the aorta in normotensive and hypertensive rats following application of high doses of methionine. Atherosclerosis 1996, 122, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraci, F.M. Hyperhomocysteinemia: a million ways to lose control. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2003, 23, 371–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamler, J.S.; A Osborne, J.; Jaraki, O.; E Rabbani, L.; Mullins, M.; Singel, D.; Loscalzo, J. Adverse vascular effects of homocysteine are modulated by endothelium-derived relaxing factor and related oxides of nitrogen. J. Clin. Investig. 1993, 91, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellamy, M.; McDowell, I.; Ramsey, M.; Brownlee, M.; Bones, C.; Newcombe, R.; Lewis, M. Hyperhomocysteinemia After an Oral Methionine Load Acutely Impairs Endothelial Function in Healthy Adults. Circulation 1998, 98, 1848–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, G.N.; Loscalzo, J.; Epstein, F.H. Homocysteine and Atherothrombosis. New Engl. J. Med. 1998, 338, 1042–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungvari, Z.; Csiszar, A.; Edwards, J.G.; Kaminski, P.M.; Wolin, M.S.; Kaley, G.; Koller, A. Increased Superoxide Production in Coronary Arteries in Hyperhomocysteinemia: role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha, NAD(P)H oxidase, and inducible nitric oxide synthase. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2003, 23, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, N.; Heydrick, S.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Bierl, C.; Cap, A.; Loscalzo, J. Cellular Redox State and Endothelial Dysfunction in Mildly Hyperhomocysteinemic Cystathionine β-Synthase–Deficient Mice. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2002, 22, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiler, H.; Isermann, B.H. Thrombomodulin. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2003, 1, 1515–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lentz, S.R.; Sobey, C.G.; Piegors, D.J.; Bhopatkar, M.Y.; Faraci, F.M.; Malinow, M.R.; Heistad, D.D. Vascular dysfunction in monkeys with diet-induced hyperhomocyst(e)inemia. J. Clin. Investig. 1996, 98, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dayal, S.; Bottiglieri, T.; Arning, E.; Maeda, N.; Malinow, M.R.; Sigmund, C.D.; Heistad, D.D.; Faraci, F.M.; Lentz, S.R. Endothelial Dysfunction and Elevation of S -Adenosylhomocysteine in Cystathionine β-Synthase–Deficient Mice. Circ. Res. 2001, 88, 1203–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, M.A.; Lalla, E.; Lu, Y.; Gleason, M.R.; Wolf, B.M.; Tanji, N.; Ferran, L.J.; Kohl, B.; Rao, V.; Kisiel, W.; et al. Hyperhomocysteinemia enhances vascular inflammation and accelerates atherosclerosis in a murine model. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 107, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werstuck, G.H.; Lentz, S.R.; Dayal, S.; Hossain, G.S.; Sood, S.K.; Shi, Y.Y.; Zhou, J.; Maeda, N.; Krisans, S.K.; Malinow, M.R.; et al. Homocysteine-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress causes dysregulation of the cholesterol and triglyceride biosynthetic pathways. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 107, 1263–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, K.H.; Jeong, M.H.; Sim, D.S.; Hong, Y.J.; Kim, J.H.; Ahn, Y.; Kang, J.C. Pulmonary thromboembolism due to severe hyperhomocysteinemia associated with a methyltetrahydrofolate reductase mutation. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2013, 28, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmadonova, N.; Shilova, A.; Kozyreva, V.; Subbotovskaya, A.; Klevanets, J.; Karpenko, A. Association of folate metabolism gene polymorphisms and pulmonary embolism: A case-control study of West-Siberian population. Thromb. Res. 2014, 135, 788–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basol, N.; Karakus, N.; Savas, A.Y.; Kaya, I.; Karakus, K.; Yigit, S. The importance of MTHFR C677T/A1298C combined polymorphisms in pulmonary embolism in Turkish population. Medicina 2016, 52, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandanpour, N.; Willis, G.; Meyer, F.J.; Armon, M.P.; Loke, Y.K.; Wright, A.J.; Finglas, P.M.; Jennings, B.A. Peripheral arterial disease and methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) C677T mutations: A case-control study and meta-analysis. J. Vasc. Surg. 2009, 49, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Silva, D.; Malone, M.V.; Seetharaman, K. MTHFR A1298C and C677T Polymorphisms Are Associated with Increased Risk of Venous Thromboembolism: A Retrospective Chart Review Study. Acta Haematol. 2017, 138, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- den Heijer M, Rosendaal FR, Blom HJ, Gerrits WB, Bos GM. Hyperhomocysteinemia and venous thrombosis: a meta-analysis. Thromb Haemost. 1998 Dec;80(6):874-7. [PubMed]
- Aday, A.W.; Duran, E.K.; Van Denburgh, M.; Kim, E.; Christen, W.G.; Manson, J.E.; Ridker, P.M.; Pradhan, A.D. Homocysteine Is Associated With Future Venous Thromboembolism in 2 Prospective Cohorts of Women. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2021, 41, 2215–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Gao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Ma, H.; Wang, W.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Xu, H.; Lu, Z. Association Between MTHFR C677T Polymorphism and Venous Thromboembolism Risk in the Chinese Population: a meta-analysis of 24 case-controlled studies. Angiology 2014, 66, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirstoveanu, C.; Calin, N.; Heriseanu, C.; Filip, C.; Vasile, C.M.; Margarint, I.; Marcu, V.; Dimitriu, M.; Ples, L.; Tarnoveanu, S.; et al. Consistent Correlation between MTHFR and Vascular Thrombosis in Neonates—Case Series and Clinical Considerations. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au-Yeung, K.K.; Woo, C.W.; Sung, F.L.; Yip, J.C.; Siow, Y.L.; O, K. Hyperhomocysteinemia Activates Nuclear Factor-κB in Endothelial Cells via Oxidative Stress. Circ. Res. 2004, 94, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigat, B., Hubert, C., Alhenc-Gelas, F., Cambien, F., Corvol, P., & Soubrier, F. (1990). An insertion/deletion polymorphism in the angiotensin I-converting enzyme gene accounting for half the variance of serum enzyme levels. The Journal of clinical investigation, 86(4), 1343–1346. [CrossRef]
- Tiret, L.; Rigat, B.; Visvikis, S.; Breda, C.; Corvol, P.; Cambien, F.; Soubrier, F. Evidence, from combined segregation and linkage analysis, that a variant of the angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) gene controls plasma ACE levels. . 1992, 51, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ueda, S.; Elliott, H.L.; Morton, J.J.; Connell, J.M.C. Enhanced Pressor Response to Angiotensin I in Normotensive Men With the Deletion Genotype (DD) for Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme. Hypertension 1995, 25, 1266–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, P.K.; Griendling, K.K. Angiotensin II cell signaling: Physiological and pathological effects in the cardiovascular system. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2007, 292, C82–C97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambien, F.; Poirier, O.; Lecerf, L.; Evans, A.; Cambou, J.-P.; Arveiler, D.; Luc, G.; Bard, J.-M.; Bara, L.; Ricard, S.; et al. Deletion polymorphism in the gene for angiotensin-converting enzyme is a potent risk factor for myocardial infarction. Nature 1992, 359, 641–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambien, F.; Costerousse, O.; Tiret, L.; Poirier, O.; Lecerf, L.; Gonzales, M.F.; Evans, A.; Arveiler, D.; Cambou, J.P.; Luc, G. Plasma level and gene polymorphism of angiotensin-converting enzyme in relation to myocardial infarction. Circulation 1994, 90, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, E.; Corneli, P.S.; Anderson, J.L.; Marshall, H.W.; Lalouel, J.-M.; Ward, R.H. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Gene Polymorphism Is Associated With Myocardial Infarction but Not With Development of Coronary Stenosis. Circulation 1995, 91, 2120–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, N.J.; Vaughan, D.E. The Renin-Angiotensin and Fibrinolytic Systems co-conspirators in the pathogenesis of ischemic cardiovascular disease. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 1996, 6, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridker, P.M.; Gaboury, C.L.; Conlin, P.R.; Seely, E.W.; Williams, G.H.; E Vaughan, D. Stimulation of plasminogen activator inhibitor in vivo by infusion of angiotensin II. Evidence of a potential interaction between the renin-angiotensin system and fibrinolytic function. Circulation 1993, 87, 1969–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Leeuwen, R.T.; Kol, A.; Andreotti, F.; Kluft, C.; Maseri, A.; Sperti, G. Angiotensin II increases plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 and tissue-type plasminogen activator messenger RNA in cultured rat aortic smooth muscle cells. Circulation 1994, 90, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaughan, D.E.; Lazos, S.A.; Tong, K. Angiotensin II regulates the expression of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in cultured endothelial cells. A potential link between the renin-angiotensin system and thrombosis. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 95, 995–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feener, E.P.; Northrup, J.M.; Aiello, L.P.; King, G.L. Angiotensin II induces plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 and -2 expression in vascular endothelial and smooth muscle cells. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 95, 1353–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-K.; Kim, J.-W.; Kim, S.; Gwon, H.-C.; Ryu, J.-C.; Huh, J.-E.; Choo, J.-A.; Choi, Y.; Rhee, C.-H.; Lee, W.-R. Polymorphism of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Gene Is Associated With Circulating Levels of Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1997, 17, 3242–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilley, A.; Austin, H.; Hooper, W.C.; Lally, C.; Ribeiro, J.A.; Wenger, N.K.; Rawlins, P.; Evatt, B. Relation of Three Genetic Traits to Venous Thrombosis in an African-American Population. Am. J. Epidemiology 1998, 147, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philipp CS, Dilley A, Saidi P, Evatt B, et al. Deletion polymorphism in the angiotensin-converting enzyme gene as a thrombophilic risk factor after hip arthroplasty. Thromb Haemost. 1998 Dec;80(6):869-73.
- Ordóñez, A.J.G.; Carreira, J.M.F.; Rodríguez, J.M.M.; Sánchez, L.M.; Díaz, R.A.; Martinez, M.V.A.; Garcia, E.C. Risk of venous thromboembolism associated with the insertion/deletion polymorphism in the angiotensin-converting enzyme gene. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2000, 11, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, A.; Brown, K.; Langdown, J.; Luddington, R.; Baglin, T. Effect of the angiotensin-converting enzyme gene deletion polymorphism on the risk of venous thromboembolism. SHORT REPORT. Br. J. Haematol. 2000, 111, 562–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, F.-C.; Hsu, L.-A. Meta-Analysis of Association Between Insertion/Deletion Polymorphism of the Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme Gene and Venous Thromboembolism. Clin. Appl. Thromb. 2009, 17, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




