Submitted:
23 April 2025
Posted:
15 May 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
- How do general diagnostic standards, AI-generated treatments, and homoeopathic approaches compare in diagnostic accuracy?
- To what extent do these modalities provide personalized and context-sensitive treatment plans?
- What is the long-term efficacy of each method in terms of sustained health outcomes and patient satisfaction?
Methodology
Scale Definition and Analysis
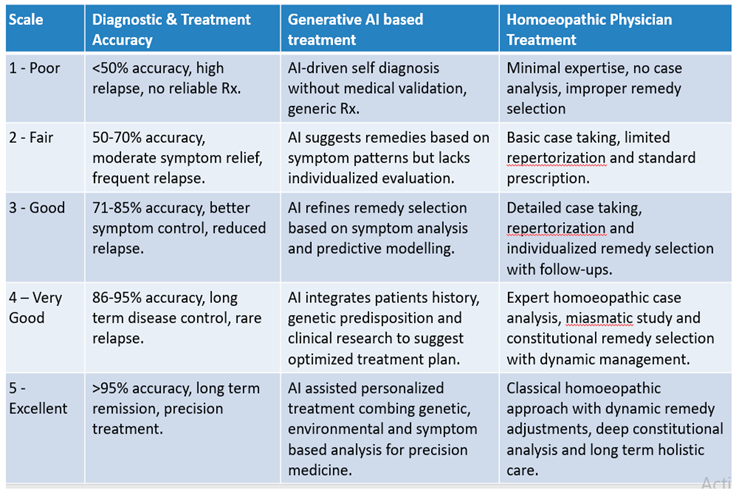
- Level 1 – Poor:
- Diagnostic & Treatment Accuracy: Less than 50% accuracy. Treatments often unreliable with frequent relapses.
- Generative AI: Basic symptom matching and generic prescriptions without clinical validation.
- Homoeopathic Physician: Minimal expertise, improper case analysis, and poor remedy selection lead to inadequate care.
- Level 2 – Fair:
- Diagnostic & Treatment Accuracy: 50–70% accuracy. Some symptom relief achieved but with frequent relapses.
- Generative AI: Uses symptom patterns to suggest possible treatments but lacks individualized patient evaluation.
- Homoeopathic Physician: Basic case taking and use of standard repertories with limited personalization.
- Level 3 – Good:
- Diagnostic & Treatment Accuracy: 71–85% accuracy. Better symptom control and reduced relapse rates.
- Generative AI: Employs predictive models and symptom analytics to refine remedy suggestions.
- Homoeopathic Physician: Detailed case taking and individualized prescriptions with regular follow-ups enhance care quality.
- Level 4 – Very Good:
- Diagnostic & Treatment Accuracy: 86–95% accuracy. Achieves long-term disease control and rare relapses.
- Generative AI: Integrates patient history, genetic predisposition, and clinical studies for optimized, data-backed treatment.
- Homoeopathic Physician: Employs expert-level miasmatic analysis, constitutional remedy selection, and dynamic management.
- Level 5 – Excellent:
- Diagnostic & Treatment Accuracy: Greater than 95% accuracy. Precision medicine approach with long-term remission.
- Generative AI: Delivers highly personalized treatment through deep integration of genetic, environmental, and clinical data.
- Homoeopathic Physician: Applies classical homoeopathic methodology with dynamic remedy adjustment and lifelong holistic care.
Discussion
- 1.
- General Diagnostic Standards: - General diagnostic practices largely fall within Level 2 (Fair) to Level 3 (Good). While protocols and clinical guidelines provide consistency, their generalized nature limits patient-specific customization. In many chronic or complex cases, standard treatments may lead to partial symptom relief but result in recurring issues or incomplete resolution. This reflects the typical outcomes seen in Levels 2 and 3, where accuracy ranges from 50% to 85%, depending on the practitioner’s experience and access to comprehensive diagnostics. However, these approaches lack the adaptability and deep personalization seen in the other modalities evaluated.
- 2.
- Generative AI-Based Treatments: - Generative AI shows a promising progression along the scale—from Level 1 (Poor) in early or minimally trained systems to Level 5 (Excellent) in advanced implementations. Basic AI models relying on symptom matching and rule-based outputs (Level 1 and 2) provide limited effectiveness, often overlooking subtle clinical nuances. However, with deeper learning models that incorporate patient history, genetic profiles, lifestyle factors, and clinical data (Levels 4 and 5), AI can deliver highly personalized treatments. These models reflect a future-oriented vision of precision medicine. Still, they face challenges regarding regulatory validation, ethical oversight, and integration into real-world clinical workflows.
- 3.
- Homoeopathic Physician-Led Treatments: - Homoeopathic care demonstrates significant variability depending on the practitioner’s expertise. Poorly trained practitioners may remain at Level 1 or 2, with generalized remedies and inadequate patient engagement leading to suboptimal outcomes. However, experienced homoeopaths who use classical methods—miasmatic analysis, constitutional case taking, and iterative follow-ups—often attain Level 4 or 5. These levels reflect long-term disease management, minimal relapses, and high patient satisfaction. The strength of homoeopathy lies in its deep personalization and holistic perspective, which aligns well with contemporary calls for integrative, patient-centered care.
- 4.
- Comparative Insights: - A notable trend across all three systems is the correlation between analytical depth and treatment efficacy. As diagnostic methods incorporate more individualized data—be it through AI algorithms or comprehensive case-taking—the outcomes shift toward Level 4 and 5. This supports the idea that personalization is a critical factor in medical success, regardless of modality. Furthermore, while AI and homoeopathy represent very different paradigms—technological and traditional respectively—both outperform standard diagnostics when practiced at advanced levels. This convergence suggests that blending the data-driven precision of AI with the human-centric nuance of classical homoeopathy could yield a hybrid model offering superior care.
- 5.
- Implications for Healthcare Practice and Policy: - These findings urge healthcare systems to consider broader evaluation frameworks that go beyond evidence hierarchies traditionally favoring pharmaceutical approaches. Embracing a pluralistic healthcare model that includes AI-enhanced diagnostics and validated alternative therapies could bridge current gaps in personalization and chronic care management. Additionally, training quality and standardization emerge as pivotal across all modalities. Whether it is an AI system being fine-tuned or a homoeopath undergoing rigorous education, the practitioner’s or system's sophistication directly affects outcomes.
- 6.
- Importance of the Research: - This research holds significant importance in the evolving landscape of healthcare innovation, especially as the medical community increasingly explores integrative approaches to enhance diagnostic and therapeutic accuracy. In an era marked by rapid technological advancement, generative AI offers immense promise for reshaping clinical decision-making through data-driven insights. However, the effectiveness of such systems needs rigorous benchmarking to ensure safety, reliability, and ethical deployment. Simultaneously, there is a resurgence of interest in holistic and individualized care systems such as homoeopathy, which emphasize deep case analysis, patient engagement, and long-term wellness over symptomatic relief. By proposing a five-level evaluative scale, this study provides a novel and structured framework that facilitates comparative analysis across fundamentally different modalities. This approach enables stakeholders—including clinicians, researchers, and policymakers—to objectively assess the strengths and limitations of both generative AI and homoeopathy based on measurable outcomes such as accuracy, relapse frequency, and personalization of care. Moreover, this framework helps bridge the gap between technological innovation and traditional wisdom, encouraging a more integrated and patient-centric model of care. As healthcare shifts from disease treatment to health management and prevention, the ability to combine precision tools like AI with the nuanced understanding of homoeopathic principles could significantly elevate treatment efficacy and patient satisfaction. From a research standpoint, this scale allows future studies to build on a consistent metric, fostering comparability and repeatability in trials and evaluations. It also invites interdisciplinary collaboration between data scientists, clinicians, and homoeopaths to refine both AI algorithms and treatment philosophies. Ethically, the framework promotes accountability by delineating clear standards for what constitutes poor, fair, or excellent practice in AI and homoeopathy. Such transparency is crucial in a healthcare environment increasingly dominated by AI startups and alternative medicine claims. In education and training, this research could serve as a foundational resource to inform curriculum development for both medical students and technology developers. Understanding how different approaches perform across a standard scale could foster mutual respect and collaboration between AI engineers and homoeopathic practitioners, improving healthcare outcomes. Ultimately, this research underscores that while technology can accelerate diagnostics and standardize treatment recommendations, the human element—represented in this study by homoeopathic expertise—remains irreplaceable in achieving true personalized care. The convergence of these modalities, when executed with excellence, offers a path toward a more holistic, accurate, and compassionate healthcare system.
- 7.
- Insights for Future AI-Homoeopathy Research: - This research lays a crucial foundation for upcoming AI-driven projects in the field of homoeopathy by providing a structured framework to evaluate efficacy, guide algorithm development, and integrate holistic principles into technological innovations. The five-level scale enables developers to measure AI system performance not only in terms of symptom matching but in delivering truly personalized, long-term treatment solutions—mirroring the ideals of classical homoeopathy. For AI researchers, this work suggests a roadmap to develop context-aware systems that can go beyond database matching to simulate in-depth case taking, miasmatic analysis, and dynamic remedy selection. It highlights the potential for AI to assist in areas like repertorization, tracking remedy responses, predicting remedy aggravations, and modeling individualized responses based on constitutional types. Furthermore, the scale encourages interdisciplinary research—bringing together AI developers, data scientists, and homoeopaths to co-create intelligent systems that are not only clinically accurate but also philosophically aligned with homoeopathic tenets. Future AI projects can leverage this structure to test and refine algorithms incrementally as they evolve from simple pattern recognition to high-level adaptive reasoning and care planning. This research also identifies key ethical and operational benchmarks, such as transparency in diagnosis, patient safety in remedy suggestions, and the necessity for human oversight in AI-assisted prescribing. These insights will be critical as AI tools are increasingly integrated into digital health platforms offering home-based care or remote consultations. Lastly, the framework can stimulate longitudinal studies evaluating how AI-homoeopathy hybrid systems impact chronic disease management, relapse rates, and patient satisfaction over time—thus providing a blueprint for evidence-based adoption of AI in complementary medicine.
Conclusion
- Supplementary: -
- Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) for Using the Five-Level Diagnostic and Treatment Evaluation Scale
- Purpose: -
- Scope: -
- Responsibilities: -
- Clinical Researchers: To apply the scale during trials and observational studies.
- AI Developers: To benchmark the performance of healthcare algorithms.
- Educators: To incorporate scale standards in training modules.
- Institutions: To use the scale for audits, certifications, and quality control.
- Physicians: To assess and improve practice levels through self-evaluation or peer review.
- Materials Required: -
- Patient outcome records
- Diagnostic accuracy logs
- Follow-up reports (relapse/frequency)
- AI output logs (if applicable)
- Evaluation checklist aligned with scale criteria
- Procedure: -
- 1.
- Data Collection: Collect diagnostic results, treatment plans, and follow-up outcomes for a defined period or sample group.
- 2.
- Performance Calculation (Percentage):
- 3.
- Grading Based on Performance Percentage:
- 4.
- Mapping Qualitative Indicators: Compare findings to qualitative descriptions under each level (e.g., personalization, relapse frequency, data depth).
- 5.
- Documentation: Record the grading level, supporting evidence, and justification in an evaluation report or audit form.
- 6.
- Review and Update: Reassess periodically or after each major system update, training cycle, or treatment revision.
- Example Application: -
- Case Evaluated: 100
- Correct Diagnoses or Effective Outcomes: 82
- Accuracy = (82/100) × 100 = 82%
- Grading: Level 3 – Good
- 7.
- Ethical Considerations: Ensure transparency and patient consent in using data, maintain confidentiality and use grading as a developmental tool, not punitive measure. The five-level diagnostic and treatment scale serves as both an evaluative and developmental tool for researchers, clinicians, and AI developers. To apply this scale effectively:
- Diagnostic Benchmarking: Assess the current level of diagnostic accuracy in a system (AI or homoeopathic) by measuring outcomes such as initial diagnosis correctness, response to treatment, and frequency of relapse.
- Treatment Planning Evaluation: Align treatment practices—whether automated or manual—to the characteristics defined in the corresponding scale level. For instance, personalized remedy selection and follow-ups align with Level 3 or higher.
- Algorithm Development: AI developers can use the scale to track their system’s growth, starting from Level 1 symptom matching to Level 5 precision medicine with multi-dimensional data integration.
- Training and Certification: Educational institutions can embed the scale in curriculums to train students in identifying and applying quality standards in diagnosis and care delivery.
- Clinical Audits: Healthcare institutions and digital health platforms can implement the scale as a quality control mechanism to continuously audit and refine diagnostic and therapeutic protocols.
- Patient Communication: Use the scale to explain the depth and sophistication of diagnostic/treatment options to patients, enhancing transparency and informed decision-making.
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References
- Singh SR, Patil AD. Bridging the Gap between Artificial Intelligence and Ancestral Intelligence in Conventional Medicine and Homeopathy. Indian Journal of Integrative Medicine. 2024 Apr 22;4(2):66-70.
- Singh SR, Patil AD. Natural Language Processing (NLP) as an Artificial Intelligence Tool and its Scope in Prognostic Factor Research Model in Homeopathy. databases.;13:15.
- Patil AD, Thopte M, Singh S. Scope of homoeopathic research based on Chat (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) GPT: An Artificial Intelligence (AI) approach. International Journal of High Dilution Research-ISSN 1982-6206. 2023;22(2):129-33. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




