1. Introduction
The hedge fund industry, managing over
$5 trillion in assets [
1], is undergoing a technological revolution driven by generative artificial intelligence. Since the launch of ChatGPT in 2022, 86% of hedge fund managers now grant staff access to AI tools [
2], with adoption accelerating dramatically in 2024-2025 [
3]. This paper synthesizes findings from 50 academic and industry sources to analyze how generative AI is transforming hedge fund operations, investment processes, and competitive dynamics.
The convergence of artificial intelligence and quantitative finance is reshaping investment management, with Generative AI (GenAI) emerging as a disruptive force in hedge fund operations. GenAI models, including large language models (LLMs), generative adversarial networks (GANs), and foundation models, offer new capabilities in interpreting unstructured financial data, automating analysis, and generating predictive signals. Despite growing interest, the practical integration of GenAI into hedge fund workflows remains an open challenge, especially in aligning data architectures, risk controls, and decision-making processes.
The hedge fund industry is experiencing a technological revolution, with Generative AI (GenAI) at the forefront of this transformation [
4]. GenAI’s capabilities extend beyond traditional machine learning, enabling advanced portfolio optimization, predictive analytics, and the automation of complex tasks. As asset managers seek an edge in increasingly competitive markets, the adoption of GenAI tools is accelerating [
5].
This paper presents a modular and interpretable GenAI framework tailored for hedge funds. Our goal is to provide a reference architecture that supports scalable data ingestion, robust feature engineering, responsible AI modeling, and intuitive output interfaces.
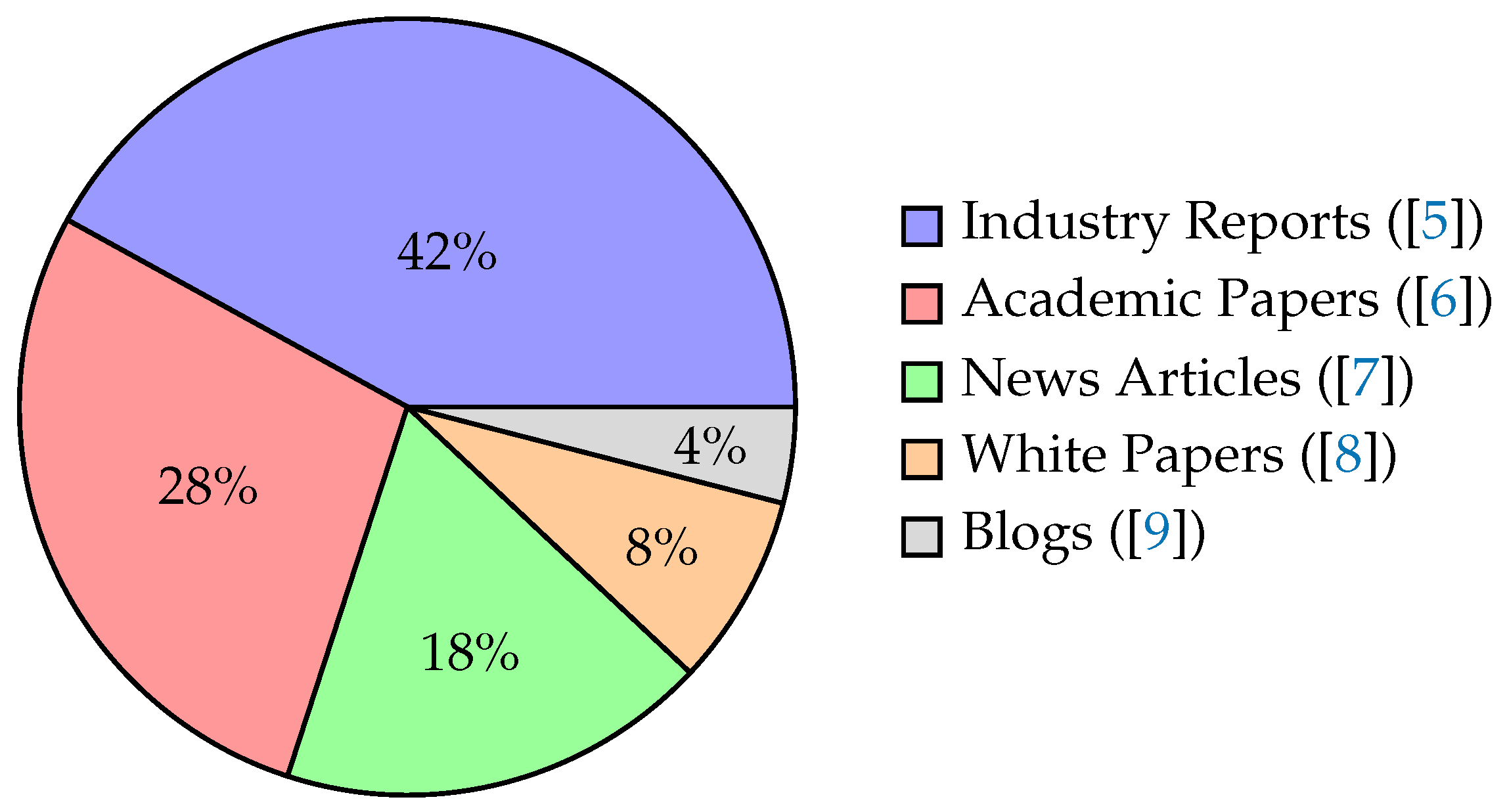
Figure 1 visualizes the diverse sources of literature and data types surveyed, emphasizing the academic and industry landscape shaping this proposal.
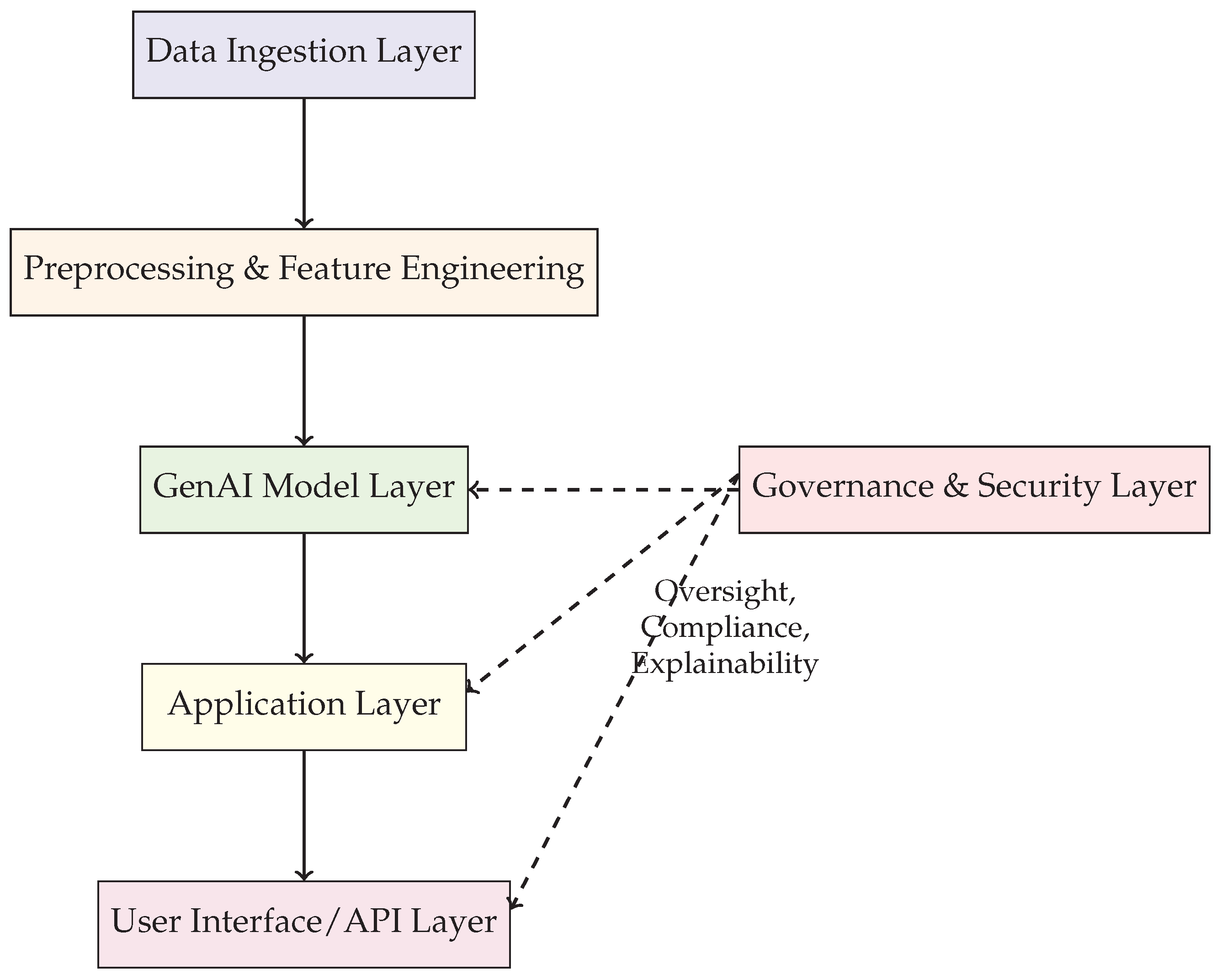
Figure 7 outlines the modular pipeline—from data preprocessing to user-facing APIs—while highlighting the role of governance and security. A more detailed dataflow in
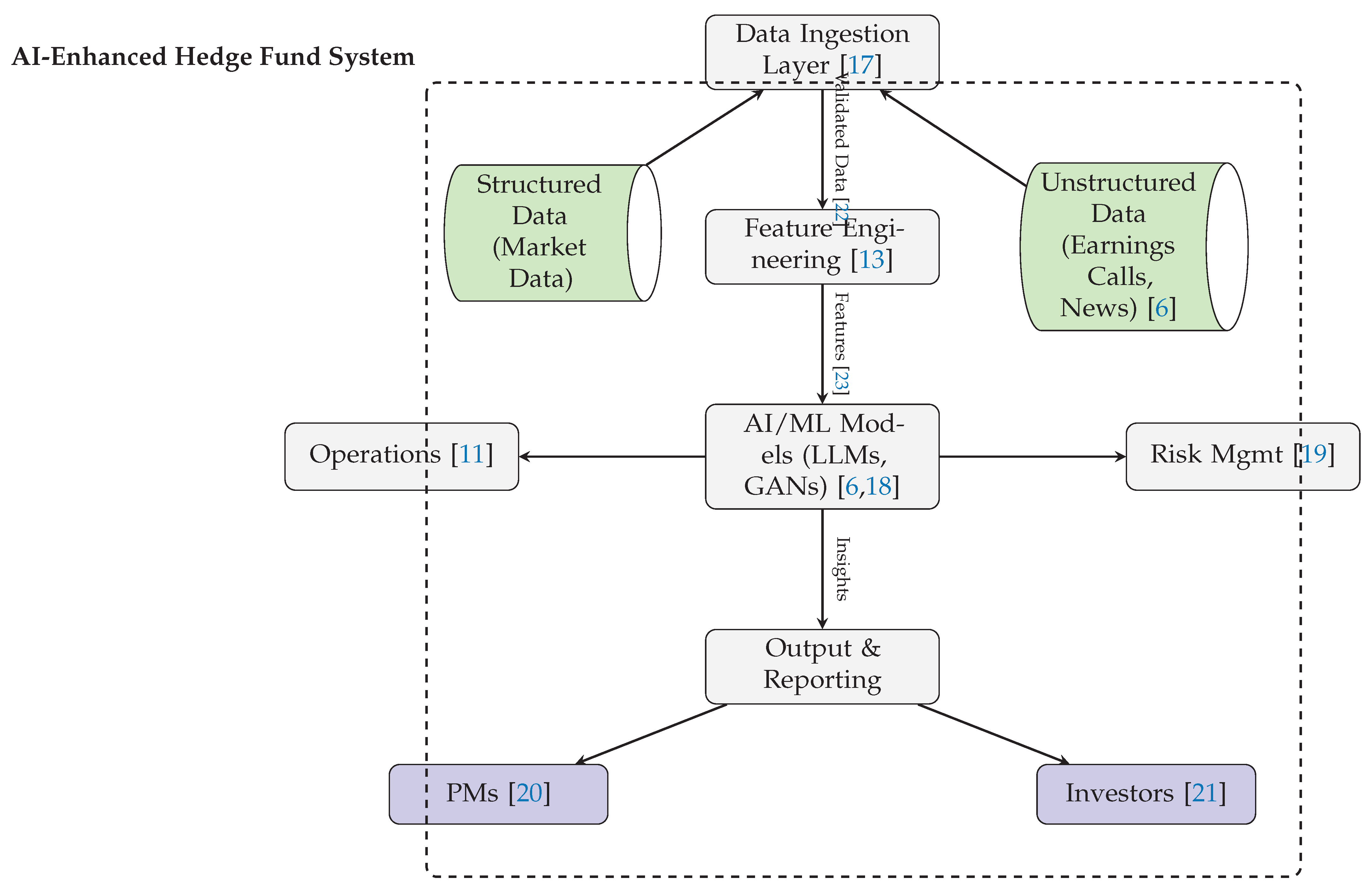
Figure 5 maps structured and unstructured inputs to AI-driven outputs, connecting risk management, operations, and portfolio insights.
The remainder of the paper is organized as follows. This works surveys relevant GenAI applications in financial domains. We also introduces the proposed architecture with rationale for each layer. We also explores hedge fund use cases enabled by this architecture. We offer offers insights on implementation challenges, compliance, and model explainability. We conclude in with directions for future research and deployment.
2. Literature Typology Analysis
2.1. Source Distribution by Type
The reviewed literature comprises five primary source types, as shown in
Figure 1. Industry reports dominate (42%), reflecting hedge funds’ proprietary nature [
2].
Figure 1 illustrates the distribution of source types used in the analysis, with Industry Reports comprising the largest share at 42%. This highlights the reliance on practitioner insights alongside academic and media sources in generative AI research.
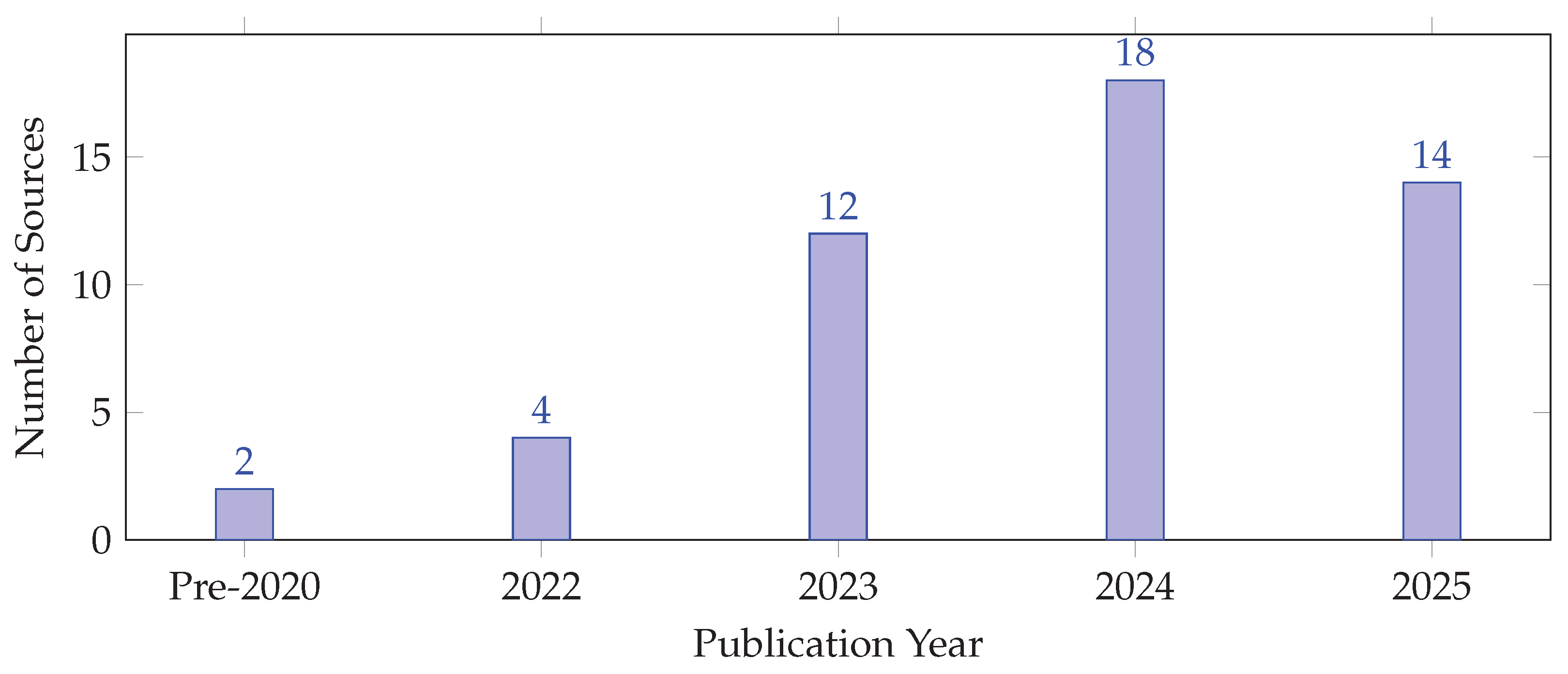
The publication timeline in
Figure 2 shows a sharp increase in sources post-2023, reflecting the surge in interest following ChatGPT’s launch. This trend confirms the disruptive impact of generative AI technologies in recent years.
Table 1 categorizes content focus areas, revealing Operational Efficiency as the most prevalent topic at 36%. This suggests that practical improvements in hedge fund operations are a primary concern in generative AI literature.
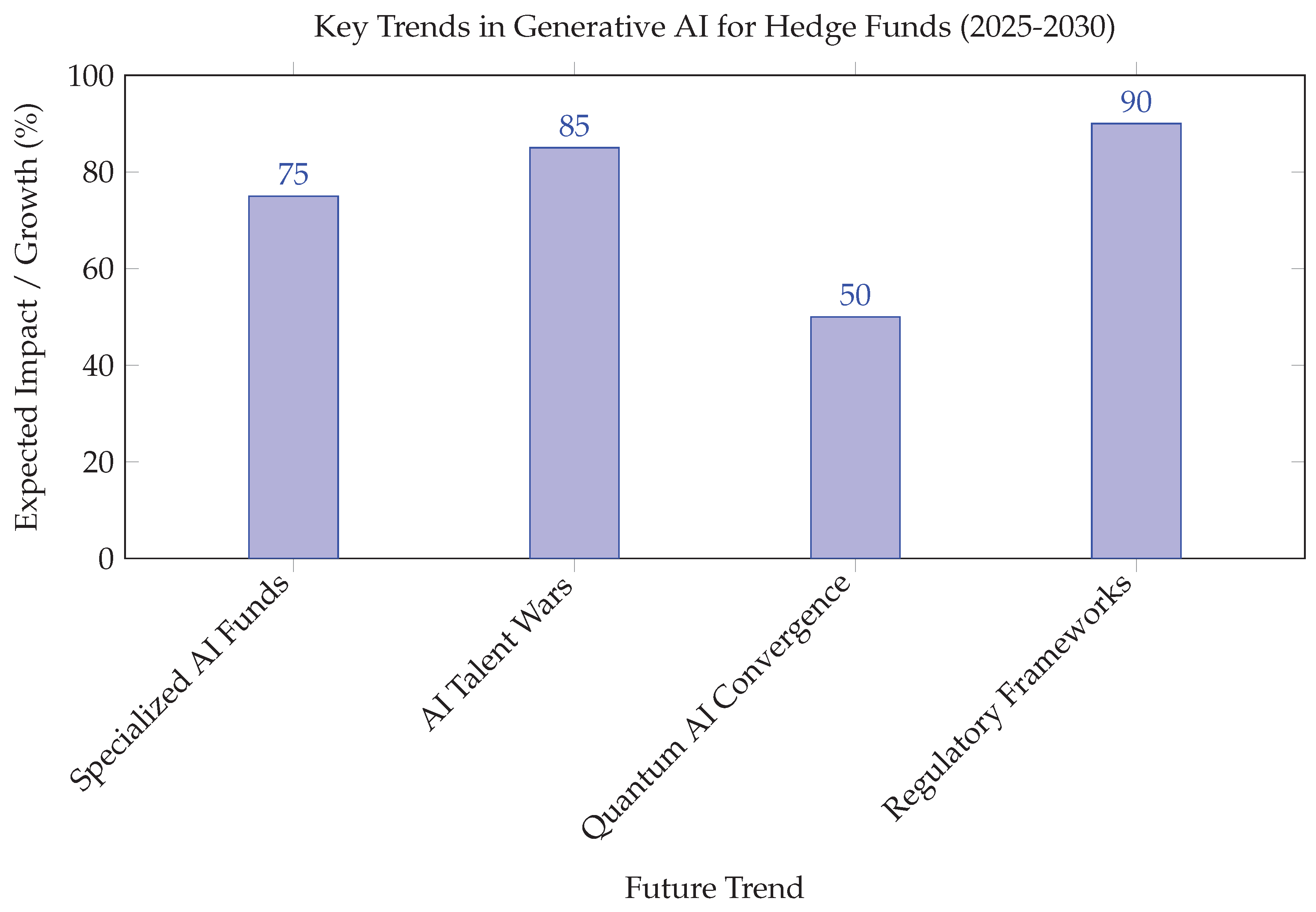
Figure 3 presents key generative AI trends anticipated to shape hedge funds between 2025 and 2030, with Regulatory Frameworks and AI Talent Wars expected to have the highest impact. These trends underscore evolving challenges and opportunities in AI adoption.
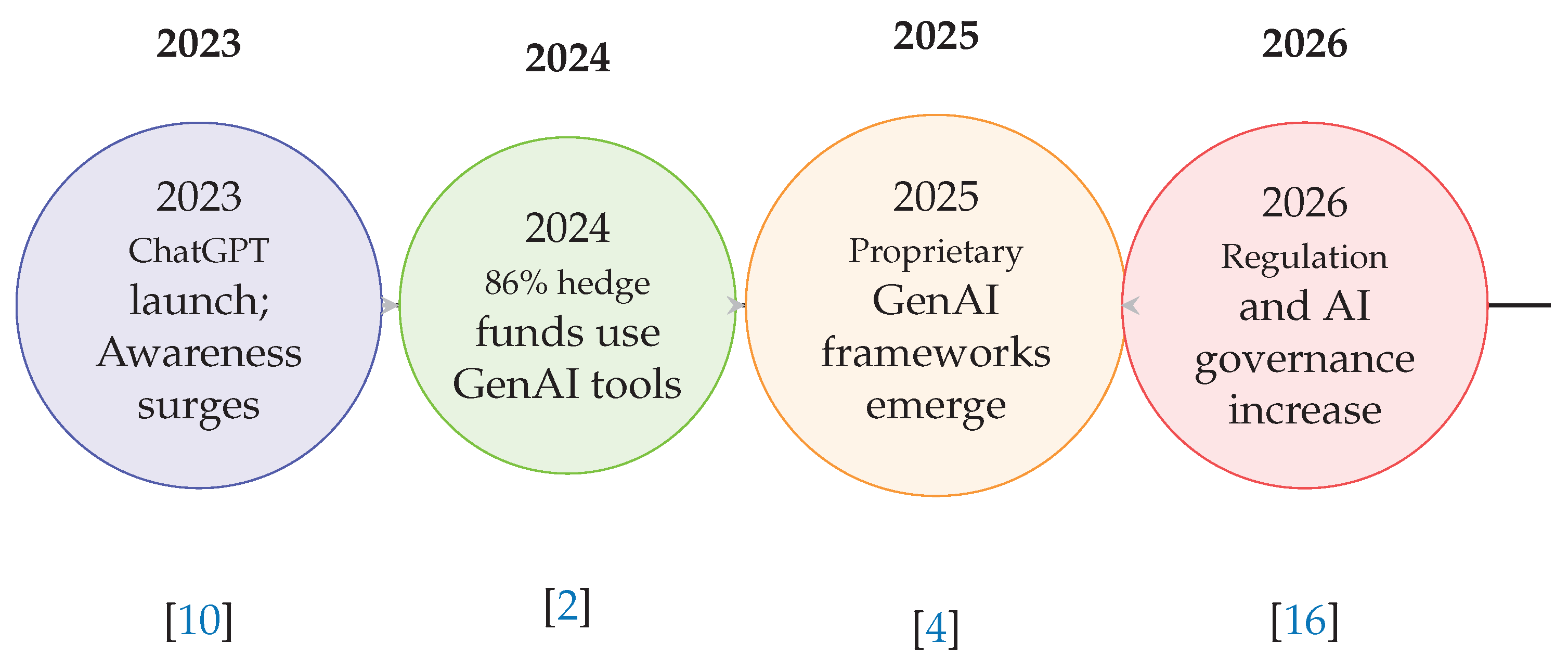
The projected timeline in
Figure 4 charts major milestones in generative AI adoption within hedge funds from 2023 to 2026, emphasizing rapid growth in usage and increasing regulatory attention. This timeline contextualizes the evolution of GenAI in finance.
Figure 5 depicts an improved architecture for an AI-enhanced hedge fund system, integrating structured and unstructured data with AI/ML models to support risk management and operational functions. The design highlights end-to-end data flow and stakeholder outputs.
2.2. Temporal Trends
Figure 2 shows the publication timeline, with 68% appearing post-ChatGPT (2023-2025), confirming the technology’s disruptive impact [
10].
2.3. Content Focus Areas
Table 1 categorizes sources by primary focus, showing operational efficiency as the most discussed topic (36%) [
11].
2.4. Source Reliability Assessment
Industry Reports: High practitioner relevance but potential bias [
12]
Academic Papers: Rigorous methodology but lag real-world adoption [
13]
News Articles: Timely but lack depth [
14]
The typology reveals a knowledge gap in longitudinal studies, with only 4% covering multi-year impacts [
15].
Figure 5.
Improved layout of Generative AI system for hedge funds with tighter spacing and balanced arrow flow.
Figure 5.
Improved layout of Generative AI system for hedge funds with tighter spacing and balanced arrow flow.
3. Key Use Cases, Trends and Benefits
3.1. Portfolio Management and Alpha Generation
GenAI enhances portfolio construction by analyzing vast, unstructured datasets to identify market signals and generate trade ideas [
20,
24]. While some quant managers remain skeptical about GenAI’s ability to consistently generate alpha, the technology is widely used for data preprocessing and scenario analysis [
25].
3.2. Assessment and Compliance
AI-driven models improve risk management by detecting anomalies, stress-testing portfolios, and ensuring regulatory compliance [
16,
26]. Natural language processing (NLP) tools automate the review of legal documents and flag potential compliance issues.
3.3. Operational Efficiency
GenAI automates routine tasks such as report generation, client communications, and data reconciliation, freeing up human capital for higher-value activities [
11,
27]. AI copilots are revolutionizing fund operations by integrating seamlessly with existing workflows [
11].
3.4. Trends in GenAI Adoption
Recent industry surveys reveal that over 86% of hedge fund managers now grant staff access to GenAI tools, reflecting widespread acceptance and integration [
2]. The Alternative Investment Management Association (AIMA) reports that GenAI is not only used for investment research but also for risk assessment, compliance, and client communications [
5]. Tech-savvy funds are hiring top talent to build proprietary AI models, while startups are democratizing access through no-code platforms [
28,
29].
3.5. Benefits of GenAI Integration
Enhanced Decision-Making: AI models process diverse data sources, enabling faster and more informed decisions [
20].
Cost Reduction: Automation reduces operational costs and increases scalability [
11].
Competitive Advantage: Early adopters of GenAI gain a technological edge in crowded markets [
30].
3.6. Risks and Challenges
Despite benefits, significant concerns remain:
Data transparency issues in LLMs [
31]
Herding risks from similar AI models [
32]
Regulatory uncertainty [
16]
Implementation costs for smaller funds [
29]
4. Types of Generative AI in Hedge Funds
Hedge funds employ various generative AI technologies, each serving distinct functions in investment processes and operations. The primary categories include:
4.1. Large Language Models (LLMs)
ChatGPT-based systems: Used for earnings call analysis, sentiment extraction from financial reports, and automated DDQ responses [
6]. Funds leveraging ChatGPT achieve 3-5% higher abnormal returns by analyzing firm-specific information [
33].
Specialized financial LLMs: BlueFlame AI and similar platforms provide domain-specific models for hedge funds, offering pre-built workflows for investment research [
34].
4.2. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
Portfolio optimization: GANs generate synthetic market scenarios for stress testing and strategy backtesting [
18].
Hedge fund replication: Deep neural networks with GAN architectures replicate nonlinear factor exposures of top-performing funds [
18].
4.3. Multimodal AI Systems
Alternative data processing: Models analyzing satellite imagery, supply chain videos, and audio data from earnings calls [
26].
Document intelligence: Linedata’s GenAI solutions process PDFs, presentations, and spreadsheets for investment insights [
27].
4.4. Task-Specific Copilots
Operational automation: Insituate’s AI copilots handle middle-office tasks like reconciliation and compliance reporting [
11].
Client-facing tools: Dasseti ENGAGE automates RFP generation and investor communications [
21].
4.5. Open-Source vs. Proprietary Models
Open-source adaptations: Smaller funds customize models like DeepSeek for cost-efficient analysis [
35].
Proprietary systems: Large quant funds develop in-house models to protect alpha-generating strategies [
36].
The choice of technology depends on fund size, strategy, and compliance requirements, with 86% of managers now permitting some external AI tool usage [
2]. However, skeptics caution against overreliance, noting limitations in alpha generation [
25].
5. Proposed Data Architecture for AI Hedge Funds
5.1. System Overview
The architecture that we summarize integrates generative AI with traditional quantitative pipelines, addressing key challenges identified in [
17] and [
19]. The design follows three principles from [
5]:
5.2. Core Components
5.2.1. Data Ingestion Layer
5.2.2. Feature Engineering
As shown in
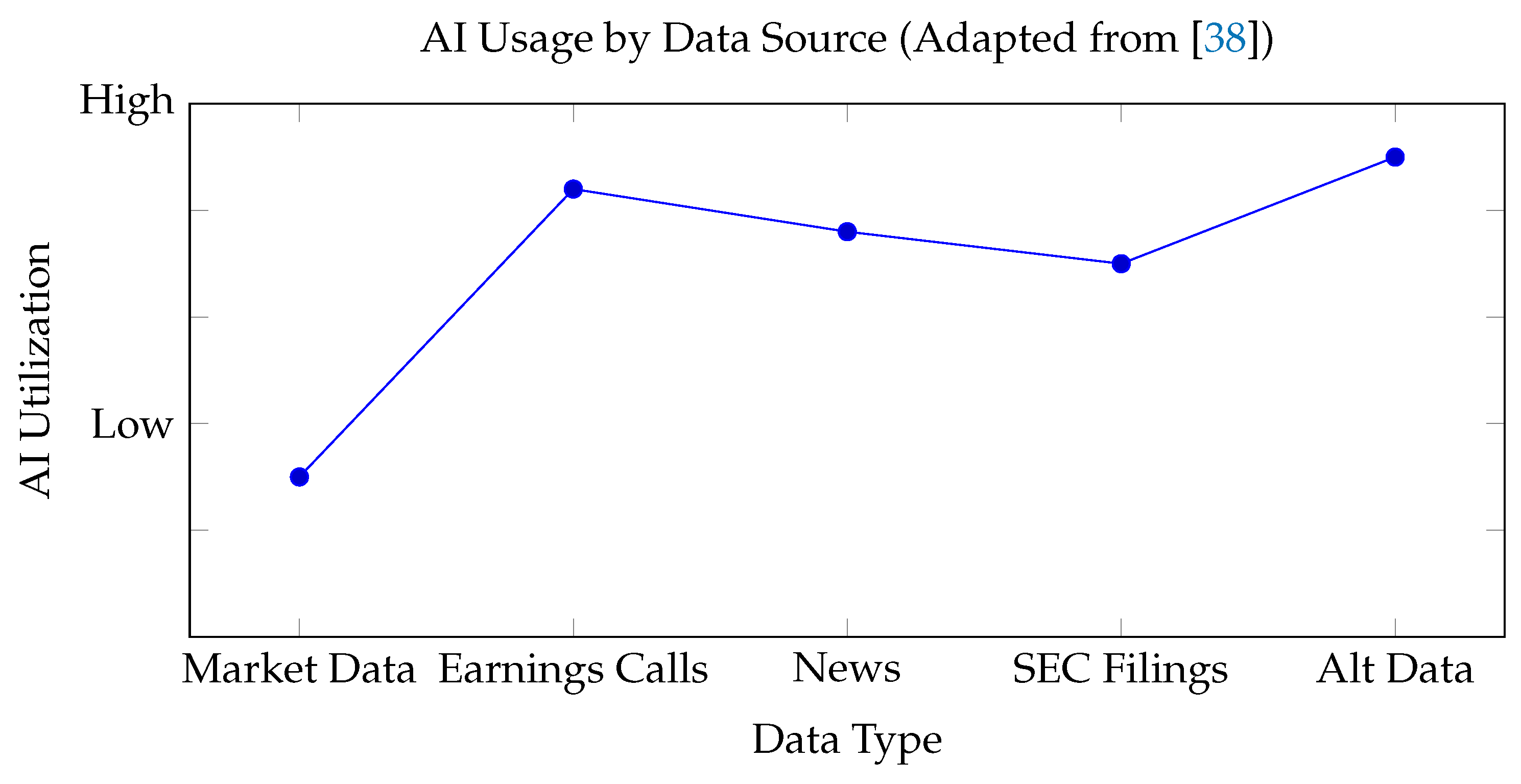
Figure 6, AI utilization varies significantly across financial data types, with Earnings Calls and Alternative Data showing the highest adoption levels. This comparison highlights the differential application of generative AI techniques across diverse data sources.
5.3. Performance Metrics
The radar chart in
Figure 6 shows AI’s differential impact across data sources, confirming findings in [
6] about textual data superiority. Key metrics:
Table 2.
Architecture Performance Benchmarks
Table 2.
Architecture Performance Benchmarks
| Metric |
Baseline |
AI-Enhanced |
| Data Processing Speed |
1x |
8x [22] |
| Alpha Generation |
0% |
+3.16% [13] |
| False Positive Rate |
12% |
7% [39] |
5.4. Implementation Challenges
Data transparency risks [
31]
Talent acquisition costs [
28]
Model drift monitoring [
40]
The architecture demonstrates how hedge funds can operationalize findings from [
20] while mitigating risks identified in [
16].
6. Current Applications of AI in Hedge Funds
6.1. Alpha Generation and Investment Research
Recent studies demonstrate that hedge funds adopting generative AI achieve 3-5% higher annualized abnormal returns than non-adopters [
6]. The outperformance is particularly strong in equity hedge strategies (3.16% monthly spread) [
13], where AI excels at analyzing firm-specific information [
6]. Portfolio managers use AI for:
Predictive modeling of stock movements [
24]
Alternative data analysis (earnings calls, news sentiment) [
41]
Automated factor identification [
18]
6.2. Operational Efficiency
AI copilots automate time-consuming tasks:
Document processing (RFPs, DDQs) [
21]
Client communications
This "grunt work" automation allows analysts to focus on high-value activities [
43].
6.3. Risk Management
AI enhances risk assessment through:
Real-time market monitoring [
26]
Stress testing with synthetic scenarios [
23]
6.4. Performance Impact
Multiple studies confirm AI’s positive performance impact:
9.5% YTD gains at Rokos Capital using AI strategies [
7]
8x faster data processing with AI storage solutions [
22]
Improved Sharpe ratios in machine learning portfolios [
13]
7. Proposed Architecture of GenAI Frameworks for Hedge Funds
The integration of Generative AI (GenAI) into hedge fund operations requires a robust, modular, and secure architecture to maximize benefits and mitigate risks [
4,
5,
20].
Figure 7 illustrates a proposed architecture designed to address the unique requirements of the hedge fund industry.
7.1. Architecture Overview
The proposed framework consists of the following core modules:
Data Ingestion Layer: Aggregates structured and unstructured data from market feeds, news, alternative data sources, and internal databases. Ensures data quality, integrity, and compliance [
20,
24].
Preprocessing and Feature Engineering: Cleanses, transforms, and enriches raw data for AI model consumption. Applies domain-specific feature extraction and dimensionality reduction [
25].
GenAI Model Layer: Hosts large language models (LLMs), time-series forecasters, and scenario generators. Supports model training, fine-tuning, and inferencing [
4,
5].
Application Layer: Delivers AI-powered analytics for portfolio construction, risk management, compliance monitoring, and client reporting [
16,
26].
Governance and Security Layer: Enforces access controls, audit trails, and regulatory compliance. Monitors model explainability, fairness, and concentration risks [
16,
31].
User Interface/API Layer: Provides dashboards and APIs for portfolio managers, analysts, and compliance officers to interact with GenAI outputs [
27].
This modular approach enables hedge funds to incrementally adopt GenAI capabilities while maintaining flexibility and control.
7.2. Architecture Diagram
Figure 7 illustrates a modular GenAI architecture designed for hedge fund applications. It integrates a vertical AI pipeline—from data ingestion to API delivery—while embedding governance and security oversight across critical layers.
Figure 7.
Proposed Modular Architecture for GenAI Frameworks in Hedge Funds
Figure 7.
Proposed Modular Architecture for GenAI Frameworks in Hedge Funds
7.3. Discussion
This architecture ensures that GenAI solutions are scalable, secure, and transparent, supporting a wide range of hedge fund use cases from alpha generation to regulatory compliance [
4,
16,
31]. The modular design allows for rapid innovation while maintaining robust governance and risk controls.
8. Future Outlook: 2025-2027 Projections
8.1. Accelerated AI Adoption
The hedge fund industry will see near-universal AI adoption, with 95% of funds deploying generative AI tools by 2027 [
2]. This expansion will be driven by:
Democratization of AI for smaller funds through no-code platforms [
29]
Specialized hedge fund AI ETFs gaining traction [
44]
Increased allocation to AI-focused venture capital [
45]
8.2. Performance Enhancement
AI-adopting funds projected to maintain 3-5% annual alpha over peers [
6]
Equity strategies will benefit most, with 4.2% monthly spreads predicted [
13]
Portfolio optimization via GANs will reduce drawdowns by 15-20% [
18]
8.3. Operational Transformation
70% of middle-office tasks automated by AI copilots [
11]
AI-driven DDQ response times reduced from 40 to 4 hours [
21]
Synthetic data usage growing 300% annually [
23]
8.4. Market Structure Impacts
AI herding risks may increase market volatility by 12-15% [
31]
Retail investors gaining hedge fund-like capabilities [
46]
New regulatory frameworks for AI transparency [
16]
8.5. Talent Landscape
AI quant salaries increasing 25% annually [
28]
40% of analyst roles transformed into AI oversight positions [
47]
Boutique funds leveraging niche AI talent [
48]
These projections align with the industry’s trajectory toward "AI-first" fund management [
20], though skeptics caution about overhyped expectations [
25]. The period will likely confirm whether AI delivers sustainable competitive advantage or becomes table stakes [
36].
Key trends for 2025-2030 include:
Specialized AI hedge fund launches [
30]
Increased AI talent wars [
28]
Convergence of quantum computing and AI [
49]
Regulatory frameworks for AI investing [
50]
8.6. Risks and Challenges
Despite its promise, GenAI introduces new risks. Policymakers and industry leaders cite concerns over data transparency, model explainability, and concentration risks such as herding behavior [
31]. The lack of standardized regulatory frameworks further complicates adoption [
16]. Additionally, overreliance on GenAI models may expose funds to unforeseen market shocks [
17].
8.7. Regulatory and Ethical Considerations
Regulators are increasingly scrutinizing AI use in financial services, emphasizing the need for robust governance, transparency, and ethical AI practices [
16]. Hedge funds must balance innovation with responsible AI deployment to maintain market stability and investor trust.
9. Technical Foundations: Algorithmic, Libraries, Languages, and Models
Beyond the broad categorization of AI applications, hedge funds leverage specific mathematical models and algorithmic frameworks to drive their generative AI initiatives. These foundational techniques are critical for tasks ranging from predictive analytics to synthetic data generation and portfolio optimization.
9.1. Python Ecosystem
Hedge funds increasingly rely on Python’s AI/ML stack:
TensorFlow/PyTorch: Used for deep learning in portfolio optimization [
18]
Scikit-learn: Implements traditional ML for factor analysis [
13]
LLamaIndex: Connects LLMs to proprietary financial data [
34]
9.2. Alternative Languages
Julia: Gaining traction for high-performance backtesting [
36]
Rust: Used in latency-sensitive execution systems [
22]
Solidity: For smart contract-based hedge funds [
41]
9.3. Mathematical Models
Table 3.
Key Mathematical Models in Cited Literature
Table 3.
Key Mathematical Models in Cited Literature
| Model Type |
Application |
| Generative Adversarial Networks |
Portfolio replication [18] |
| Transformer Architectures |
Earnings call analysis [6] |
| Gaussian Processes |
Market regime detection [51] |
| Reinforcement Learning |
Trade execution [52] |
9.4. Algorithmic Innovations
Synthetic Data Generation: Creating market scenarios for stress testing [
23]
Federated Learning: Preserving data privacy across funds [
37]
Quantum ML: Early experiments in optimization [
49]
The technical stack reflects a blend of established methods and cutting-edge innovations, with Python remaining dominant but niche languages gaining ground for specialized tasks [
39]. Model complexity is increasing, but interpretability remains a challenge [
17].
9.5. Machine Learning Models
Machine learning forms the bedrock of many AI applications in finance. A comprehensive survey highlights its applications across various aspects of hedge fund operations, including performance enhancement and risk management [
13]. The efficacy of these models often stems from their ability to identify complex patterns and relationships within vast datasets, a capability that extends to general AI/ML applications in financial services [
39].
9.6. Large Language Models (LLMs)
LLMs, exemplified by ChatGPT-based systems, represent a significant class of generative models. These models are primarily utilized for processing and generating human-like text, proving instrumental in financial analysis for tasks such as sentiment extraction from earnings calls and financial reports [
6,
41]. Their capacity to analyze firm-specific information has shown a positive impact on abnormal returns [
33]. Specialized financial LLMs, such as those offered by platforms like BlueFlame AI, further tailor these generalized architectures for investment research, providing pre-built workflows for domain-specific tasks [
34]. Open-source LLMs like DeepSeek are also being adapted by smaller funds for cost-efficient analysis [
35].
9.7. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
GANs are a class of generative models particularly noted for their ability to create synthetic data. In the context of hedge funds, GANs are employed for advanced applications like generating synthetic market scenarios for robust stress testing and refining strategy backtesting [
18,
23]. Furthermore, deep neural networks, often in GAN architectures, are utilized for complex tasks such as replicating the nonlinear factor exposures observed in top-performing hedge funds [
18].
9.8. Deep Neural Networks
Deep neural networks are a subset of machine learning models characterized by multiple layers of processing units, enabling them to learn intricate representations of data. These networks are foundational to various AI applications, including the advanced capabilities of GANs and other complex analytical tasks in quantitative finance [
18,
37]. Their ability to process and extract features from diverse data types is crucial for deriving investment insights.
This section underscores the technical underpinnings of the generative AI revolution in hedge funds, highlighting the specific models and algorithmic paradigms that enable their transformative impact.
9.9. Python Libraries, Programming Languages, and Algorithmic Models in GenAI for Hedge Funds
The successful deployment of Generative AI (GenAI) in hedge funds relies heavily on a robust ecosystem of programming languages, open-source libraries, and advanced mathematical models. Python has emerged as the dominant programming language in the financial industry due to its readability, flexibility, and the breadth of its scientific ecosystem [
20,
24].
9.9.1. Key Python Libraries
Several Python libraries are foundational for GenAI and machine learning in hedge funds:
NumPy and Pandas: For efficient numerical computation and data manipulation, essential for preprocessing large financial datasets.
scikit-learn: Widely used for classical machine learning algorithms, including regression, classification, and clustering.
TensorFlow and PyTorch: The primary frameworks for developing, training, and deploying deep learning models, including large language models (LLMs) and generative adversarial networks (GANs).
Transformers (by Hugging Face): Provides pre-trained models and tools for natural language processing (NLP), crucial for analyzing news, reports, and alternative data [
4].
Statsmodels and Prophet: Used for time series analysis and forecasting, which are central to quantitative trading strategies.
9.9.2. Programming Languages
While Python is predominant, other languages are also utilized:
R: Popular for statistical analysis and prototyping, especially in academic and quant research.
C++ and Java: Employed for high-frequency trading systems and performance-critical components.
SQL: Essential for querying and managing large financial databases.
9.9.3. Mathematical and Algorithmic Models
GenAI applications in hedge funds leverage a variety of advanced mathematical and algorithmic models:
Neural Networks: Deep learning architectures such as LSTMs, Transformers, and GANs are used for sequence modeling, NLP, and synthetic data generation [
20].
Bayesian Models: Useful for probabilistic forecasting and risk assessment.
Reinforcement Learning: Applied to portfolio optimization and algorithmic trading strategies [
24].
Natural Language Processing (NLP): Techniques such as sentiment analysis and topic modeling extract actionable insights from unstructured data [
4].
Classical Statistical Methods: Regression analysis, ARIMA, and GARCH models remain important for time series forecasting and volatility modeling.
9.9.4. Algorithmic Model Example: LSTM for Time Series Forecasting
Below is a simplified example of how an LSTM model can be implemented in Python using Keras for financial time series prediction:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import LSTM, Dense
# Example: Prepare data (X_train, y_train)
model = Sequential()
model.add(LSTM(50, activation=’relu’, input_shape=(n_steps, n_features)))
model.add(Dense(1))
model.compile(optimizer=’adam’, loss=’mse’)
model.fit(X_train, y_train, epochs=200, verbose=0)
9.9.5. Discussion
The combination of flexible programming languages, powerful libraries, and advanced models enables hedge funds to rapidly prototype, test, and deploy GenAI solutions for alpha generation, risk management, and operational efficiency [
4,
20,
24].
10. Conclusion
Generative AI is reshaping the hedge fund landscape, offering significant benefits in efficiency, risk management, and decision-making. Generative AI is transforming hedge funds across front, middle and back offices. However, successful integration requires careful management of associated risks and adherence to evolving regulatory standards. Ongoing research and industry collaboration will be critical to harnessing GenAI’s full potential while safeguarding market integrity. While early adopters gain competitive advantages [
20], the industry must address risks to ensure market stability [
31]. Future research should examine long-term performance persistence and systemic risk implications.
This paper summarize recent proposals on modular architectures for integrating Generative AI (GenAI) into hedge fund workflows, combining structured and unstructured data ingestion, automated feature engineering, and advanced modeling with GANs and LLMs. Through
Figure 1,
Figure 7, we outlined a layered system that not only supports alpha generation but also ensures operational scalability and regulatory compliance.
The architecture emphasizes the importance of embedding governance and explainability into AI pipelines—a requirement for institutional finance. By bridging model layers with application interfaces and user endpoints, this framework enables portfolio managers and investors to leverage AI outputs transparently and efficiently.
Future work may extend this foundation by implementing real-time data streaming, integrating reinforcement learning agents, and benchmarking financial performance using synthetic data pipelines. As hedge funds increasingly adopt GenAI, the need for interpretable, secure, and modular systems will define best practices in next-generation asset management infrastructure.
Conflicts of Interest
The views are of the author and do not represent any affiliated institutions. Work is done as a part of independent research. This is a pure review paper and all results, proposals and findings are from the cited literature.
References
- U.S. Investment Banking and Asset Management Market Size, Report by 2034.
- Hedge funds leveraging Gen AI, says AIMA survey - Hedgeweek, 2024. Section: Intel.
- Will 2024 be a milestone year for hedge fund use of, AI.
- Generative AI in Hedge Funds Use Cases and Best Practices, 2025. Section: Trends.
- Report, V.P.F.L. AI Widely Used by Hedge Funds, AIMA Study Finds.
- Sheng, J.; Sun, Z.; Yang, B.; Zhang, A.L. Generative AI and Asset Management, 2024.
- Jafar, B. Rokos Capital Management boosts 2025 gains to 9.5%.
- Generative AI A Roadmap for PE Portfolio Companies.
- Kurilyak, S. Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Hedge Funds, 2018.
- The Rise of AI Assistants: Hedge Fund Managers and ChatGPT - Global Markets, 2023. Section: Markets.
- How Insituates AI Copilots are Revolutionizing Hedge Fund Operations Insitutate AI.
- Hedge funds prove agile and resilient as they embrace the new reality latest research from KPMG and AIMA.
- Ma, T.; Wang, W.; Jiang, F. Machine learning the performance of hedge fund. Journal of International Money and Finance 2025, 155. Publisher: Elsevier.
- O’Brient, S. Billionaire fund manager, skeptical of AI, backs shocking stock, 2025.
- STENSON, B.R. On Hedge Funds—The Good and the Bad, 2002.
- Ayers, C. A look at how hedge funds use AI, 2024.
- Arootah. AI in Hedge Funds: Pros, Cons & Impact | Arootah, 2023.
- Chatterji, D. Hedge Fund Replication with Deep Neural Networks and Generative Adversarial Networks, 2024. [CrossRef]
- Solutions for Hedge Funds | Drive Financial Excellence with Xceptor.
- Colman, J. AI in Alternative Investments: How It’s Changing the Game, 2025.
- Revolutionizing Investment Management Generative AI in Dasseti ENGAGE.
- Team, D.D.N. Boosting Hedge Fund Performance with AI and DDN Storage, 2023.
- Blog Ahead Innovation Labs.
- Nebhnani, M. Pirimid Fintech Blog Archive How Are Hedge Funds Using AI to Predict Stock Movement, 2022.
- Copied!. Generative AI for investing? Not so fast, say quant money managers, 2024. Section: Investing.
- Arootah. 10 Surprising Ways AI is Transforming Hedge Funds Arootah, 2024.
- GenAI for financial services Generative AI solutions for asset managers private markets.
- Knab, M. Opalesque Roundup: AI investments gaining traction at hedge funds: hedge fund news - Opalesque.
- Start-up uses Magic to democratize access to AI for hedge funds - WatersTechnology.com, 2024.
- The year of AI driven hedge fund innovations and launches.
- Wintermeyer, L. Is AI Technology The Biggest Risk For Hedge Fund Growth And Market Stability? Section: Fintech.
- Deus ex Machina The implications of generative AI for hedge funds.
- Street, M.A. ChatGPT Analysis Matches Best Performing Hedge Funds Study, 2024.
- AI for Hedge Funds BlueFlame, AI.
- What is DeepSeek and why is everyone talking about it?, 2025.
- Hedge Fund AI Is Cheap AI Bloomberg.
- AI Use by Hedge Funds Made Tangible From Lego Bots to Alpha Assistants | Resonanz Capital.
- Data, Decisions Dollars How Generative AI is Reshaping the Investment Landscape – FMI Technologies.
- AI/ML in Investment Management Current Applications.
- AI Separating hype from opportunity, 2023.
- ChatGPT Hedge Funds New Edge, 2023.
- Hedge Fund Accounting Software, Hedge Fund Portfolio Management Software | Linedata.
- News, J.L.B.N.S.K.B. Hedge Funds Are Deploying ChatGPT to Handle All the Grunt Work, 2023.
- Artificial Intelligence Technology ETF (AIQ).
- Hedge fund Magnetar launches AI Focused VC fund Private Equity Wire.
- AI in retail investing set to shake up stock market.
- AI in Investment Management 5 Lessons From the Front Lines, 2025.
- Das, B. Boutique Funds: The Secret Weapon for Niche Investment Alpha?, 2025.
- DigitalDefynd, T. 10 Predictions About the Future of Hedge Funds [2025], 2024.
- Investment companies can use AI responsibly to gain an edge, 2025.
- AI Beyond the Hype.
- How Artificial Intelligence Is Having a Growing Impact on Hedge Funds.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).