Submitted:
22 October 2025
Posted:
27 October 2025
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Preface
2. Contradictions on Gravitational Redshift and Acceleration
2.1. Newtonian Gravitational Redshift
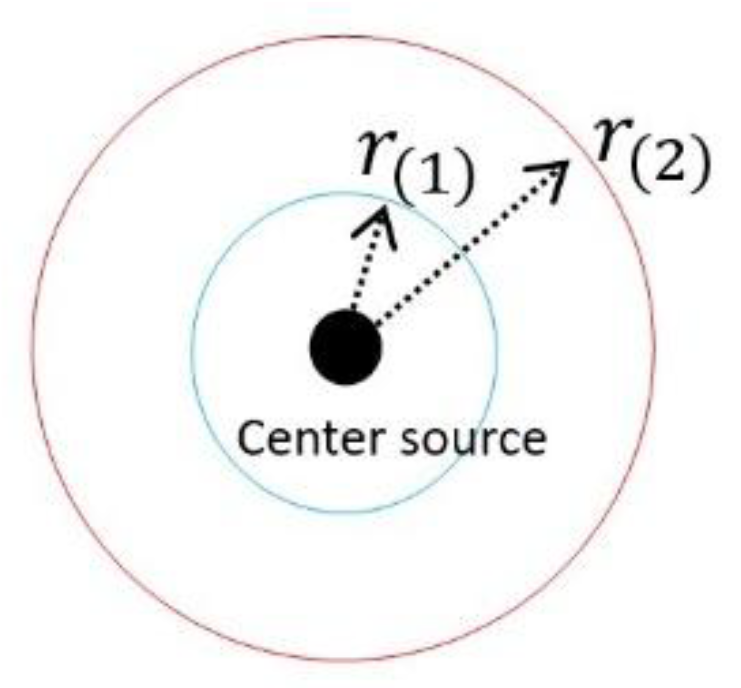
2.2. Errors in the Equation of the So-Called Revisit Gravitational Redshift
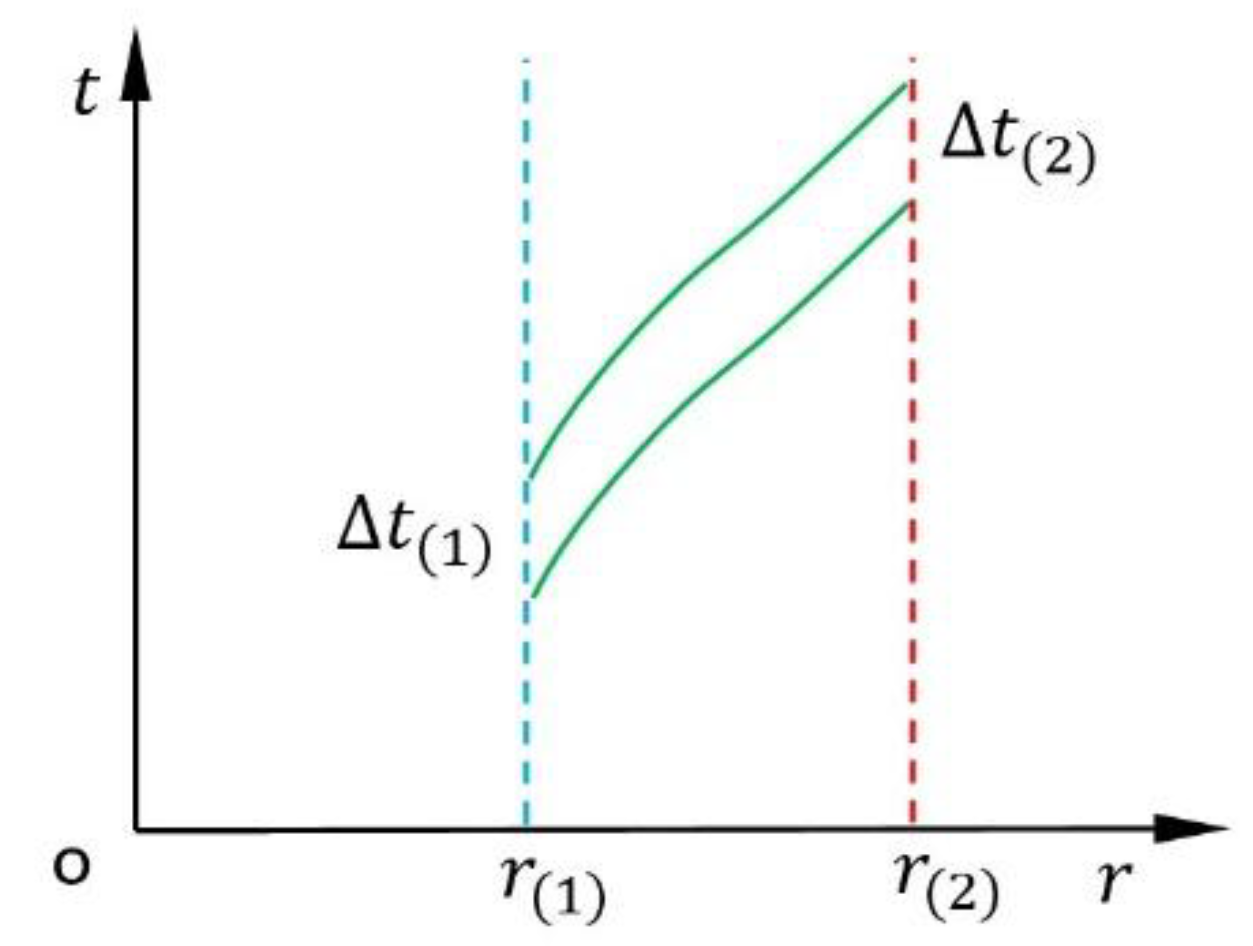
2.3. Further Investigation into the Revisit Gravitational Redshift
2.4. Additional Discussions on the Thought Experiment of Freefalling Elevator Cabin
2.5. An Investigation into Gravitational Acceleration
2.6. Discussions and Controversies
3. Theoretical Investigations on Christoffel Symbols
3.1. Classical Equations of Christoffel Symbols
3.2. The Inequality of Christoffel Symbols of Mixed Subscripts
3.2.1. Coordinate Transformations and Bases
- Example 1: Bases of Riemannian manifold of super surface
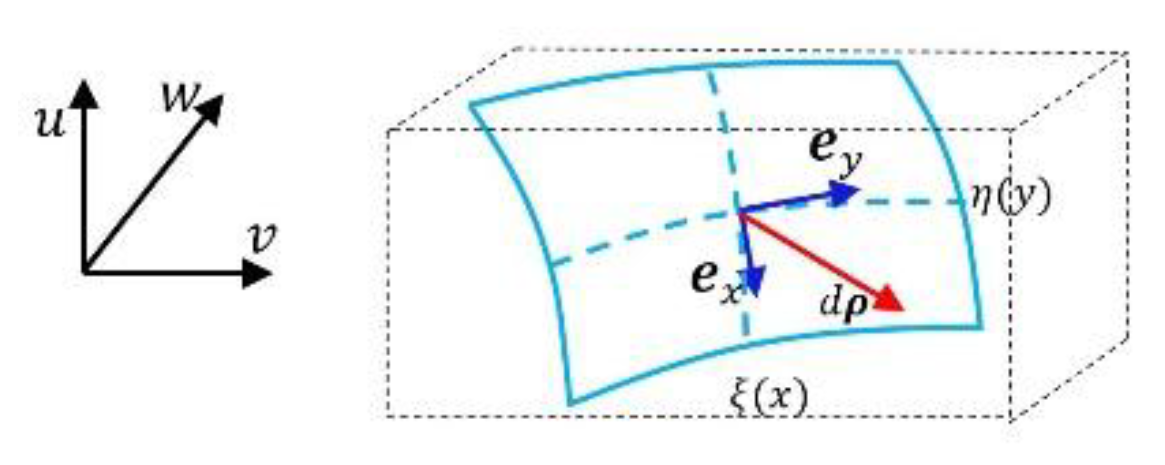
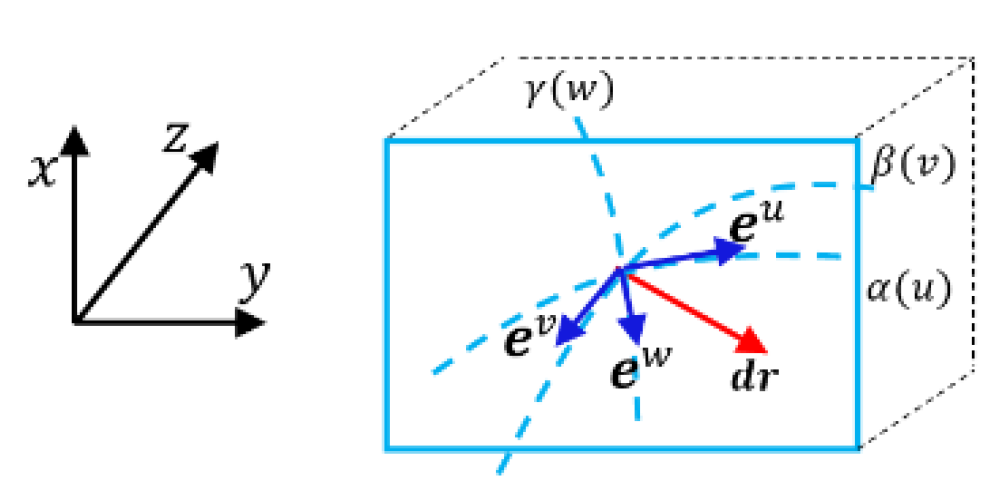
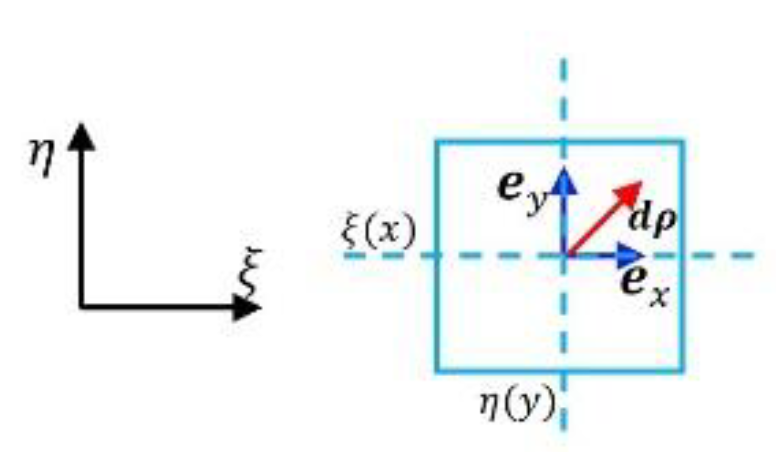
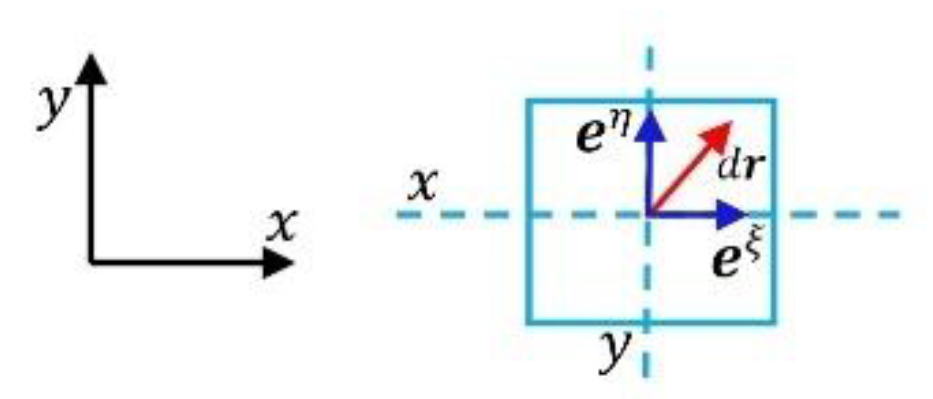
- Example 2: Bases of Riemannian manifold of equal dimension
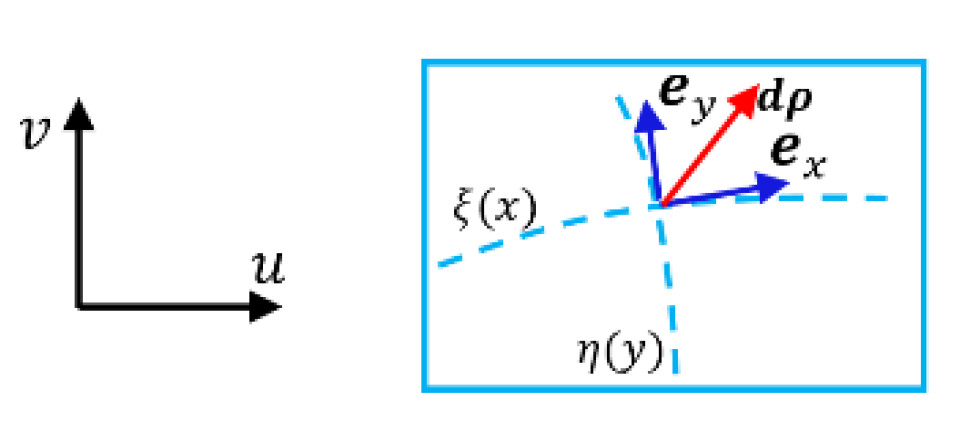
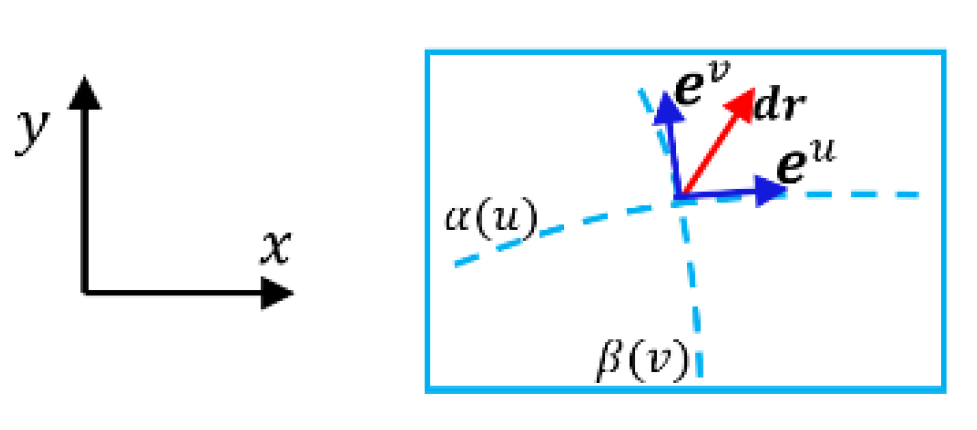
3.2.2. Inequalities of Mixed Derivatives of Bases
- Condition 1:
- Condition 2:
- Condition 3:
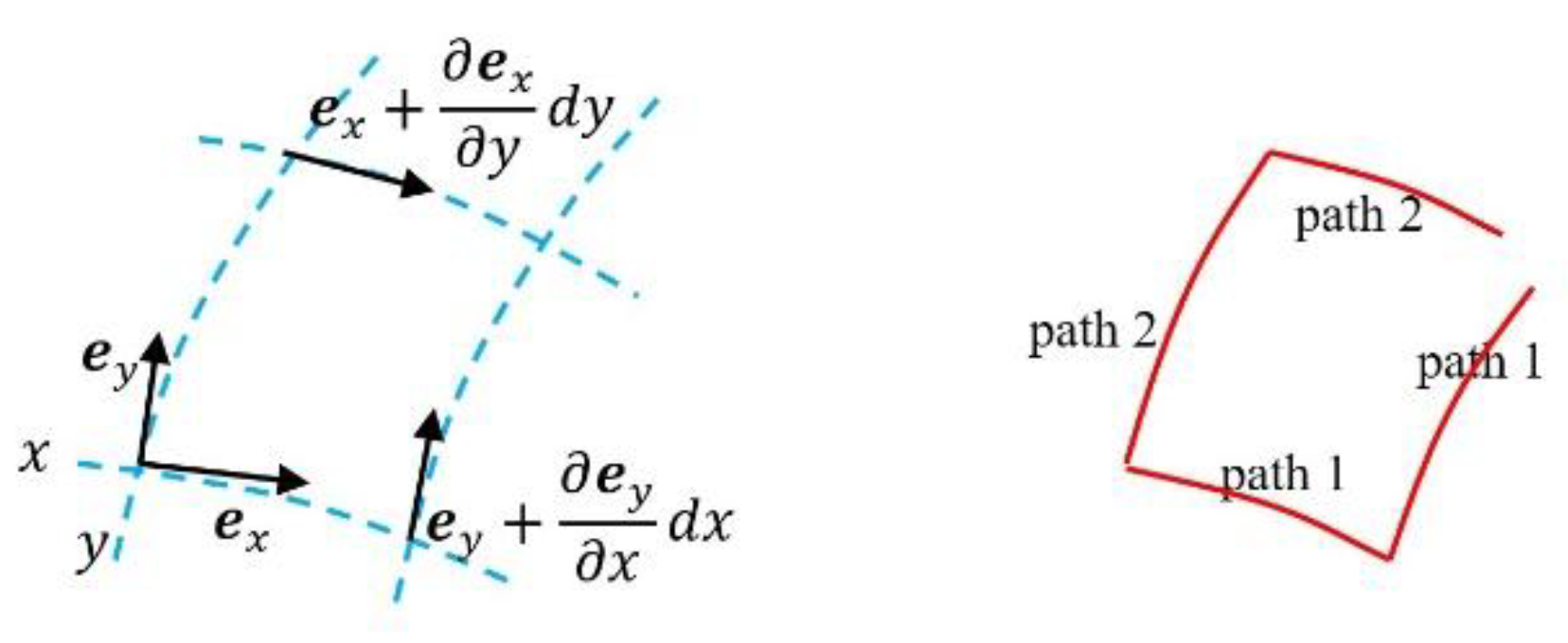
- in path 1,
3.2.3. Verifications and Discussions
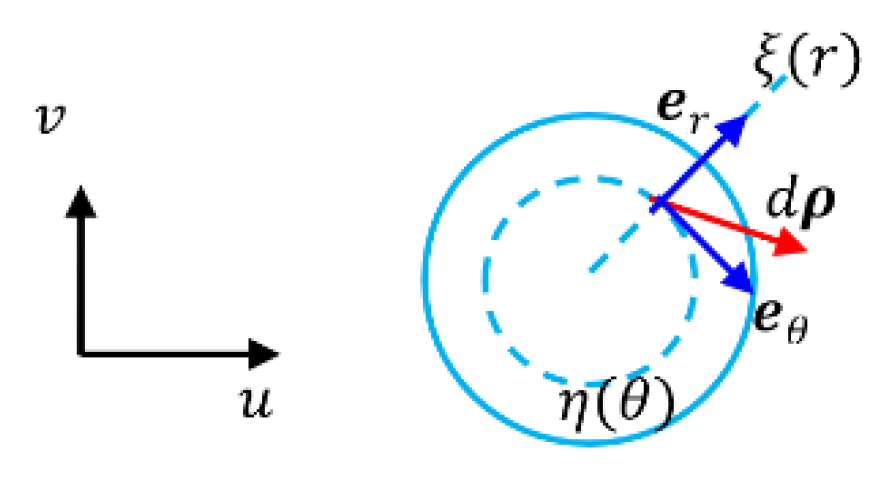
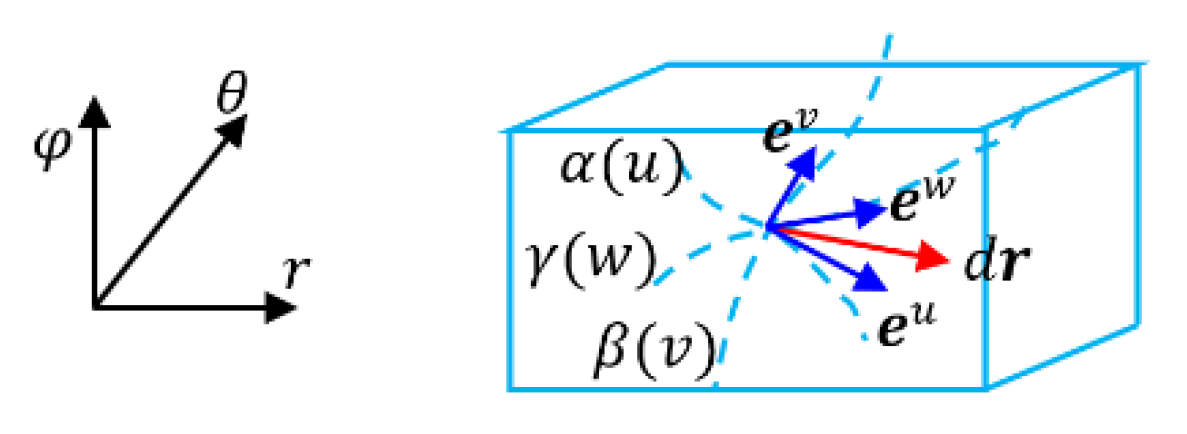
- Example 1: Polar coordinate system
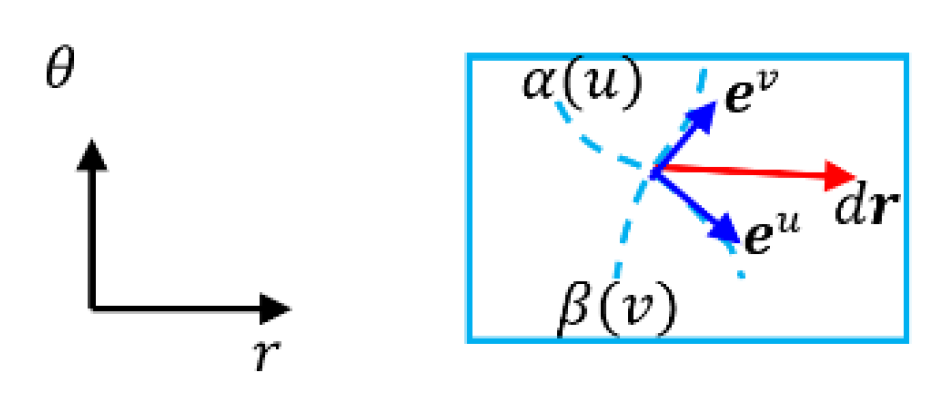
- Example 2: Spherical surface coordinate system
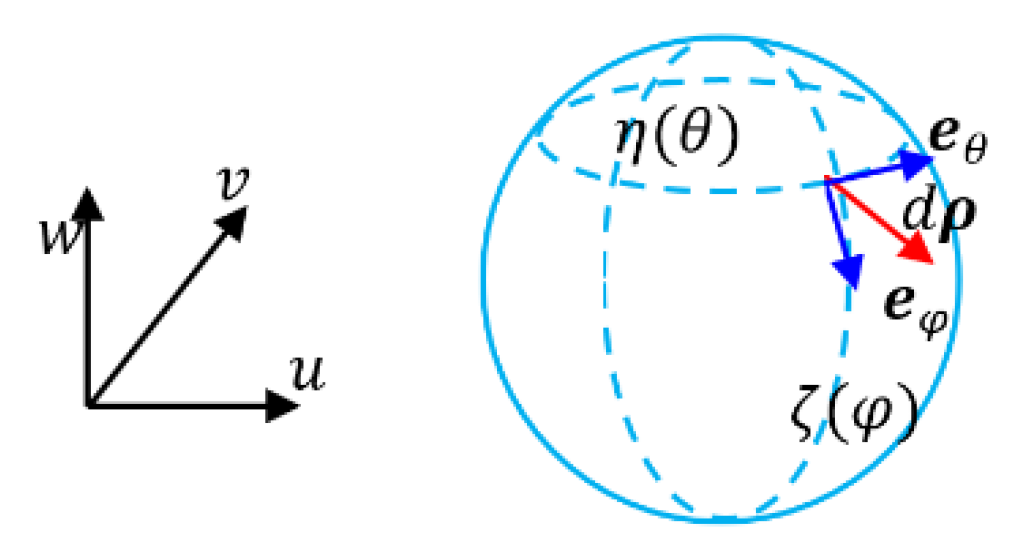
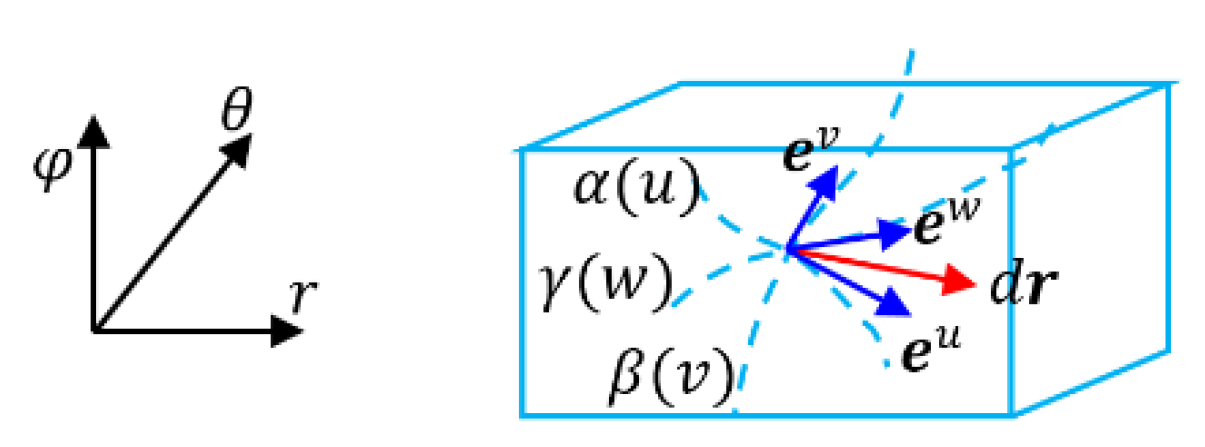
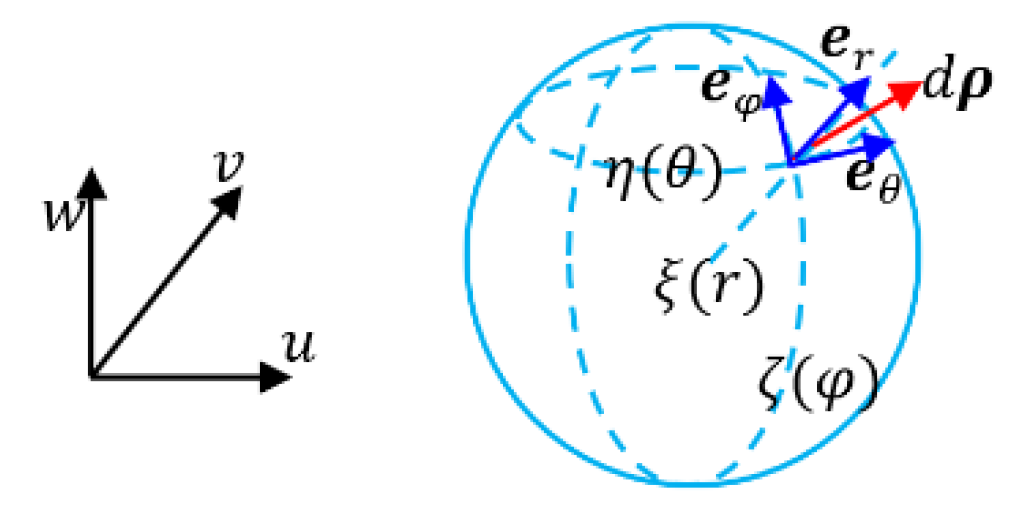
- Example 3: Spherical coordinate system
- Additional discussion: deformed bases of example 3
4. Metrics and Covariant Derivatives in Space Time
4.1. Metrics in Pseudo Riemannian Space
4.2. Discussions on Bases, Tensors, and Their Derivatives
4.3. Derivation via Christoffel Symbols
4.4. Derivatives on Matter’s Trajectory
5. Theoretical Verifications on Gravitational Redshifts and Accelerations
5.1. On Gravitational Redshifts
5.2. On Accelerations
6. Experimental Verifications on Gravitational Redshifts and Accelerations
6.1. On Measurable Experiments
6.2. Measurable Verifications for Gravitational Redshift
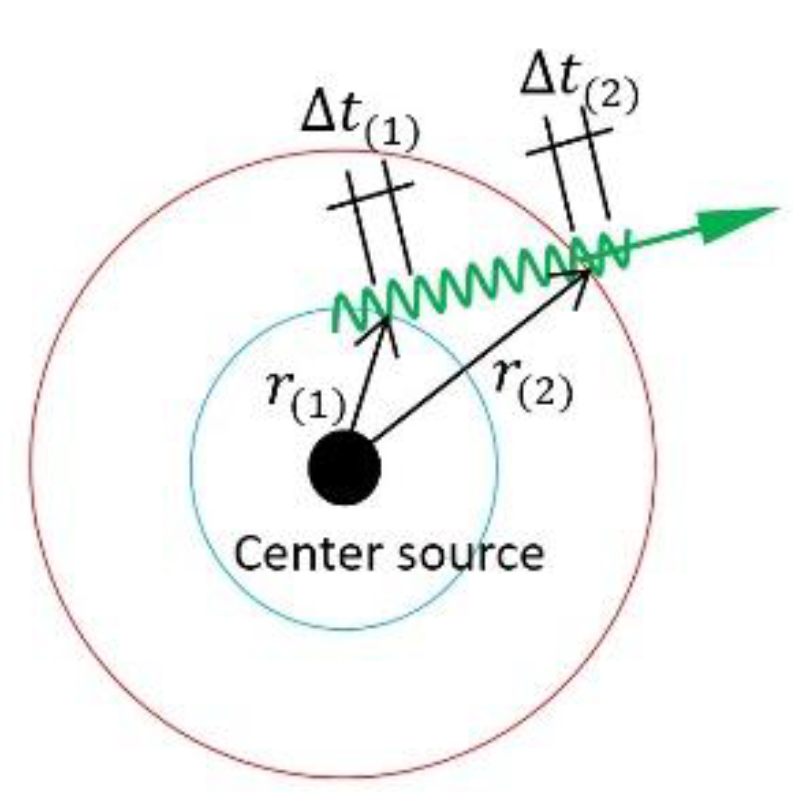
6.3. Measurable Verifications for Acceleration
6.3.1. Measurable Quantities and Measurable Acceleration
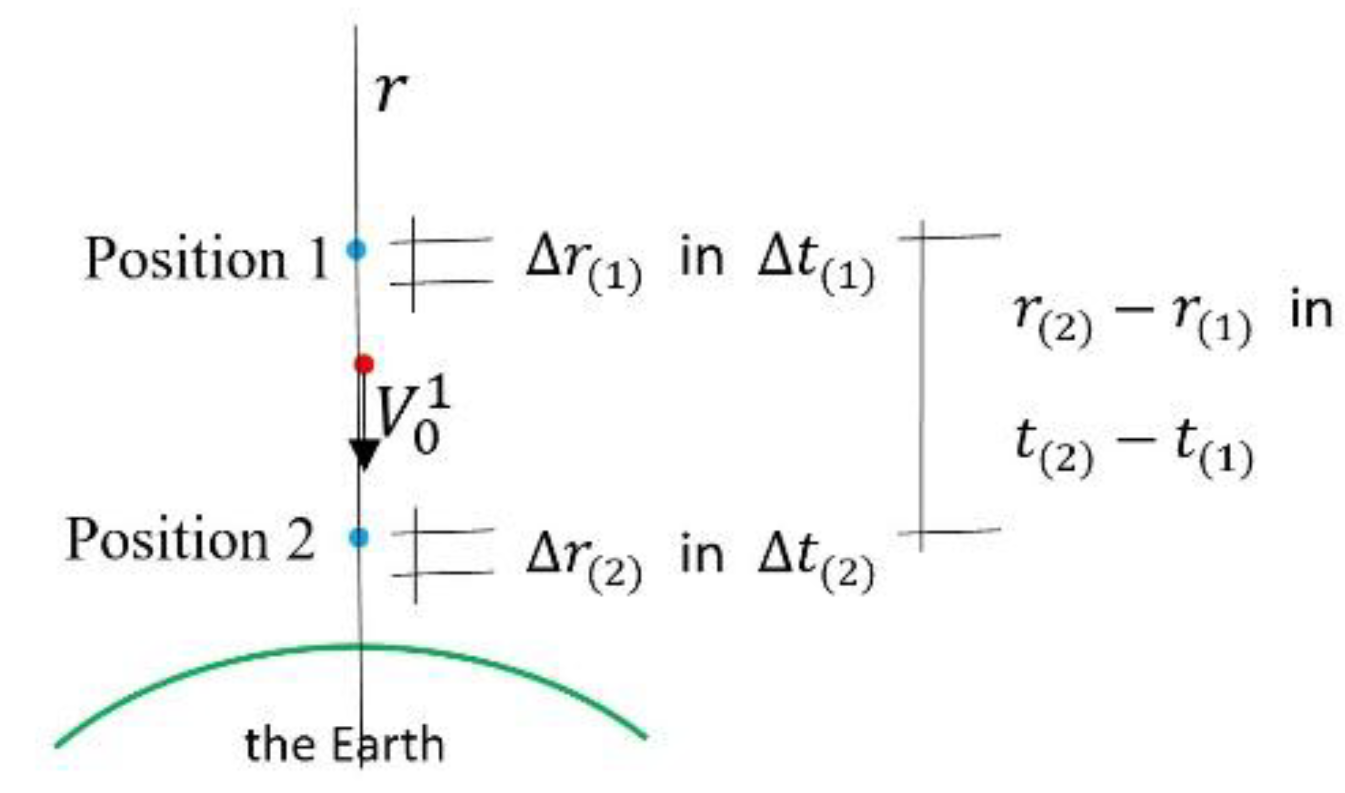
6.3.2. Examples
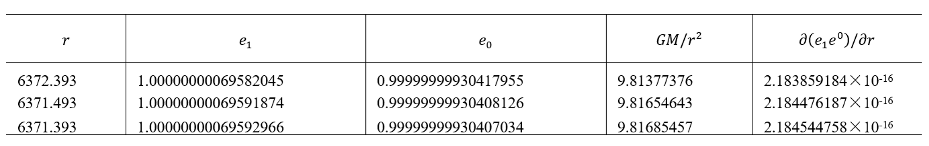 |
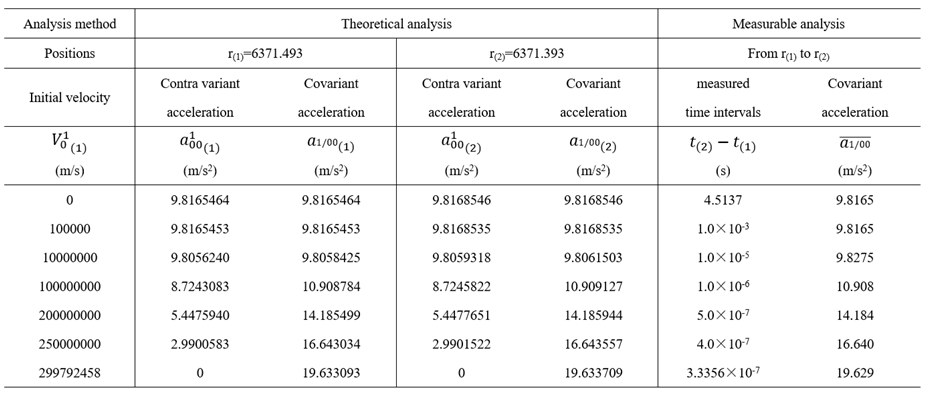 |
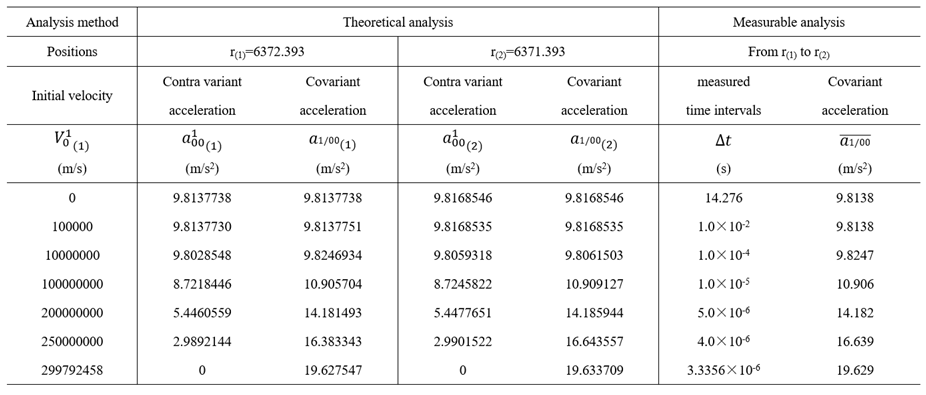 |
7. Conclusions and Inferences and Their Applications
7.1. Conclusions
7.2. Inferences
7.3. Applications
7.4. On Conservativeness
8. Kinematics and Dynamics
8.1. The Most Important
8.2. Falsification of the Employment of Geodesic Line for Kinematic Equation
8.3. Classical Equations of Light Ray Deflection
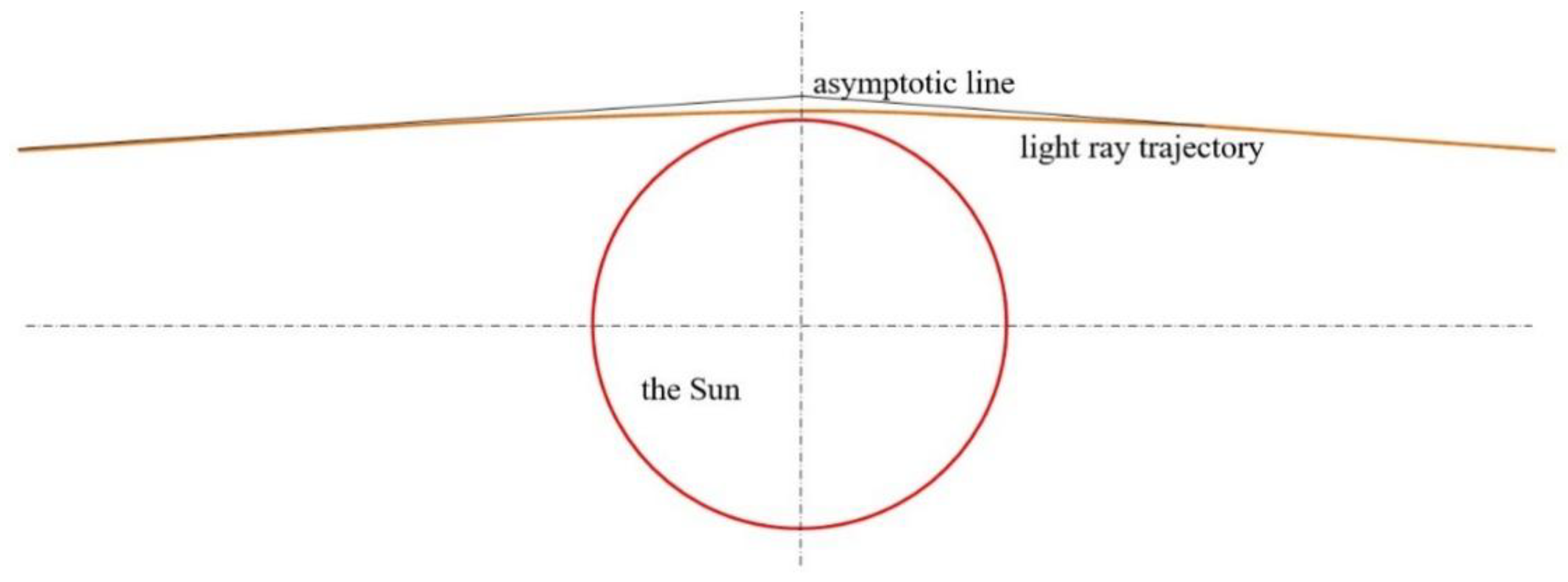
8.3.1. Classical Equations after Traditional Settings
8.3.2. Errors Hidden in the Solving Process
8.4. Momentum, Energy, and Angular Momentum Conservativeness
8.5. Revisit Equations for Light Ray Trajectory
8.5.1. Renovation and Resolution
8.5.2. Detailed Discussions on the Coordinates of the Light Ray Trajectory
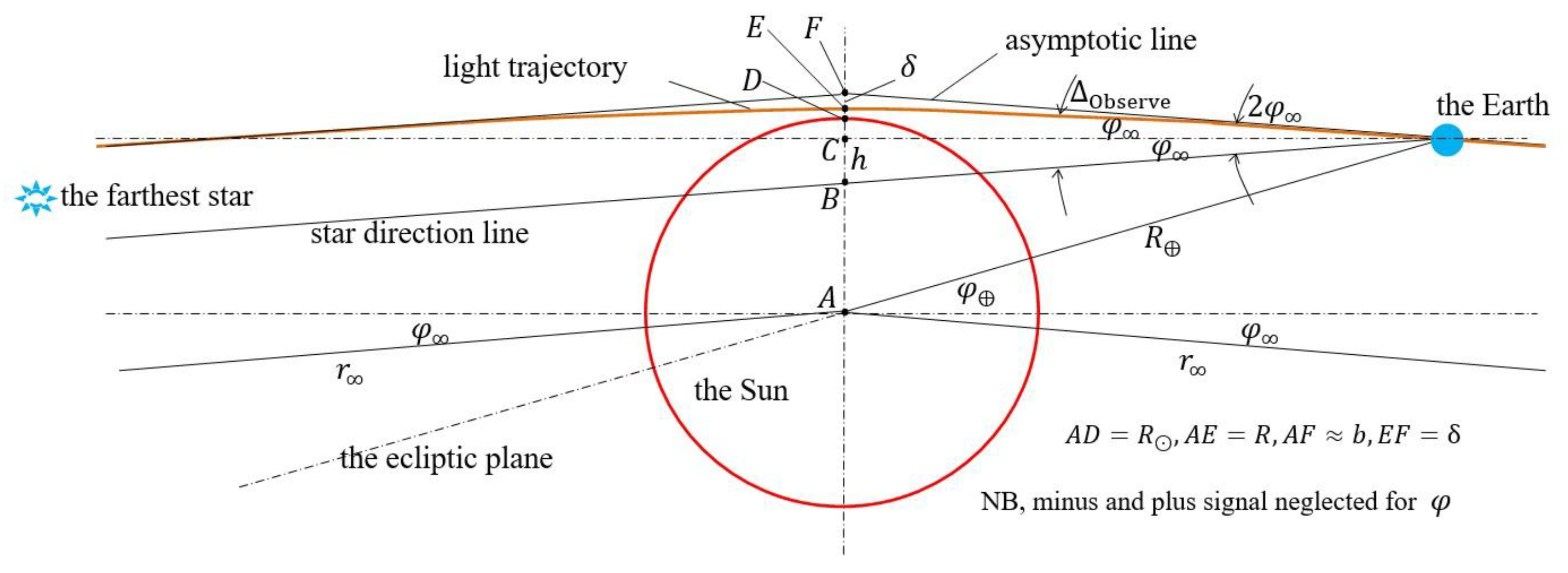
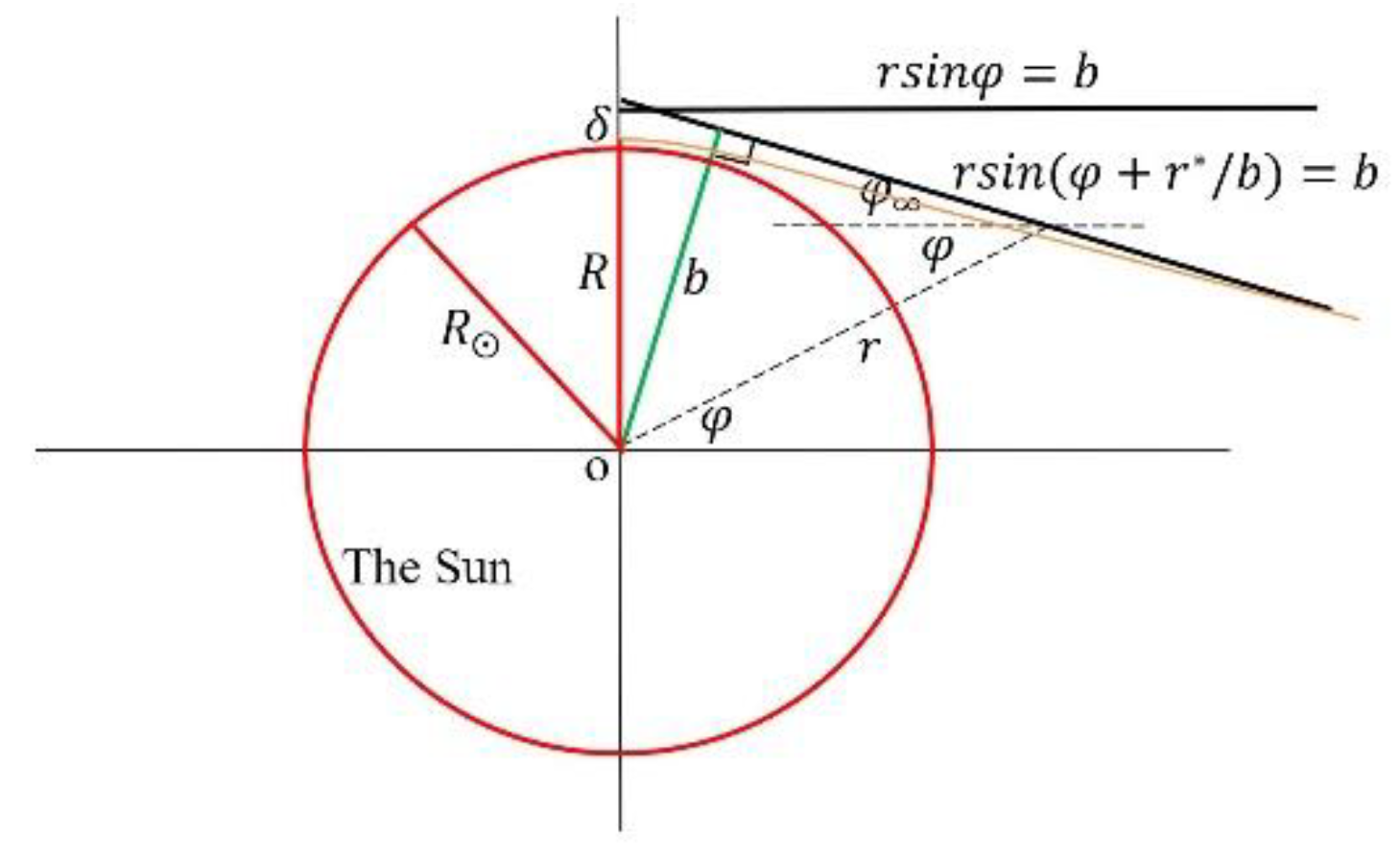
8.5.3. A Wrong Treatment for Light Propagations
8.6. Trajectories of Massive Matters
8.6.1. Discussions on Lagrangian
8.6.2. Classical Solution for Planet Orbits
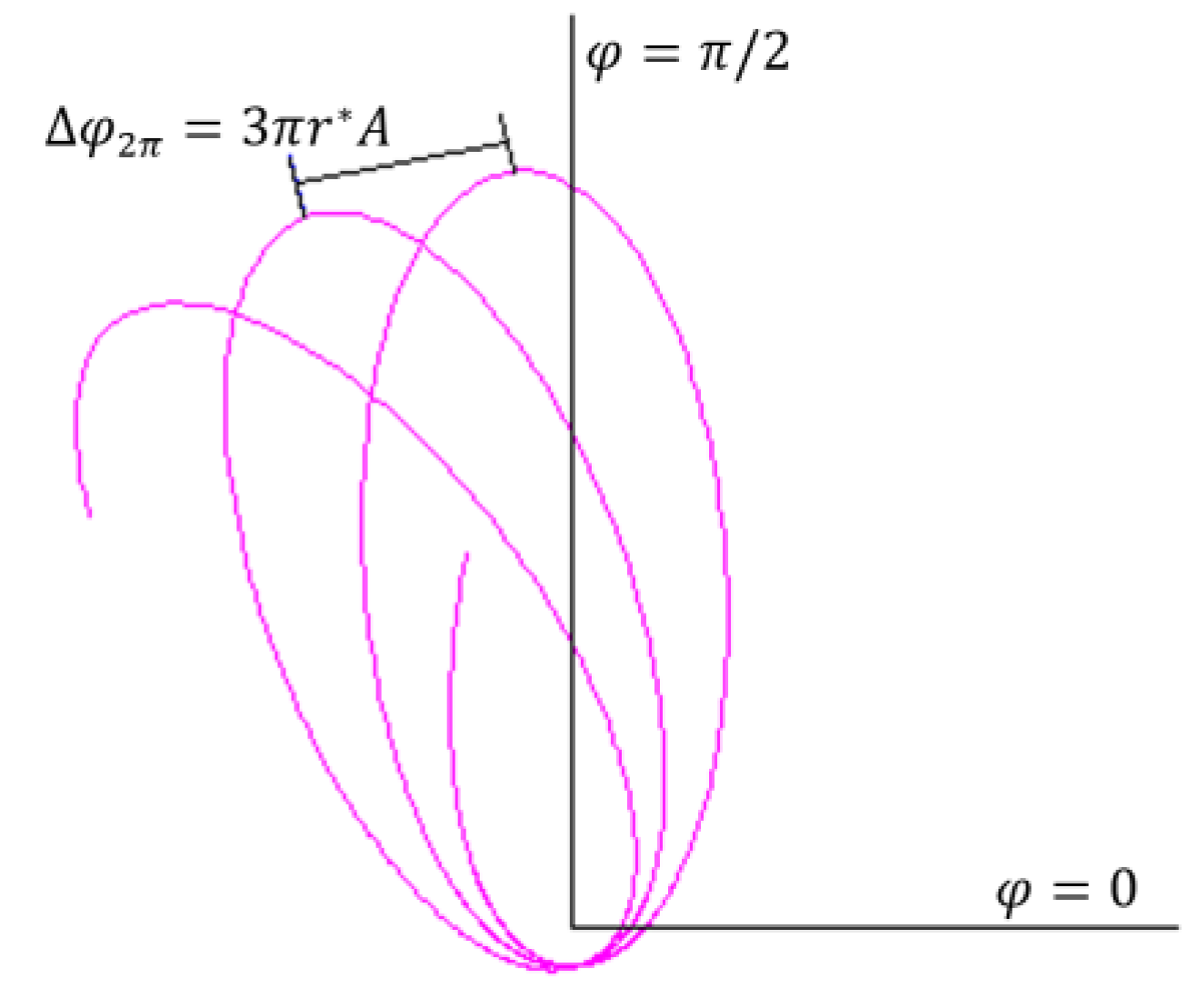
8.6.3. Traditional Treatment for Close-to-Light-Speed Particles
8.6.4. Renovated Equations for Close-to-Light-Speed Massive Particles
8.6.5. Renovated Equations for Un-Close-to-Light-Speed Massive Matters
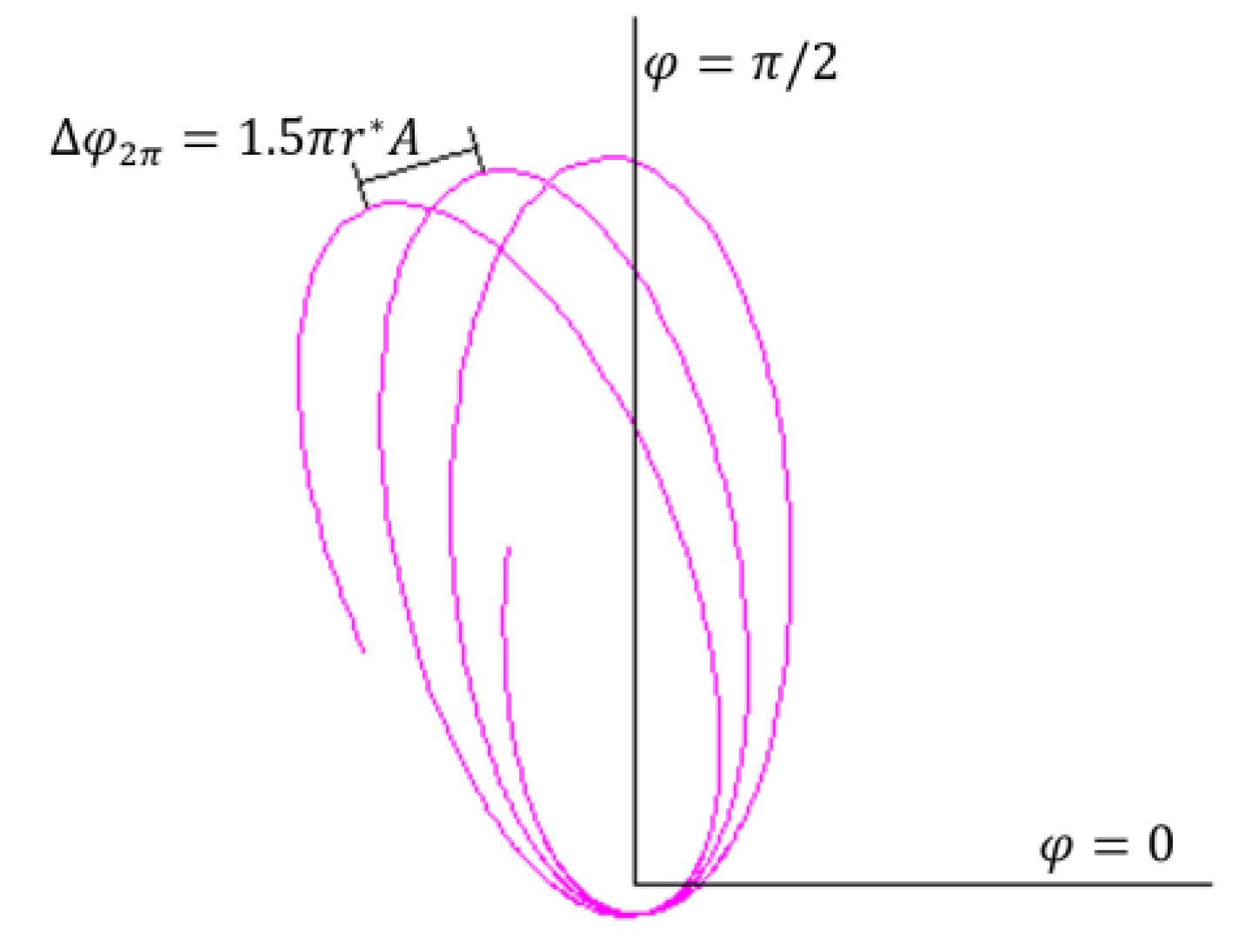
8.6.6. Dynamics within Event Horizon

8.7. Time Spending Problems
8.7.1. Classical Solution for Radar Echoes
8.7.2. Errors in
8.7.3. Renovated Equations for Radar Echoes
8.7.4. A Falsification on Traditional Methodology on Close-to-Light-Speed Particle Time Spending
8.7.5. Renovated Solution for Close-to-Light-Speed Particles
8.7.6. Equations of Time Delay
8.8. Comparative Research between Numerical Solutions and Algebraic Solutions
8.8.1. The Invalidity of Newtonian Second Law in Light Propagation
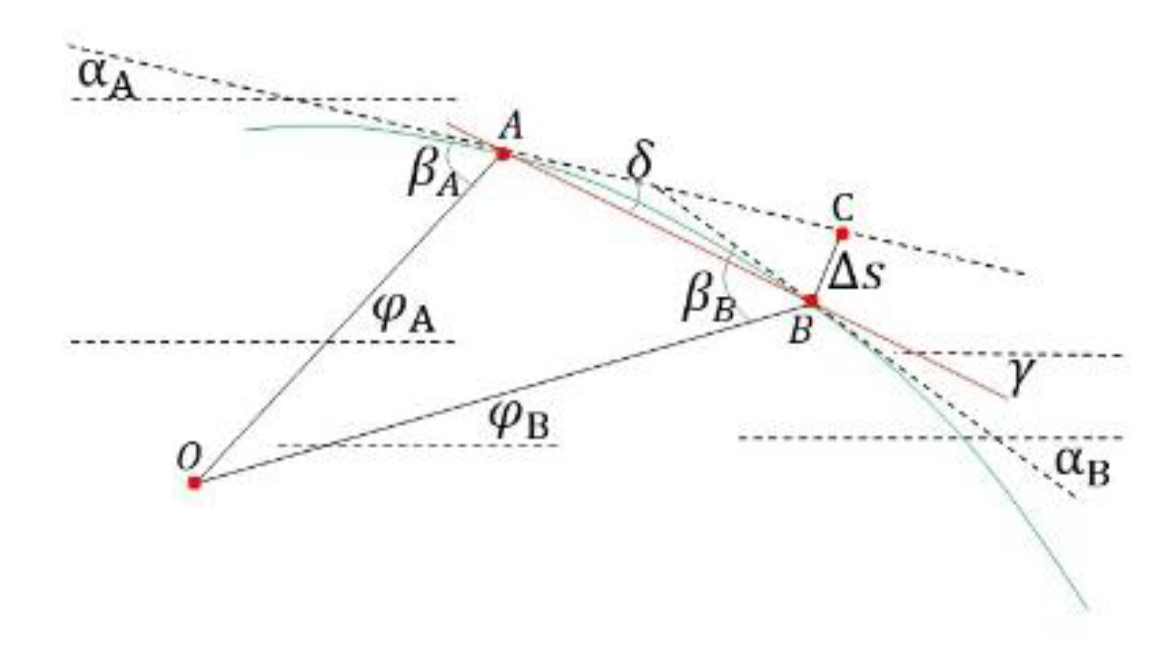
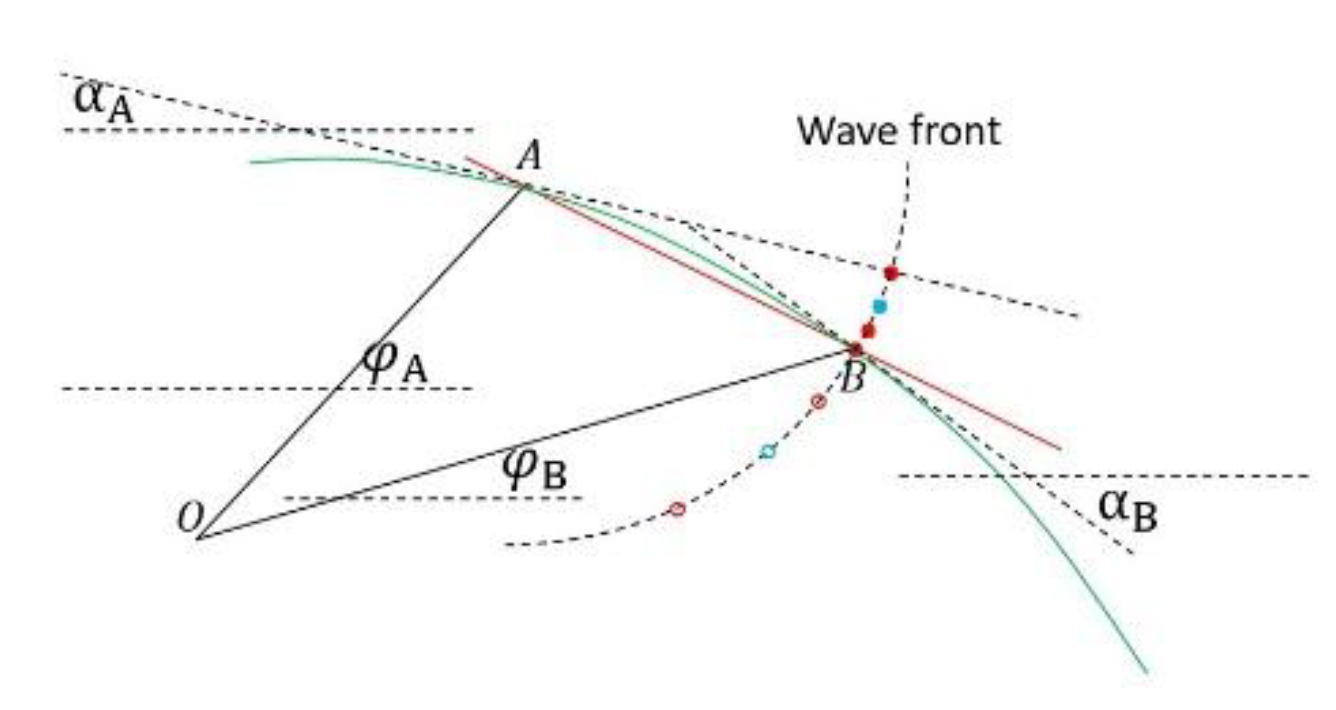
8.8.2. Comparisons of Numerical Solutions and Algebraic Solutions
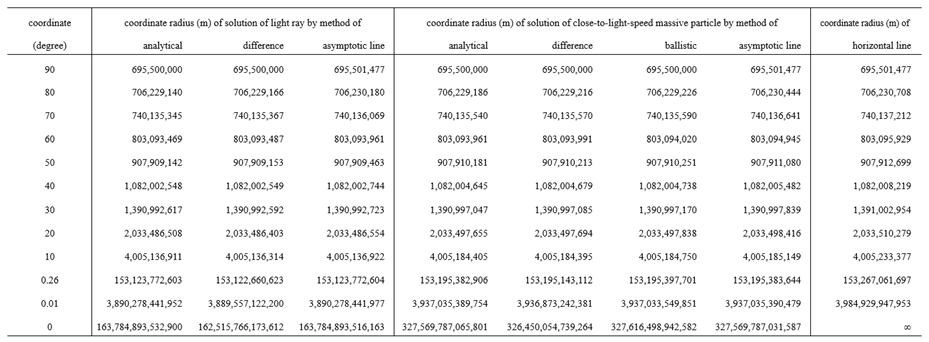
8.9. Additional Discussions
8.9.1. On Geodesic Line, Inertial Motion, and General Covariance
8.9.2. On 4-dimensional and 3-dimensional Velocities
- or the form of
8.9.3. On Light Momentum and Massive Matter’s Momentum
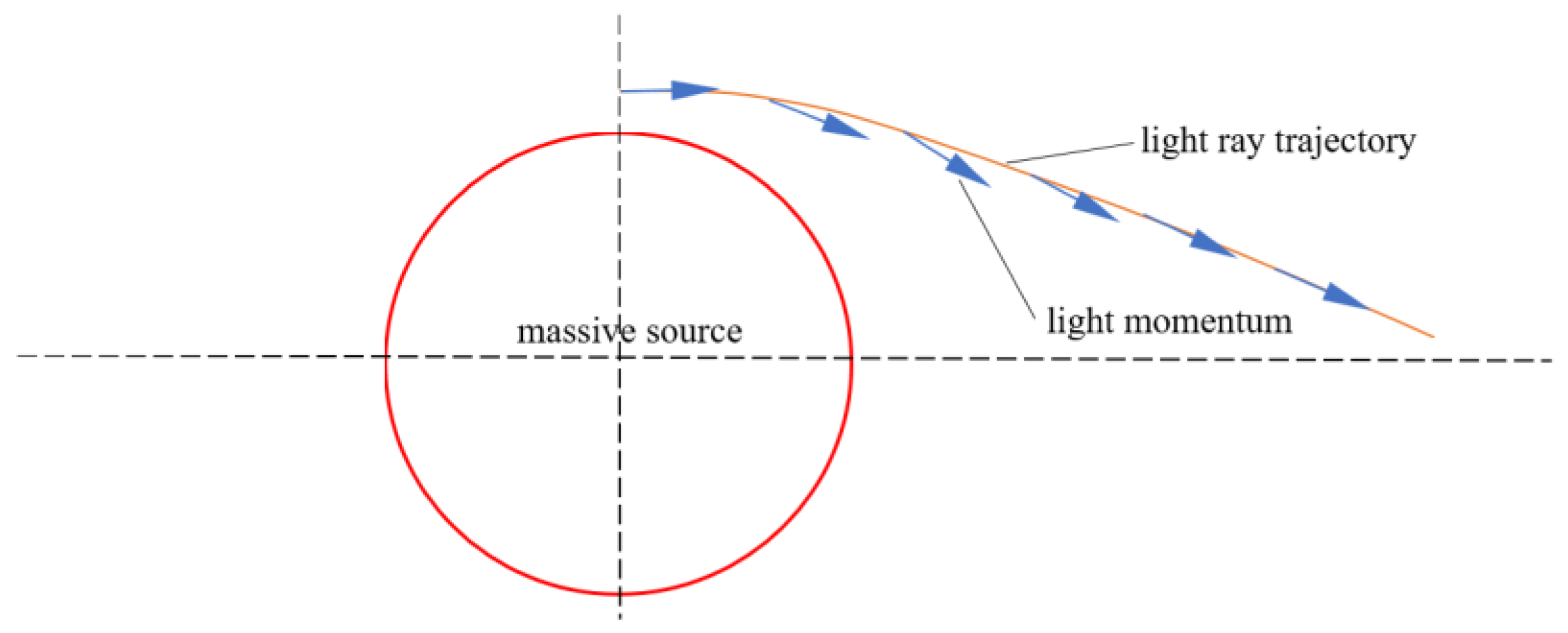
9. Relativistic Release and Relativistic Frequency Shift
9.1. Dynamics of Accretions of Quasars and Active Galactic Nuclei
9.1.1. Galactic Accretions and Planet Rings
9.1.2. The Dynamic Models of Fluid Rings
- Model 1: Central Keplerian motion with driving front and resistant front
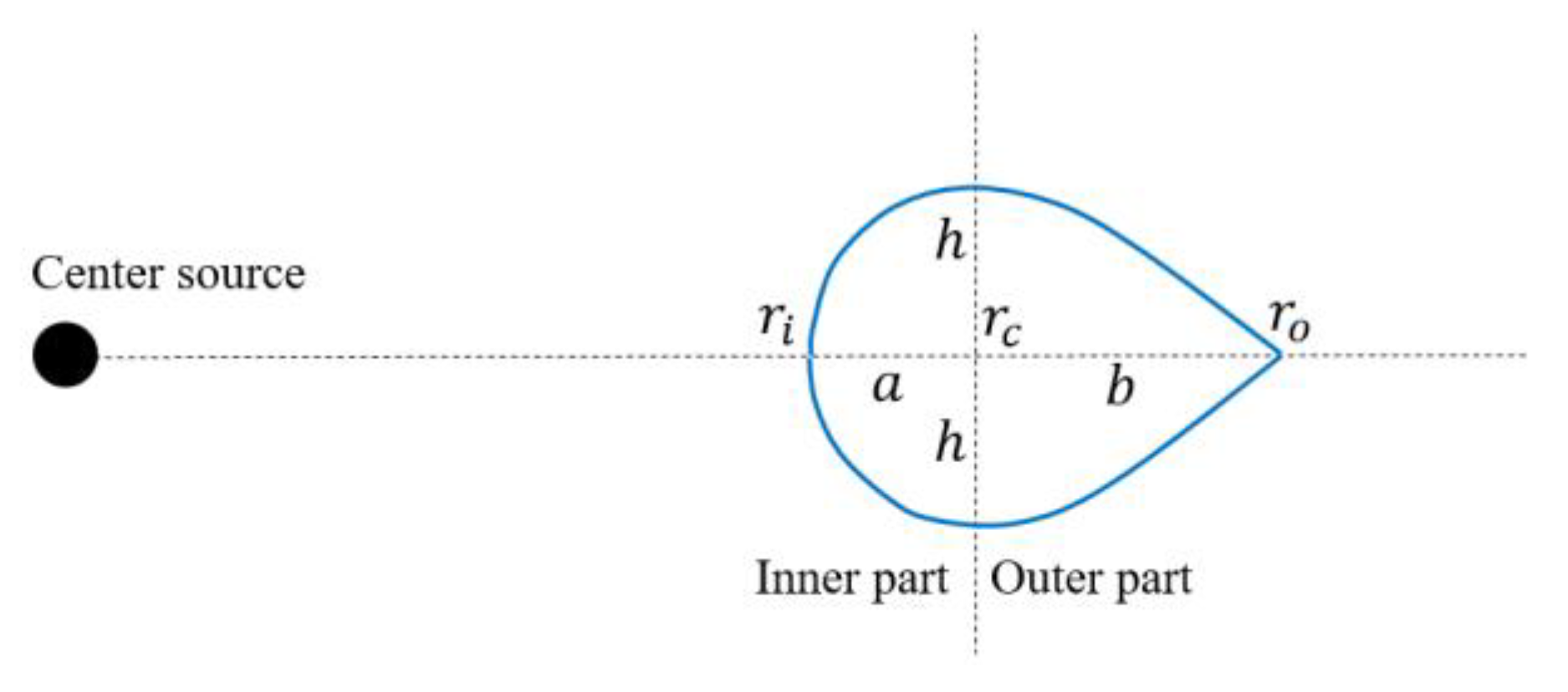
- Model 2: Driving condition with no shear motion in inner part
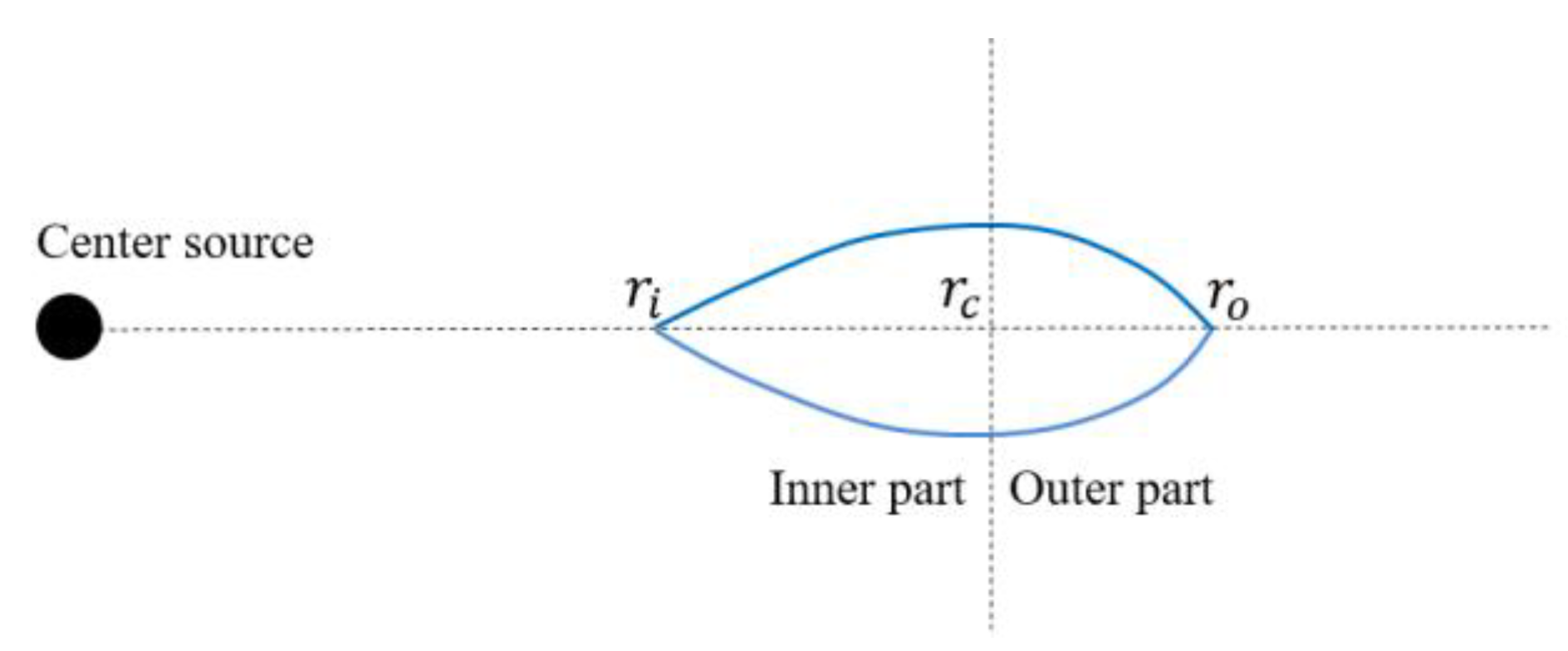
- Model 3: Momentum conversion and ring split
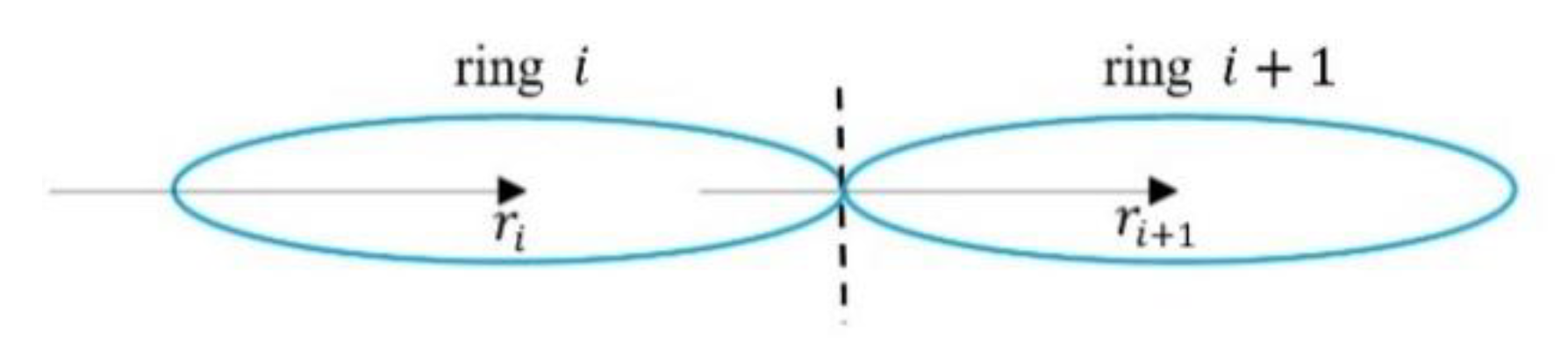
9.1.3. Shearing Dissipation in Fluid Rings
9.1.4. On Particle Rings
9.2. Relativistic Release
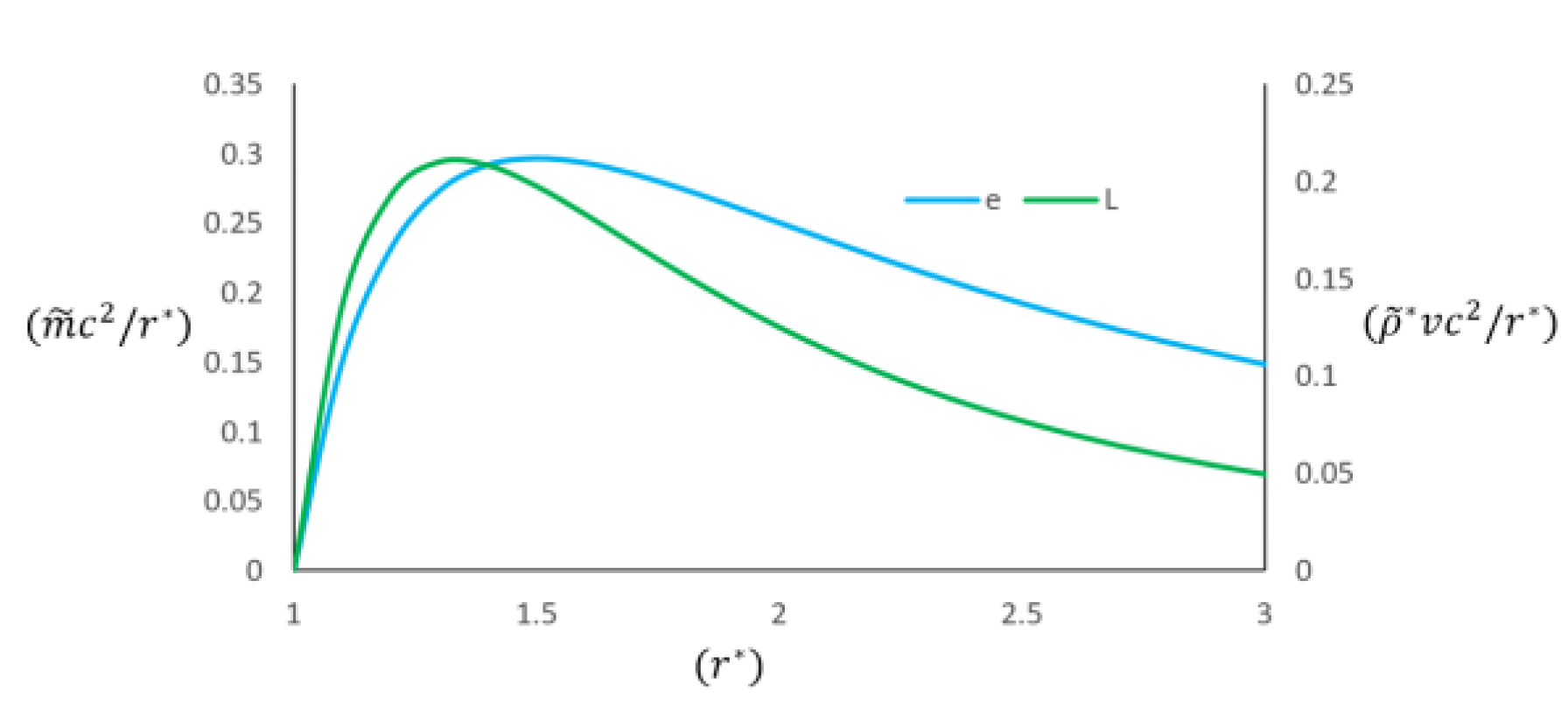
9.3. Relativistic Emission Lines and Relativistic Redshift
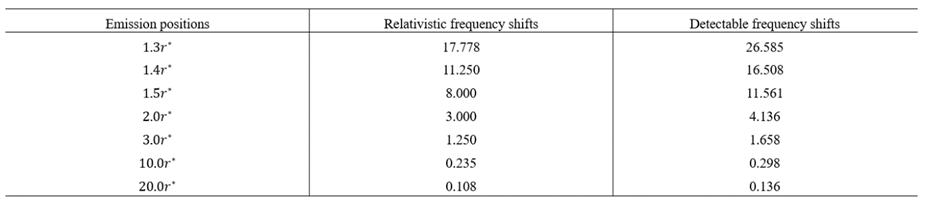
9.4. Broad Lines and Narrow Lines
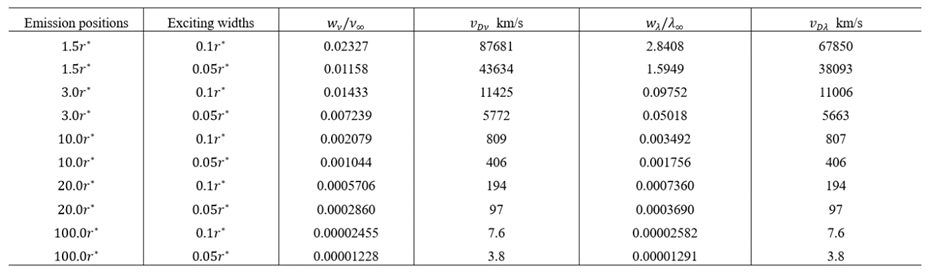
9.5. Relativistic Absorption
- or expressed by Doppler velocity in frequency as
1.66. Here, the absorption lines may show a blueshift of
Acknowledgement
References
- Einstein, A. Die Grundlage der allgemeinen Relativitätstheorie. Annalen der Phys. 1916, 49, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jost, J. Riemannian Geometry and Geometric Analysis, 6th ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, T.P. Relativity, Gravitation and Cosmology; Oxford University Press: 2005.
- Straumann, N. General Relativity; Springer Science + Business Media: Dordrecht, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Eisenhart, L.P. Riemannian geometry, Princeton University Press, Eighth Printing: 1925.
- П.К. Рашевский, Riemannian Geometry and Tensor Analysis, Technique and Theory Press, (1953).
- Huang, C. General Relativity Lecture Sheet; China Science Press:, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Einstein, A. Zur Elektrodynamik bewegter Körper. Ann. Physik 1905, 17, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minkowski, H. Nachr. Ges. Wiss. Göttn Math.-Phys. Kl. 53. 1908. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y. General Relativity; Peking University Press, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, H. Introduction to General Theory of Relativity; Zhejiang University Press, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B. General Relativity; Peking University Press, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Weatherburn, C.E. Introduction to Riemannian Geometry and the Tensor Calculus; Cambridge University Press, 1942.
- Pound, R.; Rebka, G. Gravitational Red-shift in Nuclear Resonance. Physical Review Letters 1959, 3, 439–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vessot, R.; Levine, M.; et al. Test of Relativistic Gravitation with a Space-Borne Hydrogen Maser. Physical Review Letters 1980, 45, 2081–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, T.; et al. Relativistic Redshift of the Star S0-2 Orbiting the Galactic Center Supermassive Black Hole. Science 2019, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, S. Gravitation and Cosmology, Principles and Applications of the General Theory of Relativity; John Wiley, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Peierls, R. More Surprises in Theoretical Physics; Princeton Univ. Press, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Minkowski, H. Nachr. Ges. Wiss. Göttn Math.-Phys. Kl. 53. 1908. [Google Scholar]
- Abraham, M. Rend. Circ. Matem. Palermo 1909, 28, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einstein, A. A centenary volume letter to M. Besso, 1951(p.138).
- Leonhardt, U. Optics: Momentum in an Uncertain Light. Nature 2006, 444, 823–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froeschle, M.; Miguard, F.; Arenon, F. in Proceedings of the Happarcos Venice 1997 Symposium; ESA Publications Division: Noordwijk, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro, I.I. Fourth Test of General Relativity. Physical Review Letters 1964, 13, 789–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, I.I.; Ash, M.E.; Ingalls, R.P.; et al. Fourth Test of General Relativity: New Radar Result. Physical Review Letters. 1971, 26, 1132–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, J. What is mass? European Journal of Physics 2005, 26, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z. Ordinary Differential Equations Analytical Methods and Numerical Methods; Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Perera, B.B.; McLaughlin, M.A.; Kramer, M.; et al. The Evolution of PSR J0737-3039B and a Model for Relativistic Spin Precession. Astrophysical Journal 2010, 721, 1193–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landry, P.; Kumar, B. Constraints on the Moment of Inertia of PSR J0737-3039A from GW170817, arxive: 1807. 04727v2 [gr-qc] 10 Oct 2018.
- Everitt etc, C.W.F. Gravity Probe B: Final Result of a Space Experiment to Text General Relativity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 106, 221101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.H.; Fowler, L.A.; McCulloch, P.M. Measurements of General Relativistic Effects in the Binary Pulsar PSR1913+16. Nature 1978, 277, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuter, R.; Amorim, A.; Anugu, N.; et al. Detection of the Gravitational Redshift in the Orbit of the Star S2 Near the Galactic Centre Massive Black Hole. Astronomy & Astrophysics 2018, 615, L15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victor, M.L.; Riccardo, D.M.; Ivan, M. etc. Future prospects for measuring 1PPN parameters using observations of S2 and S62 at the Galactic Center, arxive: 2410. 22864v2 [astro-ph.GA] 28 Jan 2025.
- Salpeter, E.E. Accretion of interstellar matter by massive objects. Astrophys. J. 1964, 140, 796–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dovich, Y.B.; Novikov, I.D. The radiation of gravity waves by bodies moving in the field of a collapsing star. Sov. Phys. Dokl. 1964, 9, 246. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, S.; Fukue, J. Mineshige, Black-hole Accretion Disks; Kyoto University Press, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Blandford, R.D.; Netzer, H.; Woltjer, L. Active galactic nuclei, Saas-Fee Advanced Course 20,Lecture Notes 1990, Swiss Society for Astrophysics and Astronomy; Springer, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Shakura, N.I.; Sunyaev, R.A. Black holes in binary systems. Observational appearance. Astron. Astrophys. 1973, 24, 337–355. [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro, S.L.; Lightman, A.P.; Eardley, D.M. Astrophys J. 1976, 204, 187.
- Sicardy, B. Dynamics of planetary rings. Lect. Notes Phys. 2006, 682, 183–200. [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell, J.C. On the Stability of the Motions of Saturn’s Rings, Cambridge and London: MacMillan and Company. Reprinted in Scientific Papers of James Clerk Maxwell. Cambridge University Press, 1890; Vol. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Charnoz, S.; Croda, A.; Hyodo, R. Rings in the Solar System: a Short Review. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.08963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, L.W. ; Composition; Structure; Dynamics, and Evolution of Saturn’s Rings. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2010, 38, 383–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miner, E.D.; Wessen, R.R.; Cuzzi, J.N. Planetary Ring Systems; Praxis Publishing Ltd, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, B.; Chary, R. Insights into Physical Conditions and Magnetic Fields from High Redshift Quasars, arxive: 2207. 07290v1 [astro-ph.GA] 15 Jul 2022.
- Event Horizon Telescope Collaboration, First M87 event horizon telescope results. I. The shadow of the supermassive black hole. ApJ 2019, 875, L1. [CrossRef]
- Donnan, C.T.; Mcleod, D.J.; Dulop ect, J.S. The Evolution of the Galaxy UV Luninosity Function at Reshift z≈8-15 from Deep JWST and Ground-based Near-infrared Imaging, arxive: 2207. 12356v3 [astro-ph.GA] 24 Nov 2022.
- Yung, L.Y.; Somerville, R.S.; Finkelstein ect, S.L. Are the Ultra-high-redshift Galaxies at z>10 Surprising in the Context of Standard Galaxy Formation Models? arxive: 2304. 04348v2 [astro-ph.GA] 11 Nov 2023.
- Huang, K. Quasars and Active Galactic Nuclei; China Science and Technology Press, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, B.M. An introduction to active galactic nuclei; Cambridge University Press, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Beckmann, V. Chris shrader; Active galactic nuclei, WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Boschstr. 12, 69469, Weinheim, Germany (2012).
- Osterbrock, D.E. Emission-line spectra and the nature of active galactic nuclei, proceedings of a conference held at the Georgia State University, Springer-Verlag, 1-18 (1987).
- Bentz, M.C.; Williams, P.R.; Treu, T. The Broad Line Region and Black Hole Mass of NGC 4151, arxive: 2206. 03513v1 [astro-ph.GA] 7 Jun 2022.
- Serafinelli, R.; Marinucci, A.; Rosa etc, A.D. A Remarkably Stable Accretion Disk in the Sefert Galaxy, arxive: 2309. 06092v1 [astro-ph.HE] 12 Sep 2023.
- Liu, V.; Zoghbi, A.; Miller, J.M. Dectection of Asymmetry in the Narrow Fe Kα Line in MCG-5-23-16 with Chandra, arxive: 2312. 16354v2 [astro-ph.HE] 4 Jan 2024.
- Netzer, H. The Physics and Evolution of Active Galactic Nuclei; Cambridge University Press, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lynds, R. The Absorption-line spectrum of 4c 05.34. Astrophysical Journal 1971, 164, L73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, K.; et al. Observation of a Neutrino Burst from the Supernova SN1987a. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1987, 58, 1490–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.P.; et al. GW170817: Observation of Gravitational Waves from a Binary Neutron Star Inspiral. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 119, 161101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





