Submitted:
09 June 2025
Posted:
10 June 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Setup & Preliminaries
2.1. Problem Formulation
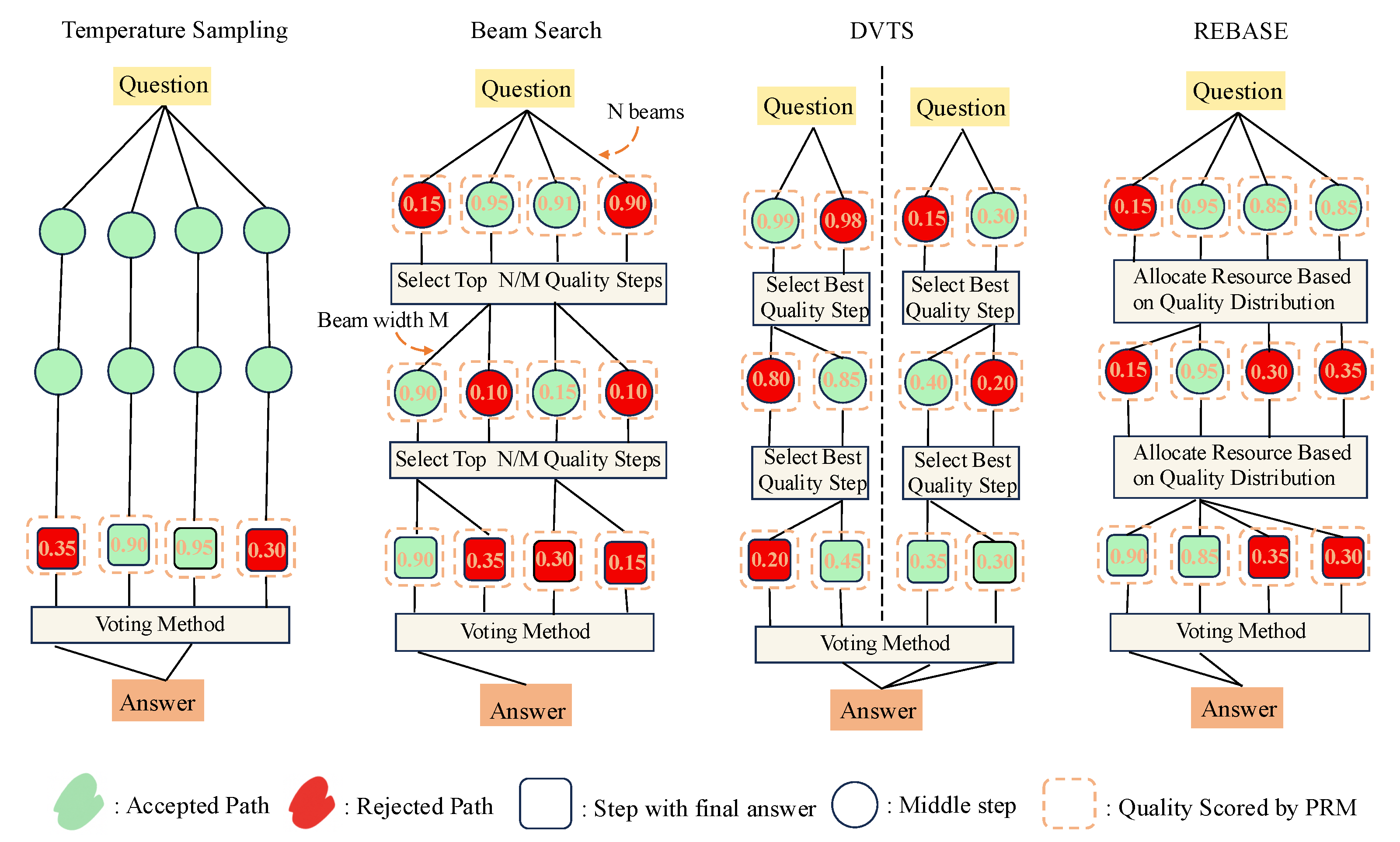
2.2. Parallel Search Method
2.2.0.1. Temperature Sampling.
Beam Search.
DVTS.
REBASE.
3. Optimal Parallel Search for Test-Time Scaling
Given a fixed rollout budget, how should one allocate resources across candidate reasoning paths to maximize performance (i.e., the success rate of achieving a correct solution)?
3.1. Theoretical Formulation of Optimal Resource Allocation
-
When , the optimal allocation assigns one rollout to each of the top- candidates with highest scores:with the remaining rollouts arbitrarily assigned.
- When , the optimal allocation converges to a deterministic allocation that assigns all rollouts to the highest-scoring candidate:
- When κ is fixed and finite, the optimal allocation approximately follows a shifted linear rule:
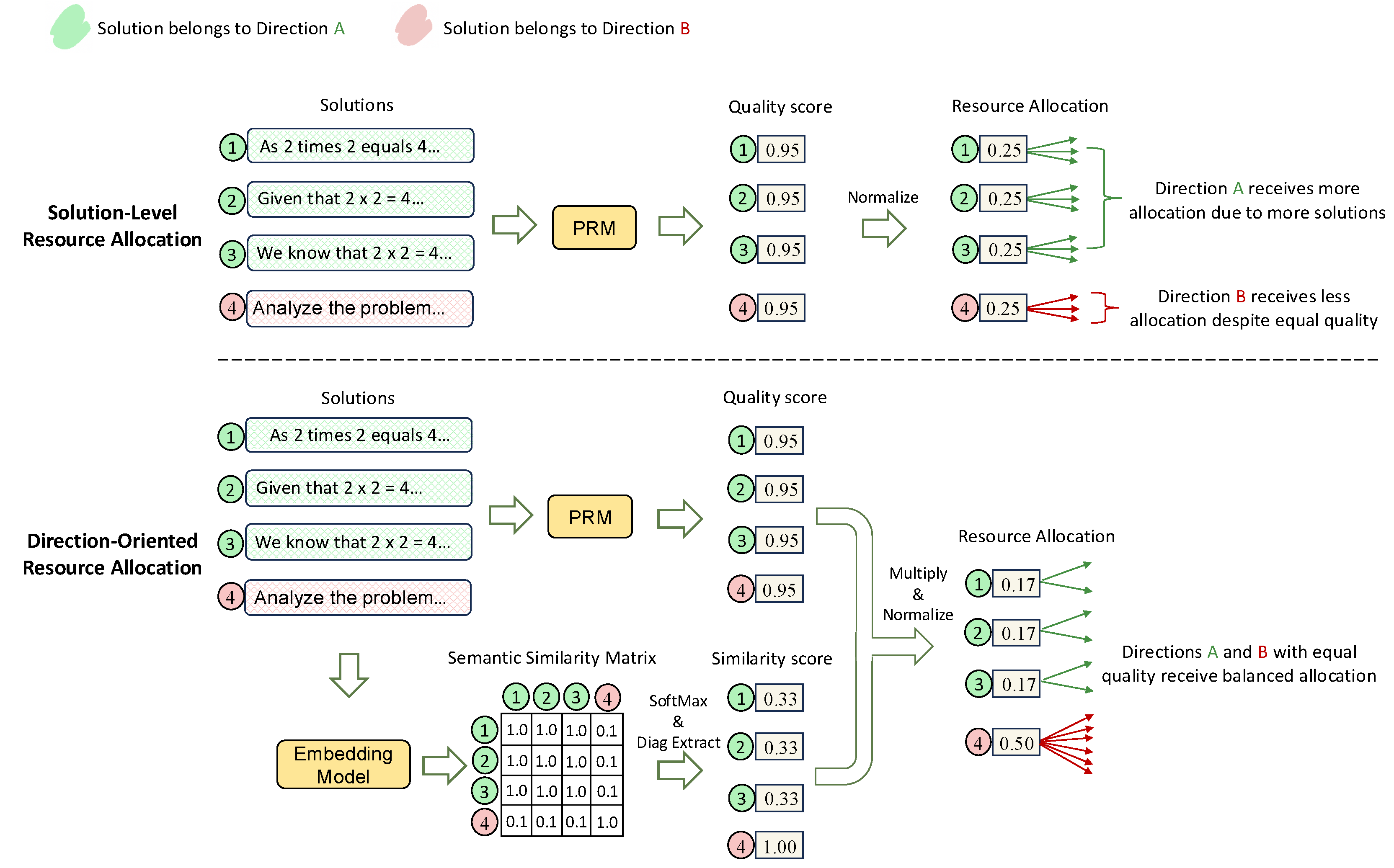
3.2. Suboptimality of Solution-Level Allocation
3.3. Direction-Oriented Resource Allocation (DORA)
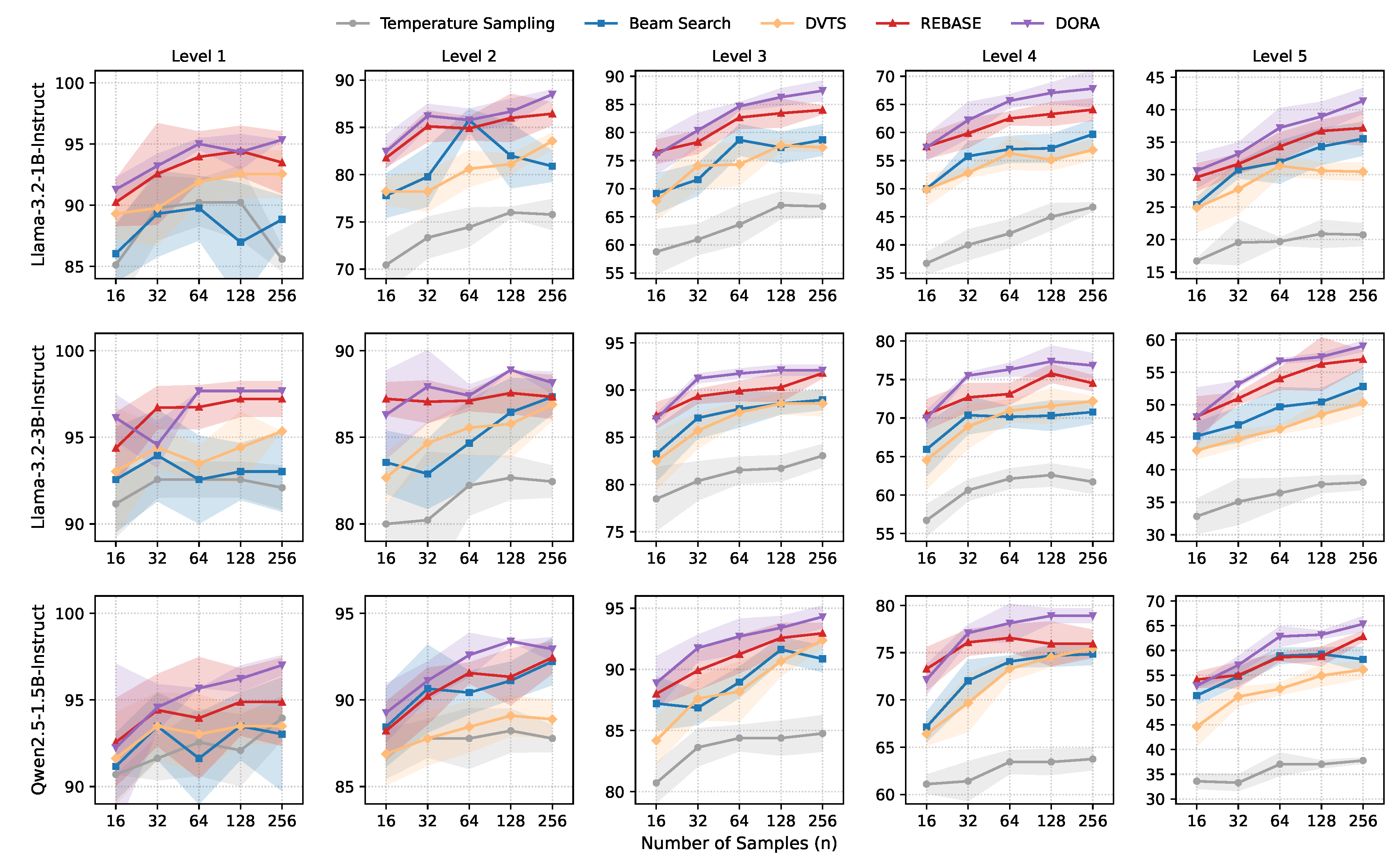
4. Experiments
4.1. Experimental Setup
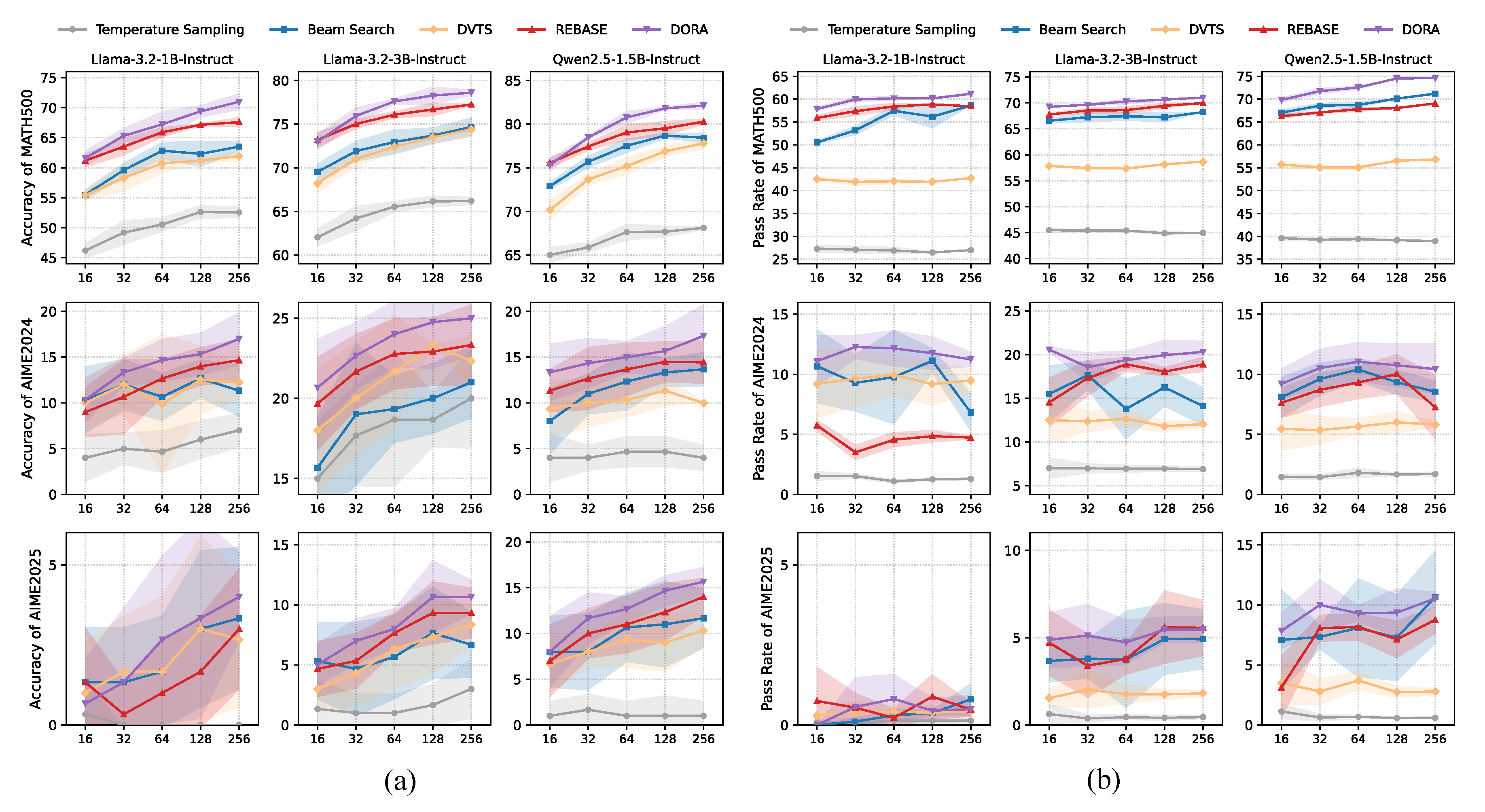
4.2. Main Results
4.3. Analysis
5. Related Work
5.0.0.5. LLM Test-Time Scaling.
5.0.0.6. Process Reward Models.
5.0.0.7. Mathematical Reasoning with LLMs.
6. Conclusions
Appendix A. Details of Parallel Search Process
| Algorithm A1:Parallel Search Process |
|
Appendix B. Proof Section
Appendix B.1. Proof of Proposition 1
Appendix B.2. Proof of Proposition 2
Appendix B.3. Proof of Theorem 1
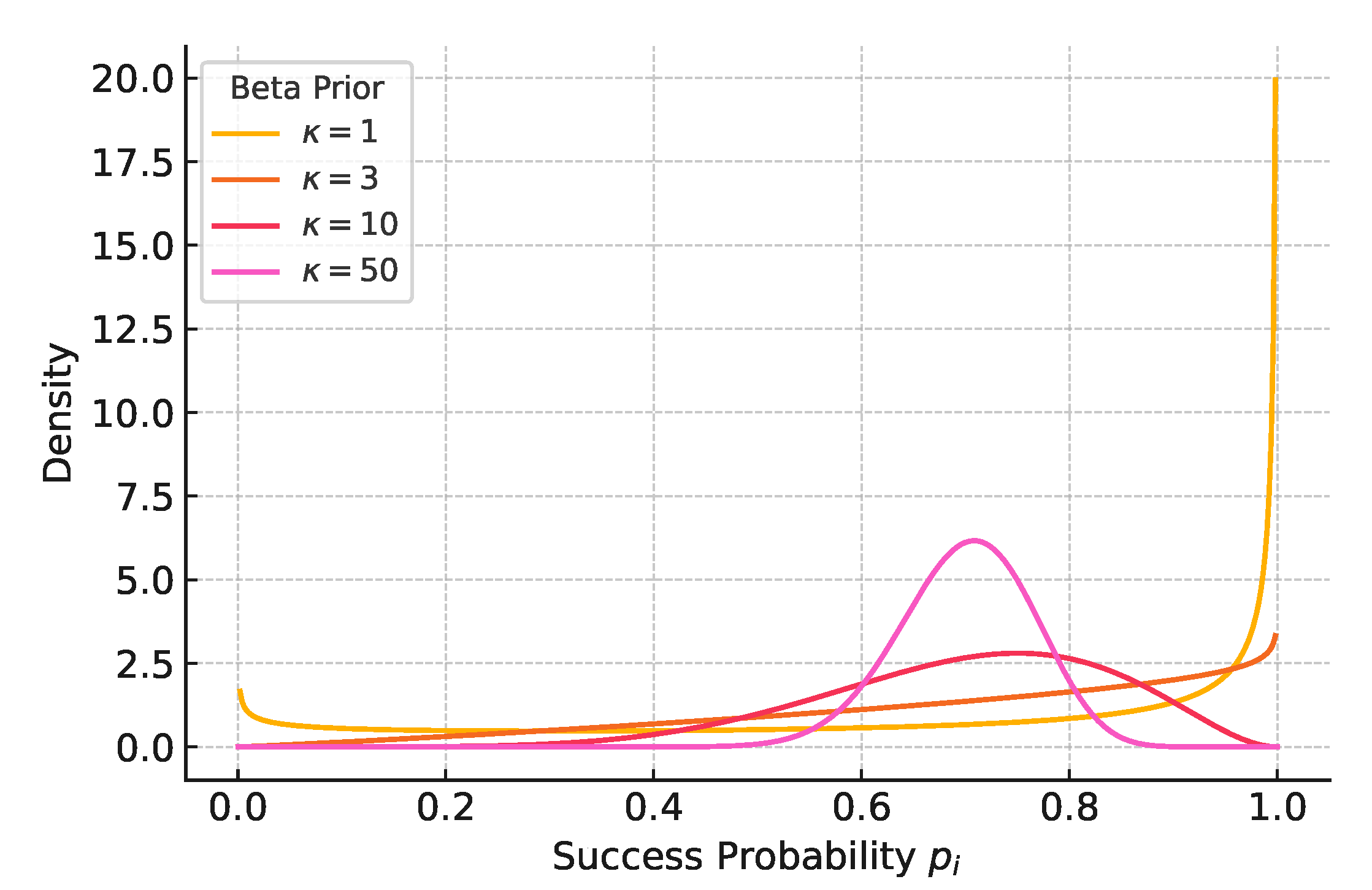
Appendix C. Details of Beta Distribution
- When is small, the distribution is diffuse and uncertain.
- When is large, the distribution is sharply peaked around , indicating high confidence.
Appendix D. Implementation Details
Appendix D.1. Experimental Hyperparameters
Appendix D.2. Details of Prompt

References
- Brown, B.; Juravsky, J.; Ehrlich, R.; Clark, R.; Le, Q.V.; Ré, C.; Mirhoseini, A. Large language monkeys: Scaling inference compute with repeated sampling. arXiv preprint arXiv:2407.21787, arXiv:2407.21787 2024.
- Snell, C.; Lee, J.; Xu, K.; Kumar, A. Scaling llm test-time compute optimally can be more effective than scaling model parameters. arXiv preprint arXiv:2408.03314, arXiv:2408.03314 2024.
- Wu, Y.; Sun, Z.; Li, S.; Welleck, S.; Yang, Y. Inference scaling laws: An empirical analysis of compute-optimal inference for LLM problem-solving. In Proceedings of the The Thirteenth International Conference on Learning Representations; 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Qwen Team. QwQ: Reflect Deeply on the Boundaries of the Unknown, 2024.
- Kimi, Team.; Du, A.; Gao, B.; Xing, B.; Jiang, C.; Chen, C.; Li, C.; Xiao, C.; Du, C.; Liao, C. Kimi k1.5: Scaling Reinforcement Learning with LLMs. arXiv preprint arXiv:2501.12599, arXiv:2501.12599 2025.
- DeepSeek-AI., *!!! REPLACE !!!*; Guo, D.; Yang, D.; Zhang, H.; Song, J.; Zhang, R.; Xu, R.; Zhu, Q.; Ma, S.; Wang, P. DeepSeek-R1: Incentivizing Reasoning Capability in LLMs via Reinforcement Learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2501.12948, arXiv:2501.12948 2025.
- Chen, L.; Davis, J.Q.; Hanin, B.; Bailis, P.; Stoica, I.; Zaharia, M.A.; Zou, J.Y. Are more llm calls all you need? towards the scaling properties of compound ai systems. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2024, 37, 45767–45790. [Google Scholar]
- Beeching, E.; Tunstall, L.; Rush, S. Scaling test-time compute with open models, 2024.
- Liu, R.; Gao, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, K.; Li, X.; Qi, B.; Ouyang, W.; Zhou, B. Can 1B LLM Surpass 405B LLM? Rethinking Compute-Optimal Test-Time Scaling. arXiv preprint arXiv:2502.06703, arXiv:2502.06703 2025.
- Setlur, A.; Rajaraman, N.; Levine, S.; Kumar, A. Scaling test-time compute without verification or rl is suboptimal. arXiv preprint arXiv:2502.12118, arXiv:2502.12118 2025.
- Bi, Z.; Han, K.; Liu, C.; Tang, Y.; Wang, Y. Forest-of-thought: Scaling test-time compute for enhancing LLM reasoning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2412.09078, arXiv:2412.09078 2024.
- Hooper, C.; Kim, S.; Moon, S.; Dilmen, K.; Maheswaran, M.; Lee, N.; Mahoney, M.W.; Shao, S.; Keutzer, K.; Gholami, A. Ets: Efficient tree search for inference-time scaling. arXiv preprint arXiv:2502.13575, arXiv:2502.13575 2025.
- Hendrycks, D.; Burns, C.; Kadavath, S.; Arora, A.; Basart, S.; Tang, E.; Song, D.; Steinhardt, J. Measuring Mathematical Problem Solving With the MATH Dataset. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the Neural Information Processing Systems Track on Datasets and Benchmarks 1, NeurIPS Datasets and Benchmarks 2021, December 2021, virtual; 2021. [Google Scholar]
- AI-MO. AIME 2024, 2024.
- Jiang, J.; Chen, Z.; Min, Y.; Chen, J.; Cheng, X.; Wang, J.; Tang, Y.; Sun, H.; Deng, J.; Zhao, W.X.; et al. Technical Report: Enhancing LLM Reasoning with Reward-guided Tree Search. arXiv preprint arXiv:2411.11694.
- Wang, P.; Li, L.; Shao, Z.; Xu, R.; Dai, D.; Li, Y.; Chen, D.; Wu, Y.; Sui, Z. Math-Shepherd: Verify and Reinforce LLMs Step-by-step without Human Annotations. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 62nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), 2024, pp.
- Luo, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, R.; Phatale, S.; Guo, M.; Lara, H.; Li, Y.; Shu, L.; Zhu, Y.; Meng, L.; et al. Improve mathematical reasoning in language models by automated process supervision. arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.06592, arXiv:2406.06592 2024.
- Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Luo, L.; Hou, L.; Yu, H.; Shang, J. Multi-step Problem Solving Through a Verifier: An Empirical Analysis on Model-induced Process Supervision. In Proceedings of the Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2024, 2024, pp. [Google Scholar]
- Setlur, A.; Nagpal, C.; Fisch, A.; Geng, X.; Eisenstein, J.; Agarwal, R.; Agarwal, A.; Berant, J.; Kumar, A. Rewarding Progress: Scaling Automated Process Verifiers for LLM Reasoning. In Proceedings of the The Thirteenth International Conference on Learning Representations; 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.H.; Yang, J.Y.; Heo, B.; Han, D.; Kim, K.; Yang, E.; Yoo, K.M. Token-Supervised Value Models for Enhancing Mathematical Problem-Solving Capabilities of Large Language Models. In Proceedings of the The Thirteenth International Conference on Learning Representations; 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Zheng, C.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Lin, R.; Yu, B.; Liu, D.; Zhou, J.; Lin, J. The Lessons of Developing Process Reward Models in Mathematical Reasoning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2501.07301, arXiv:2501.07301 2025.
- Zheng, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, B.; Lin, R.; Lu, K.; Yu, B.; Liu, D.; Zhou, J.; Lin, J. Processbench: Identifying process errors in mathematical reasoning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2412.06559, arXiv:2412.06559 2024.
- Song, M.; Su, Z.; Qu, X.; Zhou, J.; Cheng, Y. PRMBench: A Fine-grained and Challenging Benchmark for Process-Level Reward Models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2501.03124, arXiv:2501.03124 2025.
- AI, M. Llama 3.2: Multilingual Instruction-Tuned Language Models. https://huggingface.co/meta-llama/Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct, 2024. Accessed: 2025-05-14.
- Yang, A.; Yang, B.; Zhang, B.; Hui, B.; Zheng, B.; Yu, B.; Li, C.; Liu, D.; Huang, F.; Wei, H.; et al. Qwen2.5 Technical Report. arXiv preprint arXiv:2412.15115, arXiv:2412.15115 2024.
- Hochlehnert, A.; Bhatnagar, H.; Udandarao, V.; Albanie, S.; Prabhu, A.; Bethge, M. A sober look at progress in language model reasoning: Pitfalls and paths to reproducibility. arXiv, arXiv:2504.07086 2025.
- Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Du, T.; Jegelka, S.; Wang, Y. When More is Less: Understanding Chain-of-Thought Length in LLMs. arXiv preprint arXiv:2502.07266, arXiv:2502.07266 2025.
- OpenAI. Learning to Reason with LLMs, 2024.
- Wang, X.; Wei, J.; Schuurmans, D.; Le, Q.V.; Chi, E.H.; Narang, S.; Chowdhery, A.; Zhou, D. Self-Consistency Improves Chain of Thought Reasoning in Language Models. In Proceedings of the The Eleventh International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2023, Kigali, Rwanda, 2023. OpenReview.net, 2023., May 1-5.
- Xie, Y.; Kawaguchi, K.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, J.X.; Kan, M.Y.; He, J.; Xie, M. Self-Evaluation Guided Beam Search for Reasoning. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), Vol. 36; 2023; pp. 41618–41650. [Google Scholar]
- Khanov, M.; Burapacheep, J.; Li, Y. ARGS: Alignment as Reward-Guided Search. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR); 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, Z.; Feng, X.; Wen, M.; Mcaleer, S.M.; Wen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J. AlphaZero-Like Tree-Search can Guide Large Language Model Decoding and Training. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Vol. 235; 2024; pp. 49890–49920. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, S.; Yu, D.; Zhao, J.; Shafran, I.; Griffiths, T.; Cao, Y.; Narasimhan, K. Tree of Thoughts: Deliberate Problem Solving with Large Language Models. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), Vol. 36; 2023; pp. 11809–11822. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Q.; Zhou, H.; Liu, T.; Yuan, J.; Liu, P.; You, Y.; Yang, H. Let’s reward step by step: Step-Level reward model as the Navigators for Reasoning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.10080, arXiv:2310.10080 2023.
- Li, Y.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, S.; Fu, Q.; Chen, B.; Lou, J.G.; Chen, W. Making large language models better reasoners with step-aware verifier. arXiv preprint arXiv:2206.02336, arXiv:2206.02336 2022.
- Liu, J.; Cohen, A.; Pasunuru, R.; Choi, Y.; Hajishirzi, H.; Celikyilmaz, A. Don’t throw away your value model! Generating more preferable text with Value-Guided Monte-Carlo Tree Search decoding. arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.15028, arXiv:2309.15028 2023.
- Choi, S.; Fang, T.; Wang, Z.; Song, Y. KCTS: Knowledge-Constrained Tree Search Decoding with Token-Level Hallucination Detection. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 2023 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. [CrossRef]
- Uesato, J.; Kushman, N.; Kumar, R.; Song, F.; Siegel, N.; Wang, L.; Creswell, A.; Irving, G.; Higgins, I. Solving math word problems with process-and outcome-based feedback. arXiv, arXiv:2211.14275 2022.
- Polu, S.; Sutskever, I. Generative language modeling for automated theorem proving. arXiv preprint arXiv:2009.03393, arXiv:2009.03393 2020.
- Gudibande, A.; Wallace, E.; Snell, C.; Geng, X.; Liu, H.; Abbeel, P.; Levine, S.; Song, D. The false promise of imitating proprietary llms. arXiv, arXiv:2305.15717 2023.
- OpenAI. GPT-4 Technical Report. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.08774, arXiv:2303.08774 2023.
- Azerbayev, Z.; Schoelkopf, H.; Paster, K.; Santos, M.D.; McAleer, S.M.; Jiang, A.Q.; Deng, J.; Biderman, S.; Welleck, S. Llemma: An Open Language Model for Mathematics. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR); 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Z.; Wang, P.; Zhu, Q.; Xu, R.; Song, J.; Bi, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; et al. DeepSeekMath: Pushing the Limits of Mathematical Reasoning in Open Language Models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.03300, arXiv:2402.03300 2024.
- Luo, H.; Sun, Q.; Xu, C.; Zhao, P.; Lou, J.; Tao, C.; Geng, X.; Lin, Q.; Chen, S.; Zhang, D. Wizardmath: Empowering mathematical reasoning for large language models via reinforced evol-instruct. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.09583, arXiv:2308.09583 2023.
- Tang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, B.; Wei, F. MathScale: Scaling Instruction Tuning for Mathematical Reasoning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Vol. 235; 2024; pp. 47885–47900. [Google Scholar]
- Zelikman, E.; Wu, Y.; Mu, J.; Goodman, N. STaR: Bootstrapping Reasoning With Reasoning. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), Vol. 35; 2022; pp. 15476–15488. [Google Scholar]
- Gulcehre, C.; Paine, T.L.; Srinivasan, S.; Konyushkova, K.; Weerts, L.; Sharma, A.; Siddhant, A.; Ahern, A.; Wang, M.; Gu, C.; et al. Reinforced Self-Training (ReST) for Language Modeling. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.08998, arXiv:2308.08998 2023.
- Setlur, A.; Garg, S.; Geng, X.; Garg, N.; Smith, V.; Kumar, A. RL on Incorrect Synthetic Data Scales the Efficiency of LLM Math Reasoning by Eight-Fold. arXiv, arXiv:2406.14532 2024.
- Wei, J.; Wang, X.; Schuurmans, D.; Bosma, M.; Ichter, B.; Xia, F.; Chi, E.H.; Le, Q.V.; Zhou, D. Chain-of-Thought Prompting Elicits Reasoning in Large Language Models. In Proceedings of the NeurIPS; 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Yuan, J.; Yang, G.; Naseem, U. Can Pruning Improve Reasoning? Revisiting Long-CoT Compression with Capability in Mind for Better Reasoning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2505.14582, arXiv:2505.14582 2025.
- Gao, L.; Madaan, A.; Zhou, S.; Alon, U.; Liu, P.; Yang, Y.; Callan, J.; Neubig, G. PAL: Program-aided Language Models. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), 2023, Vol. 202, pp. 10764–10799.
- Chen, W.; Ma, X.; Wang, X.; Cohen, W.W. Program of Thoughts Prompting: Disentangling Computation from Reasoning for Numerical Reasoning Tasks. Transactions on Machine Learning Research (TMLR) 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Weng, Y.; Zhu, M.; Xia, F.; Li, B.; He, S.; Liu, S.; Sun, B.; Liu, K.; Zhao, J. Large language models are better reasoners with self-verification. In Proceedings of the Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2023, 2023, pp. 2550–2575.
- Chen, J.; Xiao, S.; Zhang, P.; Luo, K.; Lian, D.; Liu, Z. BGE M3-Embedding: Multi-Lingual, Multi-Functionality, Multi-Granularity Text Embeddings Through Self-Knowledge Distillation, 2024, [arXiv:cs.CL/2402.03216].
| Method | Rollout | FLOPs | Latency | Accuracy | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Policy Model | PRM | Embedding Model | Total | ||||
| Beam Search | 256 | 0 | 345 | 63.6 | |||
| DVTS | 256 | 0 | 253 | 62.0 | |||
| REBASE | 256 | 0 | 490 | 67.4 | |||
| DORA | 64 | 124 | 68.7 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





