Submitted:
02 June 2025
Posted:
02 June 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
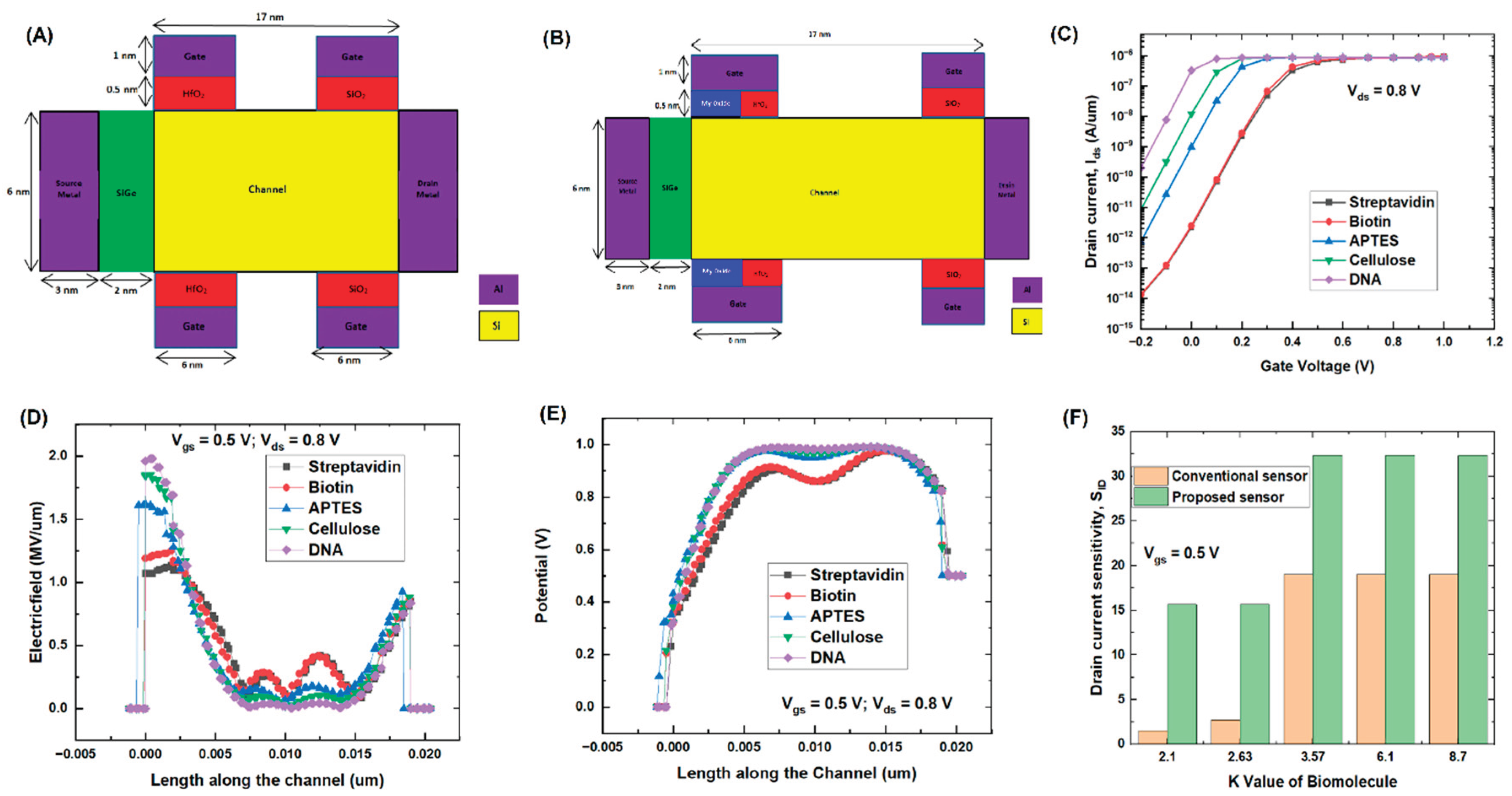
Introduction
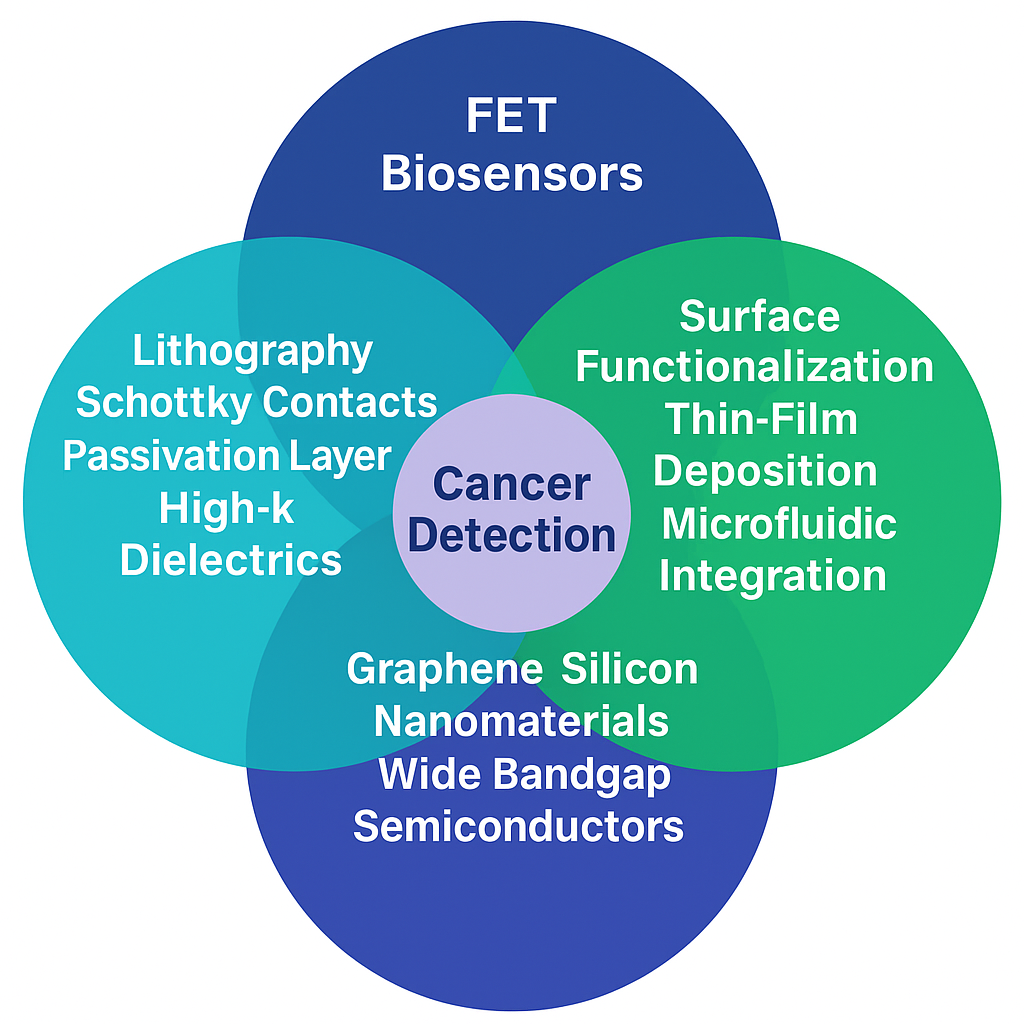
Comprehensive Strategies for Enhanced FET Biosensor Design
Advanced Lithography and Nanofabrication Techniques
Surface Functionalization and Chemical Modification
Deposition Techniques and Thin-Film Processes
Microfluidics and Integration Techniques
Passivation and Isolation Techniques
Optimizing Sensitivity and Specificity in FET Sensors
High-K Dielectrics for Enhanced Sensitivity and Specificity
Graphene and Silicon Nanomaterials for Enhanced Sensitivity and Specificity
Wide Bandgap Materials for High Sensitivity and Specificity
Schottky Barrier and Metal Contact Engineering for Enhanced Specificity
FET-Based Biosensors for Cancer Diagnostics
Pancreatic Cancer
Cancer Cell Lines Detection Using TFET
Advanced Material-Based FET Biosensors for Cancer Biomarkers
Point-of-Care and Microfluidic Integrated FET Biosensors
| Biomarker | Detection Method | Sensor Type | Functionalization | Limit of Detection | Sensitivity/Selectivity | Clinical Validation | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exosomal miRNA10b from PC-derived exosomes | Magnetic separation and reduced graphene oxide (RGO) FET biosensor | RGO FET | Magnetic beads (GPC-1 & EpCAM antibodies); PNA-functionalized RGO | 78 fM | High selectivity, capable of distinguishing single-base mismatch | Tested in 40 clinical plasma samples; effective differentiation between PC patients and healthy individuals | [42] |
| KRAS DNA and MUC1 protein markers | Single-molecule assay with large transistor (SiMoT) | Organic semiconductor FET | 3D-printed gate with b-KRAS and anti-MUC1 functionalization | KRAS: 10 zM, MUC1: 40 zM | Detection down to single-molecule level | Tested in diluted human blood serum; potential for noninvasive diagnosis of pancreatic cancer precursor cysts | [43] |
| CA 19-9 antigen | MoS2-based electrolyte-gated FET immunosensor | MoS2 nanosheets FET | Covalent immobilization of antibody 19-9 | 2.8 × 10⁻¹³ U/mL | High selectivity, linear range 1.0×10⁻¹² to 1.0×10⁻⁴ U/mL | Validated with real human serum samples; suitable for early-stage pancreatic cancer diagnosis | [44] |
| CA 19-9 antigen | TiS3 nanoribbons electrolyte-gated FET immunosensor | TiS3 nanoribbons FET | Surface modification with 1-naphthylamine, glutaraldehyde, and antibody 19-9 | 1.3 × 10⁻¹³ U/mL | High sensitivity (0.04 μA/decade), selectivity; linear range 1.0 × 10⁻¹² to 1.0 × 10⁻⁵ U/mL | Compared with ELISA in spiked real human serum samples; effective for cancer diagnosis and therapeutic monitoring | [45] |
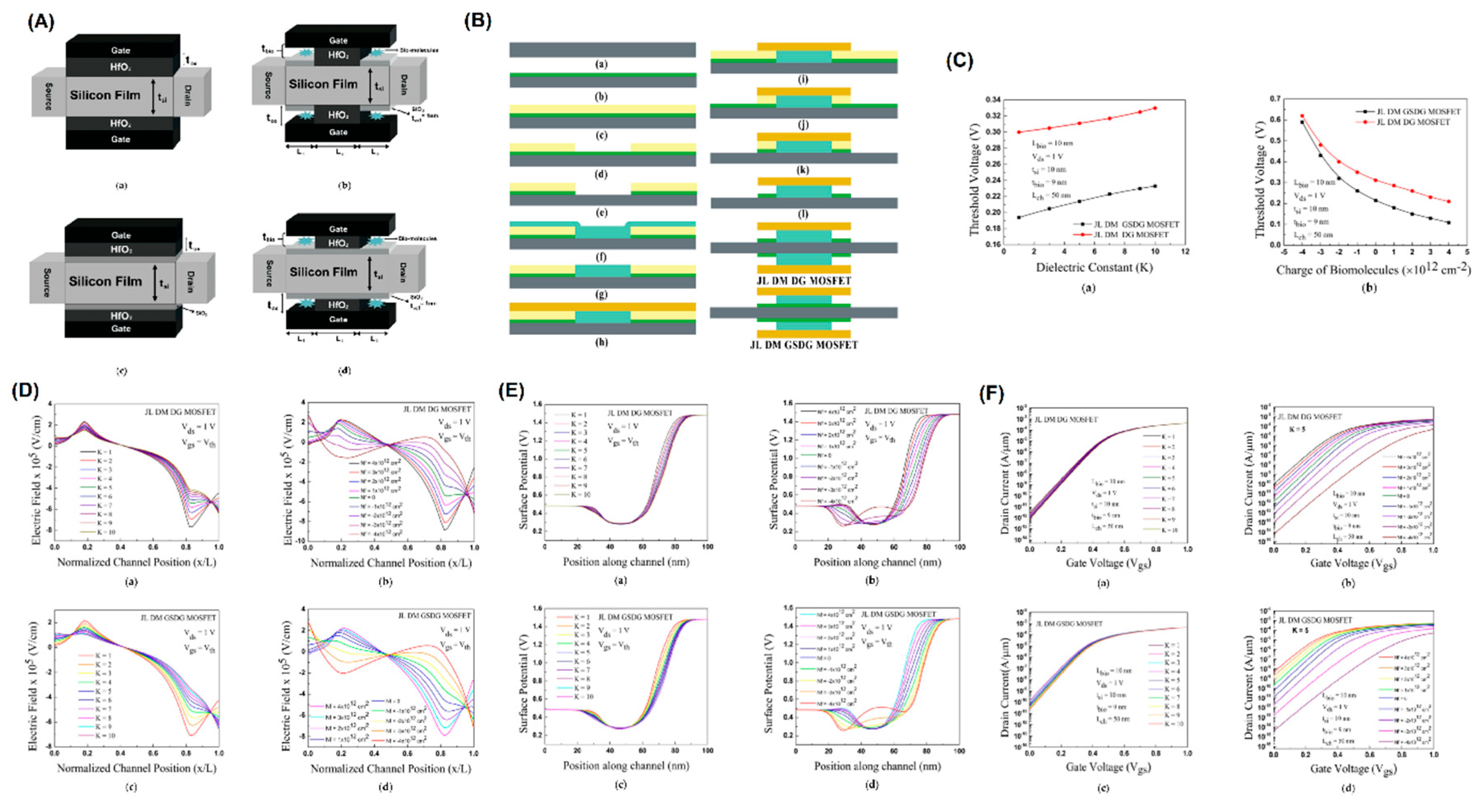
| Liver cancer cell lines (dielectric properties) | Source-Extended Tunnel FET (SE TFET) with Single-Gate Single-Metal (SGSM) and Dual-Metal (SGDM) structure | SE TFET | SiO₂ adhesive layer, modified gate oxide with nanocavities immobilizing liver samples | Not explicitly stated | Higher sensitivity in DM structure, better current differentiation in SM structure; sensitivity varies with gate work function and cavity length | Simulation-based; capable of detecting different percentages of cancerous cells in specimens | [46] |
| Exosomal microRNA-122 | Interdigitated FET incorporating metal carbide@carbon nanotubes (MC@CNT-iFETs) | MC@CNT-iFET | Metal carbide and CNT composite | 0.12 fM | High specificity, reproducibility, and stability | Differentiated 25 liver cancer patients from 25 healthy individuals; correlation with q-PCR (R²=0.8977); AUC=0.9776 | [50] |
| KRAS and BRAF gene mutations | Electrolyte-insulator-semiconductor (EIS) biosensor | YbTixOy-based EIS sensor | Functionalized with 3-aminopropyl triethoxysilane and glutaraldehyde | Sensitivity: 69.54 mV/pH; low drift and hysteresis | High sensitivity, rapid detection capability | Proposed for clinical CRC diagnostics, not yet clinically validated | [51] |
| Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) | Floating gate FET biosensor with semiconducting CNT film and Y₂O₃ dielectric layer | CNT-FET with Y₂O₃ dielectric | CNT film on undulating Y₂O₃ for enhanced probe-binding sites | 72 ag/mL (range: 1 fg/mL to 1 ng/mL) | Wide detection range, optimized sensitivity and detection limit | Validated in complex fetal bovine serum environment; potential for early lung cancer screening | [52] |
| Liver cancer cell lines (Hepatocellular carcinoma) | Source Extended Tunnel FET (SE TFET) | SG and DG SE-TFET | SiO₂ adhesive, etched oxide nanocavities; GaAs or SiGe channel | Not explicitly stated | Higher sensitivity in GaAs with gate work function 5.3 eV; better drain current differentiation at 4.2 eV; optimal cavity lengths (10 nm source, 20 nm drain) | Simulation-based; capable of detecting smaller percentages of malignant cells | [47] |
| Breast cancer cell lines (Hs578T, MDA-MB-231, MCF-7, T47D) | Junctionless dual nanocavity engraved FET | Dual Gate JLFET | Optimized nanocavity thickness and SiO₂ oxide length | Maximum sensitivity for T47D (ΔVTH=0.800 V, ΔION=0.165 mA/μm, Δgm=0.296 mA/V−μm, ΔSS=5.41 mV/decade) | Highly sensitive; sensitivity increases with cavity occupancy | Simulation-based; potentially useful for array-based diagnostics | [48] |
| Breast cancer cell lines (T-47D, MCF-7, MDA-MB-231, Hs 578T) | Dopingless dual metal gate heterojunction TFET | DM-DL-DMG-HJTFET | Immobilization in nanogap beneath gate electrode | Maximum sensitivity achieved at 0.55 V for T-47D; significant improvement in sensitivity (up to 72.40%) compared to healthy cells | Highly sensitive; differentiates even low cancer cell concentrations | Simulation-based; excellent candidate for early-stage breast cancer diagnostics | [49] |
| Ovarian cancer biomarker (HE4) | Dual-material In0.53Ga0.47As/Si charge-plasma-based extended gate TFET | DCE-HTFET | Optimized Ga mole fraction and gate extension length | Optimum SION/IOFF of 18.2 × 10⁶, sub-threshold swing sensitivity (SSS) of 95% for 'Mucinous' histological subgroup at 74 pmol/L | Highly effective; significantly better than state-of-the-art sensors | Simulation-based; highly efficient for detecting ovarian cancer biomarkers | [53] |
| Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) | Label-free graphene FET integrated with coplanar electrodes and DEP microfluidics | Graphene FET | Coplanar gate electrodes, microfluidic compact disc platform | 1 pg/mL (dynamic range up to 4 ng/mL) | Highly selective against BSA and IgG interferents; improved detection limit by 3 orders compared to existing devices | Validated with commercially available systems using human serum samples | [54] |
| CYFRA 21–1 (Oral cancer biomarker) | WO₃ thin-film FET biosensor | Tungsten oxide (WO₃) FET | Antibody immobilization on WO₃ thin film | 1.26 pg/mL (range: 1 pg/mL to 1 ng/mL) | High specificity and rapid response; maximum response 122.88 at 1 pg/mL; minimal sample requirement (2 µL) | Demonstrated capability in artificial saliva samples; batch fabrication capability | [55] |
| Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) | Microfluidic electrolyte-gated TiS₃ nanoribbon FET immunosensor | TiS₃ nanoribbon FET | Anti-PSA monoclonal antibody immobilization; microfluidic integration | 0.04 fg/mL (linear range: 0.1 fg/mL to 10 pg/mL) | High sensitivity (2.2665 nA/decade); excellent specificity; effective detection even at lower concentrations | Tested with PSA-spiked human serum; demonstrated accurate measurement in diluted serum samples | [57] |
| Glutathione (GSH) | ZnO nanoparticle-GST composite FET | ZnO nanoparticle-GST composite channel | Electrostatic binding of ZnO nanoparticles with GST enzyme | 43.96 nM; cellular detection LoD: 30 cells (HeLa cells) | Sensitivity: 60.22 μA/dec in solution, 210.86 nA/cell for cellular detection; selective differentiation between cancerous and noncancerous cells | Successfully differentiated HeLa and MCF-7 cancerous cells from noncancerous HEK cells | [56] |
Conclusion
Acknowledgments
Authors’ contributions
Funding
Availability of data and material
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Consent for publication
Competing interests
References
- Prakash, M.D., et al., A study of an ultrasensitive label free silicon nanowire FET biosensor for cardiac troponin I detection. Silicon, 2022. 14(10): p. 5683-5690. [CrossRef]
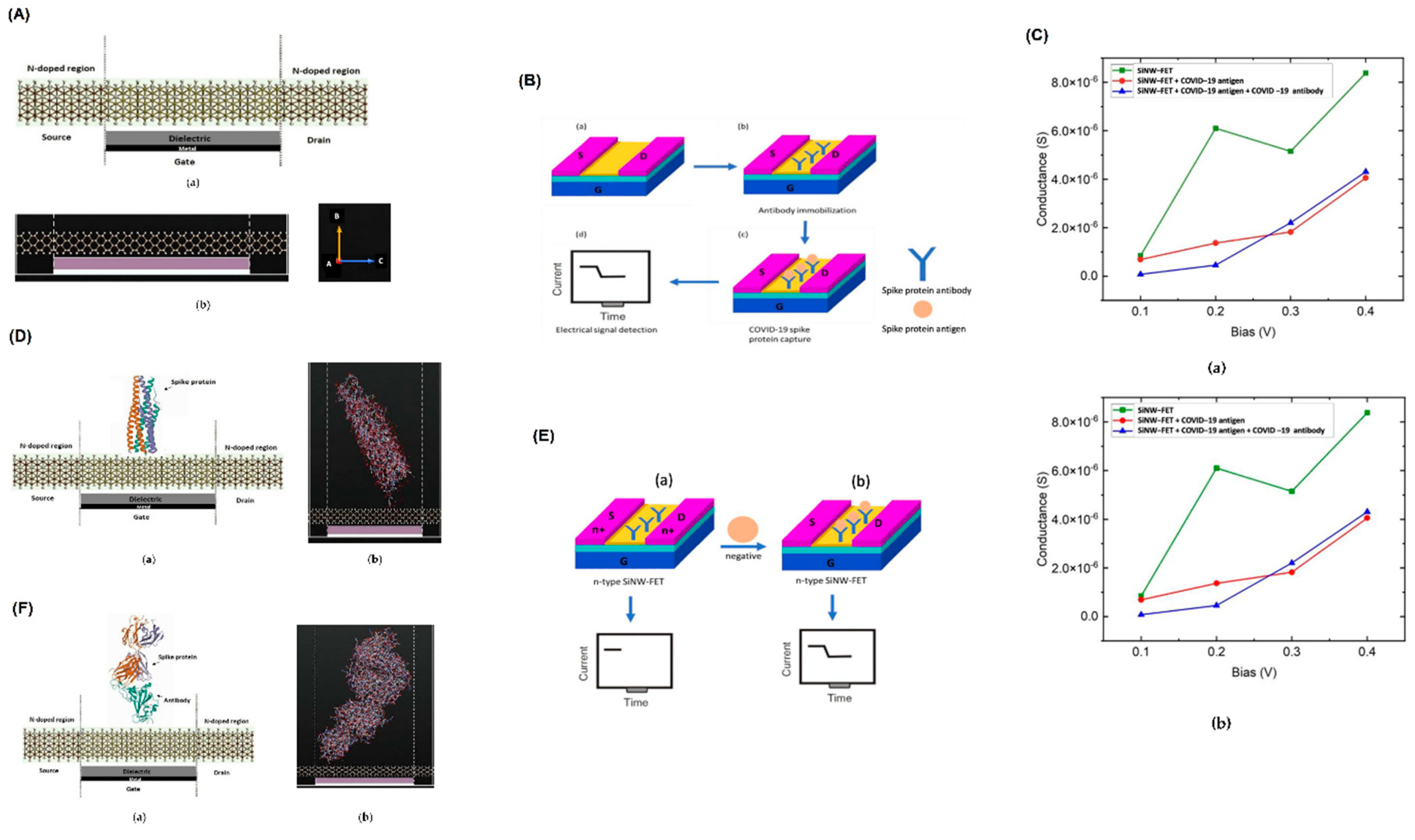
- Wasfi, A., et al., COVID-19 detection via silicon nanowire field-effect transistor: Setup and modeling of its function. Nanomaterials, 2022. 12(15): p. 2638. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W., et al., Si nanowire Bio-FET for electrical and label-free detection of cancer cell-derived exosomes. Microsystems & Nanoengineering, 2022. 8(1): p. 57. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y., et al., Integrated Urinalysis Devices Based on Interface-Engineered Field-Effect Transistor Biosensors Incorporated With Electronic Circuits. Advanced Materials, 2022. 34(36): p. 2203224. [CrossRef]
- Krsihna, B.V., et al., Design and development of graphene FET biosensor for the detection of SARS-CoV-2. Silicon, 2022: p. 1-9. [CrossRef]
- Zamzami, M.A., et al., Carbon nanotube field-effect transistor (CNT-FET)-based biosensor for rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) surface spike protein S1. Bioelectrochemistry, 2022. 143: p. 107982. [CrossRef]
- Pan, T.-M., et al., Rapid and label-free detection of the troponin in human serum by a TiN-based extended-gate field-effect transistor biosensor. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2022. 201: p. 113977. [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.-H., et al., Saliva-based COVID-19 detection: A rapid antigen test of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein using an electrical-double-layer gated field-effect transistor-based biosensing system. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2022. 357: p. 131415. [CrossRef]
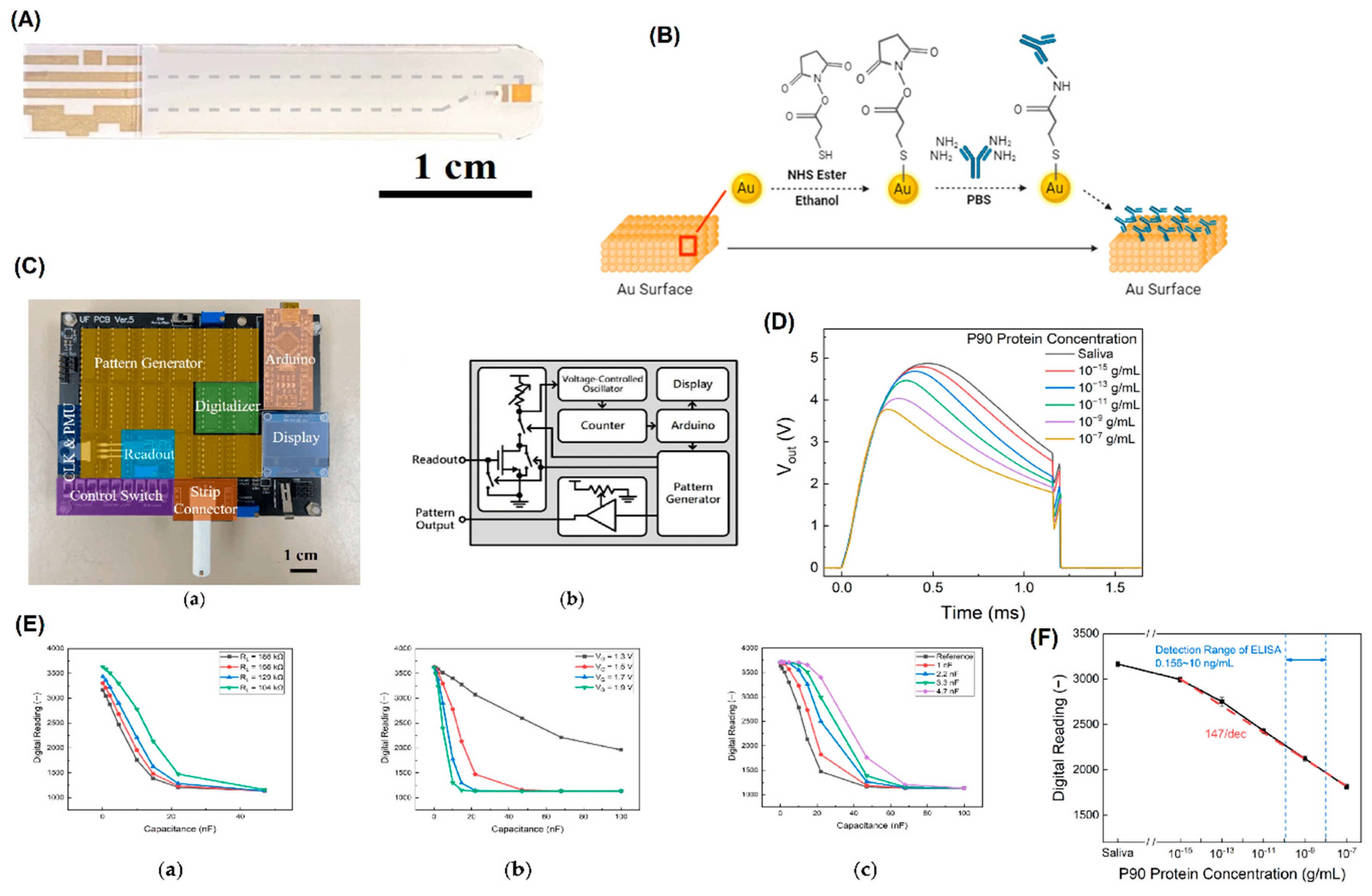
- Wan, H.-H., et al., Sensitive Detection of Oral Leukoplakia: Analyzing P90 Biomarkers in Saliva and Tissue. Biosensors, 2024. 14(6): p. 281. [CrossRef]
- Krsihna, B.V., et al., A highly sensitive graphene-based field effect transistor for the detection of myoglobin. Silicon, 2022. 14(17): p. 11741-11748. [CrossRef]
- Thakur, R.R., et al., Label-free GaN HEMT-based biosensing platform for interferon-γ detection. Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing, 2024. 178: p. 108416. [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.-H., et al., Point-of-Care Detection of HER2 and CA 15-3 in Breast Cancer Patients: Dual-Channel Biosensor Implementation. ECS Journal of Solid State Science and Technology, 2024. 13(5): p. 057003. [CrossRef]
- Samanta, S., et al., From sensing interactions to controlling the interactions: a novel approach to obtain biological transistors for specific and label-free immunosensing. Nanoscale, 2024. 16(13): p. 6648-6661. [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, R., S. Sarkhel, and P. Saha, MoS 2 based dual gate MOSFET as ultra-sensitive SARs-CoV-2 biosensor for rapid screening of respiratory syndrome. IEEE Sensors Letters, 2023.
- Wasfi, A., et al., Real-time COVID-19 detection via graphite oxide-based field-effect transistor biosensors decorated with Pt/Pd nanoparticles. Scientific reports, 2022. 12(1): p. 18155. [CrossRef]
- Kim, J., et al., An immunosensor based on a high performance dual-gate oxide semiconductor thin-film transistor for rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2. Lab on a Chip, 2022. 22(5): p. 899-907. [CrossRef]
- Johri, S., et al., ß-amyloid as a Novel Target Biomarker for the OEGFET Biosensor, Revolutionizing Non-Invasive Alzheimer's Screening. IEEE Sensors Letters, 2024.
- Wei, J., et al., Highly sensitive detection of multiple proteins from single cells by MoS2-FET biosensors. Talanta, 2022. 236: p. 122839. [CrossRef]
- Yahya, I., et al., Swcnt network-fet device for human serum albumin detection. Sensors, 2022. 22(21): p. 8212. [CrossRef]
- Kachhawa, P., et al., Antigen-antibody interaction-based GaN HEMT biosensor for C3G detection. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2022. 22(7): p. 6256-6262. [CrossRef]
- Sriramani, P., et al., Threshold and surface potential-based sensitivity analysis of symmetrical double gate AlGaN/GaN MOS-HEMT including capacitance effects for label-free biosensing. Physica Scripta, 2023. 98(11): p. 115036. [CrossRef]
- Hussian, A., et al., Metal Strip Implanted Tunneling Field-Effect Transistor Biosensor as a Label-Free Biosensor. ACS Applied Bio Materials, 2024. [CrossRef]
- Harika, P., et al., High Sensitivity of Dielectrically Modulated Tunnel Field Effect Transistor for Biosensor Applications. IEEE Transactions on NanoBioscience, 2024. [CrossRef]
- Bind, M.K. and K.K. Nigam, Sensitivity and Non-Ideal Issues Analysis of a Dielectric Modulated Electrically Doped Junctionless TFET-Based Label-Free Biosensor. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2024. [CrossRef]
- Sen, D., et al., Noise immune dielectric modulated dual trench transparent gate engineered MOSFET as a label free biosensor: proposal and investigation. Journal of Computational Electronics, 2021. 20: p. 2594-2603. [CrossRef]
- Biswas, A., C. Rajan, and D.P. Samajdar, A novel rfet sensor for label-free biomolecule detection. Silicon, 2022. 14(15): p. 9533-9541. [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, D., et al., A Novel Dielectric Modulated Gate-Stack Double-Gate Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor-Based Sensor for Detecting Biomolecules. Sensors, 2023. 23(6): p. 2953. [CrossRef]
- Peesa, R.B. and D.K. Panda, Rapid detection of biomolecules in a junction less tunnel field-effect transistor (JL-TFET) biosensor. Silicon, 2022. 14(4): p. 1705-1711. [CrossRef]
- Dash, S. and G.P. Mishra, Ambipolarity sensitivity investigation using a charge-plasma TFET with graphene channel for biomolecule detection. ECS Journal of Solid State Science and Technology, 2024. 13(1): p. 011005. [CrossRef]
- Shaleen, S. Singh, and P. Kumar, Ultrasensitive label-free electrical detection of charged biomolecules using a metal–semiconductor–metal Schottky silicon nanowire biristor. Journal of Computational Electronics, 2022. 21(1): p. 86-93. [CrossRef]
- Ashima, V. Dhandapani, and B. Raj, Design and performance assessment of graded channel gate-all-around silicon nanowire FET for biosensing applications. Silicon, 2023. 15(8): p. 3535-3542. [CrossRef]
- Esakki, P., et al., Improved Dielectrically Modulated Quad Gate Schottky Barrier MOSFET Biosensor. Micromachines, 2023. 14(3): p. 685. [CrossRef]
- Reddy, N.N. and D.K. Panda, Design and investigation of dielectric modulated triple metal gate-oxide-stack Z-shaped gate horizontal pocket TFET device as a label-free biosensor. Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering, 2022. 32(8): p. 085001. [CrossRef]
- Jia, H., et al., A P+ Pocket Doped 4H-SiC Schottky Barrier FET as Highly Sensitive Label-free Biosensor. Micro and Nanostructures, 2024: p. 207931. [CrossRef]
- Rashid, S., et al., Double gate 6h-silicon carbide schottky barrier fet as dielectrically modulated label free biosensor. Silicon, 2023. 15(8): p. 3387-3398. [CrossRef]
- Swati, J. Kaur, and A.K. Singh, Performance investigation of Ge-based dielectric modulated junctionless TFET as a label-free biosensor. Applied Physics A, 2024. 130(2): p. 133. [CrossRef]
- Chakraborti, P., A. Biswas, and A. Mallik, High sensitivity Ge-source L-shaped tunnel BioFETs for detection of high-K biomolecules. Microsystem Technologies, 2022. 28(9): p. 2131-2138. [CrossRef]
- Talukdar, J., G. Rawat, and K. Mummaneni, Highly sensitivity Non-Uniform Tunnel FET based biosensor using source engineering. Materials Science and Engineering: B, 2023. 293: p. 116455. [CrossRef]
- Biswas, A., C. Rajan, and D.P. Samajdar, A Novel HM-HD-RFET Biosensor for Label-Free Biomolecule Detection. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2022. 51(11): p. 6388-6396. [CrossRef]
- Chahardah Cherik, I. and S. Mohammadi, Fringe-fields-modulated double-gate tunnel-FET biosensor. Scientific Reports, 2024. 14(1): p. 168. [CrossRef]
- Pundir, A.K.S., et al., Electrolyte Gated based pH sensing Vertical TFET Biosensor: Design, Simulation and Noise Analysis. Micro and Nanostructures, 2024: p. 207897. [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y., et al., Integrated FET sensing microsystem for specific detection of pancreatic cancer exosomal miRNA10b. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2023. 1284: p. 341995. [CrossRef]
- Sarcina, L., et al., A large-area organic transistor with 3D-printed sensing gate for noninvasive single-molecule detection of pancreatic mucinous cyst markers. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2022. 414(18): p. 5657-5669. [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, H., S.M. Majd, and A. Salimi, Highly sensitive and selective detection of the pancreatic cancer biomarker CA 19-9 with the electrolyte-gated MoS2-based field-effect transistor immunosensor. Ionics, 2023. 29(9): p. 3769-3779. [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, H., et al., Ultrasensitive immunosensor for monitoring of CA 19-9 pancreatic cancer marker using electrolyte-gated TiS3 nanoribbons field-effect transistor. Talanta, 2023. 257: p. 124336. [CrossRef]
- Kolay, A. and A. Kumar, A Novel Liver Cancer POC Diagnostic Detection Technique by a Gate-engineered Source-extended TFET Device. Medical Engineering & Physics, 2024. 125: p. 104133. [CrossRef]
- Kolay, A. and A. Kumar, Liver cancer rapid-testing POC low-cost diagnostic unit using novel dual-gate source-extended TFET based biosensor. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 2024. 369: p. 115131. [CrossRef]
- Priyadarshani, K.N. and S. Singh, Ultra sensitive breast cancer cell lines detection using dual nanocavities engraved junctionless FET. IEEE Transactions on NanoBioscience, 2023. 22(4): p. 889-896. [CrossRef]
- Dewan, B., et al., Label-free detection of breast cancer cell lines using dopingless heterojunction TFET considering non-ideal hybridization issue. Materials Science and Engineering: B, 2024. 302: p. 117192. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W., et al., Miniaturized and portable device for Noninvasive, ultrasensitive and point-of-care diagnosis by engineered Metal-Carbide-based field effect transistor. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2025: p. 160264. [CrossRef]
- Pan, T.-M. and P.-Y. Liao, High sensitivity and rapid detection of KRAS and BRAF gene mutations in colorectal cancer using YbTixOy electrolyte-insulator-semiconductor biosensors. Materials Today Chemistry, 2022. 25: p. 100979. [CrossRef]
- Li, L., et al., Carbon nanotube field-effect transistor biosensor with an enlarged gate area for ultra-sensitive detection of a lung cancer biomarker. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2023. 15(22): p. 27299-27306. [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, A., D. De, and M. Chanda, Ovarian-cancer biomarker (HE4) recognition in serum using hetero TFET biosensor. IEEE Transactions on Nanotechnology, 2023. 22: p. 238-244. [CrossRef]
- Mandal, N., et al., PSA detection using label free graphene FET with coplanar electrodes based microfluidic point of care diagnostic device. Talanta, 2021. 222: p. 121581. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S., et al., Tungsten oxide thin film field-effect transistor based real-time sensing system for non-invasive oral cancer biomarker detection. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2024. 407: p. 135486. [CrossRef]
- Barman, U., et al., Fabrication of Glutathione-S-Transferase–ZnO Nanoconjugate Ensemble FET Device for Detection of Glutathione. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2021. 68(3): p. 1242-1249. [CrossRef]
- Majd, S.M. and A. Salimi, Microfluidic electrolyte-gated TiS3 nanoribbons-based field-effect transistor as ultrasensitive label-free immunosensor for prostate cancer marker analysis. Sensing and Bio-Sensing Research, 2024. 43: p. 100627. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





