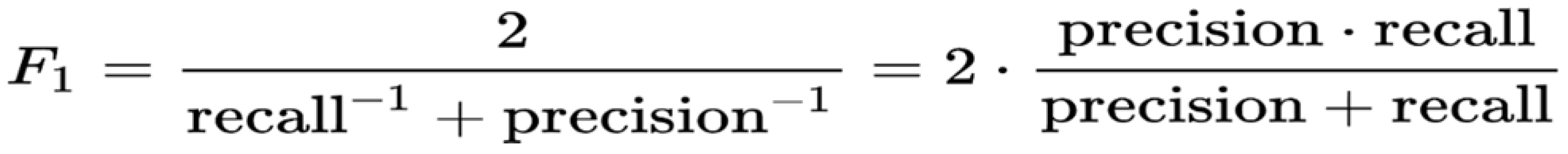1. Introduction
Deep learning has been successful in range of the domains such image processing [
1,
2,
3,
4,
6,
7,
8,
10,
12,
13,
15,
16,
17,
18,
41], natural language processing (NLP) [
14] and audio [
5,
9,
11,
19]. Particularly in question-answering systems, NLP has advanced in recent years. These algorithms play a crucial role in effectively extracting pertinent information from large amounts of written content, allowing users to receive precise and contextually relevant answers to questions.
Deep learning has been successful in a range of domains such as image processing [
1,
2,
3,
4,
6,
7,
8,
10,
12,
13,
15,
16,
17,
18,
40,
45,
47], natural language processing (NLP) [
14,
42,
43], and audio [
5,
9,
11,
19]. Particularly in question-answering systems, NLP has advanced in recent years. These algorithms play a crucial role in effectively extracting pertinent information from large amounts of written content, allowing users to receive precise and contextually relevant answers to questions.
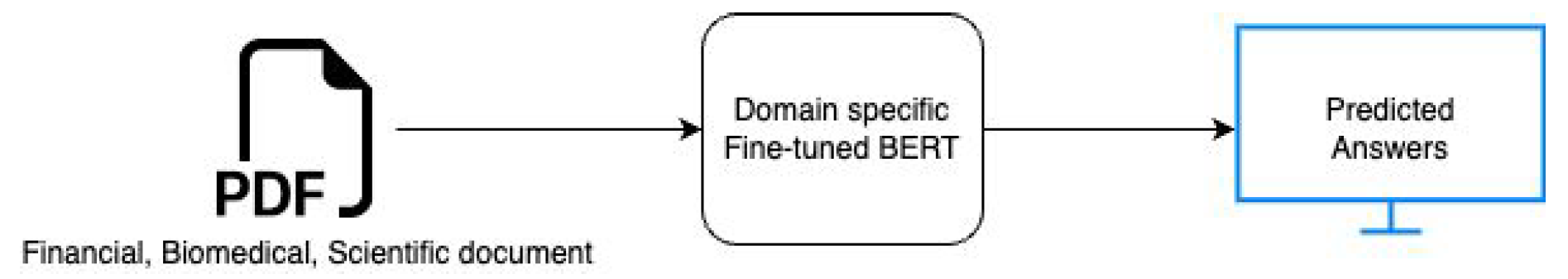
Even with end-to-end training, answering complex questions with a single machine-learning model remains challenging. The goal of this research paper is to develop a question-answering system specifically for PDF files related to scientific, financial, and biomedical literature. The technical analysis of these PDFs may be exhausting and require in-depth study of their complex text, which makes them hard to understand. On the other hand, a question-answering system can save users time and effort by rapidly retrieving the needed information. Prior research has demonstrated that machine learning models can be used to retrieve information from large documents, and these models can be evaluated using metrics like exact matches and F1 scores. Bidirectional Encoder Representations Transformers, or BERT, for short, can perform better in deep learning tasks like quality control and summarization of text with minimal to no modifications after pre-training with just one additional output layer. Medical facilities might benefit from accurate QA systems by researching disease symptoms and treatment options. Pre-trained BERT models, like Bio-BERT and Sci-BERT, seem to perform more accurately than traditional models, in line with prior research. [Unsupervised Biomedical Question-Answering Pre-Training]. This study will add to our knowledge of the effective usage of transformers in the fabrication of QA software for the selected PDFs. All things looked at, a QA system offers a more clever, effective, and user-friendly method of information extraction from huge PDFs, such as annual reports, articles, and medical documents. Research Question: The problem mentioned in the above section motivates the following research question: In the financial, biomedical, and scientific domains, how can BERT transformers be employed to effectively answer questions and retrieve knowledge from PDF files? This research intends to implement a QA system using pre-trained BERT models for the chosen domains and evaluate performance to find out the best-performing model. An overview of the question-answering system with domain-specific pre-trained BERT on documents is shown in
Figure 1.
The paper’s remaining sections are arranged as follows: The related work is discussed in
Section 2, the research methodology is shown in
Section 3, the design specification is explained in
Section 4, and the implementation aspects of the research are illustrated in
Section 5, the evaluation results are examined in
Section 6, and the conclusion and future work is highlighted in
Section 7.
2. Related Work
BERT has demonstrated Advanced results in various NLP tasks due to its conceptual simplicity and empirical effectiveness. This research aims at building a BERT-based question-answering system specifically tailored for PDF documents, aiming to address the challenges associated with extracting nuanced information from this widely used format. PDF files, prevalent in academic and professional settings, pose challenges to effective information retrieval due to their diverse structures and complex formatting. Leveraging BERT’s capabilities offers a promising solution to enhance comprehension and accessibility in PDF-based question-answering. This literature review delves into existing research on integrating BERT models for question-answering in PDFs, aiming to identify gaps and opportunities. The goal is to advance intelligent systems for document comprehension by providing insights into the creation of a BERT-based QA system based on PDFs.
Researchers in this study[
20] introduced the Transformer architecture, a sequence transduction model based on attention mechanisms. The drawbacks of conventional recurrent neural networks in encoder-decoder architectures with multi-headed self-attention were overcome by this method. Transformer architectures outperform those built on recurrent networks in terms of speed. Transformer performed more effectively for language translation tasks than even previously reported ensemble models.
This work[
21] investigates the performance of different pre-trained language models to determine if they can be fully generalized over a range of QA data sets. QA data sets vary in complexity, challenging models with various levels of reasoning. The study trains and fine-tunes pre-trained language models on a spectrum of data sets to identify models excelling in comprehensive generalization. The paper investigated whether enhanced bidirectionality improves QA model performance with BERT-BiLSTM architecture. Using the F1-score metric, the research identifies Roberta and BART are consistently outperforming others. BERT-BiLSTM also surpasses the baseline BERT model. The study sheds light on how QA models generalize and the impact of bi-directionality, contributing to robust systems for nuanced reasoning across domains. Future studies could investigate the wider effects of bidirectionality on language understanding and tailor pre-trained models for QA tasks. Covid-Twitter-BERT (CT-BERT), presented in Müller et al. (2023), was pre-trained on Covid-19-related Twitter messages, and also utilized BERT Large as a base model. The study[
23] also supports the utilization of domain-specific models.
The approach in this study[
24] involves widening the BERT architecture to consider table-inter-cell connections. A sizable table corpus taken from Wikipedia is used to retrain the parameters for these associations. Furthermore, by paying attention, to relevant text representations in the surrounding article, a novel strategy improves table representations. By considering the contextual relationship between tables and text, the suggested method seeks to offer a more practical and efficient way to answer questions from documents. They laid the groundwork for a more comprehensive understanding of complex documents by integrating text-based and table-based approaches.
Although BERT has shown an unmatched ability to comprehend language, an innovative approach is needed when applying it to language-generating problems. The research under review[
25] introduced C-MLM as a novel method that provides a mechanism to modify BERT for target generation task fine-tuning. Technique entails BERT’s fine-tuning, acting as a ”teacher” model for the goal-generation tasks. Then, this improved BERT model serves as an extra supervisory source, augmenting traditional Sequence-to-Sequence (Seq2Seq) models, also called "students," This teacher-student approach improves the performance of Seq2Seq models in text production. The experiments show notable gains in performance over robust Transformer baselines in a variety of language generation tasks, such as summarized text and automatic translation.
In [
26], BERT jointly trains on both left and right contexts across all layers to pre-train deep bidirectional representations from unlabeled text. So, by fine-tuning the previously trained BERT model with just one additional output layer, advanced models for a range of tasks, such as question answering and language inference, can be generated without necessitating significant modifications to the task-specific architecture. F1 score of 93 percent. showed empirical success for the question-answering task on SQuAD v1.1. and SQuAD v2.0 Test F1 to 83.1 percent PaperWadhwa et al. (2018) also compared the previous work done on the SQuAD dataset.
This study[
28] introduced an automated approach for extracting infra-structure damage information from textual data using BERT and question-answering (QA). The proposed method, trained on National Hurricane Center reports, demonstrates high accuracy in hurricane and earthquake scenarios, outperforming traditional methods. The method involves two steps: 1) Paragraph Retrieval using Sentence-BERT and 2) Information extraction with a BERT model. The model was trained on 533 question-answer pairs from hurricane reports and tested on diverse data sets, achieving F1 scores of 90.5 percent and 83.6 percent for hurricanes and earthquakes. This research presented an innovative BERT-based QA approach for automated infrastructure damage retrieval, contributing to improved disaster management. Researchers were optimistic about generalizing the model to other disaster types.
This study[
29] pioneered the application of BERT to document classification, achieving state-of-the-art results across four data sets. Despite initial concerns, the proposed BERT-based model surpasses previous baselines, addressing computational expenses through knowledge distillation to smaller bidirectional LSTMs. This achieves BERT base parity with 30× fewer parameters on multiple data sets. Contributions include improved baselines for future document classification research, reflecting a change in basic assumptions in NLP towards pre-trained deep language representation models like BERT. The research highlights the feasibility of distilling BERT into simpler models for competitive accuracy with reduced computational cost.
BERT has demonstrated remarkable performance across various NLP tasks. In the paper[
30] introduced BERTSUM, a simplified BERT variant tailored for extractive summarizing. For extractive summarizing, despite recent neural models, further advancements have hit a wall. This research makes the case for using BERT to improve extractive summarizing performance because of its robust design and large pre-training data set. The study investigates many BERT-based architectures for extractive summarization and finds that the best results are obtained on the job using a flat design with inter-sentence transformer layers. while the paper [
31] introduced a novel data augmentation technique, leveraging distant supervision for fine-tuning BERT in open-domain QA. challenges were noise and genre mismatch in distant supervision data and model sensitivity to diverse data sets and hyper-parameters.
This survey [
34], analyzes various BERT types, including BioBERT for biomedical texts, Clinical BERT for clinical notes, and SciBERT for scientific texts, Roberta as an enhanced version, and DistlBERT for smaller models. SCIBERT outperformed BERT-Base in scientific NLP tasks [
33], and its application Tasks like summarizing and answering questions are recommended for future research[
32].
This paper [
35] tackles bio-medical literature overload with a sequence of labeling approaches for keyword extraction, utilizing contextual embeddings from XLNET, BERT, BioBERT, SCIBERT, and RoBERTa. It avoids traditional methods, showcasing a 22 percent F1-score improvement. Similarly, study [
36] employs bioBERT and SciBERT in biomedical text. Another study[
38] stated ALBERT outperforms BERT with fewer parameters and faster training in natural language understanding benchmarks.
Conclusion: It is clear from the literature review that researchers have achieved high accuracy [
24,
25] for BERT-based models for various NLP tasks [
27], including question-answering [
21,
28]. In their study, [
22] used Roberta for PDFs containing tables and complex texts, while study [
29] illustrated the significance of domain-specific BERT models like BERT, BioBERT, and SCIBERT in the biomedical domain. The study[
26], successfully achieved better results for document classification tasks using the distilling BERT model. The reviewed papers collectively highlight the versatility and robustness of BERT-based models across various NLP tasks. From language translation to document classification and biomedical question answering, BERT has proven to be a versatile and powerful tool. Some of the challenges were model sensitivity to different datasets, scalability concerns, potential overfitting, and difficulty in applying BERT to generative tasks, underscoring the ongoing complexities in refining these models.
4. Design Specification
In this section, the foundational elements underpinning the implementation of the BERT-based QA system, catering specifically to the distinct characteristics of the financial, biomedical, and scientific domains.
4.1. Techniques
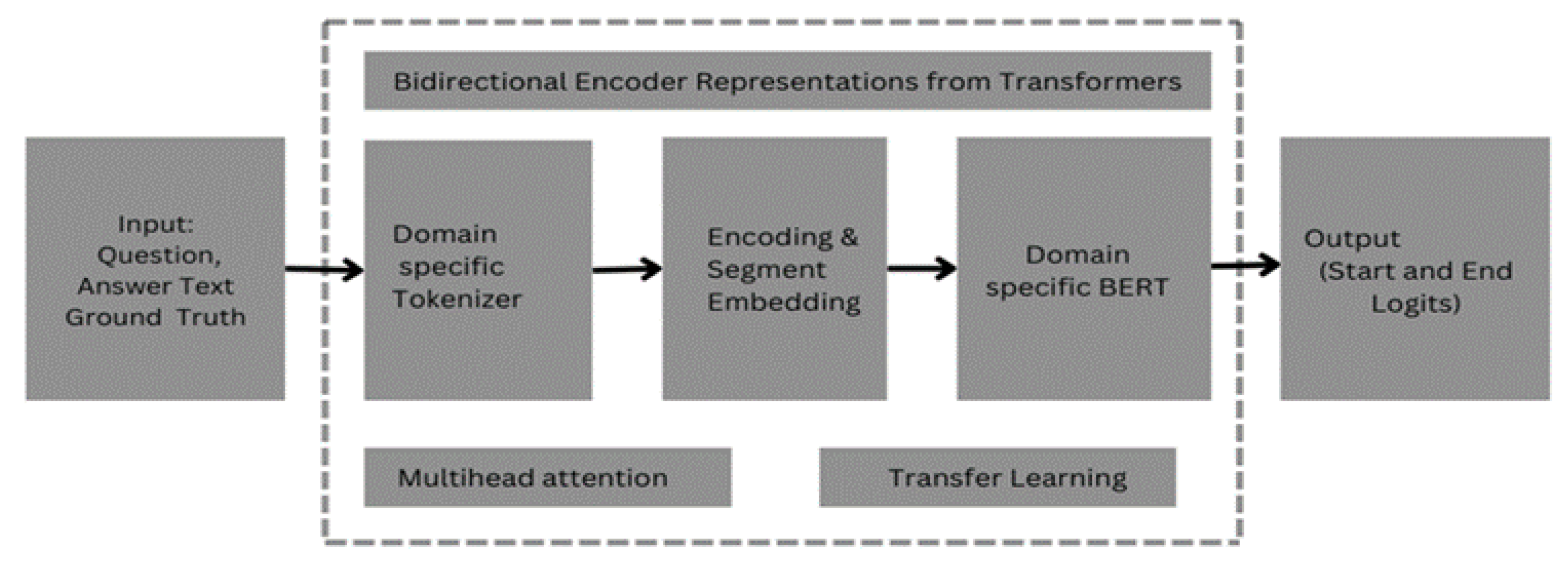
BERT-based QA system integrates several key techniques to address the unique challenges posted by diverse domains: Domain-Specific Fine-tuned BERT: For each of the domains, a domain-specific, fine-tuned BERT model was employed.
4.2. Architecture
4.2.1. Multi-Head Attention Mechanism
Multi-Head Attention Mechanism: A multi-head attention mechanism in the architecture [
20] enables the model to focus on different parts of the input text at the same time. This is especially beneficial for capturing complex relationships and context within diverse domain-specific documents.
4.2.2. Domain-Specific Embeddings
We utilize domain-specific embeddings to augment the pre-trained BERT embeddings. These embeddings are tailored to the vocabulary and context prevalent in the financial, biomedical, and scientific domains.
4.3. Framework
Implementation is built on the PyTorch framework, providing a robust and flexible platform for deep learning.
PyTorch Transformers Library: The PyTorch Transformers library was used, which facilitates seamless integration with pre-trained BERT models. This library offers a comprehensive set of tools for tokenization, model configuration, and training.
4.4. Algorithm Description
4.4.1. Algorithm Functionality
BERT-based QA system for financial, biomedical, and scientific domains introduces the following functionalities: Document Chunking Strategy: Given the potentially lengthy and complex nature of documents in these domains, our system employs a document chunking strategy to handle large texts efficiently, ensuring that relevant context is preserved.
4.4.2. Algorithm Requirements
To implement and deploy a QA system successfully, certain requirements must be met: Pre-processing Modules: Custom pre-processing modules are designed to handle data cleaning, tokenization, and embedding generation. Hardware Acceleration: For optimal performance, the system benefits from hardware acceleration, such as GPUs provided by Google Collab to expedite training and inference.
4.5. Tools and Languages
The implementation leveraged the following tools and languages: Programming Language: Python’s extensive libraries and versatility in the fields of data science and machine learning led to its selection as the main programming language. Machine Learning Frameworks: Machine learning models were implemented and trained with the help of the scikit-learn, TensorFlow, PyTorch, and Hugging Face Transformers libraries.