Submitted:
07 June 2025
Posted:
09 June 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Field Data
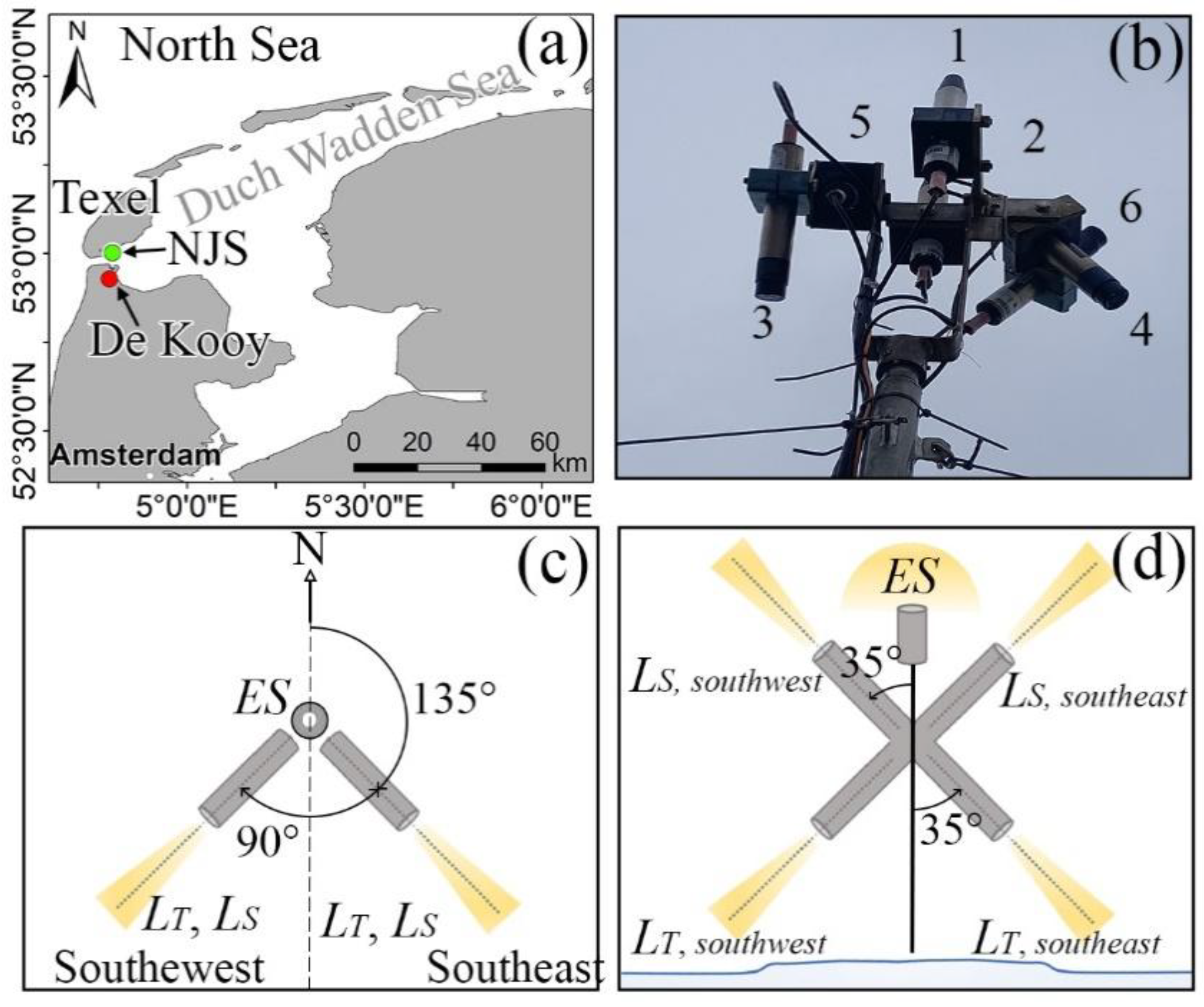
2.1. Above-Water Hyperspectral Radiometric Data
2.2. Meteorological Data
2.3. IOPs Data
2.4. Concentrations of Chla and SPM
3. Methods
3.1. Bio-Optical Models
3.2. Generating the Glint-Free Rrs(λ)
3.3. Methods of ρ and ΔL Estimation from Above-Water Radiometry
3.4. Identification of Environmental Factors
3.4.1. Sun Azimuth and Zenith Angle
3.4.2. Aerosol Optical Thickness (AOT)
3.4.3. Sky Conditions (Clear, Scattered Clouds, or Overcast)
3.5. Statistical Metrics
4. Results
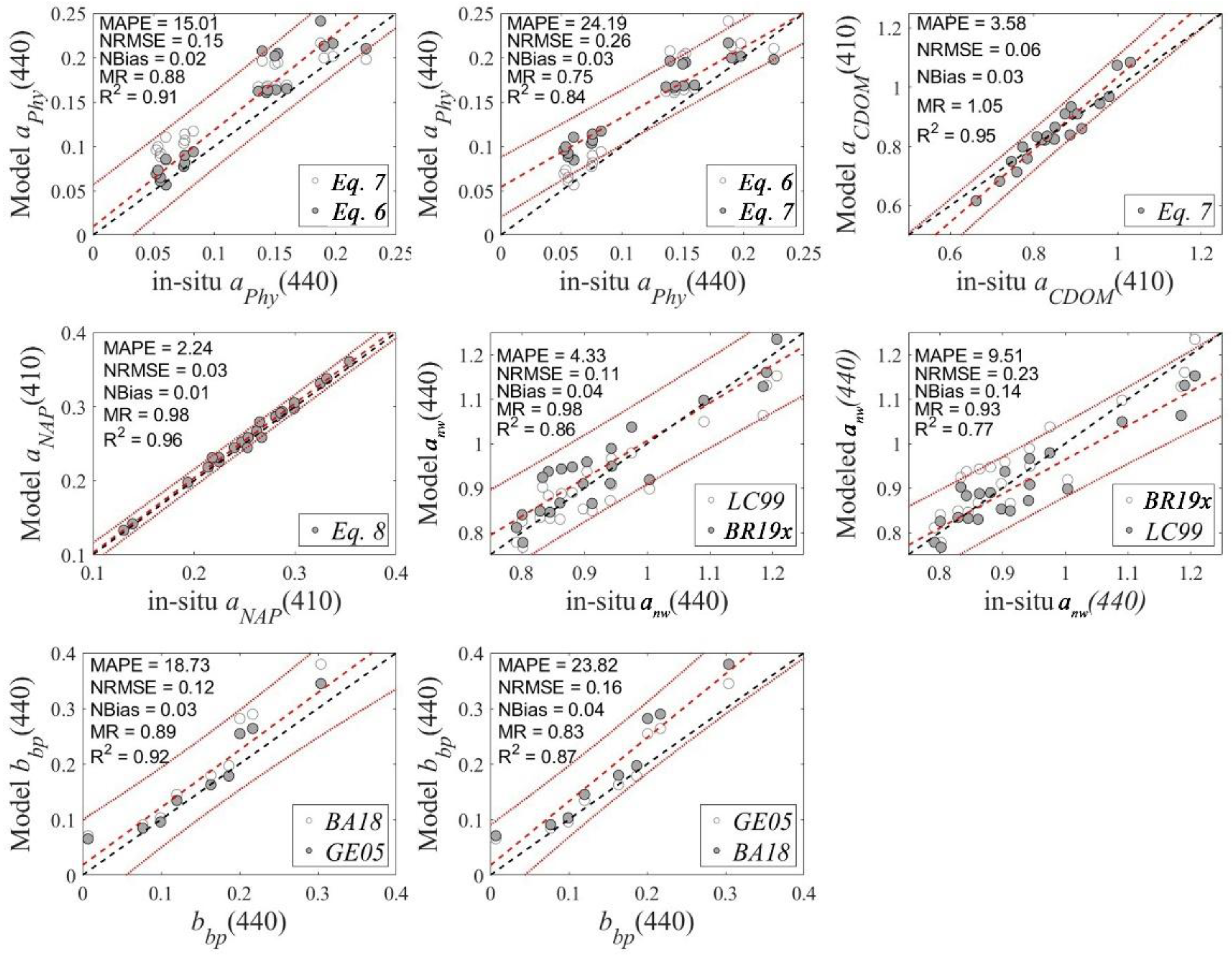
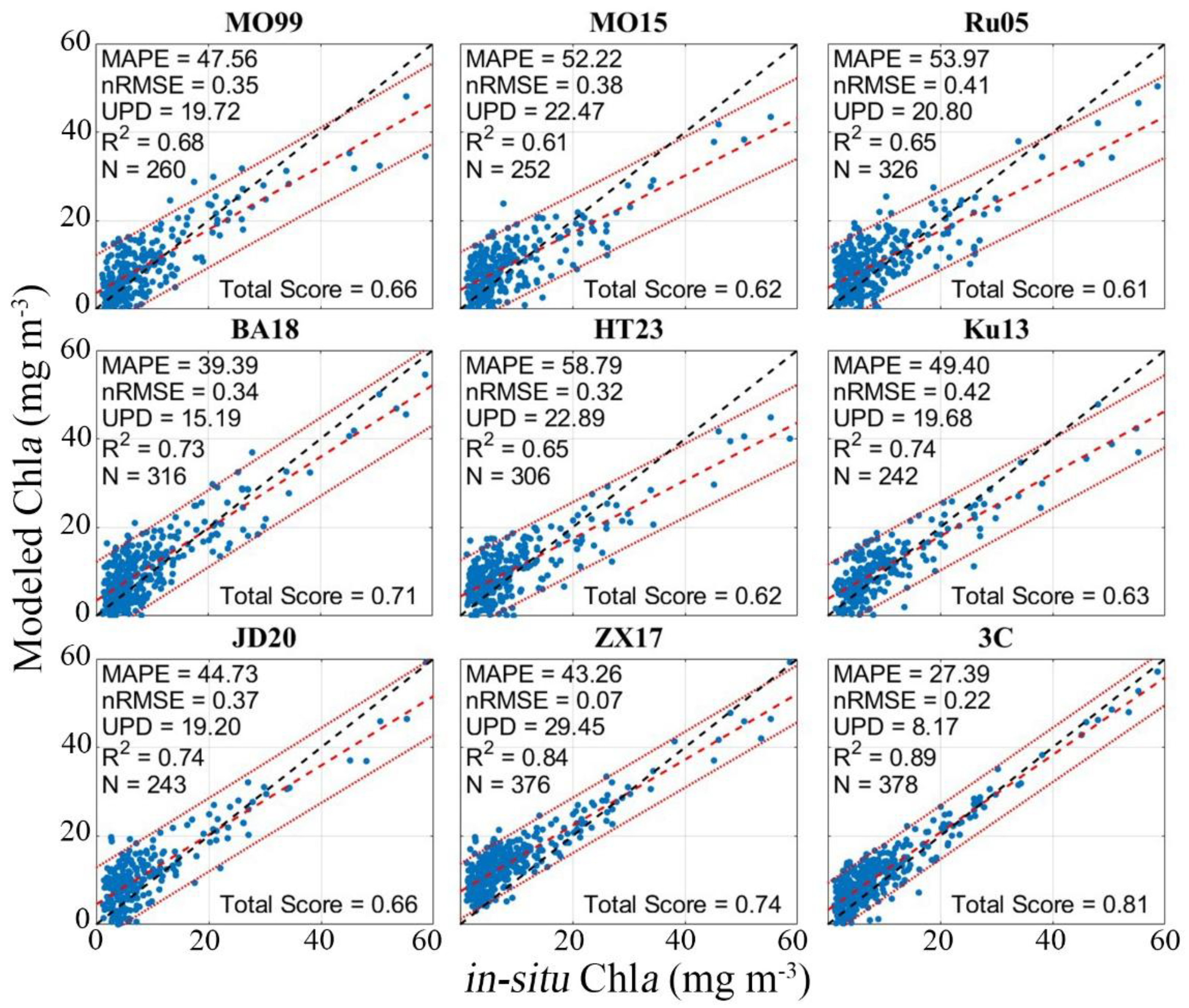
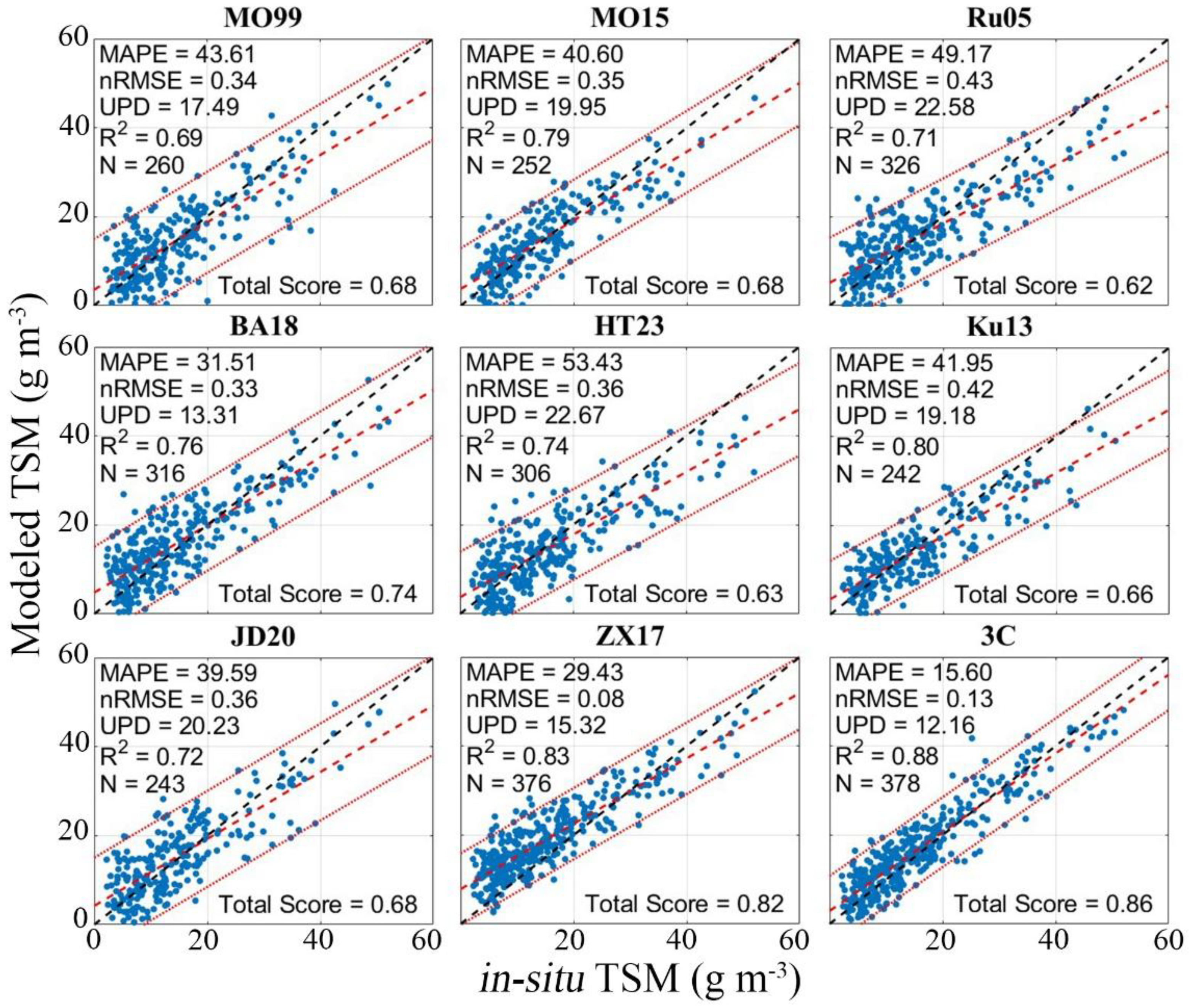
4.1. Parametrization and Validation of Bio-Optical Models
4.2. Evaluation of ρ and ΔL Estimation Methods
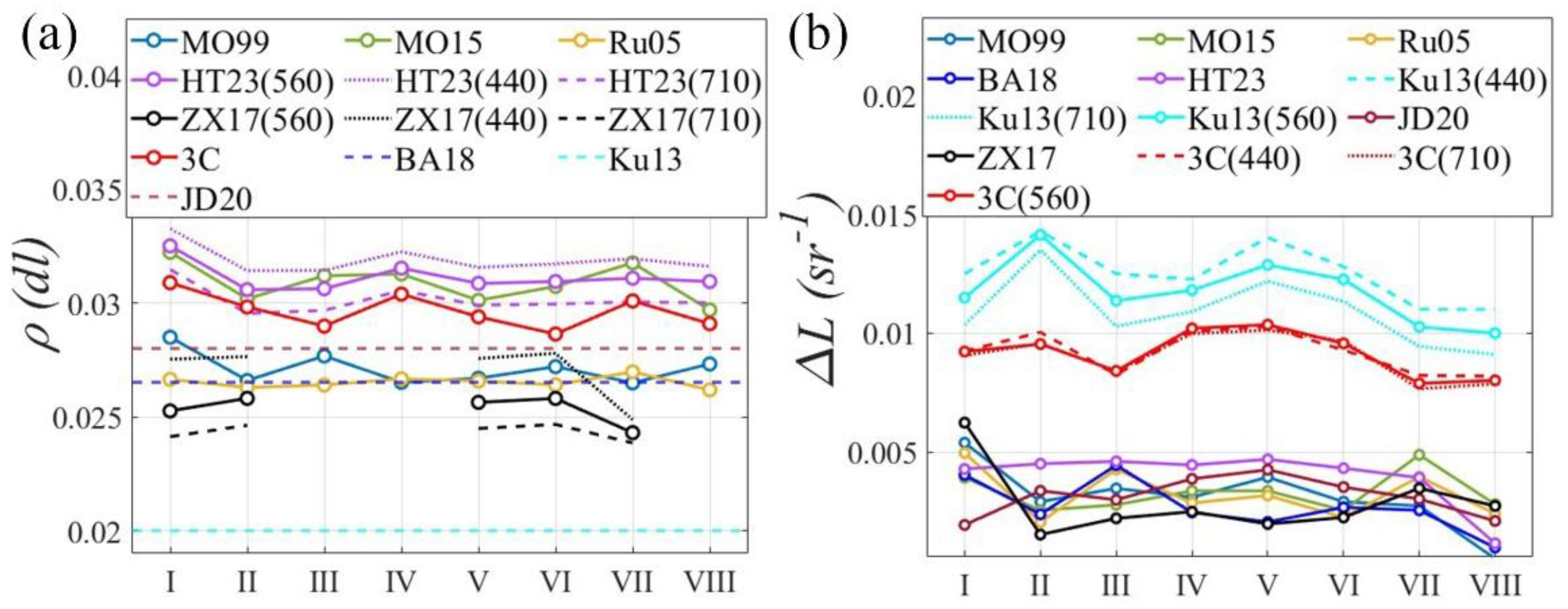
4.3. Variability of ρ and ΔL
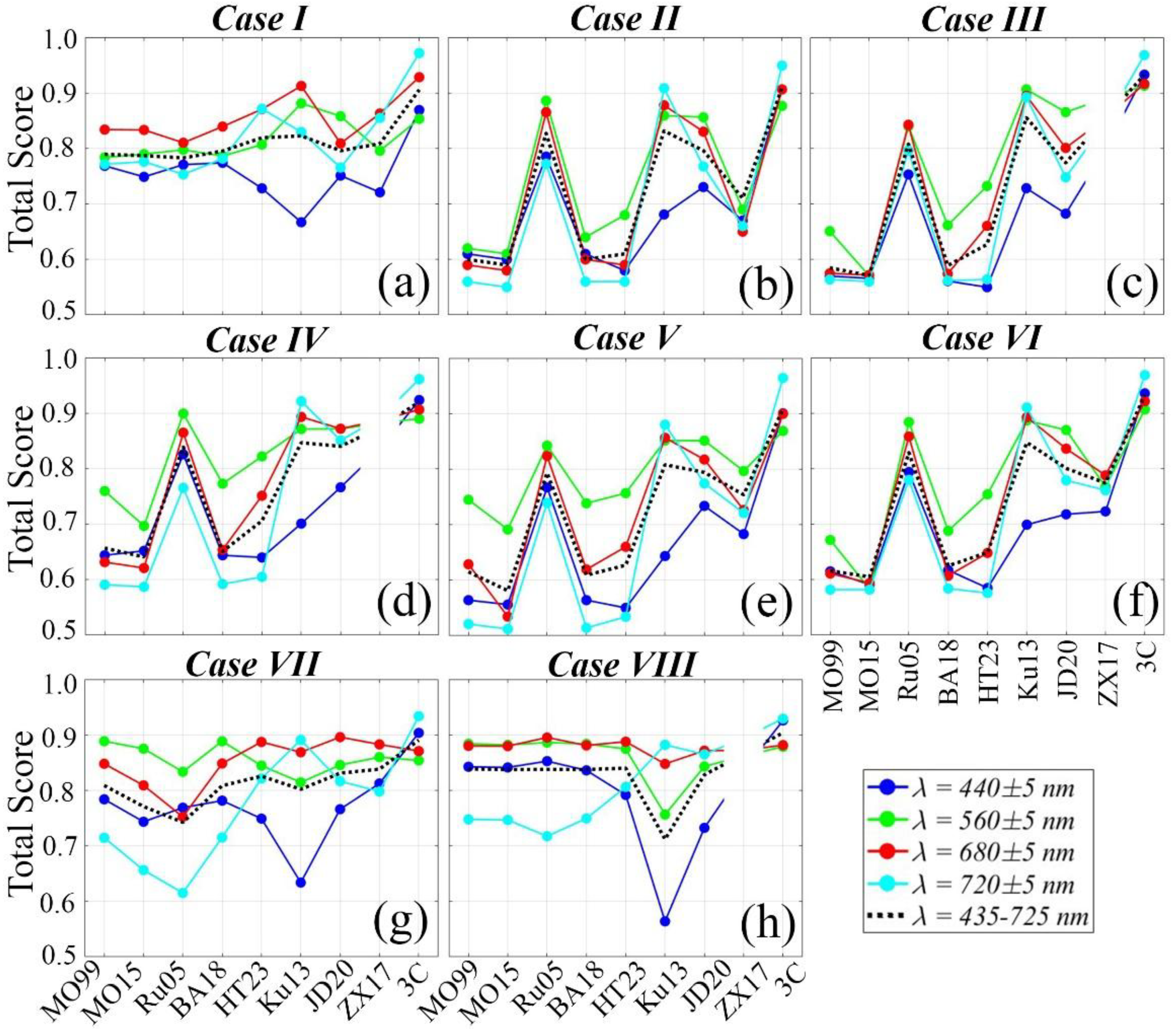
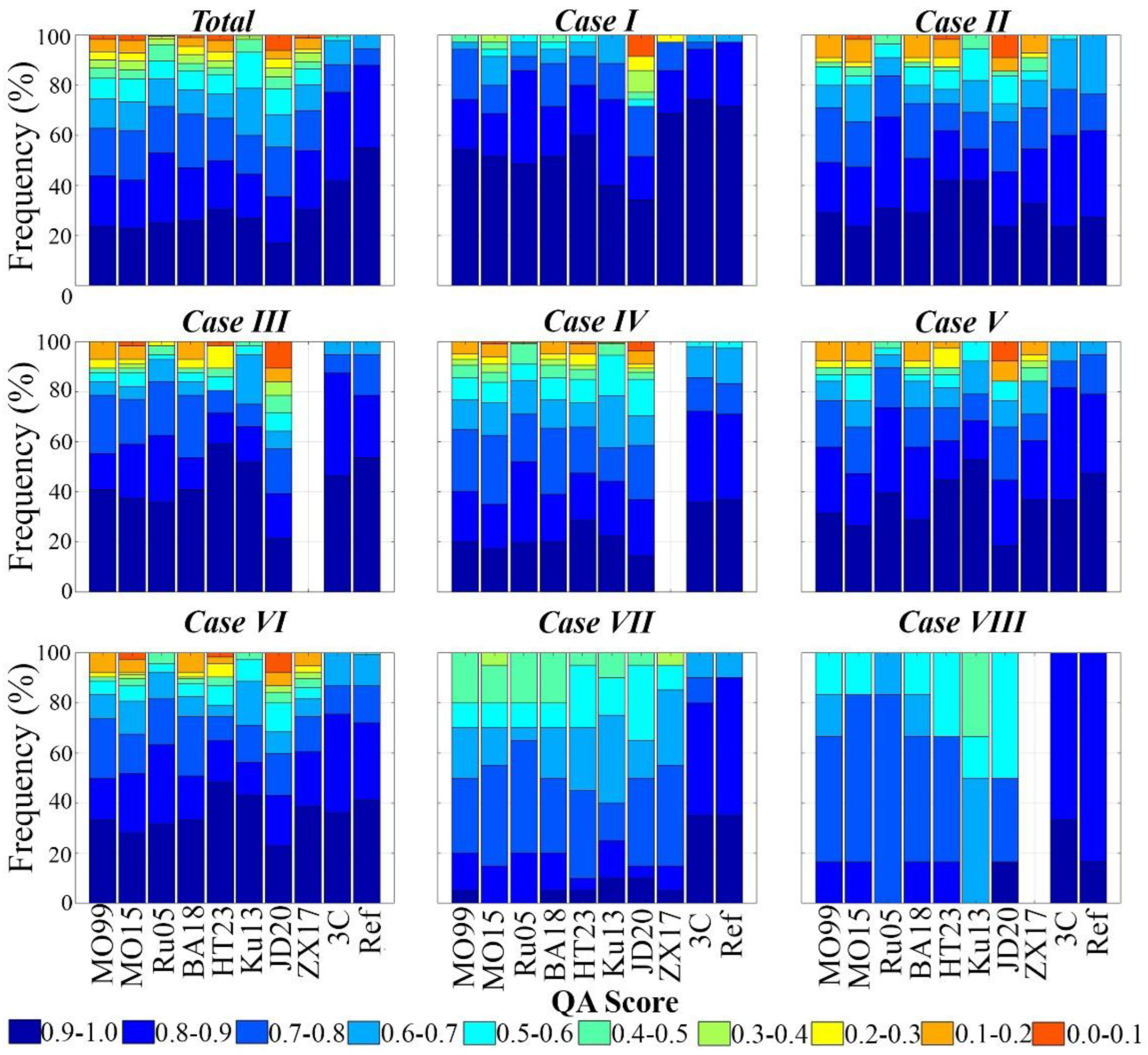
4.4. QA scores of Simulated Above-Water Rrs(λ)
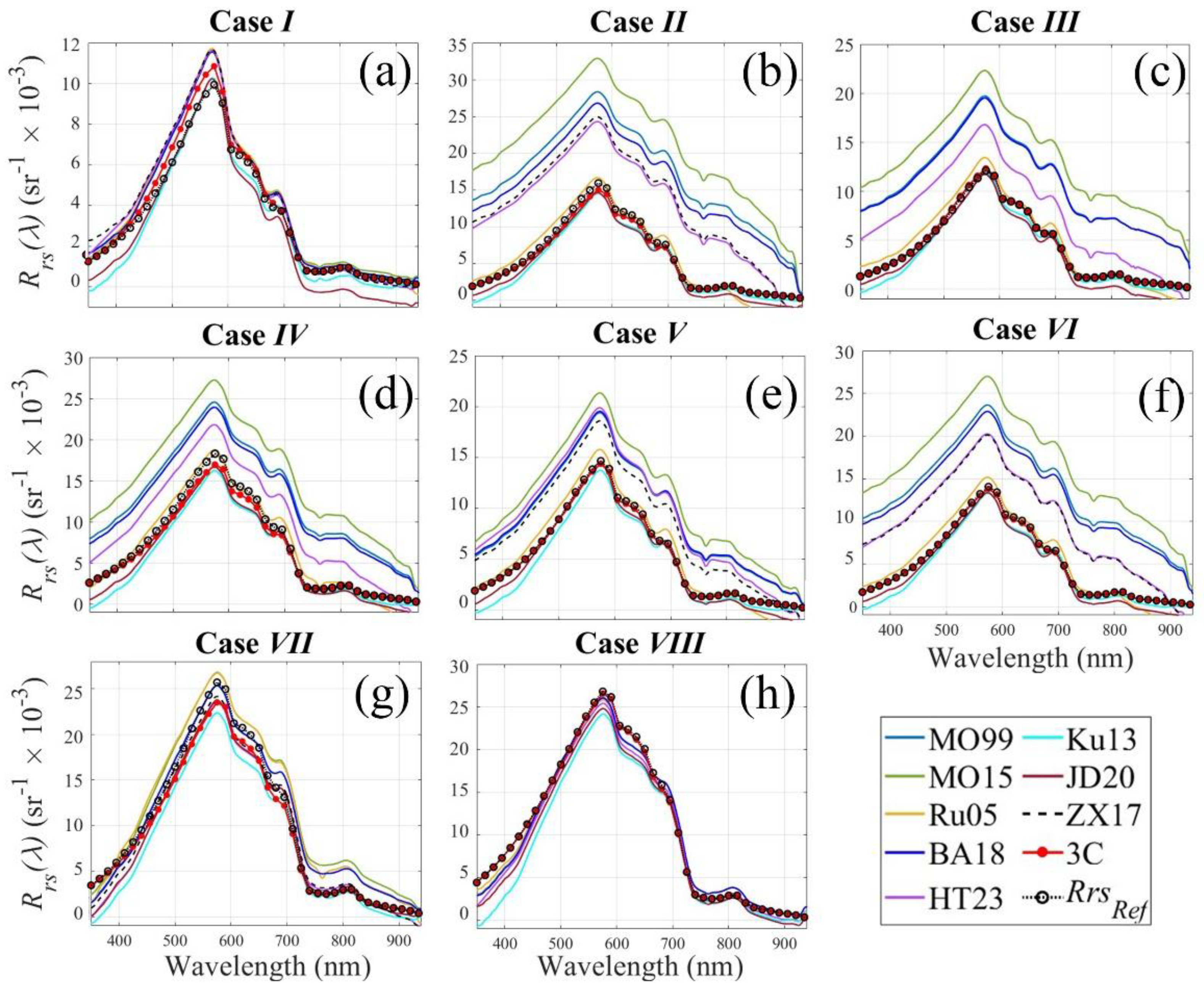
4.5. Showcases of Rrs(λ) Models
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, Z.P. Remote Sensing of Inherent Optical Properties: Fundamentals, Tests of Algorithms, and Applications. Reports and Monographs of the International Ocean-Colour Coordinating Group (IOCCG) 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; He, S.; Shabani, A.; Zhai, P.-W.; Du, K. Spectral Sea Surface Reflectance of Skylight. Optics Express 2017, 25, A1–A13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinmetz, F.; Deschamps, P.-Y.; Ramon, D. Atmospheric Correction in Presence of Sun Glint: Application to MERIS. Optics Express 2011, 19, 9783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobley, C.D. Estimation of the Remote-Sensing Reflectance from above-Surface Measurements. Applied optics 1999, 38, 7442–7455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werdell, P.J.; McKinna, L.I.W.; Boss, E.; Ackleson, S.G.; Craig, S.E.; Gregg, W.W.; Lee, Z.; Maritorena, S.; Roesler, C.S.; Rousseaux, C.S.; et al. An Overview of Approaches and Challenges for Retrieving Marine Inherent Optical Properties from Ocean Color Remote Sensing. Progress in Oceanography 2018, 160, 186–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.; Pahlevan, N.; Ahn, Y.-H.; Greb, S.; O’Donnell, D. Robust Approach to Directly Measuring Water-Leaving Radiance in the Field. Applied Optics 2013, 52, 1693–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, H.R.; Ding, K. Self-shading of In-water Optical Instruments. Limnology & Oceanography 1992, 37, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, J.P.; Zibordi, G. Optical Propagation within a Three-Dimensional Shadowed Atmosphere–Ocean Field: Application to Large Deployment Structures. Applied optics 2002, 41, 4283–4306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, S.; Röttgers, R.; Hieronymi, M. Transfer Model to Determine the Above-Water Remote-Sensing Reflectance from the Underwater Remote-Sensing Ratio. Optics Express 2023, 31, 10512–10524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruddick, K.G.; Voss, K.; Banks, A.C.; Boss, E.; Castagna, A.; Frouin, R.; Hieronymi, M.; Jamet, C.; Johnson, B.C.; Kuusk, J. A Review of Protocols for Fiducial Reference Measurements of Downwelling Irradiance for the Validation of Satellite Remote Sensing Data over Water. Remote Sensing 2019, 11, 1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zibordi, G.; Voss, K.J.; Johnson, B.C.; Mueller, J.L. IOCCG Ocean Optics and Biogeochemistry Protocols for Satellite Ocean Colour Sensor Validation. IOCCG Protocols Series 2019, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Zibordi, G.; Hooker, S.B.; Berthon, J.F.; D’Alimonte, D. Autonomous Above-Water Radiance Measurements from an Offshore Platform: A Field Assessment Experiment. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology 2002, 19, 808–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoine, D.; d’Ortenzio, F.; Hooker, S.B.; Bécu, G.; Gentili, B.; Tailliez, D.; Scott, A.J. Assessment of Uncertainty in the Ocean Reflectance Determined by Three Satellite Ocean Color Sensors (MERIS, SeaWiFS and MODIS-A) at an Offshore Site in the Mediterranean Sea (BOUSSOLE Project). J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, 2007JC004472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooker, S.B.; Morrow, J.H.; Matsuoka, A. Apparent Optical Properties of the Canadian Beaufort Sea–Part 2: The 1% and 1 Cm Perspective in Deriving and Validating AOP Data Products. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 4511–4527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.; Ahn, Y.-H.; Mobley, C.; Arnone, R. Removal of Surface-Reflected Light for the Measurement of Remote-Sensing Reflectance from an above-Surface Platform. Optics Express 2010, 18, 26313–26324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitarch, J.; Talone, M.; Zibordi, G.; Groetsch, P. Determination of the Remote-Sensing Reflectance from above-Water Measurements with the “3C Model”: A Further Assessment. Optics Express 2020, 28, 15885–15906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruddick, K.; De Cauwer, V.; Van Mol, B. Use of the near Infrared Similarity Reflectance Spectrum for the Quality Control of Remote Sensing Data. In Proceedings of the Remote Sensing of the Coastal Oceanic Environment; SPIE, 2005. Vol. 5885, p. 588501.
- Groetsch, P.M.; Foster, R.; Gilerson, A. Exploring the Limits for Sky and Sun Glint Correction of Hyperspectral Above-Surface Reflectance Observations. Applied Optics 2020, 59, 2942–2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groetsch, P.M.; Gege, P.; Simis, S.G.; Eleveld, M.A.; Peters, S.W. Validation of a Spectral Correction Procedure for Sun and Sky Reflections in Above-Water Reflectance Measurements. Optics express 2017, 25, A742–A761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Matsushita, B.; Yang, W. A Simple and Effective Method for Removing Residual Reflected Skylight in Above-Water Remote Sensing Reflectance Measurements. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing 2020, 165, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutser, T.; Vahtmäe, E.; Paavel, B.; Kauer, T. Removing Glint Effects from Field Radiometry Data Measured in Optically Complex Coastal and Inland Waters. Remote Sensing of Environment 2013, 133, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmel, T. Apparent Surface-to-Sky Radiance Ratio of Natural Waters Including Polarization and Aerosol Effects: Implications for above-Water Radiometry. Frontiers in Remote Sensing 2023, 4, 1307976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Lee, Z.; Tilstone, G.H.; Liu, X.; Wei, J.; Ondrusek, M.; Groom, S. Revised Spectral Optimization Approach to Remove Surface-Reflected Radiance for the Estimation of Remote-Sensing Reflectance from the above-Water Method. Optics Express 2023, 31, 22964–22981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arabi, B.; Salama, M.S.; Wernand, M.R.; Verhoef, W. Remote Sensing of Water Constituent Concentrations Using Time Series of In-Situ Hyperspectral Measurements in the Wadden Sea. Remote sensing of environment 2018, 216, 154–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hommersom, A.; Peters, S.; Wernand, M.R.; de Boer, J. Spatial and Temporal Variability in Bio-Optical Properties of the Wadden Sea. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 2009, 83, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruddick, K.G.; De Cauwer, V.; Park, Y.-J.; Moore, G. Seaborne Measurements of near Infrared Water-Leaving Reflectance: The Similarity Spectrum for Turbid Waters. Limnology and Oceanography 2006, 51, 1167–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobley, C.D. Polarized Reflectance and Transmittance Properties of Windblown Sea Surfaces. Applied optics 2015, 54, 4828–4849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabi, B.; Salama, M.S.; Pitarch, J.; Verhoef, W. Integration of In-Situ and Multi-Sensor Satellite Observations for Long-Term Water Quality Monitoring in Coastal Areas. Remote Sensing of Environment 2020, 239, 111632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewin, R.J.W.; Dall’Olmo, G.; Pardo, S.; van Dongen-Vogels, V.; Boss, E.S. Underway Spectrophotometry along the Atlantic Meridional Transect Reveals High Performance in Satellite Chlorophyll Retrievals. Remote Sensing of Environment 2016, 183, 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Park, Y.J.; Ahn, J.H.; Lim, H.; Eom, J.; Ryu, J. GOCI, the World’s First Geostationary Ocean Color Observation Satellite, for the Monitoring of Temporal Variability in Coastal Water Turbidity. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, 2012JC008046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z. A Simple Optical Model to Estimate Suspended Particulate Matter in Yellow River Estuary. Optics Express 2013, 21, 27891–27904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IOCCG Remote Sensing of Inherent Optical Properties: Fundamentals, Tests of Algorithms, and Applications 2006.
- Gordon, H.R. A Semianalytic Radiance Model of Ocean Color. Journal of Geophysical Research 1988, 93, 10909–10924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, A.; Maritorena, S. Bio-optical Properties of Oceanic Waters: A Reappraisal. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 7163–7180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, S.; Hieronymi, M.; Röttgers, R. Bio-Geo-Optical Modelling of Natural Waters. Frontiers in Marine Science 2023, 10, 1196352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, M.; Arabi, B.; Hommersom, A.; van der Molen, J.; Samimi, C. Quality Control Tests for Automated Above-Water Hyperspectral Measurements: Radiative Transfer Assessment. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing 2024, 215, 292–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, J.L.; Bidigare, R.R.; Trees, C.; Dore, J.; Karl, D.; Van Heukelem, L. Biogeochemical and Bio-Optical Measurements and Data... - Google Scholar. NASA/TM-2003221621. 2003, 2, 39–64. [Google Scholar]
- Pegau, W.S.; Gray, D.; Zaneveld, J.R.V. Absorption and Attenuation of Visible and Near-Infrared Light in Water: Dependence on Temperature and Salinity. Applied optics 1997, 36, 6035–6046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Hu, L.; He, M.-X. Scattering by Pure Seawater: Effect of Salinity, Optics Express, Vol. 17, No. 7, 5698-5710. 2009.
- Twardowski, M.S.; Boss, E.; Macdonald, J.B.; Pegau, W.S.; Barnard, A.H.; Zaneveld, J.R.V. A Model for Estimating Bulk Refractive Index from the Optical Backscattering Ratio and the Implications for Understanding Particle Composition in Case I and Case II Waters. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 14129–14142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaillancourt, R.D.; Brown, C.W.; Guillard, R.R.; Balch, W.M. Light Backscattering Properties of Marine Phytoplankton: Relationships to Cell Size, Chemical Composition and Taxonomy. Journal of plankton research 2004, 26, 191–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loisel, H.; Mériaux, X.; Berthon, J.-F.; Poteau, A. Investigation of the Optical Backscattering to Scattering Ratio of Marine Particles in Relation to Their Biogeochemical Composition in the Eastern English Channel and Southern North Sea. Limnology & Oceanography 2007, 52, 739–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm-Hansen, O.; Riemann, B. Chlorophyll a Determination: Improvements in Methodology. Oikos 1978, 30, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobley, C.D. Radiative Transfer in the Ocean. Encyclopedia of ocean sciences 2001, 4, 2321–2330. [Google Scholar]
- Ogashawara, I.; Li, L.; Druschel, G.K. Retrieval of Inherent Optical Properties from Multiple Aquatic Systems Using a Quasi-Analytical Algorithm for Several Water Types. Remote Sensing Applications: Society and Environment 2022, 27, 100807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bricaud, A.; Babin, M.; Morel, A.; Claustre, H. Variability in the Chlorophyll-specific Absorption Coefficients of Natural Phytoplankton: Analysis and Parameterization. J. Geophys. Res. 1995, 100, 13321–13332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.; Carder, K.L.; Mobley, C.D.; Steward, R.G.; Patch, J.S. Hyperspectral Remote Sensing for Shallow Waters: 2. Deriving Bottom Depths and Water Properties by Optimization. Applied optics 1999, 38, 3831–3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bricaud, A.; Morel, A.; Prieur, L. Absorption by Dissolved Organic Matter of the Sea (Yellow Substance) in the UV and Visible Domains. Limnol. Oceanogr 1981, 26, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gege, P. The Water Colour Simulator WASI-User Manual for Version 3. 2005.
- Doxaran, D.; Froidefond, J.-M.; Castaing, P.; Babin, M. Dynamics of the Turbidity Maximum Zone in a Macrotidal Estuary (the Gironde, France): Observations from Field and MODIS Satellite Data. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 2009, 81, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.; Carder, K.L.; Mobley, C.D.; Steward, R.G.; Patch, J.S. Hyperspectral Remote Sensing for Shallow Waters. I. A Semianalytical Model. Applied optics 1998, 37, 6329–6338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petzold, T.J. Volume Scattering Functions for Selected Ocean Waters. 1972.
- Sathyendranath, S.; Prieur, L.; Morel, A. A Three-Component Model of Ocean Colour and Its Application to Remote Sensing of Phytoplankton Pigments in Coastal Waters. International Journal of Remote Sensing 1989, 10, 1373–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babin, M.; Stramski, D.; Ferrari, G.M.; Claustre, H.; Bricaud, A.; Obolensky, G.; Hoepffner, N. Variations in the Light Absorption Coefficients of Phytoplankton, Nonalgal Particles, and Dissolved Organic Matter in Coastal Waters around Europe. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, C.; Hu, C.; English, D.; Cannizzaro, J.; Chen, Z.; Kovach, C.; Anastasiou, C.J.; Zhao, J.; Carder, K.L. Inherent and Apparent Optical Properties of the Complex Estuarine Waters of Tampa Bay: What Controls Light? Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 2013, 117, 54–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.; Wei, J.; Voss, K.; Lewis, M.; Bricaud, A.; Huot, Y. Hyperspectral Absorption Coefficient of “Pure” Seawater in the Range of 350–550 Nm Inverted from Remote Sensing Reflectance. Applied Optics 2015, 54, 546–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, R.M.; Fry, E.S. Absorption Spectrum (380–700 Nm) of Pure Water. II. Integrating Cavity Measurements. Applied optics 1997, 36, 8710–8723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loisel, H. Rrs(0+) -> Rrs(0-) & Water Coefficients. Available online: https://oceancolor.gsfc.nasa.gov/forum/oceancolor/topic_show.pl%3Ftid=2657.html (accessed on 29 July 2024).
- Wong, J.; Liew, S.C.; Wong, E.; Lee, Z. Modeling the Remote-Sensing Reflectance of Highly Turbid Waters. Applied Optics 2019, 58, 2671–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Z.; Carder, K.L.; Arnone, R.A. Deriving Inherent Optical Properties from Water Color: A Multiband Quasi-Analytical Algorithm for Optically Deep Waters. Applied optics 2002, 41, 5755–5772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.; Shang, S.; Lin, G.; Chen, J.; Doxaran, D. On the Modeling of Hyperspectral Remote-Sensing Reflectance of High-Sediment-Load Waters in the Visible to Shortwave-Infrared Domain. Applied Optics 2016, 55, 1738–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Lee, Z.; Shang, S. A System to Measure the Data Quality of Spectral Remote Sensing Reflectance of Aquatic Environments. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, C.A.; Thirumalai, K.; Kearney, K.A.; Delgado, J.M.; Schwanghart, W.; Wolfenbarger, N.S.; Thyng, K.M.; Gwyther, D.E.; Gardner, A.S.; Blankenship, D.D. The Climate Data Toolbox for MATLAB. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems 2019, 20, 3774–3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregg, W.W.; Carder, K.L. A Simple Spectral Solar Irradiance Model for Cloudless Maritime Atmospheres. Limnology and oceanography 1990, 35, 1657–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregg, W.W. A Coupled Ocean-Atmosphere Radiative Model for Global Ocean Biogeochemical Models; National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Goddard Space Flight Center, 2002.
- Slingo, A. A GCM Parameterization for the Shortwave Radiative Properties of Water Clouds. Journal of Atmospheric Sciences 1989, 46, 1419–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, J.; Smyth, T.J.; Estellés, V. Autonomous Marine Hyperspectral Radiometers for Determining Solar Irradiances and Aerosol Optical Properties. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques 2017, 10, 1723–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reno, M.J.; Hansen, C.W. Identification of Periods of Clear Sky Irradiance in Time Series of GHI Measurements. Renewable Energy 2016, 90, 520–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, H.V.; Kling, H.; Yilmaz, K.K.; Martinez, G.F. Decomposition of the Mean Squared Error and NSE Performance Criteria: Implications for Improving Hydrological Modelling. Journal of hydrology 2009, 377, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabi, B.; Salama, M.S.; Wernand, M.R.; Verhoef, W. MOD2SEA: A Coupled Atmosphere-Hydro-Optical Model for the Retrieval of Chlorophyll-a from Remote Sensing Observations in Complex Turbid Waters. Remote Sensing 2016, 8, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, S.E.; Lohrenz, S.E.; Lee, Z.; Mahoney, K.L.; Kirkpatrick, G.J.; Schofield, O.M.; Steward, R.G. Use of Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Reflectance for Detection and Assessment of the Harmful Alga, Karenia Brevis. Applied Optics 2006, 45, 5414–5425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, T.M.; Simis, S.G.; Grötsch, P.M.; Wood, J. Incorporating a Hyperspectral Direct-Diffuse Pyranometer in an Above-Water Reflectance Algorithm. Remote Sensing 2022, 14, 2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilerson, A.; Zhou, J.; Hlaing, S.; Ioannou, I.; Schalles, J.; Gross, B.; Moshary, F.; Ahmed, S. Fluorescence Component in the Reflectance Spectra from Coastal Waters. Dependence on Water Composition. Optics Express 2007, 15, 15702–15721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-C.; Miller, R.L. Spectrum Matching Method for Estimating the Chlorophyll- a Concentration, CDOM Ratio, and Backscatter Fraction from Remote Sensing of Ocean Color. Canadian Journal of Remote Sensing 2008, 34, 343–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.-G.; Zhao, D.-Z.; Liu, Y.-G.; Yang, J.-H.; Xiu, P.; Wang, L. An Overview of Remote Sensing of Chlorophyll Fluorescence. Ocean Sci. J. 2007, 42, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkart, A.; Schickling, A.; Mateo, M.P.C.; Wrobel, T.J.; Rossini, M.; Cogliati, S.; Julitta, T.; Rascher, U. A Method for Uncertainty Assessment of Passive Sun-Induced Chlorophyll Fluorescence Retrieval Using an Infrared Reference Light. IEEE Sensors Journal 2015, 15, 4603–4611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, C.; Munk, W. Measurement of the Roughness of the Sea Surface from Photographs of the Sun’s Glitter. Josa 1954, 44, 838–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, W.A.; Arnone, R.A.; Davis, C.O.; Goode, W.; Gould, R.W.; Ladner, S.; Lamela, G.; Rhea, W.J.; Stavn, R.; Sydor, M. Optical Scattering and Backscattering by Organic and Inorganic Particulates in US Coastal Waters. Applied Optics 2008, 47, 666–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lübben, A.; Dellwig, O.; Koch, S.; Beck, M.; Badewien, T.H.; Fischer, S.; Reuter, R. Distributions and Characteristics of Dissolved Organic Matter in Temperate Coastal Waters (Southern North Sea). Ocean Dynamics 2009, 59, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Sym. | Parametrization | Ref. | Eq. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chla-specific absorption | a*Chla | a* Chla(λ) = aPhy(λ)/[Chla] | [46] | (5) |
| Phy absorption | aPhy | aPhy(λ) = [Chla].a*Chla(λ) | [46] | (6) |
| Phy absorption a | aPhy |
aPhy(λ) = [a0(λ) + a1(λ) × ln(aPhy(λ1))] × aPhy(λ1) a aPhy(λ1) = 0.06 × [Chla]0.65 |
[47] | (7) |
| CDOM absorption | aCDOM | aCDOM(λ) = aCDOM(λ2) × exp[-SCDOM × (λ - λ2)] | [48] | (8) |
| NAP absorption | aNAP | aNAP(λ) = aNAP(λ2) × exp[-SNAP × (λ - λ2)] | [48] | (9) |
| Chla backscattering | bb,Chla | bb,Chla(λ) = {0.002 + 0.02 × [0.5 – 0.25 × log10[Chla] × (λ3/λ)]} × bb,Chla(λ3) , bb,Chla(λ3) = 0.416 × [Chl]0.766 | [34] | (10) |
| Chla backscattering b | bb,Chla | bb,Chla(λ) = [Chla] × b*b,Chla(λ3) × bNChla(λ) | [49] | (11) |
| NAP backscattering c | bb,NAP |
bb,NAP(λ)=bNAP(λ3)×(λ3/λ)γ - [1 – tanh(0.5 × γ2)] × aNAP(λ) bNAP(λ3) = b*SPM(λ3) × I × [SPM] |
[50] | (12) |
| NAP backscattering d | bb,NAP |
bb,NAP(λ) = [SPM] × b*b,SPM(λ) × bNNAP(λ) b*b,SPM(λ) = A × [SPM]B , bNNAP(λ) = a*Chla(λ3)/ a*Chla(λ) |
[49] | (13) |
| Parameter | Min | Max | Mean | Median | Std | N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chla (mg m-3) | 0.44 | 51.48 | 9.080 | 6.31 | 2.56 | 648 |
| SPM (g m-3) | 2.20 | 82.40 | 16.06 | 12.75 | 5.98 | 648 |
| anw(675) (m-1) | 0.073 | 0.212 | 0.134 | 0.131 | 0.037 | 22 |
| anw(440) (m-1) | 0.792 | 1.206 | 0.934 | 0.901 | 0.128 | 22 |
| aPhy(675) (m-1) | 0.030 | 0.132 | 0.069 | 0.078 | 0.032 | 22 |
| aPhy(440) (m-1) | 0.052 | 0.224 | 0.119 | 0.138 | 0.055 | 22 |
| a*Chl(675) (m2 mg-1) | 0.014 | 0.021 | 0.017 | 0.017 | 0.002 | 22 |
| a*Chl(440) (m2 mg-1) | 0.022 | 0.036 | 0.028 | 0.029 | 0.004 | 22 |
| aNAP(440) (m-1) | 0.097 | 0.264 | 0.188 | 0.189 | 0.041 | 22 |
| a*NAP(440) (m2 mg-1) | 0.004 | 0.036 | 0.015 | 0.012 | 0.009 | 22 |
| SNAP (nm-1) | -0.011 | -0.009 | -0.01 | -0.01 | 0.001 | 22 |
| aCDOM(440) (m-1) | 0.441 | 0.906 | 0.621 | 0.599 | 0.103 | 22 |
| SCDOM (nm-1) | -0.013 | -0.008 | -0.011 | -0.011 | 0.001 | 22 |
| b*SPM(λ) (m2 mg-1) | 0.182 | 1.991 | 0.401 | 0.305 | 0.395 | 12 |
| Model | ρ(λ,θv, Δφ) | ΔL | Remarks | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MO99 | Lookup table of θv, Δφ, θs, and wind speed | min of Rrs(750-800) | ρ =0.028 in overcast and full ranges of wind speeds | [4] |
| MO15 | Similar to MB99 | improved values of ρ for sky polarization | [27] | |
| Ru05 a | ρ = 0.0256 in clear skies, ρ =0.0256 + 0.00039W + 0.000034W2 in cloudy |
Similarity spectrum normalization at 780 nm | ρ fits all simulations of 30≤θs≤70 with 1% err for W=5 and 3% for W=10 | [17] |
| BA18 | ρ = 0.0265 | min of Rrs(750-950) | Rrs(λ) optimized with a two-stream RT model | [28] |
| HT23 b | Lookup table of λ,θv,Δφ, θs, wind speed, and AOT. | min of Rrs(775-850) | RT computations used for AOT, polarization, and wind effects. Wavelength-dependent ρ. | [22] |
| Ku13 | ρ = 0.020 | Fitting a power function through the 350-380 nm and 890-900 nm regions. Wavelength-dependent ΔL | [21] | |
| JD20 | ρ = 0.028 | Relative height of the water-absorption-dip-induced-reflectance-peak-at-810 nm. It assumes ΔL is wavelength independent for variable cloud covers. | [20] | |
| ZX17 | Wavelength-dependent ρ. Lookup table of θv,Δφ, θs, wind speed, and AOT | min of Rrs(775-850) | Lookup table for: Wind speed:0,5,10,15 θs ≤ 60° AOT: 0,0.05,0.10, 0.20, 0.50 Clear Sky (cloud cover = 0) |
[2] |
| 3C | ρ and ΔL were estimated through optimization of LT(λ)/Ed(λ) modeling against measured LT(λ)/Ed(λ) using the fit parameters of IOPs and WCCs | It needs an overview of IOPs and WCCs, flexible for all environmental conditions. Wavelength-dependent ΔL | [16] | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





