Introduction
Social media has become a vital tool for sharing information. It plays a significant role in the preservation and promotion of traditional Malay music, particularly among the younger generation, who can now easily access related content through platforms such as Facebook, Instagram, TikTok, and YouTube. Moreover, social media functions as a medium for mass communication, facilitating the rapid and widespread dissemination of information. It also enables individuals to connect with one another regardless of their geographical location. The accessibility and user-friendliness of social media allow anyone to navigate it effortlessly and without limitations (Ananda, 2018).
In addition, social media has become an important platform for the preservation of traditional Malay music. Various forms of traditional music such as kompang, ghazal, and joget can be shared in diverse formats, making them more accessible and appealing to the younger generation today.
The role of music within the cultures and communities of the Malays, Chinese, Indians, Dayaks, Kadazan-Dusun, Portuguese, Eurasians, and other ethnic groups is reflected in the nation’s musical genres, despite Malaysia’s multicultural nature. However, the musical styles of these diverse ethnic communities have yet to be prominently showcased, and the distinctions between the Chinese, Indian, and Malay communities, as well as other indigenous groups, remain highly pronounced. Generally, Malaysian music can be classified into five categories: art music, popular music, folk music, syncretic music, and classical or modern music. These categories often overlap in terms of their characteristics (Matusky & Tan, 2004, p. 5).
According to sources from traditional musical instrument publications, traditional music has existed since ancient times. It was inspired by observations of the natural environment and utilised raw materials from nature to create instruments. In addition, it began with simple systems such as hand clapping, whistling, and foot stomping, which are collectively known as body sounders.
Objective
To analyse how social media expands the exposure of traditional Malay music to the younger generation.
To examine the types of social media platforms frequently used by the younger generation when engaging with tradisional music.
To indentify the challenges in promoting tradisonal Malay music through social media.
Literature Review
This literature review aims to examine the role of social media in the preservation of traditional Malay music. Traditional Malay music, which incorporates instruments such as the gamelan, kompang, and seruling (flute), represents a vital cultural heritage and reflects the identity of the Malay community. However, with the advancement of globalization and technology, this traditional music faces challenges in maintaining its relevance, particularly among the younger generation who tend to gravitate more towards modern music.
Social media platforms such as YouTube, Instagram, Facebook, and TikTok have emerged as significant channels for promoting and disseminating traditional Malay music to a global audience. These platforms not only provide spaces for traditional musicians to share their performances, but also serve as mediums for documentation and direct engagement with younger audiences from diverse cultural backgrounds. By employing creative approaches that align with modern interests and lifestyles, social media offers valuable opportunities to present traditional music in more engaging and appealing formats.
1. Traditional
Traditional arts are often regarded as expressions and cultural identities rooted in the wisdom and uniqueness of a particular community. In addition, traditional arts have existed and evolved through customs and practices within society, playing a vital role in preserving social collectivity. They are also associated with activities believed to integrate physical expression with elements of the mystical, serving as a bridge between ritual values and the concept of moderation (Nurhasanah et al., 2021).
1.1. Traditional Malay
1.1.1. Definition and History
According to Award (2023), traditional music is often regarded as a universal language capable of transcending cultural boundaries and uniting communities. For centuries, music has been used as a medium to celebrate cultural events, express emotions, and preserve as well as transmit cultural traditions. As a medium that crosses cultural frontiers, music serves not only as a form of entertainment but also as a vehicle for conveying values, customs, and historical narratives to future generations, thus ensuring the continuity of cultural heritage.
1.1.2. Traditional Malay Musical Instrument
Malay music is one of the most treasured cultural heritages, featuring a variety of traditional musical instruments that play significant roles and serve specific functions in various aspects of Malay community life. The following are several traditional Malay musical instruments (Understanding the Rich Heritage of Malay Music: Traditional Musical Instruments and Their Functions, 2024).
- i.
Gamelan Melayu
The Gamelan Melayu is a musical ensemble consisting of various instruments such as the gong, saron, kenong, and bonang. This ensemble is often performed in a variety of cultural contexts, including traditional ceremonies, wedding celebrations, and cultural events.
- ii.
Kompang
The kompang is a traditional musical instrument played by striking it with the palm of the hand. It is commonly used during events such as the Maulid Nabi (the celebration of the Prophet Muhammad’s birthday), weddings, and thanksgiving ceremonies.
- iii.
Rebab
The rebab is a bowed string instrument with two or three strings. It plays a vital role in traditional Malay music, particularly in accompanying traditional dances such as the Zapin.
1.2. Characteristics of Traditional Malay Music
1.2.1. Melody and Rhythm
Traditional music such as gamelan, zapin, and keroncong reflects the cultural values and creativity of the Malay community, where each musical element carries its own meaning. Studies on musical sound reinforce the view that music is an autonomous entity that plays a vital role in preserving cultural heritage (Jahnichen & Chieng, 2021).
1.2.2. Use of Acoustic Musical Instruments
Traditional Malay music primarily uses handcrafted acoustic instruments such as the gendang, serunai, rebab, and gong, which produce natural sounds. These instruments contribute to the music’s unique identity and highlight its strong connection to nature.
For instance, the rebab plays a significant role in various forms of traditional performances and symbolizes the refinement of Malay culture. According to Matusky & Tan Sooi Beng (2017), natural materials such as wood and animal skin are commonly used in the making of these instruments, demonstrating the connection between musical art and elements of nature.
1.3. Social Media
According to Barger (2024), social media serves as an effective platform for building relationships with audiences and customers, enhancing the quality of customer service, increasing awareness of products or services, and supporting marketing and sales activities.
1.3.1. Types of Social Media
- i.
Facebook
These platforms support the democratization of music by introducing artists who may be unfamiliar to users but have the potential to be appreciated based on their listening habits. Through algorithms that analyze listening patterns, users are provided with artist recommendations that align with their musical interests, thereby offering opportunities to discover a wider variety of music and enriching the listening experience. This approach benefits not only listeners but also provides emerging artists with the chance to reach a broader audience (Hutchison, 2012).
- ii.
Instagram
Instagram provides photo editing tools that allow users to enhance image quality, add captions, and comment on pictures. The name “Instagram” is a combination of the words “instant” and “telegram,” reflecting the app’s ability to facilitate fast and intuitive interactions. Launched on October 6, 2010, Instagram has brought about significant changes in the way users share visual content, making it one of the leading platforms in the digital world (Mattern, 2016).
- iii.
Tiktok
This application offers a variety of tools for content creators, including visual filters similar to those found on Snapchat and options to select background sounds or music for videos. Additionally, TikTok encourages user interaction through features such as “reply” or “duet” videos, where users can replicate original content while creatively adding their own elements. This approach has made TikTok a highly interactive and engaging platform within the social media landscape (Herrman, 2019).
- iv.
Youtube
According to Fuchs (2017), YouTube is owned by Google, and the revenue generated through online advertising on YouTube does not directly belong to content creators, but to Google’s shareholders. YouTube is an online video-sharing platform that allows users to upload, watch, share, and comment on videos.
1.4. The Role of Social Media in Traditional Malay Music
1.4.1. A Platform for Cultural Heritage Preservation
Social media platforms such as YouTube, Facebook, and Instagram provide a space for traditional Malay musicians to share their performances with a global audience. This facilitates the documentation and dissemination of traditional music, thereby introducing this cultural art form to younger generations who may have limited direct exposure to such traditions. The role of social media in promoting the heritage of traditional music also broadens access to Malay cultural arts, reinforcing the continuity of tradition in the modern era (Saari, 2010).
1.4.2. Increasing Awareness and Popularity
Social media platforms such as YouTube and Instagram play a vital role in increasing awareness and appreciation of traditional Malay music among the younger generation. By offering engaging features like video sharing, tutorials, and interactive tools, these platforms make traditional music more accessible, relevant, and appealing. They also serve as effective channels for promoting cultural heritage to a global audience (Hutchison, 2012).
Research Methodology
Research methodology refers to the overall philosophical framework within which research is conducted (Brown, 2006). The term “research” implies a systematic investigation into a particular topic. One definition of research is the scientific and methodical inquiry into a subject. The research methodology serves as the foundation of this study and plays a crucial role in ensuring the effectiveness and accuracy of the analysis related to the younger generation and society.
Research Design
This study employs a quantitative approach as its primary research design. The quantitative method is chosen because it allows for the collection of statistically measurable data and offers objective and systematic analysis. This approach is suitable for gathering large-scale data related to the topic, “The Role of Social Media in the Preservation of Traditional Malay Music Among the Younger Generation.”
Quantitative research focuses on the collection and analysis of numerical data. In this approach, data is collected through instruments such as surveys, questionnaires, or objective measurements involving numerical calculation and statistical analysis. The data obtained is then analysed using statistical techniques to systematically organise and interpret the research findings.
Sampling Method and Respondents
Sampling in this study involves the selection of individuals from the younger generation who use social media to understand the role of digital platforms in the preservation of traditional Malay music. The sample represents youths aged between 15 and 25 years old. It includes social media users on platforms such as TikTok, Instagram, Facebook, and YouTube, regardless of whether they come from urban or rural backgrounds, as long as they have access to the internet.
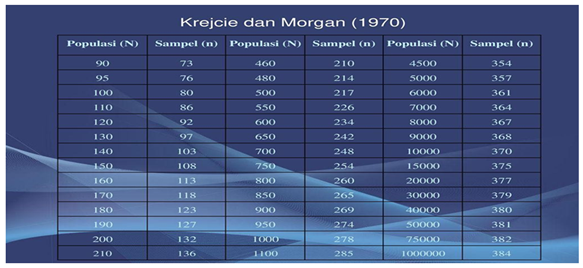
Sampling is a method used to collect information about individuals from a larger population. A population refers to a group of individuals, objects, or events that share certain characteristics of interest to the study. In this research, the study population consists of 100 individuals from the younger generation.
The researcher referred to the Krejcie and Morgan (1970) table as a guideline to determine an appropriate sample size for the study population. This table was used to ensure that the sample size would be sufficient to produce accurate and reliable findings. Based on Table 7 in Krejcie and Morgan’s (1970) study, a population of 100 individuals was identified, and the sample size for this research was determined to be 80 individuals.
Research Instrument
The primary data collection method in this study will be conducted through a survey approach. This survey involves the preparation of an online questionnaire (Google Form) containing a wide range of questions aligned with the objectives of the study. The questionnaire will explore respondents’ demographic aspects as well as specifically examine the involvement of the younger generation in the use of social media for traditional Malay music.
This study employs the Likert scale as the primary measurement tool to examine how social media expands the exposure of traditional music to the younger generation. The Likert scale is a widely used approach in quantitative research that allows respondents to express their level of agreement with various statements using a graded rating scale, as shown in
Table 1 below:
This study adopts a quantitative approach, enabling large-scale data collection in an objective and systematic manner through a structured questionnaire based on a Likert Scale. The instrument consists of 20 questions divided into four main sections: respondent demographics, the extent of exposure to traditional Malay music through social media, commonly used platforms, and challenges in promoting traditional music. The sample size was determined using Krejcie and Morgan’s table (1970), with 80 respondents selected from a population of 100. Data were analyzed using Microsoft Excel to generate descriptive statistics such as frequency, percentage, and mean. Additionally, secondary data collection was conducted through online sources such as journals, articles, official websites, and blogs to strengthen the understanding and context of the findings. The combination of primary and secondary data provides a comprehensive overview of the role of social media in preserving traditional Malay music among the younger generation.
Data Analysis Method
In this study, descriptive statistical techniques are used to analyze data obtained from the questionnaire. The data collected through the Likert scale are analyzed to identify patterns, trends, and distributions of respondents’ responses in examining the role of social media in preserving traditional Malay music.
In addition, visual tools such as pie charts or bar graphs may be used to illustrate the percentage distribution of responses for each question. This allows the researcher to easily identify dominant patterns among respondents, which may indicate trends in the use of social media for introducing traditional music. For example, if the majority of respondents state that they frequently use the TikTok platform, this will be clearly presented in a graphic format that integrates the percentage data.
Research Finding
Respondent Demographic Profile
Out of the 100 respondents involved in this study, (60%) were female while the remaining (40%) were male. This finding indicates that female respondents were more active in participating in the online questionnaire. This gender difference may reflect varying levels of interest, awareness, or inclination towards the use of social media in the preservation of traditional Malay music.
Based on the demographic analysis, the majority of respondents were aged between 21 and 23 years, accounting for (51%) of the total sample. Respondents aged between 24 and 25 years comprised (24%,) followed by 18–20 years at (15%), and the remaining (10%) were aged between 15 and 17 years. This diverse age representation provides a comprehensive view of the younger generation’s perspectives on the role of social media in preserving traditional music, particularly among early adulthood groups.
This study also involved respondents from various ethnic backgrounds. A total of 41 respondents (41%) were Bumiputera from Sabah and Sarawak, while 35% were of Malay ethnicity. Respondents from the Indian community accounted for 13%, and the Chinese community was represented by 11%. This ethnically diverse composition reflects the multicultural nature of Malaysia’s youth and offers a broader perspective on the acceptance and engagement of different ethnic groups in efforts to preserve traditional Malay music through social media platforms.
Realibility Analysis
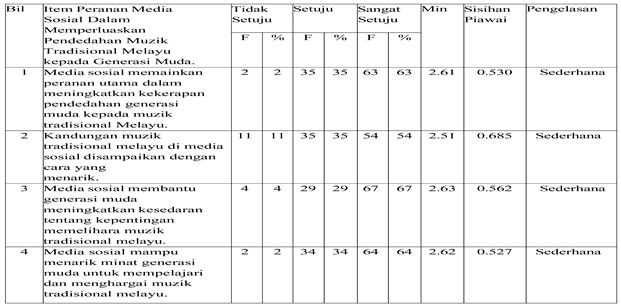
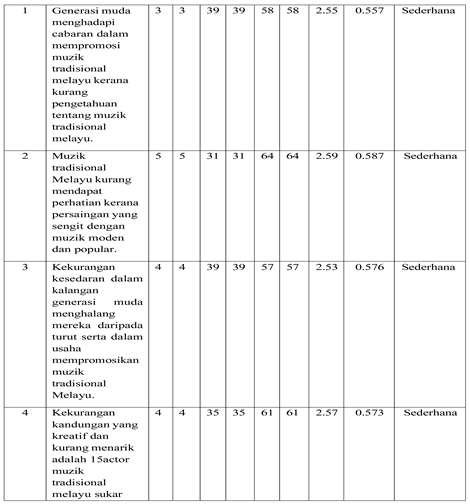
Social media plays an important role in expanding the exposure of traditional Malay music to the younger generation, with all survey items recording mean values at a moderate level (2.51–3.50). The most prominent aspect is the role of social media in raising awareness about the importance of preserving traditional music, where (67%) of respondents strongly agreed and (29%) agreed, reflecting the recognition of social media as a medium for cultural empowerment. Additionally, 54% of respondents strongly agreed and (35%) agreed that the presentation of traditional music content on social media is engaging; however, the low mean score (2.51) indicates a lack of visual appeal and interactive presentation. In terms of frequency of exposure, (63%) strongly agreed and (35%) agreed that social media effectively introduces traditional music to the younger generation. Meanwhile, for the item related to interest and appreciation, (64%) strongly agreed and (34%) agreed that social media is capable of attracting young people’s attention. Overall, social media is seen as an effective platform for delivering and promoting traditional Malay music, but content strategies need to be enhanced to be more creative and aligned with the digital preferences of today’s youth.
Table 1.
Social Media Helps Broaden the Exposure of Traditional Malay Music. Petunjuk: F= Kekerapan, %= Peratus.
Table 1.
Social Media Helps Broaden the Exposure of Traditional Malay Music. Petunjuk: F= Kekerapan, %= Peratus.
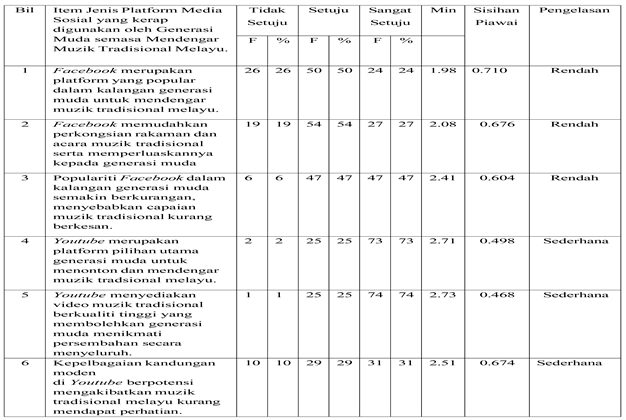
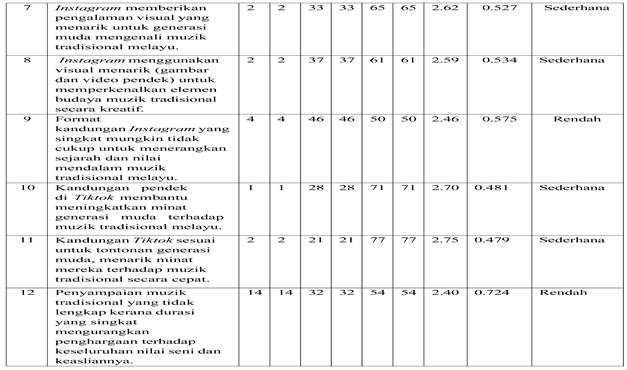
Table 2.
The Use of Social Media Platforms by the Younger Generation in Listening to Traditional Malay Music. Petunjuk: F= Kekerapan, %= Peratus.
Table 2.
The Use of Social Media Platforms by the Younger Generation in Listening to Traditional Malay Music. Petunjuk: F= Kekerapan, %= Peratus.
This section evaluates the preferences of the younger generation toward various social media platforms in enjoying traditional Malay music. Findings reveal that YouTube and TikTok are the most effective platforms, recording the highest mean scores (2.73 and 2.75), indicating their popularity due to easy access, high visual quality, and relaxed presentation styles. YouTube is recognized for offering high-quality and comprehensive content, while TikTok quickly attracts interest with short, engaging video though there are concerns about its limitations in conveying deeper artistic and cultural values. Instagram also shows moderate effectiveness in visual engagement, with mean scores around (2.59–2.62). However, its brief content format is seen as insufficient for delivering in-depth information about traditional music. In contrast, Facebook recorded the lowest mean scores (1.98–2.41), indicating that it is less relevant among the younger generation due to limited interactivity and less appealing visual content. Overall, the study suggests that promotional efforts for traditional Malay music should focus on platforms like YouTube, TikTok, and Instagram, which align better with the digital lifestyles of today’s youth while ensuring that the content remains engaging, high-quality, and informative.
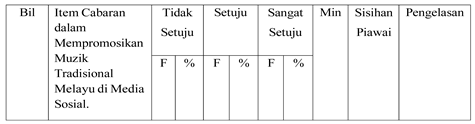
Table 3.
Challenges in Promoting Traditional Malay Music on Social Media. Petunjuk: F= Kekerapan, %= Peratus.
Table 3.
Challenges in Promoting Traditional Malay Music on Social Media. Petunjuk: F= Kekerapan, %= Peratus.
This questionnaire includes Section D, which focuses on the challenges in promoting traditional Malay music on social media. This section aims to identify the difficulties faced by the younger generation in promoting traditional Malay music through digital platforms. Several major challenges in promoting traditional Malay music on social media. The main issue is competition from modern music, with (64%) of respondents strongly agreeing and (31%) agreeing. A lack of engaging content was noted by (61%) strongly agree and (35%) agree, while (58%) strongly agreed and (39%) agreed that limited knowledge about traditional music hinders youth participation. Lastly, (57%) strongly agreed and (39%) agreed that low awareness is also a challenge. These results underscore the need for creative, informative, and youth-friendly strategies to enhance the appeal and visibility of traditional Malay music in the digital age.
Discussion
This study successfully addressed all three research objectives. Firstly, social media platforms such as TikTok, Instagram, YouTube, and Facebook were found to significantly enhance exposure to traditional Malay music among the younger generation through interactive and accessible content. Secondly, YouTube and TikTok emerged as the most frequently used platforms, with YouTube offering in-depth content and TikTok attracting attention through concise and engaging videos. Lastly, the main challenge identified was the dominance of modern music, which overshadows traditional genres. These findings underscore the importance of strategic and innovative efforts to preserve and promote traditional Malay music in the digital era.
References
- Alat Muzik Tradisional - Kraftangan. (2022, October 28). Kraftangan.
- Awards, I. M. (2023). How Music Helps Preserve Cultural Heritage. InterContinental Music Awards. Available online: https://www.intercontinentalmusicawards.com/how-music-helps-preserve- cultural-heritage/.
- Barger, C. (2024). The Social Media Strategist: Build a Successful Program from the Inside Out.
- Brown, R. B. (2006). Doing your dissertation in business and management: the reality of researching and writing. Doing Your Dissertation in Business and Management, 1- 128.
- Cook, N. (2000). Music: A Very Short Introduction. In Amazon (1st edition). Oxford University Press.
- Fuchs, C. (2017). Social Media: A Critical Introduction.
- Hanafi, L. H., Mohamad Al-Bakri, Z., & Raja Shaharuddin, R. R. (2018). Hiburan: Muzik, Nyanyian, Nasyid Menurut Perspektif Fiqh dan Fatwa. Journal of Fatwa Management and Research, 3(1), 83–108. [CrossRef]
- Herrman, J. (2019). How TikTok Is Rewriting the World. Available online: http://res.tigerge.cn/20200713/%E8%A1%A5%E5%85%851%20How%20TikTok%2 0Is%20Rewriting%20the%20World.pdf.
- Hutchison, T. W. (2012). Web Marketing for the Music Business. In Routledge eBooks. [CrossRef]
- Jahnichen, G., & Chieng, J. (2021). Music Local Culture in Global Mind.
- Kautzar, A. (2019). Karakteristik Bentuk Musik Melayu Di Kota Palembang Pada Lagu Melati Karangan. Resital: Jurnal Seni Pertunjukan, 18(2), 88–94. [CrossRef]
- Mattern, J. (2016). Instagram. Google Books. Available online: https://books.google.com.my/books?id=0BvPDAAAQBAJ&printsec=frontcover#v=o nepage&q&f=false.
- Matusky, P. (1985). An Introduction to the Major Instruments and Forms of Traditional Malay Music. Asian Music, 16(2), 121– 182. [CrossRef]
- Matusky, P. A.,& Tan, S. B (2017). The music of Malaysia: The classical, folk, and syncretic traditions. Taylor and Francis.
- Memahami Kekayaan Warisan Musik Melayu: Alat Musik Tradisional dan Fungsinya. (2024). Jurnal Intelek Dan Cendikiawan Nusantara, 1(3), 3233-3241. Available online: https://jicnusantara.com/index.php/jicn/article/view/369.
- Mohd Hamizi, M. A. F. (2023). Penggunaan Media Sosial Sebagai Media Baharu dan Impaknya Terhadap Masyarakat Malaysia. Perspektif Jurnal Sains Sosial Dan Kemanusiaan, 15, 24–37.
- Nurhasanah, L., Siburian, B. P., & Fitriana, J. A. (2021). Pengaruh Globalisasi Terhadap Minat Generasi Muda Dalam Melestarikan Kesenian Tradisional Indonesia. Jurnal Global Citizen: Jurnal Ilmiah Kajian Pendidikan Kewarganegaraan, 10(2), 31–39. [CrossRef]
- Saari, N., Sarji, A., & Basri, F. K. H. (2010). Muzik dan pembangunan sosial: Paparan dasar industri hiburan dalam akhbar-akhbar di Malaysia. Jurnal Komunikasi, Malaysian Journal of Communication, 26(2), 47-65. Available online: https://journalarticle.ukm.my/1905/1/V26_2_4.pdf.
- Safir, R. (2020). Make your music video and put it online.
- Shah, S. M. (2013). Contextualizing the Transmission of Malaysian Traditional Music. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 93, 1000–1004. [CrossRef]
- Vizcaino-Verdu, A., Aguaded, I., & Contreras-Pulido, P. (2021). Understanding transmedia music on YouTube through Disney storytelling. Sustainability, 13(7), 3667. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/13/7/3667.
- Wang, J. (2021). Preservation and promotion of China’s musical cultural heritage . Heritage Science, 9(1). [CrossRef]
- Yusof, A., & Bidin, A. (2024). Perkembangan Seni Muzik Dalam Peradaban Islam Di Nusantara. Um.edu.my. Available online: https://jice.um.edu.my/index.php/JAT/article/view/7844/6056.
Table 1.
Three-Point Likert Scale for Survey Questions.
Table 1.
Three-Point Likert Scale for Survey Questions.
| Strongly Disagree |
Agree |
Strongly Agree |
| 1 |
2 |
3 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).